Abstract
Treated effluent from a wastewater treatment plant can be further reused as a water resource for a water supply treatment plant. In this case, the treated sewage gathered in the study of the Class V National Water Quality Standard (NWQS) of Malaysia would be treated for use as a water resource for a water treatment plant. In a moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) with a 500-L working volume, organic pollutants, undesirable nutrients, and bacteria were removed without disinfectant. At 24-h hydraulic retention time (HRT), the maximum removal efficiency of 5-day biological oxygen demand, ammonia–nitrogen (NH3-N), and total phosphorus were 71%, 48%, and 12%, respectively. The biofilm thickness, which was captured using scanning electron microscopy, increased from 102.6 μm (24-h HRT) to 297.1 μm (2-h HRT). A metagenomic analysis using 16S rRNA showed an abundance of anaerobic bacteria, especially from the Proteobacteria phylum, which made up almost 53% of the total microbes. MBBR operated at 24-h HRT could improve effluent quality, as its characteristics fell into Class IIA of the NWQS of Malaysia, with the exception of the NH3-N content, which indicated that the effluent needed conventional treatment prior to being reused as potable water.
1. Introduction
Treated wastewater is a viable option for managing a state’s scarce water resources. Opportunities for adopting technological innovations for water reuse are particularly significant due to the fact that reclaimed water has economic value as a water supply resource [1]. Furthermore, while the disposal of treated effluent is subject to stringent pollution control measures, water reuse can allow for greater flexibility and water quality management benefits. Extra treatment stages are required in order to polish secondary effluent to high-quality standards outlining very stringent discharge or unrestricted reuse [2]. These stages enable the reclamation of municipal wastewater, which is suitable for raw water supply resources.
Standard A of the Malaysia Sewage Discharge standard and classes of the National Water Quality Standard (NWQS) has been tabulated in Table 1 [3,4]. It can be shown that the water quality must be in Class IIA in order for the water to be used as a water resource needing conventional water treatment for potable use. The table lists the regulations for each class based on five parameters: total suspended solid (TSS), 5-day biological oxygen demand (BOD5), chemical oxygen demand (COD), ammonia–nitrogen (NH3-N), and colony-forming units per 100 mL (CFU/100 mL), which are considered essential for controlling the quality of treated water. A TSS of under 10 mg/L indicates clear effluent. BOD5 values ranging from (10–20) mg/L and a COD of around 100 mg/L are the limits of the required nutrients for microbial growth [5].

Table 1.
Standard A of the Malaysia Sewage Discharge standard and classes of the National Water Quality Standard (NWQS) for Malaysia [3,4]
Pathogens below the detection limit appear to be a common standard for graywater treatment in most countries. Some researchers have used combined low-frequency ultrasound and ozonation technology to produce treated effluent, which can be used for agricultural irrigation and fertilization [2]. Elwakeel et al. [6] pointed out that magnetic thiourea-formaldehyde polymer loaded with silver ion provides a promising disinfectant activity against microbial pathogens in the water and wastewater samples with high magnetic-separation ability. Additionally, since there are many modern technologies available, appropriate polishing treatment for water reuse can be selected based on a “fit-for -purpose” approach [7].
Effluent polishing should be adopted after discharge in order to protect the environment and public health. The unique advantages and disadvantages of conventional treatment systems have been reported, e.g., slow sand filter [8], rapid sand filter, activated carbon [9], and microfiltration [10]. A comparison of widely-used treatment technologies will help engineers select treatment technologies based on efficiency, energy, operation, performance, land requirement, cost, etc. Biological treatments of waste and wastewater using different microorganisms have become desirable and are required for reducing many industrial and environmental wastes. Ibrahim et al. [11] reported that about 2.5 mg/L of the identified bacterial consortium—such as Pediococcus acidilactici, Pediococcus pentosaceus, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Bacillus subtilis—was the optimum dose with 6-h contact time for wastewater treatment.
Among the biological treatment systems used, the moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) system has been operated in more than 1200 wastewater treatment plants in at least 50 countries [12]. The MBBR was first developed to treat municipal wastewater, especially for the purpose of removing nitrogen [13]. Afterwards, other applications of the MBBR were developed, such as for BOD removal, phosphorus removal, and nitrification and denitrification in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment [14]. MBBR is a complete mix, continuous flow process that combines the advantages of fixed film and suspended growth processes such as high and stable removal activity, low head loss, more robust to overloading conditions and toxic components, no sludge bulking, and a large surface area for colonization, leading to a more compact design [15,16].
Many works have identified MBBR technology as an appropriate technology for upgrading the performance and treatment capacity of existing plants, particularly if space limitations constrain the plant expansion [17,18,19]. The work of Zafarzadeh et al. [20] was successful in showing that fluctuations in the concentration of dissolved oxygen (DO) had no negative influence on the COD removal rate in the reactor, and complete soluble organic carbon removal of about 99% efficiency was achieved and occurred in the total moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) system. Yang et al. [16] verified MBBR technology as being an alternative and successful method for treating different kinds of effluents under different conditions.
Some experiments have shown that biological phosphorus, nitrogen, and organic matter can be removed in a MBBR operating in continuous flow, along with concurrent aerobic nitrification/denitrification and phosphorus uptake, without some of the problems of activated sludge [13,14,21]. Regmi et al. [22] studied nitrogen polishing of main stream nitritation-denitritation system effluent via anammox at 25 °C in a fully anoxic MBBR in a volume of 0.45 m3 over 385 days. This study demonstrated the feasibility of anammox nitrogen polishing in an MBBR for nitritation-denitration systems at limited COD availability.
Following a thorough evaluation of related literature, most past studies on MBBR have investigated raw wastewater treatment with high pollutant concentrations. However, none have investigated the ability of MBBR to treat low effluent concentration or polish treated effluent. Hence, this study introduces the concept of effluent polishing to bridge the technology gap between the bulk removal and fine polishing of organic and inorganic compounds in order to obtain better water quality. This study also presents a unique system design that reduces the footprint size, making the system suitable for polishing treated water on-site within a small area.
2. Materials and Methods
This experimental study investigates the possibility of removing low concentrations of pollutants (organic matters, nitrogen, and phosphorus) from treated sewage using an MBBR polishing system for the purpose of using the treated water as a water resource.
2.1. Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) Polishing System
2.1.1. System Design and Installation
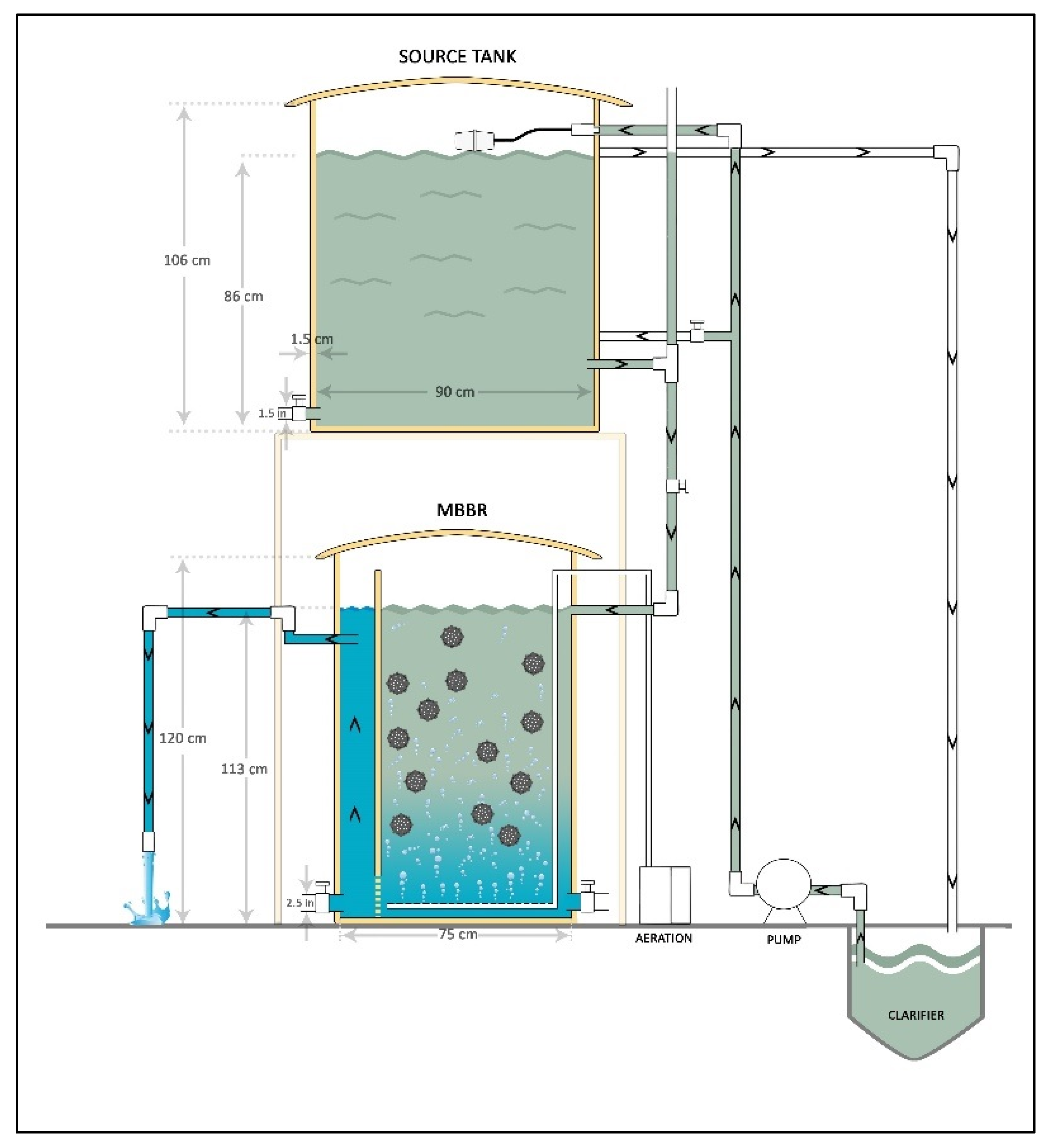
The MBBR polishing system consisted of MBBR and a source tank, as shown in Figure 1. The MBBR was a cylindrical column with an inside diameter of 0.75 m and a total height of 1.2 m, in which 1.13 m was the effective reactor height. In this study, non-exposure to light was important for reducing phototropic organism proliferation in the MBBR, such as algae. Therefore, the reactors were made from a black and thick (1.5 cm) high density polyethylene (HDPE) material in order to enable operation in darkness, except for periods of sampling or reactor maintenance. The MBBR and the source tank were both closed at the top using a HDPE convex cover.
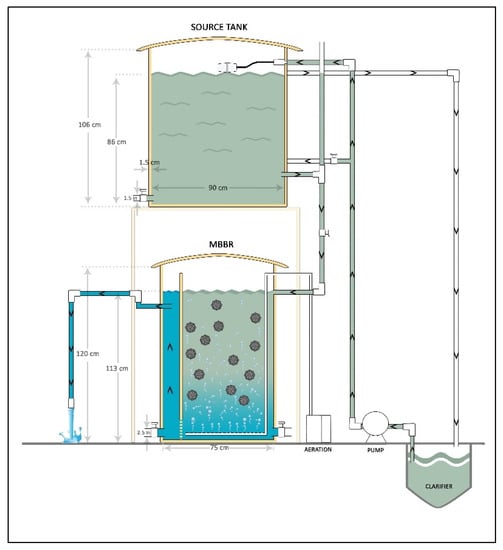
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram of the moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) polishing system.
A variable flow rate (gravity-dependent) (Table 2) was used for the reactor, without a pump and using a hand valve, which enabled the flow rates to be adjusted. The MBBR inlet pipe was occasionally flushed to remove built-up solids and biofilm inside the pipe. This step enabled the researcher to maintain a continuous flow of treated wastewater supply at all times. The MBBR had two sampling ports, which were located on the MBBR inlet line and outlet line.

Table 2.
Variation in flow rate (Q) and HRT during the experimental runs.
The bottom section of the MBBR was the most vital part, as this was where both the air distributor and the perforation barrier were installed. The bottom section had four fine bubble walls and air stone tube diffusers mounted on it. Diffusers were placed at an equal distance from the center to facilitate equal distribution. Outside the reactor, these diffusers were connected to a central air supply with rubber tubes. This connection made it easy to orient the air supply pipes around the reactor.
The pumps also provided sufficient mixing and kept the biomass suspended. Additionally, a stable base was used to support the reactor. The aeration system provided coarse bubbles and kept the media in circulation. The up-flow configuration was chosen, due to the fact that it could treat high influent flow rates and had a longer operating cycle. It could also reduce the ‘smelly water’ issue at the top of the reactor when the air reacted with the treated effluent [23].
The source tank was a 550-L cylindrical vessel with 1.5 cm thickness located above the MBBR using a stand. This gave the liquid some height to flow under gravity through a 2.54 cm diameter pipe into the MBBR. The stand and the elevation along the source tank’s cylindrical sidewall for the gravity overflow port were chosen to provide a 550-L operational volume for the vessel.
The gravity overflow allowed the excess mixed-liquor to flow into a 2.54 cm T-connector, providing equalized atmospheric pressure, before exiting the system via a 2.54 cm clear tubing, vertically downward to the external clarifier. The influent was pumped from a sewage treatment plant (STP) final clarifier through a 2.50-cm internal diameter polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tube, connected to pump head tubes by fittings to the source tank.
2.1.2. Biofilm Carrier
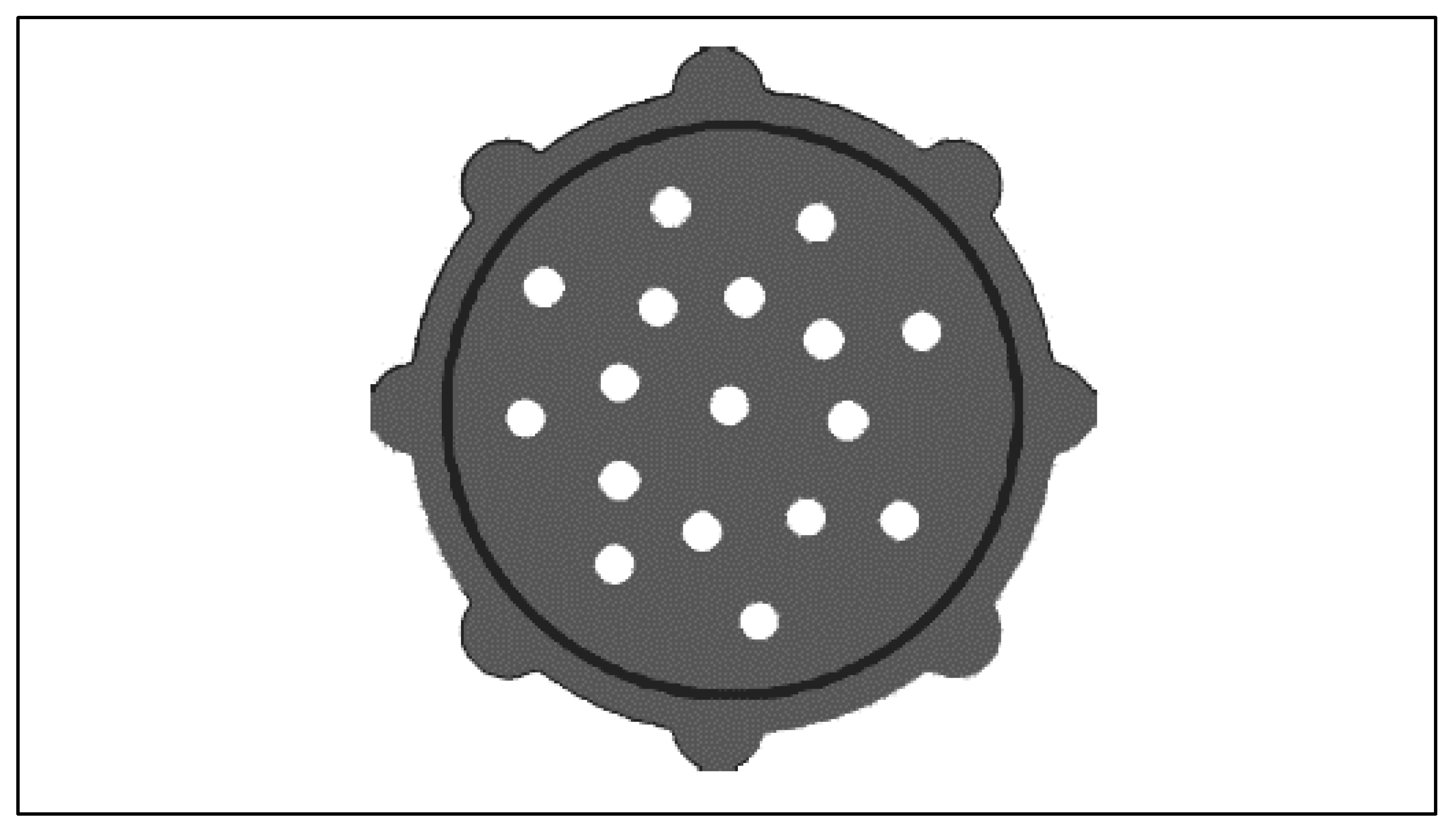
Envirosource Multimedia (EMM, Malaysia)—the three-dimensional (3-D) HDPE medium—was used as a biofilm carrier in this study. The EMM is a cylinder that is perforated on both sides. Figure 2 and Table 3 show the structure and the physical properties of the medium, respectively.
Figure 2.
Front section of the three-dimensional Envirosource Multimedia (3-D EMM).

Table 3.
The physical characteristics of 3-D EMM.
The 3-D EMM carries numerous advantages. For example, the medium’s lighter density allows lower liquid superficial velocity, which suits a longer hydraulic retention time (HRT) and reducing aero pumping energy. This medium is manufactured using HDPE material and is appropriate for a long service life that allows microorganisms to grow and attach. In this study, the bulk medium volume was 5% of the reactor volume, as the EMM medium has a specific structure and size, as well as a higher surface area, compared to other media.
In this study, the density of the 3-D EMM was adjusted so that these plastic media would be suspended in the tank. This was because the treated wastewater had a lower density (1.02–1.04 g/cm3) than the EMM. Consequently, to reduce the media density, a small ball of low-density polyethylene (used for packaging) was placed inside each EMM in order to suspend it or to make it float.
The 3-D EMM protects sensitive bacteria, such as nitrifiers, from being washed-out. The oxygen profile of biofilm layers enabled the survival of anaerobic, anoxic, and aerobic microorganisms in one system. Therefore, the system could perform both oxidative and reductive reactions, such as nitrification-denitrification and azo-bond cleavage, thus yielding excellent water-polishing capabilities.
2.1.3. Characteristics of the Feed (Treated Sewage)
In this work, treated domestic sewage, with very low concentrations of pollutants, was used as the feed. Real treated sewage was used because it is easier to biodegrade than synthetic wastewater and because it contains ubiquitous microbial community. The raw sewage from the facility was first treated by using an aerobic STP designed for a work capacity of 5000 population equivalent (p.e.). However, the STP was not fully operational yet and, at present, caters to only approximately 100 people. This meant that the effluent (treated sewage) had low concentrations of pollutants.
The temperature of the treated wastewater was consistent at approximately 30 °C. The aeration agitator was kept running throughout the study, to achieve complete mixing and homogeneous wastewater. The specifications of the treated wastewater as the MBBR system’s influent were as shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Characteristics of the feed (treated wastewater) entering the MBBR polishing system.
2.2. Experimental Operations
The MBBR polishing system was designed and set up to operate in an outdoor facility with an open environment. It was decided that the complete research work must be carried out under realistic conditions. Effluent from the aerobic STP clarifier (please refer to Figure 1) was used as the influent for MBBR. Firstly, the MBBR polishing system was assembled and tested for any leakage, to ensure that the system functioned properly. Then, the MBBR was filled with treated sewage for the seeding process.
Afterwards, the MBBR was continuously fed with treated wastewater at 24-h HRT, to minimize shock load and to avoid the wash-out of the initial bacteria. After three weeks, noticeable biofilm growth was observed. The MBBR was then sequentially operated at different HRTs (please refer to Table 2) by changing the HRT once a steady state had been obtained. Toet et al. [1] additionally evaluated the pollutant-removal performance of a surface-flow wetland system for polishing tertiary effluent from an STP at HRT of 0.3, 0.8, 2.3, and 9.3 days.
A fine diffuser was used for the MBBR aeration and mixing. The air was diffused from the bottom of the reactor at a constant aeration rate of 15 L/min at all stages in order to supply oxygen to the microbial mass to facilitate biological activity and mix the carriers. A dissolved oxygen (DO) meter probe (ODEON, Caudan, France) was utilized to periodically check the DO levels in the reactor. If necessary, the air flow rate was adjusted to maintain an adequate DO concentration, which was maintained at 5–7 mg/L to minimize adverse effects on nitrification, and the temperature was maintained at 27 °C to 30 °C.
2.3. Analytical Methods
After attaining a steady state, the sample matrix from the MBBR was tested for various physicochemical and microbiological parameters. This sample matrix was divided into two parts: the MBBR influent and the MBBR effluent. To maintain sampling consistency, the wastewater samples were taken from 10.00 a.m. to 11.00 a.m. on sampling days. All samples were collected in sterile 1000 mL polyethylene bottles, which had been soaked and cleaned prior to sampling.
The samples were then kept in ice storage and processed at the lab. The BOD5 samples were collected in black bottles. The analysis was carried out in the Environmental Laboratory of the Civil Engineering Department, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM). Most tests were carried out in triplicate and filtered through a 0.45 μm filter before testing, to reduce the effect of suspended solids on the measured values. Table 5 lists the parameters and methods used.

Table 5.
List of parameters and methods of analysis.
The analysed physicochemical parameters focused in this study were BOD5, COD, NH3-N, nitrate–nitrogen (NO3-N), pH, DO, TSS, and total phosphorus. The methods used for the analyses were the Standard Method for the Examination of Water and Wastewater from the American Public Health Association (APHA) [24], along with the HACH methods, as described by the Water Analysis Handbook [25].
The pH was continuously recorded using a pH probe (ODEON, Caudan, France), whereas for the temperature, an ODEON range open x model, temperature sensor probe with automatic temperature correction, was used. The DO in MBBR reactor was maintained above 2.0 mg/L throughout the study period using an ODEON range open x model, dissolved oxygen sensor. To determine the attached solids fixed in EMM carriers (include attached biomass), three pieces of the PE carriers were taken out of the reactor and kept in three separate beakers with milli-q water.
The beakers were inserted into an ultrasonic cleaner, POWER SONIC 405 (Hwashin Technology Co., Seoul, Korea) until the attached solids and biomass on the carriers were slugged off from the carriers. Then, the solution of biomass and milli-q water was filtered through a GFC Whatman’s 0.45 μm filter paper. The retained solid residue on the filter paper was dried by placing inside an oven at 105 °C for 1 h, followed by desiccation for 20 min, and finally weighted to calculate the mixed liquor suspended solid (MLSS). The main details of the cadmium reduction method (spectrophotometer HACH DR 6000, Method 8039) and spectrophotometry measurement is that 10 mL of the sample was used. The reagent was NitraVer 5 Nitrate Reagent Powder Pillow.
For the microbiological parameters, the coliform-forming analysis was conducted on the effluent and influent of MBBR as a requirement for the water quality assessment (please refer to Table 5). Aside from that, the identification of bacterial communities inside the MBBR was additionally performed by extracting the biofilm attached on the selected 3-D EMM, and the samples were then sent to the external molecular laboratory to run the 16S rRNA gene sequencing analysis. Biofilm thickness and the morphology of the biofilm attached to the 3-D EMM were also investigated via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) at the SEM Laboratory, UKM.
The 3-D EMM was randomly selected from the reactor at each phase of the study. For sample preparation, the 3-D EMM was cut without detaching the biofilm from the medium itself, to enable the visualization of all sections of the media and the respective attached biofilm. Images were captured at random locations on the biofilm medium, and a minimum of 20 thickness measurements total—per medium—were acquired and analyzed for each experimental phase.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Monitoring of Basic Parameters
The influent and effluent temperature for the MBBR polishing system ranged between 27.6 °C to 34.7 °C. These temperature values were within the optimal biodegradation temperature, which generally ranges from 20 °C to 35 °C [26,27]. The pH value for the MBBR effluent during subsequent HRT operations ranged between 6.8 and 8.1, which corresponded with the typical values of pH in the wastewater, 6.5 to 8.5 [28]. The aeration process inside the MBBR was kept above 2.0 mg/L throughout operation in order to ensure that the MBBR was fully functioning for nitrification. The DO readings decreased from 8.47 mg/L during 24-h HRT to 3.0 mg/L (2-h HRT) due to the microorganisms’ growth inside the biofilms attached on the media.
3.2. Effect of HRT on Removal Efficiency
3.2.1. TSS Removal
The concentration of total suspended solids (TSS) is one of the most important parameters for evaluating pollution in wastewater treatment systems, especially when no secondary clarifiers are installed. In this experiment, the storage tank constructed from a perforated polyethylene buffer running vertically from the top to the reactor floor also worked as a primary sedimentation tank, even though the treated wastewater from STP was also previously clarified before undergoing the MBBR process in the reactor. The bottom section of the buffer was perforated, to keep media out of the reactor outlet and maintain a less-turbulent region for the physical settling of residual suspended solids via gravitational force, as well as to allow for only the effluent to flow out. The average TSS effluent over the study course was 10.1 mg/L. No sludge was discharged from the MBBR throughout the experimental period. In all cases of HRT, the TSS effluent concentration was always less than that of the influent concentration.
The behavior of TSS concentrations gradually reduced with increasing HRTs, because the long time provided the particle a chance to settle and get attached on the EMM surfaces. The results demonstrated that the optimum condition of retention time ranges between 6 and 24 h for obtaining the greatest removal efficiency of TSS. High TSS removal efficiency was observed in the MBBR with effluent concentrations less than 3 mg/L at 24-h HRT. The average MBBR effluent TSS over the course of the study was 10.1 mg/L (SD = 8.3, N = 57), and the maximum reduction efficiency was 84.91%. In general, the TSS concentration gradually reduced with increasing HRT, because the long amount of time provided the particles the chance to settle and attach to the 3-D EMM surface.
3.2.2. Organic Pollutants Removal
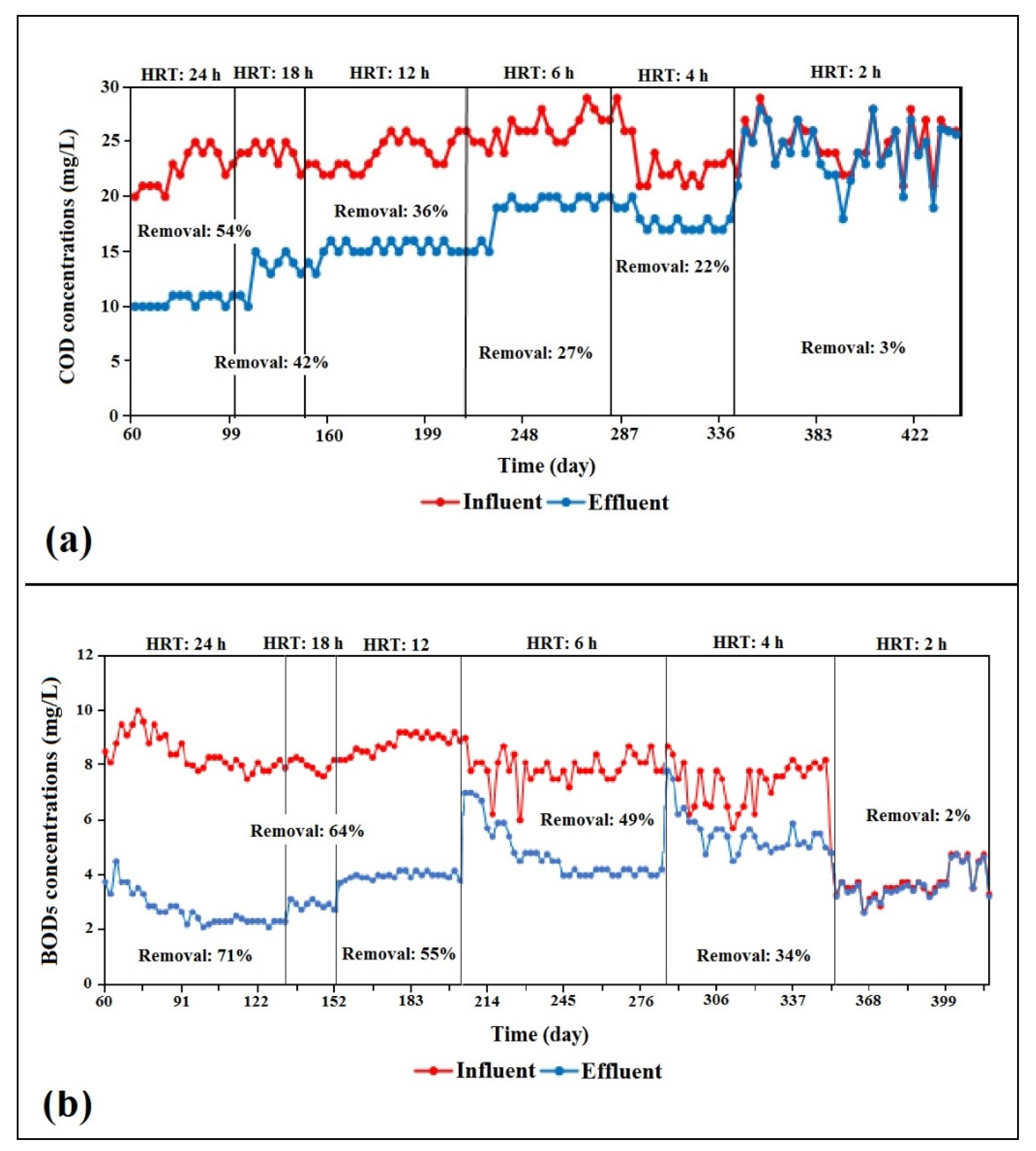
The MBBR polishing system showed sufficient organic-pollutant removal, with both COD and BOD5 presenting the highest removal efficiency, of 54% and 71%, respectively, during the 24-h HRT (please refer to Figure 3). According to a recent study by Gulhane and Kotangale [19]—who employed the MBBR system to remove BOD5, COD, and total solids from wastewater with 24-h HRT—their system demonstrated a minimum BOD5 removal efficiency of 75.48% (average 78.2 ± 1.95%), which appeared to be comparable to the current study results.
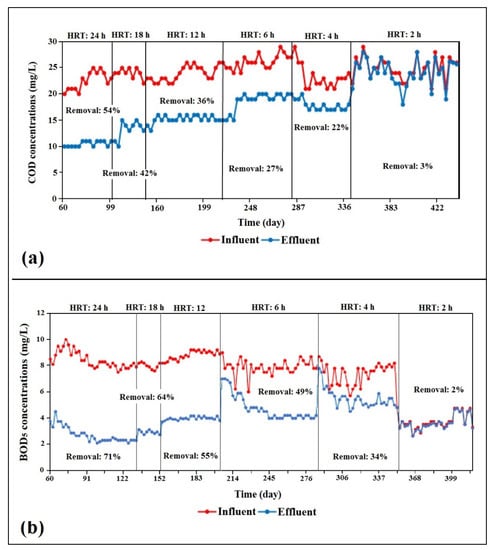
Figure 3.
(a) Chemical oxygen demand (COD) and (b) 5-day biological oxygen demand (BOD5) values throughout the MBBR polishing system operation.
Other than wastewater treatment, the MBBR system used in a river-purification treatment plant performed by Sidek et al. [21] also showed similar results, with a BOD5 removal efficiency of 68% during 24-h HRT. These findings showed that the MBBR system is generally capable of treating water and wastewater with high or low concentration of organic pollutants, with more than 50% removal efficiency within 24 h. However, the subsequent operations with lower HRTs displayed constant decreases in removal efficiency for both COD and BOD5 as the influent’s flow rate was being increased (see Figure 3).
It became too apparent during 2-h HRT, when the removal efficiency was only 2% due to the hydraulic overload. When the reactor was operated at a high flow rate (short retention time), the water flow or movement in the reactor led to a high water velocity in the reactor and a short duration of contact between the organic matter, along with less time for biofilm formation [28,29]. Consequently, the organisms’ ability to oxidize organic substances was reduced. The findings suggested that 50% BOD5 removal is 50% effective within 12 h.
3.2.3. Nutrients Removal
The concentration of nitrogen in the wastewater can be from low to high content, which requires an appropriate treatment process for its removal [17]. A bacteria known as Nitrosomonas converts NH3 and ammonium to nitrite (NO2). Next, a bacteria species called Nitrobacter complete the conversion of NO2 to nitrate (NO3). These types of bacteria—known as nitrifiers—must consume free DO in order to perform their work. Nitrification only occurs under aerobic conditions at DO levels of 2.0 mg/L or more.
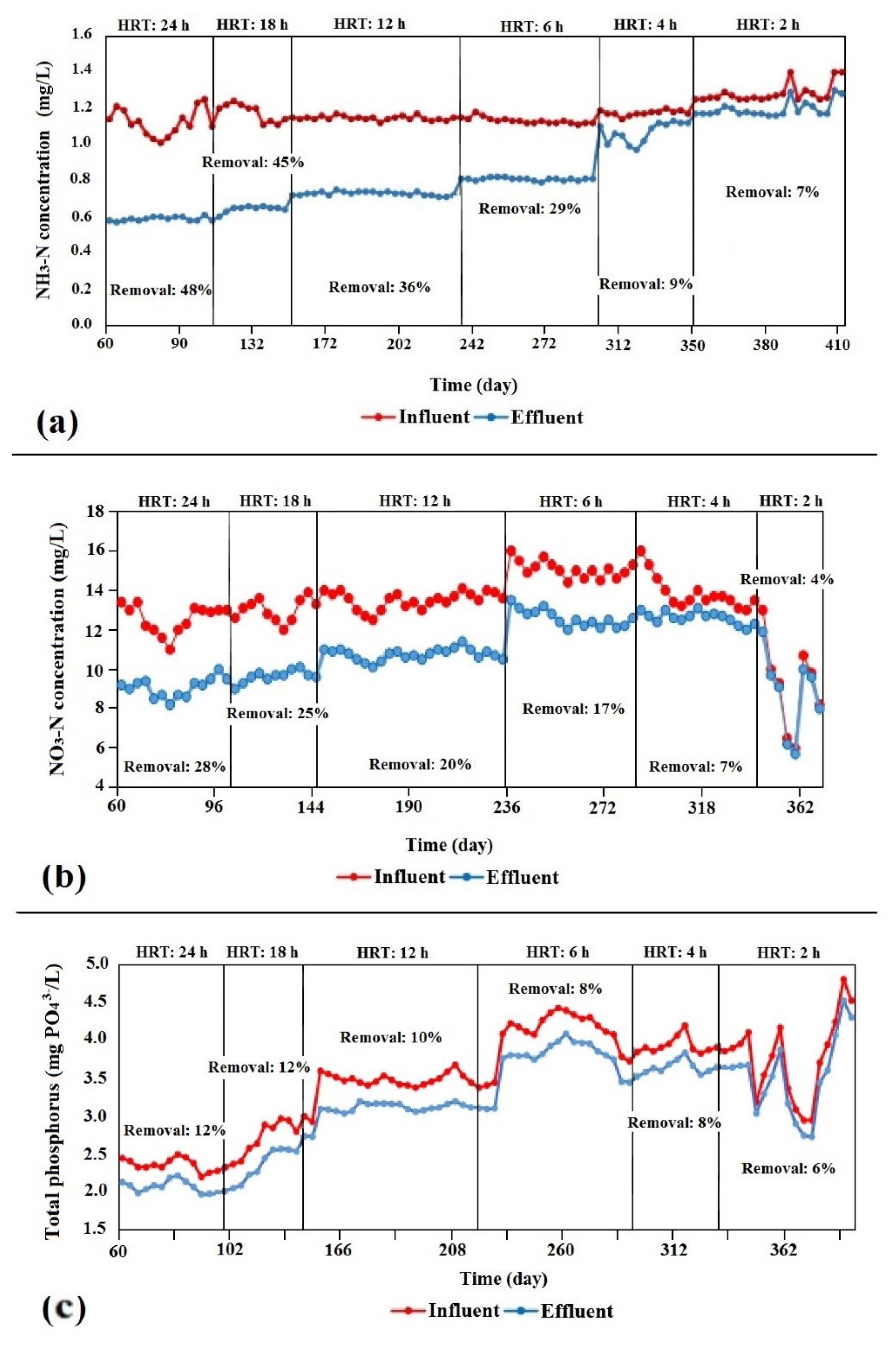
The two-step nitrification conversion process requires sufficient time to occur. The growth of the nitrifying bacteria (autotrophic) is much slower than the growth of denitrifying bacteria (heterotrophic) [30]. The MBBR in this study showed low NH3-N removal efficiency at 4-h and 2-h HRTs (please refer to Figure 4a). The reason for this could be that, in low HRT, the nitrifying bacteria do not receive sufficient time to accomplish nitrification.
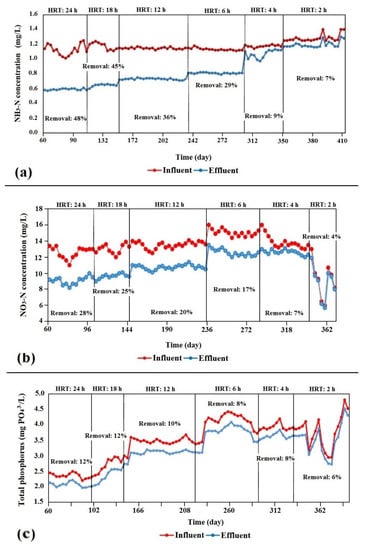
Figure 4.
(a) Ammonia–nitrogen (NH3-N), (b) nitrate–nitrogen (NO3-N), and (c) total phosphorus values throughout the MBBR polishing system operation.
Kutty et al. [31] said that, to encourage nitrification, the reactor must operate at a high retention time for the nitrifiers to grow. Therefore, the MBBR showed higher NH3-N removal efficiency at a high HRT (i.e., 24 h), which was 47% on average. Moreover, at a low HRT, Nitrosomonas had insufficient time to accomplish nitrification. Water temperature also affects the nitrification rate. The MBBR polishing system ran at temperatures ranging from 30–35 °C, as previous studies have recorded this range as being the optimum temperature for nitrification [32,33].
Hasan et al. [34] used a biologically-aerated filter (BAF) system for drinking water treatment and achieved a removal efficiency of 40% at 24-h HRT and a NH3 loading rate of 0.04 kg/m3·d. The current study results are a bit higher in comparison, with NH3-N removal performance of 47% at 24-h HRT. Thus, the MBBR has satisfactory NH3-N removal efficiency and stability compared to BAF.
The denitrification process is a conversion of NO3 to nitrogen gas that is carried out by facultative heterotrophic bacteria, which obtains oxygen by taking DO out of the water or by otherwise taking it out of NO3 molecules. In general, the gradual decrease in NH3-N concentrations also correlated to an increase in NO3 concentrations. The sudden reduction in the NH3-N concentrations during the 4 h retention time corresponded with a jump in NO3 concentration (please refer Figure 4a,b).
Treated wastewater contains a significant nutrient load, particularly in regard to nitrogen and phosphorus. Using treated wastewater for irrigation could reduce the amount of commercial fertilizer for gardens and lawns. Phosphorus is mainly produced from chemical products, particularly powdered soap. The MBBR polishing system demonstrated low total-phosphorus removal efficiency, with a maximum removal efficiency of 12% recorded at 24-h HRT (please refer to Figure 4c). This finding was supported by a study conducted by Kim et al. [35], who investigated the effect of MBBR at 8 h of HRT on phosphate ion (PO43−) removal and found only 9% removal effectiveness at 0.6 days of HRT.
3.2.4. Fecal Coliforms Removal
The microbial quality of greywater is measured from the presence of fecal coliforms (thermotolerant coliforms) such as E. coli, which also indicates the presence of pathogens such as Salmonella sp., Shigella sp., Giardia lamblia Cryptosporidium parvum, and enteric viruses [36]. Graywater can contain at least 104/100 mL of potentially pathogenic microorganisms [37]. The number of thermotolerant coliforms increases with increased storage time.
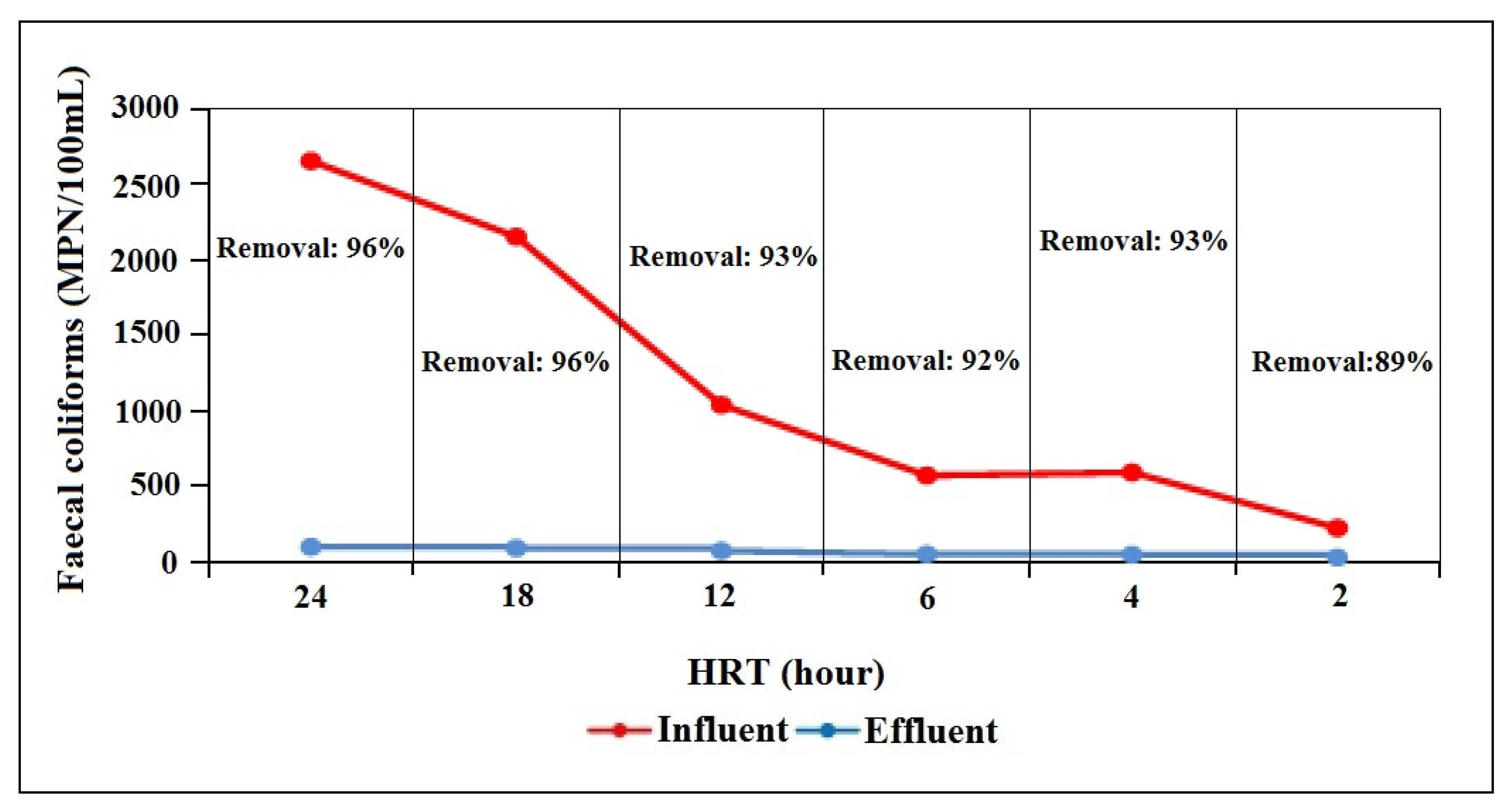
The coliforms have been found to multiply by 10 to 100 times during the first 24 to 48 h of storage. Therefore, graywater must not be stored in order to prevent it from reaching anaerobic conditions [38]. Figure 5 supports this theory, as the MBBR influent water contained fecal coliform concentrations that were substantially greater as HRT increased. However, the percentage of fecal-coliform-removal efficiency exhibited by the MBBR polishing system ranged from between 89% to 96%, and the highest removal efficiency occurred during 24-h and 18-h HRT.
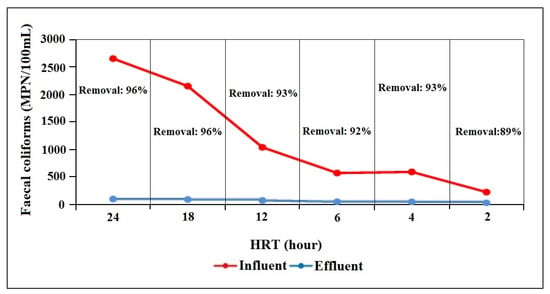
Figure 5.
Fecal coliform concentration in treated wastewater before and after being subjected to the MBBR polishing system.
3.3. Bacterial Morphology and Community
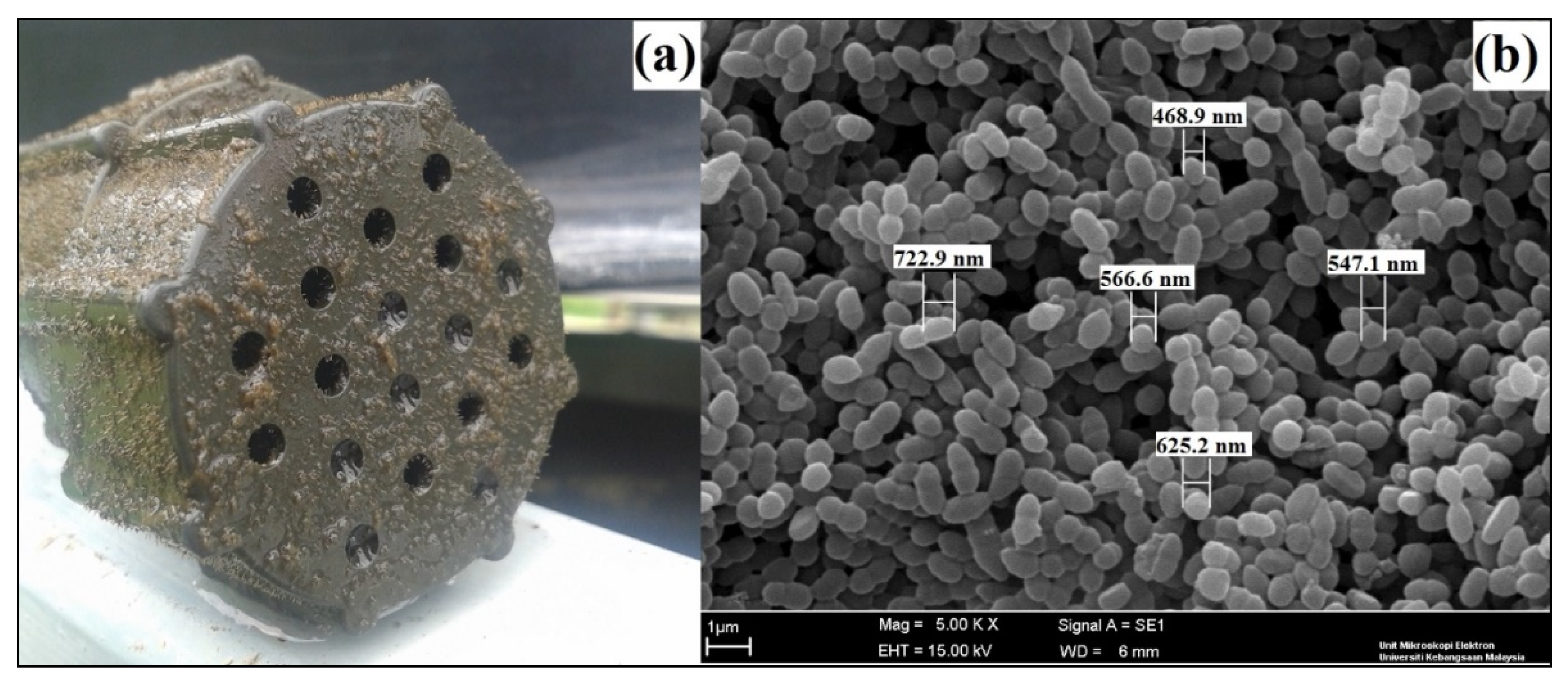
A key property that is believed to influence the community structure and function of biofilms is thickness. Here, in the MBBR polishing system, during subsequent HRT operations, biofilms with different thicknesses were grown in a single reactor and subjected to similar external conditions. The biofilm biomass can increase or decrease over time, until the growth rate is balanced by the decay rate and the shear loss rate [39]. Since biofilm density is assumed to be constant, the biofilm volume and thickness must increase over time as the biofilm grows. Figure 6a demonstrates a uniformly thin biofilm and an unsmooth biofilm surface on the surface of 3-D EMM. Both thick and thin ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOBs) achieved high-rate performance in terms of acetonitrile removal [40].
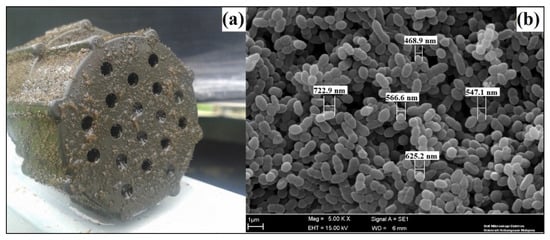
Figure 6.
The 3-D EMM from the MBBR displayed (a) uniformly thick biofilm on its surface, and (b) the thickness of the attached bacteria on its biofilm was measured using scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
To maintain effective gas and nutrient transfer, the ideal biofilm should be relatively thin and evenly distributed over the carrier surface [41]. The thickness of the biofilm formed on the media should be in the range of effective biofilm thickness (the depth of the biofilm to which the substrates have penetrated) [42]. Throughout the experiments under different HRTs, the SEM images of biofilm morphology did not display any notable changes. During each phase of the study, a carrier was randomly selected from the reactor for the sample preparation. Due to its large size, the 3-D EMM was cut without detaching the biofilm from the carrier itself in order to enable thickness measurements.
Figure 6b illustrates the measured bacteria thickness, with its value around 0.5 μm. These layers of bacteria were shaped into biofilm, which was attached onto the surface of EMM. For this study, the biofilm thickness measured was 102.6 μm, 107.8 μm, 135.4 μm, 178.5 μm, 212.6 μm, and 297.1 μm at 24-h, 18-h, 12-h, 6-h, 4-h, and 2-h HRT, respectively. The results showed that the biofilm was slowly generated at 24-h HRT after 2 months since the reactor startup. However, the biofilm at 2-h HRT was significantly thicker than the biofilm at 24-h HRT was. These SEM images showed phylotypes with different morphologies, such as cocci (round shape) and bacilli (rod shape), as well as filamentous bacteria and extracellular polymeric substances layers, which formed the basis of the attached biomass [43].
This is because a lower HRT resulted in a high flow rate that increased the biofilm’s contact with the substrate, enabling rapid biofilm growth. At 2-h HRT, the maximum layers of bacteria were observed due to the maximum amount of biofilm produced. Additionally during this time, the biofilm slough-off increased, thus adding to the amount of suspended biomass—indicated as the MLSS—inside the MBBR.
No difference was observed in the biomass morphology for every HRT, but this was not so for the biofilm thickness. However, the amount of biomass at steady state was greater than that at the beginning of the HRT period. Biofilm communities from the MBBR showed limited bacterial diversity, because the MBBR influent had already been treated, and was then categorized as tertiary wastewater treatment plant effluent.
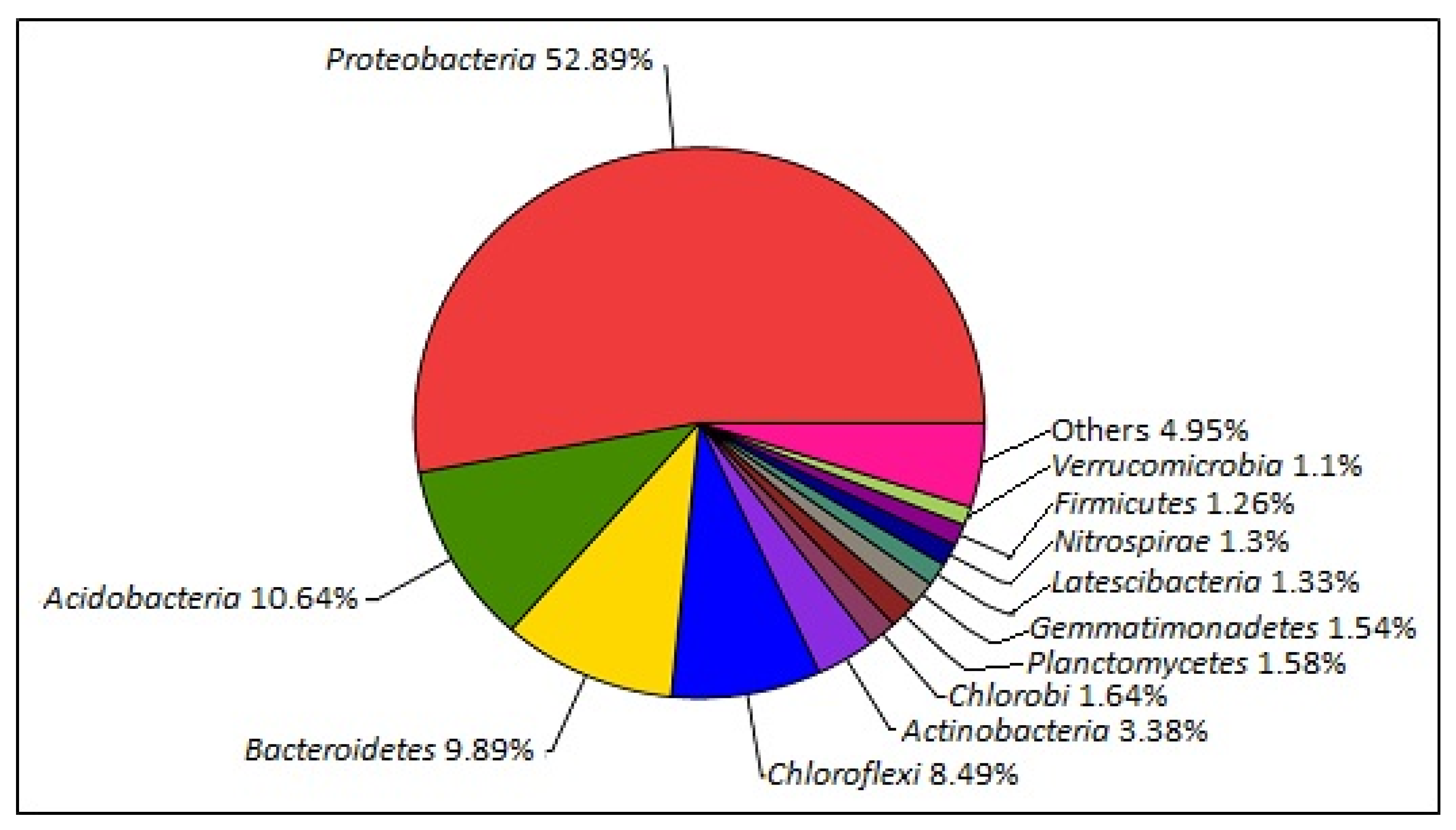
The sequencing result of the 16S rRNA gene-based analysis of the 3-D EMM samples showed only 389 ± 32 operational taxonomic units. The most abundant phylum in the sample was Proteobacteria, with a relative abundance of 52.89%, represented mainly by the families Bradyrhizobiaceae and Rhodoplanes. This was followed by Acidobacteria and Bacteroidetes, with an abundance percentage of 10.6% and 9.9%, respectively (please refer to Figure 7). The composition analysis of the sample’s micro biota at the phylum level has been presented in Table 6.
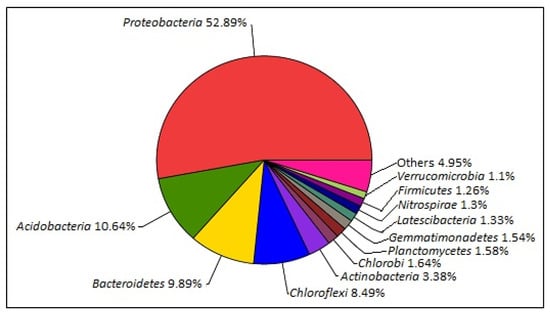
Figure 7.
Relative abundance value at the phylum level for the analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequencing.

Table 6.
The phylum’s reads for samples collected from 3-D EMM.
Most of the phyla were shown to have come from anaerobic or facultative (aerobic and anaerobic) bacteria groups. This was because the feed used as MBBR influent was taken from the clarifier of anaerobic STP (please refer to Section 2.1.3). MBBR is effective at being used as a polishing system due to the abundance of aerobic, anaerobic, and facultative bacteria in the same vessel at the same time.
3.4. Compliance for Raw Water Resource
In this study, the treated wastewater (influent), which was used as the feed for the MBBR polishing system, came from the clarifier of the aerobic STP. The characteristics of the influent showed lower values of parameters than Standard A of the Malaysia Sewage Discharge (please refer to Table 1) standard, indicating it is safe to be discharged into any inland waters within catchment areas [4]. However, this influent could not be reused directly due to its characteristics falling into Class V of the NWQS of Malaysia (please refer to Table 1), thus classifying it as not suitable and with low beneficial usage as a water supply [43].
Hence, the MBBR polishing system was fabricated in order to further treat this Standard A-compliant wastewater so that it could at least be reused as non-potable water instead (for example, toilet flushing and irrigation for parks and landscapes for domestic use or as cooling water for industrial use). The characteristics of MBBR effluent during 24-h HRT as listed in Table 7 were compared to the classes of the NWQS, and it was shown that the effluent fell under Class III, which requires the effluent to be treated extensively prior to being supplied as potable water [4,43].

Table 7.
Comparison of parameter values between MBBR effluents during 24-h HRT, Standard A of the Malaysia Sewage Discharge standard and classes of the National Water Quality Standard (NWQS) for Malaysia [4,5]
From the comparisons of all the parameters listed in Table 7 between MBBR effluents during 24-h HRT, Standard A of the Malaysia Sewage Discharge and classes of the NWQS for Malaysia [4,5], only NH3 concentration in the treated effluent exceeds the stipulated value for Category IIA. The value at 24-h HRT is almost comparable with the effluent from the covered lagoon treatment process alone, which contains less than 10 mg/L of NH3-N [13,44].
In this study, the bulk media volume to reactor volume is only 5%, which will affect the SRT values and will then affect the removal of ammonia nitrogen. A comparative study to explore the characteristics of partially and fully packed biological aerated filters (BAFs) in the removal of carbon pollutants reveals that the partial-bed reactor can perform comparably well with that of the full-bed reactor, with an organic removal rate of 5.34 kg COD m−3d−1 for organic loading rate (OLR) of 5.80 ± 0.31 kg COD m−3d−1 for the full-bed and 5.22 kg COD m−3d−1 at OLR 5.79 ± 0.29 kg COD m−3d−1 for the partial-bed (half of the reactor) [39].
The SRTs of the partial-bed, however, were always lower than those in the full-bed, where the SRT was reduced from 20.08 days at OLR 4.18+/−0.20 kg COD m−3d−1 to 7.62 days at OLR 5.80+/−0.31 kg COD m−3d−1 in the full-bed and from 7.17 days to 4.21 days in the partial-bed [39]. As autotrophic nitrifiers grow very slowly, a long SRT is needed in order to maintain a certain amount of nitrifiers and ensure effective nitrification, as well as affect the removal of ammonia in this study.
Aside from 24-h HRT, the effluents discharged from MBBR during 18-h, 12-h, and 6-h HRTs also showed characteristics that were compliant with Class III of the NWQS. The MBBR effluent during 24-h HRT fell under Class IIA of the NWQS for Malaysia, except for the parameter on NH3-N. The volume of biofilm media could be increased so as to provide more space for biofilm, while at the same time, the solids retention time (SRT) of the system increased. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria favors high SRT, so higher removal efficiency of ammonia can be obtained.
However, based on the removal efficiency of most parameters listed, 24-h HRT displayed the highest removal percentage compared with those of other subsequent HRTs. Thus, it is recommended that 24-h HRT effluent be reused as non-potable water or potable water after further treatment. The polishing process of treated wastewater for water reuse could help in cutting the usage of clean water supply other than supporting zero discharge for a more sustainable lifestyle.
4. Conclusions
The monitoring undertaken at the MBBR polishing system indicated that it showed the highest removal efficiency of organic pollutants and nutrients during 24-h HRT, with COD, BOD5, NH3-N, NO3-N, total phosphorus, and fecal coliform removal percentages of 54%, 71%, 48%, 28%, 12%, and 96%, respectively. The findings on biofilm morphology using SEM displayed a constant increase of the biofilm thickness, as the HRT was subsequently shortened. The bacterial community on the 3-D EMM was identified using 16S rRNA gene-sequencing, which exhibited a majority of 52.89%, of the phylum Proteobacteria, as the main bacteria residing inside the reactor. The MBBR effluent during 24-h HRT fell under Class IIA of the NWQS for Malaysia, which requires only conventional treatment prior to being used as potable water but could be reused directly as non-potable water. MBBR is a highly modular system and can be used either for high concentrations of organic loading or for very low concentrations, as for polishing. With a compact design and small footprint, it can be placed in any wastewater treatment plant to ensure that the water that comes out meets local standards. For the continuity of this MBBR polishing technology to be used for commercial applications, techno-economic analysis and research on a larger scale must be carried out.
Author Contributions
Project administration (J.A.K.); writing & editing (F.S.); validation (S.K.P. & A.Y.); investigation (R.A.R.); formal analysis (H.A.H.). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Ministry of Higher Education (LRGS MRUN/F2/01/2019/3).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research was partially supported by the Ministry of Higher Education with grant number LRGS MRUN/F2/01/2019/3.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Toet, S.; Van Logtestijn, R.S.P.; Kampf, R.; Schhreijer, M.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. The effect of hydraulic retention time on the removal of pollutants from sewage treatment plant effluent in a surface-flow wetland system. Wetlands 2005, 25, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Fit-for-purpose urban wastewater reuse: Analysis of issues and available technologies for sustainable multiple barrier approaches. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 1619–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Environment Malaysia. Environmental Quality Act 1974: Environmental Quality (Sewage) Regulations; Department of Environment Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2009. Available online: https://www.doe.gov.my/portalv1/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/Environmental_Quality_Sewage_Regulations_2009__P.U.A_432-2009.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Department of Environment Malaysia. National Water Quality Standards for Malaysia. Malaysia. 2009. Available online: https://www.doe.gov.my/portalv1/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Standard-Kualiti-Air-Kebangsaan.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Chaillou, K.; Gerente, C.; Andres, Y.; Wolbert, D. Bathroom greywater characterization and potential treatment for reuse. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 215, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwakeel, K.Z.; El-Liethy, M.A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Ezzat, S.M.; Kamel, M.M. Facile synthesis of magnetic disinfectant immobilized with silver ions for water pathogenic microorganism’s deactivation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22797–22809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Mainardis, M.; Aneggi, E.; Weavers, L.K.; Goi, D. Combined ultrasound-ozone treatment for reutilization of primary effluent—A preliminary study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, F.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Eslami, H.; Ghaneian, M.T.; Fallahzadeh, H.; Talebi, P.; Fard, R.F.; Ebrahimi, A.A. Removal of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate and turbidity from greywater by a hybrid multi-layer slow sand filter microfiltration ultrafiltration system. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, A.; Liu, Y. Mechanisms and kinetics of greywater treatment using biologically active granular activated carbon. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 45–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; El-Liethy, M.A.; Elwakeel, K.Z.; Hasan, M.A.E.G.; Al Zanaty, A.M.; Kamel, M.M. Role of identified bacterial consortium in treatment of Quhafa Wastewater Treatment Plant influent in Fayuom, Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 192, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, K.; Taylor, M.W.; Turner, S.J. Successional development of biofilms in moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) systems treating municipal wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegaard, H.; Rusten, B.; Westrum, T. A new moving bed biofilm reactor-applications and results. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helness, H. Biological Phosphorus Removal in a Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi, A.; Dargahi, A.; Almasi, A. Biological removal of diazinon in a moving bed biofilm reactor—Process optimization with central composite design. Toxin Rev. 2019, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; He, Q.; Ibrahim, H. Review on moving bed biofilm processes. Pak. J. Nutr 2012, 11, 804–811. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, B.K.; Fatihah, S.; Shahrom, Z.; Ahmad, E. Biological aerated filters (BAFs) for carbon and nitrogen removal: A review. JESTEC 2012, 7, 428–446. [Google Scholar]
- Biase, A.D.; Kowalski, M.S.; Devlin, T.R.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A. Moving bed biofilm reactor technology in municipal wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulhane, M.L.; Kotangale, A.J. Hybrid Moving Bed Bio Film Reactor. In Proceedings of the 3rd IRF International Conference, Goa, India, 10 May 2014; pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zafarzadeh, A.; Bina, B.; Nikaeen, M.; Attar, H.M.; Hajian nejad, M. Performance of moving bed biofilm reactors for biological nitrogen compounds removal from wastewater by partial nitrification-denitrification. Process. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Sidek, L.M.; Mohiyaden, H.A.; Basri, H.; Salih, G.H.A.; Birima, A.H.; Ali, Z.; Sabri, A.F.M.; Noh, M.N.M. Experimental comparison between moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) and conventional activated sludge (CAS) for river purification treatment plant. Adv. Mat. Res. 2015, 1113, 806–811. [Google Scholar]
- Regmi, P.; Holgate, B.; Fredericks, D.; Miller, M.W. Optimization of a mainstream nitritation-denitritation process and anammox polishing. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H. An Evaluation of Biological Aerated Filtration for Wastewater Treatment through Pilot and Laboratory Scale Experiments. Master’s Thesis, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- HACH. Water Analysis Handbook, 5th ed.; Hach Company: Loveland, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, H. Biodegradation of petroleum oil achieved by bacteria and nematodes in contaminated water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, F.; Ma, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, G.; Lu, X. Influence of temperature on biogas production efficiency and microbial community in a two-phase anaerobic digestion system. Water 2019, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arij, Y.; Fatihah, S.; Rakmi, A.R.; Sarifah, Y. Optimization of operation conditions for the start-up of a pilot-scale anaerobic biofilm digester treating leachate. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 86, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosg, B. Process Monitoring in Biogas Plants; IEA Bioenergy: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Biplob, P.; Fatihah, S.; Shahrom, Z.; Ahmed, E. Monitoring and control of a partially packed biological aerated filter (BAF) reactor for improving nitrogen removal efficiency. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2011, 1, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, S.; Mohammed, N.; Som, S.; Dawam, A. Formulation of Nitrification, BOD and COD Kinetics in Compact Extended Aeration Reactor (CEAR). In Recent Advances in Urban Planning and Construction; Lee, K.C., Ed.; WSEAS Press: Athens, Greece, 2013; pp. 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaskar, K.V.; Charyulu, P.B.B.N. Effect of environmental factors on nitrifying bacteria isolated from the rhizosphere of Setaria italica (L.) Beauv. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 1145–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Luo, W.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L. Effects of temperature on the characteristics of nitrogen removal and microbial community in post solid-phase denitrification biofilter process. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassan, H.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Kofli, N.T.; Anuar, N. Kinetic evaluation of simultaneous COD, ammonia and manganese removal from drinking water using a biological aerated filter system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 130, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Chang, D.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, J.K.; Yeon, H.J.; Yeon, C.Y.; Fan, Y.; Lim, S.Y.; Hong, K.H. Wastewater treatment in moving bed biofilm reactor operated by flow reversal intermittent aeration system, WASET. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 5, 867–870. [Google Scholar]
- Hachich, E.M.; Bari, M.D.; Christ, A.P.G.; Lamparelli, C.C.; Ramos, S.S.; Sato, M.I.Z. Comparison of thermotolerant forms and Escherichia coli densities in freshwater bodies. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, K.-W.; Wang, C.-W.; Jiang, S.C. Quantitative microbial risk assessment of greywater on-site reuse. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Matos, C.; Silva-Alfonso, A. Health Issues and Security of Water Saving Systems. In Frontiers in Civil Engineering: Water Savings in Building; Ghisi, E., Ed.; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, UAE, 2017; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Fatihah, S.; Donnelly, T. Effect of full and partial-bed configuration on carbon removal performance of biological aerated filters. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatihah, S.; Donnelly, T. Spatial distribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in the biofilm and suspended growth biomass of the full- and partial-bed biological aerated filters. Can. J. Civil. Eng. 2009, 36, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusten, B.; Eikebrokk, B.; Ulgenes, Y.; Lygren, E. Design and operations of the Kaldnes moving bed bio film reactors. Aquacult. Eng. 2006, 34, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, K.; González-Martínez, A.; Montero-Puente, C.; Reboleiro-Rivas, P.; Poyatos, J.M.; Juárez-Jiménez, B.; Martínez-Toledo, M.V.; Rodelas, B. Bacterial community structure and enzyme activities in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) using pure oxygen as an aeration source. Biores. Tech. 2012, 103, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainuddin, Z. Benchmarking river water quality in Malaysia. JURUTERA 2010, 12, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Lemna Environmental Technologies Inc. Integrating Lagoon Technologies to Solve Every Treatment Challenge from Influent to Effluent. Available online: https://www.lemnatechnologies.com/ammonia-nitrogen-removal (accessed on 1 November 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).