Abstract
Fluoride (iF) is an inorganic element commonly present in groundwater in central Mexico and is considered a health risk when it exceeds the Mexican drinking water standard of 1.5 mg/L. Prolonged exposure to iF can cause various adverse health effects, such as dental fluorosis and neurological effects, particularly in children. A rapid and cost-effective strategy to identify possible areas where the resident population may be at risk of exposure to this contaminant is the health risk estimation methodology of the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO). The aim of this study was to estimate the environmental risk of iF exposure in residents of Jerez, Zacatecas, Mexico, and subsequently construct risk maps to identify areas of the city where there is a higher risk of exposure. Fifty-five tap water samples were collected from households to determine iF concentrations using the ion-selective electrode method. Based on these environmental values, the hazard quotient (HQ) was estimated following the health risk estimation methodology. Subsequently, risk maps were generated from these values to visualize the spatial distribution of high-risk areas within the city. The iF concentrations in tap water ranged from 1.3 to 7.3 mg/L (ppm), with only one sample below the standard of 1.5 mg/L. We estimated HQ values ranging from 0.63 to 3.73. Exposure to iF in tap water is a health problem that must be addressed, necessitating risk communication actions that enable the population to safeguard its health through simple measures, thereby avoiding future health costs.
1. Introduction
Access to water of adequate quality and quantity for the entire population is an inalienable human right, which is essential for human development and health care. In Mexico, efforts have been made to ensure that the majority of households have access to piped water. In the central state of Zacatecas, 94.4% of households are reported to have access to piped water [1] while in the city of Jerez, 93.2% of households are reported to have such access [2]. It is important to note that the quality of the water that reaches homes through the supply system remains constant under routine operating conditions; however, it has been reported that when wells are overused or during dry periods, water is drawn from lower levels of the wells, causing an increase in the concentration of toxic compounds.
Fluorine (iF) is an inorganic compound abundantly found in the Earth’s crust. It typically occurs in groundwater as a fluoride ion, which leaches from minerals such as fluorite and apatite when in contact with rocks. The maximum allowable concentration of fluoride in drinking water, adopted by many countries including Mexico, is based on the WHO guideline of 1.5 mg/L [3]. This standard is established due to the association of fluoride exposure with dental fluorosis at doses as low as 0.06 mg/kg/day [4]. Additionally, fluoride exposure has been linked to endocrine and neurological effects, as well as skeletal fluorosis [5,6,7,8,9].
iF has high bioavailability, which is why the consumption of water with this element is a cause of concern for public health, especially considering the vulnerability of the child population and pregnant women [10,11,12]. In areas where there are high concentrations of iF in the tap water, there is a high prevalence of dental fluorosis [13,14]. In Mexico, 3.05 million people are exposed to fluoride in water [10]. This is a historical problem in the state of Zacatecas [10,15], where it is estimated that approximately 22% of the population is at risk of suffering health effects from exposure to iF [16].
The availability of a tool for identifying geographical regions with increased risk enables decision-makers to optimize resource allocation and improve public health. Thus, the aim of this study is to highlight areas requiring intervention due to elevated fluoride concentrations in water intended for human consumption, employing risk maps as an analytical tool. The geospatial risk information generated in this study is a novel visual tool that can be very useful in decision making, since there is a lack of information that is available and usable for the population.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
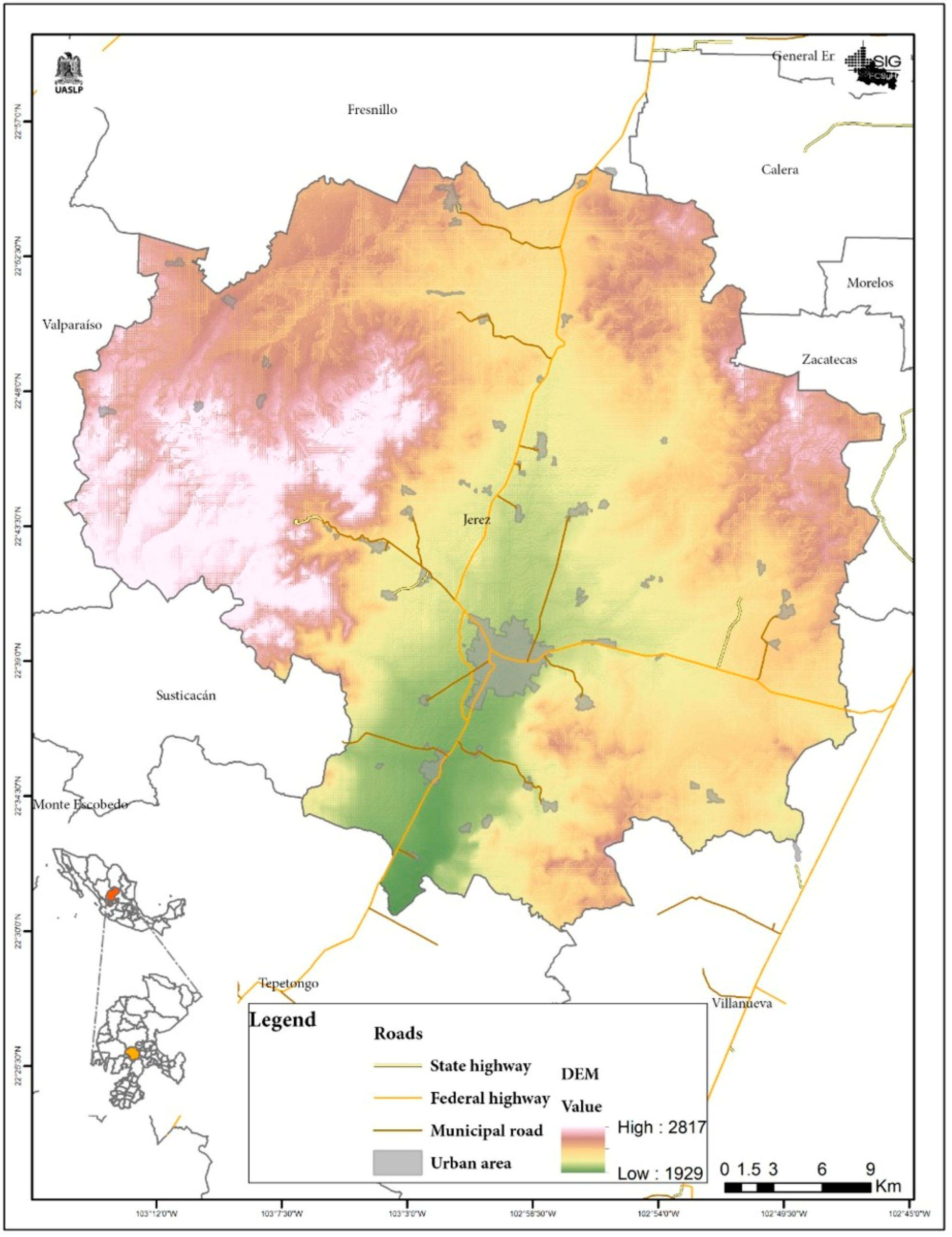
The municipality of Jerez is located in the Central Region of the State of Zacatecas, with an average elevation of 2027 m above sea level. It borders to the north with the municipalities of Fresnillo and Calera, to the south with Villanueva and Tepetongo, to the east with Zacatecas, and to the west with Valparaiso and Susticacan, approximately 50 km from the state capital: see Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Location of the municipality of Jerez de Garcia Salinas, Zacatecas, Mexico.
Jerez has a population of 43,046 inhabitants, representing slightly over 74% of the total municipality, and it largey ily concentrates economic activity. Traditionally, it is a city where tourism holds significant economic value, leading to its designation as a “Pueblo Magico”, granting access to specially allocated economic resources. However, its residents persist in primary economic activities such as livestock farming and agriculture, making it a region conducive to the production of apples and peaches [17].
2.2. Physiography and Geology
The city is located, according to the physiographic regionalization of the National Institute of Statistics and Geography [1], in the Sierra Madre Occidental Province, Sub-province of Zacatecan Sierras and Valleys. These are characterized by their high mountain ranges, with elevations ranging from 2300 to 2700 m above sea level. According to the Köppen classification, the climate is semi-arid temperate BS1kw, with an annual mean temperature varying between 18 and 22 °C. The mean temperature of the coldest month is below 18 °C, with cool winters and a summer rainfall regime. Winter precipitation accounts for between 5 and 10.2 percent of the total precipitation. The rainy season typically features two periods of occurrence: one in summer from June to September, when peak values are recorded, and another of winter rains from November to February, with less significant precipitation mainly due to cold fronts affecting the region. The dry season spans from March to May.
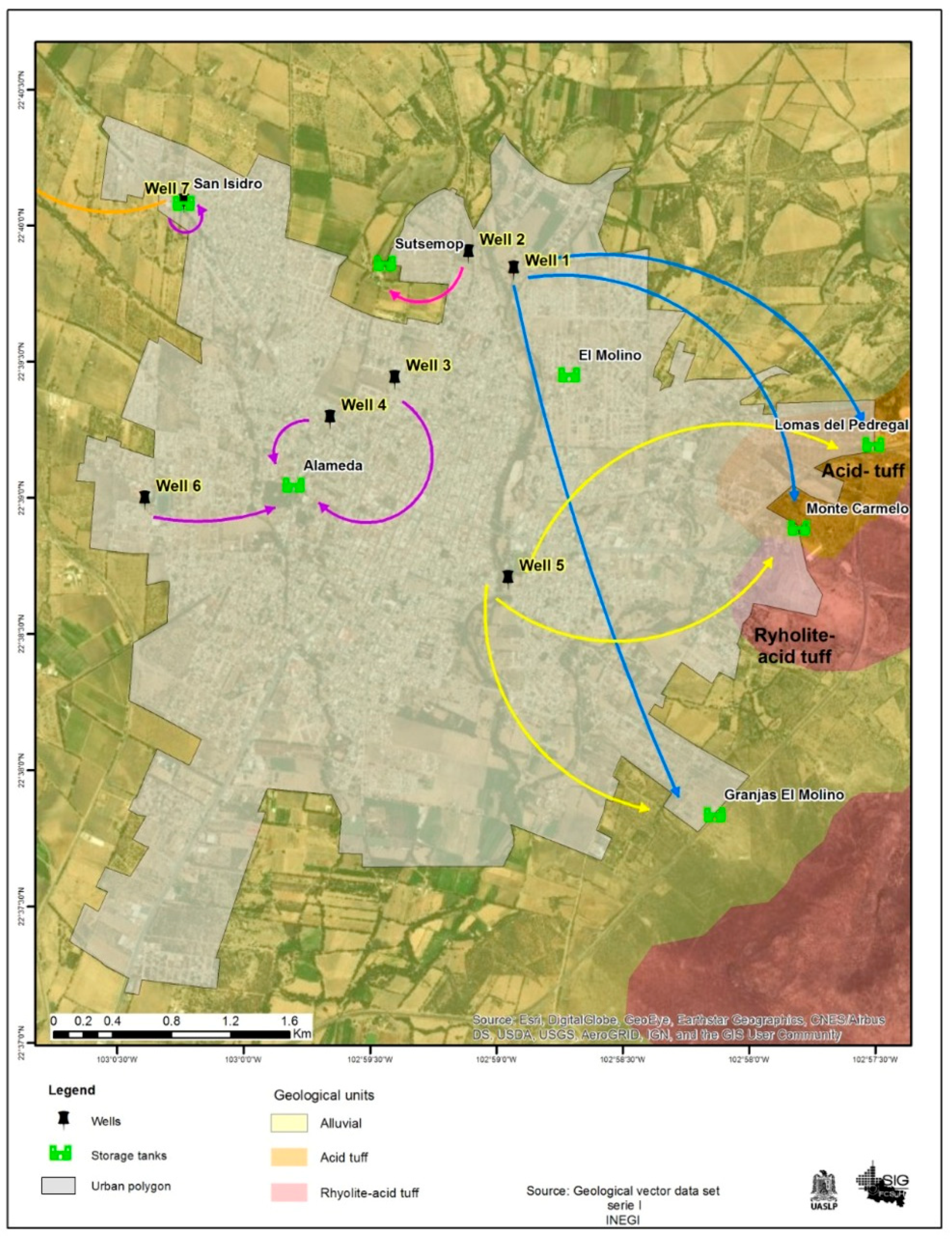
The most significant superficial water in the area is the Jerez River, a tributary of the Colotlan River, which converges into the Grande de Santiago River. Jerez is part of a broad valley floor with some nearby hills. Its stratigraphy is represented by lithostratigraphic units of volcanic sedimentary origin with regional low-grade metamorphism (green schist facies), sequences of calcareous-clayey and sandy-clayey rocks, intermediate and acidic, with ages ranging from the upper Triassic to the quaternary. Within the area, there are seven active wells with two pumping systems and eight elevated tanks: Figure 2 shows the city map with the ubication of wells.
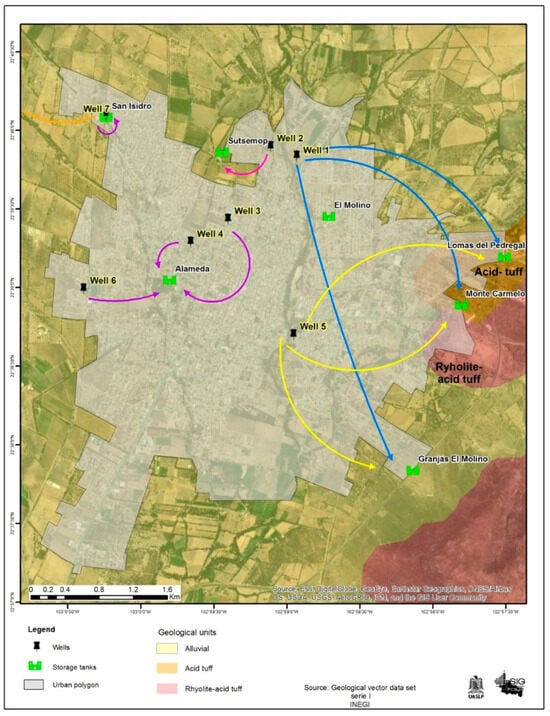
Figure 2.
Stratigraphy with extraction points, pumping systems, and elevated water tanks.
According to Nuñez et al. [18] in their study of the hydrogeochemical characteristics and quality of the Jerez aquifer, specifically focusing on wells in the municipal seat city (see Table 1), it can be stated that the origin of the groundwater corresponds to water families circulating through fractured volcaniclastic rocks at depths exceeding 300 m. This suggests that the behavior of ions such as Na+, Li+, As+, and F− results from an interaction between groundwater and the vitreous mesostasis of volcaniclastic rocks, leading to their devitrification. This process involves an exchange of hydrogen ions from the solution primarily for Na+ and Li+, with a concentration of Li observed to correlate with those of F−. These ions are considered to originate from a regional flow system.

Table 1.
Wells of supply system of the city of Jerez.
2.3. Sampling
A cluster sampling method was employed by overlaying a grid on the city map, resulting in a total of 36 squares each 1 km2. Only 14 squares, where the highest population density was concentrated, were considered. In each of the selected quadrants, 5 water samples were taken from different households, recording the geolocation of each one using a Garmin™ eTrex 20 GPS locator (Olathe, KC, USA), as well as the elevation above sea level. Full sampling data are in Supplementary Materials.
Tap water samplers were provided directly by the residents of the households, who were instructed to follow the protocol and were given appropriate containers according to the Mexican standard NOM-230-SSA1-2002 [19]. The standard requires a one-liter water sample to be collected from the tap after letting the water flow for at least 30 s.
The sample was stored in an amber plastic bottle with a capacity of one liter. The samples were kept at a temperature below 5 degrees Celsius during transportation and were refrigerated until analysis. The pH of each sample was measured at the time of collection using an portable pH detector (Thermo Scientific Orion™, Waltham, MA, USA). The time between sampling and the fluoride analysis did not exceed 24 h.
2.4. Determination of Fluorides in Tap Water
Fluoride levels were determined using the ion-selective electrode method described in the Mexican standard NMX-AA-077-SCFE-2001 [20]. A ISE meter with the 9609BNWP fluoride electrode combinate was used to determine the fluoride in the water (Thermo Scientific Orion™, Waltham, MA, USA). The electrode response follows the Nernst equation. Direct calibration was used, and a series of solutions ranging from 0.5 to 8 ppm were prepared from a 100-ppm standard solution (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) to construct a calibration curve. These solutions were mixed with TISAB (Sigma Aldrich, USA) ionic strength adjuster solution in a 1:1 ratio. This solution adjusts the pH and facilitates the formation of metal complexes with ions that could interfere with the measurement [21].
Three aliquots (50 mL each) of each water sample were taken, and 50 mL of TISAB™ was added to each aliquot. Measurements of both standards and samples were conducted by immersing the ion-selective electrode in the solutions with continuous stirring for 3 min; the electrode was rinsed with deionized water and carefully dried between each measurement and the final reading (mV) was recorded. The electrode potentials of standard solutions were plotted on the linear axis against their concentrations on the log axis.
As a quality control, it was monitored that the slope of the calibration curve was between −54 to −60 mV as an indicator of the proper functioning of the electrode. Precision was assessed by determining the coefficient of variation of the repeated measurements for each triplicate standard, which should have been less than 15%. Accuracy was evaluated by determining the concentration of the certified fluoride standard (CLINICHECK II™ IRIS Technologies International GmbH, Papillion, NE, USA). All the standards were at the same temperature as the samples, i.e., between 20 and 25 °C.
2.5. Environmental Health Risk Estimation
To estimate the environmental health risk from fluoride exposure in tap water, the PAHO method [22] was used, which allows for the estimation of health risks based on environmental contaminant concentrations. This method is designed for application in regions with limited resources for conducting population biomonitoring. Health risk estimation is a valuable tool for generating information that enables the rapid and cost-effective identification and classification of areas requiring urgent attention.
The steps followed to estimate the environmental risk are as follows: conduct a dose-response analysis by searching for reference values for health effects due to oral exposure to fluoride in the literature; then, estimate the population exposure and the risk quotient as detailed below. These estimations were performed for the pediatric population due to its significant vulnerability window, and allow for rapid and cost-effective results.
2.6. Dose–Response Analysis
Several reference values are available for fluorides that are useful for estimating environmental risks. However, due to insufficient evidence supporting their carcinogenic effects, only non-carcinogenic risk can be estimated. The No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) is 0.06 mg/kg/day; the Low Observed Adverse Effect Level LOAEL is 0.12 mg/kg/day and the reference dose is 0.06 mg/kg/day, calculated for the critical effect of dental fluorosis. The Minimal Risk Level (MRL) is 0.05 mg/kg-day for the same critical effect [4,23,24].
2.7. Exposure Estimation
To estimate the Average Daily Dose (ADD) for the pediatric population, Equation (1) is used:
The average body weight of the school-age child population was assumed to be 33.9 kg for this risk estimation. This value was derived from a previous study that involved children residing in the same area [16]. The water ingestion rate for this population was assumed to be 0.960 L/day; these data are estimated in the Mexican National Survey of Health and Nutrition (ENSANUT) [25]. The environmental concentration corresponds to each water sample, so the ADD was calculated for each of the sampling points.
2.8. Risk Characterization
For the characterization of non-carcinogenic risk, the hazard quotient (HQ) was calculated using Equation (2):
HQ = ADD((mg/kg)/day)/RfD((mg/kg)/day) × EF
The reference dose (RfD) for the critical effect, in this case, dental fluorosis [4], was 0.06 mg/kg/day [23], The exposure factor (EF) is defined by the duration of exposure and the bioavailability of the toxicant. In this case, it was assumed to be 1, as the contaminant is continuously present in the water, which is consumed daily, and the oral bioavailability of fluoride is very high [4]. We calculated the HQ for each of the sampling points. HQ allows us to estimate how many times the exposure dose exceeds the reference dose; a value greater than one signifies that the population is at risk, and the greater the estimated value, the greater the risk. A value equal to or less than one is interpreted as meaning that the population is not at risk due to exposure to iF in water in that area.
2.9. Risk Mapping
The mapping of risk areas was based on the fluoride concentration levels detected in tap water samples. These concentration data were used to create a spatial distribution map, highlighting areas with higher fluoride levels. The aim was to identify regions with a potential health risk, particularly for the pediatric population. The cartography of fluorine concentrations and water well distribution was elaborated in the ArcMap 10.8.2 Geographic Information System (GIS). In particular, the fluorine concentration map was obtained using the inverse distance weighted (IDW) method, an interpolation process that is widely used and highly adaptable. The interpolation method uses the average values to estimate the importance of the cells. Thus, the values for each cell never exceed the minimum or maximum values of a point. This method assumes that each value in the space has an influence that decreases with distance. The IDW uses the measured values surrounding the prediction location to predict a value for any unmeasured location [26,27].
The fluorine concentrations were captured in a database, exported, and displayed in the GIS. Through the IDW method, the punctual values were interpolated to obtain a layer with continuous concentration values. The map of the water well distribution and its relationship with storage water tanks was obtained using the geographic location of each element and the related tool of ArcMap™.
3. Results
3.1. Fluoride Concentration
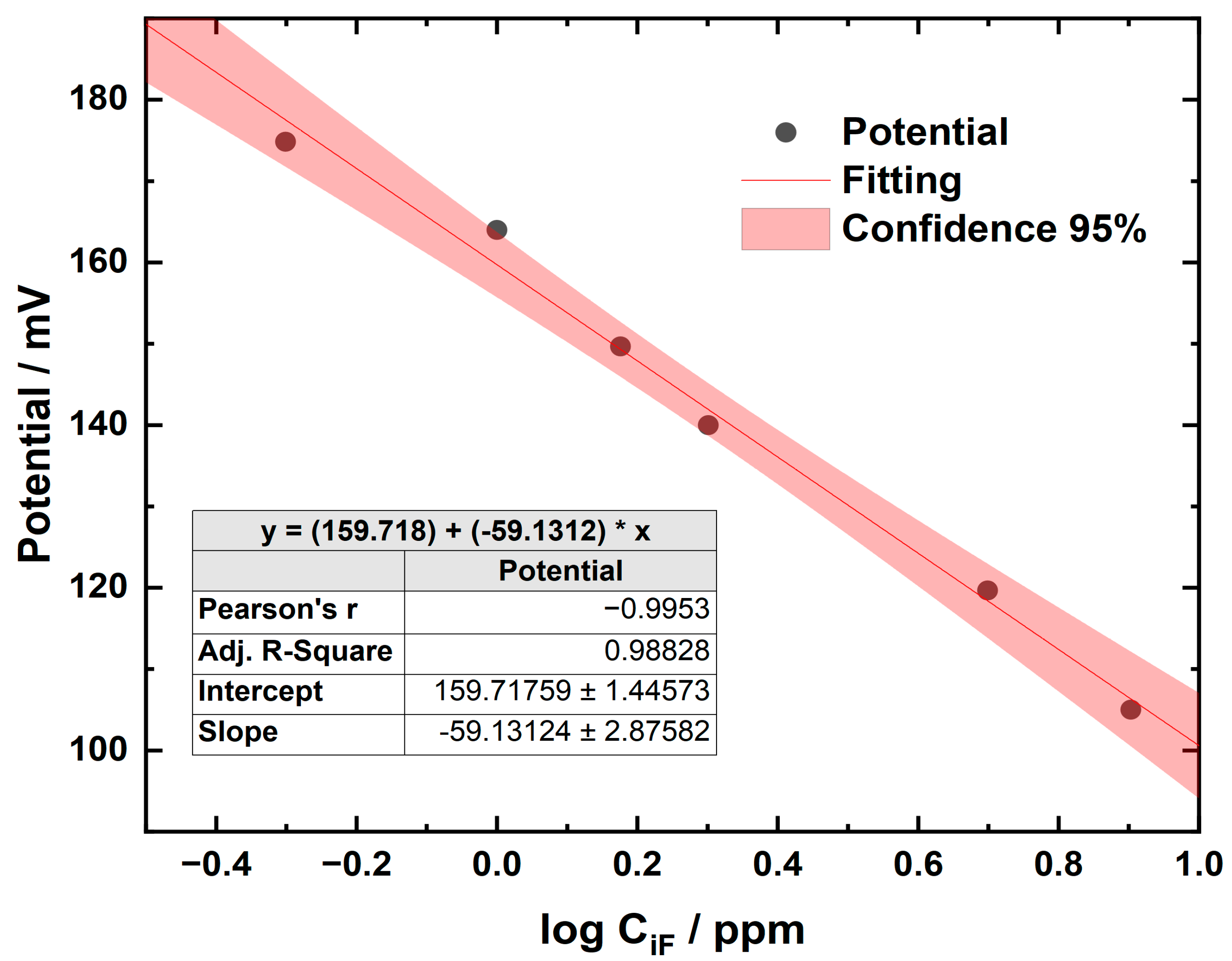
The concentrations of the samples were calculated from the equation of the straight line obtained by plotting the log concentration (log CiF [ppm]) of the standards on the x-axis against the instrument response (potential, mV) on the y-axis. It was verified that the slope was between −54 and −60 mV when the standards were at a temperature between 20 and 25 °C, as a control of the proper functioning of the system [21]. An accuracy percentage of 98% was achieved using Clinicheck II™ (IRIS Technologies International GmbH, Papillion, NE, USA) level II as the reference material. Figure 3 shows an example of a calibration curve; these curves were prepared for each work session.
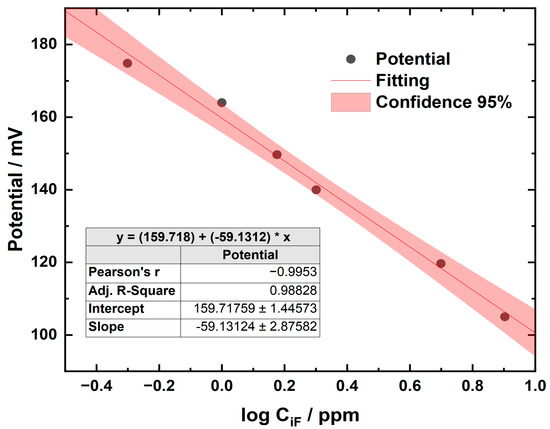
Figure 3.
Calibration curve using the ion-selective electrode method for determining the concentration of fluoride.
The concentration of each sample was obtained by interpolating the response of the electrode against the x-axis of the calibration curve. This value corresponds to the logarithm of the concentration, so the antilogarithmic transformation was carried out to obtain the iF concentration expressed in mg/L. which is the same as in ppm units. As each sample was prepared in triplicate, the mean and standard deviation were calculated as a control for the precision of the measurements.
Most of the samples taken (69 out of 70) showed fluoride concentrations exceeding the limit allowed by NOM-127-SSA1-2021 of 1.5 mg/L [28]. The measured values ranged from 1.34 to 7.30 mg/L.
In Table 2, the results of the fluoride concentration in each quadrant sampled are summarized. The pH of water samples means of 7.8 at the interval of 7.3–8.4.

Table 2.
Wells of supply system of the city of Jerez.
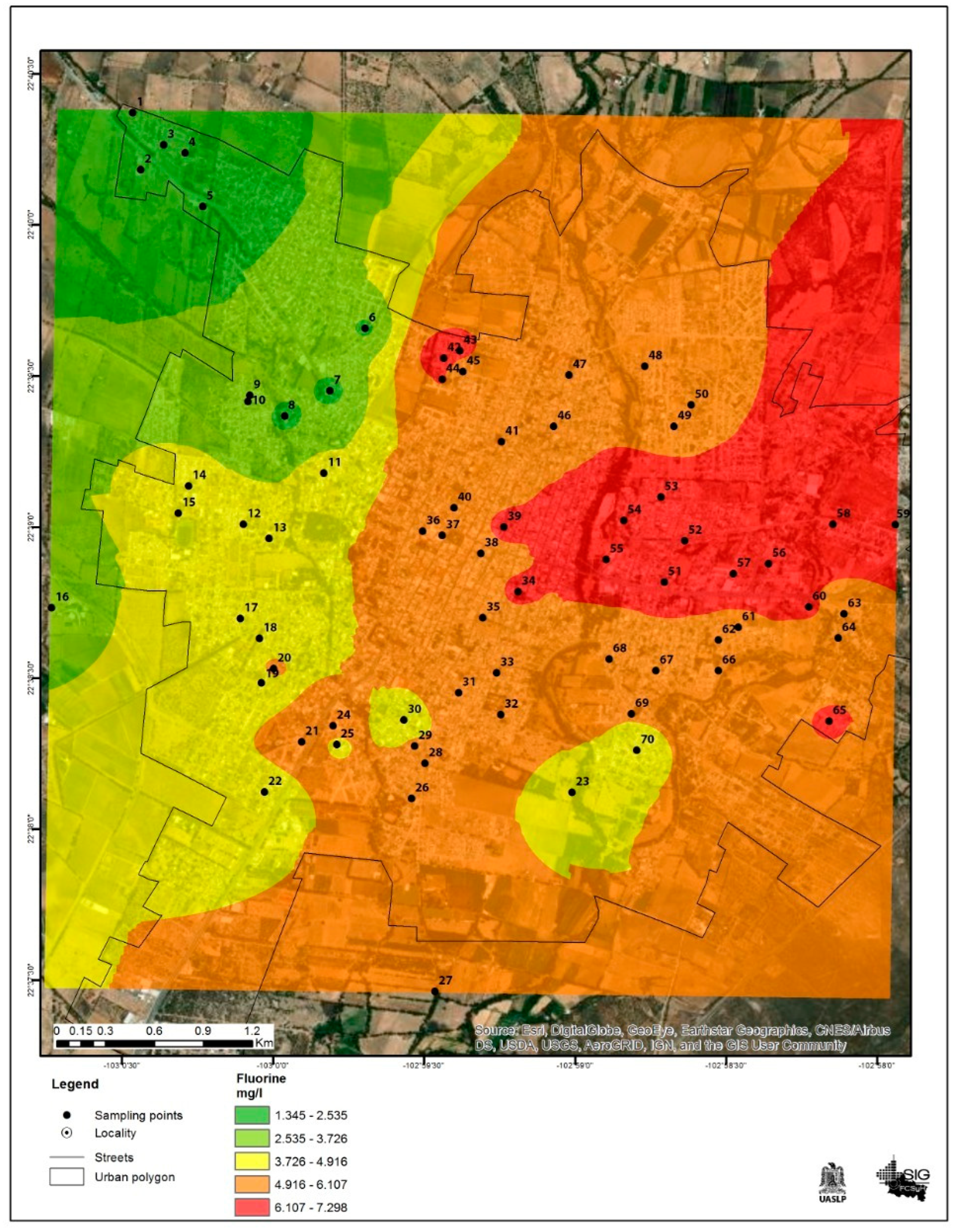
Only the northwest part of the city had a sample below the permitted limit according to the Mexican Official Standard [28], with a concentration of 1.34 mg/L. This area also showed the lowest fluoride values compared to the other quadrants.
Conversely, the area with the highest fluoride levels was the east to northeast part of the city, with concentrations significantly above the permitted limit, the highest being 7.30 mg/L. This information is shown in Figure 4.
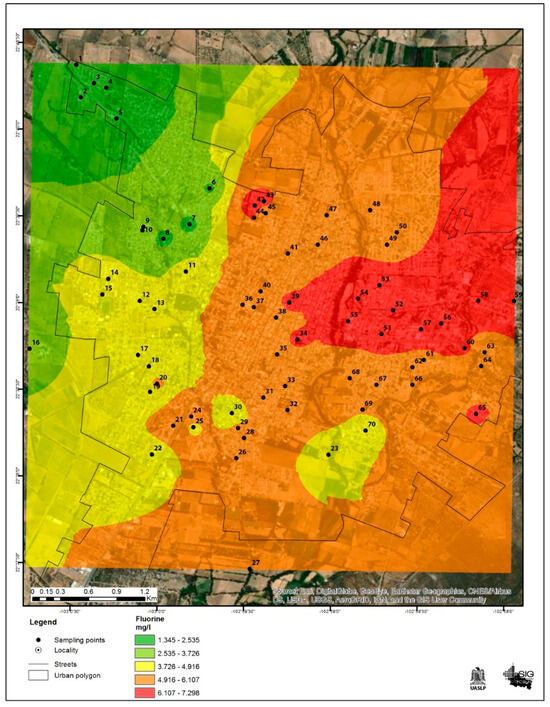
Figure 4.
Fluoride concentrations in drinking water in the city of Jerez, Zacatecas Mexico. The black dots represent the sampling sites, and the colors indicate the fluoride concentration.
3.2. Exposure Estimation
To estimate the fluoride exposure from tap water in children, the exposure dose was calculated, as previously described, based on the fluoride concentrations determined in the water. The results can be seen in Table 2. The ADD estimated was in the range of 0.04–0.22 mg/kg/day.
3.3. Hazard Quotient
The hazard quotient was calculated using data from the school-age population of the city, as they are considered the most vulnerable group to adverse effects from elevated fluoride consumption in the water.
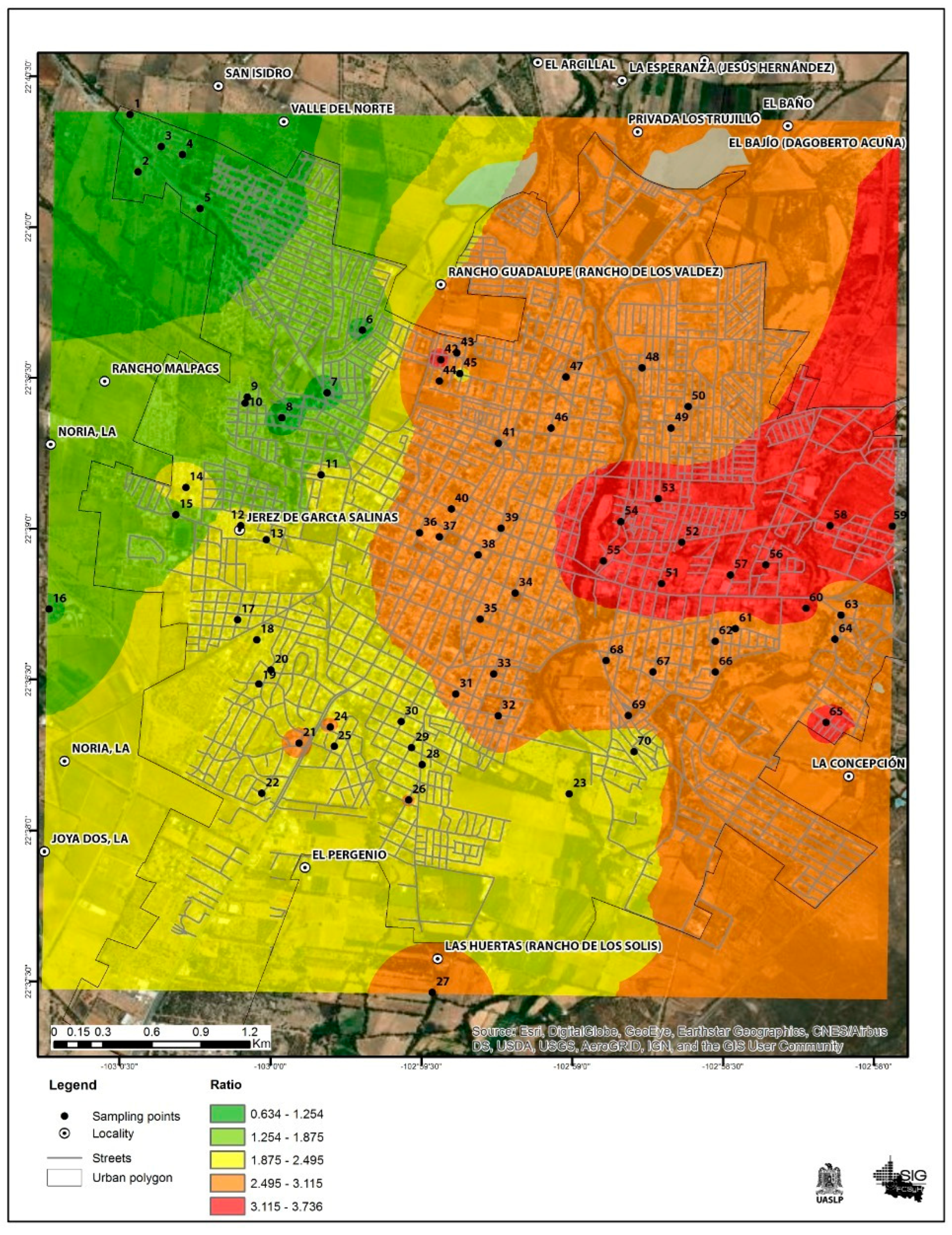
In only 4 out of the 70 analyzed points, the risk quotient was less than 1.0, corresponding to the northwest part of the city. The remaining 66 points were distributed in the city and exceed the value of 1.0; in general, the HQ ranged from 0.6 to 3.7. Table 2 depicts the detailed HQ for each quadrant. This indicates that the majority of the school-age population is at risk of experiencing some type of adverse effect due to tap water consumption. These results can be seen in Figure 5.
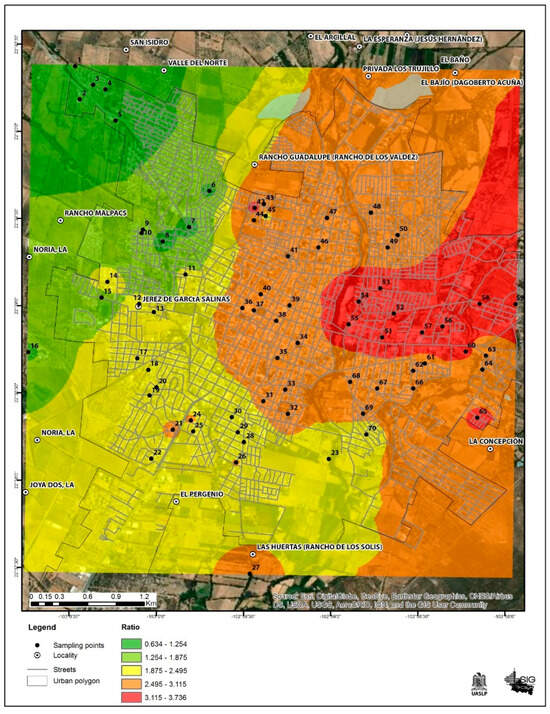
Figure 5.
Environmental estimation risk map for Jerez, Zacatecas city.
4. Discussion
It was found that the fluoride levels in the tap water of the city of Jerez, Zacatecas, exceeds the limit allowed by the Mexican Official Standard NOM-127-2021 [28] and the WHO of 1.5 mg/L in almost all the samples. Only 1 out of the 70 analyzed points complied with this value. Therefore, it can be stated that 98.57% of the analyzed samples are above the permissible limit. It is important to note that the U.S. Public Health Service recommends a fluoride concentration of 0.7 mg/L to maintain caries prevention benefits and reduce the risk of dental fluorosis; the iF values in this study are more than double this recommendation [29]. It must be mentioned that the highest fluoride concentrations are near the rhyolite-acid tuff geological units.
In a previous study conducted in the state of Zacatecas to measure fluoride and arsenic levels, 10 aliquots of tap water were taken, resulting in an average fluoride level of 1.8 mg/L [16]. Although this is above the levels permitted by the NOM and the WHO, it is below the results obtained in this study. In the city of San Luis Potosi, SLP, 190 km from the study site, Perez et al. [30] found areas where the mean iF concentration was 2.55 mg/L, estimating an HQ of 1.4 ± 0.980. These data are consistent with the exposure values, as the pediatric population living in this area exhibited the highest iF levels. Another study conducted by Farias [31] estimated an HQ of 1.5 for children exposed to fluoride in tap water in the state of Guanajuato, Mexico. Tap water was identified as the primary source of exposure compared to other drinking water sources. The average concentration of fluoride in tap water was 4.2 mg/L in their study.
On the other hand, Jarquin et al. [6] reported, in a rural population of the state of San Luis Potosí, Mexico, that children exposed to fluoride with mean urinary levels of 3.14 ± 1.09 mg/L all presented dental fluorosis, with 95% of the cases being severe. All these studies were conducted in the north-central region of the country; Alarcón [10] reported a high presence of this element in alluvial aquifers in the arid zones of this region, where volcanics rocks are abundant. The area where the city of Jerez is located is mostly volcaniclastic, so it is possible that, due to the depth of the wells from which the water is pumped, the fluoride comes from the types of rocks and sediments that make up the soil.
The calculation of the HQ was based on the critical effect of dental fluorosis, for which the reference dose is estimated [23]. In this regard, Gamarra et al. [32] mention that in areas with higher concentrations of fluoride in drinking water, there is a higher prevalence of dental fluorosis, which is consistent with the estimated HQ values. However, health effects have been reported in the literature that still lack reference doses, such as a reduction in IQ scores in children, thyroid dysfunction, kidney dysfunction, and a disruption effect [33], indicating that the HQ might be underestimated. Moore et al. [34] suggest considering not only dental fluorosis but also the reduction in children’s IQ scores as critical health effects for calculating a safety level for fluoride in drinking water.
Furthermore, the effects of oral fluoride exposure on the human microbiome have not been fully studied [35]. India et al. [36] reported an association between early dietary fluoride exposure and adverse cardiometabolic outcomes in school-aged Mexican children. Qiao et al. [37] reported that oral exposure to sodium fluoride produces immunotoxicity, disrupted riboflavin metabolism, and transport and mitochondrial function in mouse models. In humans, Avila, et al. [38] refer to chronic fluoride exposure having harmful effects on human health. Besides, preclinical studies associate fluoride toxicity with oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Therefore, these health effects should also be considered a risk for the resident population, although the reference doses for these effects are not yet available.
There is evidence of the co-occurrence of iF and arsenic (As) in ground water sources [10,11], which could indicate that the population is at risk of suffering the combined or enhanced toxic effects of these two contaminants, which are still under study. However, the greatest risk is to the pediatric population; therefore, it is necessary to take remediation actions to provide them with safe water sources [39]. Locksley F. Castañeda and co-workers reviewed an electrochemical technology to solve this problem, where electrocoagulation proved a promising technology for the removal of iF from natural groundwater samples [40]. However, many remediation technologies are still in the development stage or are very expensive to implement [39].
In a community in central Mexico, an association with biomarkers of early kidney damage was found in a pediatric population exposed to water contaminated with inorganic elements, including As and iF [41], Limon et al. [42] estimated 6 million children of school age would be exposed to fluoride over the Mexican official standards, which the authors suggest should be adjusted and enforced to preserve health.
Various methodological approaches have been proposed to implement interventions in communities to mitigate the health risks associated with environmental risk [43,44]. For example, risk communication is useful for involving the community in health care by providing them with educational tools that enable them to take simple actions [45]. In this case, actions such as avoiding the consumption of boiled water for drinking and for food preparation could reduce exposure to iF. These strategies require working with the community to understand residents’ perceptions of risk and to tailor the intervention to the community’s knowledge, culture, and needs. This educational tool, along with providing access to safe drinking water sources, can have a beneficial impact on the population’s health in the short and medium term, while also reducing economic and social costs.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that the population of Jerez, especially children, is at risk of health problems due to exposure to and ingestion of tap water. Ninety-nine percent of the tap water samples are above the reference values of 1.5 mg/L. The risk quotient for this age group ranges from 0.63 to 2.73, and the majority of the HQs estimated are above 1. The risk map shows that about 99 percent of the city’s resident population is at risk of exposure to fluoride through tap water consumption. It is necessary to implement risk-mitigation strategies in the areas with the highest HQ identified on the map in order to provide safe water sources for the population. It is suggested that a health risk communication program be carried out focusing on educating the population to adopt habits such as not consuming tap water directly, neither for drinking nor for food preparation, as well as reducing the use of products with added fluoride. Additionally, new measures should be promoted for water treatment and ways to reduce the fluoride levels in it to comply with the NOM standards and protect public environmental health.
In addition, it is necessary to consider routine epidemiological surveillance of diseases associated with exposure to fluoride to prevent and intervene in a timely manner in the exposed population, in order to reduce the environmental burden of these diseases, using the risk maps generated in this work as a basis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16172428/s1, Table S1, Full sampling data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.I.M.-A.; Data curation, L.A.E.-W.; Investigation, R.A.M.-E.; Project administration, M.I.M.-A.; Visualization, H.R.-H.; Writing—original draft, M.I.M.-A.; Writing—review & editing, S.A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially funded by Instituto Politécnico Nacional (Reference No. SIP-20231815, SIP-20240967).
Data Availability Statement
Data set available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Priscila Medrano and Alejandro Carlos Arjon for their assistance in conducting the sampling and laboratory analysis. Luis A. Estudillo-Wong thanks Instituto Politécnico Nacional for the financial support through the SIP-projects.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rivera, P.; Aguilar, A.G. La gestión integral del agua en zonas urbanas: Caso de estudio Zacatecas-Guadalupe, México. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2015, 6, 125–142. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2007-24222015000300009&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- INEGI. Panorama Sociodemográfico de Zacatecas: Censo de población y Vivienda; Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI): Madrid, México, 2020. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/productos/prod_serv/contenidos/espanol/bvinegi/productos/nueva_estruc/702825198053.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Fawell, J.; Bailey, K.; Chilton, J.; Dahi, E.; Fewtrell, L.; Magara, Y. Fluoride in Drinking-Water; WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; Issue. I. Publishing; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9241563192 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- EPA. Fluorine (Soluble Fluoride); E. P. Agency: Woollahra, Australia, 1987. Available online: https://iris.epa.gov/ChemicalLanding/&substance_nmbr=54 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Del Razo, L.M.; García-Vargas, G.G.; Valenzuela, O.L.; Castellanos, E.H.; Sánchez-Peña, L.C.; Currier, J.M.; Drobná, Z.; Loomis, D.; Stýblo, M. Exposure to arsenic in drinking water is associated with increased prevalence of diabetes: A cross-sectional study in the Zimapán and Lagunera regions in Mexico. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarquín-Yañez, L.; Mejía-Saavedra, J.d.J.; Molina-Frechero, N.; Gaona, E.; Rocha-Amador, D.O.; López-Guzmán, O.D.; Bologna-Molina, R. Association between urine fluoride and dental fluorosis as a toxicity factor in a rural community in the state of San Luis Potosi. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 647184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Frechero, N.; Gaona, E.; Angulo, M.; Sanchez Perez, L.; Gonzalez Gonzalez, R.; Nevarez Rascon, M.; Bologna-Molina, R. Fluoride exposure effects and dental fluorosis in children in Mexico City. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 3664–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Amador, D.; Navarro, M.E.; Carrizales, L.; Morales, R.; Calderón, J. Decreased intelligence in children and exposure to fluoride and arsenic in drinking water. Cad. Saude Publica 2007, 23 (Suppl. 4), S579–S587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, J.S.; Perez, V.; Garry, M.R.; Alexander, D.D. Association of low-level arsenic exposure in drinking water with cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and risk assessment. Toxicology 2014, 323, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon-Herrera, M.T.; Martin-Alarcon, D.A.; Gutierrez, M.; Reynoso-Cuevas, L.; Martin-Dominguez, A.; Olmos-Marquez, M.A.; Bundschuh, J. Co-occurrence, possible origin, and health-risk assessment of arsenic and fluoride in drinking water sources in Mexico: Geographical data visualization. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Macias, J.C.; Ochoa-Martínez, Á.C.; Orta-García, S.T.; Varela-Silva, J.A.; Pérez-Maldonado, I.N. Probabilistic human health risk assessment associated with fluoride and arsenic co-occurrence in drinking water from the metropolitan area of San Luis Potosí, Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Flora, S.J.S. Fluoride in drinking water and skeletal fluorosis: A review of the global impact. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2020, 7, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Díaz, F.d.C.; Morales-Corona, F.; Cintra-Viveiro, A.C.; de la Fuente-Hernández, J. Prevalence of dental fluorosis in Mexico 2005–2015: A literature review. Salud Pública Méx. 2017, 59, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt-Lineares, A.; Irigoyen-Camacho, M.E.; Mejía-González, A.; Zepeda-Zepeda, M.; Sánchez-Pérez, L. Prevalencia de fluorosis dental en localidades mexicanas ubicadas en 27 estados y el D.F. a seis años de la publicación de la Norma Oficial Mexicana para la fluoruración de la sal. Rev. Investig. Clín. 2013, 65, 237–247. Available online: https://www.medigraphic.com/cgi-bin/new/resumen.cgi?IDARTICULO=43865 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Armienta, M.A.; Segovia, N. Arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater of Mexico. Environ. Geochem. Health 2008, 30, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Acuña, M.I.; Mercado-Reyes, M.; Alegría-Torres, J.A.; Mejía-Saavedra, J.J. Preliminary human health risk assessment of arsenic and fluoride in tap water from Zacatecas, México. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INEGI. Estado de Zacatecas: Municipio de Jerez. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/app/indicadores/?ind=5300000007&tm=6#divFV5300000007#D5300000007 (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Nuñez Peña, E.P.; Escalona Alzázar, F.d.J.; Bluhm Gutiérrez, J.; Ramos De la Cruz, G.A.; de la Torre Guerrero, A.; Ortega Martínez, E.; Cardona Benavides, A. Caracterización hidrogeoquímica del acuífero Jerez, estado de Zacatecas, México. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2015, 6, 105–124. Available online: https://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2007-24222015000300008 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- SSA. NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-230-SSA1-2002, Salud Ambiental. Agua para uso y Consumo Humano, Requisitos Sanitarios Que Se Deben Cumplir en los Sistemas de Abastecimiento Públicos y Privados Durante el Manejo del Agua. Procedimientos Sanitarios para el Muestreo. Diario Oficial de la Federación. 2002. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=2081772&fecha=12/07/2005 (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- SE. NMX-AA-077-SCFI-2001: Determinación de Fluoruros en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas; Secretaria de Economía, Diario Oficial de la Federacion (DOF): Mexico City, México, 2001; Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166793/NMX-AA-077-SCFI-2001.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Thermo Scientific Orion Fluoride Electrodes—pH and Electrochemistry, Probes and Electrodes. (s. f.). Available online: https://www.fishersci.com/shop/products/orion-fluoride-electrodes-1/13642265 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Díaz-Barriga, F. Metodología de Identificación y Evaluación de Riesgos para la Salud en Sitios Contaminados; CEPIS: Brussels, Belgium; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999; Available online: https://toxicologia.org.ar/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Manual-Sitios-Contaminados.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Fluorine (Soluble Fluoride) CASRN 7782-41-4 | IRIS | US EPA, ORD. (s. f.). Available online: https://iris.epa.gov/ChemicalLanding/&substance_nmbr=53 (accessed on 22 July 2024).
- Tylenda, C.A.; Dennis, J.; Ingerman, L.; Sage, G.; Chappell, L. Toxicological Profile for Fluorides, Hydrogen Fluoride, and Fluorine, 2nd ed.; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2003. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp.asp?id=22&tid=3 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Gaona-Pineda, E.B.; Martínez-Tapia, B.; Arango-Angarita, A.; Valenzuela-Bravo, D.; Gómez-Acosta, L.M.; Shamah-Levy, T.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, S.; Gaona-Pineda, E.B.; Martínez-Tapia, B.; Arango-Angarita, A.; et al. Consumo de grupos de alimentos y factores sociodemográficos en población mexicana. Salud Pública Méx. 2018, 60, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.N.; Yu, X.Y.; Jia, L.F.; Wang, Y.S.; Song, Y.C.; Meng, H.D. The influence of distance weight on the inverse distance weighted method for ore-grade estimation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setianto, A.; Triandini, T. Comparison of kriging and inverse distance weighted (IDW) interpolation methods in lineament extraction and analysis. J. Appl. Geol. 2013, 5, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SSA. Modificación a la Norma Oficial Mexicana. NOM-127-SSA1-2021, Salud Ambiental. Agua Para uso y Consumo Humano. Límites Permisibles de Calidad y Tratamientos a Que Debe Someterse el Agua Para Su Potabilización. Diario Oficial de la Federación. 2021. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5650705&fecha=02/05/2022#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Federal Panel on Community Water Fluoridation. U.S. Public Health Service recommendation for fluoride concentration in drinking water for the prevention of dental caries. Public Health Rep. 2015, 130, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Vázquez, F.J.; González-Martell, A.D.; Fernández-Macias, J.C.; Rocha-Amador, D.O.; González-Palomo, A.K.; Ilizaliturri-Hernández, C.A.; González-Mille, D.J.; Cilia-Lopez, V.G. Health risk assessment in children living in an urban area with hydrofluorosis: San Luis Potosí Mexico case study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 68, 126863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farías, P.; Estevez-García, J.A.; Onofre-Pardo, E.N.; Pérez-Humara, M.L.; Rojas-Lima, E.; Álamo-Hernández, U.; Rocha-Amador, D.O. Fluoride exposure through different drinking water sources in a contaminated basin in Guanajuato, Mexico: A deterministic human health risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra, J.; Álvarez-Ordaz, D.; Molina-Frechero, N.; Sánchez-Pérez, L.; Pierdant-Rodriguez, A.; Isiordia-Espinoza, M.A.; Espinosa-Cristóbal, L.F.; Gómez Palacio-Gastelum, M.; González-González, R.; Salas-Pacheco, J.; et al. Association between fluoride intake from drinking water and severity of dental fluorosis in Northern and Western Mexico: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taher, M.K.; Momoli, F.; Go, J.; Hagiwara, S.; Ramoju, S.; Hu, X.; Jensen, N.; Terrell, R.; Hemmerich, A.; Krewski, D. Systematic review of epidemiological and toxicological evidence on health effects of fluoride in drinking water. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2024, 54, 2–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.; Glenny, A.M. Fluoride and children’s IQ: Evidence of causation lacking. Evid.-Based Dent. 2024, 25, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, G.P.; Zgaga, L.; Daly, B.; Harding, M.; Montgomery, T. Does fluoride exposure impact on the human microbiome? Toxicol. Lett. 2023, 379, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- India Aldana, S.; Colicino, E.; Cantoral Preciado, A.; Tolentino, M.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Wright, R.O.; Téllez Rojo, M.M.; Valvi, D. Longitudinal associations between early-life fluoride exposures and cardiometabolic outcomes in school-aged children. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhuang, C.; Li, X.; Yong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Cai, M.; Yang, J.; et al. Fluoride induces immunotoxicity by regulating riboflavin transport and metabolism partly through IL-17A in the spleen. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Rojas, S.H.; Aparicio-Trejo, O.E.; Sanchez-Guerra, M.A.; Barbier, O.C. Effects of fluoride exposure on mitochondrial function: Energy metabolism, dynamics, biogenesis and mitophagy. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 94, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Sánchez, A.G.; Castillo-Suárez, L.A.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Linares-Hernández, I.; Teutli-Sequeira, E.A. As and cooccurrence in drinking water: Critical review of the international scenario, physicochemical behavior, removal technologies, health effects, and future trends. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 38768–38796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.F.; Rodríguez, J.F.; Nava, J.L. Electrocoagulation as an affordable technology for decontamination of drinking water containing fluoride: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Romero, M.; Jiménez-Córdova, M.I.; Barrera-Hernández, Á.; Sepúlveda-González, M.E.; Narvaez-Morales, J.; Aguilar-Madrid, G.; Juárez-Pérez, C.A.; Del Razo, L.M.; Cruz-Angulo, M.D.C.; Mendez-Hernández, P.; et al. Relationship between urinary biomarkers of early kidney damage and exposure to inorganic toxins in a pediatric population of Apizaco, Tlaxcala, Mexico. J. Nephrol. 2023, 36, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limón-Pacheco, J.H.; Jiménez-Córdova, M.I.; Cárdenas-González, M.; Sánchez Retana, I.M.; Gonsebatt, M.E.; Del Razo, L.M. Potential co-exposure to arsenic and fluoride and biomonitoring equivalents for mexican children. Ann. Glob. Health 2018, 84, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corpus-Espinosa, C.A.; Cilia-López, V.G.; Nieto-Caraveo, L.M.; Cubillas-Tejeda, A.C. Desarrollo de la capacidad de comunicar riesgos relacionados con la exposición infantil a fluoruros, a través de una estrategia educativa en línea [Development of the capacity to communicate risks related to childhood exposure to fluorides through an online educational strategy]. Cad Saude Publica 2024, 40, e00215723. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Health Organization. Communicating Risk in Public Health Emergencies: A WHO Guideline for Emergency Risk Communication (ERC) Policy and Practice; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Meza-Lozano, B.; Ortiz-Pérez, M.D.; Ponce-Palomares, M.; Castillo-Gutiérrez, S.G.; Flores-Ramírez, R.; Cubillas-Tejeda, A.C. Implementación y evaluación de un programa de comunicación de riesgos por exposición a flúor en la comunidad de El Fuerte, Santa María del Río, San Luis Potosí, México. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2016, 32, 87–100. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0188-49992016000100087&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 5 May 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).