Abstract
The multi-reservoir flood control operation (MRFCO) problem is characterized by high dimensions and multiple constraints. These features pose significant challenges to algorithms aiming to solve the MRFCO problem, requiring them not only to handle high-dimensional variables effectively but also to manage constraints efficiently. The Horned Lizard Optimization Algorithm (HLOA) performs excellently in handling high-dimensional problems and effectively integrates with penalty functions to manage constraints. However, it still exhibits poor convergence when dealing with certain benchmark functions. Therefore, this paper proposes the Enhanced Horned Lizard Optimization Algorithm (EHLOA), which incorporates Circle initialization and two strategies for avoiding local optima, thereby enhancing HLOA’s convergence performance. Firstly, EHLOA was tested on benchmark functions, where it demonstrated strong robustness and scalability. Then, EHLOA was applied to the MRFCO problem at the upper section of Lanzhou of the Yellow River in China, showing excellent convergence capabilities and the ability to escape local optima. The reduction rates of flood peaks achieved by EHLOA for the two millennial floods and two decamillennial floods were 55.6%, 52.8%, 58.1%, and 56.4%, respectively. Additionally, the generated operation schemes showed that the reservoir volumes changes were reasonable, and the discharge processes were stable under EHLOA’s operation. Overall, EHLOA can be considered a reliable algorithm for addressing the MRFCO problem.
1. Introduction
As global warming intensifies, the enhancement of the hydrological cycle has led to an increased frequency of extreme precipitation events [1]. The amount of rainfall and the areas affected by these extreme precipitation events have become larger than before [2]. Moreover, some studies suggest that by the end of this century, the frequency of extreme precipitation events will increase globally by approximately 1.8 times, with a significant rise in the frequency of extreme precipitation also expected between 2041 and 2070 [3,4]. With the rising frequency and intensity of extreme precipitation, the frequency of flood events has also increased accordingly [1]. Over the past three years, several countries have experienced devastating floods. From December 2021 to early 2022, Malaysia faced one of the most severe floods in its history, with approximately 70,000 victims evacuated daily, 54 fatalities, and total losses amounting to approximately $1.46 billion [5]. In July 2021, catastrophic floods struck western Germany and Henan Province, China. In Germany, over 107,000 people were affected, 205 lives were lost, and economic losses reached $40 billion [6]. In Henan Province, the floods impacted 14.786 million people, resulting in 398 deaths and losses of $18.9 billion [6]. In 2022, unprecedented massive floods hit southern Pakistan, displacing 33 million people [7]. In summary, climate warming has led to an increase in the frequency of extreme precipitation, which directly results in a higher probability of extreme flood events. Moreover, as the frequency of extreme precipitation is expected to rise significantly in the coming decades, the losses caused by extreme flood events to humanity may become increasingly severe.
Reservoirs are crucial tools for flood control. By utilizing their flood storage capacity to store more floodwaters while ensuring their own safety, reservoirs can effectively reduce peak flood flows and mitigate downstream flood damages. When a reservoir operates independently, its flood detention capacity can be limited when dealing with large flood volumes, increasing the risk of downstream flooding [8]. Therefore, with the development of socio-economic conditions, there is a tendency to use multiple reservoirs for flood control, and a flood control system often includes several reservoirs [9]. Multi-reservoir systems are categorized into cascade reservoirs and parallel reservoirs. Both types can reduce maximum discharge, enhance flood control capacity, and lower flood risks in downstream areas through coordinated operating of multiple reservoirs [10,11]. However, this approach introduces several challenging issues during the operation process, such as how to rationally utilize the flood storage capacities of the various reservoirs and how to ensure the safety of each reservoir. Consequently, multi-reservoir flood control operation (MRFCO) is a high-dimensional, multi-constraint problem.
There are two main approaches to solving the problem of multi-reservoir flood control operation. The first approach involves the use of metaheuristic optimization algorithms [12,13,14], while the second approach uses mathematical algorithms that divide the flood control operation process into several stages for optimization [15,16]. The latter can be time-consuming and difficult to converge when dealing with long-duration flood events. In contrast, metaheuristic algorithms perform exceptionally well in high-dimensional optimization problems and are widely applied in commercial, engineering, and economic fields [17].
Solving the MRFCO problem using metaheuristic algorithms requires the establishment of an appropriate mathematical model, which typically comprises three components: the objective function, the variable bounds and constraints, and the handling of constraint violations. There are two primary methods for addressing constraint violations: employing metaheuristic algorithms with built-in constraint handling techniques [18] and adding a penalty function to the objective function [19]. The former method, though proven to work, tends to become trapped in local optima and struggles to converge, especially in high-dimensional optimization problems where the feasible region is small [20]. Additionally, it demonstrates inefficiency in high-dimensional contexts, making it less suitable for complex optimization tasks [21,22]. The latter method, the penalty function approach, is generally more efficient [23]. It assigns high penalty values to infeasible solutions, thereby forcing the algorithm to search within the feasible solution space. However, the performance of different metaheuristic algorithms when combined with penalty functions can vary [24]. Penalty functions can also cause the algorithm to get stuck in local optima in high-dimensional problems [25]. The ability to escape these local optima depends on the algorithm’s inherent capacity to overcome local optima challenges. Therefore, to effectively solve the MRFCO problem, it is crucial to find a metaheuristic algorithm that not only integrates well with the penalty function approach but also possesses a strong ability to escape local optima.
The Horned Lizard Optimization Algorithm (HLOA), proposed by Vázquez et al. [26] achieves global optimization by mathematically simulating various defensive behaviors of horned lizards. The performance of HLOA was tested on the optimization problems from IEEE CEC 2017 “Constrained Real-Parameter Optimization” [27], with variable dimensions of 10, 30, 50, and 100. The results indicated that HLOA performed best at dimensions of 50 and 100 and ranked second at dimensions of 30 and 10. It suggests that HLOA excels in handling high-dimensional constrained problems even more than low-dimensional ones. Additionally, HLOA was tested on five real-world constrained optimization problems using the penalty function method to handle constraints. The results demonstrated that HLOA delivered competitive results across all five problems and provided the best solutions for three of them. It indicates that the performance of HLOA combined with the penalty function approach is reliable.
However, HLOA still has areas for improvement. In their study on 63 commonly used unconstrained test functions, Vázquez et al. [26] found that HLOA performed poorly on some functions, becoming trapped in local optima, demonstrating that its global search capability and ability to escape local optima need enhancement.
Therefore, this paper combines three strategies to enhance HLOA’s performance, aiming to improve the algorithm’s ability to escape local optima, ensuring that it demonstrates strong robustness and convergence when handling both benchmark problems and the MRFCO problem. The novelties of this work are as follows:
- EHLOA demonstrates better robustness compared to widely used algorithms and highly cited algorithms from the past three years on both benchmark functions and the MRFCO problem.
- EHLOA exhibits superior convergence compared to widely used algorithms and highly cited algorithms from the past three years on both benchmark functions and the MRFCO problem.
- The flood control scheduling process provided by EHLOA is reasonable, making it a reliable algorithm for flood control operations.
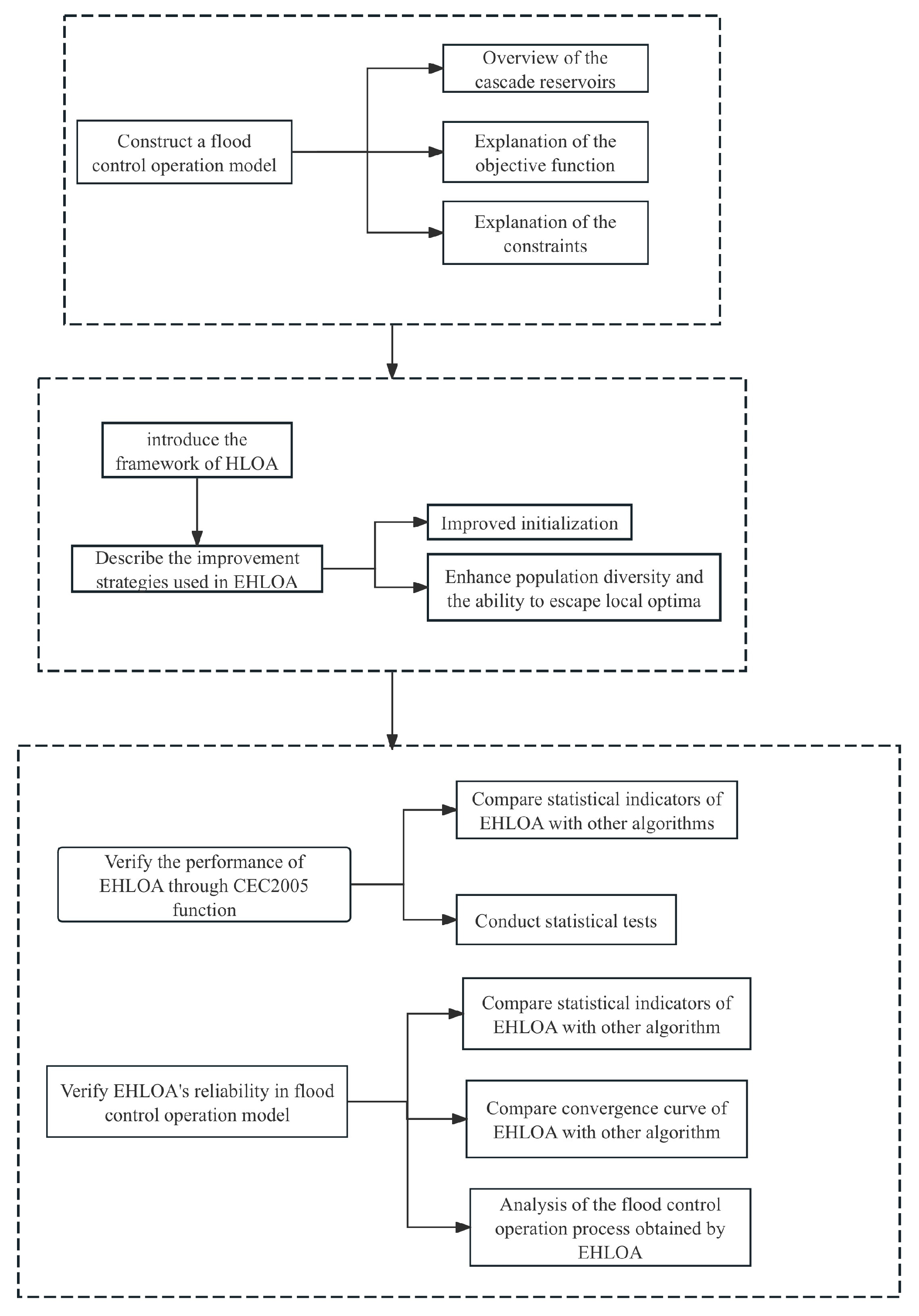
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces an overview of the study area and constructs the flood control operation model. Section 3 presents the basic framework of HLOA and explains the improvement strategies used in EHLOA. Section 4 tests the performance of EHLOA and its reliability in flood control operation through simulations on benchmark functions and the flood control operation model. Section 5 discusses the main findings of the study, and Section 6 presents the main conclusions of the paper. The flowchart of this study is presented in Figure 1.
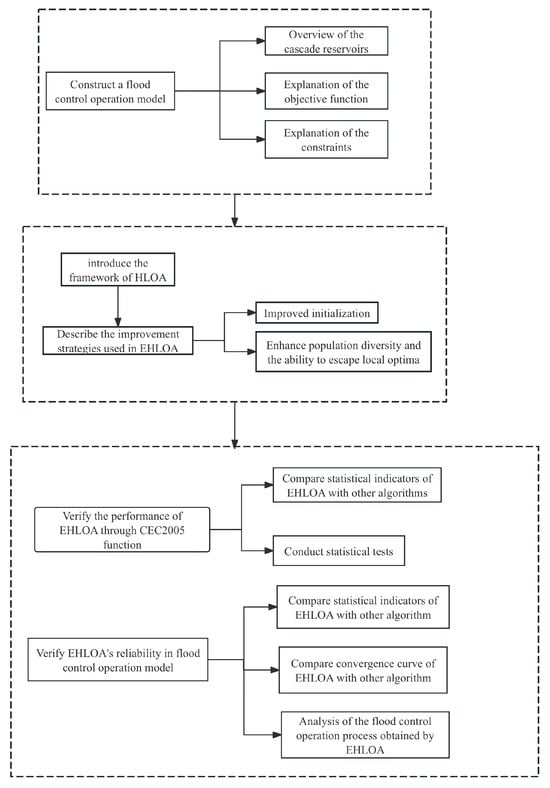
Figure 1.
Flowchart of this study.
2. Study Area and Flood Control Operation Model
2.1. Cascade Reservoirs and Flood Data
This section will introduce the study area of this paper, including the geographic location and composition of the cascade reservoirs, as well as the flood data used in this paper.
The Yellow River, the second longest river in China, traverses nine provinces and plays a crucial role in the agriculture, industry, and ecology of northern China. Floods in the upper reaches of the Yellow River generally take place between July and September. While the fluctuations of these floods are relatively mild, they tend to last for an extended period, approximately 40–45 days.
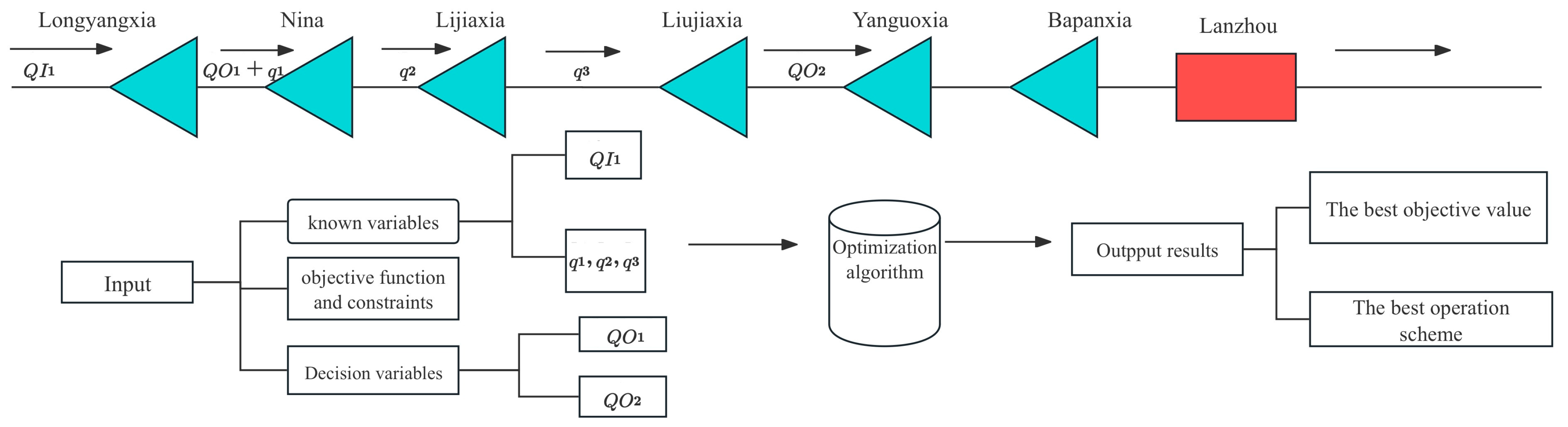
The cascaded reservoirs formed by Longyangxia (LYX) and Liujiaxia (LJX) bear the primary flood control tasks in the upper Yellow River due to their excellent flood mitigation capacity, playing a significant role in protecting the safety of Lanzhou, the second largest city in northwest China. This study is centered at the upper section of Lanzhou of Yellow River in China, where it conducts an in-depth analysis of flood control operation for the LYX and LJX cascade reservoirs across four different design floods.
The design floods used in this paper are based on typical floods from 1964 and 1967, provided by the Yellow River Conservancy Commission of China (http://www.yrcc.gov.cn, accessed on 20 May 2024). The 1964 flood is characterized by a sharp and narrow peak shape, while the 1967 flood features a flat-topped peak shape. Their characteristics include long durations (45 days) and large flood volumes. This study includes four different design floods: flood 1 (a millennial flood based on the typical 1964 flood), flood 2 (a millennial flood based on the typical 1967 flood), flood 3 (a decamillennial flood based on the typical 1964 flood), and flood 4 (a decamillennial flood based on the typical 1967 flood). Figure 2 illustrates the flood evolution process in the upper section of the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River. Table 1 details the characteristic parameters used in this study, including the reservoir capacity at the dead water level (VL), the reservoir capacity at the design flood level (VD) and the reservoir capacity at the check flood level (VC), and the maximum allowable discharge flow (QOM).
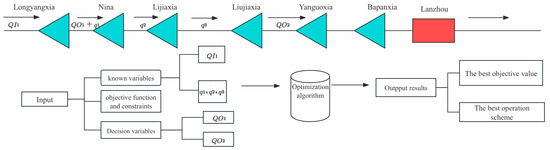
Figure 2.
Cascade reservoirs and model operation flowchart.

Table 1.
Parameter values used for flood control operation.
2.2. Flood Control Operation Model of Cascade Reservoirs
2.2.1. Objective Function of Flood Control Operation
This section will present the objective function for flood control operation and explain the rationale for its use. As shown in Figure 2, the primary flood protection target for the cascade reservoirs in the upstream of the Yellow River is Lanzhou. The last large reservoir upstream of Lanzhou is LJX, and its maximum discharge directly impacts the safety of Lanzhou. If the maximum discharge from LJX is relatively low, the operation is considered successful during the process of a large flood. Therefore, the decision variables (variables to be optimized) in this model are the outflow of LYX during the operation process (QO1) and the outflow of LJX during the operation process (QO2). The known variables input into the model include the inflow rate of LYX (QI1) and the interval flows between the reservoirs during flood propagation (q1, q2, q3). The decision variables and known variables will be input into the optimization algorithm along with the objective function and constraints. The optimization algorithm will output the minimum value of the objective function and the outflow processes of LYX and LJX during the flood operation period. The operation period (T) for this model is 45 days, and there are two decision variables (QO1, QO2), making the problem dimension for this model 90 (45 × 2). Simultaneously, the reservoirs must ensure their own safety, and the maximum storage capacity during the operation process should not exceed the flood control standards for the corresponding flood frequency. The objective function and the corresponding penalty function are as follows:
where QO2(t) represents the discharge of LJX at the end of t period; V1 and V2 represent the reservoir volumes of LYX and LJX, respectively; and Vmax,1 and Vmax,2 represent the maximum storage capacities that LYX and LJX can reach during the flood control process, respectively.
2.2.2. Constraints of Flood Control Operation
- (1)
- Water balance constraint
- (2)
- Outflow constraint
To ensure the safety of downstream protection objects and the stability of the downstream river channel of a reservoir, two constraints are set as follows:
where QOi,max is the maximum allowable outflow of reservoir i; and ΔQOi,max is the maximum allowable fluctuation constraint for reservoir i.
- (3)
- Interval flow constraint
- (4)
- Reservoir storage capacity constraint
- (5)
- Initial condition constraint
- (6)
- Non-negative constraint
All variables in the flood control operation model of cascade reservoirs are non-negative.
3. HLOA Algorithm
3.1. Basic HLOA Algorithm
This section will introduce the basic HLOA algorithm, including its main framework and how it is inspired by the behavior of horned lizards. There is a type of horned lizard that inhabits the region from south central United States to northeastern Mexico. These lizards are adapted to extreme temperatures in arid or semi-arid areas. Their primary passive defense method is camouflage, which includes the ability to blend into their surroundings through changes in color, pattern, and shape. Another passive defense strategy is relocation or fleeing. Additionally, when threatened, these lizards can adopt aggressive strategies such as squirting blood to deter predators. The horned lizard’s skin can lighten or darken depending on whether it needs to reduce or increase solar gain. In high temperatures, they adopt a lighter color, while in low temperatures, their skin darkens. Dark skin does not reflect any color; instead, it absorbs all wavelengths of light and converts them into heat. The rapid change in the horned lizard’s skin color is due to the effect of temperature on its alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH). Inspired by these horned lizards, Vázquez et al. [26] proposed the HLOA algorithm, which incorporates a mathematical model based on the behaviors.
3.1.1. Crypsis Behavior
The horned lizard’s skin color often changes with its external environment, this behavior can help it better hide from predators. To simulate the horned lizard’s constantly changing colors, the variability of sine and cosine functions is utilized. This variability increases the algorithm’s randomness, enhancing its ability to perform global searches. The mathematical formula for this is as follows [26]:
where is the new search agent position in the solution search space for the generation t + 1; is the best search agent for the generation t; Max_iter represent the maximum number of iterations; and r1, r2, r3 and r4 are random numbers generated within the range of 1 to the population size. , , and are the r1, r2, r3, r4-th search agent selected; σ is a binary value, which can be either 0 or 1; and, c1, c2, with c1 ≠ c2, are random numbers.
3.1.2. Skin Darkening or Lightening
Horned lizards can lighten or darken their skin depending on whether they need to reduce or increase their solar heat gain. The color changes in horned lizard skin are described by Equations (10) and (11), where Equation (10) represents the skin-lightening strategy, and Equation (11) represents the skin-darkening strategy [26].
where is the worst search agent for the generation t; and Light1, Light2, Dark1, Dark2 are random numbers.
3.1.3. Blood-Squirting
Horned lizards defend themselves by squirting blood from their eyes to deter predators. This defensive behavior is defined as a projectile motion. By utilizing projectile motion, the current solution is combined with the best solution, allowing the algorithm to move closer to the optimal solution while maintaining population diversity. The mathematical formula as follows [26]:
where ε1 is set to 1 × 10−6 g is set to 0.009807 to represent the gravity of the earth; and is the current search agent.
3.1.4. Move-to-Escape
Horned lizards can move quickly and randomly in nature to evade predators. A function that includes both local and global movements is introduced to simulate this behavior. This combination of local and global movements reduces the likelihood of the algorithm becoming trapped in local optima [26]:
where walk is a random number generated between −1 and 1; ε2 is a random number generated from a standard Cauchy distribution with the mean and standard deviation set to 0 and 1.
3.1.5. Alpha Melanophore Stimulating Hormone (α-MSH) Rate
The color change in horned lizard skin can be attributed to the effect of temperature on melanophore. Inspired by this behavior, the rate of melanophore is introduced to assess the quality of the current solution, determining whether the solution enhancement procedure needs to be executed. The rate of melanophore activity in horned lizards is defined as follows [26]:
where Fitnessmin and Fitnessmax are the best and the worst fitness values in the current t generation, respectively; and Fitness(i) is the current fitness value of the i-th search agent.
The melanophore activity rate is a value within the interval [0, 1]. If its value is less than 0.3, the search agent will be replaced.
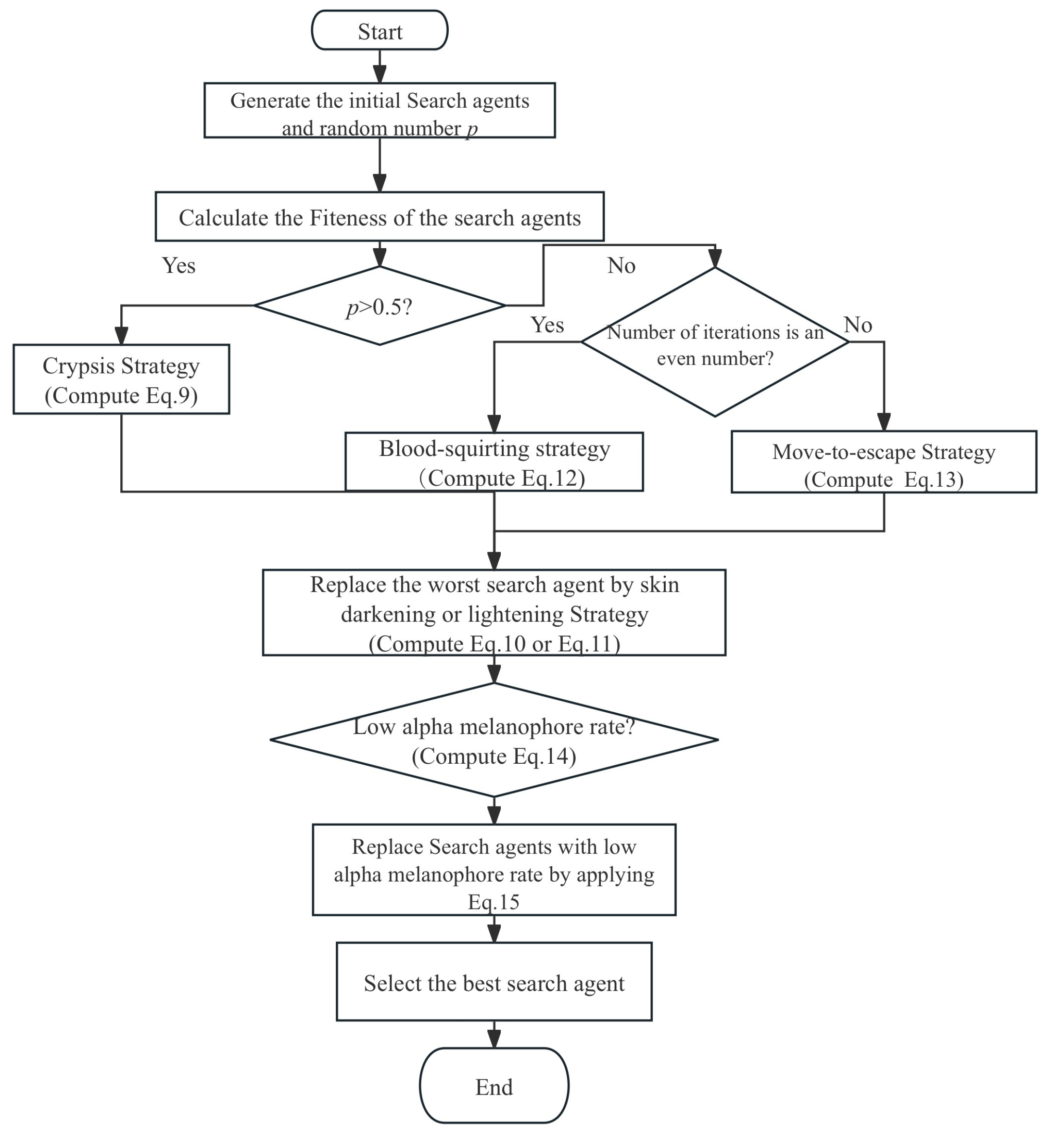
The flowchart of HLOA is shown in Figure 3.
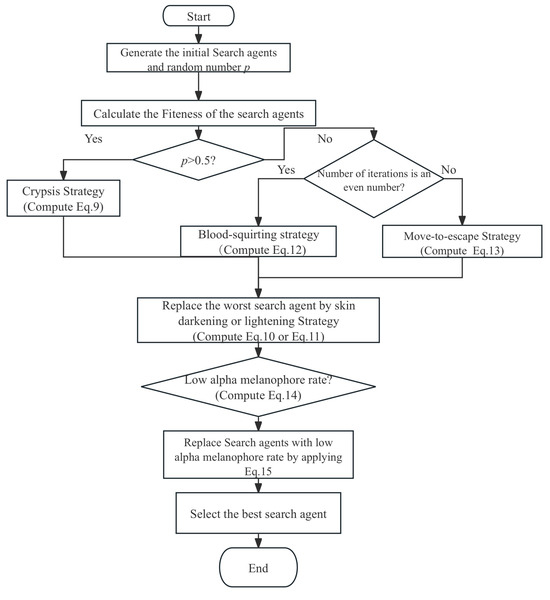
Figure 3.
Flowchart of HLOA.
3.2. Enhanced HLOA Algorithm
To enhance HLOA’s convergence capability, chaotic initialization and two solution enhancement strategies were adopted. Chaotic initialization can generate higher-quality initial solutions, helping the algorithm converge to smaller values within a limited number of iterations. The two solution enhancement strategies can increase the algorithm’s ability to escape local optima.
3.2.1. Circle Map Initialization
Circle map initialization is a type of chaotic initialization that effectively helps the algorithm generate higher-quality solutions during the initialization phase. Due to the ergodicity and randomness of chaotic search, it can easily escape local optima. Therefore, chaotic initialization is often incorporated into metaheuristic optimization algorithms [28]. Chaos can enhance the algorithm’s performance on benchmark functions [29,30] and improve its efficiency in solving engineering problems [31]. It also makes the algorithm perform exceptionally well in handling high-dimensional optimization problems [32]. The Circle map has been proven to be one of the better chaotic mapping methods [33]. Therefore, in EHLOA, the Circle map is used for initialization instead of random initialization [33].
where a and b are set to 0.5 and 0.2, respectively; xi+1 is a number obtained through the circle map; xi is a number obtained through random initialization. The mod (1) ensures that the value of xi+1 stays within the range of 0 to 1; represents the initial position of the n th search agent’s j th search variable; lb and ub represent the lower and upper bounds of the problem to be solved, respectively; NP represents the population size of the algorithm; and dim represents the number of decision variables.
3.2.2. Trap Escaping Operator (TEO)
Trap Escaping Operator (TEO) is a strategy designed to help the algorithm avoid becoming trapped in the local optima. In HLOA, Strategies 4 and 5 can be considered as enhancing the quality of the population to increase the likelihood of escaping local optima. However, regarding Strategy 5 in HLOA and its Equation (15), although it includes random numbers, it may not be sufficient to allow the population to escape local optima. Moreover, it completely ignores the role of the current solution, which may reduce the diversity of the population in the early stages of iteration. Therefore, TEO is used to replace Equation (15). The essence of TEO is to generate enhanced quality solutions by combining the best position, the current velocity position, and the average position of each dimension. The parameters μ1 and μ2 in TEO are highly random, making it easier for the population to escape local optima and contributing to increased diversity within the population. The parameter δ is designed to maintain a balance between exploration and exploitation within the population. The TEO formula is inspired by the TAO strategy in the Newton–Raphson-based optimizer [34]. The mathematical expression of the TEO is as follows:
where t represents the current iteration number; μ1 and μ2 are random numbers based on β; β denotes a binary number, either 1 or 0; rand denotes the random number; and is a vector obtained by combining the average positions of all search agents in each dimension.
3.2.3. Sudden Attack Model
Horned lizards possess the ability to crypsis, which not only confuses predators but also serves as an excellent tool for hunting prey. Their color closely matches their surroundings, making them difficult to detect. When they spot their prey, they often lie in wait, seizing the moment when the prey is unaware, and then use their tongues to capture and devour the prey. Inspired by this unique hunting behavior, a sudden attack mathematical model was established to mimic this behavior. The sudden attack can enable the algorithm to systematically change the search step length and direction, helping to increase population diversity and escape local optima. The mathematical model for sudden attack is as follows:
where γ is set to 6.
The pseudocode of EHLOA is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Pseudo code of the EHLOA algorithm.
4. Experiments and Results
The experimental simulations in this section were conducted on a laptop equipped with the macOS Sonoma operating system, featuring 8 GB of RAM and an Apple M1 chip. The simulations were carried out using MATLAB R2023a. To evaluate the performance of EHLOA, it will be compared with HLOA and three classical algorithms widely used in engineering problems: Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) [35], Whale optimization algorithm (WOA) [36], Particle swarm optimization (PSO) [37], as well as three highly cited algorithms proposed in the last three years: Honey badger algorithm (HBA) [38], Golden jackal optimization algorithm (GJO) [39], and Dwarf mongoose optimization algorithm (DMO) [40].
4.1. Experiments 1: In Benchmark Functions
In this section, the tests will be conducted using the F1–F13 functions from the CEC2005 benchmark set [41], where F1–F7 are unimodal test functions and F8–F13 are multimodal test functions. To assess the robustness of the algorithms, these test functions will have dimensions of 30, 100. All algorithms will independently run 30 times on these test functions. The maximum number of iterations for each algorithm will be set to 1000, and the population size will be set to 30. The detailed expressions and optimal values of the test functions are provided in Table A1 in the Appendix A, and the important parameter settings for the algorithms are consistent with the settings in their references—please refer to [35,36,37,38,39,40]. Table A2 and Table A3 in the Appendix A present the minimum values, mean values, and standard deviations obtained by eight algorithms after 30 independent runs on benchmark functions with 30 and 100 dimensions, respectively. To enhance readability, the best results for each of the three statistical indicators on each benchmark function are highlighted.
As shown in Table A2 in the Appendix A, EHLOA achieved the best minimum values for all benchmark functions except F12. It also obtained the best mean values for all benchmark functions except F6 and F12, and the best standard deviations for all benchmark functions except F6, F8, and F12. From Table A3 in the Appendix A, it can be seen that EHLOA achieved the best minimum values and mean values in all cases under the 100-dimensional benchmark functions. Additionally, EHLOA obtained the best standard deviations for all benchmark functions except F6 and F13.
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of EHLOA, Wilcoxon signed-rank tests [42] were conducted to compare EHLOA’s results on each benchmark function with those of the comparison algorithms. This test determines whether there are statistically significant differences between EHLOA and the comparison algorithms on the benchmark functions. The tests were performed at the 5% significance level. When the p-value is less than 0.05, the result is denoted as “+” or “−”. “+” indicates that EHLOA performs better on the given benchmark function, while “−” indicates that EHLOA performs worse. When the p-value is greater than 0.05, the result is denoted as “=“, indicating that EHLOA and the comparison algorithm have similar performance on the given benchmark function. Table A4 and Table A5 in Appendix A present the p-values and Wilcoxon signed-rank test results for the 30-dimensional and 100-dimensional benchmark functions, respectively.
It can be found from Table A4 in Appendix A that EHLOA performs worse than the comparison algorithm HBA only on F6 and F12 for the 30-dimensional benchmark functions. The remaining results indicate that EHLOA’s performance is not inferior to the comparison algorithms, and it outperforms them in most cases. Specifically, EHLOA outperforms HLOA and HBA 8 times, GWO and PSO 12 times, WOA and GJO 10 times, and it outperforms DMO on all benchmark functions. In Table A5 in the Appendix A, EHLOA does not perform worse than any of the comparison algorithms on any benchmark function for the 100-dimensional benchmark functions. Specifically, EHLOA outperforms HLOA 8 times, GWO 12 times, WOA, HBA, and GJO 10 times, and it outperforms PSO and DMO on all benchmark functions.
4.2. Experiment 2: In the Flood Control Operation Model
In this section, the performance of 8 algorithms will be analyzed after independently running the flood control operation model 30 times under the conditions of a population size of 100 and a maximum of 1000 iterations.
Table 3 presents the minimum and mean values of the objective function obtained by EHLOA and the comparison algorithms after 30 independent runs on four typical flood datasets. In Table 3, the best value in each row is highlighted in bold, and N/A indicates that the algorithm could not find a feasible solution. As shown in Table 3, EHLOA achieved the best minimum and mean values across all four floods. Except for Flood 2, EHLOA’s minimum values after 30 runs were more than 40 lower than the second-best algorithm’s minimum values in the other three floods. However, in Flood 2, EHLOA’s minimum value was only slightly lower than that of HLOA. In Flood 1, EHLOA had the largest lead in mean value, outperforming the second-best HLOA by more than 100. In Flood 3, EHLOA’s lead in the mean value was the smallest, just slightly better than GWO. In both Flood 2 and Flood 4, EHLOA’s mean values were more than 20 lower than the second-best mean values.

Table 3.
Optimization results of EHLOA and comparison algorithms on benchmark flood control operation model.
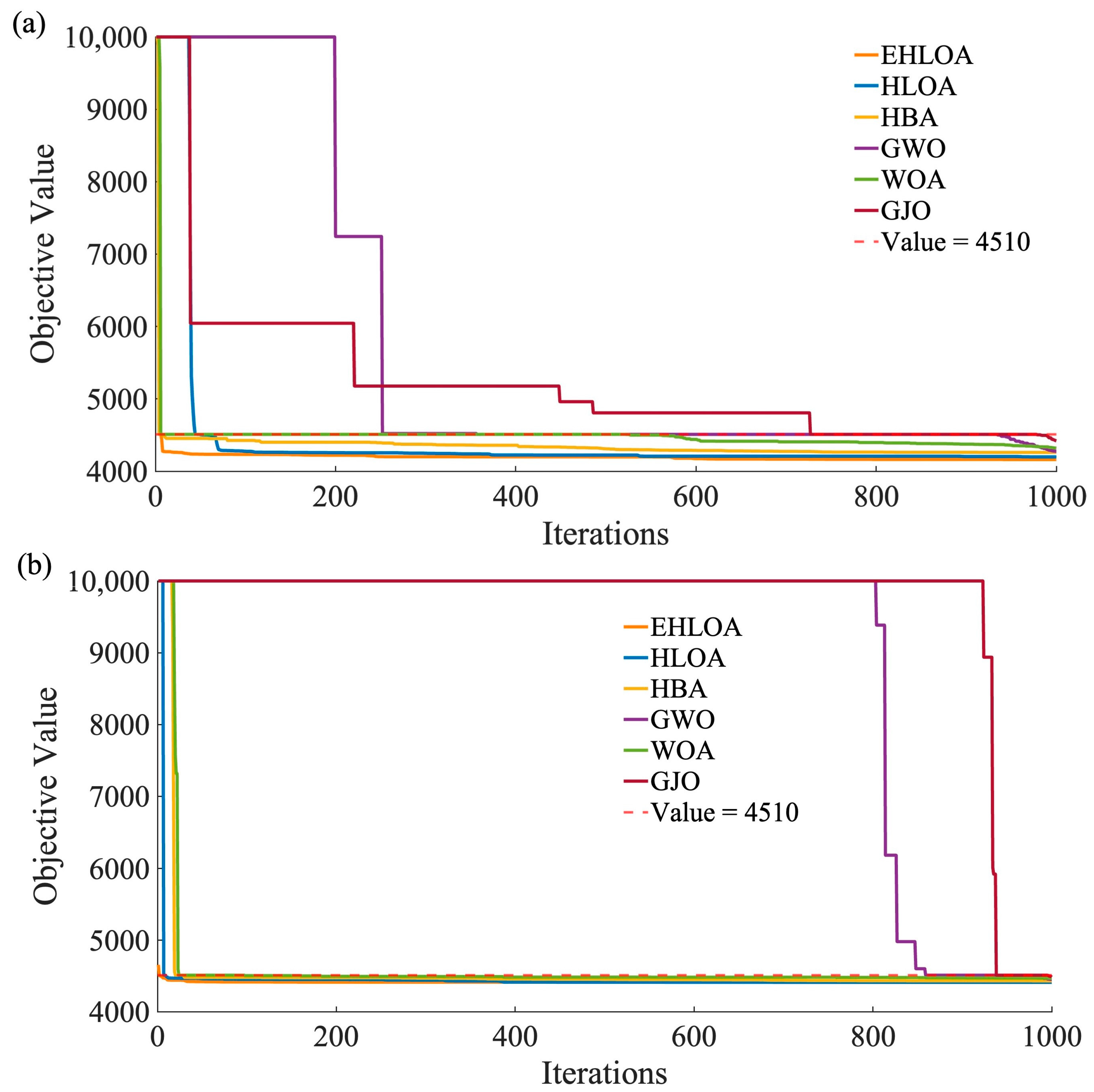
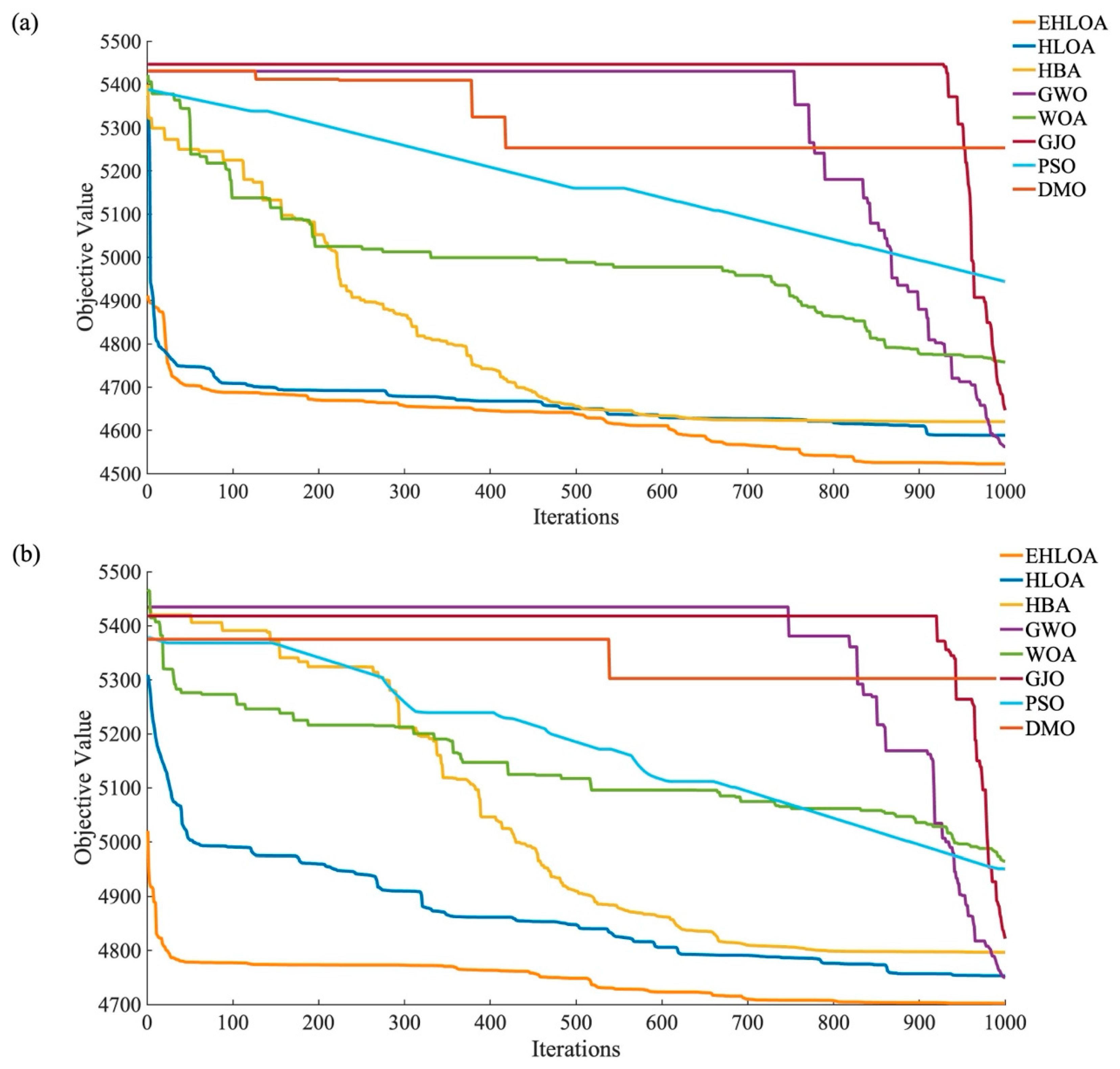
Figure 4a,b shows the iterative processes of EHLOA, HLOA, HBA, GWO, WOA, and GJO when operating flood 1 and flood 2, respectively. These figures present the iterative process for the minimum fitness values. Please note that due to the large penalty function coefficients, fitness values exceeding 10,000 are uniformly replaced with a fitness value of 10,000. Additionally, the value 4510 is marked in the figure, representing the discharge limit of LJX under a millennial flood. Values below 4510 indicate that the algorithm has found a feasible region. From Figure 4a, it can be seen that the fitness values for all six algorithms exceed 10,000 at the start of the iterations. However, EHLOA quickly converges to below 4510 and achieves the best fitness value at the end of the iterations. Observing the iterative curves of GWO, GJO, and WOA, it is evident that they remain at the value of 4510 for an extended period, Additionally, GJO and GWO converge to 4510 significantly slower than the other four algorithms. As observed in Figure 4b, EHLOA starts with a fitness value around 4510, while the other five algorithms have initial fitness values exceeding 10,000. Moreover, the fitness values for both GWO and GJO do not drop below 10,000 until after 800 iterations. By the end of the iterations, the fitness values of EHLOA and HLOA are nearly the same and are better than those of the other four algorithms.
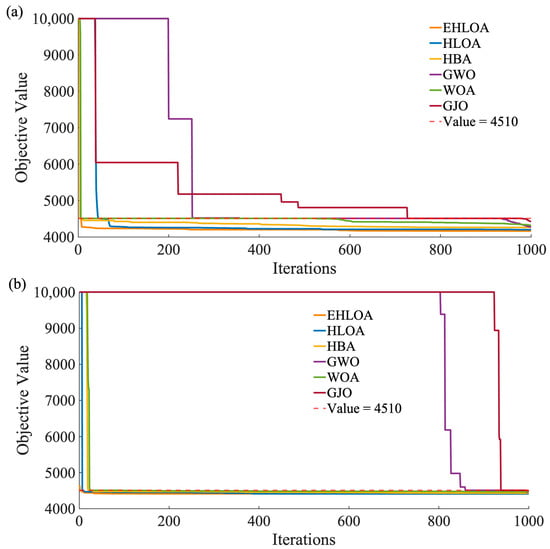
Figure 4.
Iterative process for the minimum fitness values after 30 runs of each algorithm on flood 1 (a) and flood 2 (b). Note: flood1 and flood 2 denote a millennial flood based on the typical 1964 and 1967 flood, respectively.
Figure 5a,b shows the iterative processes of EHLOA, HLOA, HBA, GWO, WOA, GJO, PSO, and DMO when operating flood 3 and flood 4, respectively. These figures present the iterative process for the minimum fitness values too. As shown in Figure 5a,b, EHLOA starts with a fitness value that is more than 300 lower than the other seven algorithms at the beginning of the operation process. Except for DMO, EHLOA has the fastest convergence rate. Although DMO converges quickly, its final fitness values in Figure 5a,b are much higher than those of EHLOA. Additionally, EHLOA achieves the best fitness values for both flood 3 and flood 4, maintaining a noticeable lead over the second-best algorithm.
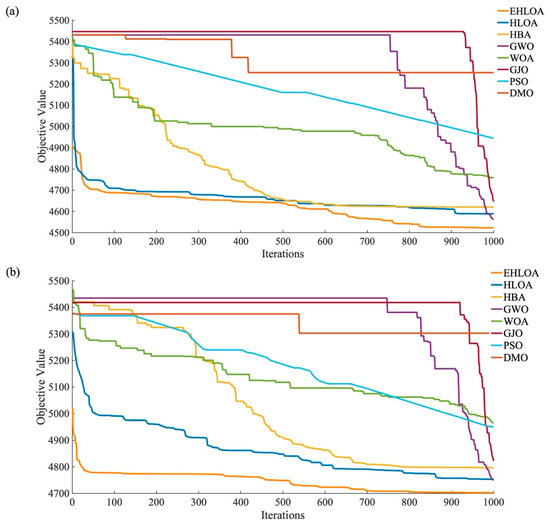
Figure 5.
Iterative process for the minimum fitness values after 30 runs of each algorithm on flood 3 (a) and flood 4 (b). Note: flood 3 and flood 4 denote a decamillennial flood based on the typical 1964 and 1967 flood, respectively.
4.3. Analysis of the Flood Control Operation Process Obtained by EHLOA
In this section, the scheme with the smallest fitness value obtained by EHLOA when operating four floods will be analyzed. Table 4 presents the best peak reduction rates achieved by EHLOA for four floods. As shown in Table 4, under EHLOA operation, the peak reduction rates of the cascade reservoirs are all above 50%, with higher peak reduction rates for the peak-shaped floods compared to the flat-topped floods.

Table 4.
Best peak reduction rates achieved by EHLOA for four floods.
Figure 6 and Figure 7 illustrate the variations in reservoir storage capacity, inflow, and discharge flow for floods 1 to 2, respectively. To better demonstrate the flood control effectiveness of the reservoir, the inflow of LJX uses the design flood, rather than the outflow from LYX during the operating process. Due to the peak shape and operating process of the decamillennial floods (flood 3 and flood 4) being essentially the same as those of the millennial floods, their detailed operating processes are included in Appendix B without further analysis.
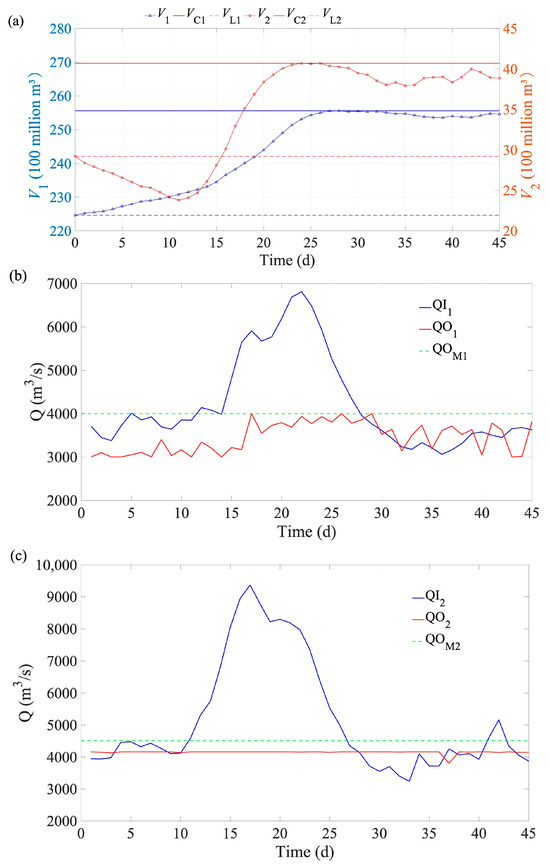
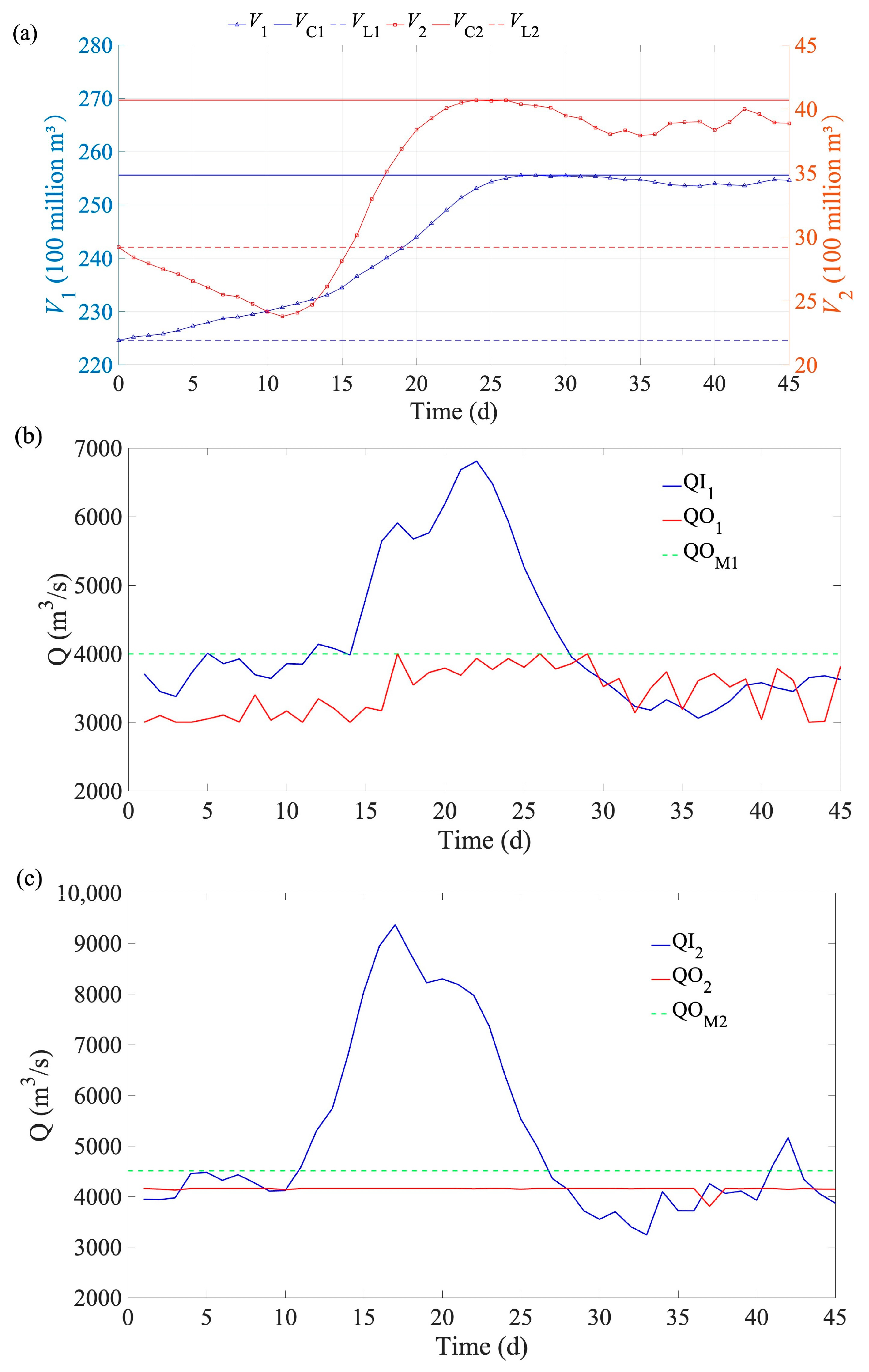
Figure 6.
Changes in reservoir volume (a) and discharge flow of LYX (b) and LJX (c) reservoirs for flood 1 (a millennial flood based on the typical 1964 flood). Note: V denotes the reservoir volume at the time t; VL denotes the reservoir capacity at the dead water level; VC denotes the reservoir capacity at the check flood level; QI denotes the reservoir inflow at the time t; QOM denotes the maximum allowable discharge flow; and subscripts 1 and 2 denote LYX and LJX reservoirs, respectively.
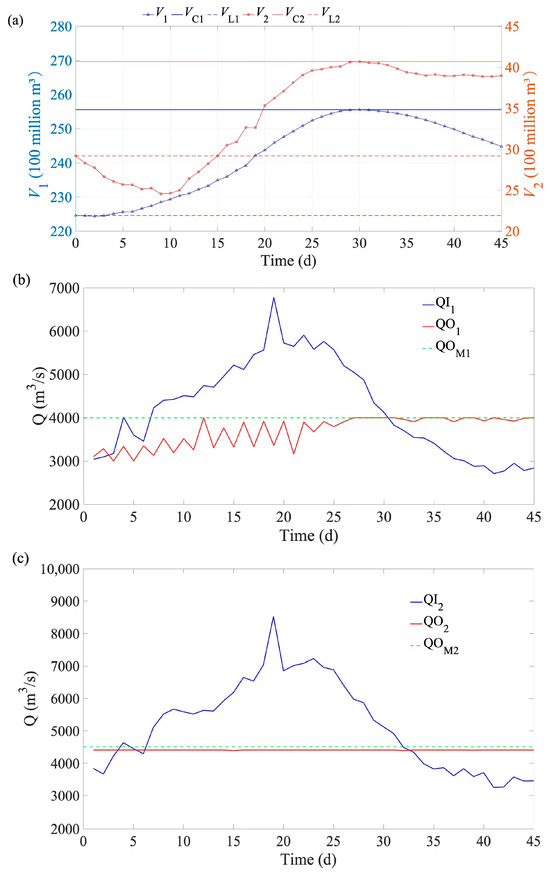
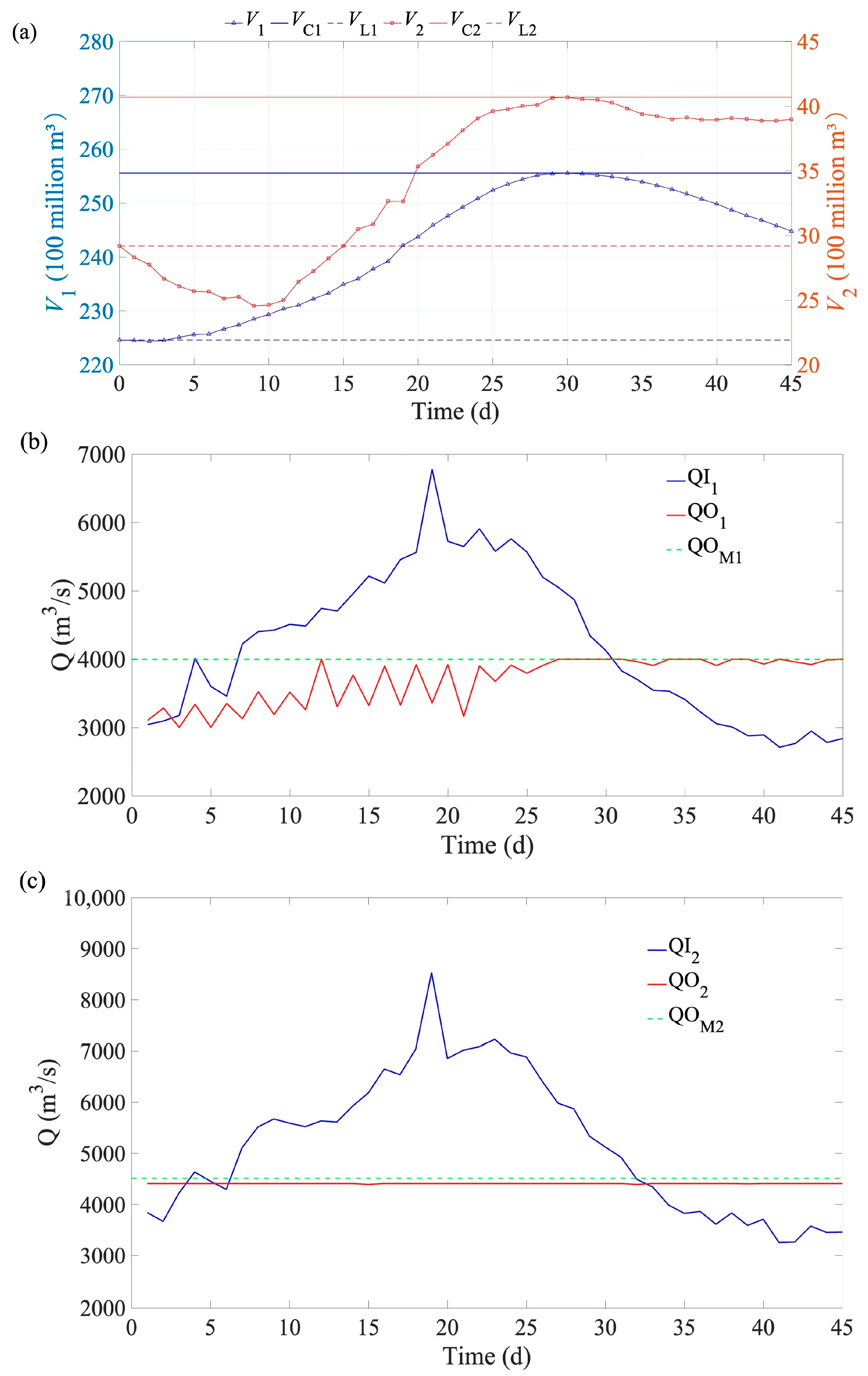
Figure 7.
Changes in reservoir volume (a) and discharge flow of LYX (b) and LJX (c) reservoirs for flood 1 (a millennial flood based on the typical 1967 flood). (Note: the signs are the same with Figure 6).
Figure 6a shows that the pre-release period for LJX lasts up to 11 days, with its storage capacity being pre-released to 2.38 million m3 on the 11th day. LYX and LJX approach their flood control storage capacities (VL), on the 27th and 24th days, respectively. After this, the storage capacities gradually decrease, but LYX’s storage capacity rises again on the 40th day, while LJX’s storage capacity rises again on the 41st and 42nd days. Figure 5b indicates that LYX’s maximum inflow occurs on the 22nd day, after which the inflow gradually decreases. However, LYX’s inflow rate significantly increases again between the 38th and 41st days. The discharge process for LYX exhibits noticeable fluctuations but does not exceed the fluctuation constraint of 1000 m3/s. Figure 6c illustrates that LJX’s maximum inflow occurs on the 17th day, after which the inflow gradually decreases. However, LJX’s inflow rate significantly increases again on the 41st and 42nd days, rising to 5164 m3/s on the 42nd day. Overall, the discharge process for LJX is stable, with no significant fluctuations except on the 37th day.
Figure 7a shows that the pre-release period for LJX lasts 9 days, with its storage capacity being pre-released to 2.46 billion m3 on the 9th day. LYX and LJX approach their flood control storage capacities (VL), on the 29th day, and there is no significant rebound in their storage capacities afterward. Figure 7b indicates that LYX’s maximum inflow occurs on the 19th day. Although the inflow decreases between the 20th and 24th days, there are noticeable increases on the 22nd and 24th days. After the 24th day, LYX’s inflow declines rapidly, with a slight increase on the 43rd day, but it does not exceed 3000 m3/s. LYX’s discharge exhibits considerable fluctuations from the 1st to the 27th day, but these do not exceed the fluctuation constraint. After the 27th day, LYX’s discharge becomes stable with no significant fluctuations. Figure 7c illustrates that LJX’s maximum inflow occurs on the 20st day, followed by a gradual decrease. However, there is a noticeable increase on the 23rd day. Although there are rebounds after the 35th day, the inflow does not exceed 3600 m3/s.
5. Discussion
5.1. Robustness and Scalability of EHLOA
EHLOA demonstrates a good scalability. Comparing the results from Table A2, Table A3, Table A4 and Table A5 in the Appendix A, it can be seen that EHLOA’s performance on the 100-dimensional benchmark functions is even better than on the 30-dimensional ones. For the 30-dimensional benchmark functions, HBA was able to achieve the best minimum values and means on F6 and F12. However, for the 100-dimensional benchmark functions, EHLOA achieved the best minimum values and means across all benchmark functions. Additionally, according to the Wilcoxon test results in Table A4 and Table A5 in Appendix A, EHLOA outperformed the comparison algorithms three more times on the 100-dimensional problems than on the 30-dimensional ones. Interestingly, according to the results from Table A2 and Table A3 in Appendix A, EHLOA’s average and minimum values on benchmark functions F5 and F13 are lower for the 100-dimensional problems than for the 30-dimensional ones. This demonstrates that EHLOA’s performance does not degrade with increasing problem dimensionality and may even excel in handling high-dimensional problems.
EHLOA has demonstrated a good robustness. As shown in Table A2 and Table A3 in Appendix A, the comparison algorithms performed poorly on the unimodal function F5 and the multimodal function F8, with the minimum and mean values after 30 runs being significantly distant from the theoretical optimal values. On F5, the mean value of EHLOA is below 0, while the mean values of all comparison algorithms are above 20. On F8, the minimum values of all comparison algorithms, except for WOA, are more than 10,000 away from the theoretical optimal value after 30 runs, whereas the minimum value of EHLOA equals the theoretical optimal value. F5 and F8 present a substantial challenge due to the presence of numerous local optima, causing many algorithms to become trapped in these local optima, resulting in poor performance [43,44]. EHLOA’s excellent performance on the most challenging unimodal and multimodal functions in the CEC2005 test set demonstrates its ability to handle different types of problems, verifying its robustness and ability to escape local optima.
5.2. Reliability of EHLOA in a Multi-Reservoir Flood Control Operation
From Table 3, it can be seen that whether it is a millennial flood (flood 1, flood 2) or a decamillennial flood (flood 3, flood 4), the mean objective function value for operating peak-shaped floods (flood 1, flood 3) are lower than those for operation flat-topped floods (flood 2, flood 4) for all algorithms. This indicates that flat-topped floods are more difficult to operate than peak-shaped floods. EHLOA achieved the lowest mean fitness values and lowest minimum values in all four floods, demonstrating its good robustness in the MRFCO problem. It performs best regardless of whether it is operation peak-shaped or flat-topped floods. The fitness curves corresponding to the best fitness values of each algorithm for the four floods show that EHLOA consistently obtained the lowest best fitness values, further illustrating its excellent robustness in the MRFCO problem.
The significantly lower initial fitness values of EHLOA compared to the other algorithms when operating floods 2 to 4 suggest that the Circle map initialization strategy likely enables EHLOA to find feasible solutions in less time for the MRFCO problem. EHLOA exhibited the fastest convergence speed and the highest convergence accuracy (lowest fitness value) across all four floods, indicating strong convergence performance in the MRFCO problem.
Additionally, when operating flood 1, the fitness values of GWO, WOA, and GJO remained at 4510 for an extended period. This is because 4510 is the discharge limit of LJX for a millennial flood; a fitness value of 4510 implies that the algorithm releases a large flow to prevent LYX and LJX from exceeding their flood control capacity, resulting in a penalty function value of 0. However, the final operation results show that fitness values can be below 4510, indicating that 4510 is a local optimum. The iterative curve of EHLOA did not stay at 4510, illustrating that EHLOA has a strong ability to escape local optima in the MRFCO problem and can effectively integrate with penalty functions to handle constraints.
From the flood operation results and the operation process, the schemes provided by EHLOA are reliable. Firstly, under the operation of EHLOA, the peak reduction rates of the cascade reservoirs for all four floods are above 50%, proving that EHLOA has strong peak reduction capabilities for different types of floods. Secondly, the discharge processes of LJX are very stable, which greatly protects the stability of downstream slopes of the cascade reservoirs.
Finally, the changes in storage capacity of LYX and LJX during the operating of flood 1 and flood 2 show significant differences. The pre-release period for flood 1 is two days longer than that for flood 2, due to the much larger total flood volume in the first 10 days of the 1967 design flood compared to the 1964 design flood. During the operating of flood 1, both LYX and LJX exhibit a noticeable rebound in storage capacity towards the end of the operating period, whereas this phenomenon does not occur during the operating of flood 2. This is because the total flood volume in the last 10 days of the 1964 design flood is much larger than that of the 1967 design flood. Therefore, the 1964 design flood is characterized by smaller early and peak flows but larger later flows, while the 1967 design flood has larger early and peak flows but smaller later flows. EHLOA can flexibly adjust the pre-release duration and provide different operating schemes based on the varying flood patterns of these two types of floods.
6. Conclusions
The main conclusions of this paper are summarized as follows:
(1) EHLOA has excellent robustness and scalability.
(2) EHLOA can be considered a reliable algorithm for solving multi-reservoir flood control operation problems.
The methods used in this paper to enhance EHLOA’s performance are improving the quality of initial solutions and strengthening the ability to escape local optima. However, balancing exploration and exploitation is also crucial for metaheuristic algorithms. Therefore, future work will analyze the exploration-to-exploitation ratio of HLOA to determine if improvements are needed. Additionally, EHLOA will be tested on more benchmark functions and applied to parallel reservoir flood control operation to further validate its performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L. and Y.X.; methodology, C.L.; software, S.L.; validation, C.L., Y.X. and S.L.; formal analysis, J.Q.; investigation, Y.X.; resources, C.L.; data curation, J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.X.; visualization, H.F.; supervision, H.D.; project administration, Y.X.; funding acquisition, Y.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by 2024 Yangzhou University Humanities and Social Sciences Research Fund Project (Grant No. xjj2024-38), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42401010), The Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (Grant No. 24KJB570005), Chongqing Water Conservancy Science and Technology Project (Grant No. CQSLK-2023007), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52379027; and Grant No. 52379016).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The processed data are not publicly available as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jiyao Qin was employed by the company Chongqing Western Water Resources Development Co., Ltd., author Jianfeng Wei was employed by the company Chongqing Yufa Hydraulic Research Institute Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
Common abbreviations and their full names used in this paper:
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Type |
| EHLOA | Enhanced Horned Lizard Optimization Algorithm | Algorithm |
| HLOA | Horned Lizard Optimization Algorithm | Algorithm |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimizer | Algorithm |
| WOA | Whale optimization algorithm | Algorithm |
| PSO | Particle swarm optimization | Algorithm |
| HBA | Honey badger algorithm | Algorithm |
| GJO | Golden jackal optimization algorithm | Algorithm |
| DMO | Dwarf mongoose optimization algorithm | Algorithm |
| LYX | Longyangxia | Reservoir |
| LJX | Liujiaxia | Reservoir |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Details of the benchmark function.
Table A1.
Details of the benchmark function.
| Fun | Dimension | Range | Theoretical Optimization Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30/100 | [−100, 100] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−10, 10] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−100, 100] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−100, 100] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−30, 30] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−100, 100] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−1.28, 1.28] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−500, 500] | 418.9829 × Dimension | |
| 30/100 | [−5.12, 5.12] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−32, 32] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−600, 600] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−50, 50] | 0 | |
| 30/100 | [−50, 50] | 0 |

Table A2.
Optimization results of EHLOA and comparison algorithms on benchmark functions (dimensions = 30).
Table A2.
Optimization results of EHLOA and comparison algorithms on benchmark functions (dimensions = 30).
| Fun. | Index | EHLOA | HLOA | GWO | WOA | PSO | HBA | GJO | DMO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Min | 0 | 0 | 2.85 × 10−61 | 7.49 × 10−167 | 3.25 × 10−6 | 5.06 × 10−288 | 4.08 × 10−117 | 1.02 × 10−4 |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 7.68 × 10−59 | 1.48 × 10−148 | 4.50 × 10−5 | 1.33 × 10−276 | 1.25 × 10−110 | 4.35 × 10−4 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 2.25 × 10−58 | 7.39 × 10−148 | 6.73 × 10−5 | 0 | 6.81 × 10−110 | 3.35 × 10−4 | |
| F2 | Min | 0 | 8.99 × 10−264 | 1.58 × 10−35 | 9.65 × 10−115 | 8.69 × 10−5 | 8.21 × 10−152 | 2.99 × 10−68 | 3.21 × 10−4 |
| Mean | 0 | 1.06 × 10−243 | 1.16 × 10−34 | 2.79 × 10−100 | 0.33 | 1.06 × 10−146 | 2.20 × 10−66 | 7.69 × 10−3 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 9.46 × 10−35 | 1.53 × 10−99 | 1.83 | 2.68 × 10−146 | 3.49 × 10−66 | 1.28 × 10−2 | |
| F3 | Min | 0 | 0 | 3.92 × 10−20 | 2.29 × 103 | 1.76 × 102 | 4.71 × 10−218 | 1.34 × 10−49 | 1.81 × 104 |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 7.19 × 10−14 | 2.04 × 104 | 8.11 × 102 | 4.01 × 10−200 | 5.9 × 10−38 | 5.14 × 104 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 3.73 × 10−13 | 1.06 × 104 | 1.29 × 103 | 0 | 2.47 × 10−37 | 1.45 × 104 | |
| F4 | Min | 0 | 3.62 × 10−255 | 1.05 × 10−15 | 7.7 × 10−1 | 2.47 | 6.05 × 10−124 | 1.66 × 10−36 | 3.54 × 102 |
| Mean | 0 | 2.71 × 10−239 | 2.03 × 10−14 | 3.50 × 101 | 4.55 | 5.23 × 10−117 | 5.88 × 10−33 | 4.54 × 102 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 3.68 × 10−14 | 2.93 × 101 | 9.6 × 101 | 2.12 × 10−116 | 2.08 × 10−32 | 4.82 | |
| F5 | Min | 2.95 × 10−12 | 4.13 × 10−4 | 2.62 × 101 | 2.69 × 101 | 2.02 × 101 | 2.11 × 101 | 2.62 × 101 | 3.57 × 102 |
| Mean | 4.25 × 10−2 | 2.2 × 101 | 2.71 × 101 | 2.73 × 101 | 1.83 × 102 | 2.18 × 101 | 2.75 × 101 | 2.43 × 103 | |
| Std | 2 × 10−2 | 1.23 × 101 | 7.62 × 10−1 | 6.28 × 10−1 | 5.42 × 102 | 4.56 × 10−1 | 7.43 × 10−1 | 2.24 × 103 | |
| F6 | Min | 3.13 × 10−11 | 5.89 × 10−6 | 1.64 × 10−5 | 1.04 × 10−2 | 4.07 × 10−6 | 2.62 × 10−9 | 1.5 | 9.28 × 10−5 |
| Mean | 1.95 × 10−5 | 1.72 × 10−4 | 5.24 × 10−1 | 1.09 × 10−1 | 6.39 × 10−5 | 1.97 × 10−8 | 2.75 | 4.93 × 10−4 | |
| Std | 2.55 × 10−5 | 1.91 × 10−4 | 2.89 × 10−1 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 9.14 × 10−5 | 1.06 × 10−7 | 4.71 × 10−1 | 2.99 × 10−4 | |
| F7 | Min | 1.54 × 10−6 | 3.44 × 10−6 | 2.05 × 10−4 | 4.28 × 10−5 | 9.03 × 10−3 | 3.71 × 10−5 | 4.99 × 10−5 | 5.1 × 10−2 |
| Mean | 4.70 × 10−5 | 1.53 × 10−4 | 9.20 × 10−4 | 1.36 × 10−3 | 2.41 × 10−2 | 1.65 × 10−3 | 1.89 × 10−5 | 8.25 × 10−2 | |
| Std | 3.94 × 10−5 | 1.48 × 10−4 | 4.43 × 10−4 | 1.52 × 10−3 | 7.63 × 10−3 | 1.02 × 10−4 | 1.31 × 10−4 | 1.74 × 10−2 | |
| F8 | Min | −12,569.487 | −10,417.75 | −7318.73 | −12,569.486 | −8897.80 | −10,291.76 | −6410.95 | infinity |
| Mean | −11,525.40 | −7412.19 | −6039.21 | −11,330.87 | −7793.66 | −8865.33 | −3928.43 | infinity | |
| Std | 1548.62 | 995.25 | 718.53 | 1633.55 | 539.36 | 952.32 | 1053.01 | infinity | |
| F9 | Min | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.36 × 101 | 0 | 0 | 1.25 × 102 |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 8.1 × 10−1 | 0 | 4.38 × 101 | 0 | 0 | 2.02 × 102 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 2.13 | 0 | 1.67 × 101 | 0 | 0 | 2.56 × 101 | |
| F10 | Min | 4.4 × 10−16 | 4.4 × 10−16 | 7.55 × 10−15 | 4.4 × 10−16 | 3.1 × 10−4 | 4.4 × 10−16 | 3.99 × 10−15 | 5.91 × 10−3 |
| Mean | 4.4 × 10−16 | 4.4 × 10−16 | 1.59 × 10−14 | 4.1 × 10−15 | 8.1 × 10−3 | 4.4 × 10−16 | 4.47 × 10−15 | 1.53 × 10−2 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 3.02 × 10−15 | 2.37 × 10−15 | 1.86 × 10−2 | 0 | 1.23 × 10−15 | 1.63 × 10−2 | |
| F11 | Min | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.05 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | 1.49 × 10−3 |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 1.38 × 10−3 | 0 | 1.85 × 10−2 | 0 | 0 | 5.98 × 10−2 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 4.55 × 10−3 | 0 | 8.08 × 10−3 | 0 | 0 | 1.1 × 10−1 | |
| F12 | Min | 1.98 × 10−9 | 9.66 × 10−8 | 9.14 × 10−3 | 6.33 × 10−4 | 7.28 × 10−8 | 4.55 × 10−10 | 7.84 × 10−2 | 6.21 |
| Mean | 1.69 × 10−6 | 6.92 × 10−3 | 4.24 × 10−2 | 6.08 × 10−3 | 6.22 × 10−2 | 1.66 × 10−8 | 2.63 × 10−1 | 1.53 × 101 | |
| Std | 2.16 × 10−6 | 2.6 × 10−2 | 2.56 × 10−2 | 5.29 × 10−3 | 1.03 × 10−1 | 3.97 × 10−8 | 1.79 × 10−1 | 5.03 | |
| F13 | Min | 4.49 × 10−8 | 6.04 × 10−7 | 1.00 × 10−1 | 3.83 × 10−2 | 2.63 × 10−6 | 1.12 × 10−7 | 1.20 | 9.91 |
| Mean | 1.73 × 10−2 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 5.34 × 10−1 | 2.44 × 10−1 | 3.49 × 10−3 | 1.51 × 10−1 | 1.61 | 2.86 × 101 | |
| Std | 6.55 × 10−2 | 3.81 × 10−1 | 2.10 × 10−1 | 1.50 × 10−1 | 5.06 × 10−3 | 1.85 × 10−1 | 2.41 × 10−1 | 3.37 × 101 |

Table A3.
Optimization results of EHLOA and comparison algorithms on benchmark functions (dimensions = 100).
Table A3.
Optimization results of EHLOA and comparison algorithms on benchmark functions (dimensions = 100).
| Fun. | Index | EHLOA | HLOA | GWO | WOA | PSO | HBA | GJO | DMO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Min | 0 | 0 | 1.58 × 10−30 | 1.17 × 10−166 | 1.60 × 102 | 5.26 × 10−262 | 4.55 × 10−62 | 1.97 × 105 |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 2.63 × 10−29 | 1.05 × 10−148 | 6.46 × 102 | 7.56 × 10−248 | 5.52 × 10−60 | 2.51 × 105 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 4.42 × 10−29 | 5.75 × 10−148 | 1.83 × 103 | 0 | 1.19 × 10−59 | 2.27 × 105 | |
| F2 | Min | 0 | 8.25 × 10−259 | 2.19 × 10−18 | 8.62 × 10−113 | 6.06 | 8.56 × 10−138 | 5.51 × 10−38 | 1.62 × 1016 |
| Mean | 0 | 2.36 × 10−239 | 6.54 × 10−18 | 3.83 × 10−103 | 2.08 × 101 | 6.82 × 10−132 | 4.71 × 10−37 | 7.98 × 1034 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 3.04 × 10−18 | 1.99 × 10−102 | 1.20 × 101 | 3.41 × 10−131 | 1.65 × 10−36 | 2.96 × 1035 | |
| F3 | Min | 0 | 0 | 2.00 × 10−2 | 5.44 × 106 | 4.34 × 104 | 1.57 × 10−186 | 3.85 × 10−19 | 7.15 × 105 |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 9.95 | 8.87 × 106 | 6.45 × 104 | 4.02 × 10−165 | 2.00 × 10−4 | 1.06 × 106 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 1.92 × 101 | 1.58 × 106 | 1.30 × 104 | 0 | 6.00 × 10−3 | 2.23 × 105 | |
| F4 | Min | 0 | 3.40 × 10−256 | 3.87 × 10−5 | 1.79 × 101 | 2.60 × 101 | 9.63 × 10−89 | 6.92 × 10−13 | 9.27 × 101 |
| Mean | 0 | 5.82 × 10−241 | 1.00 × 10−2 | 7.67 × 101 | 3.34 × 101 | 7.27 × 10−83 | 1.53 | 9.53 × 101 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 4.00 × 10−2 | 2.26 × 101 | 3.09 | 2.18 × 10−82 | 5.20 | 1.04 | |
| F5 | Min | 9.09 × 10−11 | 4.13 × 10−4 | 9.59 × 101 | 9.67 × 101 | 1.61 × 104 | 9.24 × 101 | 9.62 × 102 | 9.64 × 108 |
| Mean | 8.59 × 10−4 | 2.20 × 101 | 9.77 × 101 | 9.77 × 101 | 5.59 × 104 | 9.57 × 101 | 9.82 × 101 | 1.12 × 109 | |
| Std | 2.58 × 10−3 | 1.23 × 101 | 8.00 × 10−1 | 4.40 × 10−1 | 3.23 × 104 | 1.99 | 6.02 × 10−1 | 8.29 × 107 | |
| F6 | Min | 2.91 × 10−10 | 5.89 × 10−6 | 6.74 | 9.10 × 10−1 | 1.23 × 102 | 2.24 | 1.55 × 101 | 1.99 × 105 |
| Mean | 9.21 × 10−5 | 1.72 × 10−4 | 9.11 | 2.13 | 6.74 × 102 | 4.16 | 1.68 × 101 | 2.43 × 106 | |
| Std | 1.15 × 10−5 | 1.91 × 10−4 | 1.02 | 9.51 × 10−1 | 1.83 × 103 | 8.41 × 10−1 | 8.36 × 10−1 | 2.11 × 105 | |
| F7 | Min | 1.34 × 10−6 | 3.44 × 10−6 | 1.14 × 10−3 | 6.55 × 10−5 | 5.33 × 10−1 | 2.44 × 10−5 | 5.31 × 10−5 | 1.06 × 103 |
| Mean | 9.21 × 10−5 | 1.53 × 10−4 | 2.43 × 10−3 | 1.31 × 10−3 | 8.10 × 10−1 | 2.68 × 10−4 | 5.98 × 10−4 | 1.77 × 103 | |
| Std | 1.15 × 10−5 | 1.48 × 10−4 | 1.21 × 10−3 | 1.53 × 10−3 | 1.70 × 10−1 | 2.92 × 10−4 | 4.33 × 10−4 | 2.08 × 102 | |
| F8 | Min | −41,898.29 | −25,513.15 | −20,216.25 | −41,897.14 | −25,484.57 | −28,539.74 | −16,502.35 | Inf |
| Mean | −37,887.25 | −22,227.35 | −15,699.06 | −37,799.01 | −21,852.99 | −24,870.91 | −9351.13 | Inf | |
| Std | 5381.91 | 1793.71 | 3511.17 | 5440.29 | 1453.26 | 3297.17 | 3940.74 | Inf | |
| F9 | Min | 0 | 0 | 2.27 × 10−13 | 0 | 2.09 × 102 | 0. | 0 | 1.45 × 103 |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 3.71 × 10−1 | 3.78 × 10−15 | 2.94 × 102 | 0 | 0 | 1.57 × 103 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 1.12 | 2.07 × 10−14 | 3.97 × 101 | 0 | 0 | 5.36 × 101 | |
| F10 | Min | 4.44 × 10−16 | 4.44 × 10−16 | 9.99 × 10−14 | 4.44 × 10−16 | 3.58 | 4.44 × 10−16 | 7.55 × 10−15 | 2.05 × 102 |
| Mean | 4.44 × 10−16 | 4.44 × 10−16 | 1.13 × 10−13 | 3.28 × 10−15 | 4.81 | 2.66 | 9.44 × 10−15 | 2.08 × 102 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 1.10 × 10−14 | 2.36 × 10−15 | 1.28 | 6.89 | 2.91 × 10−15 | 9.45 × 10−2 | |
| F11 | Min | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.47 | 0 | 0 | 1.91 × 103 |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 2.8 × 10−3 | 0 | 6.47 | 0 | 0 | 2.24 × 103 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 8.6 × 10−3 | 0 | 1.65 | 0 | 0 | 1.53 × 102 | |
| F12 | Min | 1.33 × 10−13 | 9.66 × 10−8 | 1.38 × 10−1 | 7.23 × 10−3 | 1.96 × 101 | 2.59 × 10−2 | 4.71 × 10−1 | 1.76 × 109 |
| Mean | 5.43 × 10−7 | 1.04 × 10−3 | 2.55 × 10−1 | 1.68 × 10−2 | 9.66 × 101 | 4.52 × 10−2 | 6.19 × 10−1 | 2.71 × 109 | |
| Std | 6.12 × 10−7 | 5.68 × 10−3 | 7.55 × 10−2 | 6.3 × 10−3 | 2.25 × 102 | 1.45 × 10−2 | 7.49 × 10−2 | 3.07 × 108 | |
| F13 | Min | 2.49 × 10−9 | 1.28 × 10−5 | 5.58 | 7.62 × 10−1 | 6.23 × 102 | 5.77 | 7.88 | 3.89 × 109 |
| Mean | 7.60 × 10−3 | 9.41 × 10−3 | 6.29 | 1.97 | 7.32 × 103 | 7.41 | 8.46 | 4.93 × 109 | |
| Std | 4.06 × 10−2 | 2.61 × 10−2 | 3.38 × 10−1 | 7.41 × 10−1 | 7.50 × 103 | 7.95 × 10−1 | 2.95 × 10−1 | 3.96 × 109 |

Table A4.
Wilcoxon signed-rank test simulation results: EHLOA and comparative algorithms on benchmark functions (dimensions = 30).
Table A4.
Wilcoxon signed-rank test simulation results: EHLOA and comparative algorithms on benchmark functions (dimensions = 30).
| Fun. | Index | HLOA | GWO | WOA | PSO | HBA | GJO | DMO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | p-value | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F2 | p-value | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F3 | p-value | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F4 | p-value | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F5 | p-value | 1.74 × 10−4 | 4.86 × 10−5 | 4.86 × 10−5 | 2.35 × 10−6 | 5.31 × 10−5 | 2.35 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F6 | p-value | 2.16 × 10−5 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.04 × 10−3 | 1.92 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | |
| F7 | p-value | 5.31 × 10−5 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 2.13 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 3.18 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F8 | p-value | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 6.64 × 10−4 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | = | + | + | + | + | |
| F9 | p-value | 1 | 3.13 × 10−2 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | + | = | + | = | = | + | |
| F10 | p-value | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 7.12 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | + | + | + | = | + | + | |
| F11 | p-value | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | = | = | + | = | = | + | |
| F12 | p-value | 8.31 × 10−4 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 9.32 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | |
| F13 | p-value | 1.25 × 10−2 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 6.98 × 10−6 | 0.32 | 2.22 × 10−4 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | = | + | + | + | |
| Total | (+/=/−) | 8/5/0 | 12/1/0 | 10/3/0 | 12/1/0 | 8/3/2 | 10/3/0 | 13/0/0 |

Table A5.
Wilcoxon signed-rank test simulation results: EHLOA and comparative algorithms on benchmark functions (dimensions = 100).
Table A5.
Wilcoxon signed-rank test simulation results: EHLOA and comparative algorithms on benchmark functions (dimensions = 100).
| Fun. | Index | HLOA | GWO | WOA | PSO | HBA | GJO | DMO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | p-value | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F2 | p-value | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F3 | p-value | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F4 | p-value | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F5 | p-value | 2.35 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 4.86 × 10−5 | 2.35 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F6 | p-value | 4.45 × 10−5 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.04 × 10−3 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F7 | p-value | 2.11 × 10−3 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 2.13 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 4.45 × 10−5 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F8 | p-value | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | = | + | + | + | + | |
| F9 | p-value | 1 | 1.48 × 10−6 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | + | = | + | = | = | + | |
| F10 | p-value | 1 | 1.61 × 10−6 | 2.93 × 10−5 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 0.12 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | + | + | + | = | + | + | |
| F11 | p-value | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1 | 1 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | = | = | = | + | = | = | + | |
| F12 | p-value | 2.35 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| F13 | p-value | 1.39 × 10−2 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 1.73 × 10−6 |
| +/=/− | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Total | (+/=/−) | 8/5/0 | 12/1/0 | 10/3/0 | 13/0/0 | 10/3/0 | 10/2/0 | 13/0/0 |
Appendix B
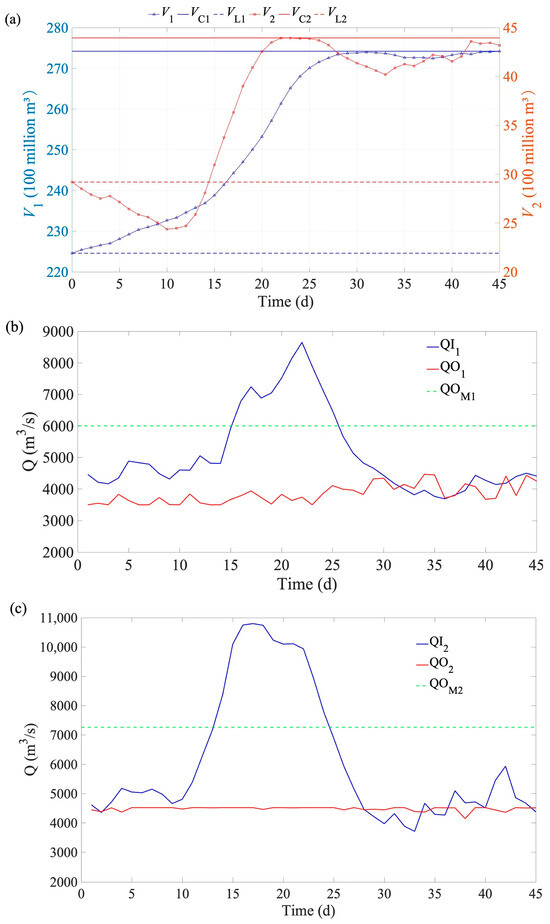
Figure A1.
Changes in reservoir volumes (a) and discharge flow of LYX (b) and LJX (c) reservoirs for flood 3 (a decamillennial flood based on the typical 1964 flood). Note: V denotes the reservoir volume at the time t; VL denotes the reservoir capacity at the dead water level; VC denotes the reservoir capacity at the check flood level; QI denotes the reservoir inflow at the time t; QOM denotes the maximum allowable discharge flow; and subscripts 1 and 2 denote LYX and LJX reservoirs, respectively.
Figure A1.
Changes in reservoir volumes (a) and discharge flow of LYX (b) and LJX (c) reservoirs for flood 3 (a decamillennial flood based on the typical 1964 flood). Note: V denotes the reservoir volume at the time t; VL denotes the reservoir capacity at the dead water level; VC denotes the reservoir capacity at the check flood level; QI denotes the reservoir inflow at the time t; QOM denotes the maximum allowable discharge flow; and subscripts 1 and 2 denote LYX and LJX reservoirs, respectively.
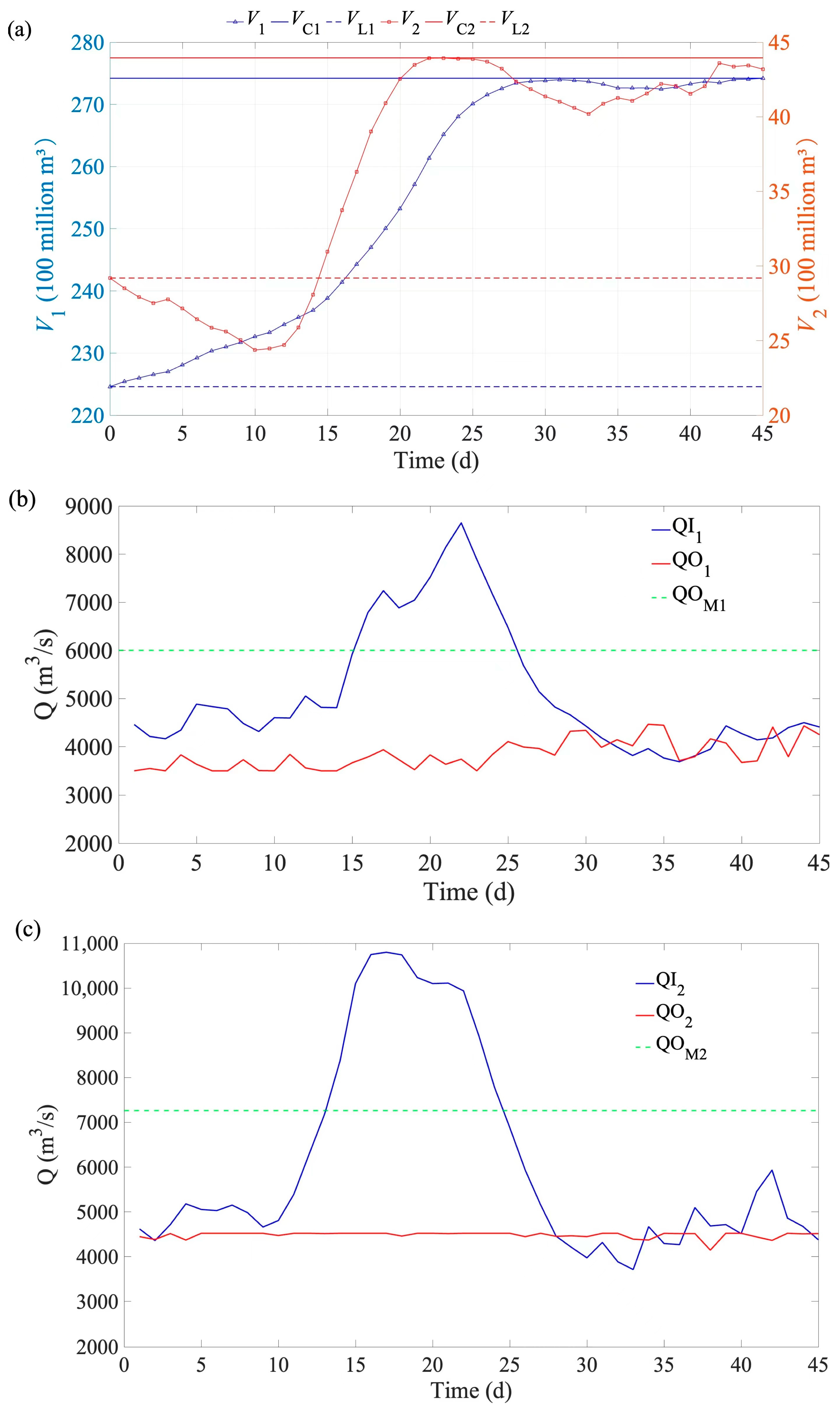
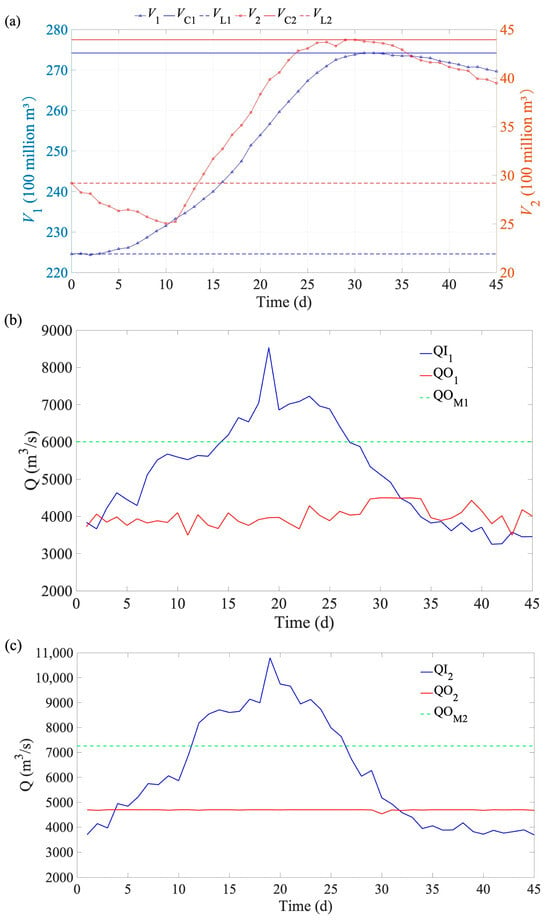
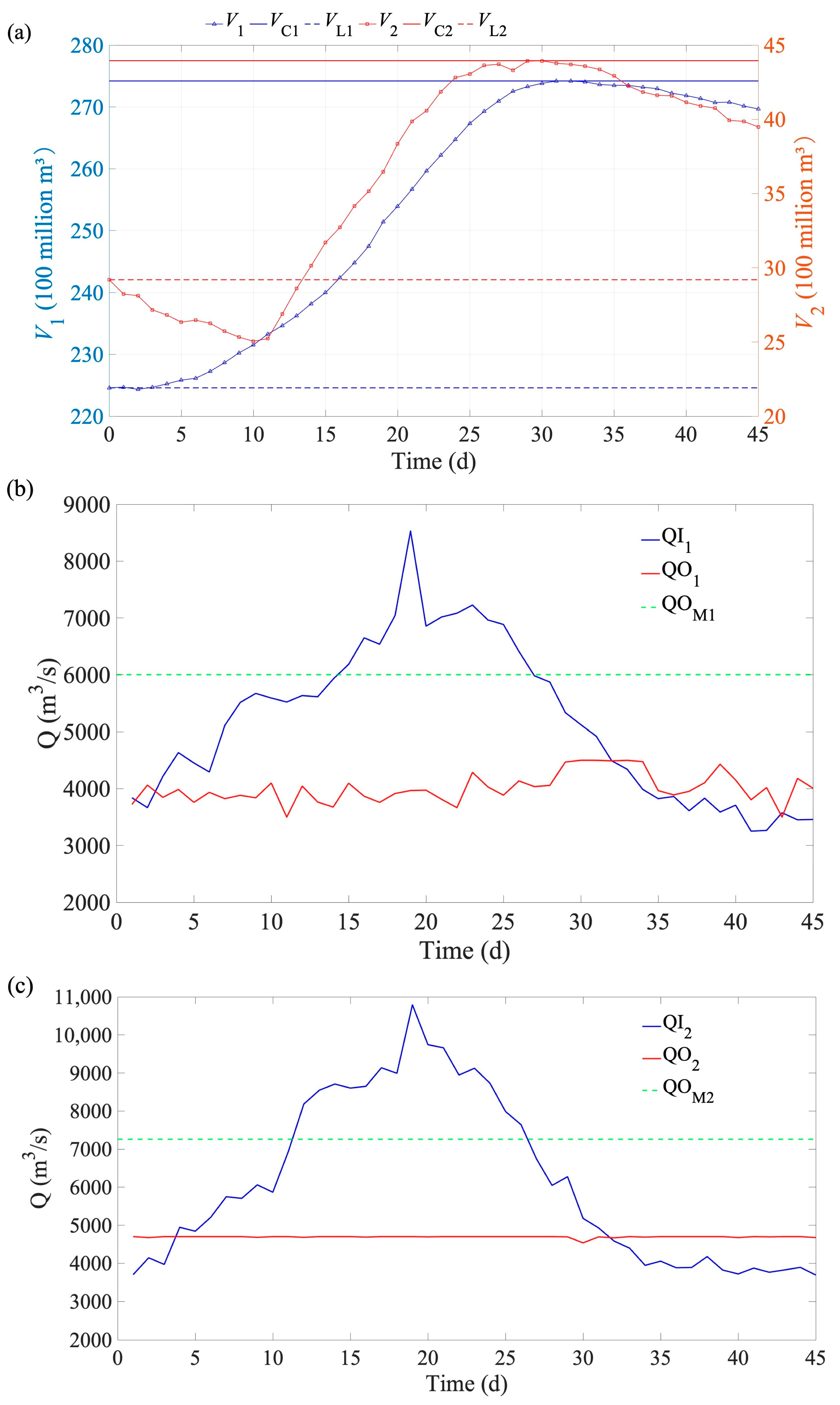
Figure A2.
Changes in reservoir volume (a) and discharge flow of LYX (b) and LJX (c) reservoirs for flood 4 (a decamillennial flood based on the typical 1967 flood). (Note: the signs are the same with Figure A1).
Figure A2.
Changes in reservoir volume (a) and discharge flow of LYX (b) and LJX (c) reservoirs for flood 4 (a decamillennial flood based on the typical 1967 flood). (Note: the signs are the same with Figure A1).
References
- Tabari, H. Climate change impact on flood and extreme precipitation increases with water availability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Chen, L. Quantitative attribution of historical anthropogenic warming on the extreme rainfall event over Henan in July 2021. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J. Significant increase of the global population exposure to increased precipitation extremes in the future. Earth’s Future 2021, 9, e2020EF001941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.H.; Eum, H.I.; Park, J.; Cho, J. Assessment of climate change impacts on extreme precipitation events: Applications of CMIP5 climate projections statistically downscaled over South Korea. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 4720523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, Y.L.; Tan, M.L.; Juneng, L.; Chun, K.P.; bin Hassan, M.H.; bin Osman, S.; Samat, N.; Chang, C.K.; Kabir, M.H. Rapid extreme tropical precipitation and flood inundation mapping framework (RETRACE): Initial testing for the 2021–2022 Malaysia flood. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, B.; Cui, S.; Wang, L.; Shrestha, S. Post-flood resilience assessment of July 2021 flood in western Germany and Henan, China. Land 2023, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanditha, J.S.; Kushwaha, A.P.; Singh, R.; Malik, I.; Solanki, H.; Chuphal, D.S.; Dangar, S.; Mahto, S.S.; Vegad, U.; Mishra, V. The Pakistan flood of August 2022 causes and implications. Earth’s Future 2023, 11, e2022EF003230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowski, A. Optimal control of single retention reservoir during flood: Solution of deterministic, continuous-time problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1991, 69, 55–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, G.; Zhou, J.; Yang, X.; Fang, W.; Dai, L.; Wang, Q.; Ding, X. Modeling and solving of joint flood control operation of large-scale reservoirs: A case study in the Middle and Upper Yangtze River in China. Water 2021, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Zhang, R.; Bao, H.; Zhang, S. Joint flood control scheduling strategy of large cascade reservoirs: A case study of the cascade reservoirs in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River in China. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2022, 15, e12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhong, P.A.; Liu, W.; Wan, X.Y.; Yeh, W.W.G. A multi-objective risk management model for real-time flood control optimal operation of a parallel reservoir system. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Mo, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T. Optimization of Cascade Reservoir Operation for Power Generation, Based on an Improved Lightning Search Algorithm. Water 2023, 15, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Pan, J.; Qiu, Q. Optimal flood-control operation of cascade reservoirs using an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Water 2022, 14, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Guo, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Guo, X.; Li, S. Application of Multi-Strategy Based Improved DBO Algorithm in Optimal Operation of Reservoir Groups. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 38, 1883–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Mei, Y.; Xu, X.; Guo, S. A triple-stage operation method for deriving operation rules for cascade reservoirs during catastrophic flood events. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 4863–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Mei, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Cai, H. Optimal operation of a parallel multireservoir system for flood control using a stagewise compensation method. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 1689–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, S.; Shiri, M.E.; Rahnamayan, S. Metaheuristics in large-scale global continues optimization: A survey. Inf. Sci. 2015, 295, 407–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tian, W.; Chau, K.; Zang, H.; Ma, M.; Feng, Z.; Xu, D. Multi-reservoir flood control operation using improved bald eagle search algorithm with ε constraint method. Water 2023, 15, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, V.; Huang, Y.F.; Koo, C.H.; Ahmed, A.N.; El-Shafie, A. A review of reservoir operation optimisations: From traditional models to metaheuristic algorithms. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 3435–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig, M.; Beyer, H.G. A modified matrix adaptation evolution strategy with restarts for constrained real-world problems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Fang, Y.; Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bian, X. LSHADE44 with an improved ε constraint-handling method for solving constrained single-objective optimization problems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Garibaldi, J.M. A novel memetic algorithm for constrained optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Basharu, M.; Arana, I.; Ahriz, H. Escaping local optima: Constraint weights vs. value penalties. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Techniques and Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Cambridge, UK, 10–12 December 2007; Springer: London, UK, 2007; pp. 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Çınar, A.; Kıran, M. The performance of penalty methods on tree-seed algorithm for numerical constrained optimization problems. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 2020, 17, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefa AR, A.S.; Kahraman, H.T.; Gedikli, E. Determination of the effects of penalty coefficient on the meta-heuristic optimization process. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Processing (IDAP), Malatya, Turkey, 28–30 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Peraza-Vázquez, H.; Peña-Delgado, A.; Merino-Treviño, M.; Morales-Cepeda, A.B.; Sinha, N. A novel metaheuristic inspired by horned lizard defense tactics. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Mallipeddi, R.; Suganthan, P.N. Problem Definitions and Evaluation Criteria for the CEC 2017 Competition on Constrained Real-Parameter Optimization; Technical, Report; National University of Defense Technology: Changsha, China; Kyungpook National University: Daegu, Republic of Korea; Nanyang Technological University: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Atali, G.; PehlIvan, İ.; Gürevin, B.; Şeker, H.İ. Chaos in metaheuristic based artificial intelligence algorithms: A short review. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2021, 29, 1354–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouertani, M.W.; Manita, G.; Korbaa, O. Chaotic lightning search algorithm. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 2039–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, S.; Yildirim, M.; Alatas, B. CIDO: Chaotically initialized dandelion optimization for global optimization. Int. J. Adv. Netw. Appl. 2023, 14, 5696–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezici, H.; Livatyalı, H. Chaotic Harris hawks optimization algorithm. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2022, 9, 216–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B.; Gao, S. Chaotic Mapping Genetic Algorithm with Multiple Strategies. In Proceedings of the 2023 15th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 6–9 May 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Z.; Yi, P. Computational efficiency of accelerated particle swarm optimization combined with different chaotic maps for global optimization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 1245–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, R.; Premkumar, M.; Jangir, P. Newton-Raphson-based optimizer: A new population-based metaheuristic algorithm for continuous optimization problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 128, 107532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, F.A.; Houssein, E.H.; Hussain, K.; Mabrouk, M.S.; Al-Atabany, W. Honey Badger Algorithm: New metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems. Math. Comput. Simul. 2022, 192, 84–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, N.; Ansari, M.M. Golden jackal optimization: A novel nature-inspired optimizer for engineering applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 198, 116924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agushaka, J.O.; Ezugwu, A.E.; Abualigah, L. Dwarf mongoose optimization algorithm. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 391, 114570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganthan, P.N.; Hansen, N.; Liang, J.J.; Deb, K.; Chen, Y.P.; Auger, A.; Tiwari, S. Problem Definitions and Evaluation Criteria for the CEC 2005 Special Session on Real-Parameter Optimization; KanGAL report, 2005005; Nanyang Technological University: Singapore, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Woolson, R.F. Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Encycl. Biostat. 2005, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.; Wen, M. Multi-threshold image segmentation research based on improved enhanced arithmetic optimization algorithm. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 4045–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Liu, S. Cooperation search algorithm: A novel metaheuristic evolutionary intelligence algorithm for numerical optimization and engineering optimization problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 98, 106734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).