Abstract
This study explored the characteristics of benthic animal communities in different water functional areas and the driving factors affecting changes in the community structure of four water functional zones of the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River: the protection, buffer, reserve, and development and utilization zones. The results showed that the alpha diversity of the benthic animal communities in the protected and reserved zones was significantly higher than that of the buffer and development and utilization zones, and the benthic animal community structure differed significantly across different water functional zones. These zones indirectly affected the community of benthic fauna due to their environmental heterogeneity. Furthermore, the average degree, map density, and average clustering coefficient of the molecular ecological network were highest in the protected zone. The average path length was shorter, and there were more types and numbers of key species in the benthic animal community in the protected zone, indicating high levels of connectivity and efficiency in transferring substances, energy, and information between benthic animals. These results will provide a scientific basis for studying the characteristics and driving factors of benthic animal communities in the Yangtze River and have important significance for assessing and restoring aquatic ecology in the Yangtze River Basin.
1. Introduction
The Yangtze River, the longest river in China, stretches approximately 6300 km. Its total water resources reach 961.6 billion cubic meters, accounting for approximately 36% of the country’s total river runoff. It plays a crucial role in power generation, ecology, shipping, and irrigation [1,2,3]. For the rational development, utilization, conservation, and protection of water resources, the Yangtze River was divided into four first-level water functional zones: the protection, buffer, reserve, and development and utilization zones. The protection zone includes water bodies that are crucial for preserving water resources, natural ecosystems, and rare or endangered species and therefore require special protection. The buffer zone is designated to manage water use conflicts between provinces and regions where water disputes are significant. The reserve zone consists of water bodies that are not yet heavily developed, serving as reserves for sustainable water resource use in the future. Finally, the development and utilization zone is designated for areas that meet various needs such as industrial and agricultural production, urban life, fishing, and recreation [4]. Given the requirement to conduct a comprehensive water ecological assessment of the Yangtze River Basin by 2025, increasing attention is being paid to the river’s water ecology across various regions. Benthic animals are an important part of aquatic ecosystems, with diverse species, a wide distribution, and small individuals. These species exhibit varying levels of sensitivity and tolerance to water quality and therefore have been widely used in water quality evaluations of rivers and lakes [5,6,7]. Understanding the characteristics and driving factors of the benthic animal community in the Yangtze River can reveal the ecological laws of the community’s composition, helping to improve benthic animal diversity and ecological zoning management.
However, much of the current research on benthic animals in rivers primarily focuses on their community distribution characteristics and influencing factors. For example, Zhang et al. focused on the diversity and community structure characteristics of large benthic animals in Hengsha Dongtan [8]. Mu et al. elucidated the community structure characteristics of large benthic animals in the northern waters of the Beibu Gulf [9]. Li et al. focused on the community structure and influencing factors of large benthic animals in urban rivers in Dongguan [10]. The above-mentioned scholars found that conditions such as temperature, water quality, turbidity, and flow rate can have a significant impact on the structure of benthic animal communities. Currently, the impact of environmental differences caused by different functional sections of the Yangtze River and related factors on benthic animals is unclear. Furthermore, there is a lack of research on the response of interspecific interactions and key species using spatial distribution data of benthic animals, limiting our understanding of the characteristics and driving factors of benthic animal communities, community interactions, and functional composition in different water functional zones of the Yangtze River.
There are 100 first-level water functional zones within the management scope of the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River, with a length of 1021 km. Among them, there are eight protected zones with a total length of 77.7 km, accounting for 7.61% of the total length, fifteen reserved zones with a total length of 233.9 km, accounting for 22.90% of the total length, three buffer zones with a length of 30.3 km, accounting for 2.97% of the total length, and seventy-four development and utilization zones with a total length of 679.4 km, accounting for 66.52% of the total length [11]. This study investigated the benthic animal communities and environmental factors at 21 typical locations along the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River to reveal the characteristics of benthic animal communities in this section. Simultaneously, a constraint ranking analysis was used to identify the main environmental factors affecting the structure of benthic animal communities in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River, and an ecological network was constructed to analyze the interspecies interactions and interaction patterns of benthic animals to provide a theoretical basis for the assessment and restoration of aquatic ecology in the Yangtze River Basin.
2. Materials and Methods
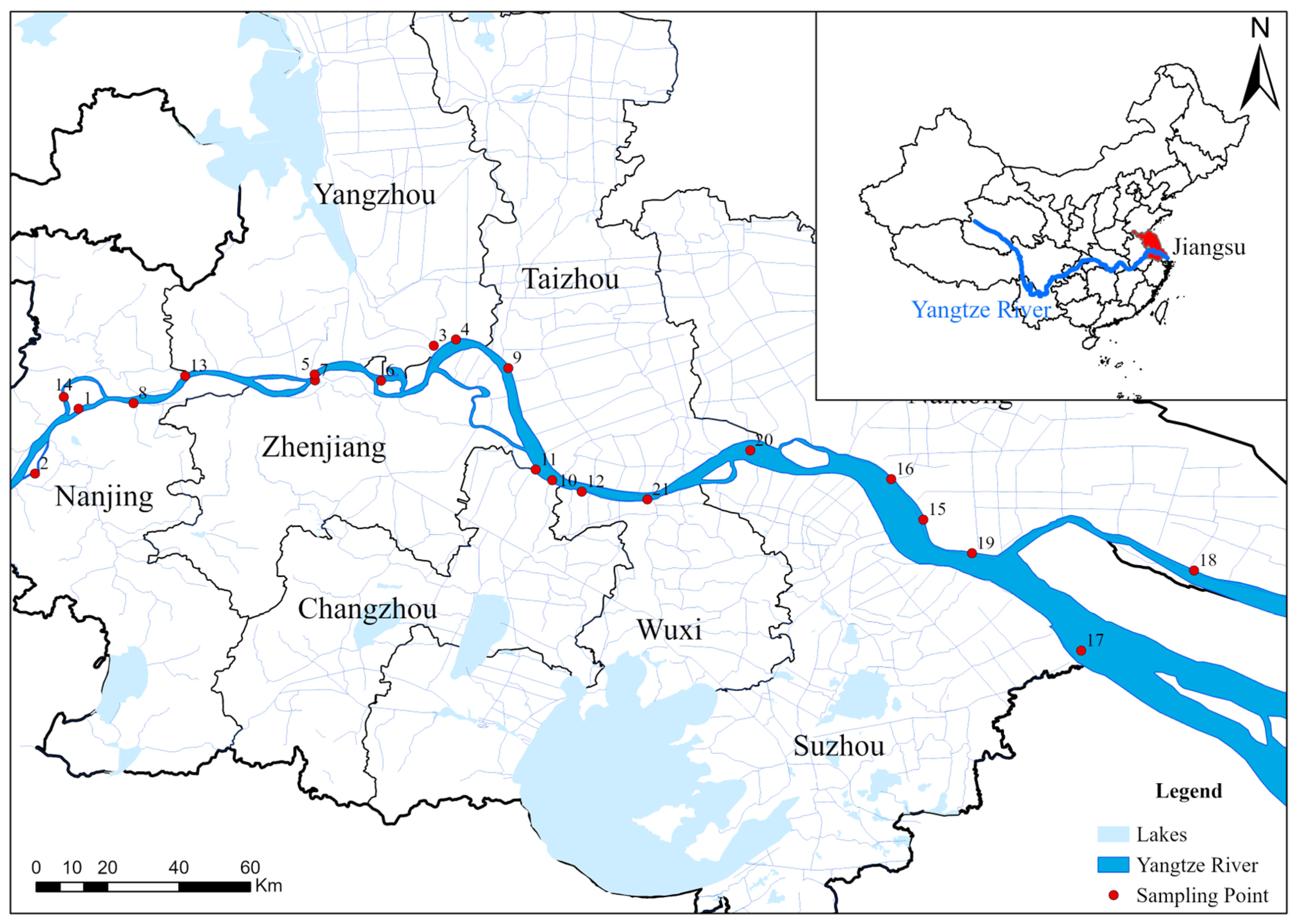
2.1. Study Area
The research section was the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River, with a sampling length of 1021 km. Figure 1 shows the specific locations and sampling points. Table 1 provides a detailed display of the latitude and longitude coordinates of 21 points. The sampling period was 2021–2023, with a sampling frequency of twice yearly, i.e., April–June in the first half of the year and September–October in the second half of the year. These two seasons are more suitable for the growth of benthic animals. The sampling range was 118°29′51″ E–121°52′38″ E longitude and 31°30′3″ N–32°20′3″ N latitude. In this study, the four water functional zones were designated by the management department, and sampling points were randomly determined based on the river sections of each water functional zone; there were 21 sampling points in total. Flowing through 8 prefecture-level cities, including Nanjing, Yangzhou, Zhenjiang, Taizhou, Changzhou, Wuxi, Suzhou, and Nantong, as well as 12 counties (cities), including Yizheng, Jurong, Yangzhong, Danyang, Taixing, Jingjiang, Jiangyin, Zhangjiagang, Rugao, Changshu, Taicang, and Qidong, the route involves four major water functional zones: protected, reserved, buffer, and development and utilization zones.
Figure 1.
Distribution diagram of sampling points for benthic animals in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River.

Table 1.
Longitude and latitude of sampling points.
2.2. Collection and Identification of Benthic Animals
A 0.03125 m2 Peterson mud collector was used to collect sediment samples in the shallow waters along the shore of each sampling point, which were then cleaned and filtered using a 250 μm sieve. All benthic animals were collected on white porcelain plates and fixed with 75% alcohol for preservation. They were brought back to the laboratory for classification and identification under dissecting or optical microscopes, counted, and weighed [12]. The final results were converted into density and biomass per unit area. They were classified as much as possible to identify genera or species, and a small number could be classified into families [13].
2.3. Determination of Physical and Chemical Indicators of Water Bodies
At each sampling site, a portable water quality detector (YSI ProPlus multiparameter water quality monitor) was used to measure water temperature (T, °C), conductivity (EC, μs/cm), dissolved oxygen (DO, mg/L), pH, and redox potential (ORP, mV), whereas turbidity (TU, NTU) was measured using a turbidity meter (WZB-170) [14]. Another LB-800L water sampler was used to collect 2 L of water samples at a surface depth of 0.5 m. The samples were refrigerated and transported to the laboratory as soon as possible to determine the total organic carbon (TOC, mg/L), total phosphorus (TP, mg/L), phosphate (PO43−, mg/L), total nitrogen (TN, mg/L), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−, mg/L), nitrite nitrogen (NO2−, mg/L), ammonium salt (NH4+, mg/L), and silicate (SiO44−, mg/L) contents. Three parallel samples were set up for each indicator measurement, taking the average of both annual sampling rounds for subsequent analysis; there were a total of 63 data points across 21 locations in 3 years.
In the laboratory, the water sample was first filtered through a Whatman filter membrane (NJ, USA) with a 0.45 μm pore size, and the TOC concentration was determined using a liquid TOC analyzer (Elementar, Frankfurt, Germany). The dissolved SiO44− concentration was measured using molybdate blue spectrophotometry, whereas the TN and TP contents were determined using the colorimetric method after acid hydrolysis via persulfate digestion [15]. Then, NO3−, NO2−), NH4+, and PO43− were measured using an AA3 Seal automatic analyzer (Norderstedt, Germany).
2.4. Determination of the Physical and Chemical Indicators of Sediments
The organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (STN), and total phosphorus (STP) levels in the sediments were measured using the “Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods” (Fourth Edition) for detection. The steps mainly include sediment dehydration and air drying, sample screening to remove large particulate impurities, sediment sample decomposition and leaching, and measurement of the leached solution using the same water quality method [15]. Three parallel samples were set up for each indicator measurement, and 63 sediment samples were measured.
2.5. Measurement of Hydrodynamic Indicators
The flow velocity (μ) was measured on-site using an acoustic Doppler current profiler at each sampling point [16]. Using an ultrasonic depth gauge (LB-S100) to measure water depth (h), the instrument was placed on the water surface or at a certain position during the depth measurement. By using the fixed sound velocity (v) of the ultrasonic waves in water and the time (t) from ultrasonic wave transmission to reception, the instrument automatically converts water depth (h) [17].
2.6. Data Statistics and Analysis
To understand the species diversity within the samples, this study used the Chao1, Pielou, and Simpson indices to characterize the community alpha diversity, principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) to characterize the community beta diversity, and a nonparametric multivariate statistical function (ANOSIM) to further indicate whether there are differences in benthic animal communities in the different water functional zones. Firstly, we can use the vegdist function in the vegan package of R language (V3.2.1) to calculate the Bray–Curtis distance matrix. Then we use the cmdscale function to perform PCoA analysis on the Bray–Curtis distance matrix. Finally, we use the ggplot2 package to draw the PCoA graph.
We use analysis of variance to test the significance of intergroup differences in various indicators. To analyze the differences in environmental factors among these zones, PCA was first performed to visually represent them before ANOSIM was then used for intergroup difference analysis. To investigate the impact of environmental heterogeneity on benthic animals, the differences in benthic community structure (Bray–Curtis distance) among the different water functional zones were calculated for each site. For correlation analysis, the Euclidean distance of the environmental factors and the heterogeneity of group differences served as the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively, and a linear relationship was established between the environmental factors and the heterogeneity of group differences. These analyses were implemented using the vegan package in R language (V3.2.1).
Meanwhile, Mantel analysis, coefficient of expansion analysis, redundancy analysis (RDA), and Monte Carlo permutation test were used to identify important factors affecting changes in benthic animal community structure. First, Mantel and coefficient of expansion analyses were used to preliminarily screen the environmental factors that affect community structure, retaining those with p < 0.05 Next, RDA and Monte Carlo permutation test were conducted to screen for the most significant influencing factors among the environmental variables with a variance inflation factor (VIF) of <20 and a value of 05. These analyses were implemented using the vegan package in R language (V3.2.1).
The network construction method was performed using the Conet plugin in Cytoscape software (V3.8.0) to calculate and determine node and edge data. Subsequently, Gephi (V0.9.2) software was used for visualization processing to construct an ecological network diagram, and topology parameters, including the number of network nodes, average degree, network diameter, and average path length, were calculated and obtained. Simultaneously, using the R language WGCNA and rnetcarto packages, the p-values of the correlation matrix were calculated, and the positions of each point in the network were analyzed to obtain the intramodule connectivity (Zi) and intermodule connectivity (Pi) of each species, thereby identifying key species in the benthic community.
3. Results
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of the Physical and Chemical Indicators of Water Bodies and Sediments
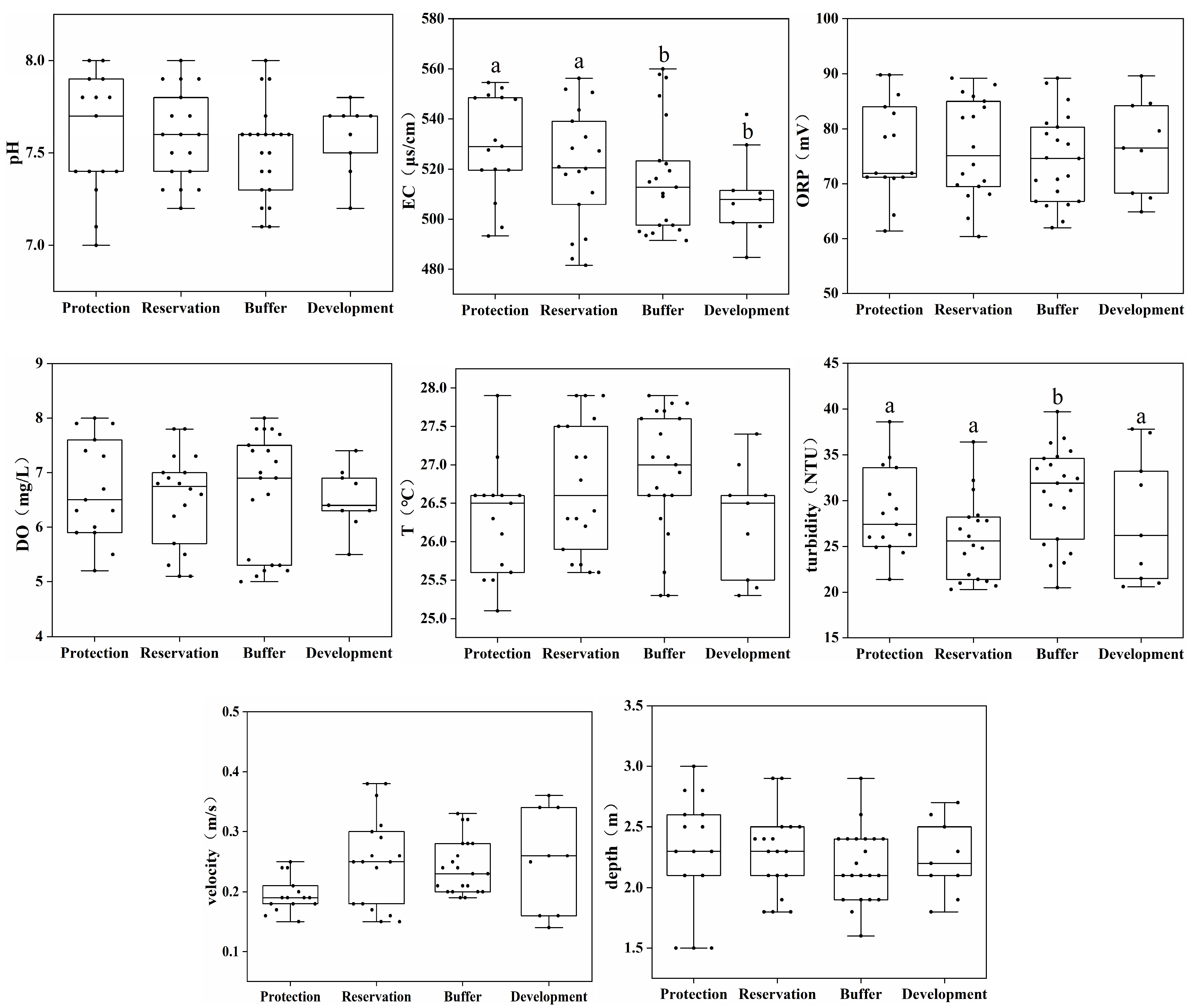
This study analyzed the distribution of the physical and chemical indicators in the water bodies of different water functional zones. Figure 2 shows the physical and chemical indicators of water bodies at the 21 sampling points in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River. The pH of each point fluctuated, but the difference in the overall pH of the four water functional zones was insignificant; the water bodies were generally neutral. The EC of the protected and reserved zones was significantly higher than that of the buffer and development zones (p < 0.05), and the TU of the buffer zone was significantly higher than that of the other three water functional zones (p < 0.05). The mean values of DO, ORP, and T differed insignificantly among the four water functional zones. The flow velocity at the sampling points was 0.2–0.3 m/s, and the water depth was 2–3 m. The mean values of the flow velocity and the water depth differed insignificantly among the four water functional zones.
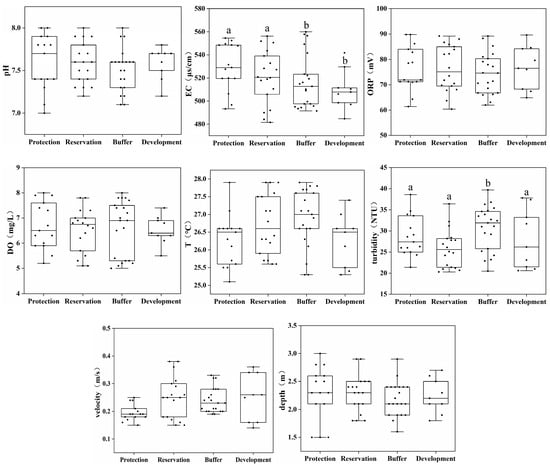
Figure 2.
Distribution of the physical and chemical indicators of water bodies across different water functional zones. (Annotations a and b indicate significant differences between the two).
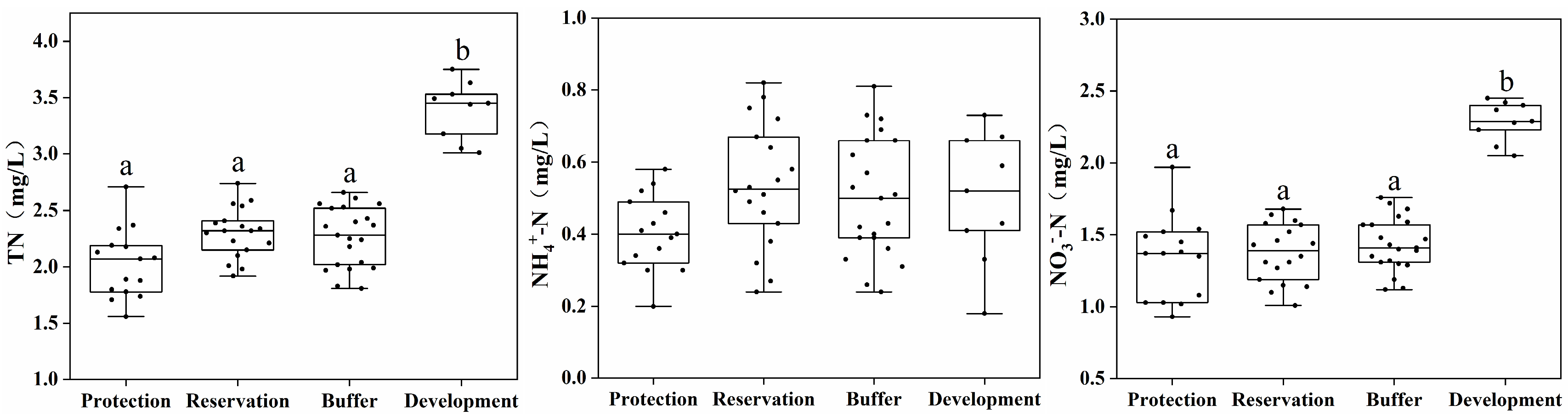
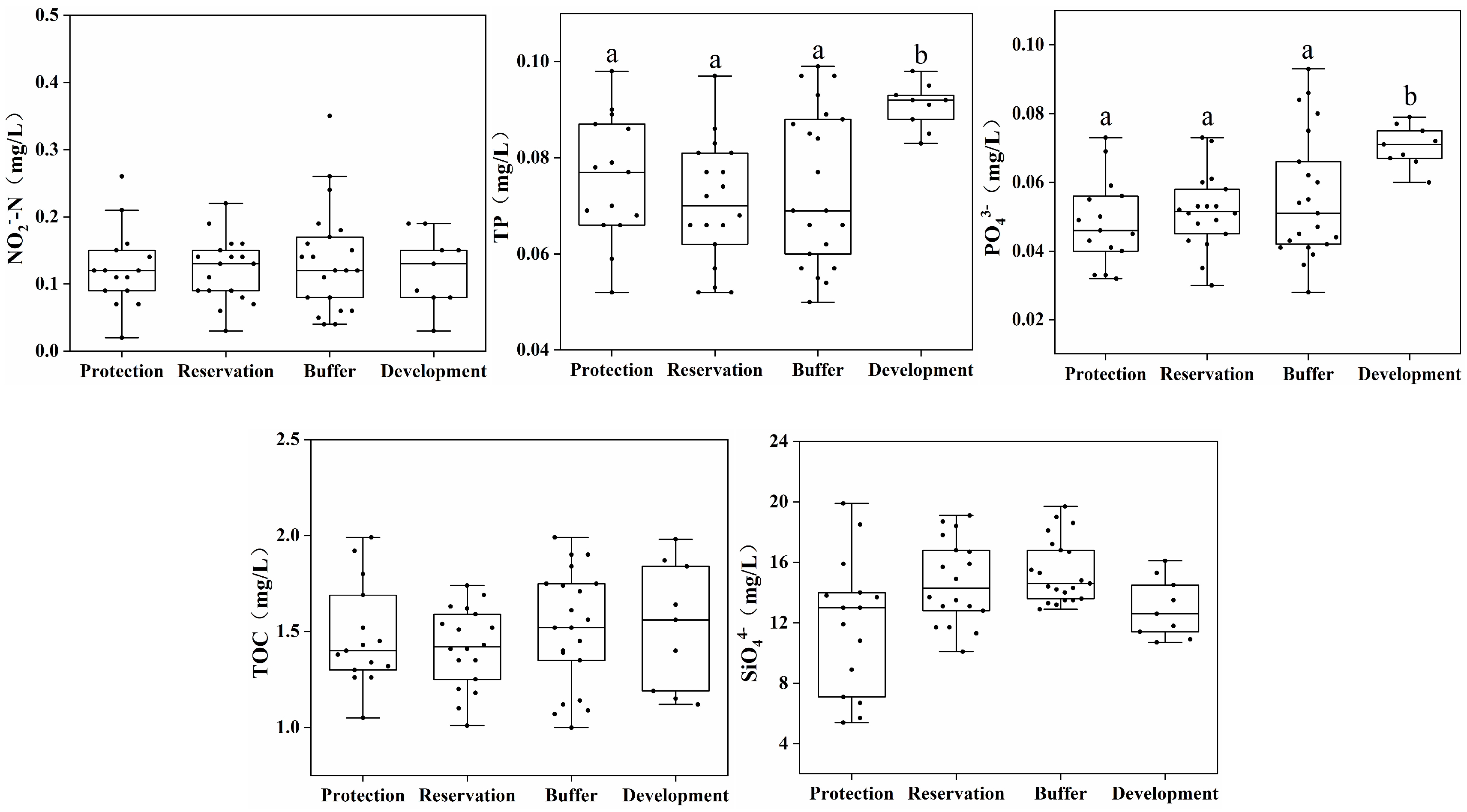
This study analyzed the concentration distribution of biogenic substances such as TN, NH4+-N, NO3−-N, NO2−-N, TP, and PO43− in four water functional zones. Figure 3 shows the results of the water source material indicators. The average TN, NO3−-N, TP, and PO43− concentrations in the water of the development and utilization zone were 3.39, 2.28, 0.091, and 0.072 mg/L, respectively, which are significantly higher than those in the protected, reserve, and buffer zones (p < 0.05). The concentrations of NH4+-N, NO2−-N, TOC, and SiO44− differed insignificantly between the different water functional zones.
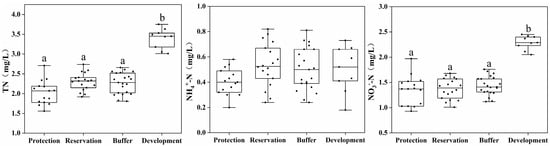
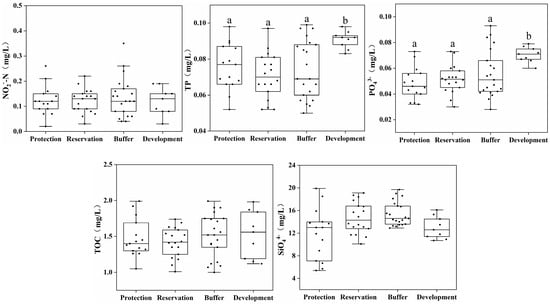
Figure 3.
Distribution of biogenic substances across different water functional zones. (Annotations a and b indicate significant differences between the two).
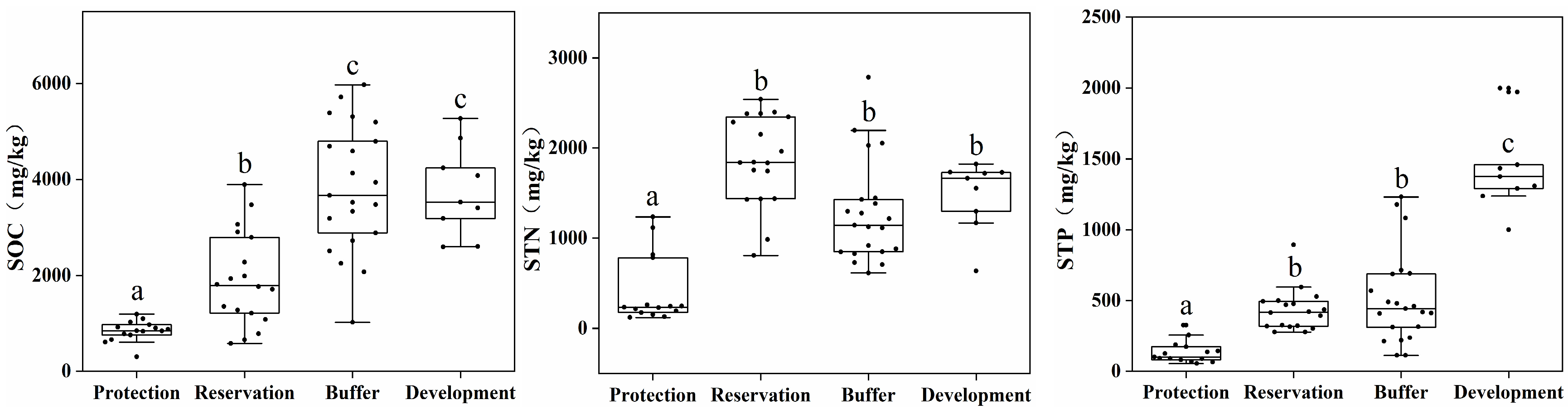
This study analyzed the distribution of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus contents in sediments from different water functional areas. Figure 4 shows the measurement results of the sediment carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous indicators. The average organic carbon contents in the protected, reserve, buffer, and development and utilization zones were 840, 1921, 3829, and 3754 mg/kg, respectively. The average TN contents were 411, 1865, 1280, and 1481 mg/kg, respectively. The average total phosphorous contents were 134, 433, 515, and 1453 mg/kg, respectively.
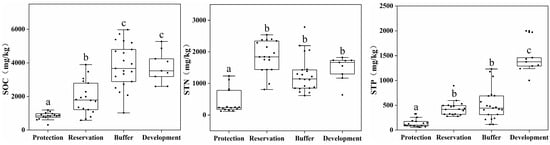
Figure 4.
Distribution of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus contents in sediments from different water functional zones. (Annotations a, b, and c indicate significant differences between each pair).
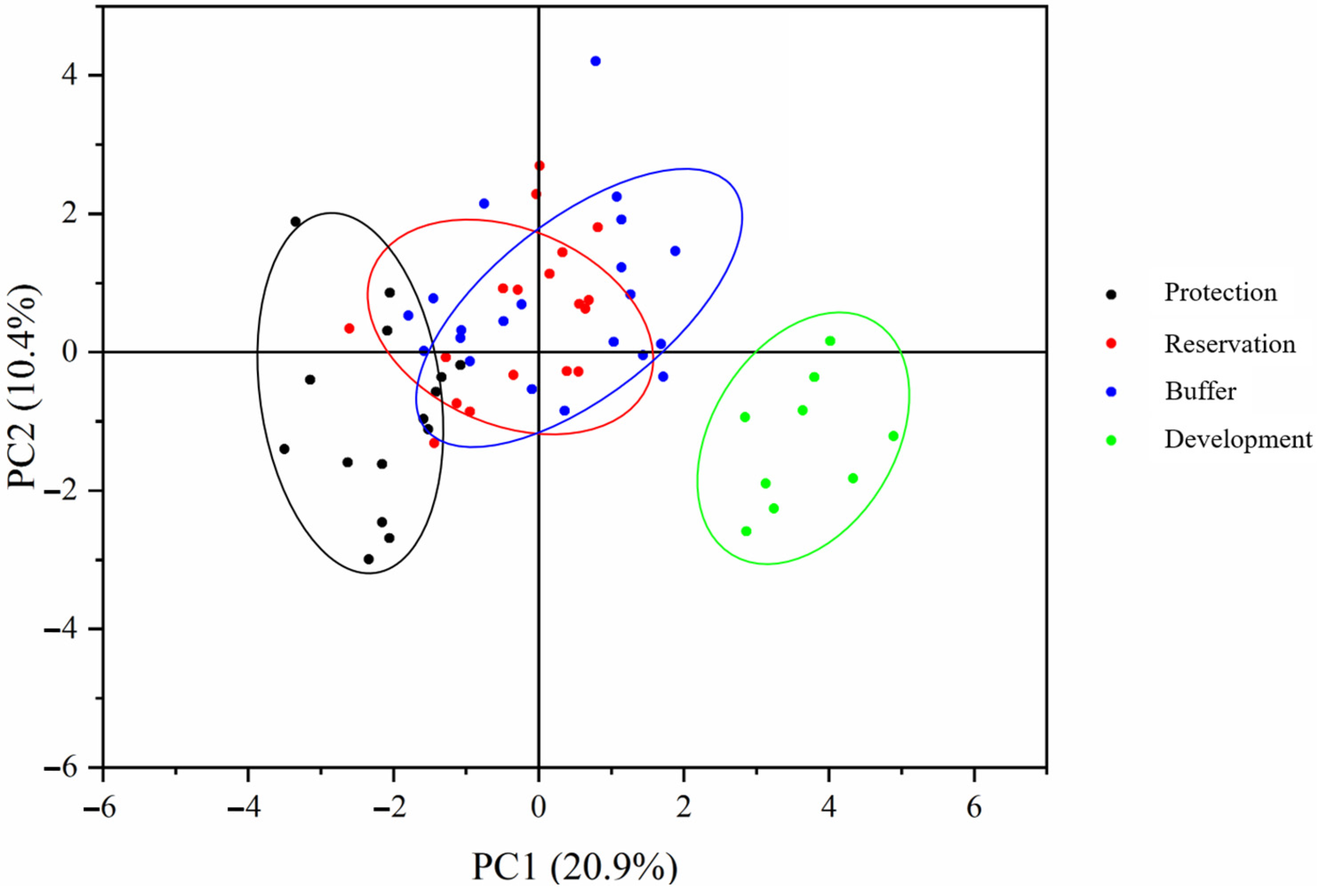
To investigate the comprehensive impact of the different water functional zones on environmental factors in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River, a PCA was conducted on the physical and chemical properties, biogenic substances, and sediment carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus indicators of the protected, reserved, buffer, and development and utilization zones. As shown in Figure 5, the PC1 axis explains 20.9% of the changes in environmental factor composition, whereas the PC2 axis explains 10.4%. The sampling points of the four water functional zones in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River were relatively concentrated. Comparing the clustering of the sampling points in the protected, reserve, buffer, and development and utilization zones, significant differences were found between the two axes (ANOSIM, p < 0.05). This indicates that the composition of environmental factors significantly differed among the different water functional zones, further demonstrating that the delineation of water functional zones affects the heterogeneity of the water environment.
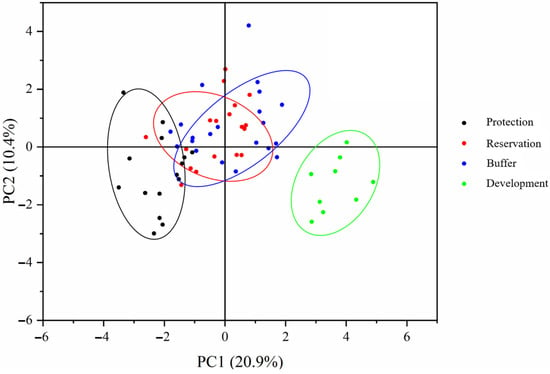
Figure 5.
Analysis of the environmental heterogeneity across different water functional zones.
3.2. Distribution Characteristics of Benthic Animal Communities
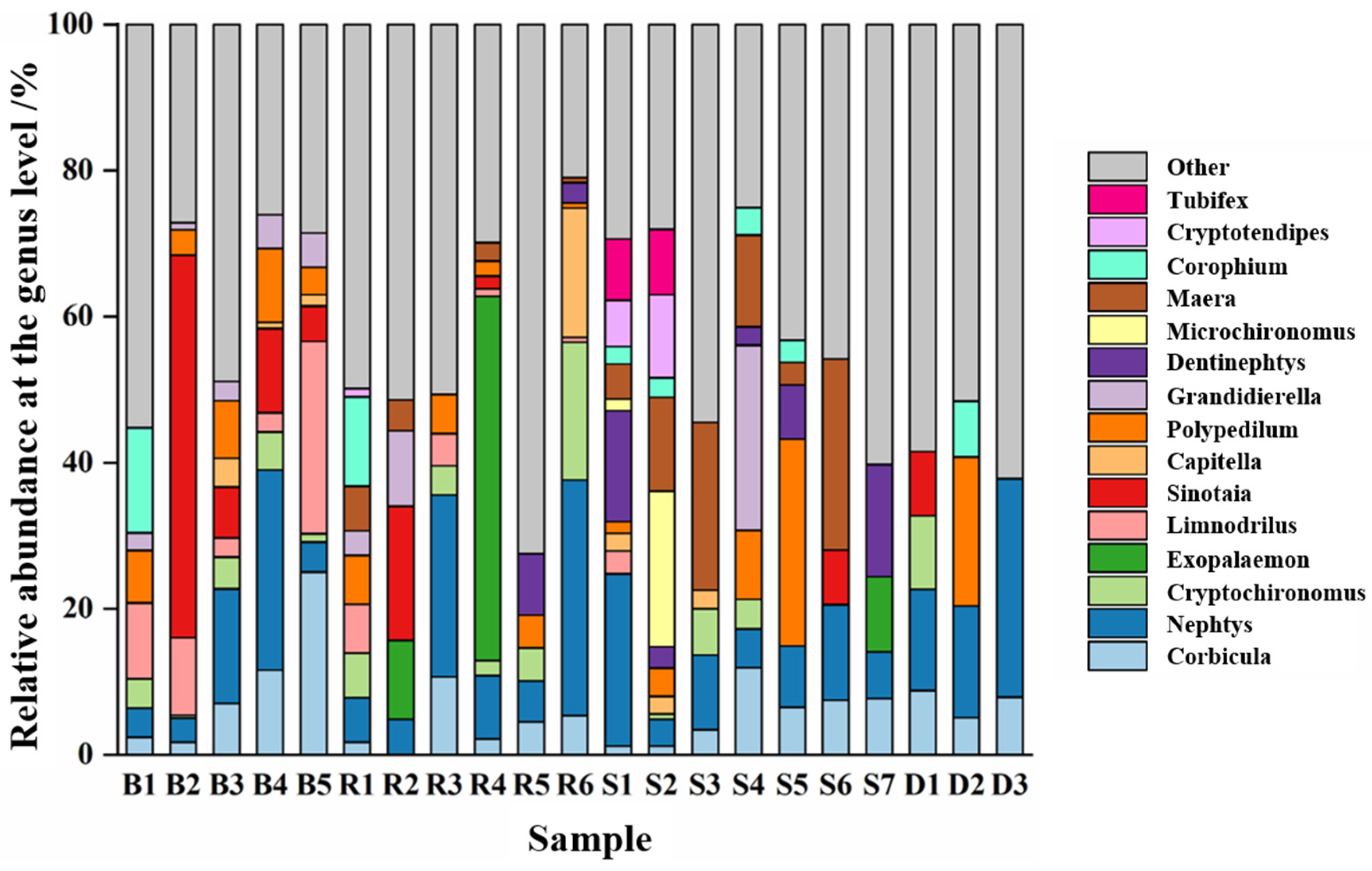
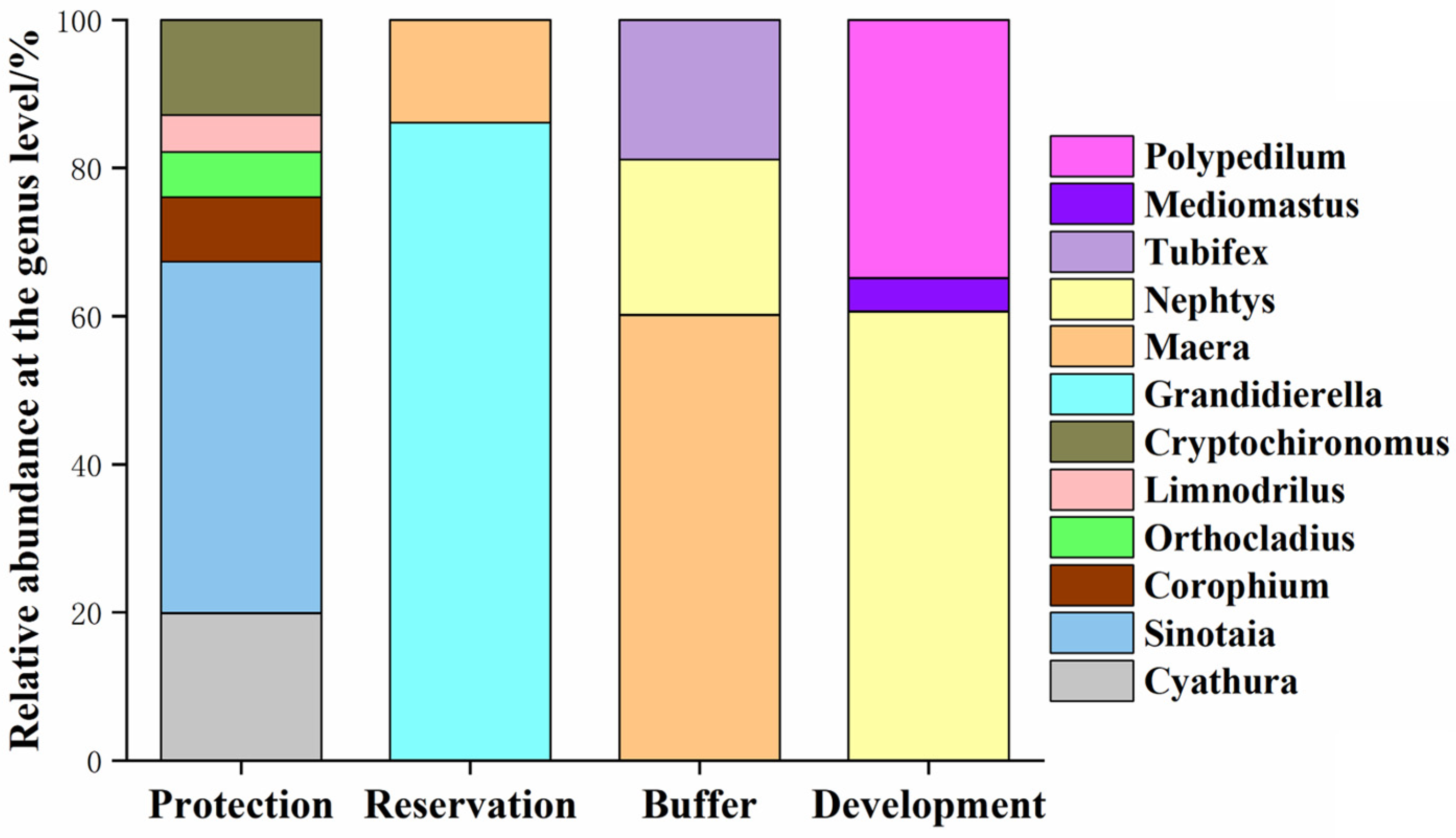
Through a taxonomic analysis, the composition and relative abundance changes in benthic animal species at the genus level can be obtained (Figure 6). A total of 15 genera of dominant benthic animals were found in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River, and there were certain differences in the relative abundance of species in the different water functional zones. For example, the relative abundance of Limnodrilus, Sinotaia, Nephtys, and Polypedilum was highest in the protected zone, whereas that of Sinotaia, Nephtys, Exopalaemon, and Cryptochironomus was highest in the reserved zone. The relative abundance of Nephtys, Dentinephtys, Polypedilum, and Grandidierella was highest in the buffer zone, whereas that of Nephtys and Polypedilum was highest in the development and utilization zone.
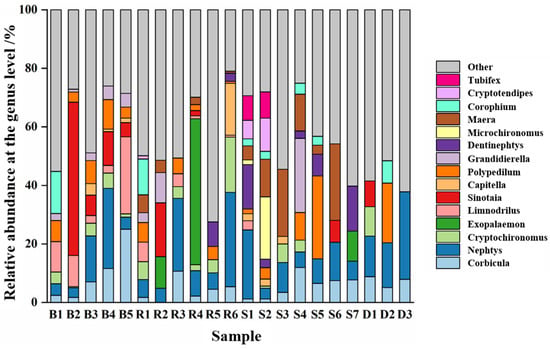
Figure 6.
Relative abundance of benthic animal communities in different water functional zones at the genus level. B denotes the protected zone, R denotes the reserved zone, S denotes the buffer zone, and D denotes the development and utilization zone.
3.3. Alpha Diversity of Benthic Animals
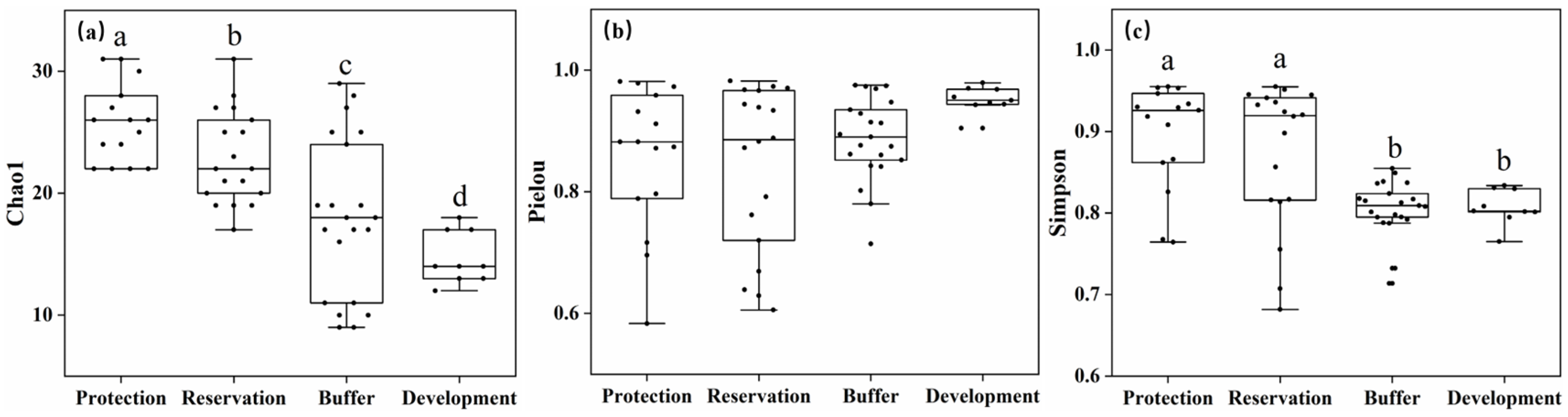
This study selected three indices to characterize the alpha diversity of benthic animal communities, with the Chao1 index representing benthic animal richness, the Pielou index representing benthic animal evenness, and the Simpson index being a comprehensive indicator of benthic animal richness and evenness. As shown in Figure 7a, the benthic animal richness in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River was highest in the protected zone and lowest in the development and utilization zone. Figure 7b shows that the benthic animal evenness differed insignificantly among the water functional zones. As shown in Figure 7c, the Simpson index of the protected and reserved zones was significantly higher than that of the buffer and development and utilization zones. According to the comprehensive analysis of these indices, the alpha diversity of benthic animal communities in the protected and reserved zones was significantly higher than that in the buffer and development and utilization zones (p < 0.05).
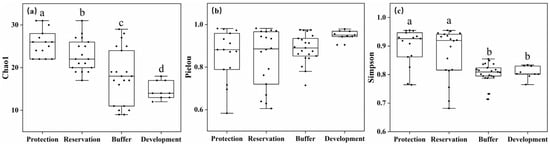
Figure 7.
Differences in the alpha diversity index across different water functional zones (Annotations a, b, c and d indicate significant differences between each pair). (a) Chao1; (b) Pielou; (c) Simpson.
3.4. Beta Diversity of Benthic Animals
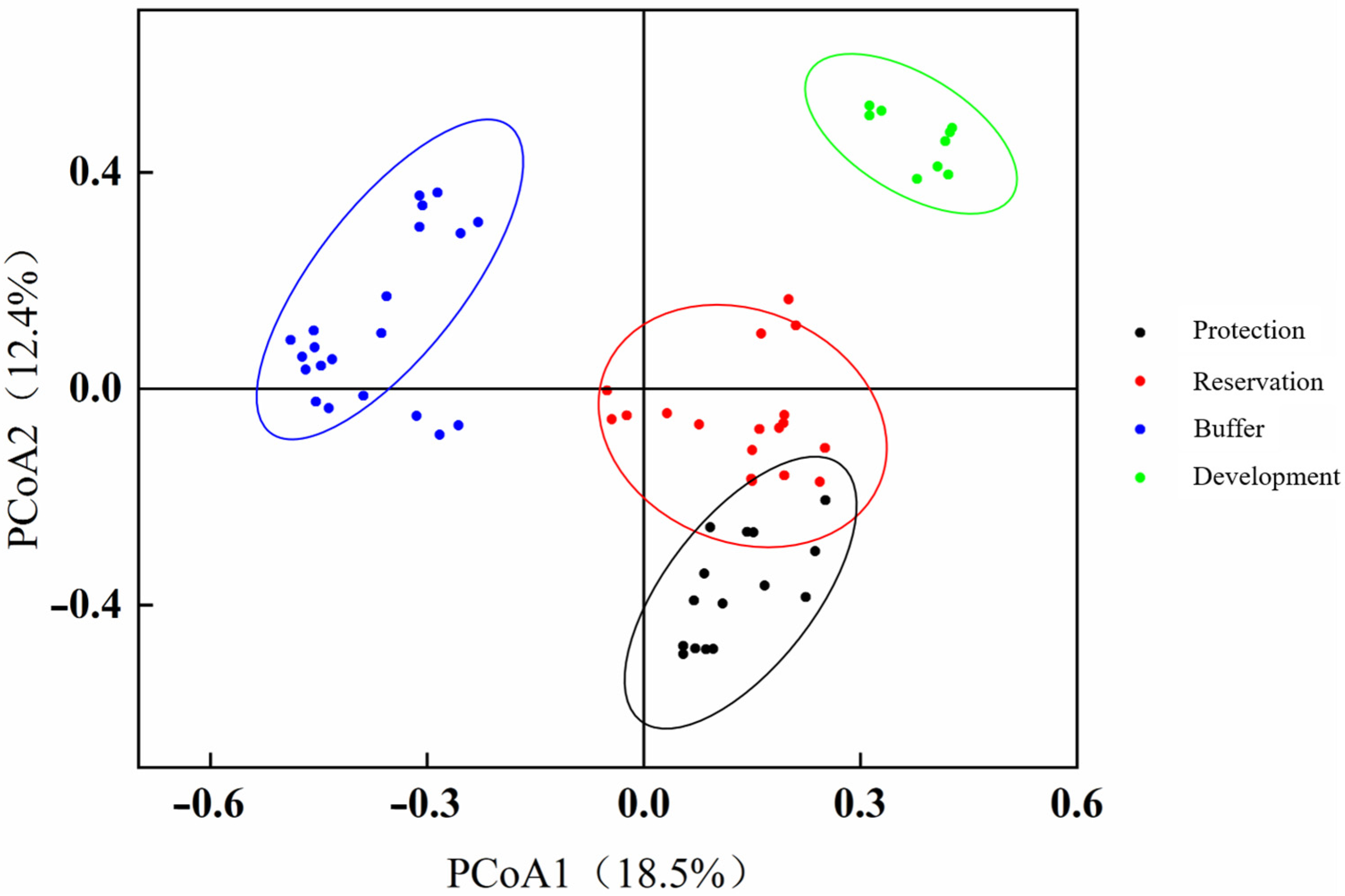
A PCoA was used to cluster the benthic animal community structure at each adoption point. As shown in Figure 8, the explanatory power of the PCoA1 axis for changes in benthic community structure was 18.5%, whereas that of the PCoA2 axis was 12.4%. The sampling points in the four water functional zones of the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River were relatively concentrated, and the benthic animal community structures at each sampling point in these zones were similar. A further comparison of the clustering of sampling points in the protected, reserved, buffer, and development and utilization zones revealed significant differences (ANOSIM, p < 0.05) in the benthic community structure between each pair of the four water functional areas, indicating significant differences in the benthic community structure in the different water functional zones.
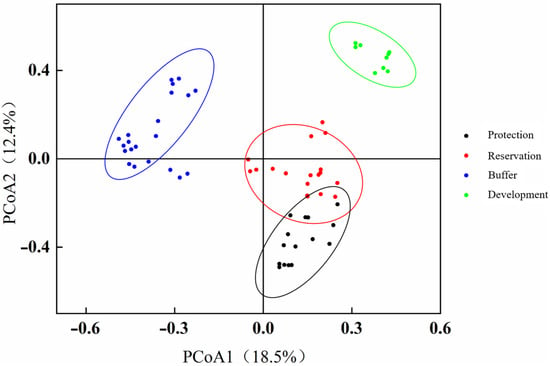
Figure 8.
PCoA map of the benthic animal communities in different water functional zones.
3.5. Relationship between Benthic Animal Communities and Environmental Variables
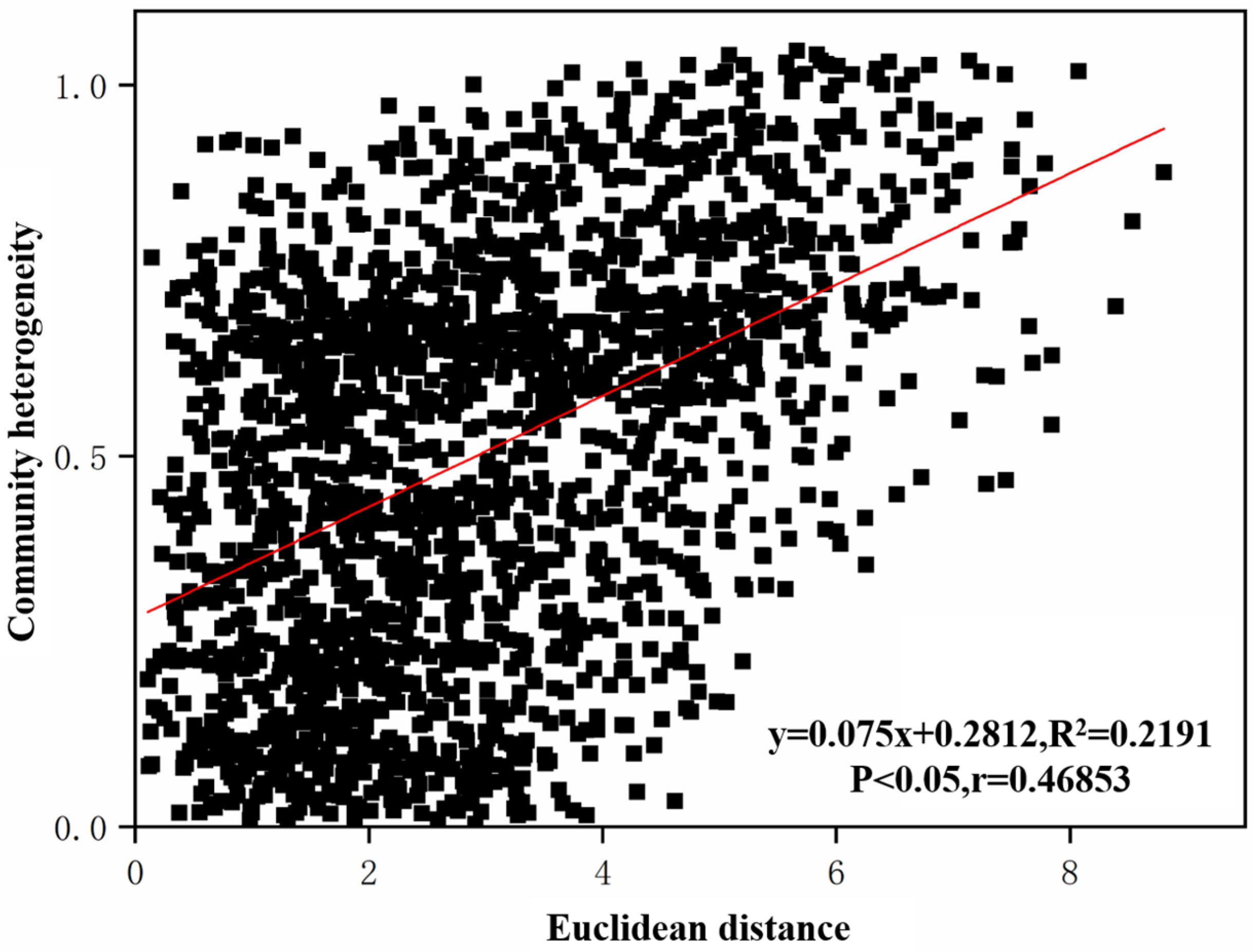
To explore the important factors affecting the structural changes in benthic animal communities in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River, this study conducted a correlation analysis between the changes in benthic animal community structure and the environmental heterogeneity of the water and sediment. As shown in Figure 9, the changes in benthic community structure were significantly positively correlated with changes in environmental heterogeneity (r = 0.47, p < 0.05), indicating that the differences in benthic community structure increased significantly with an increase in the differences in environmental factors, suggesting that environmental heterogeneity affected the benthic community structure in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River.
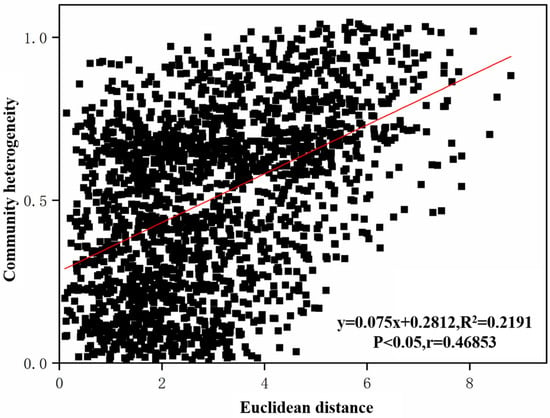
Figure 9.
Correlation analysis between benthic animal communities and environmental variables.
To identify significant environmental factors that affect changes in benthic animal community structure, this study used Mantel and VIF analyses to conduct a preliminary screening of environmental factors. As shown in Table 2, when p < 0.05 and VIF < 20, the six environmental factors of TU, TN, NO3−, SOC, STN, and STP significantly affected the structure of the benthic animal communities. To further screen important environmental impact factors from the six factors mentioned above, a DCA (detrended correspondence analysis) was used to determine the correlation between the benthic community structure and the six environmental factors initially screened (the maximum gradient length of the first four axes in the DCA was 4.7826 > 3.0).

Table 2.
Mantel and variance inflation factor analyses.
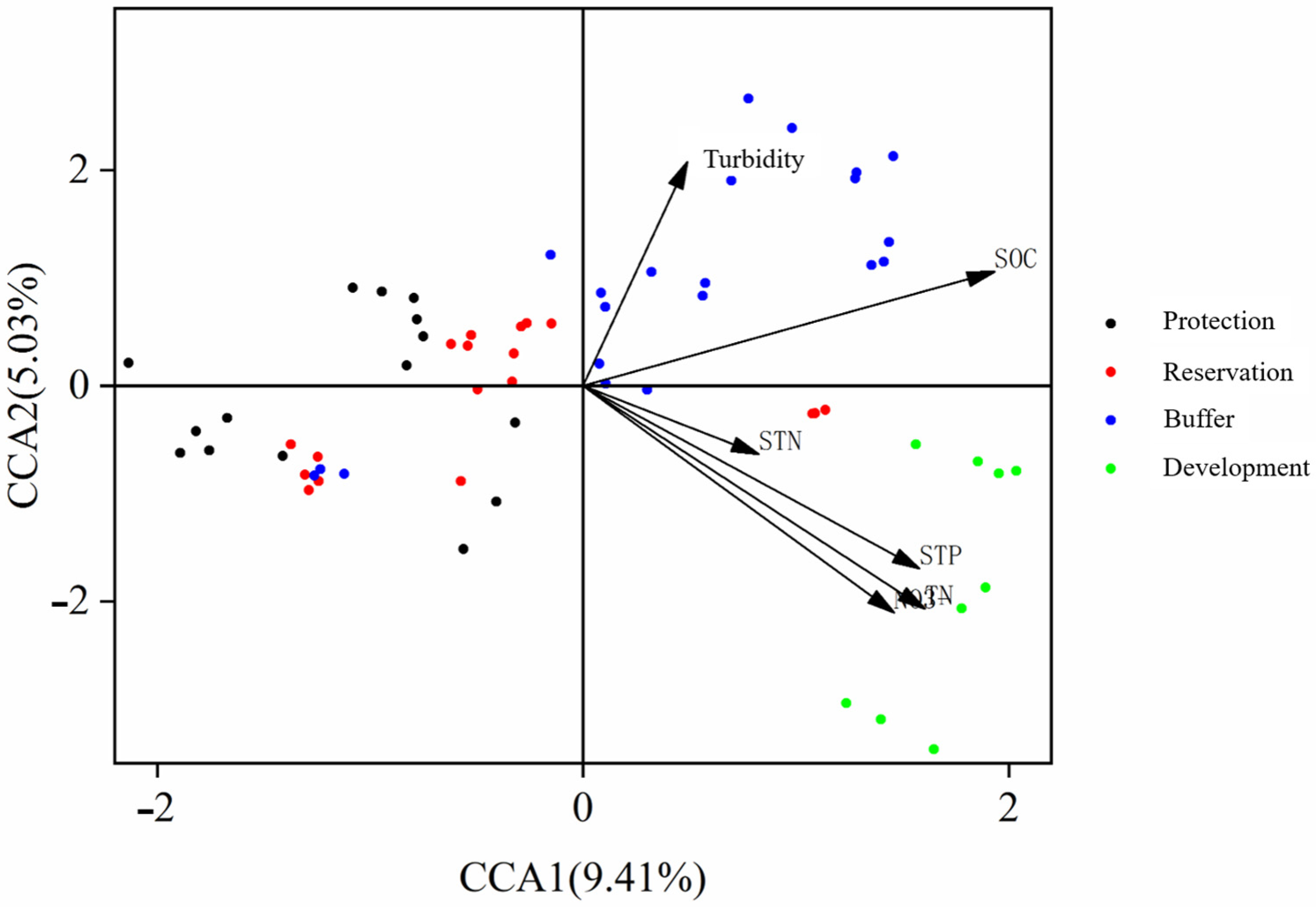
This study analyzed the impact of environmental factors on the structure of benthic animal communities using a canonical correspondence analysis (CCA). Figure 10 shows the canonical correspondence analysis of the environmental factors and benthic animal communities, with explanatory powers of 9.41% and 5.03% for the CCA1 and CCA2 axes. The Monte Carlo permutation test results indicated a significant correlation between SOC, STP, TN, and NO3− environmental factors. The community structure of the benthic animals in the different water functional zones of the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River was mainly influenced by SOC, STP, TN, and NO3−, with SOC having the most significant impact. Therefore, the changes in the mineral content of the sediments in the different water functional zones of the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River significantly influence the changes in the benthic animal community structure.
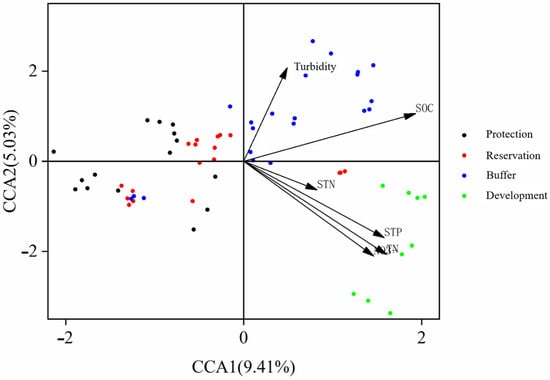
Figure 10.
CCA analysis of environmental factors and benthic animal communities.
3.6. Analysis of Network Structure and Topological Characteristics
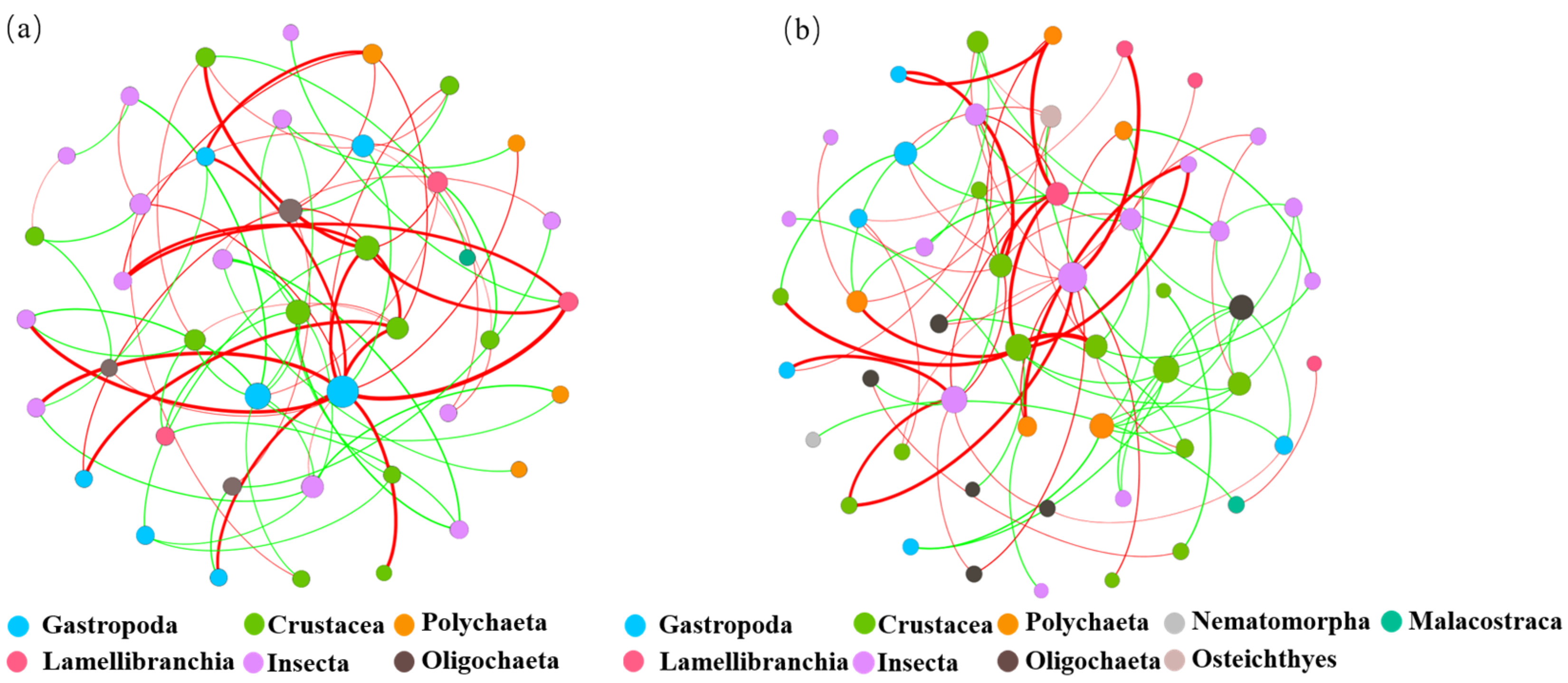
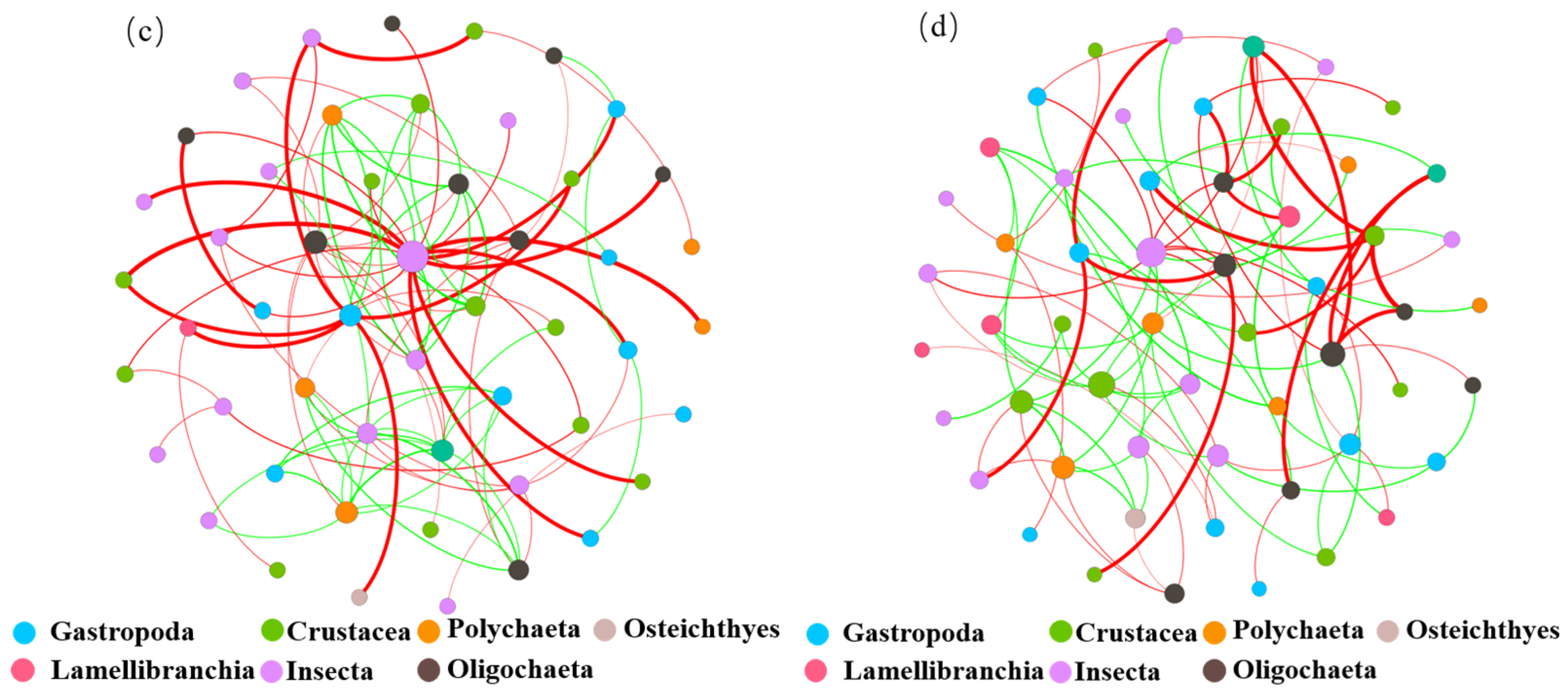
To explore the interspecies interactions of benthic animal communities, this study constructed an ecological network of benthic animal communities in the different water functional zones of the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River at the taxonomic level (Figure 11). As shown in Figure 11a, six species, including Gastropoda, Crustacea, Polychaeta, and Entomophthorales, were found in the protected zone network. As shown in Figure 11b, nine species, including Gastropoda, Crustacea, Ironworms, and Malacostraca, were found in the reserve zone. As shown in Figure 11c, seven species, including Gastropoda, Oligochaeta, Polychaeta, and Entomophthorales, were found in the buffer zone. As shown in Figure 11d, seven species, including Branchiopsida, Oligochaeta, Polychaeta, and Entomophthorales, were found in the development and utilization zone. Node size is related to connection number (i.e., degrees), with more connections resulting in larger nodes. Figure 11 shows that the gastropod class in the protected zone has the most connected relationships in the ecological network. The crustaceans in the reserve zone have the most connected relationships in the ecological network. Both the buffer and the development and utilization zones are the most interconnected in the ecological network of insects.
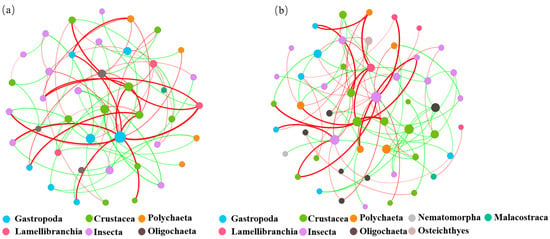
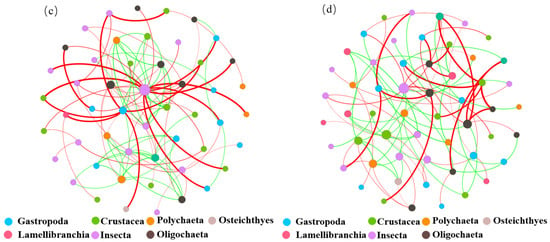
Figure 11.
Ecological network of benthic animals in different water functional zones of the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River at the class level. (a) Protected, (b) reserve, (c) buffer, (d) development and utilization zones, with nodes of different colors representing different classes and node sizes set according to degree. The green line represents a positive correlation, and the red line represents a negative correlation.
To further explore the characteristics of the benthic animal networks in the different water functional zones, this study calculated the topological structure of the ecological network. The results are shown in Table 3. The number of edges in the ecological network of the four water functional zones was the same, whereas the number of nodes in the development and utilization zone was higher than that of the other three water functional zones, indicating a larger network size. The negative correlation between benthic animals in the different water functional zones was higher than the positive correlation, though the difference was insignificant (p < 0.05). Additionally, the network modularity index of the four water function zones was > 0.5, indicating that the four networks have modular structures, and the biological communities of the same module can be regarded as having similar ecological niches. This study found that the modularity index of the development and utilization zone network was higher than the ecological networks of the other three water functional zones, indicating that the development and utilization zone network forms larger node modules to maintain network structure and function. Furthermore, the average degree, graph density, and average clustering coefficient of the protected zone network were relatively high, indicating that the ecological network of benthic animals in the protected zone is more complex and has a higher degree of aggregation. Simultaneously, the average path length of the protected zone network was shorter, further indicating that the degree of species separation of the benthic animal community in the protected zone was low and the connectivity was high. Therefore, the efficiency of transferring substances, energy, and information between benthic animals in the protected zone is higher, and their response to external changes is faster, whereas benthic animals in the development and utilization zone have a greater level of resistance to environmental interference.

Table 3.
Topological attributes of the benthic animal ecological networks in different water functional zones.
3.7. Impacts of the Different Water Functional Zones on Key Species of Benthic Animal Communities
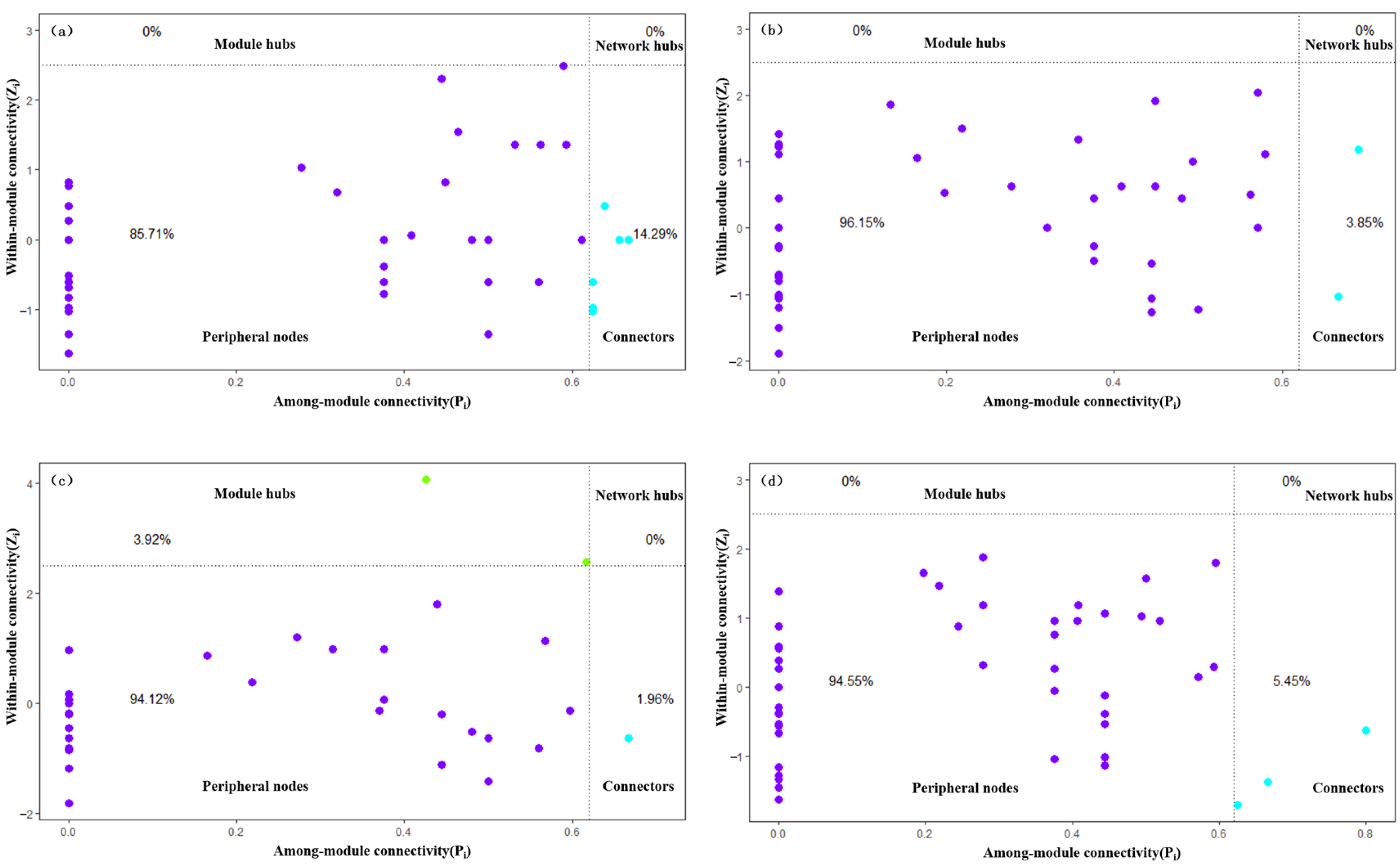
Zi represents a node’s role within the module, whereas Pi represents the degree to which the node participates in other modules. Generally, nodes can be divided into four roles: peripherals, connectors, module hubs, and network hubs. The peripheral nodes (Zi < 2.5, Pi < 0.62) indicate only a few connections and are mostly connected to nodes within the module. Connectors (Zi < 2.5, Pi ≥ 0.62) indicate a high level of connectivity with other modules. Module hubs (Zi ≥ 2.5, Pi < 0.62) indicate relatively close connections with nodes within the module. Network hubs (Zi ≥ 2.5, Pi ≥ 0.62) indicate a high level of connectivity with nodes within the module and a high level of connectivity with nodes in other modules. Nodes with Zi ≥ 2.5 or Pi ≥ 0.62 are generally considered key species and can have roles as connectors, module hubs, or network hubs [18].
As shown in Figure 12, most nodes in the benthic animal ecological networks of the four water functional zones were peripheral nodes, and none of the four ecological networks had network hubs, indicating that none of the four ecological networks had highly connected nodes both within and between modules. Only the ecological network of the buffer zone had module hubs, indicating that the connections between species within the modules of the buffer zone network were closer. The four ecological network connectors differed significantly, with the highest in the protected zone at 14.29% and the lowest in the buffer zone at 1.96%, indicating that nodes in the protected zone network have stronger interconnectivity and can better support and promote the functions and processes of the entire ecosystem. This high connectivity helps improve the stability of ecological networks, enabling them to better cope with external disturbances and changes and maintain system health and balance. The comprehensive results indicate that the network structures of the different water functional zones differ.
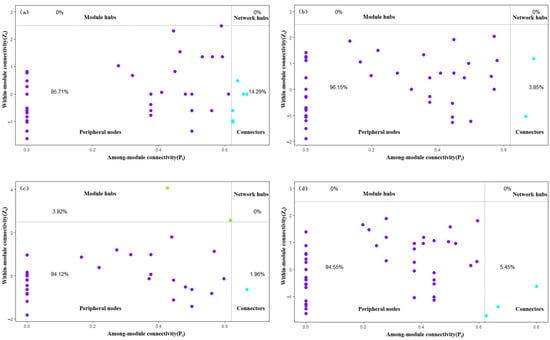
Figure 12.
Zi–Pi diagram of benthic animals in different water functional zones. (a) Protected, (b) reserve, (c) buffer, (d) development and utilization zones. The numbers in the figure represent the proportions of the four node types. (Purple is the point inside the peripherals, fluorescent blue is the point inside the connectors, and green is the point inside the module hubs).
This study analyzed the key species composition of benthic animals in different water functional zones. Figure 13 shows that the number of key species in the benthic animal community of the protected zone was significantly higher than that of the other three water functional zones, indicating that the benthic animal community in the protected zone is more complex. Most of the connectors in the protected zone network belonged to the Cyathura and Sinotaia genera. The connectors in the reserved zone network belonged to the Grandidierella and Gammaridea genera. The connectors in the buffer zone network belonged to the Gammaridea, Nephtys, and Tubifex genera. The connectors in the development and utilization zone network belonged to the Nephtys, Mediomastus, and Polypedilum genera. According to Figure 6 in Section 3.2, the relative abundances of Sinotaia, Nephtys, Grandidierella, and Polypedilum in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River were relatively high, indicating their importance in maintaining community stability. Furthermore, although the relative abundance of species, such as Cyathura, Gammaridea, Tubifex, and Mediomastus, was relatively low in the community, they are key species that play important roles in the interspecific interactions of benthic animals in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River.
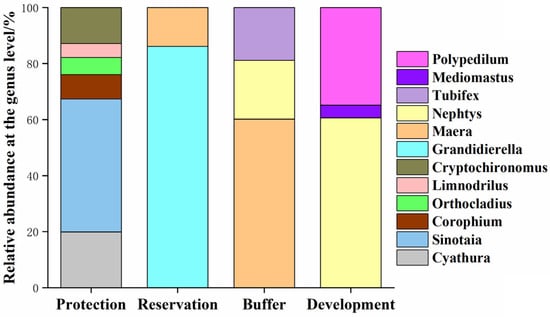
Figure 13.
Key species composition of benthic animals in the different water functional zones.
4. Discussion
This study found that the concentrations of some biogenic substances differed significantly in the water bodies of the different water functional zones in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River. The concentrations of biogenic substances, including TN, TP, and phosphate, in the development and utilization zone were significantly higher than those in the protected, reserve, and buffer zones. Different water functional zones had different purposes; for example, the development and utilization zones were water bodies that were used for industrial and agricultural production, urban life, fisheries, entertainment, etc., whereas the protected zones were water bodies of great significance for water resource protection, natural ecosystem protection, and rare and endangered species protection [18]. This study also found that the organic carbon, TN, and TP contents in the sediments differed significantly in the different water functional zones. The content of minerals, including carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, in the sediments from the development and utilization zones was significantly higher than that in protected zones, indicating that the mineral content was low in sediments from zones with less human activity. Similarly, a study by Wang et al. found that the concentration of biogenic substances differed significantly in the different water ecological environment functional zones, mainly due to different land use patterns. Land use patterns may drive the loss of minerals, including nitrogen and phosphorus, in watersheds, and these minerals flow into water bodies [19].
This study found significant heterogeneity in the environments of the different water functional zones, and the environmental heterogeneity was significantly correlated with the changes in benthic animal communities. Therefore, the delineation of water functional zones alters benthic animal diversity and community structure. Chen et al. found that human interference in urban rivers in Wenzhou is becoming increasingly severe and compared the impact of four land use patterns, namely forest land, farmland, urban areas, and industrial zones, on the benthic community structure in river sections. The lowest level of species diversity of benthic animals was found in industrial areas, which are most affected by human activity intensity [20]. Di et al. found that the key environmental factors affecting the spatial distribution of benthic animal species in the Chishui River were TN, TU, and DO. With the advancement of downstream industrialization and urbanization, the degree of eutrophication in the Chishui River has increased, and the dominant species have transformed into pollution-tolerant groups, represented by dipteran chironomid larvae and oligochaete water worms [21]. In summary, the benthic animal community in the Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River will differ significantly according to the different functional zones, resulting from community adaptability, environmental factors, and human activity intensity.
Previous studies have shown that the higher the average degree and clustering coefficient of ecological network topology, the lower the average path length and the more complex the interactions between species [22,23,24]. This study found that the ecological network of benthic animal communities in protected zones is more complex, with a low species separation degree and a high level of connectivity. A previous study found that a high level of network connectivity may be related to the rapid response of benthic animals to environmental disturbances [25,26,27]. In this study, the connectivity of the benthic animal community network in the protected zone was relatively high, indicating that the benthic animal community in the protected zone is more susceptible to environmental disturbances. The negative correlation between benthic animals in the different water functional areas was higher than the positive correlation, but the difference was insignificant (p < 0.05), indicating that the synergistic and predatory relationships between benthic animals play a similar role in maintaining ecosystem stability [28]. Conversely, benthic animals as decomposers can collaborate to decompose substances that are difficult to utilize in the environment. Moreover, there is a predation relationship between large and small benthic animals, which forms a natural food chain that maintains ecological stability. These relationships can be influenced to maintain ecosystem balance [29,30,31].
From the proportion of connectors and module hubs, it can be seen that the different water functional zones have different topological effects and significant changes in the module properties. The species and numbers of key benthos species were higher in the reserve zone than in the other three water functional zones. This model shows that the benthos community in the reserve zone is more stable and invulnerable to the collapse of the entire community resulting from the disappearance of key species [32]. Key species play an important role in maintaining community stability and function. Although there is currently no relevant research on the role of key species, including Cyathura, Sinotaia, and Gammaridea, in maintaining community stability and function, studies have shown that benthic ciliates, as a key species in ecosystems and an important source of food for benthic animals, play an important role in maintaining community stability [33]. Ma et al. also found that as a key species in the ecosystem, chironomid larvae have the best ability to degrade COD, and their activities in water sediments produce a large number of migration traces and water channels, which can increase the exchange flux of dissolved substances, such as nutrients, between the sediments and water, thereby playing an important role in maintaining community function [34]. This study might encourage management departments to focus on the impact of indicators such as organic carbon, total phosphorus in the sediment, total nitrogen, and nitrate nitrogen in the water on the structure of benthic animal communities, providing a good habitat for the growth of benthic animals.
5. Conclusions
(1) The delineation of water functional zones significantly changes environmental heterogeneity, thereby affecting benthic animal communities. The alpha diversity of benthic animal communities in the protected and reserved zones was significantly higher than that in the buffer and development and utilization zones, and the benthic animal community structure differed significantly among the four water functional zones.
(2) The results of the ecological network analysis showed that the average degree, graph density, and average clustering coefficient of the protected zone network were high, and that the average path length was shorter, indicating that the species separation degree of the benthic animal community in the protected zone was low, the connectivity was high, the efficiency of material, energy, and information transmission between benthic animals was high, and the response speed to external changes was fast.
(3) Most of the connectors in the protected zone network belong to the Cyathura and Sinotaia genera. The connectors in the reserved zone network belong to Grandidierella and Gammaridea genera. The connectors in the buffer zone network belong to the Gammaridea, Nephtys, and Tubifex genera. The connectors in the development and utilization zone network belong to the Nephtys, Mediomastus, and Polypedilum genera. The proportion of key species in the benthic animal community was highest (at 14.29%) in the protected zone.
Author Contributions
M.S., methodology, software, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft, visualization, graph drawing; M.L. and J.W., investigation, data curation; G.L., resources, supervision, project administration; H.G. and M.G., resources, software, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Research Fund of State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Aquatic Ecosystem Health in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River (AEHZK2023004).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Lu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Fang, G.H.; Deng, M.; Sun, C. Ecological risk assessment and management for riverfront development along the Yangtze River in Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhang, A.G.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Dou, Y.; He, J.; Kong, D. Perfluoroalkyl substances in drinking water sources along the Yangtze River in Jiangsu Province, China: Human health and ecological risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 218, 112289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.C.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.J.; Hu, S.-P.; Gao, M.-Y.; Liu, M. Thoughts and suggestions on water ecological environment protection in Jiangsu reach of the Yangtze River. Jiangsu Water Resour. 2021, S2, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.K.; Tan, Y.; Xu, X.B.; Lin, Y. Identifying ecological degradation and restoration zone based on ecosystem quality: A case study of Yangtze River Delta. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 162, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.C. Deeply grasp the core essence of the assessment index system for water ecology in the Yangtze River Basin. China Environ. Superv. 2023, 8, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Peng, Y.C.; Shi, B.C.; Liu, T.; Dong, H.B.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.C.; Xi, Y.L. Assessing the ecological health of the Qingyi River Basin using multi-community indices of biotic integrity. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, A.; Pipko, I.; Pugach, S. On the water circulation and chemical parameter distributions in the western and central Chukchi Sea in summer 2002 and summer 2019. Polar Sci. 2023, 37, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.S.; Chen, M.; Ding, L.; Li, S. Diversity and community structure of macrobenthos in the Hengsha East Shoal. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2024, 30, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, W.D.; Pei, L.Y.; Zhu, Z.H.; Zhang, L.; Jia, R.; Zhang, Q. Community structure of macrobenthos in the northern waters of Beibu Gulf. J. South. Agric. 2024, 55, 299–310. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, M.Y.; Yu, M.Q.; Li, X.-X.; Chang, M.; Chen, L.-B.; Ding, S. Community structure and influencing factors of macroinvertebrate in urban rivers of Dongguan. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Pei, Z.P.; Zhou, Q. Layout and regulation planning of into-river sewage outlets in the Yangtze River economic zone. Ecol. Environ. Monitor. Three Gorges. 2018, 3, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.X.; Chen, J.H. Atlas of Freshwater Microbes and Benthic Animals, 3rd ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.L.; Gao, L.; Ding, L.J.; Lv, L.; Yu, Y. Trophodynamics and bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in marine food web from Laizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.F.; Chen, J.; Miao, L.; Feng, T.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, S. How bacterioplankton community can go with cascade damming in the highly regulated Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 4444–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Environmental Protection Administration; Editorial Committee for Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods. Monitoring and Analysis Methods for Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.Z.; Gu, J.H.; Wei, T.Y. Principle of acoustic Doppler velocity profiler and its application in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Mar. Sci. 2004, 10, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, X.M.; Wang, B.Y.; Yi, A.M.; Xie, K. Accuracy analysis of bathymetry for prototype observation of the Yangtze River waterway. Des. Water Resour. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2024, 43, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.L.; Li, D.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, R.; Huang, F.; Wu, J. Temporal trend and source apportionment of water pollution in different functional zones of Qiantang River, China. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1781–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.-Q.; Cai, Y.-J. Water quality assessment of rivers in aquatic eco-environmental function regions in Changzhou city. Pearl River 2022, 43, 64–73+103. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Tang, Q.C.; Zhao, B.X.; Chen, Y.-X.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Wang, B.-Q. Impact of different land-use patterns of urban river on benthic communities: A case study of Wen-Rui Tang River and Yong-Qiang Tang River. J. Hydroecol. 2023, 10, 112–121. [Google Scholar]
- Di, F.; Han, D.H.; Zhao, W.B.; Zhou, D.-K.; Wang, G.; Zhao, R.; Liang, R.-C. Macroinvertebrate community characteristics and driving factors in the Chishui River (Renhuai section). Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 17, 3988–3995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Tu, Q.; Zhi, X. Functional molecular ecological networks. mBio. 2010, 1, e00169-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Shang, J.H.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Cai, W.; Wang, L. Redox gradients drive microbial community assembly patterns and molecular ecological networks in the hyporheic zone of effluent-dominated rivers. Water Res. 2024, 248, 120900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.B.; Lu, Z.D.; Zhao, Z.N.; Cao, W.; Wang, W.; Ke, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, W. Molecular ecological networks reveal the spatial-temporal variation of microbial communities in drinking water distribution systems. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, D.T.; Guo, Y.Q.; Zhang, B.G.; Zhang, C.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wei, G. Rare prokaryotic sub-communities dominate the complexity of ecological networks and soil multinutrient cycling during long-term secondary succession in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, H.W.; Huang, C.; Lin, H.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Lv, S. Microbial compositions, ecological networks, and metabolomics in sediments of black-odour water in Dongguan, China. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.B.; Roley, S.S.; Duncan, D.S.; Guo, J.; Quensen, J.F.; Yu, H.Q.; Tiedje, J.M. Long-term excess nitrogen fertilizer increases sensitivity of soil microbial community to seasonal change revealed by ecological network and metagenome analyses. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, E.; Morais, P.; Antunes, C.; Hoffman, J.C. The benthic food web connects the estuarine habitat mosaic to adjacent ecosystems. Food Webs 2023, 35, e00282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Cameron, T.C.; Couce, E.; Garcia, C.; Hicks, N.; Thomas, G.E.; Thompson, M.S.A.; Whitby, C.; O’Gorman, E.J. Oil and gas platforms degrade benthic invertebrate diversity and food web structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.F.; Feng, C.L.; Xu, Y.P.; Wang, J.; Huang, N.; Jin, X.; Wu, F.; Bai, Y. Water temperature governs organophosphate ester dynamics in the aquatic food chain of Poyang Lake. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 21, 100401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lv, X.C.; Zhu, W.X.; Gao, Y.; Dong, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Li, X. The aquatic benthic food webs: The determinants of periphyton biofilms in a diversion canal and its upstream reservoir. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 170, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The modularity of pollination networks. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W. Study on the Driving Factors of Benthic Ciliate Diversity and Community Composition in Zhejiang Intertidal Wetland. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.M. Study on the Effect of Plant–Benthic Fauna–Fish Functional Group on Self-Purification in Micropolluted Water. Master’s Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).