Mechanisms of Irrigation Water Levels on Nitrogen Transformation and Microbial Activity in Paddy Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Soil Samples
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Experiments
2.4. Microbial Sample Testing and Analysis
2.4.1. DNA Extraction
2.4.2. 16S rDNA Amplicon Pyrosequencing
2.4.3. Sequence Analysis
2.5. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
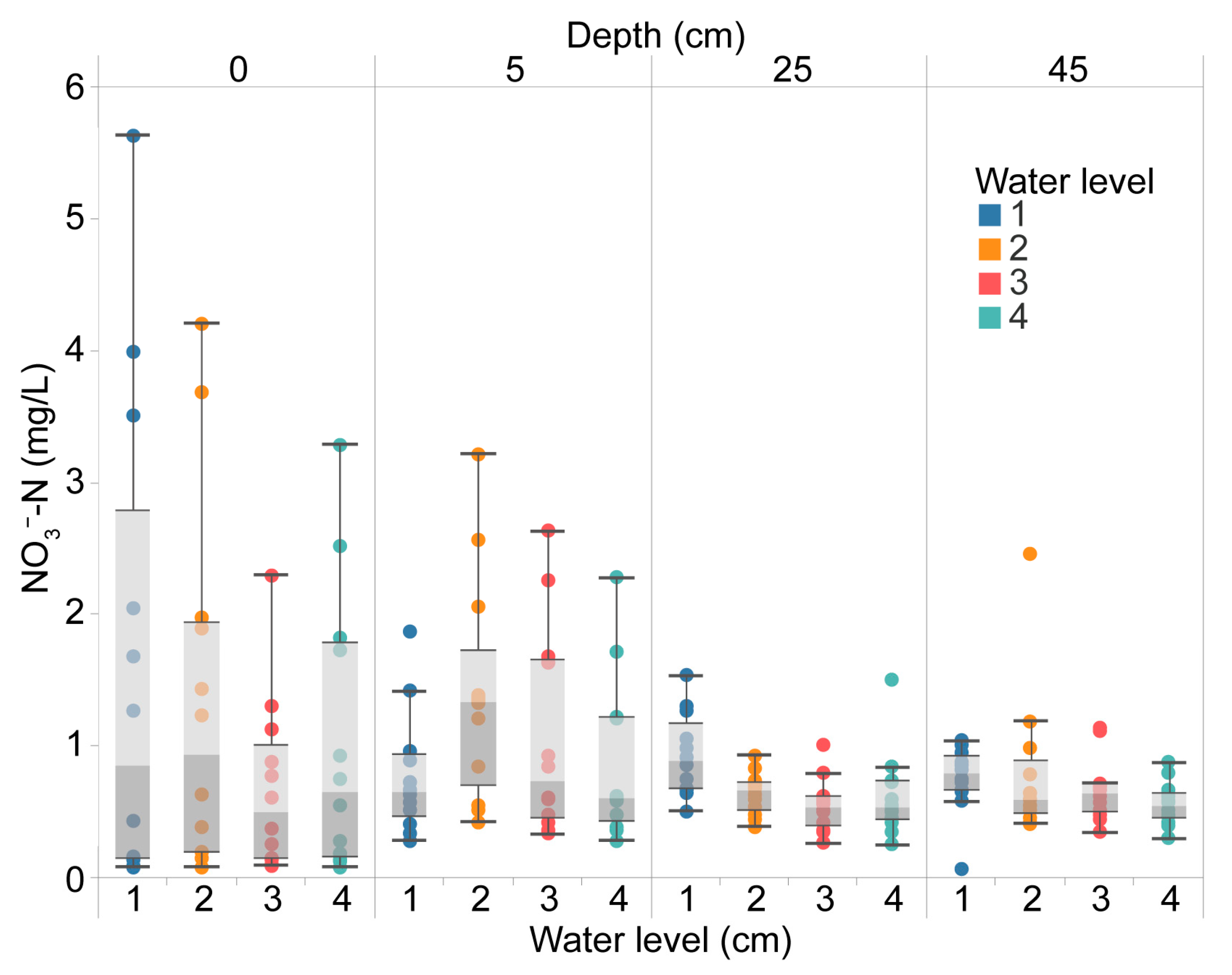
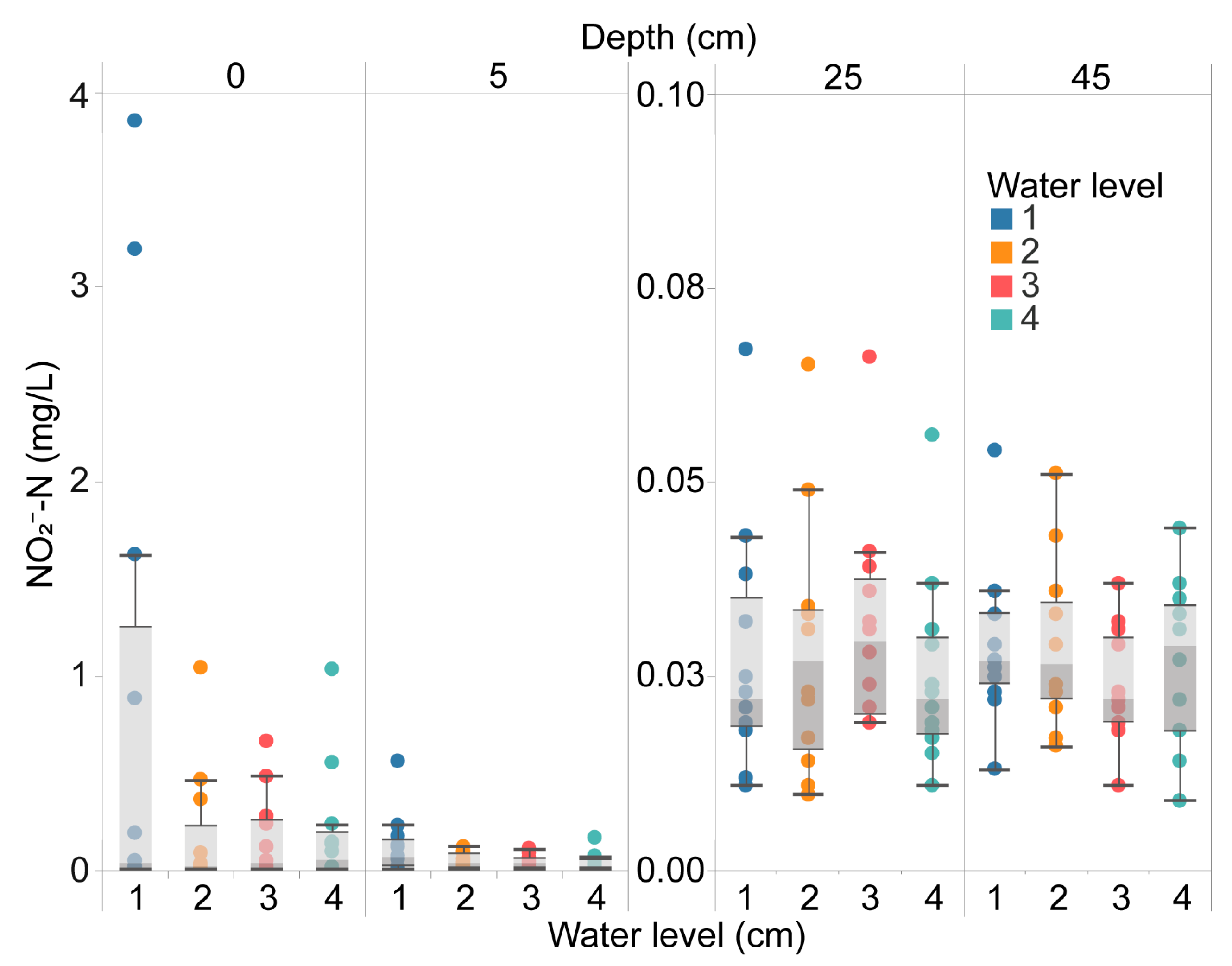
3.1. Distribution of Nitrogen Concentration at Different Depths of Rice Paddy Soil and Water System under Different Field Water Level Conditions
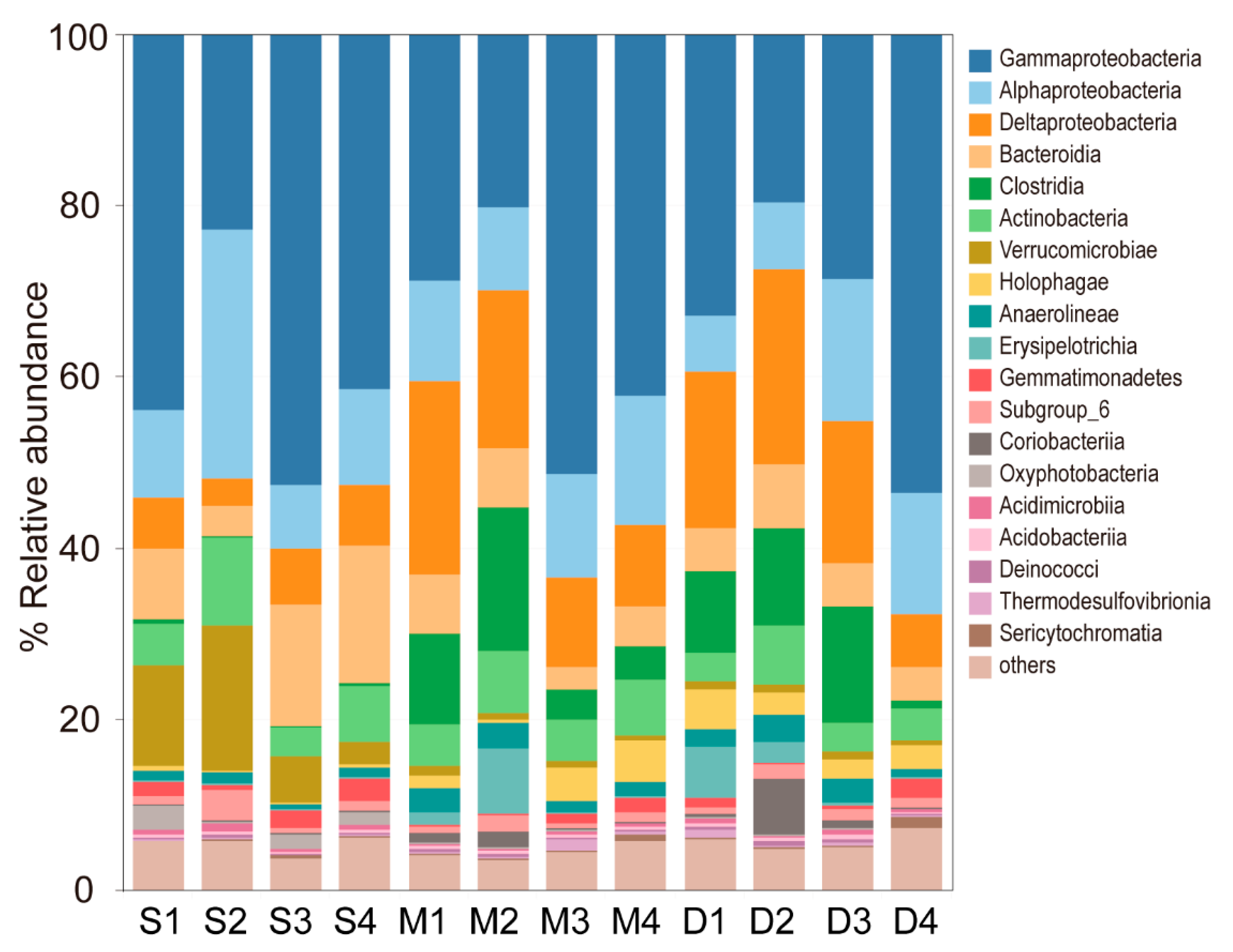
3.2. Distribution of Microbial Composition of Paddy Soil Under Different Field Water Level Conditions
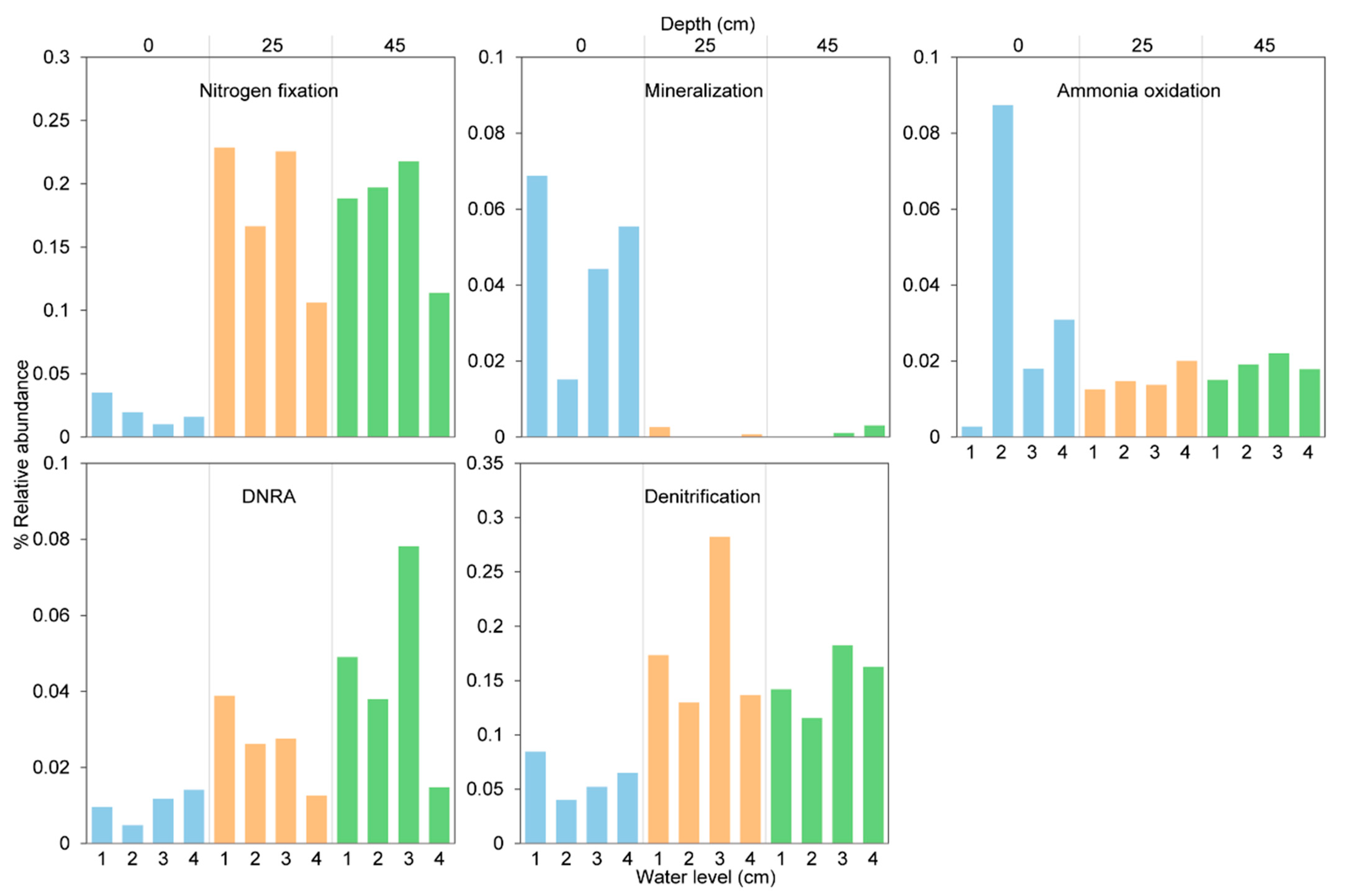
3.3. Microbial-Mediated Nitrogen Biochemical Responses Under Different Field Water Level Conditions
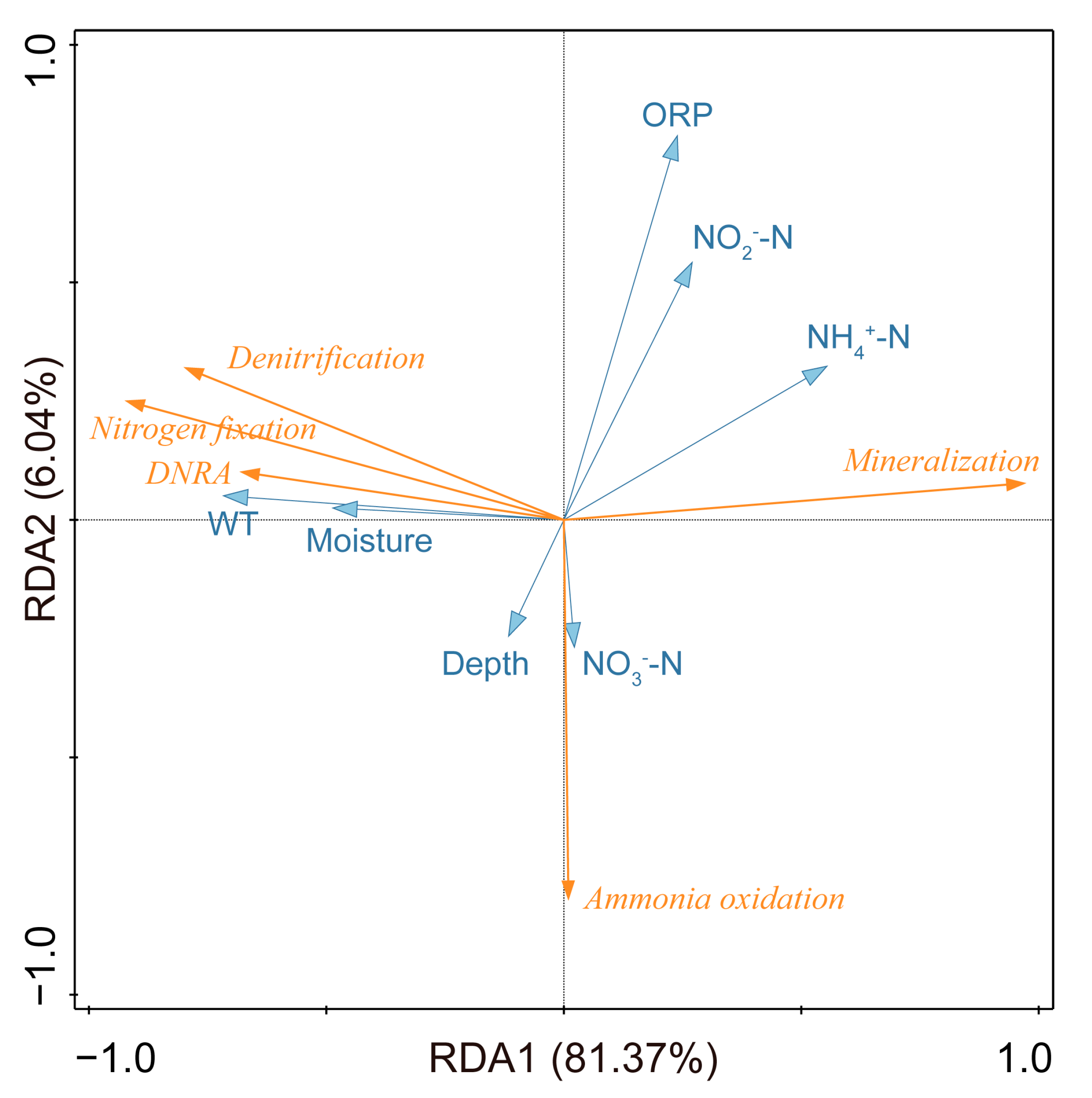
3.4. Nitrogen-Cycling Pathways and Relative Abundance Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Water Levels on Nitrogen Transformation in Surface Soils
4.2. Influence of Water Levels on Microbial Communities in Surface Soils
4.3. Impact of Water Levels on Nitrogen Cycling in Middle and Deep Soils
4.4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, N.; Ronga, X.; Xie, G.; Chang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, J.; Luo, G. Effectiveness of a 10-Year Continuous Reduction of Controlled-Release Nitrogen Fertilizer on Production, Nitrogen Loss and Utilization of Double-Cropping Rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, W.; Zhu, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Gu, J. Coated and Un-Coated Urea Incorporated with Organic Fertilizer Improves Rice Nitrogen Uptake and Mitigates Gaseous Active Nitrogen Loss and Microplastic Pollution. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 375, 109201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Huang, J.; Xie, R.; Di, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, G. Synergistic Effects of N Fertilization and Irrigation on Soil Bacterial Community in Super Rice Paddies. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Peng, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, W. Ammonia Volatilization Losses from a Rice Paddy with Different Irrigation and Nitrogen Managements. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 104, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Chen, X.; Shamsi, I.H.; Fang, P.; Lin, X.-Y. Effects of Irrigation Patterns and Nitrogen Fertilization on Rice Yield and Microbial Community Structure in Paddy Soil. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Qian, W.; He, M.; Chen, P.; Zhou, X.; Qi, Z. Nitrogen Losses from Soil as Affected by Water and Fertilizer Management under Drip Irrigation: Development, Hotspots and Future Perspectives. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 296, 108791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, D. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses by surface runoff and soil microbial communities in a paddy field with different irrigation and fertilization managements. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.-Z.; Yang, S.-H.; Xu, J.-Z.; Luo, Y.-F.; Hou, H.-J. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Leaching Losses from Paddy Fields with Different Water and Nitrogen Managements. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Jiao, X. Effect of Irrigation and Fertilizer Management on Rice Yield and Nitrogen Loss: A Meta-Analysis. Plants 2022, 11, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-Z.; Peng, S.-Z.; Hou, H.-J.; Yang, S.-H.; Luo, Y.-F.; Wang, W.-G. Gaseous Losses of Nitrogen by Ammonia Volatilization and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Rice Paddies with Different Irrigation Management. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yu, S.; Ma, T.; Ding, J.; He, P.; Dai, Y.; Zeng, G. Effects of Water and Nitrogen Management on Water Productivity, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Leaching Loss in Rice Paddies. Water 2022, 14, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.A.; Yu, S.; Zou, X.; Batool, I.; Castellano-Hinojosa, A.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, Q. Unraveling Nitrogen Loss in Paddy Soils: A Study of Anaerobic Nitrogen Transformation in Response to Various Irrigation Practice. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devkota, K.P.; Manschadi, A.; Lamers, J.P.; Devkota, M.; Vlek, P.L. Mineral Nitrogen Dynamics in Irrigated Rice-Wheat System under Different Irrigation and Establishment Methods and Residue Levels in Arid Drylands of Central Asia. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 47, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Hu, K.; Batchelor, W.D.; Liang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, J.; Cui, X.; Zhou, F. Exploring Optimal Nitrogen Management Strategies to Mitigate Nitrogen Losses from Paddy Soil in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-W.; Lim, S.-S.; Kwak, J.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Yoon, K.-S.; Kim, H.-Y.; Baek, W.-J.; Choi, W.-J. Further Understanding of the Impacts of Rainfall and Agricultural Management Practices on Nutrient Loss from Rice Paddies in a Monsoon Area. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Peng, S.; Xu, J.; Hou, H.; Gao, X. Nitrogen Loss from Paddy Field with Different Water and Nitrogen Managements in Taihu Lake Region of China. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 2393–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, S.; Yao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Gschwendtner, S.; Schloter, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Dannenmann, M. Enhanced Nitrogen Cycling and N2O Loss in Water-Saving Ground Cover Rice Production Systems (GCRPS). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Z.; Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Melching, C.S.; Shang, X. Critical Period and Pathways of Water Borne Nitrogen Loss from a Rice Paddy in Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.C.Y.; Kieft, T.L.; Kuloyo, O.; Linage-Alvarez, B.; Van Heerden, E.; Lindsay, M.R.; Magnabosco, C.; Wang, W.; Wiggins, J.B.; Guo, L.; et al. An Oligotrophic Deep-Subsurface Community Dependent on Syntrophy Is Dominated by Sulfur-Driven Autotrophic Denitrifiers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7927–E7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME Allows Analysis of High-Throughput Community Sequencing Data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, W. Application of High-Throughput Sequencing in Understanding Human Oral Microbiome Related with Health and Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast Length Adjustment of Short Reads to Improve Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and Clustering Orders of Magnitude Faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a Chimera-Checked 16S rRNA Gene Database and Workbench Compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; He, Y.; Yue, H.; Wang, Q. Microbial Structures and Community Functions of Anaerobic Sludge in Six Full-Scale Wastewater Treatment Plants as Revealed by 454 High-Throughput Pyrosequencing. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.-Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A Web Server for Annotation and Identification of Enriched Pathways and Diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39 (Suppl. S2), W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.-X.; Lin, H.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Rowley, G.; Todd, J.D.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.-H. DiTing: A Pipeline to Infer and Compare Biogeochemical Pathways from Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Data. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 698286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragahawewa, U.H.; Doole, G.J.; Bower, B. Is Dilution the Solution for Water Pollution? An Economic Analysis. In Proceedings of the 59th AARES Annual Conference, Rotorua, New Zealand, 10–13 February 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Nishiyama, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Hosomi, M. Nitrogen Budget and Ammonia Volatilization in Paddy Fields Fertilized With Liquid Cattle Waste. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2009, 201, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Hua, Z.; Xue, H.; Mei, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, S. Comparison of Nitrogen Loss Weight in Ammonia Volatilization, Runoff, and Leaching Between Common and Slow-Release Fertilizer in Paddy Field. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J. Study on the Integrated Distribution Coefficient of Ammonium N Migration in Layered Soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25340–25352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaviraj, M.; Kumar, U.; Chatterjee, S.; Parija, S.; Padbhushan, R.; Nayak, A.K.; Gupta, V.V. Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction to Ammonium (DNRA): A Unique Biogeochemical Cycle to Improve Nitrogen (N) Use Efficiency and Reduce N-Loss in Rice Paddy. Rhizosphere 2024, 30, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, S.Z.; Jiao, J.; Kong, W.L. Research on Nitrogen Dynamics in Paddy Field under Different Levels of Water and Fertilizer during Whole Growing Period. Water Sav. Irri 2009, 9, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Deng, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.; Hu, C. Nitrification Performance and Bacterial Community Dynamics in a Membrane Bioreactor with Elevated Ammonia Concentration: The Combined Inhibition Effect of Salinity, Free Ammonia and Free Nitrous Acid on Nitrification at High Ammonia Loading Rates. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J. Variations of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Surface Water Body of a Paddy Field. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2005, 24, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Yao, D.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Zhu, B. Immediate Response of Paddy Soil Microbial Community and Structure to Moisture Changes and Nitrogen Fertilizer Application. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1130298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Wang, Q.; She, Z.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Jin, C. Nitrogen Removal Pathway and Dynamics of Microbial Community with the Increase of Salinity in Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrification Process. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Su, Z.; Zhang, H. Community Composition and Co-Occurrence Patterns of Diazotrophs along a Soil Profile in Paddy Fields of Three Soil Types in China. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 82, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Ye, X.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Chen, D.; Gao, N.; Huang, M. Responses of Microbial Community Composition and Function to Biochar and Irrigation Management and the Linkage to Cr Transformation in Paddy Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.J.; Liesack, W.; Janssen, P.H. Opitutus Terrae Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., to Accommodate Novel Strains of the Division “Verrucomicrobia” Isolated from Rice Paddy Soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1965–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Luo, X.; Liao, H.; Nie, H.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. Nitrospira Are More Sensitive than Nitrobacter to Land Management in Acid, Fertilized Soils of a Rapeseed-Rice Rotation Field Trial. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Suter, H.; He, J.-Z.; Hu, H.-W.; Chen, D. Dissimilatory Nitrate Ammonification and N2 Fixation Helps Maintain Nitrogen Nutrition in Resource-Limited Rice Paddies. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, D.; Deng, Q.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Song, C. DNRA Was Limited by Sulfide and nrfA Abundance in Sediments of Xiamen Bay Where Heterotrophic Sulfide-Producing Genus (Pelobacter) Prevailed among DNRA Bacteria. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3493–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhuang, X.; Ahmad, S.; Lee, T.; Cao, C.; Ni, S.-Q. Investigation of Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction to Ammonium (DNRA) Microbial Communities in Sediments of Urban River Network Along the Huangpu River, China. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y.; Shiratori, Y.; Ohba, H.; Ishida, T.; Takano, R.; Satoh, S.; Shen, W.; Gao, N.; Itoh, H.; Senoo, K. Enhancement of the Nitrogen-Fixing Activity of Paddy Soils Owing to Iron Application. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 67, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; He, Y.; Yue, H.; Wang, Q. Metagenomic and Quantitative Insights into Microbial Communities and Functional Genes of Nitrogen and Iron Cycling in Twelve Wastewater Treatment Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, J.; De Rosa, D.; Rowlings, D.W.; Grace, P.R.; Müller, C.; Scheer, C. Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction to Ammonium (DNRA), Not Denitrification Dominates Nitrate Reduction in Subtropical Pasture Soils upon Rewetting. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Hou, H.; Xu, J.; Mao, Z.; Abudu, S.; Luo, Y. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Paddy Fields under Different Water Managements in Southeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Harhangi, H.R.; Zhu, B.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Yin, C.; Op Den Camp, H.J.M. Co-Occurrence and Distribution of Nitrite-Dependent Anaerobic Ammonium and Methane-Oxidizing Bacteria in a Paddy Soil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 336, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| pH | TOC | TN | TP | TK | NH4+-N | Available K | Available P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.45 ± 0.08 | 5.31 ± 0.77 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 706.63 ± 3.88 | 1.86 ± 0.03 | 218.9 ± 4.5 | 250.8 ± 0.10 | 2.35 ± 0.05 |
| Water Level | 1 cm | 2 cm | 3 cm | 4 cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shallow soil (5 cm) | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 |
| Medium soil (25 cm) | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 |
| Deep soil (45 cm) | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Li, X. Mechanisms of Irrigation Water Levels on Nitrogen Transformation and Microbial Activity in Paddy Fields. Water 2024, 16, 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213021
Fang Y, Qiu J, Li X. Mechanisms of Irrigation Water Levels on Nitrogen Transformation and Microbial Activity in Paddy Fields. Water. 2024; 16(21):3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213021
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Yunqing, Jiangping Qiu, and Xudong Li. 2024. "Mechanisms of Irrigation Water Levels on Nitrogen Transformation and Microbial Activity in Paddy Fields" Water 16, no. 21: 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213021
APA StyleFang, Y., Qiu, J., & Li, X. (2024). Mechanisms of Irrigation Water Levels on Nitrogen Transformation and Microbial Activity in Paddy Fields. Water, 16(21), 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213021






