Delineating Urban Functional Zones Using U-Net Deep Learning: Case Study of Kuancheng District, Changchun, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
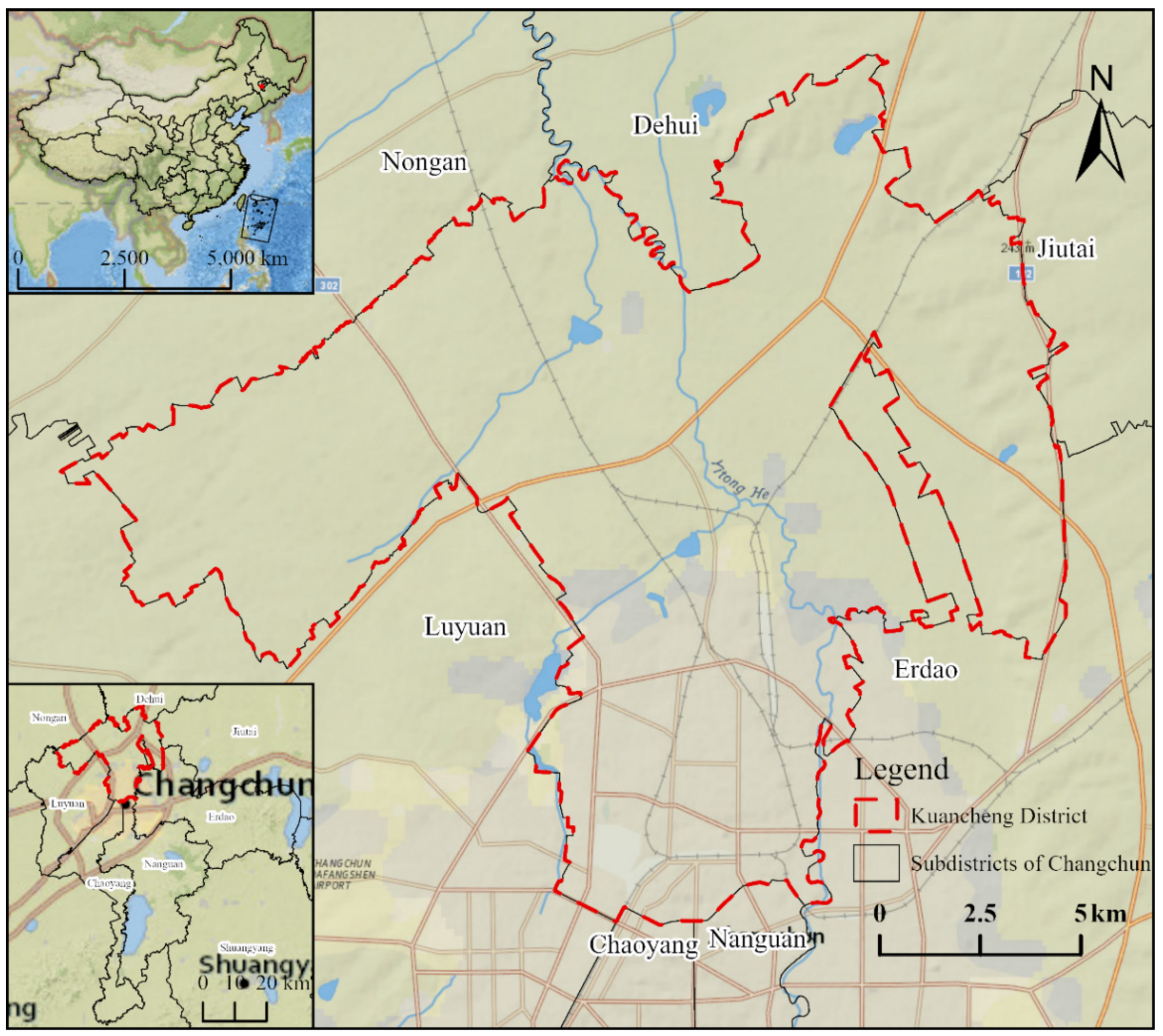
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Processing
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Unit Division of Urban Functional Zones
2.3.2. Classification System
2.3.3. U-Net Deep Learning
2.3.4. Verification
3. Results
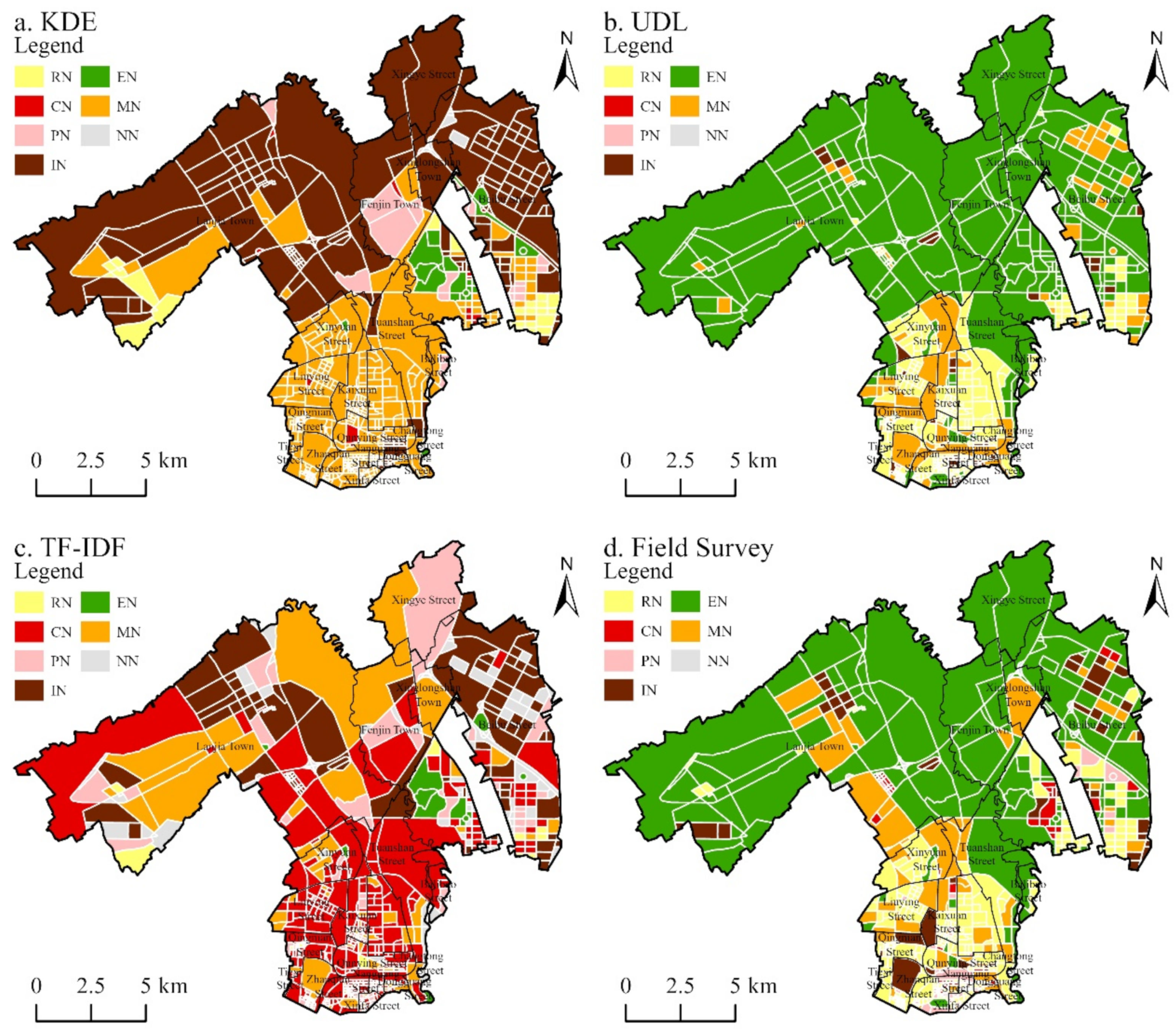
3.1. Identification of Functional Zones
3.1.1. Single Functional Zone
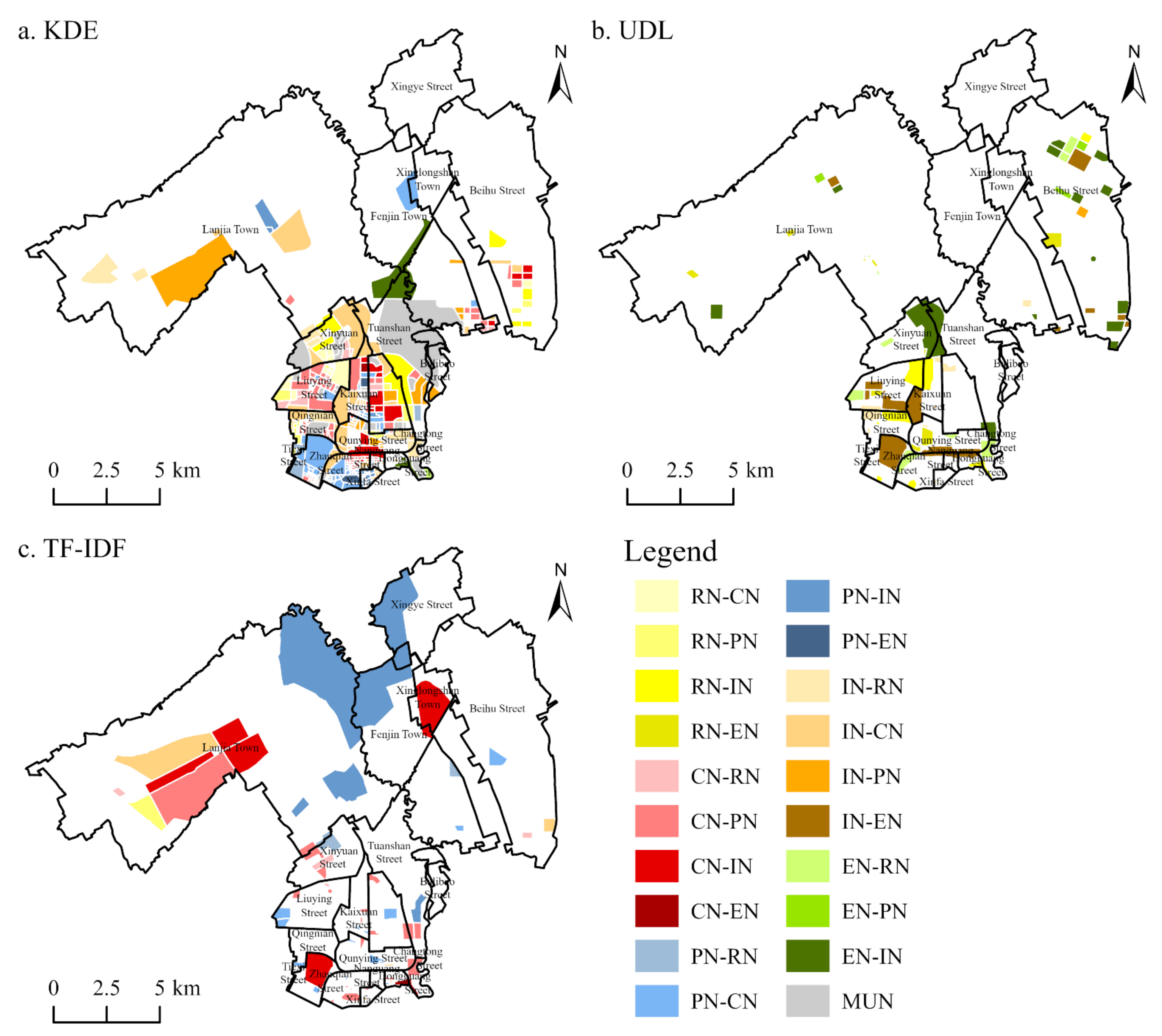
3.1.2. Mixed Functional Zones
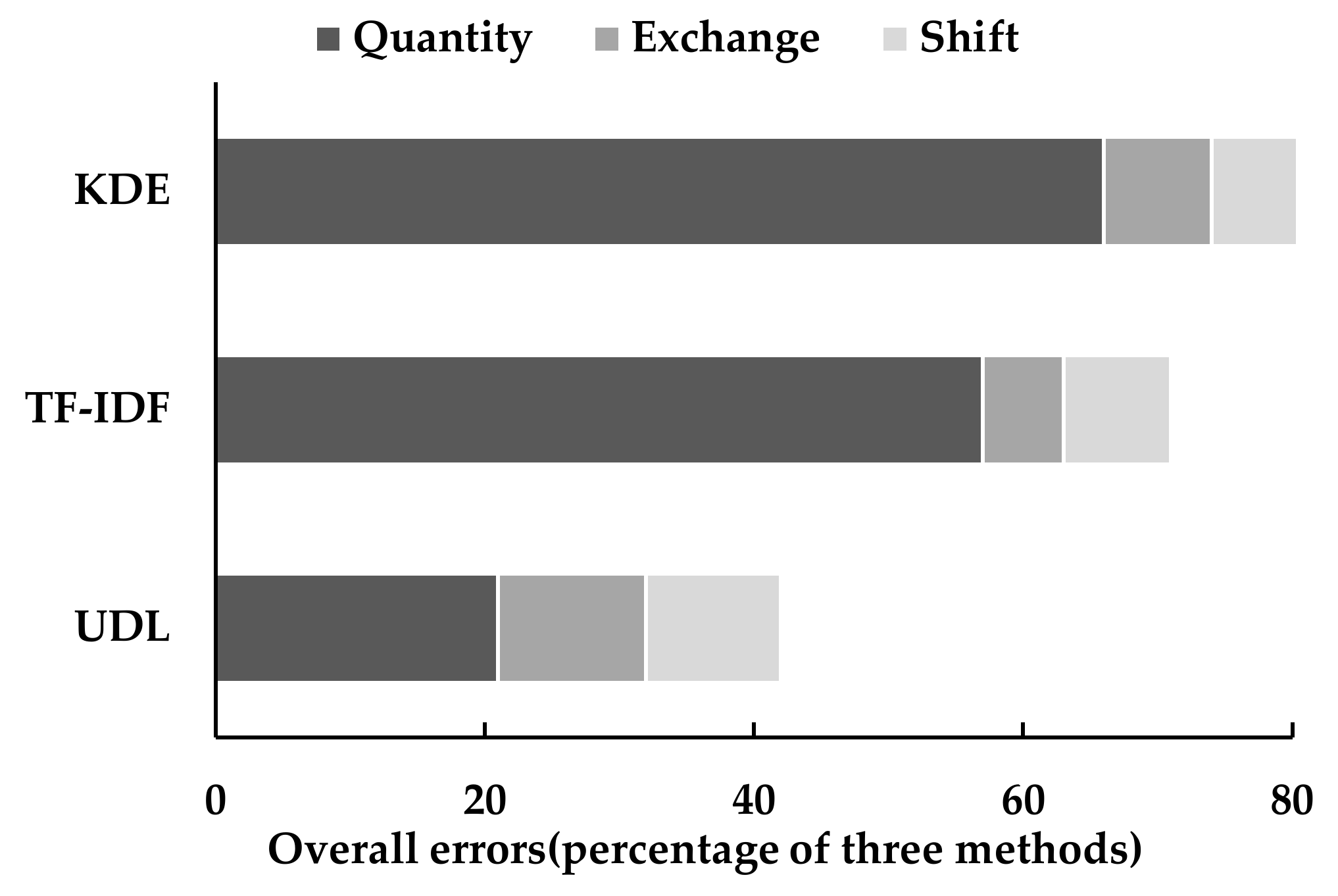
3.2. Verification
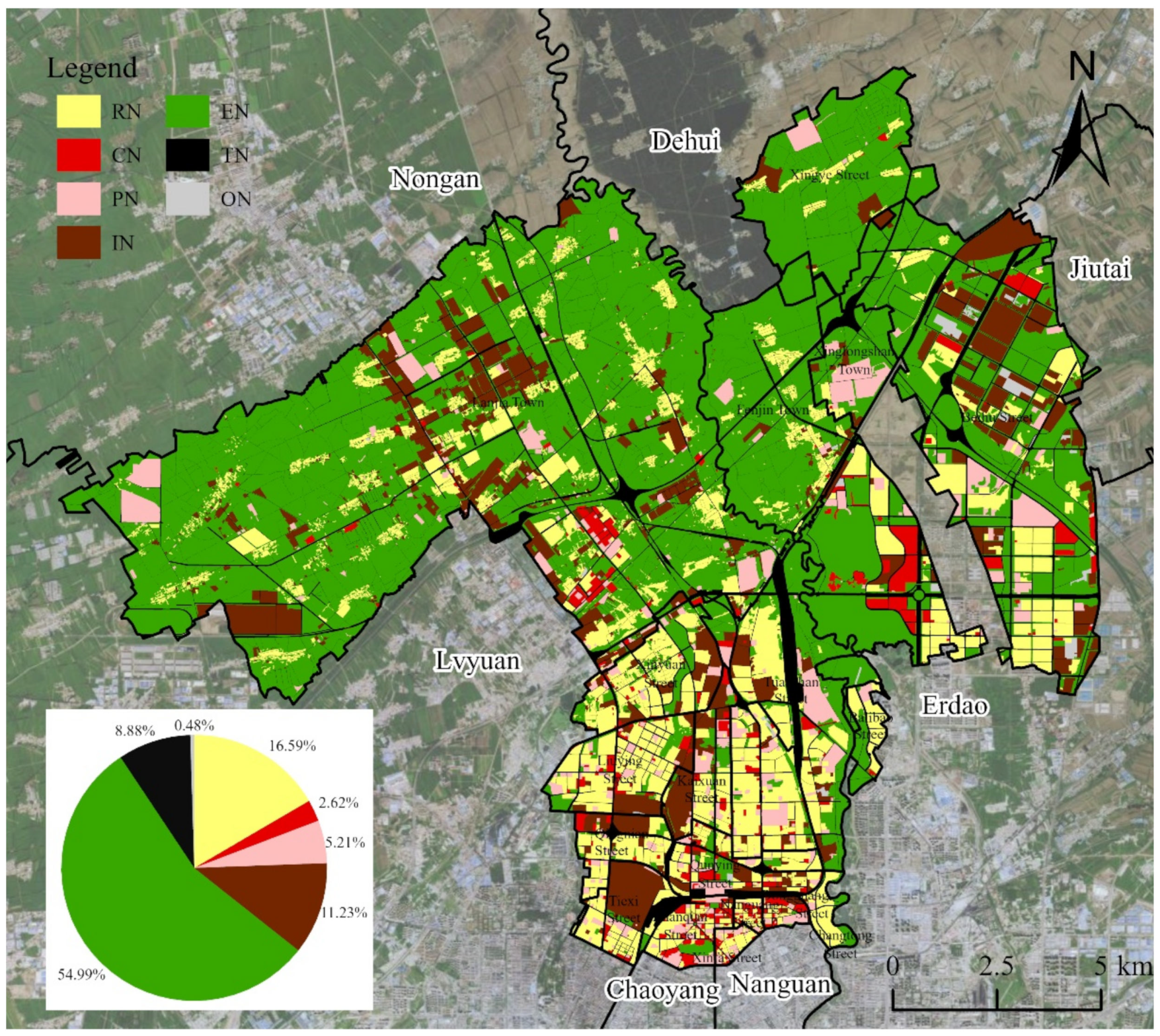
3.3. Spatial Pattern of Urban Functional Zones
4. Discussion
4.1. Development Current Situation
4.2. Comparison with Exiting Studies
4.3. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Aggregated Type | Big Category * | Mid Category * |
|---|---|---|
| Residential | Residential Area | Residential Area |
| Commercial And Commercial Services Facilities | Accommodation Service | Hotel, Hostel, Accommodation Service Related |
| Auto Dealers | Audi Franchised Sales, BMW Franchised Sales, Porsche Franchised Sales, Beiben Trucks Sales, BAIC MOTOR Sales, Honda Franchised Sales, Peugeot Citroen Franchised Sales, Peugeot Citroen, Chengdu Dayun Automotive Sales, Volkswagen Franchised Sales, MAN Sales, Dongfeng Truck Sales, DFM Franchised Sales, Ferrari Franchised Sales, Fiat Franchised Sales, Toyota Franchised Sales, Ford Franchised Sales, Foton Truck Sales, Qoros Sales, GAC Trumpchi Sales, Haima Sales, Hongqi Sales, CAMC Sales, Truck Sales, Geely Franchised Sales, JAC Truck Sales, JAC Sales, JAGUAR Franchised Sales, Chrysler Franchised Sales, Renault Franchised Sales, Land Rover Franchised Sales, Mercedes-Benz Truck Sales, Mercedes-Benz Franchised Sales, MG Sales, Luxgen Sales, Chery Franchised Sales, KIA Franchised Sales, Automobile Sales, Nissan Franchised Sales, ROEWE Sales, Mitsubishi Franchised Sales, Shaanxi Heavy-duty Truck Sales, Subaru Franchised Sales, SCANIA Sales, General Motors Franchised Sales, Volvo Truck Sales, Hyundai Franchised Sales, FAW Jiefang Sales, Chang’an Sales, Great Wall Sales, SINOTRUK Sales | |
| Auto Repair | Audi Franchised Repair, BMW Franchised Repair, Porsche Franchised Repair, Beiben Trucks Repair, BAIC MOTOR Repair, Honda Franchised Repair, Peugeot Citroen Franchised Repair, Peugeot Citroen, Chengdu Dayun Automotive Repair, Volkswagen Franchised Repair, MAN Repair, Dongfeng Truck Repair, DFM Franchised Repair, Ferrari Franchised Repair, Fiat Franchised Repair, Toyota Franchised Repair, Ford Franchised Repair, Foton Truck Repair, Qoros Repair, GAC Trumpchi Repair, Haima Repair, Hongqi Repair, CAMC Repair, Truck Repair, Geely Franchised Repair, JAC Truck Repair, JAC Repair, JAGUAR Franchised Repair, Chrysler Franchised Repair, Renault Franchised Repair, Land Rover Franchised Repair, Mercedes-Benz Truck Repair, Mercedes-Benz Franchised Repair, MG Repair, Luxgen Repair, Chery Franchised Repair, KIA Franchised Repair, Automobile Repair, Automobile Comprehensive Repair, Nissan Franchised Repair, ROEWE Repair, Mitsubishi Franchised Repair, Shaanxi Heavy-duty Truck Repair, Subaru Franchised Repair, SCANIA Repair, General Motors Franchised Repair, Volvo Truck Repair, Hyundai Franchised Repair, FAW Jiefang Repair, Chang’an Repair, Great Wall Repair, SINOTRUK Repair | |
| Auto Service | Charging Station, Used Automobile Dealer, Filling Station, Filling Station, Other Energy Station, Automobile Service Related, Automobile Rescue, Automobile Club, Automobile Parts Sales, Automobile Maintenance/Decoration, Automobile Rental, Car Wash | |
| Commercial House | Industrial Park, Building, Commercial House Related | |
| Daily Life Service | Move Service, Lottery Store, Electric Supply Service Office, Telecom Office, Travel Agency, Beauty and Hairdressing Store, Job Center, Funeral Facilities, Photo Finishing, Daily Life Service Place, Professional Service Firm, Ticket Office, Repair Store, Logistics Service, Laundry, Bath & Massage Center, Information Centre, Baby Service Place, Post Office, Agency, Water Supply Service Office | |
| Finance & Insurance Service | Insurance Company, Finance Company, Finance & Insurance Service Institution, Bank, Bank Related, Securities Company, ATM | |
| Food & Beverages | Food & Beverages Related, Tea House, Bakery, Coffee House, Fast Food Restaurant, Icecream Shop, Dessert House, Foreign Food Restaurant, Leisure Food Restaurant, Chinese Food Restaurant | |
| Motorcycle Service | Motorcycle Service Related, Motorcycle Repair, Motorcycle Sales | |
| Shopping | Convenience Store, Supermarket, Clothing Store, Personal Care Items Shop, Shopping Related Places, Plants & Pet Market, Home Electronics Hypermarket, Home Building Materials Market, Shopping Plaza, Commercial Street, Special Trade House, Sports Store, Stationary Store, Franchise Store, Comprehensive Market | |
| Public Government And Public Service | Culture & Education | School |
| Governmental Organization & Social Group | Industrial and Commercial Taxation Institution, Public Security Organization, Traffic Vehicle Management, Democratic Party, Social Group, Foreign Organization, Governmental Organization, Governmental & Social Groups Related | |
| Medical Service | Veterinary Hospital, Emergency Center, Disease Prevention Institution, Medical and Health Care Service Place, Pharmacy, Clinic, Special Hospital, Hospital | |
| Public Facility | Newsstand, Public Toilet, Public Facility, Public Phone, Emergency Shelter | |
| Science, Culture & Education Service | Museum, Media Organization, Archives Hall, Convention & Exhibition Center, Driving School, Science & Technology Museum, Science & Education Cultural Place, Research Institution, Art Gallery, Training Institution, Planetarium, Library, Cultural Palace, Arts Organization, School, Exhibition Hall | |
| Sports & Recreation | Holiday & Nursing Resort, Golf Related, Sports & Recreation Places, Recreation Place, Theatre & Cinema, Recreation Center, Sports Stadium | |
| Industrial And Mining Storage | Enterprises | Factory, Company, Enterprises, Farming, Forestry, Animal Husbandry and Fishery Base, Famous Enterprise |
| Ecological | Tourist Attraction | Scenery Spot, Tourist Attraction Related, Park & Square, Park & Plaza |
| Transportation | Pass Facilities | Gate of Buildings, Gate of Street House, Pass Facilities, Virtual Gate |
| Road Furniture | Road Furniture, Service Area, Traffic Light, Warning Sign, Signpost, Toll Gate | |
| Transportation Service | Commuter Bus Station, Taxi, Subway Station, Port & Marina, Bus Station, Border Crossing, Railway Station, Airport Related, Transportation Service Related, Ferry Station, Light Rail Station, Ropeway Station, Parking Lot, Coach Station |
References
- Seto, K.C.; Reenberg, A.; Boone, C.G.; Fragkias, M.; Haase, D.; Langanke, T.; Marcotullio, P.; Munroe, D.K.; Olah, B.; Simon, D. Urban land teleconnections and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7687–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, S.; Xue, G.; Gong, D. Soft Sensor with Deep Learning for Functional Region Detection in Urban Environments. Sensors 2020, 20, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaco, M.; Royuela, V.; Xavier, V. Identifying functional urban areas in ecuador using a varying travel time approach. Geogr. Anal. 2020, 52, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Long, Y. Functional urban area delineations of cities on the Chinese mainland using massive Didi ride-hailing records. Cities 2020, 97, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Silva, E.A. Delineating urban functional use from points of interest data with neural network embedding: A case study in Greater London. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 88, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Wen, D. Urban functional zone mapping by integrating high spatial resolution nighttime light and daytime multi-view imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Dong, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Chen, G.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, T. Heavy metal pollution in urban river sediment of different urban functional areas and its influence on microbial community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Tong, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, C.; Prishchepov, A.V. Monitoring finer-scale population density in urban functional zones: A remote sensing data fusion approach. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2019, 190, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Men, H.; Zhou, T.; Li, Z.; Zhu, F. Variance of the impact of urban green space on the urban heat island effect among different urban functional zones: A case study in Wuhan. Urban. For. Urban. Green. 2021, 62, 127159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhao, C.; Lin, T.; Li, X.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatio-temporal patterns of traffic-related air pollutant emissions in different urban functional zones estimated by real-time video and deep learning technique. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, L.; Yao, L.; Rong, J. Impact analysis of land use on traffic congestion using real-time traffic and POI. J. Adv. Transp. 2017, 2017, 7164790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiden, U.; Heldens, W.; Roessner, S.; Segl, K.; Esch, T.; Mueller, A. Urban structure type characterization using hyperspectral remote sensing and height information. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2012, 105, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Yao, Y.; Hu, G.; Xu, X.; Pei, F. Delineating urban functional areas with building-level social media data: A dynamic time warping (DTW) distance based k-medoids method. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 160, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Cao, J.; Yue, Y.; Shaw, S.-L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Z.; Chang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q. Coupling mobile phone and social media data: A new approach to understanding urban functions and diurnal patterns. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 2331–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiao, P.; Yuan, N.; Wang, W. Identification of multi-attribute functional urban areas under a perspective of community detection: A case study. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 462, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapka, P.; Halás, M.; Erlebach, M.; Tonev, P.; Bednář, M. A Multistage agglomerative approach for defining functional regions of the czech republic: The use of 2001 commuting data/Vícestupňový aglomerační přístup k vymezení funkčních regionů České republiky: Využití údajů o dojížďce z roku 2001. Morav. Geogr. Rep. 2014, 22, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Janowicz, K.; Couclelis, H. Extracting urban functional regions from points of interest and human activities on location-based social networks. Trans. GIS 2017, 21, 446–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Analyzing urban spatial patterns and functional zones using sina weibo POI data: A case study of Beijing. Sustainability 2021, 13, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; Yin, L.; Xu, Y.; Cui, H. A framework for extracting urban functional regions based on multiprototype word embeddings using points-of-interest data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 80, 101442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Yao, Y. Hierarchical community detection and functional area identification with OSM roads and complex graph theory. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 1569–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Du, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z. Large-scale urban functional zone mapping by integrating remote sensing images and open social data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Tu, W.; Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Qiu, G. Deep learning-based remote and social sensing data fusion for urban region function recognition. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Quantitative estimation of urbanization dynamics using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A comparative case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Hu, Z.; Li, L.; Cao, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, Q. Portraying urban functional zones by coupling remote sensing imagery and human sensing data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Du, S.; Wang, Q. Hierarchical semantic cognition for urban functional zones with VHR satellite images and POI data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 132, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Tsou, M.-H.; Li, H.; Jiang, W.; Guo, F. Mapping dynamic urban land use patterns with crowdsourced geo-tagged social media (Sina-Weibo) and commercial points of interest collections in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Zhou, F.; Xu, L.; Meng, D.; Xu, Z.; Paisley, J. Hyperspectral image classification with markov random fields and a convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2354–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Wang, L.; Meng, X. Image Semantic Segmentation Based on Deep Learning; Maritime Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Deep Learning Image Recognition Technology; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.-Y.; Xia, G.-S.; Lu, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, S.; You, S.; Zhang, L. Land-cover classification with high-resolution remote sensing images using transferable deep models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Wan, G.; Cheng, G.; Meng, L.; Han, J. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sahoo, D.; Hoi, S.C.H. Recent advances in deep learning for object detection. Neurocomputing 2020, 396, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Yin, G.; Johnson, B.A. Deep learning in remote sensing applications: A meta-analysis and review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakogiannis, F.I.; Waldner, F.; Caccetta, P.; Wu, C. ResUNet-a: A deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, H.; Ming, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, K.; Du, S. DFCNN-based semantic recognition of urban functional zones by integrating remote sensing data and POI data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.; Sun, T.; Wang, L. Evolving urban spatial structure and commuting patterns: A case study of Beijing, China. Transp. Res. Part. D Transport. Environ. 2018, 59, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Meng, Y. Integrating landscape metrics and socioeconomic features for urban functional region classification. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 72, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Han, Y. Identification of urban functional areas based on POI data: A case study of the Guangzhou economic and technological development zone. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, W.; Bai, X.; Shi, Y.; Han, Y.; Peng, Z.-R.; Gu, C. Beyond Word2vec: An approach for urban functional region extraction and identification by combining Place2vec and POIs. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Fu, Y.; Liu, B.; Hu, W.; Xiong, H. Representing urban functions through zone embedding with human mobility patterns. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-18), Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Halás, M.; Klapka, P.; Tonev, P. The use of migration data to define functional regions: The case of the Czech Republic. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 76, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, S. The study of Changchun city function subarea and the adjustive problems of the industry space structure. J. Northeast. Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2004, 3, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Long, Y. Automated identification and characterization of parcels with OpenStreetMap and points of interest. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2015, 43, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J. Spatial organization pathway for territorial function-structure: Discussion on implementation of major function zoning strategy in territorial spatial planning. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Liu, Y.; Du, M.; Gao, S.; Wang, P.; Liu, X. The influence of spatial grid division on the layout analysis of urban functional areas. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, I.; Dewancker, B. Identification of population growth and distribution, based on urban zone functions. Sustainability 2018, 10, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Berlin, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H. End-to-end change detection for high resolution satellite images using improved UNet++. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, N.; Fang, L.; Plaza, A. Hybrid first and second order attention Unet for building segmentation in remote sensing images. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontius, R.G. Component intensities to relate difference by category with difference overall. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 77, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.G.; Bartolo, R.E. Use of WorldView-2 time series to establish a wetland monitoring program for potential offsite impacts of mine site rehabilitation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 42, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ye, X.; Ren, F.; Du, Q. Check-in behaviour and spatio-temporal vibrancy: An exploratory analysis in Shenzhen, China. Cities 2018, 77, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Cutchan, M.; Comber, A.J.; Giannopoulos, I.; Canestrini, M. Semantic boosting: Enhancing deep learning based LULC classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Du, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X. Mapping large-scale and fine-grained urban functional zones from VHR images using a multi-scale semantic segmentation network and object based approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 261, 112480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhou, Z.; Jiao, L.; Zhao, R. Compact urban form and expansion pattern slow down the decline in urban densities: A global perspective. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Sodoudi, S. A new method to quantify surface urban heat island intensity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakali, L.; Kwon, T.J.; Fu, L. Identification of crash hotspots using kernel density estimation and kriging methods: A comparison. J. Mod. Transp. 2015, 23, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Tian, K.; Hu, X.; Xia, F. CoPFun: An urban co-occurrence pattern mining scheme based on regional function discovery. World Wide Web 2018, 22, 1029–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zhang, F.; Mu, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y. Urban function recognition by integrating social media and street-level imagery. Environ. Plan. B Urban. Anal. City Sci. 2020, 48, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Gong, P. Mapping urban land use by using landsat images and open social data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Shao, G.; Xu, Z.; Tang, L.; Sun, L. Measuring urban compactness based on functional characterization and human activity intensity by integrating multiple geospatial data sources. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




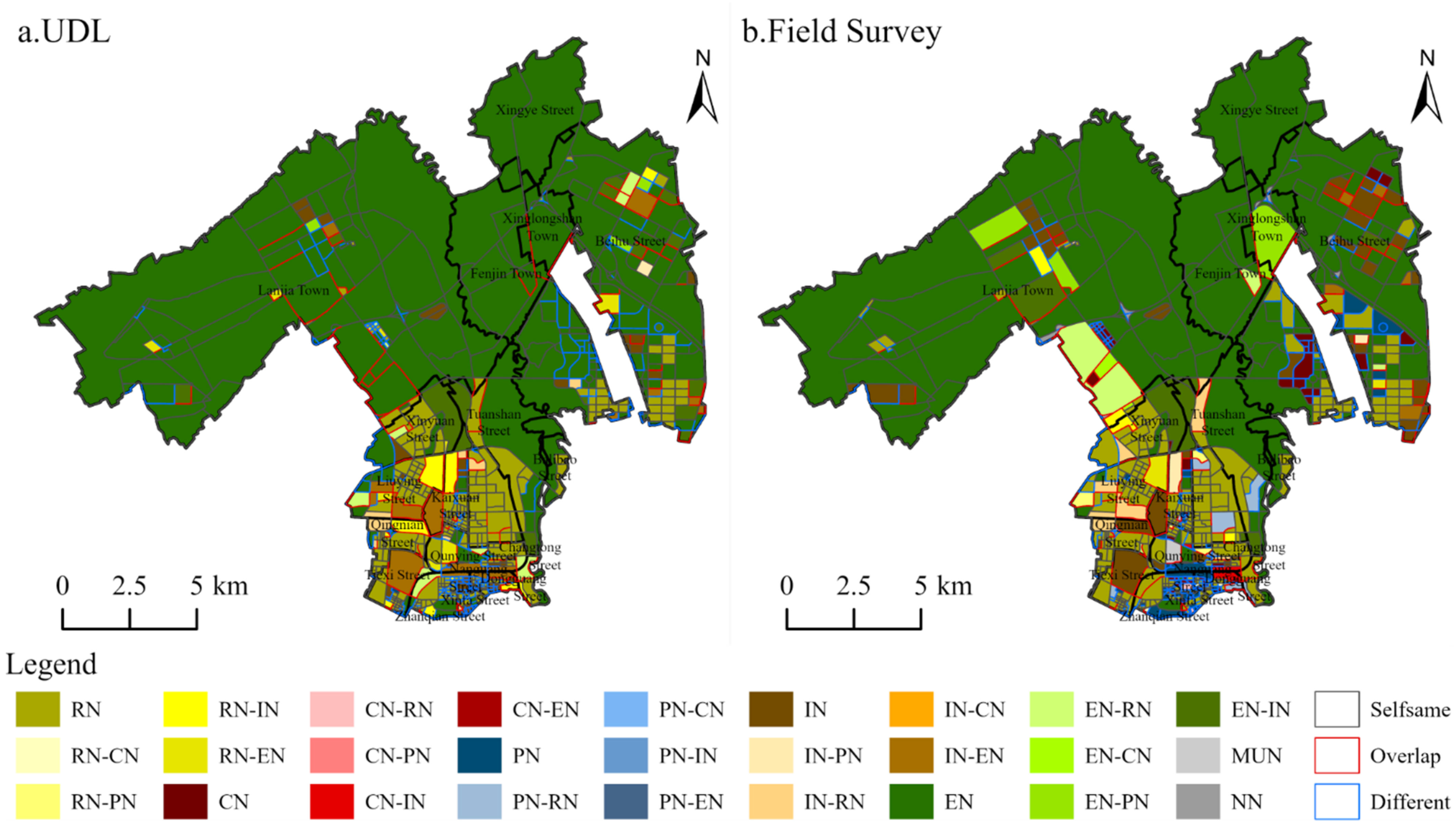

| Order | Functional Classifications | Authors |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diplomatic and political zone, science and education zone, mature residential zone, new residential zone, commercial and entertainment zone, tourist attraction zone, area to be developed, unclassified area | Miao et al. [19] |
| 2 | Commercial zone, campuses, parks and greenbelts, industrial zone, residential districts, shantytowns | Zhang et al. [26] |
| 3 | Corporate business area or factory, shopping mall, tourism attraction place, public facility, transportation facility, science and education place, medical service place, food and beverage place and daily life service place, governmental and public organizations | Hu et al. [20] |
| 4 | Residential, education and training, recreation and entertainment, medical and public health, commercial and finance, incorporated and business, party and government organization, scenic areas | Luo et al. [46] |
| 5 | Office building/space, financial services, medical/education, entertainment, life services, residence communities, government | Hong and Yao [21] |
| 6 | Ecological area, transit region, urban buffer, suburbs, subcenter, urban center | Tu et al. [25] |
| 7 | Urban green, industrial districts, public services, residential districts, commercial districts, hospitals, schools, shantytowns | Bao et al. [36] |
| 8 | Developed working and industrial regions, developed public service region, emerging working and industrial regions, emerging residential region, developed residential region, nature park, developing rural region, undefined region | Zhai et al. [40] |
| 9 | Mixed use, residential, industry, business, conservation | Malik and Dewancker [47] |
| The Largest Functional Area | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RN | CN | PN | IN | EN | MUN | NN | Total | ||
| The second functional area | a. KDE | ||||||||
| RN | 30 | 19 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 70 | |||
| CN | 12 | 16 | 54 | 43 | 125 | ||||
| PN | 12 | 72 | 28 | 24 | 136 | ||||
| IN | 9 | 41 | 32 | 190 | 3 | 275 | |||
| EN | 1 | 3 | 2 | 26 | 32 | ||||
| MUN | 40 | 40 | |||||||
| NN | 29 | 29 | |||||||
| Total | 63 | 149 | 127 | 269 | 30 | 40 | 29 | 707 | |
| b. TF-IDF | |||||||||
| RN | 11 | 5 | 3 | 19 | |||||
| CN | 295 | 16 | 4 | 315 | |||||
| PN | 1 | 22 | 77 | 2 | 102 | ||||
| IN | 8 | 4 | 83 | 95 | |||||
| EN | 2 | 16 | 18 | ||||||
| MUN | |||||||||
| NN | 158 | 158 | |||||||
| Total | 12 | 332 | 100 | 89 | 16 | 158 | 707 | ||
| c. UDL | |||||||||
| RN | 300 | 7 | 9 | 316 | |||||
| CN | |||||||||
| PN | 2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | |||||
| IN | 10 | 67 | 16 | 93 | |||||
| EN | 11 | 15 | 264 | 290 | |||||
| MUN | |||||||||
| NN | 2 | 2 | |||||||
| Total | 321 | 2 | 90 | 292 | 2 | 707 | |||
| Field Survey Data | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RN | CN | PN | IN | EN | MN | NN | ON | Total | ||
| Prediction data | a. KDE | |||||||||
| RN | 17 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 30 | |||||
| CN | 7 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 16 | ||||
| PN | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 15 | 3 | 3 | 28 | ||
| IN | 22 | 21 | 6 | 39 | 68 | 24 | 10 | 190 | ||
| EN | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 19 | 1 | 26 | |||
| MN | 236 | 43 | 34 | 9 | 31 | 29 | 6 | 388 | ||
| NN | 1 | 10 | 18 | 29 | ||||||
| Total | 286 | 68 | 45 | 54 | 157 | 58 | 38 | 1 | 707 | |
| b. TF-IDF | ||||||||||
| 9 | 2 | 11 | ||||||||
| CN | 199 | 35 | 11 | 8 | 16 | 25 | 1 | 295 | ||
| PN | 26 | 8 | 17 | 3 | 15 | 8 | 77 | |||
| IN | 3 | 13 | 3 | 31 | 25 | 8 | 83 | |||
| EN | 2 | 2 | 12 | 16 | ||||||
| MN | 33 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 12 | 11 | 67 | |||
| NN | 16 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 75 | 6 | 38 | 158 | ||
| Total | 286 | 68 | 45 | 54 | 157 | 58 | 38 | 1 | 707 | |
| c. UDL | ||||||||||
| RN | 233 | 27 | 14 | 4 | 8 | 13 | 1 | 300 | ||
| PN | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||
| IN | 13 | 19 | 13 | 12 | 2 | 8 | 67 | |||
| EN | 27 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 143 | 23 | 35 | 1 | 264 | |
| MN | 13 | 10 | 6 | 25 | 4 | 14 | 72 | |||
| NN | 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| Total | 286 | 68 | 45 | 54 | 157 | 58 | 38 | 1 | 707 | |
| Authors | Data Source | Study Area | Mapping Unit | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xin et al. [6] | MHRI SHRI | Beijing and Wuhan | Roads | BOVW (bag of visual word) model and SDA (semi-supervised discriminant analysis) dimensionality reduction approach |
| Du et al. [55] | MHRI | Beijing and Shanghai | Objects | Multi-scale semantic segmentation network |
| Heiden et al. [12] | MHRI | Munich | Pixels | Automated multi-stage processing system |
| Myint et al. [13] | SHRI | Phoenix, Arizona | Objects | Object-based classifier |
| Chen et al. [14] | MPPD | Yuexiu District, Guangzhou | Buildings | Improved k-medoids method |
| Du et al. [22] | MHRI POI | Three districts in Beijing | Roads | LDA, SVM |
| Hong and Yao [21] | POI | Guangzhou | Roads | Infomap community detection algorithm |
| This study | SHRI POI | Kuancheng District, Changchun | Roads | UDL, KDE, TF-IDF |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, S. Delineating Urban Functional Zones Using U-Net Deep Learning: Case Study of Kuancheng District, Changchun, China. Land 2021, 10, 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111266
Yang Y, Wang D, Yan Z, Zhang S. Delineating Urban Functional Zones Using U-Net Deep Learning: Case Study of Kuancheng District, Changchun, China. Land. 2021; 10(11):1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111266
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuewen, Dongyan Wang, Zhuoran Yan, and Shuwen Zhang. 2021. "Delineating Urban Functional Zones Using U-Net Deep Learning: Case Study of Kuancheng District, Changchun, China" Land 10, no. 11: 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111266
APA StyleYang, Y., Wang, D., Yan, Z., & Zhang, S. (2021). Delineating Urban Functional Zones Using U-Net Deep Learning: Case Study of Kuancheng District, Changchun, China. Land, 10(11), 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111266





