Abstract
Urban land is the primary location for manufacturing and services, facilitating the expansion and interconnectedness of economic activities and factor flows to shape various urban land-use performances (ULUP). Exploring these spatial linkages of urban land-use performance can play a crucial role in fostering cohesive urban development. Taking 109 prefecture-level cities as research samples, this paper explores the characteristics and influencing factors of the spatial network associated with ULUP in the Yangtze River Economic Belt through modified gravity model, network analysis and QAP analysis. The analysis shows that ULUP has shown an N-shaped trend over the past two decades. It has formed a network of correlations, with Chongqing, Shanghai, and Wuhan emerging as central nodes. Notably, the correlation predominantly occurs between geographically adjacent cities, with weaker links between the Yangtze River Economic Belt’s upstream, midstream, and downstream regions. The network can be divided into four distinct types: main inflow plate, main outflow plate, agent plate, and bidirectional spillover plate. Geographic location is the most significant factor influencing network formation, followed by resource mismatch, economic development, and openness. The study provides theoretical guidance and empirical support for improving the utilisation of urban land and promoting coordinated development.
1. Introduction
Urban land is a fundamental pillar for urban development, encompassing significant economic, social, and environmental values. Its effective utilisation is pivotal in promoting economic growth and enhancing life quality while mitigating resource consumption and environmental impact [1]. Existing research primarily concentrates on the efficiency of urban land use [2]. However, an overemphasis on efficiency can engender issues like housing congestion, elevated living expenses, and environmental degradation. Urban land use performance (ULUP), as a critical urban land use metric, offers a more expansive and meaningful perspective than mere efficiency. It underscores a holistic and comprehensive representation of land use benefits, effects, and impacts, integrating multiple objectives [3]. Conducting a ULUP evaluation has important practical significance for realizing urban land functions and transforming urban development.
Originally, performance evaluation aimed to provide an unbiased and accurate assessment of a business’s operational efficiency [4]. As performance evaluation evolved, it has transcended economic assessments for enterprises and institutions to public management, thus leading to the emergence of ULUP evaluation. Currently, academics have studied ULUP from different perspectives, including environmental regulation [5], environmental performance [6], and land consolidation performance [7]. Due to the varied perspectives of the research, the performance evaluation index system is also different. Prominent among these is the “4E” evaluation framework, which integrates considerations of Economy, Effectiveness, Efficiency, and Equity [8]. In terms of evaluating models, various methods are employed to calculate performance values, such as the Comprehensive Evaluation Method [9], the TOPSIS Model [10], and the Structural Equation Model [11]. Recent studies delve into the regional correlation of ULUP using statistical models, including the econometric model, spatial autocorrelation, and hot–cold spot analysis. Researchers have noted a pattern of clustered distribution in ULUP, suggesting notable inter-city correlations. However, the study of these performance linkages and spatial structure remains underexplored despite its critical importance for regional coordinated development. For this reason, it is necessary to identify an appropriate methodology for examining the spatial correlation structures in ULUP.
Spatial structure, which refers to the distribution and combination of economic elements, has evolved from urban network development, typically exhibiting single or multi-centre patterns [12]. Governments have recognized its impact on economic growth, acknowledging that an optimal urban structure can enhance factor mobility and boost productivity [13]. However, large cities face issues like traffic congestion and environmental harm, prompting a shift towards a polycentric spatial structure to foster sustainable regional development [14,15]. Many studies have explored the social and economic impacts of the development of polycentric spatial structures, focusing mainly on economic growth [16], urban carbon emissions [17], and environmental performance [12]. Despite extensive research on the socio-economic impacts of polycentric structures, their influence on ULUP remains underexplored. Hence, to achieve the synergistic enhancement of ULUP and regional coordinated development, it is imperative to analyse the impact of regional spatial structure on ULUP and its effectiveness.
The Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREB) encompasses 11 provinces and cities, covering over 20% of China’s area. The growth strategy of the YREB is a significant national strategy aimed at connecting the north and south and coordinating the development of the regions of eastern, central and western China. This study aims to investigate the spatial correlations of ULUP and the factors influencing the formation of spatial correlation networks using the YREB as a study area. By addressing these issues, we can promote the rational use of land resources within the YREB and gain valuable insights for refining the regional urban governance system and promoting coordinated and sustainable development. Based on a comprehensive measurement of ULUP, this paper delves into the characteristics of its spatial correlation networks by employing an Improved Gravity Model (IGM) coupled with Social Network Analysis (SNA). Subsequently, the Quadratic Assignment Procedure (QAP) is applied to explore the association mechanisms of ULUP. This research furnishes a dependable reference for shaping future urban land use policy improvements and contributes to the refinement of strategies for regional coordinated development.
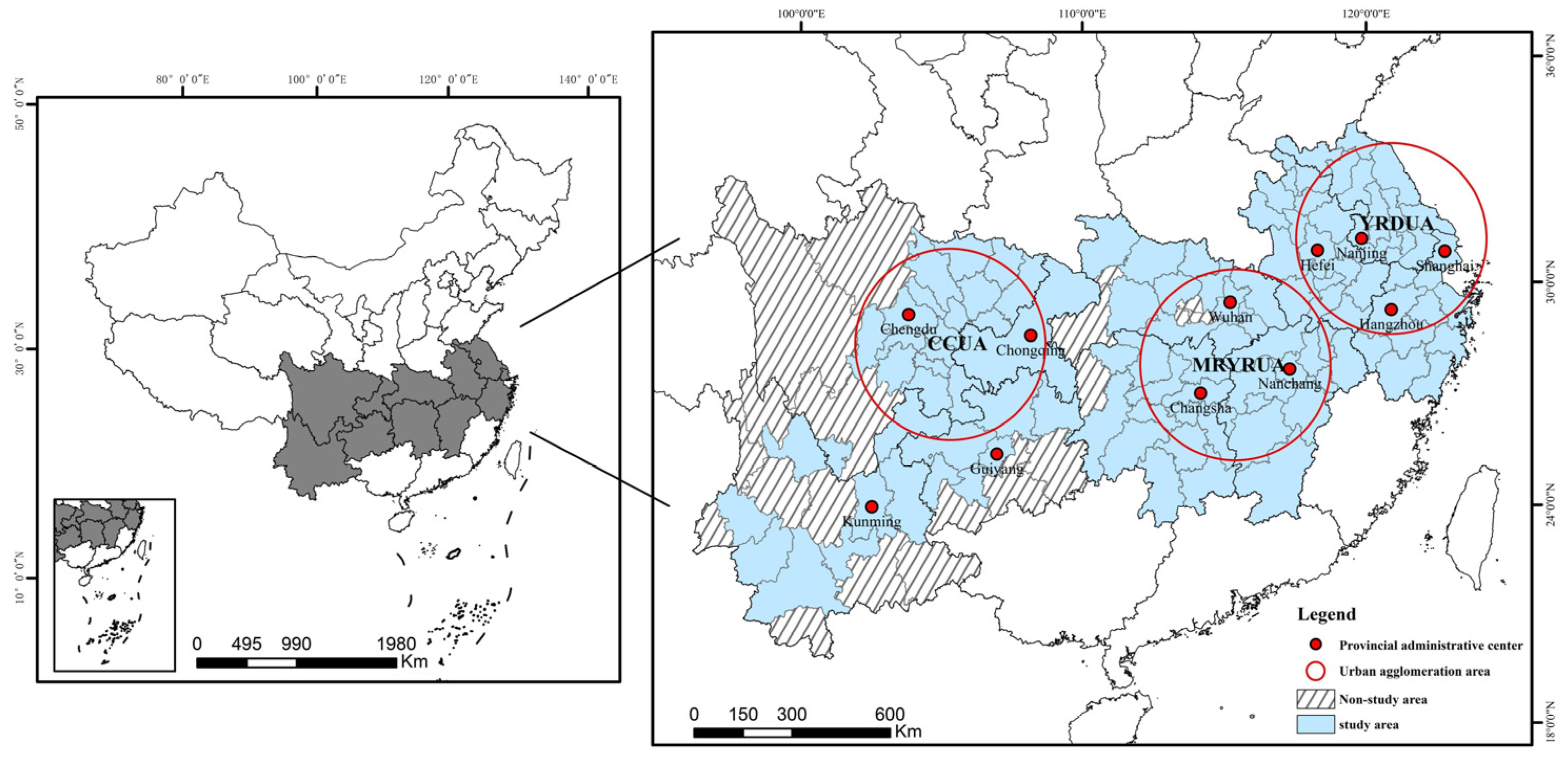
2. Study Area
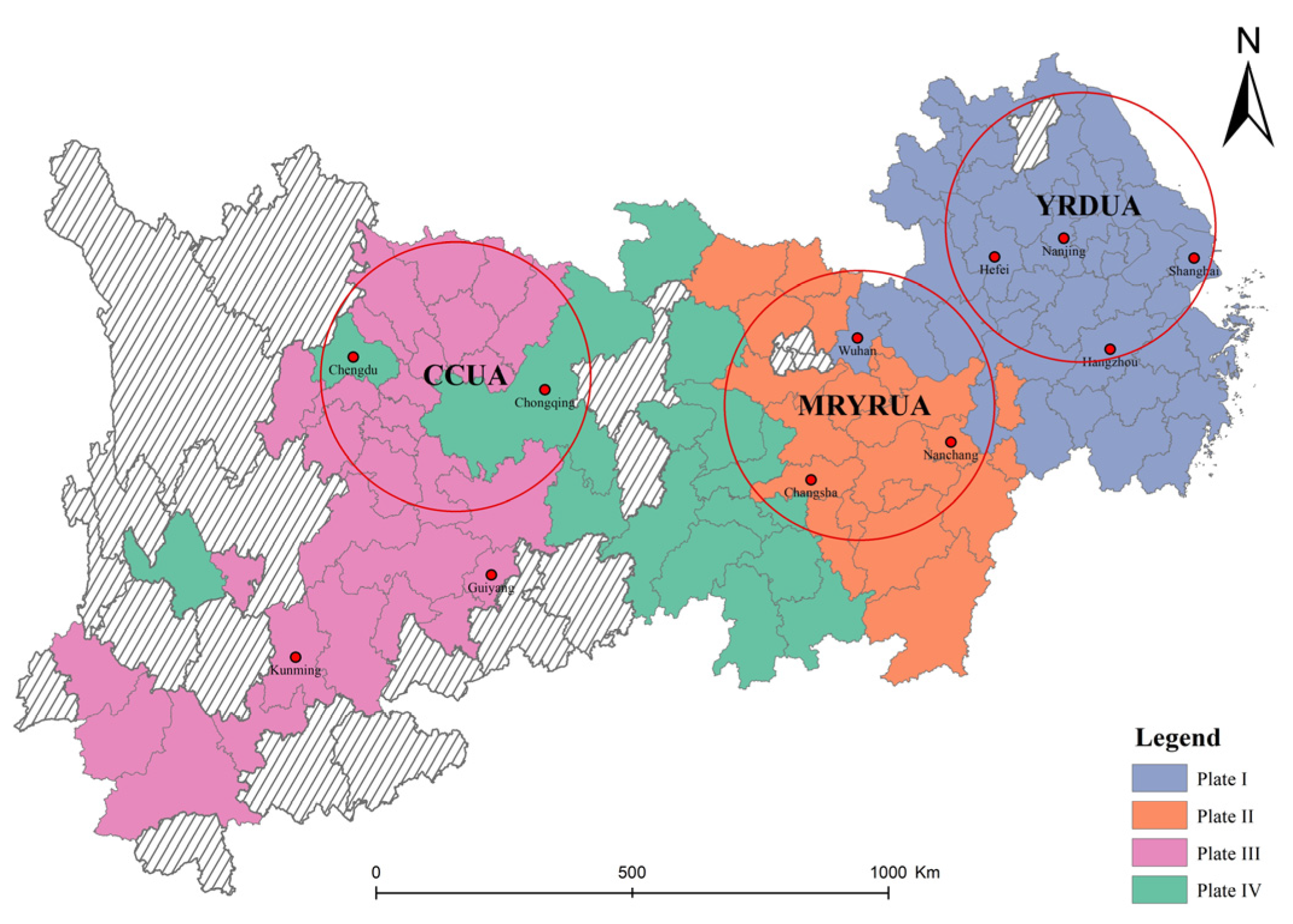
The YREB is the world’s largest inland river basin economic belt open for development, accounting for over 40% of the country’s population and GDP. The YREB comprises three major metropolitan areas: the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River (MRYR), and the Chengdu–Chongqing (CC) urban agglomerations (Figure 1). Despite its significance, the YREB still faces challenges such as uncoordinated regional development, irrational urban land use structure, and regional factor mismatch, which seriously obstructs its green and sustainable development. The study of ULUP can provide essential scientific insights to optimise land resource utilisation and enhance urbanisation quality. To ensure representative findings, we selected 109 cities in the YREB as study areas, taking into account the extensive coverage of the YREB and the administrative district adjustments.
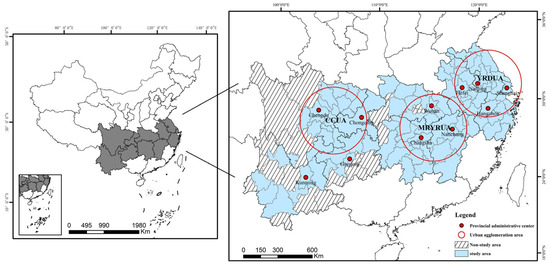
Figure 1.
Study area.
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Data Sources
The paper uses data from the statistical yearbooks, economic and social statistical yearbooks, statistical bulletins on national economic and social development, and local government offices of the 109 prefecture-level cities in the study area for the period 2000–2020 (Table 1). Land use data for the years 2000–2020 are acquired from the Geographic Data Sharing Infrastructure, Resource and Environment Science and Data Centre (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 16 June 2013). The land use data utilized is in the form of raster data with a precision of 30 m. The spatial distances between cities are obtained using straight-line distance measurements from their geometric centres, calculated by the ArcGIS 10.2 platform. In order to ensure the comparability of the data in different years, this study adjusted the relevant data and interpolation was used to supplement some of the missing data.

Table 1.
Data sources and collection methods.
3.2. ULUP Measurement
3.2.1. Measurement Models
Evaluation models are crucial in ensuring the scientific rigour and accuracy of results. This paper adopts the Projection Pursuit Model (PPM) to assess ULUP, recognizing the limitations of traditional evaluation methods in handling high-dimensional data. PPM excels in capturing and analyzing intricate urban land use patterns, offering a novel and effective approach to evaluation that enhances understanding and optimisation of the dynamic influences on urban land use. PPM, an emerging statistical method, is mainly used to deal with nonlinear data [18,19,20]. PPM has been widely used in many studies, such as cultivated land system security [21], carbon emission efficiency [22], and environmental vulnerability assessment [23].
The process for creating a comprehensive evaluation model of ULUP using PPM is as follows:
- (1)
- Projection Index Functions
In order to project the high-dimensional data into a one-dimensional space, an m-dimensional unit projection vector ‘a’ is assumed, expressed as a = (a1, a2, …, am). The resulting one-dimensional projected value zi of xij can then be expressed as follows:
where zij = aj × x*ij is the projected component of indicator j for sample i, and z = (z1, z2, …, zn) is the vector of projected eigenvalues.
- (2)
- Optimisation Function
We use the following constraints to determine the optimal projection direction:
where Sz and Dz are the standard deviation and the local density. is the average value of zi. R is the window radius of the local density, r(i,j) is the distance between the evaluation indicators, and μ(x) is a step function.
- (3)
- Solution of the optimal projection direction
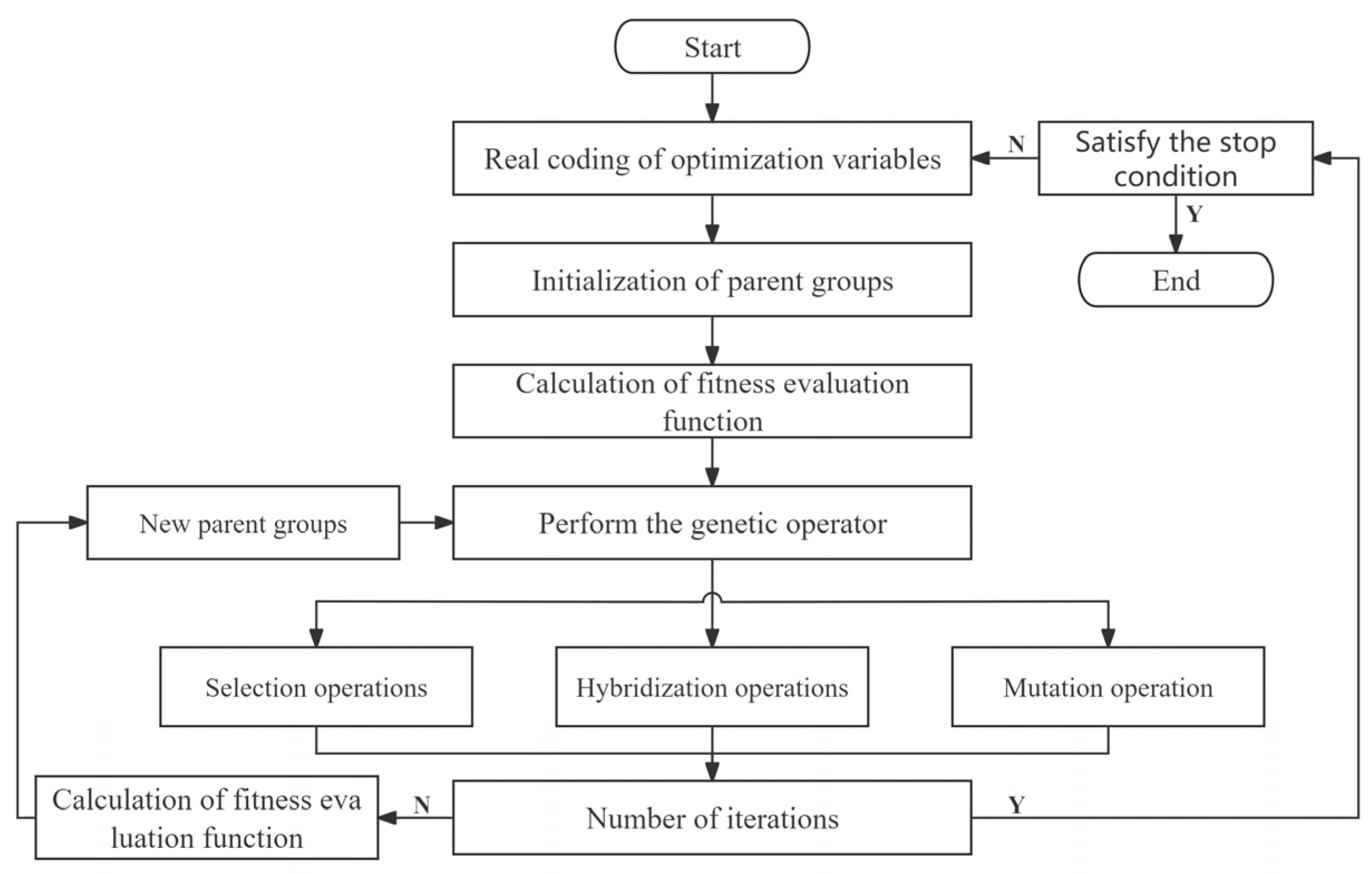
This is essentially a complex non-linear optimisation problem that is difficult to solve using conventional optimisation methods. Numerous well-established algorithms exist for solving nonlinear optimisation problems, some of which are inspired by natural phenomena, such as genetic algorithms [24], whale algorithms [25], and sparrow search algorithms [26]. In this paper, the Real coding-based Accelerating Genetic Algorithm (RAGA) is used for global optimisation using MATLAB 2019 software, resulting in the identification of the optimal projection direction vector. RAGA processes data in parallel, which allows it to cover a wide search range and increases the likelihood of finding the best solution. The RAGA loop can progressively refine and narrow down the optimisation range for the variable. As the number of loops increases, the solution’s accuracy is expected to gradually improve. The specific process of RAGA is as follows (Figure 2):
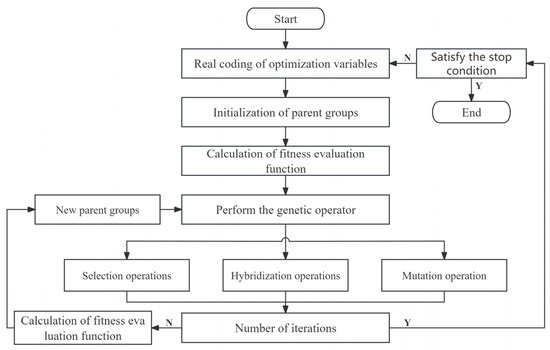
Figure 2.
The flow chart of RAGA.
- (4)
- Projection Value
After obtaining the optimal projection direction vector aj = (a1, a2, a3, …, aj), the projection values for each sample can be calculated by calculating Equation (1). Based on the magnitude of these sample projection values, it is possible to rank the samples in terms of their relative quality.
3.2.2. System of Evaluation Indicators
ULUP encompasses not only rational utilisation and structural optimisation but also the realisation of functional goals. However, the inherent characteristics of land use systems have been overlooked in much of the existing research, which has focused on performance metrics. Studies on the interdependent relationship between structure and function in ULUP are still in their infancy. In this paper, we introduced an evaluation system that incorporates indicators from both land structure and function. This approach offers a more comprehensive definition of ULUP.
- (1)
- Urban Land Structure
Urban land structure refers to urban land use characteristics, which reflect the efficiency and rationality of land allocation. It can be divided into two levels: static structural conditions and dynamic structural changes. Static structural conditions are assessed through land balance and land diversity. Land balance is measured as the ratio of the information entropy to the maximum entropy of the land pattern, while land diversity is measured by the Gibbs–Martin Diversity Index. Dynamic structural changes include the relationship between population and land elasticity, measured by the coefficient of elasticity of build-up area to population growth [27]. It reflects the sensitivities of population growth to the demand for urban build-up areas. Additionally, the land consumption per unit of GDP growth is calculated by the area of new urban construction land divided by new GDP, assessing the extent to which economic growth consumes land resources.
- (2)
- Urban Land Function
The functions of urban land are determined by its economic, social, humanistic and ecological dimensions. The economic functions of urban land are assessed by the investment in fixed assets and the production value of secondary and third-sector industries. Social functions are determined by the number of health facilities and jobs provided. The humanistic functions are reflected in the popularisation of books and the ability to cultivate talents in colleges and universities per unit of urban land. Finally, ecological functions are measured by indicators such as sewage discharge and waste emissions per unit of urban land. The ULUP evaluation indicator system and types of indicators are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
System of ULUP Evaluation Indicator System.
3.3. Spatial Correlation Network of ULUP
SNA is a typical method for studying relational data [28,29,30]. We use SNA to reveal the spatial network structure of ULUP. Within this framework, a network consists of “nodes” interconnected by “lines”. In our context, the “nodes” represent individual cities, while the “lines” symbolise the connections between these cities.
3.3.1. Spatial Correlation of ULUP
The IGM has been chosen for the analysis of the ULUP correlation in this paper [31,32]. The specific model is as follows:
The spillover impact of a city’s ULUP on another city can be represented by fij. The total population of city j is denoted by Pj. At the same time, its ULUP is represented by Cj. Qj refers to the gross product of city j, and Mij is the geographical distance between city i and city j. Rij represents the gravity matrix, which is calculated by fij.
3.3.2. Overall Network Characteristics
The network density is equal to dividing the number of relationships by the theoretical maximum number of connected relationships.
where M is the count of relationships; N represents the total number of node cities.
Network connectedness is the extent to which any two city nodes can be directly or indirectly linked.
where V is the number of cities that are not connectable.
Network efficiency can reflect how many redundant links exist in the network.
where E denotes the count of redundant lines in the network.
Network reciprocity measures the extent to which ULUP networks are symmetrically accessible.
where T denotes the number of symmetrically reachable node cities in the network.
3.3.3. Centrality
Degree centrality measures the number of cities directly associated with others in the network, highlighting their importance. There are two forms of degree centrality: Indegree and Outdegree. The greater the degree of centrality, the more extensive the city’s connections with others in the network, indicating a higher likelihood of it being a central node. The formula is as follows:
If cities i and j are correlated, Xij = 1, otherwise 0.
Closeness centrality measures the shortest connection distance between a node and other nodes.
where dij is the distance of the shortest path between two node cities.
Betweenness centrality is a measure of the degree of control a city has over the connections between other cities.
where gjk(i) is the number of shortest paths between cities j and k through city i; and gjk is the number of shortest paths between cities j and k.
3.3.4. Block Model
A standard way of analyzing the role of various cities within a ULUP interconnection network is the block model. It categorizes cities into distinct blocks based on their respective role within the network [33,34,35]. As a result, the delineation results will often have different representations of meaning. We employ this method to divide the network and examine the interactions between and within these defined blocks.
In the interpretation of block attributes, Wasserman and Faust (1994) put forward indicators to evaluate the relationships within and among blocks, which relevant researchers have widely adopted in social network analysis. According to the presence or absence of the internal and external relations of the plates, this paper divides the plates in the correlation network of ULUP into four types: “main inflow” plate, “main outflow” plate, “agent” plate, and “bidirectional spillover” plate.
3.4. Formation Mechanism of Correlation Network
Grasping the underlying mechanism of the interconnection network in ULUP within YREB is pivotal. This understanding is essential for constructing a comprehensive network of correlation and interaction aimed at enhancing ULUP across the region. The ULUP spatial correlation matrix is constructed using data such as the GDP of provinces and cities, which makes it highly correlated with the matrix of the explanatory variables. Common analytical methods have limitations in dealing with highly correlated matrices, which can affect the measurement results. In contrast, the QAP analysis method takes the relationship between variables as the basis of research, does not require variables to be independent of each other, and does not need to consider the problem of multiple covariance among the influencing factors. This makes the analysis of the relationship data more stable and the conclusions more effective. Therefore, we use QAP regression to examine the drivers of the network, which is more reliable than traditional tests [36,37,38]. The QAP regression equation is presented as follows:
Proxies for drivers are as follows: P for ULUP; Distcity for geographic proximity between cities. Pgdp for economic disparity. Indus for the difference in the industrial structure. Imp for the degree of openness to the outside world. Lrea for the degree of mismatch of land resources.
4. Result
4.1. Assessment of ULUP
The evaluation process for the projection tracing model involved inputting data into MATLAB 2019 software to create the projection index function and the projection objective function. Then, the accelerated genetic algorithm (RAGA) performed an optimisation operation on the projection objective function for the urban land use micro-performance evaluation. The crossover probability was set at 0.8, the variance probability at 0.2, the number of optimisation variables at 12, and the number of acceleration iterations at 20. Using the PPM, we derive the optimal projection values. The results were obtained in the Table 3.

Table 3.
Optimal Projection Values.
Subsequently, we calculated the projection values for each indicator, thereby determining the ULUP levels of the cities in the YREB. Table 4 shows the general characteristics of the evaluation results. In general, there are noticeable disparities in the ULUP among urban areas, although these gaps have been narrowing over time. The deviation in ULUP was 0.254 in 2000 but decreased to 0.236 in 2020. Since 2000, ULUP has exhibited a fluctuating pattern that resembles the letter “N”, with periods of improvement and decline. The highest average ULUP was recorded in 2020, at 1.45, while the lowest was 1.33 in 2005.

Table 4.
Overall Evaluation of ULUP.
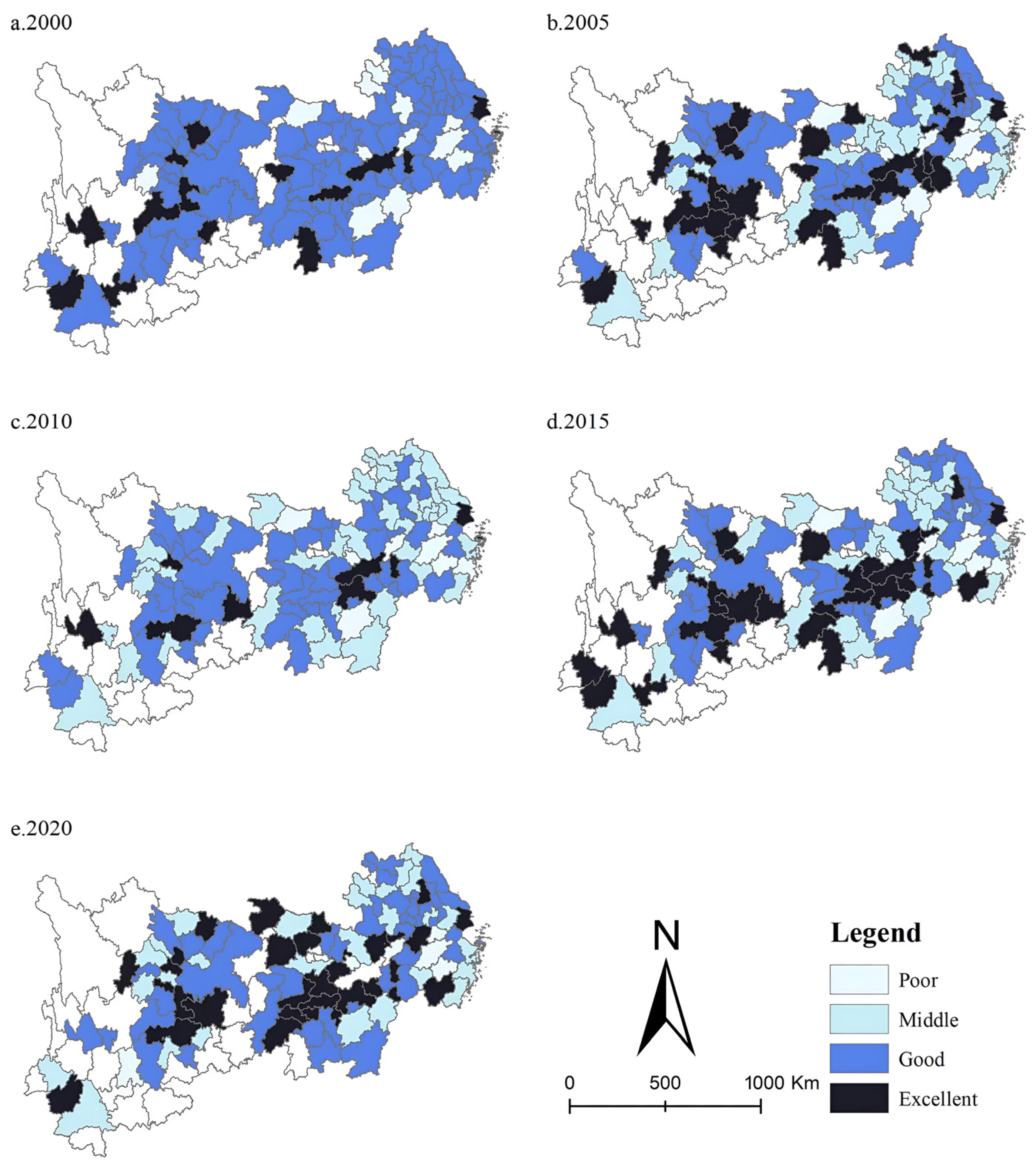
This paper applies the natural break point method to classify ULUP. The natural breakpoint method is based on clustering. It aims to maximise similarity within each group while maximizing dissimilarity between different groups. Unlike traditional clustering, this method minimises the differences in the number and range of features between each group, which will help us analyse the spatio-temporal variation of ULUP. The classification system has four levels: poor, average, good, and excellent. Table 5 displays the classification criteria. Figure 3 shows the spatial distribution of ULUP.

Table 5.
Criteria for grading ULUP.
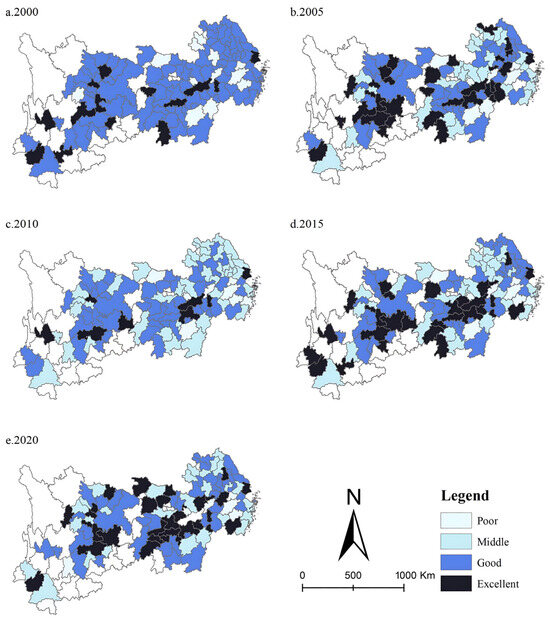
Figure 3.
Spatial Distribution of ULUP.
Cities with excellent ULUP are mainly in the three nationally significant city clusters. Shanghai, Chongqing, Changsha, and Chengdu are among the cities with the highest ULUP and form the top performers. Most cities are located at medium and good levels and are mainly distributed in regional urban agglomerations such as the Wanjiang Urban Belt, Qianzhong Urban Agglomeration, and Dianzhong Urban Agglomeration. However, a few cities are in the poor category, mainly in the middle region of the connecting line between the Yangtze River Delta metropolitan area and the metropolitan area of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River and in the western part of the YREB. Cities like Jinhua, Ji’an, and Chizhou have lower ULUP, constituting the third echelon of performers. The spatial autocorrelation analysis of ULUP reveals that the mean value of Moran’s index is 0.12. The significance test passed for all five years, and all were positive. It suggests that ULUP is spatially distributed in a clustered distribution.
4.2. Characterisation of the Structure of Spatial Association Networks
4.2.1. Strength Analysis of Spatial Correlation Networks
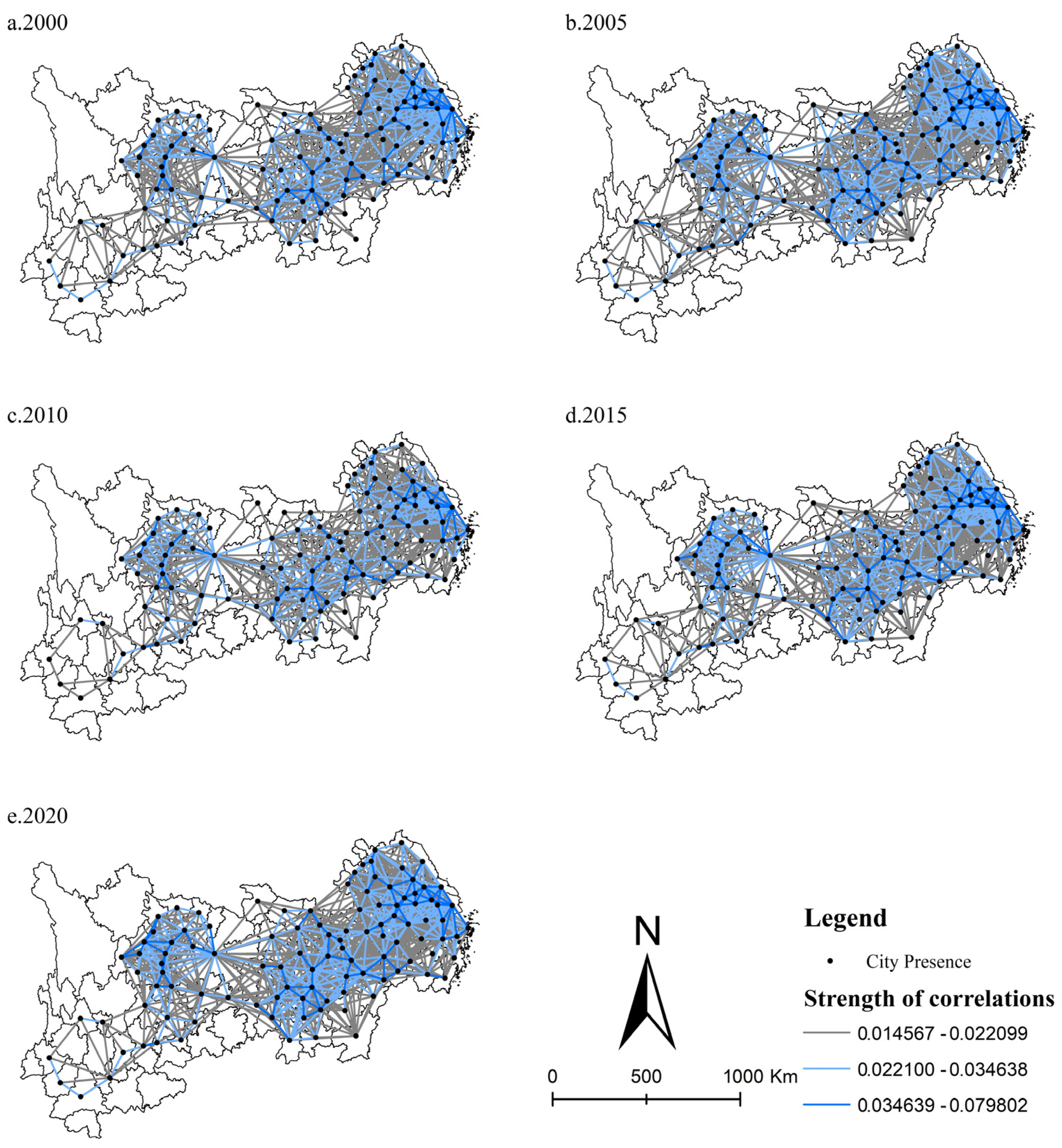
The degree of spatial association in ULUP is calculated using IGM. The spatial correlation paths and linkage strength of ULUP are drawn depending on the ArcGIS platform. In this paper, the natural breaking point method is used to classify the strength of ULUP. In addition, to achieve a better graphical effect, linkage pairs below 0.014 were deleted concerning related studies [39]. The results are shown in Figure 4. Overall, the spatial correlation intensity of ULUP has increased from 2000 to 2020. The average value rose from 0.008 to 0.01, suggesting an escalating interactivity among cities to improve ULUP.
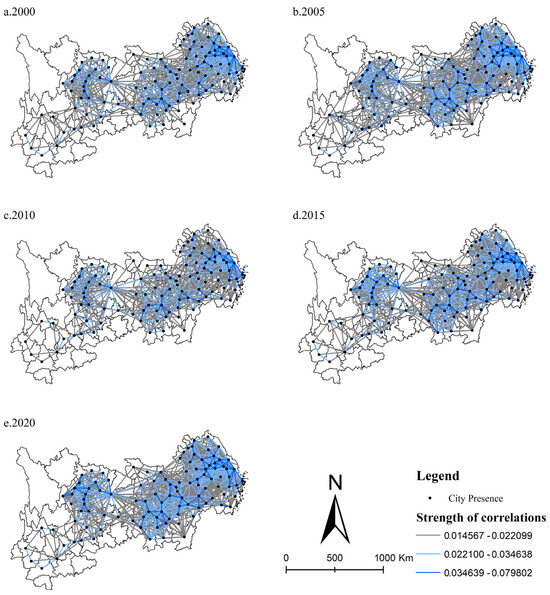
Figure 4.
Spatial correlation network of ULUP.
The downstream region of the YREB has the most vital spatial correlation strength, with a mean value of 0.012. The middle reaches of the YREB have the second most substantial ties between cities, with a mean value of 0.009. The relationship between the middle and lower reaches gradually strengthened during the study period. In contrast, the upstream region has the weakest strength of spatial association, with a mean value of only 0.006. For example, Baoshan, Lincang, and Lijiang have less than 0.007 links with other cities. These cities are less connected to other cities in improving ULUP and hardly participate in exchanges within the network of spatial connections. In general, the regions with high spatial connectivity intensity are still concentrated in the three major metropolitan areas, and the correlation between the metropolitan areas and the peripheral areas of the study area needs to be strengthened.
The strength analysis of spatial correlations reveals a growing interconnectedness in ULUP among cities. However, the linkages between the YREB’s upper, middle, and lower regions must be strengthened. The strong correlations of ULUP are predominantly observed in cities with neighbouring geographic locations. In response, local governments should take the lead in inter-regional cooperation through a range of policy measures.
4.2.2. Overall Network Characteristics
Based on the formula (3.7~3.10), we calculated the overall characteristics of spatial association networks, as shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Overall network characteristics.
The density of the urban land use performance networks in the YREB tends to decrease and then increase between 2000 and 2020. The density of the correlation network was at its lowest in 2005, then started to increase, reaching its peak in 2020. It shows that the correlation in ULUP between cities in the YREB has become more pronounced. However, the current density of the correlation network is only 27.1%, which means there is still a need to improve the degree of ULUP linkage further.
From 2000 to 2020, network connectedness and reciprocity showed a similar trend. They remained stable between 2000 and 2015, then increased in 2020. In the first four years, network connectedness was at 0.9455; in 2020, it increased to 0.9817. It indicates that more cities are now involved in the linked interaction of ULUP. In the first four years, network reciprocity was relatively low (0.0189), suggesting that the urban land use performance correlation was symmetric across most cities. However, the network reciprocity rises to 0.0367 in 2020, indicating that the ranking structure of the correlation network is gradually becoming more important.
Between 2000 and 2020, there was an overall fluctuating upward trend in network efficiency. The most significant increase in network efficiency was between 2015 and 2020, from 0.7002 to 0.7096. It suggests that the cost of conduction and spillover of ULUP has decreased, and the correlation of ULUP among cities is more easily realized. All characteristics changed significantly between 2015 and 2020, possibly due to implementing the Yangtze River Economic Belt Development Program in 2016. This program promoted the proper and free movement of economic factors and the efficiency of resource allocation, thereby improving the ULUP.
Over the past two decades, an increasing number of cities have been collaborating to improve ULUP. This collaboration has helped to bridge the development gaps within the region, underscoring the necessity for coordinated growth. The spillover effects of ULUP are being felt in more areas across the region, benefiting more cities. However, it is also becoming clear that there is a hierarchical structure to the network of ULUP linkages, with regions with high-performance levels dominating the network. This dominance is likely due to the polarisation effect of more developed cities, which attracts factors of land production, leaving less developed cities struggling to keep up. Local governments have also been implementing implicit subsidy measures, such as financial and land support, which restrict capital movement across regions. Finally, while increased network efficiency implies a reduction in redundant correlation paths, enabling cities to rely on fewer paths between them to achieve correlation in ULUP, it also potentially reduces the stability of the network.
4.2.3. Analysis of Centrality
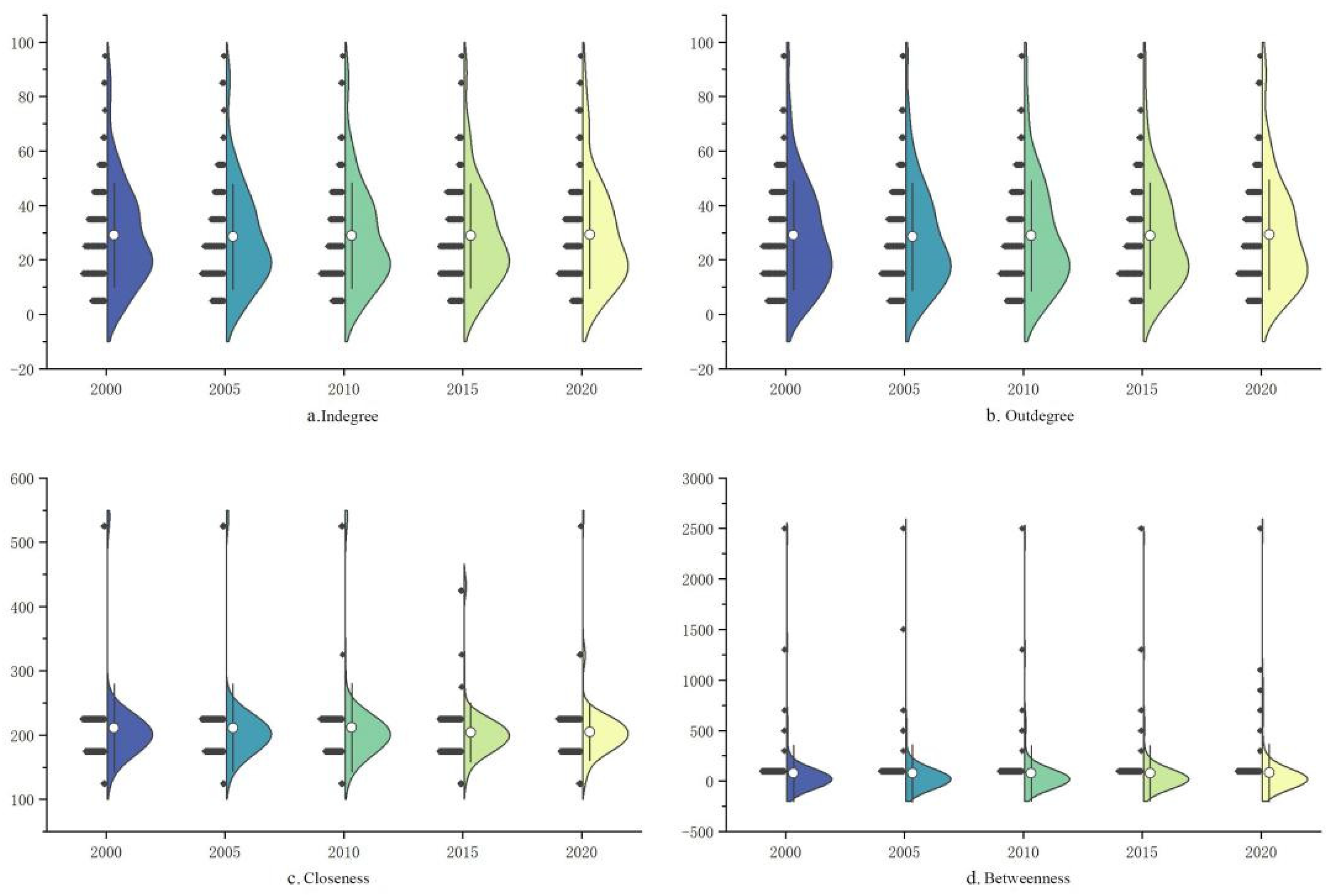
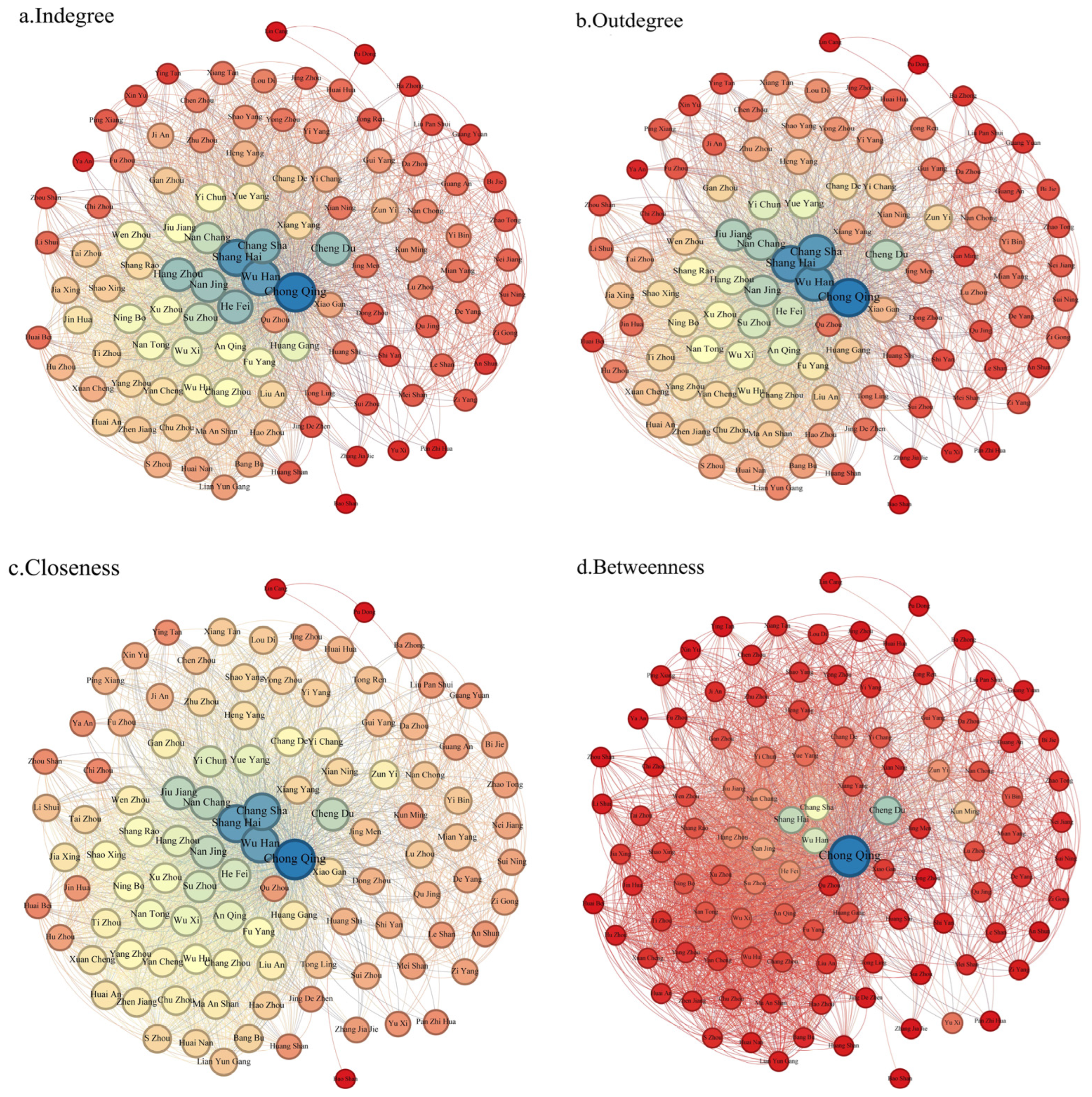
Based on the formula (3.11~3.13), we calculated the centrality of spatial association networks, as shown in Figure 5. The violin plot depicts the distribution of different centrality types over the years. It was observed that the shape and mean value of the centrality distribution did not change significantly. Therefore, this paper focuses on the correlation network of ULUP in 2020 to report the measurement results. The centrality of the network is represented by nodes and is mapped using the Gephi platform, as shown in Figure 6. Each circle represents a city, with the size of the circle indicating its centrality.
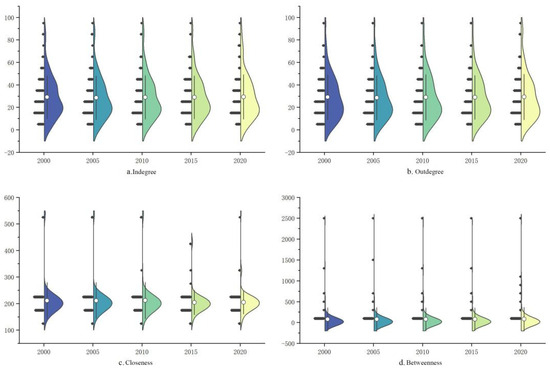
Figure 5.
Centrality violin plot.
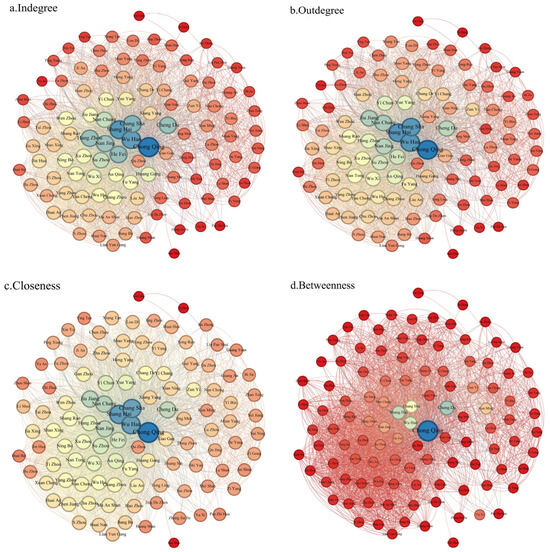
Figure 6.
Spatial correlation network node centrality in 2020. (Note: Red means the least centrality, blue means the most centrality).
- (1)
- Degree Centrality
In directed graphs, degree centrality can be divided into indegree and outdegree, which respectively measure a node’s ability to receive and transmit relationships. The average degree centrality value in 2020 was 29.26, with 48 nodes having values higher than the average. Additionally, 58 nodes have an outdegree greater than their in-degree, indicating a network characterized by more spillover than benefit in ULUP.
The top ten cities in terms of outdegree are Chongqing, Shanghai, Wuhan, Changsha, Nanjing, Nanchang, Suzhou, Jiujiang, Wuxi, and Anqing. These cities are primarily located in the three major nationally significant urban clusters and exhibit a strong external radiation capacity, placing them at the centre of the network. Meanwhile, the nodes with the lowest outdegree are mainly situated in the upper reaches of the YREB, such as Pu’er, Lincang, Panzhihua, and Anshun, with an average outdegree of less than 5. This pattern indicates that the spatial spillover paths of ULUP are mainly concentrated in more economically developed areas.
The top ten cities in terms of indegree are Chongqing, Shanghai, Wuhan, Changsha, Suzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Hefei, Nanchang, and Chengdu. These nodes are central to the spatial correlation in ULUP, as evidenced by their high indegree and outdegree. Chongqing, Shanghai, Wuhan, Changsha, and Suzhou stand out with exceptionally high values, indicating their pivotal significance.
- (2)
- Closeness Centrality
The network’s average closeness centrality is 204.72, with 53 cities exceeding this average. Among these, the top ten nodes—Changsha, Chongqing, Nanchang, Jiujiang, Jingdezhen, Shanghai, Yichun, Xianning, Yueyang, and Wuhan—are the centre cities in their respective regions. This indicates that these cities have high spatial spillover capacity and maintain closer proximity to other nodes, facilitating swift and efficient spatial associations within the network. Conversely, the cities with lower closeness centrality are mainly concentrated in the upper part of the YREB, consistent with the degree of centrality. It indicates that these cities have a poor level of ULUP and are far from other node cities in the correlation network, which poses a challenge to their participation in ULUP correlation transmission.
- (3)
- Betweenness Centrality
The average betweenness centrality is 96.72. It shows significant bipolar characteristics, with only 33 cities above the average. The top ten nodes in terms of betweenness centrality are Chongqing, Changsha, Yichang, Chengdu, Tongren, Nanchang, Jiujiang, Shanghai, Jingdezhen, and Yongzhou. Notably, six of these nodes are located in the middle reaches and three in the upper reaches. These nodes account for 46.2% of the total betweenness centrality, indicating their significant role in controlling other cities in the correlation network of ULUP. On the contrary, the cities in the bottom 80 positions account for only 20.8% of the total betweenness centrality. These cities are at the periphery of the correlation network and rarely serve as conduits for spatial correlation paths, resulting in a diminished influence over other nodes.
Developed cities such as Chongqing, Shanghai, Wuhan and Changsha play an important part in the ULUP correlation network. The network is characterized by a few nodes governing the majority of correlations, with Chongqing acting as an essential intermediary node for bridging the upstream, middle, and downstream regions of the YREB. Accurately identifying the central actors, along with the cities that serve as bridges and intermediaries in their spatial transmission paths, is essential for promoting the development of a ULUP spatial correlation network.
4.2.4. Analysis of Block Model
This study analyses the clustering features of each city by applying a block model. As shown in Figure 7 and Table 7. In 2020, there were four major clusters (Plates I–IV), with Plate I having 43 cities and Plate IV having 11 cities. Additionally, this study analysed data from four other years, revealing that the distribution of these clusters remained relatively consistent with the 2020 pattern. Notably, Plate I mainly includes cities in the lower reaches of the YREB. In contrast, Plate II and Plate IV are mainly situated in the middle reaches, while Plate III is located in the upper reaches.
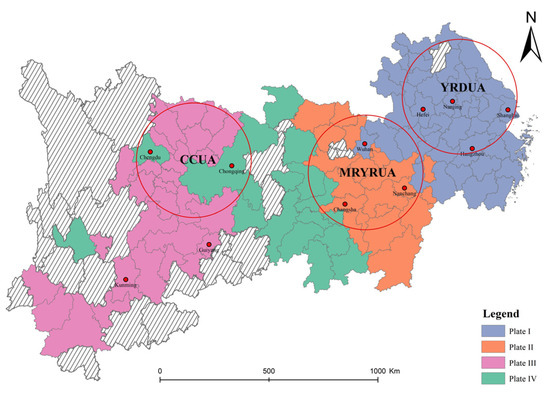
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of plates in 2020.

Table 7.
Spatial correlations between plates.
In 2020, the urban land use performance correlation network encompassed 5696 relationships, with 2538 interactions occurring within plates and 3158 between them, illustrating a robust correlation in ULUP. Plate I has the largest number of members, with 1428 contacts within the plates. It has more intra-plate contacts than inter-plate contacts, having received 465 and sent 439 contacts. Plate I thus functions as a bidirectional spillover plate, actively using its development to forge links with other plates and facilitate collective progress. Plate II serves as a pivotal intermediary in the network, acting as a bridge for connections. It accounted for 425 internal contacts, with 614 incoming and 612 outgoing spillover interactions. The balance between its received and dispatched contacts reveals its dual role: being influenced by and influencing other plates. Plate III is characterized as an inflow plate. The amount of relations within Plate III is 583. It received and sent 167 and 125 contacts, respectively. The actual internal relations of Plate III exceed the expected proportion, underscoring its strong internal dynamics. Finally, Plate IV is the main outflow plate, receiving and sending 333 and 403 contacts. The number of internal relationships is less than the count of spillover relationships, highlighting its role in extending influence beyond its boundaries.
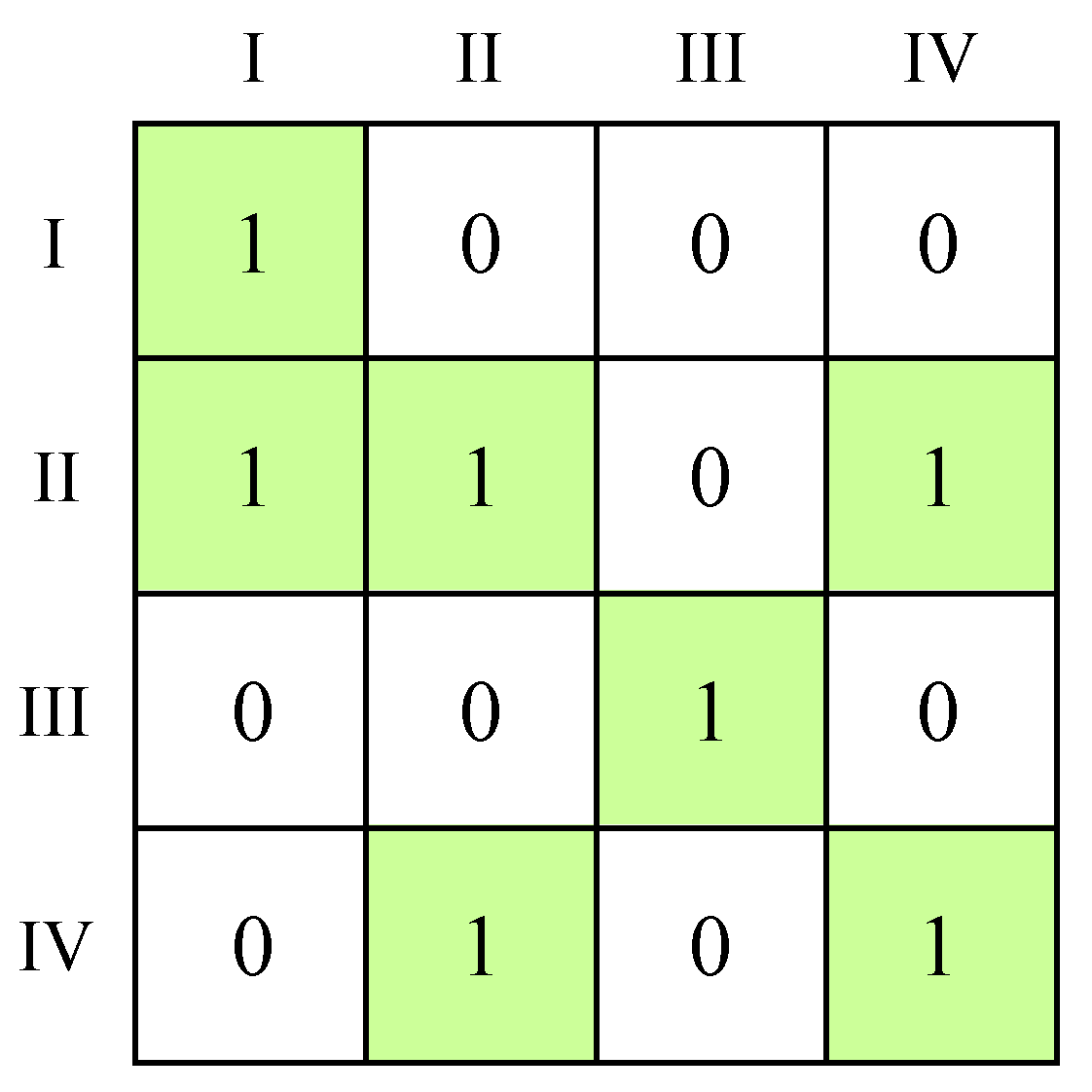
In addition, we calculated the density of the network between the four plates as follows, as shown in Figure 8. A value of 1 is assigned if the density of a plate is greater than the overall network density, indicating a spatial correlation between the row plate and column plate. Conversely, a value of 0 indicates the absence of spatial correlation between the row plate and column plate. Notably, all the main diagonal elements in this matrix are all assigned a value of 1, indicating that the correlation of ULUP exhibits a significant “club” effect. Specifically, Plate I and III have spillover effects exclusively within themselves. Plate II demonstrates spillover effects impacting all three other plates, while Plate IV influences both itself and Plate II.
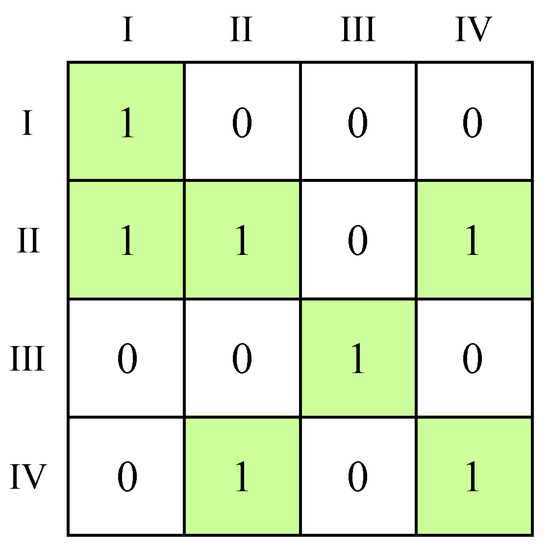
Figure 8.
Image matrix of plates.
4.3. Formation Mechanism
The results of the QAP correlation analysis for the urban land use performance correlation network (Table 8). The results reveal positive correlations for all variables except Pgdp and Lrea. And the variables Distcity, Imp, and Lrea have passed the 1% significance level test. The Pgdp variable has achieved significance at the 10% level, while the Indus variable did not reach statistical significance. However, it is essential to note that the correlation does not imply causation. Therefore, further regression analysis is required to comprehensively discern the impact of regional disparities in each variable on the spatial correlation of ULUP.

Table 8.
QAP correlation analysis results.
The standardized regression coefficients, as shown in Table 9, reveal that the Distcity, Indus, and Imp coefficients are positive. Distcity and Imp achieved statistical significance at the 1% level, whereas Indus is not statistically significant. This suggests that cities in close geographical proximity are more likely to show spatial correlations in ULUP. Furthermore, a city’s openness to external interactions enhances its potential for spatial correlation spillovers. The coefficient values of the Pgdp and Lrea variables are negative. The Lrea variable is significant at the 5% test, and the Pgdp variable passes the 10% significance test. This suggests a tendency for urban land use performance correlations to occur more frequently between cities with comparable economic profiles. In contrast, cities with a high degree of land resource mismatch tend to have weaker spatial spillovers in ULUP.

Table 9.
Regression results of the impact factors by the QAP method.
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison and Progress with Existing Research
At present, the spatial correlation of ULUP has been partially explored, and several scholars have pointed out that ULUP shows a clustered distribution pattern in space, aligning with the findings of this paper. However, the detailed spatial correlation structure of ULUP needs further exploration. Based on the previous studies [40,41], this study adopts social network analysis to identify the spatial correlation structure of ULUP. The factors affecting the spatial correlation of ULUP include the structure of urban land use and the factor flow between cities. Based on this assessment, this paper examines the drivers of the network of spatial correlations. Particular attention is paid to the impact of land resource mismatches. Previous research has highlighted the losses to total factor productivity and land use efficiency due to mismatched land resources [42]. Consistently, our findings indicate that the mismatch of land resources diminishes the correlation of ULUP. This study’s results reveal the challenges of ULUP at the regional level and provide policy recommendations to enhance ULUP, which will eventually lead to sustainable and coordinated regional development.
5.2. Discussion of Research Findings
ULUP in a city is significantly influenced by the socio-economic dynamics and industrial structures of its surrounding cities. This interdependence underlies the tight correlations in ULUP among cities within the YREB. In order to promote the coordinated growth of regional ULUP, the optimisation of the spatial network structure emerges as a critical aspect. It is important to acknowledge the different roles cities play t within the spatial correlation network. The cities with high ULUP have a more substantial influence on other cities. However, there still are many cities positioned on the network’s periphery, and expecting them to impact the network as significantly as central cities is impractical. Therefore, policy formulation must take into account the diverse characteristics of different regions.
Moreover, attention should be paid to the imbalanced correlation between central and peripheral cities to resolve mismatches between urban land resources and socio-economic conditions. Interactions between cities, primarily driven by the exchange of factors, can enhance the complementary strengths among cities. These flows reflect the quality of coordinated development of the region to some extent [43]. However, they may also lead to irrational distribution of resources and unbalanced development [44]. These factors impede the improvement of ULUP and contribute to the gradual increase of asymmetric correlations within the network, which poses a challenge to the coordination development of regional ULUP.
5.3. Policy Implications
First, it is essential to recognise the structural characteristics of the spatial correlation network in ULUP. This involves identifying the core cities that play an important role in the network of associations. For instance, the core cities, like Shanghai and Chongqing, have more significant spillover and radiative effects on other cities. Therefore, the influence of these core cities should be strengthened, consolidated, and expanded to promote the better performance of urban land use performance networks. Secondly, the rise in network reciprocity means an increase in asymmetric correlations in ULUP. This trend signals a potential crisis between edge and core cities, especially in the upstream areas of the YREB. The “Construction Planning Outline of Shuangcheng Economic Circle in Chengdu-Chongqing Area” acknowledges the importance of enhancing collaboration among central cities and promoting cooperation in adjacent areas. However, it is also essential to facilitate industrial interaction to prevent regional industrial homogeneity. Improving the exchange and interaction of factors and fostering a conducive environment in the western regions are also necessary. Thirdly, problems such as congestion, social development space, and land resource mismatch impede ULUP. The Government should eliminate unfavourable factors, allocate land resources equitably, and optimise land resource allocation. Additionally, transitioning from inter-governmental competition to win-win cooperation, characterized by increased openness and reduced protectionism, is recommended. At last, the Government should formulate and implement regionally differentiated land regulation policies based on the distinct characteristics of the four correlation plates. For the “bidirectional spillover” and “agent” plates, innovative technologies should be utilized to promote synergistic development across cities. For the “main outflow” and “main inflow” plates, the Government should continue to optimise land use structures and strengthen transportation and other infrastructure construction. Through these means, spatial correlations in ULUP can be supported via interregional industrial transfers and technology exchanges.
5.4. Limitations
This paper extensively explores the spatial network structure and formation mechanisms of ULUP, yielding a series of specific research findings. However, there remain areas where further refinement is warranted. Regarding indicator selection, we mainly measure ULUP from the two aspects of land structure and function, which have specific innovations in theory. However, land use is a comprehensive and complex system involving different resource trade-offs. ULUP evaluation should be conducted using a more comprehensive system. Energy–resource–water systems show promise as a new direction, with a focus on the interdependencies among energy, food, and water to better utilise urban land resources. Balancing these aspects more accurately would better reflect the actual conditions and developmental trends of ULUP. During the data collection phase, extensive data were gathered from multiple sources and subjected to rigorous accuracy checks to ensure the reliability and scientific validity of the study findings. Nevertheless, addressing data errors requires further in-depth analysis and validation to ensure precise measurement and understanding of the various facets of ULUP. In addition, the paper thoroughly analyses the interconnected network among ULUPs, initially uncovering complex and extensive spatial associations across different regions. However, further refinement and deeper analysis are necessary to study the impacts of these interrelationships, particularly in understanding how they influence urban development, resource allocation, and environmental sustainability. In conclusion, future research should build upon these foundations to further refine and expand the in-depth understanding of ULUP’s spatial structure, data accuracy, and the impacts of interrelationship networks. This would provide a more comprehensive basis for enhancing urban planning strategies and sustainability initiatives.
6. Conclusions
This study uses the data from 109 cities in the YREB, spanning from 2000 to 2020, to construct an Improved Gravity Model to calculate the spatial association matrix of ULUP. Then, the spatial network structure and spatial clustering of ULUP are explored utilizing SNA. Furthermore, QAP is applied to investigate the factors influencing the spatial correlation network. The main conclusions are as follows:
The ULUP has followed an N-shaped trend for the past two decades, with regional disparities gradually diminishing. Notably, the ULUP within this region is characterized by significant spatial clustering and interconnectivity. This external interconnectedness must be a central consideration in policy development aimed at enhancing ULUP. The interaction of ULUP across cities is increasingly pronounced, with stronger interactions observed among geographically proximate cities. Nonetheless, there exists a weak linkage among the upper, middle, and lower regions of the YREB. The network structure of ULUP in the YREB is complex. The network density is gradually increasing, but there is much room for improvement in the number of linkages. The network reciprocity is still being strengthened, showing a more prominent “Matthew effect”.
The cities in the YREB are divided into four plates, each fulfilling specific roles in sustaining the operational dynamics of the correlation network. The central actors of the correlation network are the “bidirectional spillover” and “agent” plates, mainly located in the middle and lower reaches of the YREB. The “main outflow” plate receives spillover relationships from eastern cities and spills ULUP effects to western cities. The “main inflow” plate is located in the upstream region of the YREB, mainly accepting spillover relationships from other cities and hardly spilling outward.
According to the QAP regression results, the geographic proximity and openness levels exhibit a positive influence on spatial associations. In contrast, economic conditions and land resource mismatch negatively affect these spatial correlations. The industrial structure, however, does not significantly influence the spatial association.
Author Contributions
Methodology, H.F., J.C., Z.W., R.Z., C.H. and M.L.; Software, C.H.; Validation, J.C. and Z.W.; Formal analysis, H.F.; Investigation, H.F. and R.Z.; Resources, J.C. and Z.W.; Writing—original draft, H.F.; Writing—review and editing, H.F.; Visualization, M.L.; Supervision, J.C.; Project administration, J.C.; Funding acquisition, J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant number 72004209).
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. Research on the impact of green finance and abundance of natural resources on China’s regional eco-efficiency. Resour. Policy 2022, 76, 102579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, V.J.P.D. Efficiency, total factor productivity and returns to scale in a sustainable perspective: An analysis in the European Union at farm and regional level. Land Use Policy 2017, 68, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Qiu, R.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of regional land use performance based on entropy TOPSIS model and diagnosis of its obstacle factors. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Xu, C.; Xue, X.; Zhu, H. Can digital innovation improve firm performance: Evidence from digital patents of Chinese listed firms. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2023, 89, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Q. Performance evaluation, environmental regulation, and urban land green use efficiency: Evidence from China. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2023, 42, e14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauleit, S.; Duhme, F. Assessing the environmental performance of land cover types for urban planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 52, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Timothy, D.J. An assessment of farmers’ satisfaction with land consolidation performance in China. Land Use Policy 2017, 61, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, T.; Feng, T.; An, P. Evaluation and correlation analysis of land use performance based on entropy-weight TOPSIS method. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Wei, C.; Yin, K. Recent 10-year land use change and evaluation of their performance, in Chongqing, China. Energy Procedia 2011, 5, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Niu, L.; Wang, J. Study on Big Data Based Land Use Performance in Yunnan Province. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Transportation, Big Data & Smart City (ICITBS), Changsha, China, 12–13 January 2019; pp. 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Xiao, Y.; Luan, S. Study on Influencing Factors of Urban Land Use System Performance in Heilongjiang Province. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Environmental Science and Material Application, Singapore, 21–23 June 2019; p. 440. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Lie, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Li, S.; Luo, G.; Wang, Z. City-level environmental performance and the spatial structure of China’s three coastal city clusters. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, G.; Liu, J. The Impact of Spatial Structure on Economic Efficiency of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Megalopolis in China. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6038270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneri, P.; Burgalassi, D. Questioning Polycentric Development and its Effects. Issues of Definition and Measurement for the Italian NUTS-2 Regions. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2012, 20, 1017–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qiu, B.; Sun, S.Q. Polycentric spatial structure and energy efficiency: Evidence from China’s provincial panel data. Energy Policy 2021, 149, 112012. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, Y. Industrial agglomeration, spatial structure and economic growth: Evidence from urban cluster in China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Hui, E.C.M.; Lin, Y. Relationship between urban spatial structure and carbon emissions: A literature review. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y. The Improvement of Projection Pursuit Model and the Application in Evaluating Water Conservancy Projects. In Proceedings of the 2012 Fifth International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID 2012), Hangzhou, China, 28–29 October 2012; Volume 2, pp. 450–453. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, T. Research on the evaluation of the resilience of subway station projects to waterlogging disasters based on the projection pursuit model. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2020, 17, 7302–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, P.; Sha, D. A spatial projection pursuit model for identifying comprehensive urban vitality on blocks using multisource geospatial data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 100, 104998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Hu, L.; Chen, Z. Evaluation on Cultivated Land System Security in Chang-Zhu-Tan Region Based on Quantum Genetic Projection Pursuit Method. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Khan, M.I.; Li, T.; Cui, S. Calculation and analysis of agricultural carbon emission efficiency considering water–energy–food pressure: Modeling and application. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Sun, X.; Tao, S.; Xiang, Z.; Xian, W. Environmental vulnerability assessment in middle-upper reaches of dadu river watershed using projection pursuit model and gis. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2015, 10, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, W.; Wu, J.; Cao, H.; Kang, Q.; Ali, S.S.S.; Xing, Z. Flood risk assessment of subway stations based on projection pursuit model optimized by whale algorithm: A case study of Changzhou, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 98, 104068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.J.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.S. A novel evaluation method for renewable energy development based on improved sparrow search algorithm and projection pursuit model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 244, 122991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wang, J.; Jing, Z.R. Tempo-spatial changes of ecological vulnerability in resource-based urban based on genetic projection pursuit model. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Jin, W. New perspectives and new methods on the research of intensive urban land use in China: Literature review and prospect. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 21, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre-López, J.M.; Díaz-José, J.; Chaloupková, P.; Guevara-Hernández, F. Unraveling Innovation Networks in Conservation Agriculture Using Social Network Analysis. In Challenges in Social Network Research: Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Tao, F.; Wu, Q.; Han, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T. Structural Differences of PM2.5 Spatial Correlation Networks in Ten Metropolitan Areas of China. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Chen, J.; Qin, T.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Kang, J. Spatial Correlation Network of Water Use in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 924246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Xie, B.Y.; Han, M.Y. Unpacking the Sub-Regional Spatial Network of Land-Use Carbon Emissions: The Case of Sichuan Province in China. Land 2023, 12, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Li, C.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Peasant households’ land use decision-making analysis using social network analysis: A case of Tantou Village, China. J. Rural Stud. 2020, 80, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, K.; Liu, Z.; Chai, S.; Li, K.; Li, Y. Spatial correlation network structure of green innovation efficiency and its driving factors in the Bohai Rim region. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; An, L.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y. Spatial Correlation and Influencing Factors of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in the Urban Agglomeration of the Yangtze River Delta Based on Social Network Analysis. Land 2022, 11, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, J.; Chong, D.; Niu, X. Analysis on the Housing Price Relationship Network of Large and Medium-Sized Cities in China Based on Gravity Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Zheng, X.; Han, F.; Yang, Z. The Structure and Evolution of the Tourism Economic Network of the Tibetan Plateau and Its Driving Factors. Land 2022, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vidal, I. Determinants of inter-organizational network formation in the cultural sector. Rae-Rev. De Adm. De Empresas 2018, 58, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huang, S.S.; Fu, H. An application of network analysis on tourist attractions: The case of Xinjiang, China. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Weng, A. Spatial correlation network and its formation mechanism of urban water utilization efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 2353–2373. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Li, T.; Yu, J.; Sun, Y.; Xie, S. Spatial Correlation Network Structure of Carbon Emission Efficiency in China’s Construction Industry and Its Formation Mechanism. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Qin, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, X. Structure of low-carbon economy spatial correlation network in urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 394, 136359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhao, H.; Xie, B.; Li, Z.; Li, K. The impacts of land misallocation on urban industrial green total-factor productivity in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 1865–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Xinyi, Z.; Xiang, L. Revisiting the regional sustainable development from the perspective of multi-system factor flows–Evidence in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18893. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, Y.; Gao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, R. Sustainable network analysis and coordinated development simulation of urban agglomerations from multiple perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 413, 137378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).