Abstract
Wildfires present a major global environmental issue, exacerbated by climate change. The Iranian Northern Zagros Forests, characterized by a Mediterranean climate, are particularly vulnerable to fires during hot, dry summers. This study investigates the impact of climate change on forest fires in these forests from 2006 to 2023. The analysis revealed significant year-to-year fluctuations, with notable fire occurrence in years 2007, 2010, 2021, and 2023. The largest burned area occurred in 2021, covering 2655.66 ha, while 2006 had the smallest burned area of 175.27 ha. Climate variables such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind speed, heat waves, and solar radiation were assessed for their effects on fire behavior. Strong correlations were found between higher average temperatures and larger burned areas, as well as between heat waves and increased fire frequency. Additionally, higher wind speeds were linked to larger burned areas, suggesting that increased wind speeds may enhance fire spread. Multiple linear regression models demonstrated high predictive accuracy, explaining 84% of the variance in burned areas and 69.6% in the variance in fire frequency. These findings document the growing wildfire risk in the Northern Zagros region due to climate change, highlighting the urgent need to integrate scientific research with policies to develop effective wildfire management strategies for sustainable forest management.
1. Introduction
Forest fires are an important ecological phenomenon with profound impacts on biodiversity, climate, and human health [1,2]. Understanding the factors that contribute to the occurrence and intensity of forest fires is essential for effective forest management and mitigation strategies [3]. In recent decades, the global climate has changed dramatically, with rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and the increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events [4]. This change significantly influences forest ecosystems, affecting the frequency and behavior of forest fires [5,6]. Scientists, politicians, and the public have increasingly focused on the complex interactions between climate change and wildfires due to their far-reaching implications for biodiversity, ecological services, human health, and socioeconomic well-being [7].
Wildfires have long been a natural part of many ecosystems, performing essential ecological processes such as nitrogen cycling, restoration, and habitat preservation [8]. However, climate change has disrupted these ecosystems’ equilibrium, leading to a surge in wildfires that are more frequent, prolonged, and catastrophic than before. From the northern forests of Canada to the tropical rainforests of the Amazon, no area has been untouched. The Northern Zagros region of Iran, a biological treasure and a significant barrier against soil erosion, drought, and desertification, has also experienced an increase in forest fires [9,10]. This trend raises concerns about the underlying causes and potential impact of environmental and climatic variability on fire dynamics [11].
Several studies have highlighted the impact of climate change on global fire regimes, particularly in temperate and Mediterranean ecosystems like the Zagros forests. Rising temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and the increased frequency of extreme weather events have been identified as major factors affecting fire behavior and occurrence [12]. Temperature and relative humidity are critical in influencing fire behavior. High temperatures increase vegetation flammability, while low humidity levels reduce moisture content, making plants more susceptible to ignition [13]. Studies indicate that rising temperatures and decreasing humidity significantly elevate the risk of forest fires in many regions [14]. In the Zagros region, recent trends have shown rising temperatures and decreasing humidity, potentially exacerbating fire risks [15,16]. Additionally, wind plays a pivotal role in fire spread by driving flames and carrying embers over long distances, often transforming small fires into large outbreaks [17]. Understanding local wind dynamics is crucial for predicting fire behavior and developing effective management strategies. Heat waves, defined by extended periods of extreme heat, have also been linked to increased fire activity, significantly drying out vegetation and enhancing its flammability [18]. Current climate research indicates an increase in the frequency and severity of heat waves globally [19], underscoring the need to assess their impact on regional fire regimes.
Forest fires caused by climate change have far-reaching consequences, affecting the human communities connected to these forests [20]. Rural communities relying on forest resources face vulnerabilities, including loss of croplands and pastures, displacement, and economic hardship. Additionally, the decline of forest ecosystem services such as water management and soil fertility impairs people’s ability to cope with environmental pressures [21].
Despite the evident connections between climatic and environmental variables and forest fire activity, comprehensive statistical analysis is needed to quantify these relationships in the Northern Zagros region and other areas with a Mediterranean climate. This study aims to fill this gap by investigating the impact of climatic and environmental factors on forest fire occurrence and the extent of burned areas. Using statistical methods such as Multiple Linear Regression, this research seeks to identify significant variables influencing fire dynamics and develop predictive models for wildfire management and prevention [22].
Through this study, we aim to deepen the understanding of the interplay between climate variability and forest fire risks in the Northern Zagros. Our findings will provide valuable insights for policymakers, forest managers, and conservationists working to mitigate the adverse effects of forest fires and promote sustainable forest management practices in this ecologically sensitive region. Therefore, this study addresses the following research questions:
- How have the frequency and intensity of wildfires in the Zagros forests changed over the past few decades?
- Which climatic variables have the most significant correlation with wildfire occurrences in the Zagros forests?
- How do changes in climatic conditions impact the likelihood and intensity of fires in the Zagros forests?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
This study was carried out in the Zagros forests of northwest Iran, encompassing regions within the West Azarbaijan and Kurdistan provinces. The continuous vegetation of the Zagros forests extends from West Azarbaijan to the Fars province in southwestern Iran and spans nine other provinces [23]. The specific areas of focus include Sardasht city in West Azarbaijan and the cities of Baneh, Sarvabad, Sanandaj, Kamyaran, and Marivan in Kurdistan (Figure 1), where the Zagros forests are located. These locations are situated between latitudes 34°43′ and 36°28′ N and longitudes 45°14′ and 47°20′ E, covering altitudes ranging from 593 to 3122 m above sea level. In 2023, the forest land area in West Azarbaijan was 122,197.50 ha, while in Kurdistan it was 202,261.03 ha [23].
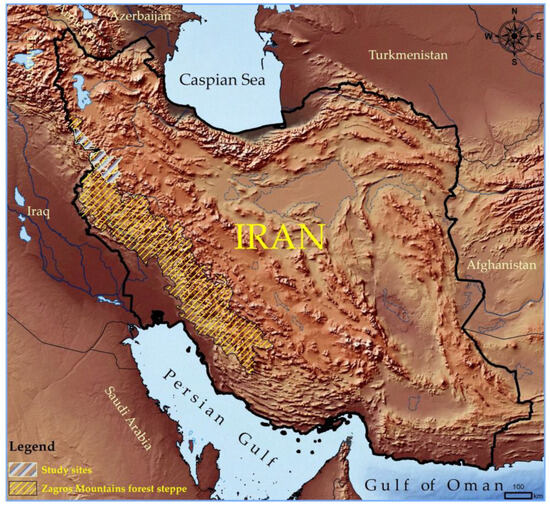
Figure 1.
Distribution of Zagros forests in western Iran (polygon with yellow hatching), as well as the geographic location of the studied regions in the north of Zagros (polygon with gray hatching).
The region is characterized by a Mediterranean climate, featuring hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, which significantly influence the local vegetation and fire patterns. The dominant vegetation includes oak species (Quercus spp., occurring mostly as coppice stands), alongside pistachio (Pistacia spp.), almond (Amygdalus spp.), and juniper (Juniperus spp.) [24]. The mountainous topography of the Zagros range creates diverse microclimates, contributing to the rich biodiversity of the area [25].
The local population primarily comprises rural Kurdish communities whose livelihoods depend on agriculture, livestock, and forest resources. These forests are culturally important and play an essential role in preventing soil erosion, supporting biodiversity, and regulating the regional climate.
2.2. Data Collection: Fire Data and Climatic Variables Sources
The Natural Resources Departments of the West Azarbaijan and Kurdistan provinces provided data and information on all fires documented in the Iranian Northern Zagros forests (i.e., studied sites) between 2006 and 2023. These statistics included the number (frequency) and extent of fires (in hectares) during this period.
To explore the effect of climate variables on the frequency and intensity of forest fires, a multifaceted strategy was employed, utilizing data from several sources and platforms. Meteorological factors significantly impact fuel accumulation and humidity, which in turn affect the probability, timing, and location of fires [26]. This study focuses on the following climatic variables for the period from 2006 to 2023, selected based on data availability and their established influence on fire dynamics (see references for details on their effects on forest fires): Minimum Temperature (°C) [27], Maximum Temperature (°C) [28], Average Temperature (°C) [29], Average Relative Humidity (%) [30], Average Precipitation (mm) [31], Average Wind Speed (m/s) [32], Wind Direction (°) [33], Heat Waves (including: Heat Wave Magnitude and Frequency) [34], and Surface Solar Radiation (kW-hr/m2/day) [35].
Annual maximum, minimum, and average temperatures, annual average precipitation, relative humidity, wind direction, and surface solar radiation data were obtained from the NASA POWER (Prediction of Worldwide Energy Resources) project [36]. This data source provides high-resolution, globally available meteorological data derived from satellite observations and reanalysis models [37], integrating both satellite and ground-based observations.
To analyze wind speed in the study area, the u and v wind components of the ERA5 reanalysis dataset were used, which was accessed via the Google Earth Engine platform [38]. The ERA5 dataset provides high-resolution climate and weather data, which are useful for accurately modeling and analyzing meteorological variables. Produced by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), ERA5 offers comprehensive atmospheric data with a spatial resolution of approximately 27 km [39]. The dataset includes hourly values of u (zonal wind component) and v (meridional wind component) at various pressure levels [40]. The u and v wind components were extracted for the study period (2006–2022), and wind speed at each grid point was calculated using Equation (1):
where u is the zonal wind component and v is the meridional wind component [41].
To analyze heat waves in the Northern Zagros forests of Iran, the Heat Wave Magnitude Index (HWMI) was used. This index is specifically designed to assess the intensity and duration of heat waves and can aid in understanding thermal impacts on forest ecosystems [42]. For the calculation of HWMI, temperature data were used from NASA POWER, including daily maximum and minimum temperatures from 2006 to 2023. The baseline temperature was defined as the average of daily maximum temperatures during non-heat wave days, typically derived from the 30-year average of maximum temperatures under normal climatic conditions [43]. For each day, the deviation of the maximum temperature from the baseline was calculated, with positive deviations indicating heat wave conditions [44]. The intensity of the heat wave was computed using the deviations in temperature with Equation (2):
where Ti is the daily maximum temperature on day i and Tbase is the baseline temperature [45].
To identify heat waves, HWMI values were compared to predefined thresholds. In this study, the threshold was defined as the maximum of three consecutive days with maximum temperatures exceeding the 90th percentile. This threshold was derived empirically using historical data [46]. The analysis and computation of the HWMI were performed using the R software environment (version 4.4.1). Specifically, the data were processed and analyzed using the “dplyr” and “lubridate” packages in R [47].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
To explore the impact of climatic variables on the number and extent of forest fires in the Northern Zagros forests, several statistical methods were used. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was first used to assess the normality of the fire data and climatic variables, since normality of data is a prerequisite for many other statistical analyses. The test indicated that the data followed a normal distribution.
Pearson’s correlation and multiple linear regression (MLR) analyses were used to investigate the relationships between fire frequency, extent, and climate variables. MLR allows for the simultaneous evaluation of the relationship between a dependent variable (the number or the extent of forest fires) and multiple independent variables (climate variables) [48]. In this study, the coefficients of the independent variables were calculated to understand their individual influences on the dependent variable. The MLR model assumes a linear relationship between the dependent variable and the independent variables, as expressed in Equation (3):
where Y is the dependent variable, x1, x2, …, xn are the independent variables, and b1, b2, …, bn are their coefficients. The constant a reflects the value of Y when all independent variables are zero, while the coefficients bi indicate the change in Y for a unit increase in the corresponding independent variable [49]. The error term (ϵ) represents the difference between the observed values and the values predicted by the model, calculated as:
Additionally, the assumptions of the MLR were checked to ensure the validity of the model. Linearity was verified to confirm a linear relationship between the independent and dependent variables (burned area and fire frequency). This Appendix A is presented in Figure A1 and Figure A2. Homoscedasticity was assessed by plotting the residuals against the fitted values, with Appendix A shown in Figure A3 and Figure A4. Multicollinearity was checked using the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF), with values less than 10 indicating acceptable levels (Table A1). The independence of residuals was verified using the Durbin–Watson statistic, with values close to 2 indicating no autocorrelation (Table A2). The effectiveness of the MLR model was assessed using several statistical metrics. The coefficient of determination (R2) quantifies the proportion of variance in the dependent variable that is explained by the independent variables [50]. An R2 value approaching 1 suggests that the model accounts for a significant portion of the variance, indicating a good fit. However, R2 does not adjust for the number of predictors in the model, which may result in overfitting, particularly in models with many predictors [51]. To address this limitation, the Adjusted R2 was also calculated. The Adjusted R2 refines the R2 value by considering both the number of predictors and the sample size, offering a more accurate assessment of the model’s explanatory power, especially when comparing models with different numbers of predictors. Unlike R2, the Adjusted R2 only increases if the added predictor enhances the model’s predictive capability by more than what would be expected by chance [52]. Additionally, the correlation coefficient (R) was employed to evaluate the strength and direction of the linear relationship between the observed and predicted values. The R value ranges from −1 to 1, with values close to 1 or −1 indicating a strong linear relationship, while values near 0 suggest a weak or no linear relationship [53]. Furthermore, the p-value was used to assess the statistical significance of the relationships between the independent variables and the dependent variable. The p-value indicates the probability that the observed results occurred by chance. A p-value less than 0.05 typically suggests that the relationship is statistically significant, meaning the independent variables have a meaningful impact on the dependent variable [54]. By integrating these metrics—R, R2, Adjusted R2, and p-value—the effectiveness and predictive capacity of the model were comprehensively evaluated. These measures collectively provide a robust understanding of how well the independent variables explain the variance in the dependent variable and of how the model will generalize with new data. The statistical analyses in this study were carried out using SPSS version 27 [55].
3. Results
3.1. Trends in Fire Frequency and Intensity
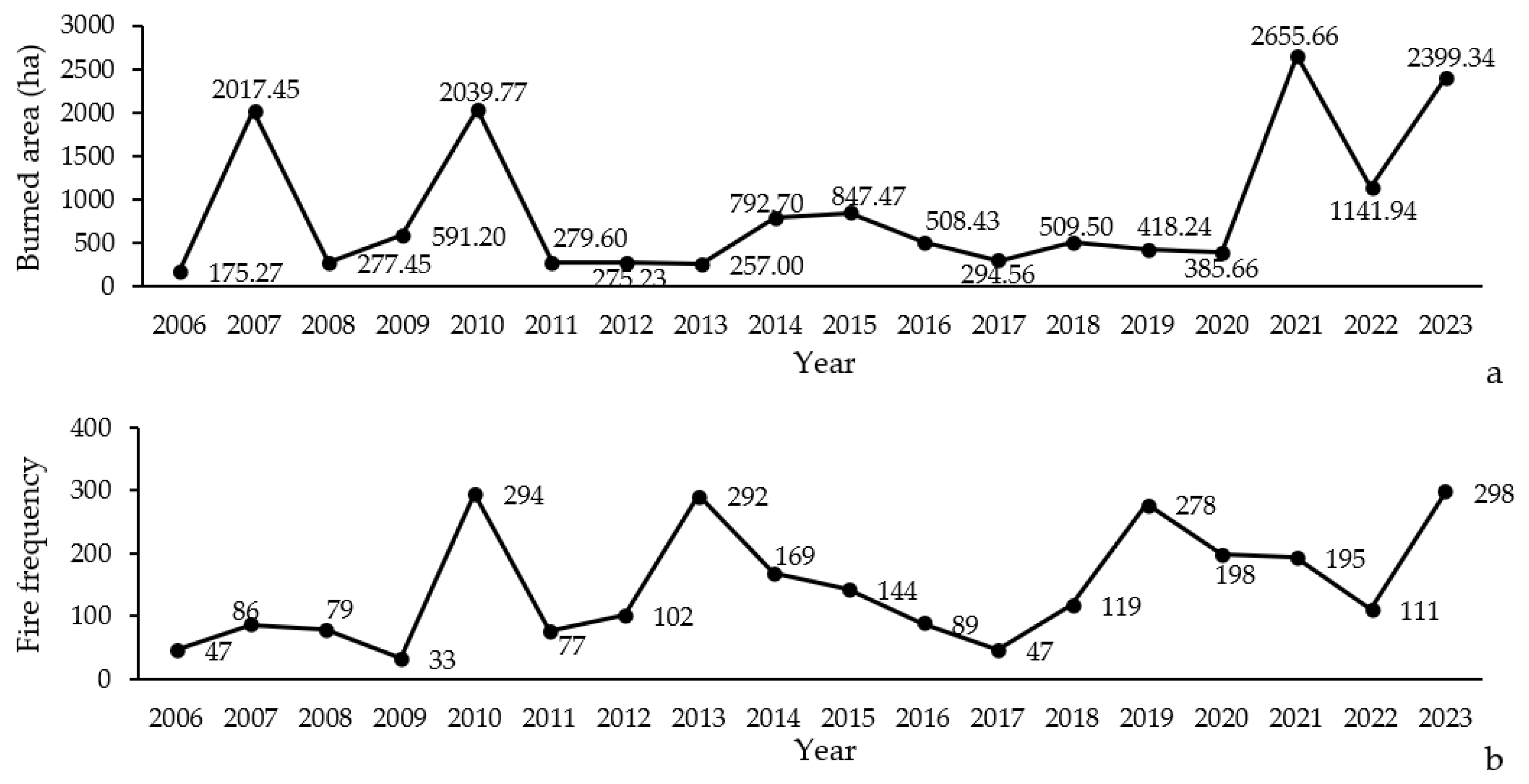
The analysis of burned areas in the Northern Zagros forests from 2006 to 2023 shows a significant variability in the extent of the affected areas (Figure 2a). These data illustrate several important trends: First, there is considerable fluctuation in the burned area from year to year, with peaks occurring in 2007, 2010, 2021, and 2023. The largest burned area was recorded in 2021, with 2655.66 ha, while the smallest was in 2006, with 175.27 ha.
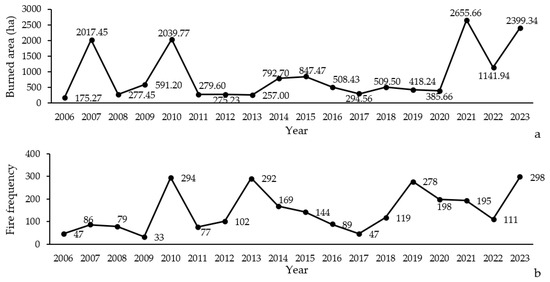
Figure 2.
Variation in extent (a) and frequency (b) of forest fires occurring in Northern Zagros from 2006 to 2023.
The data show that the number of wildfires in the Northern Zagros forests varied between 2006 and 2023 (Figure 2b). Overall, the highest number of wildfires was observed in the years 2006, 2015, and 2021, reaching 294, 278, and 298 incidents, respectively. In contrast, the years with the lowest number of wildfires, such as 2009 and 2012, recorded 33 and 47 incidents, respectively, reflecting a significant decrease during this period.
3.2. Annual Changes in Weather Variables
3.2.1. Temperature
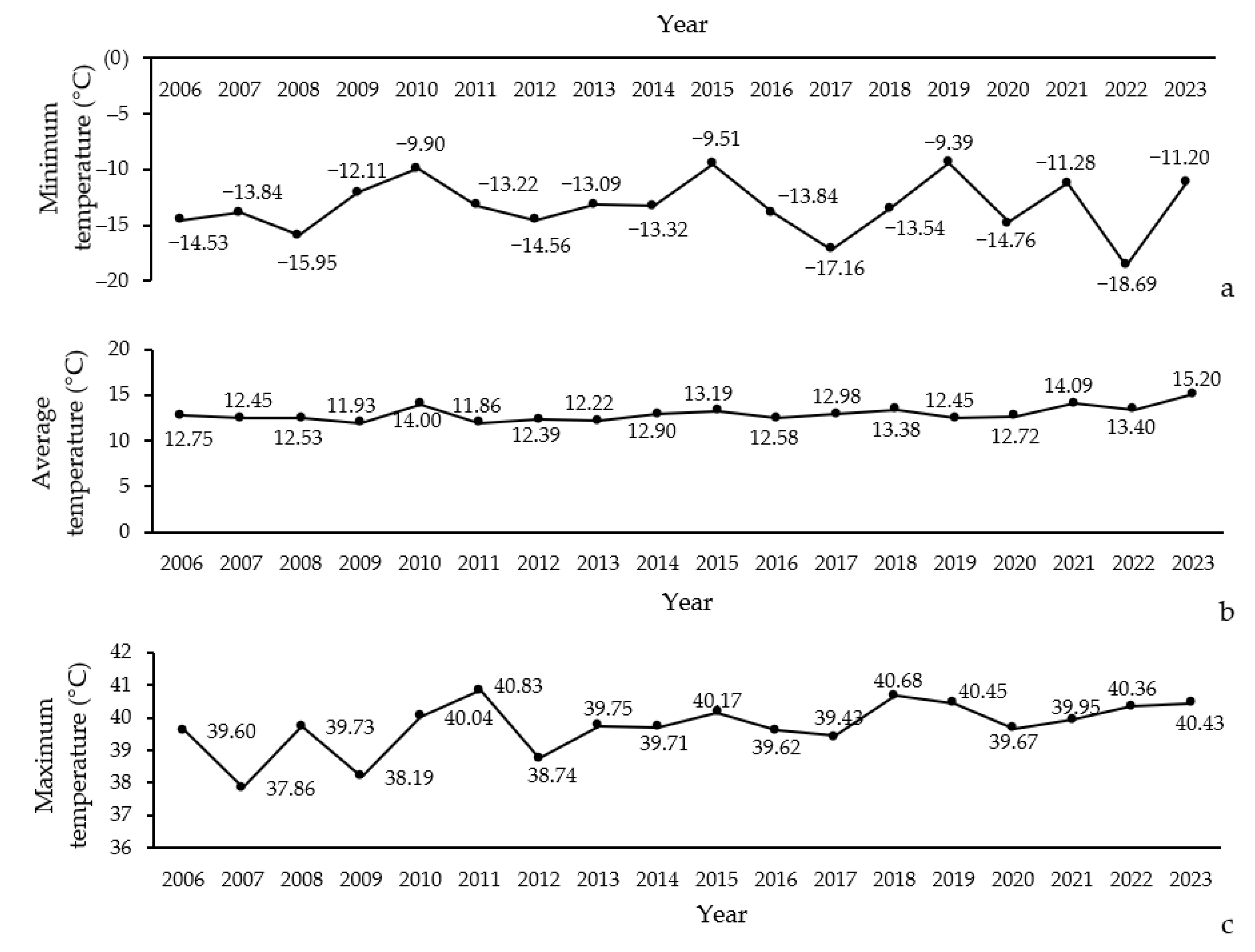
The results indicate that temperature variables in the Northern Zagros forests from 2006 to 2023 have shown notable fluctuations. The minimum temperatures ranged from −18.66 °C to −9.39 °C (Figure 3a), while the maximum temperatures varied between 37.86 °C and 40.83 °C (Figure 3c). The average temperatures ranged from 11.86 °C to 15.20 °C (Figure 3b).
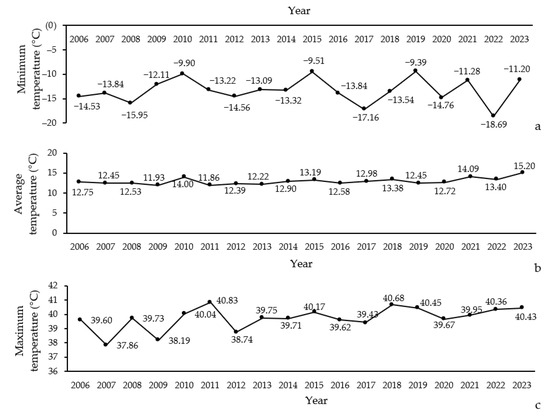
Figure 3.
Trends in minimum (a), average (b), and maximum (c) temperatures over time (2006–2023) in Northern Zagros.
Significant variations can be observed in both the minimum and maximum temperatures throughout the study period. For instance, the highest minimum temperature was recorded in 2020, whereas the lowest was in 2018. Similarly, maximum temperatures peaked in 2021, with the lowest recorded in 2007. The average temperatures also reflect this variability, with the highest values noted in 2021 and the lowest in 2018.
3.2.2. Precipitation and Humidity
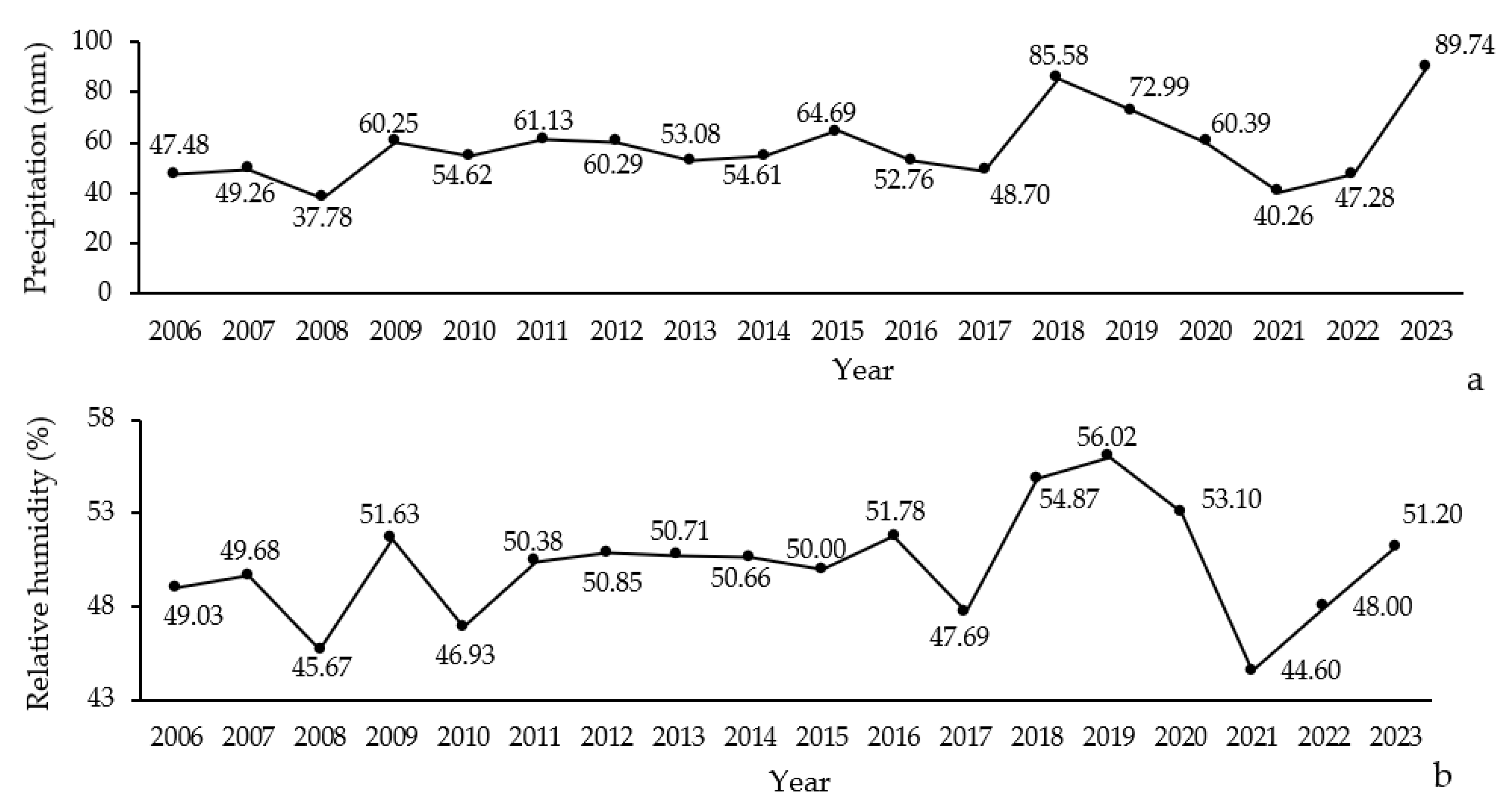
Significant shifts in average relative humidity and precipitation were recorded in northern Zagros forests between 2006 and 2023. The average relative humidity varied between 44.60% and 56.02%, with the highest value recorded in 2015 and the lowest in 2014 (Figure 4b). This indicates a considerable variability in moisture levels over the years. Similarly, the average precipitation ranged from 37.78 mm to 89.74 mm, with notable peaks in 2015 and 2022 (Figure 4a).
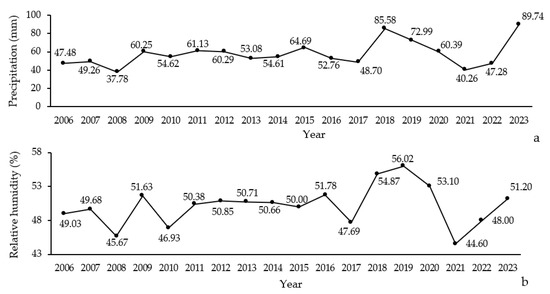
Figure 4.
Annual variation in precipitation (a) and relative humidity (b) levels (2006–2023) in Northern Zagros.
3.2.3. Wind
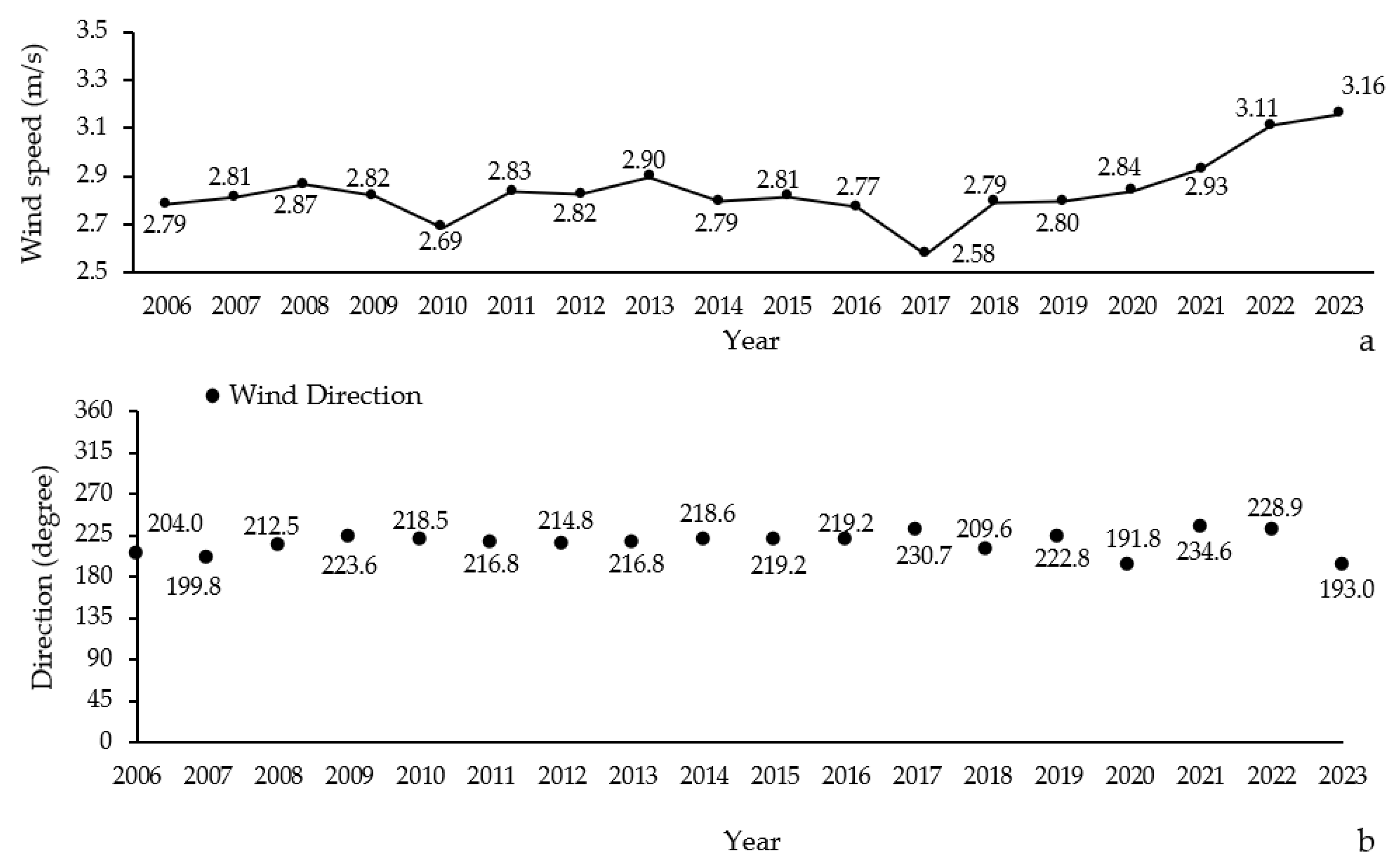
Throughout the study period (2006–2023), the average yearly wind speed fluctuated significantly. The lowest average wind speed was recorded in 2017 at 2.58 m/s, while the highest was in 2023 at 3.16 m/s (Figure 5a). Over the years, there appears to be a general increasing trend in wind speed, particularly notable in the last few years of the study. The results indicate that the predominant wind direction in the northern Zagros forests varied over the study period from 2006 to 2023. Specifically, in the years 2007, 2020, and 2023, the prevailing wind direction was southern, whereas in the remaining years, it was predominantly southwestern (Figure 5b).

Figure 5.
Annual variations in wind speed (a) and the prevailing wind direction (b) in Northern Zagros from 2006 to 2023.
3.2.4. Heat Wave Characteristics and Surface Solar Radiation
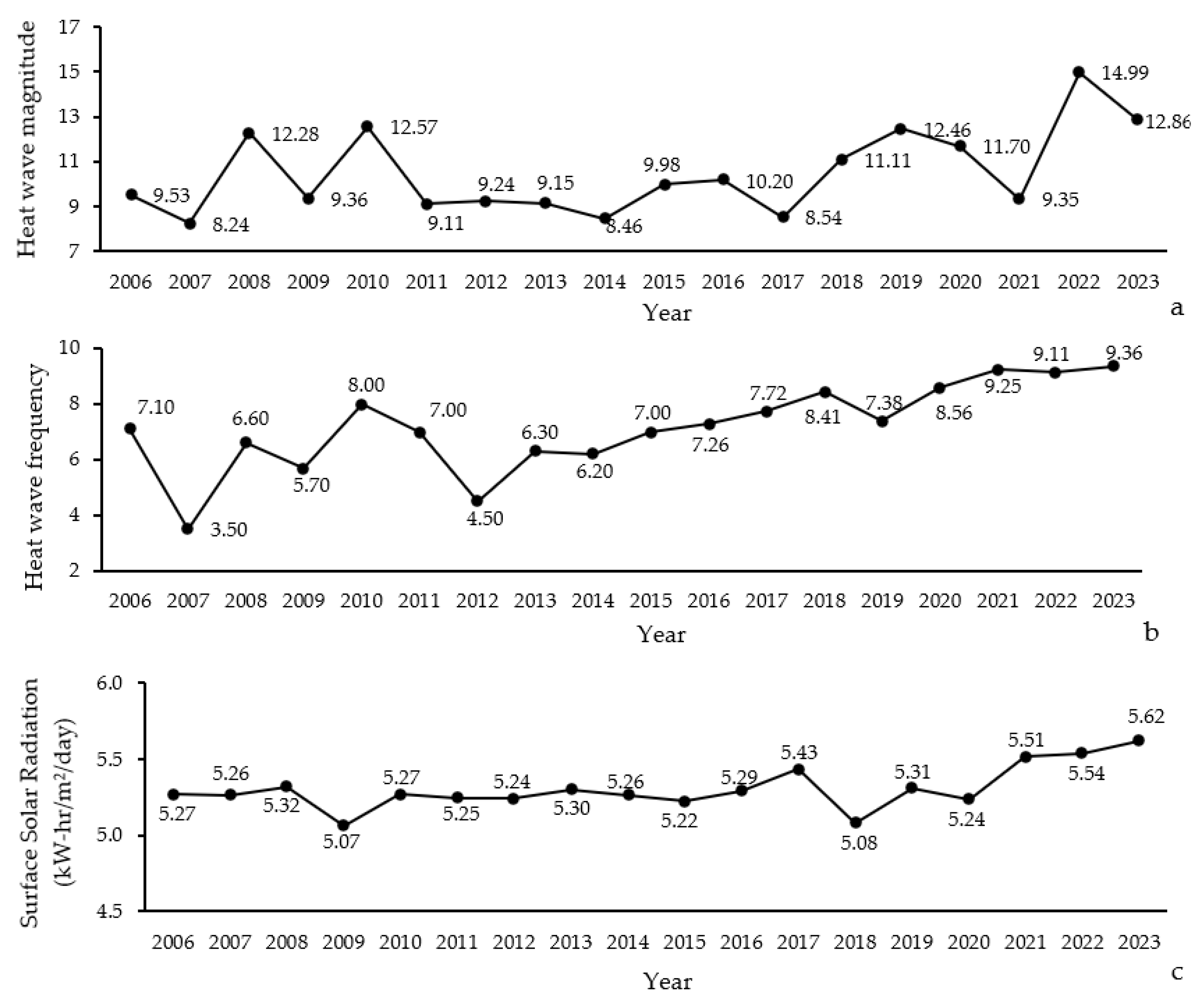
The magnitude of heat waves showed a considerable variability, with values ranging from 8.24 to 14.99. The highest heat wave magnitudes were recorded in the most recent years, specifically 2022 (14.99) and 2023 (12.86), indicating an increasing trend in heat wave intensity (Figure 6a). This suggests that the region has experienced more severe heat waves in recent years.
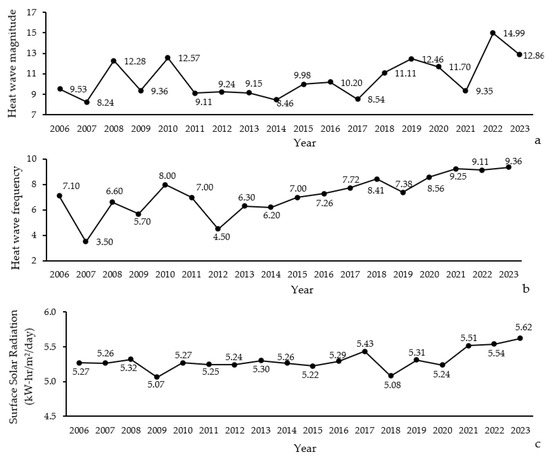
Figure 6.
Annual variation in heat wave magnitude (a), frequency (b), and surface solar radiation (c) in Northern Zagros from 2006 to 2023.
Similarly, the frequency of heat waves varied across the study period, with a minimum of 3.50 and a maximum of 9.36 occurrences per year (Figure 6b). The years 2022 and 2023 also saw the highest frequencies, at 9.11 and 9.36, respectively. This trend indicates that not only have heat waves become more intense, but they have also become more frequent, particularly in the last few years of the study.
The average surface solar radiation levels remained relatively stable, but showed slight variations ranging from 5.07 to 5.62 kWh/m2/day (Figure 6c). The highest levels of solar radiation were observed in 2022 and 2023, with values of 5.54 and 5.62 kW-h/m2/day, respectively. This increase in solar radiation could be contributing to the higher magnitude and frequency of heat waves observed.
3.3. Relationships between Fire and Climate Variables
The analysis of the Pearson correlation between the dependent variables (fire frequency and burned area) and various climatic and environmental factors yielded meaningful findings. A strong positive correlation was found between the annual average temperature and the burned area, significant at the 99% confidence level (r = 0.746, p-value < 0.001) (Table 1). This suggests that higher average temperatures are strongly associated with larger burned areas, highlighting the role of temperature in influencing fire spread and intensity.

Table 1.
Correlation between burned area, fire frequency, and climatic/environmental factors in northern Zagros forests.
The annual average wind speed demonstrated a significant positive correlation with the burned area at the 95% confidence level (r = 0.740, p-value = 0.036) (Table 1). This indicates that higher wind speeds are associated with larger burned areas, likely due to fires spreading more rapidly across a wider area, thereby increasing the total burned area. Additionally, surface solar radiation showed a significant positive correlation with the burned area at the 95% confidence level (r = 0.519, p-value = 0.027) (Table 1), implying that increased solar radiation, likely due to its effect on drying vegetation, contributes to larger burned areas.
Regarding fire frequency, a significant positive correlation was observed between the annual minimum temperature and the frequency of fires at the 95% confidence level (r = 0.573, p-value = 0.013) (Table 1). This indicates that higher minimum temperatures, which can prevent nocturnal cooling and contribute to the persistence of fire-prone conditions, are linked to a higher frequency of fires. Similarly, the annual average temperature also showed a significant positive correlation with fire frequency at the 95% confidence level (r = 0.501, p-value = 0.034) (Table 1), reinforcing the impact of overall warmer conditions on the likelihood of fire occurrences.
Moreover, the magnitude of heat waves demonstrated a significant positive correlation with fire frequency at the 95% confidence level (r = 0.479, p-value = 0.021) (Table 1). This finding suggests that more intense heat waves contribute to an increased number of fires, likely due to the extreme drying and stress on vegetation during such periods. No significant correlations were found between the dependent variables and other climatic factors such as maximum temperature, average relative humidity, average precipitation, wind direction, or heat wave frequency, indicating that these factors did not have a strong direct impact on the burned area or fire frequency in this study.
The Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) models yielded R values of 0.916 and 0.834 (Table 2), indicating strong positive correlations between the observed and predicted values of the dependent variables (i.e., burned area and fire frequency, respectively). These high R values suggest that the models fit the data well.

Table 2.
Summary of MLR analysis for climatic and environmental factors predicting burned area and fire frequency in northern Zagros forests.
The R2 values of 0.840 and 0.696 indicate that approximately 84% and 69.6% of the variance in the dependent variables (burned area and fire frequency, respectively) can be explained by the independent variables included in the model (Table 2). These high R2 values demonstrate that the model is effective in capturing the variability of the dependent variables based on the selected predictors.
The Adjusted R2 values of 0.546 and 0.139, although lower than the R2 values, still indicate that around 54.6% and 13.9% of the variability in the dependent variables (burned area and fire frequency, respectively) is explained by the model when taking into account the number of predictors and the sample size.
The ANOVA results for both multiple linear regression models suggest that the independent climatic and environmental variables are significant predictors of both burned area and fire frequency in the Northern Zagros forests. The statistically significant p-values (0.034 for burned area and 0.048 for fire frequency) indicate that these models effectively capture the variability in the dependent variables based on the selected predictors (Table 3). This finding underscores the importance of climatic and environmental factors in understanding and predicting wildfire dynamics in this region.

Table 3.
ANOVA results for MLR models assessing burned area and fire frequency in northern Zagros forests.
The MLR analysis indicates that several climatic variables significantly predict burned area and fire frequency in the northern Zagros forests (Table 4). For the burned area, higher average temperatures, lower precipitation, higher wind speeds, and increased surface solar radiation are significant predictors. For fire frequency, higher minimum and average temperatures, lower precipitation, and greater heat wave magnitude are significant predictors. These findings highlight the importance of specific climatic factors in influencing wildfire dynamics in this region.

Table 4.
MLR analysis coefficients for predicting burned area and fire frequency in northern Zagros forests.
The MLR equations for predicting burned area and fire frequency are presented in Equations (5) and (6).
Burned Area = 3738.379 + (125.494 × Minimum Temperature) + (−277.873 × Maximum Temperature) + (809.017 × Average Temperature) + (−5.711 × Average Relative Humidity) + (−18.975 × Average Temperature) + (−1410.154 × Average Wind Speed) + (2.093 × Wind Direction) + (−24.356 × Heat Wave Magnitude) + (−69.383 × Heat Wave Frequency) + (200.314 × Surface Solar Radiation)
Fire Frequency = −2725.357 + (22.978 × Minimum Temperature) + (32.669 × Maximum Temperature) + (46.586 × Average Temperature) + (18.814 × Average Relative Humidity) + (−4.155 × Average Precipitation) + (−122.269 × Average Wind Speed) + (−1.200 × Wind Direction) + (8.927 × Heat Wave Magnitude) + (−15.259 × Heat Wave Frequency) + (238.614 × Surface Solar Radiation)
4. Discussion
The analysis of the Northern Zagros forests from 2006 to 2023 reveals notable trends in fire frequency and intensity. The fluctuations in burned area, with significant peaks in 2007, 2010, 2021, and 2023 underscore the variability in fire activity over the study period. The largest burned area was recorded in 2021 (2655.66 ha), highlighting a concerning increase in fire intensity. These findings are consistent with previous studies that have documented regional variability in fire occurrence, influenced by climatic and environmental factors [56].
The temperature data indicated a considerable variability, with minimum temperatures ranging from −18.69 °C to −9.39 °C and maximum temperatures between 37.86 °C and 40.83 °C. These fluctuations reflect the broader climatic variability in the region. The highest minimum temperature in 2020 and peak maximum temperatures in 2021 align with the global trends of rising temperatures [57], corroborating the hypothesis that temperature increases are linked to heightened fire risks [58]. Precipitation and humidity data show significant changes, with an average relative humidity of between 44.60% and 56.02%, and precipitation ranging from 37.78 mm to 89.74 mm. These variations suggest that moisture levels have been highly variable, influencing fuel moisture content and fire potential. The peaks in precipitation in 2015 and 2022, along with the variability in humidity, highlight the dynamic nature of the region’s climate. Wind speed analysis reveals a general increasing trend, with the highest average wind speed in 2023. This trend, alongside the predominant southern wind direction in certain years, underscores the role of wind in fire dynamics, affecting fire spread and intensity [59]. The heat wave data indicate a significant increase in both magnitude and frequency, with values ranging from 8.24 to 14.99. The years 2022 and 2023 experienced the highest heat wave magnitudes and frequencies, highlighting an increasing trend in heat wave severity. This aligns with global trends showing more frequent and intense heatwaves due to climate change [45]. The increase in surface solar radiation, particularly in 2022 and 2023, reinforces the link between solar radiation and heat wave intensity, contributing to the drying of vegetation and increasing fire risk.
Pearson correlation analysis reveals strong correlations between temperature variables and the burned area. The significant positive correlation between the annual average temperature and burned area (r = 0.746, p-value < 0.001) confirms that higher temperatures are strongly associated with larger burned areas, consistent with previous findings [56,60]. Interestingly, wind speed shows a positive correlation with the burned area (r = 0.740, p-value = 0.036), suggesting that higher wind speeds are associated with larger burned areas. This finding highlights the role of wind in fire dynamics, where higher winds can promote fire spread and increase the total burned area, supporting the complexity of fire behavior under varying environmental conditions [61]. Surface solar radiation’s positive correlation with the burned area (r = 0.519, p-value = 0.027) indicates that increased solar radiation contributes to greater fuel drying, enhancing fire spread and intensity. The significant positive correlation between minimum temperature and fire frequency (r = 0.573, p-value = 0.013), along with the average temperature’s correlation (r = 0.501, p-value = 0.034), reinforces the link between warmer temperatures and increased fire occurrences. Moreover, the magnitude of heat waves shows a positive correlation with fire frequency (r = 0.479, p-value = 0.021), highlighting the role of extreme heat in increasing fire frequency. These findings underscore the importance of temperature and heat wave characteristics in shaping fire dynamics in the northern Zagros forests.
The MLR analysis reveals several significant predictors for both the burned area and fire frequency in the northern Zagros forests. For the burned area, the model highlights that higher average temperatures (p-value = 0.023) significantly increase the burned area, indicating the strong influence of temperature on fire spread. Lower average precipitation (p-value = 0.032) also significantly correlates with larger burned areas, emphasizing the role of moisture in fire dynamics. Additionally, higher average wind speeds (p-value = 0.028) are associated with larger burned areas, suggesting that wind can exacerbate fire spread by providing additional oxygen and facilitating the movement of embers. Increased surface solar radiation (p-value = 0.012) significantly correlates with larger burned areas, likely due to its effect on drying out vegetation and making it more susceptible to burning.
For fire frequency, higher minimum temperatures (p-value = 0.005) are significant predictors, suggesting that even night-time temperatures contribute to the likelihood of fires. Higher average temperatures (p-value = 0.028) also increase fire frequency, reinforcing the importance of overall warming trends. Conversely, lower average precipitation (p-value = 0.012) significantly increases fire frequency, underlining the critical role of moisture in preventing fires. Higher heat wave magnitude (p-value = 0.033) is another significant predictor, indicating that extreme temperature events are crucial in driving fire occurrences.
MLR analysis shows that climate and environmental variables are effective predictors of the burned area. These results are consistent with those from earlier studies that highlighted these variables as critical factors in fire activity [60,62,63]. The MLR model’s strong coefficients and predictive capability suggest its potential to improve fire management policies and prediction accuracy. Including climate and environmental variables provides a clearer understanding of the complex relationship between weather conditions and fire behavior. The role of heat wave magnitude, precipitation, surface solar radiation, temperature, and wind speed in the regression model underscores its importance in influencing fuel moisture, affecting fire spread and intensity [64,65]. Thus, integrating these variables into prediction models can enhance fire risk assessment accuracy and refine prevention strategies.
Various factors, such as vegetation type, topography, and human activities, influence fire behavior [62,66]. Future research should incorporate these factors into comprehensive models to better capture the diverse dynamics of fire in the northern Zagros forests. Also, effective fire control requires a multifaceted approach combining scientific research, policy making, and community involvement. Strategies like controlled burns, fuel reduction, and optimized land use can help mitigate fire risks and enhance ecosystem resilience [67]. Investing in early detection, response capabilities, and public education is crucial to minimizing the adverse impacts of wildfires on human health, infrastructure, and natural resources [68]. Additionally, fostering international collaboration and information sharing can facilitate the exchange of best practices and lessons learned in fire management across borders [69]. By adopting transdisciplinary approaches and leveraging technological and modeling advancements, stakeholders can better predict forest fire trends and develop adaptive strategies to reduce their impact [70].
These findings have significant implications for fire management and climate change adaptation in the northern Zagros forests and beyond. As temperatures continue to rise, proactive measures like fuel reduction, early warning systems, and community preparedness are becoming increasingly essential. Moreover, integrating climate change considerations into forest management can enhance ecosystem resilience to fire disturbances.
This research has several important limitations. Data quality and availability issues, particularly in historical climate and fire data, can affect the reliability of the findings. The multiple linear regression models used may not fully capture the complexities of fire behavior, and the exclusion of key variables such as vegetation types, land use changes, and human activities restricts the analysis. Additionally, while significant correlations were found between climatic variables and fire metrics, these do not establish causation. Future research should address these limitations by incorporating a broader range of variables, utilizing advanced modeling techniques, and including longer temporal and wider geographic scopes.
5. Conclusions
This study provides valuable insights into the relationship between climate change and forest fires in the Northern Zagros, Iran. The observed trends in fire frequency, intensity, and climatic variables underscore the increasing vulnerability of this region to wildfires. The significant correlations and predictive power of the climatic variables highlight the need for targeted fire management strategies that account for the changing climate. The findings emphasize the importance of incorporating climate change considerations into forest management practices. Strategies such as fuel reduction, early warning systems, community preparedness, and the promotion of adaptive land use practices are essential. Enhancing collaboration at the national and international levels will also be important in sharing knowledge and best practices to mitigate the impact of wildfires. Future research should continue to refine predictive models, incorporating additional factors such as vegetation type, topography, and human activities to improve our understanding of fire dynamics. This will enable the development of more effective and sustainable fire management and climate adaptation strategies in the Northern Zagros forests and similar regions worldwide.
Author Contributions
H.B.H.: Conceptualization, methodology, software, formal analysis, data curation, project administration. M.G.B.: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. S.A.B.: methodology, validation, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting this study may be provided by the first author upon a reasonable request. The data are not publicly available due to privacy of parts of the data.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the Department of Natural Resources and Watershed Management of West Azarbaijan and Kurdistan Provinces of Iran for providing statistics related to the occurrence of fires, which were instrumental to this study. We also extend our heartfelt thanks to the NASA POWER Project team for their invaluable support in supplying the meteorological data that significantly contributed to our research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Assumptions Validation for Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
1. Normality of Residuals
The normality of residuals was assessed using Normal P-P plots of regression standardized residuals. For both dependent variables, the burned area and fire frequency, the results are shown in Figure A1 and Figure A2, respectively. In these plots, the points generally follow a straight diagonal line, suggesting that the residuals are normally distributed. This finding supports the assumption of normality, which is essential for the validity of the regression model.
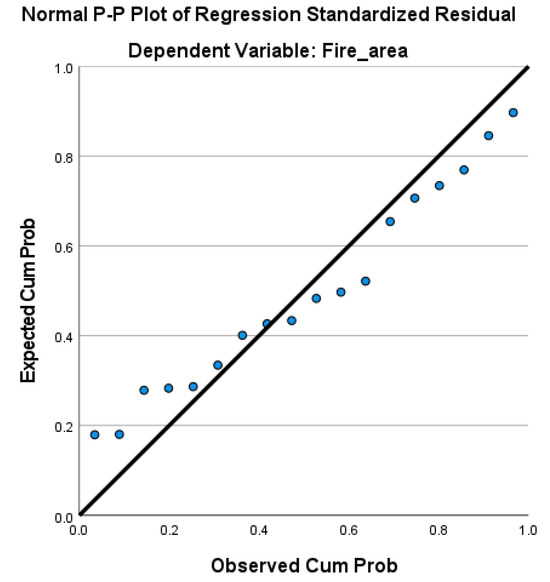
Figure A1.
Normal P-P plot of regression standardized residuals for the burned area.
Figure A1.
Normal P-P plot of regression standardized residuals for the burned area.
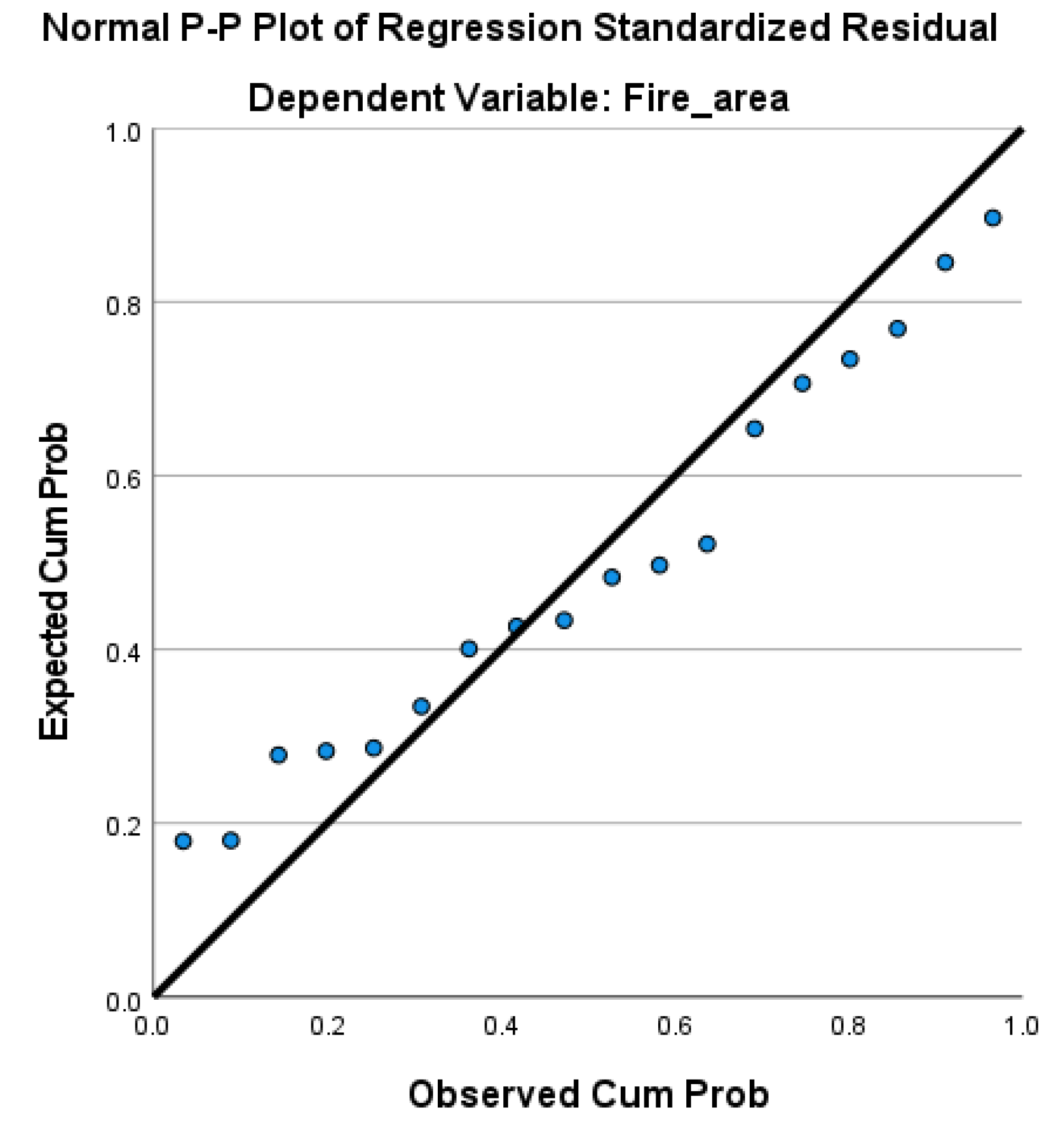
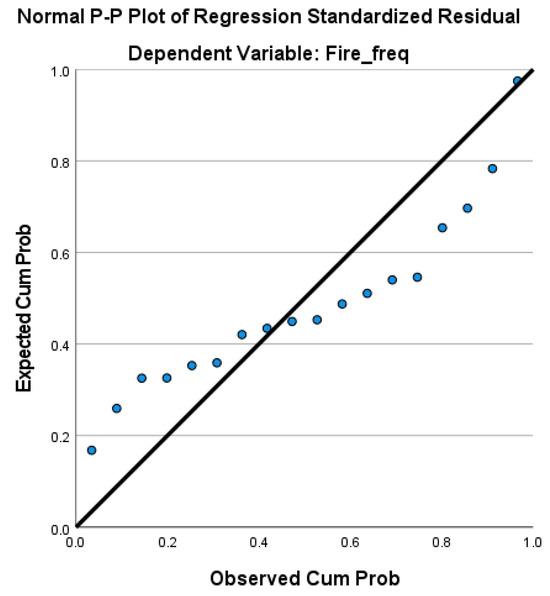
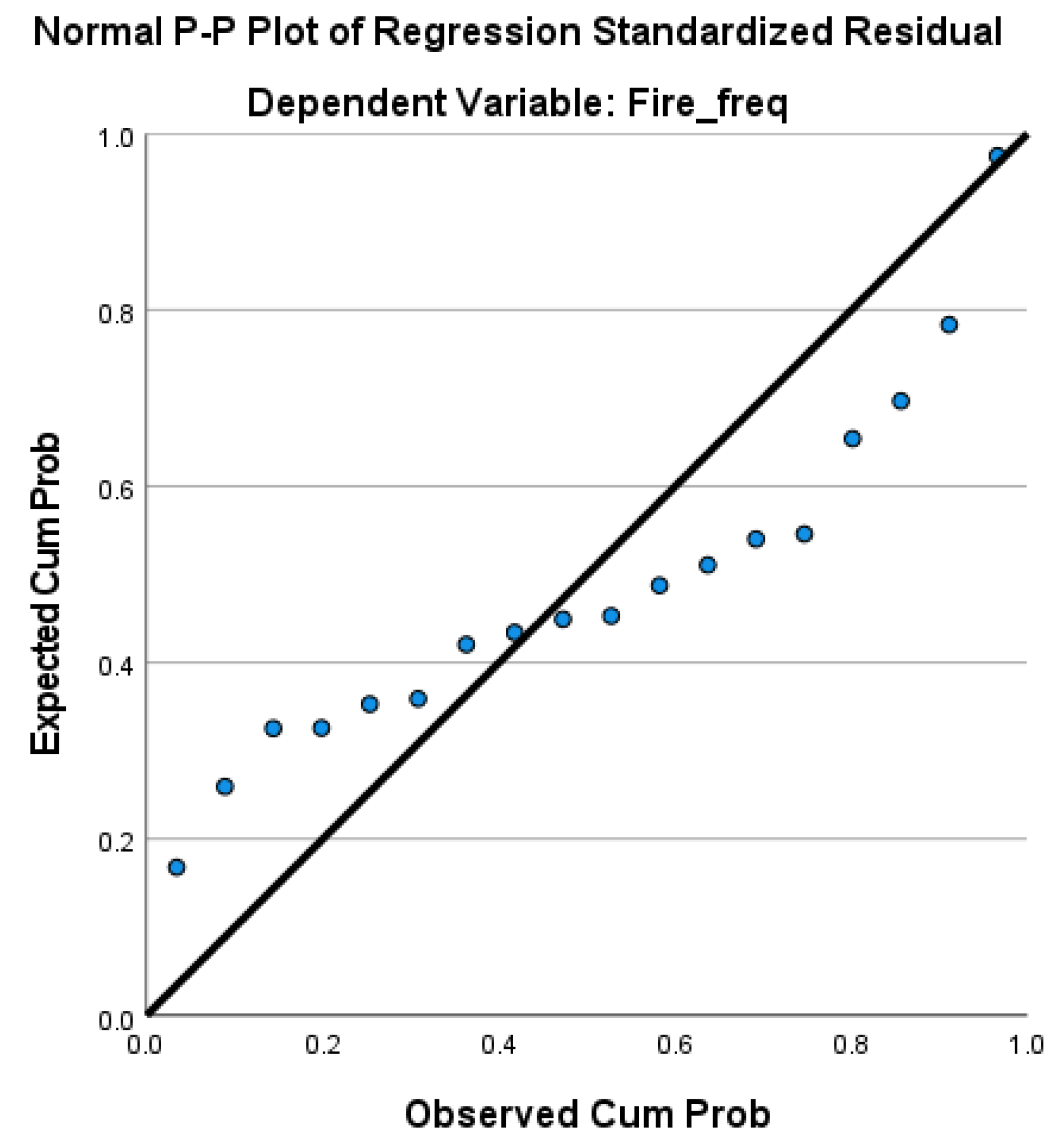
Figure A2.
Normal P-P plot of regression standardized residuals for the fire frequency.
Figure A2.
Normal P-P plot of regression standardized residuals for the fire frequency.
2. Homoscedasticity
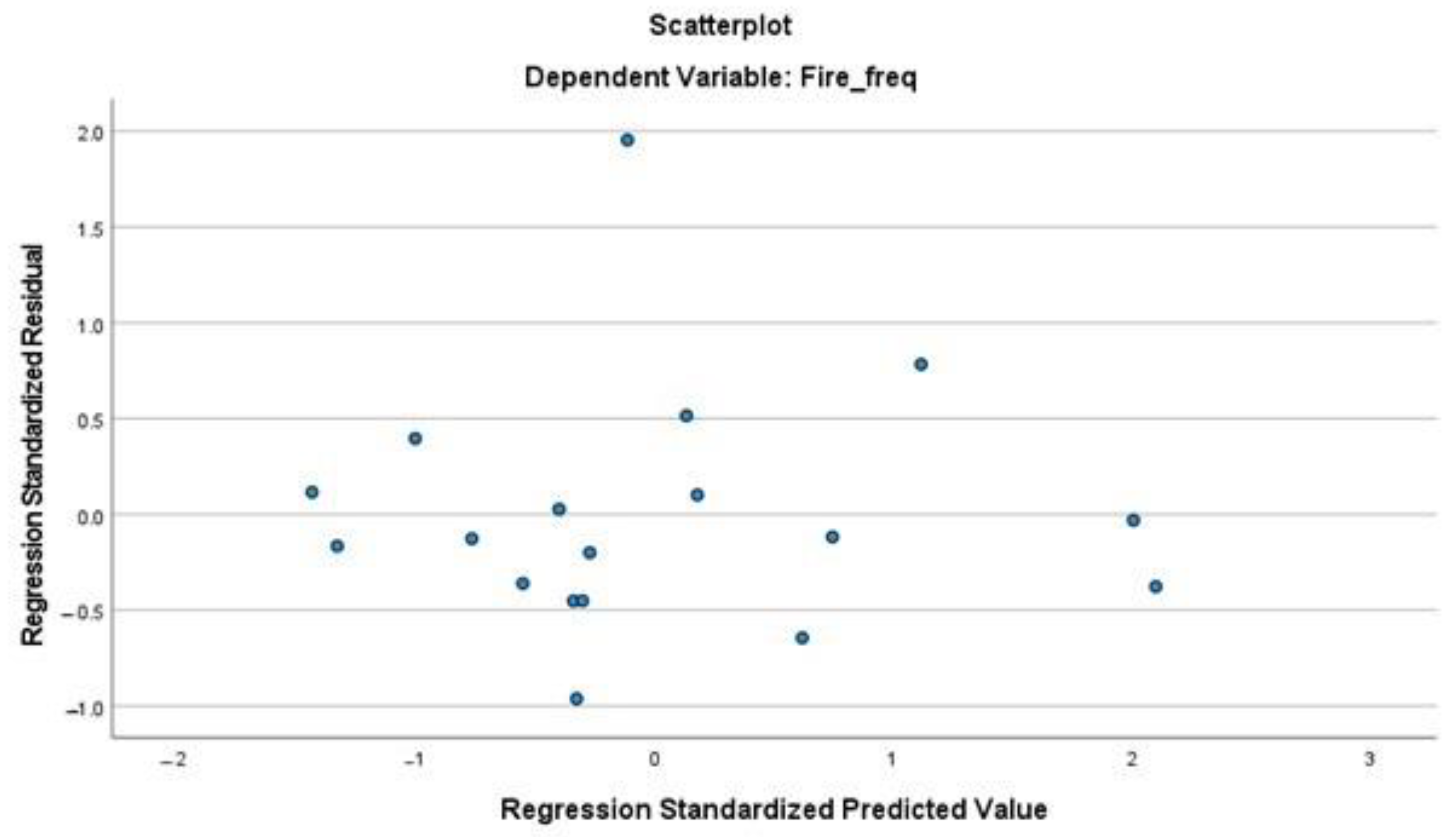
The assumption of homoscedasticity, which means that the variance of the residuals is constant across all levels of the predicted values, was evaluated using scatter plots of residuals. Figure A3 and Figure A4 show the homoscedasticity plots for the burned area and fire frequency, respectively. The plots reveal a random distribution of residuals around the horizontal axis without any discernible pattern, indicating that the variance of the errors is homoscedastic and that this assumption holds true.
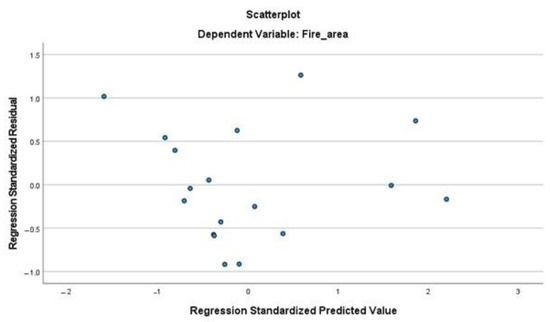
Figure A3.
Homoscedasticity plot of residuals for the burned area.
Figure A3.
Homoscedasticity plot of residuals for the burned area.
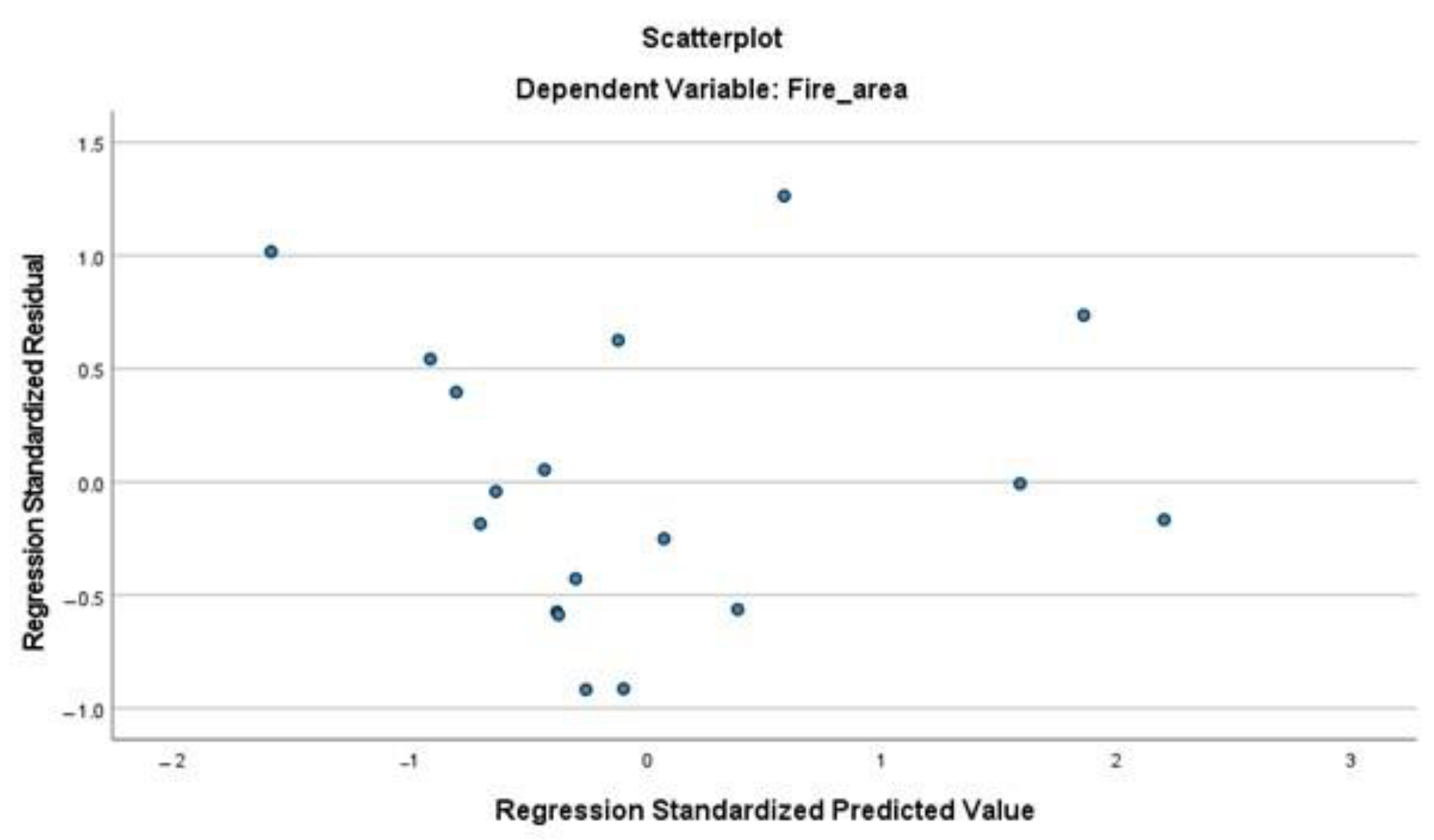
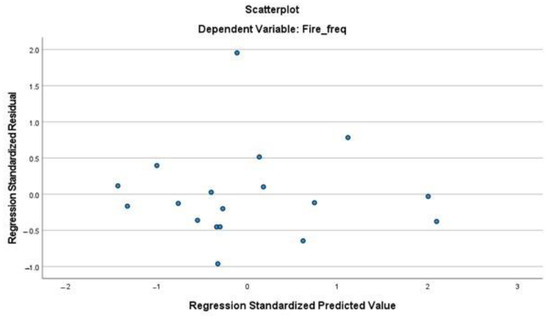
Figure A4.
Homoscedasticity plot of residuals for the fire frequency.
Figure A4.
Homoscedasticity plot of residuals for the fire frequency.
3. Multicollinearity
To detect potential multicollinearity issues, the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) was calculated for each independent variable, as presented in Table A1. The VIF values for all variables are below the commonly accepted threshold of 10, with most values being significantly lower. This indicates that multicollinearity is not a concern in this model, allowing for reliable interpretation of the regression coefficients.

Table A1.
Results of the multicollinearity test using the variance inflation factor (VIF).
Table A1.
Results of the multicollinearity test using the variance inflation factor (VIF).
| Independent Variables | Dependent Variable | |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Frequency | Burned Area | |
| Minimum Temperature | 1.684 | 1.716 |
| Maximum Temperature | 2.378 | 2.362 |
| Average Temperature | 2.967 | 2.643 |
| Average Relative Humidity | 1.119 | 2.887 |
| Average Precipitation | 2.445 | 2.066 |
| Average Wind Speed-GEE | 1.175 | 1.209 |
| Wind Direction | 2.741 | 1.513 |
| Heat Wave Magnitude | 2.112 | 1.779 |
| Heat Wave Frequency | 1.206 | 1.333 |
| Surface Solar Radiation | 2.432 | 2.512 |
4. Independence of Errors
The independence of errors was tested using the Durbin–Watson statistic, with the results provided in Table A2. The Durbin–Watson values were 2.789 for the burned area and 1.618 for fire frequency. Both values are close to the ideal value of two, suggesting that there is no significant autocorrelation in the residuals for either dependent variable, thereby fulfilling the assumption of independent errors.

Table A2.
Durbin–Watson statistic for the regression model with dependent variables.
Table A2.
Durbin–Watson statistic for the regression model with dependent variables.
| Dependent Variable | Durbin-Watson Value |
|---|---|
| Burned area | 2.789 |
| Fire frequency | 1.618 |
These analyses collectively confirm that the assumptions required for performing a valid Multiple Linear Regression are largely satisfied, ensuring the robustness and reliability of the regression results.
References
- Goldammer, J.G.; Statheropoulos, M.; Andreae, M.O. Impacts of vegetation fire emissions on the environment, human health, and security: A global perspective. Dev. Environ. Sci. 2008, 8, 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, F.H.; Williamson, G.; Borchers-Arriagada, N.; Henderson, S.B.; Bowman, D.M. Climate Change, Landscape Fires, and Human Health: A Global Perspective. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2024, 45, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adámek, M.; Jankovská, Z.; Hadincová, V.; Kula, E.; Wild, J. Drivers of forest fire occurrence in the cultural landscape of Central Europe. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 2031–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Stjern, C.W.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Marelle, L.; Samset, B.H.; Sillmann, J.; Schaller, N.; Fischer, E.; Schulz, M. Frequency of extreme precipitation increases extensively with event rareness under global warming. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canadell, J.G.; Meyer, C.; Cook, G.D.; Dowdy, A.; Briggs, P.R.; Knauer, J.; Pepler, A.; Haverd, V. Multi-decadal increase of forest burned area in Australia is linked to climate change. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.W.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Veraverbeke, S.; Andela, N.; Lasslop, G.; Forkel, M.; Smith, A.J.; Burton, C.; Betts, R.A.; van der Werf, G.R. Global and regional trends and drivers of fire under climate change. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2020RG000726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, C.R.; Innes, J.L. Interactions between fire, climate change and forest biodiversity. CABI Rev. 2007, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausas, J.G.; Keeley, J.E. Wildfires as an ecosystem service. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2019, 17, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, P.; Banj Shafiei, A.; Barin, M.; Khezri, K. Effect of surface fire on dynamic of some chemico-physical properties of forest soil, Sardasht, West Azarbayjan. For. Res. Dev. 2020, 6, 395–410. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Beygi Heidarlou, H.; Banj Shafiei, A.; Nasiri, V.; Niţă, M.D.; Borz, S.A.; Lopez-Carr, D. Impact of Iran’s Forest Nationalization Law on Forest Cover Changes over Six Decades: A Case Study of a Zagros Sparse Coppice Oak Forest. Sensors 2023, 23, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzipour, B. Climate Change: Impacts on Forest Fires in Iran; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, D.M.; Balch, J.K.; Artaxo, P.; Bond, W.J.; Carlson, J.M.; Cochrane, M.A.; d’Antonio, C.M.; DeFries, R.S.; Doyle, J.C.; Harrison, S.P. Fire in the Earth system. Science 2009, 324, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, D.; Gedalof, Z.E.; Peterson, D.L.; Mote, P. Climatic change, wildfire, and conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2004, 18, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannigan, M.D.; Logan, K.A.; Amiro, B.D.; Skinner, W.R.; Stocks, B.J. Future area burned in Canada. Clim. Chang. 2005, 72, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleemahmoodi Sarab, S.; Feghhi, J.; Jabbarian Amiri, B.; Danehkar, A.; Attarod, P. Applying the regression models to assess the influences of climate factors on forest fires (case study: Izeh). J. Nat. Environ. 2013, 66, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Beygi Heidarlou, H.; Karamat Mirshekarlou, A. Understanding the effects of climate change on wildfires in the Iranian Northern Zagros Forests. For. Res. Dev. 2024, 10, 289–303. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Rothermel, R.C. A Mathematical Model for Predicting Fire Spread in Wildland Fuels; Intermountain Forest & Range Experiment Station, Forest Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture: Ogden, UT, USA, 1972; Volume 115.
- Moritz, M.A.; Parisien, M.-A.; Batllori, E.; Krawchuk, M.A.; Van Dorn, J.; Ganz, D.J.; Hayhoe, K. Climate change and disruptions to global fire activity. Ecosphere 2012, 3, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; Haunschild, R.; Bornmann, L. Heat waves: A hot topic in climate change research. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 146, 781–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. Climate change caused by human activities is happening and it already has major consequences. J. Energy Nat. Resour. Law 2018, 36, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, B.M.; Balch, J.K.; Goetz, S.J.; Lehmann, C.E.; Turetsky, M. Focus on changing fire regimes: Interactions with climate, ecosystems, and society. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 030201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayum, A.; Ahmad, F.; Arya, R.; Singh, R.K. Predictive modeling of forest fire using geospatial tools and strategic allocation of resources: eForestFire. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2020, 34, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beygi Heidarlou, H.; Karamat Mirshekarlou, A.; Lopez-Carr, D.; Borz, S.A. Conservation policy and forest transition in Zagros forests: Statistical analysis of human welfare, biophysical, and climate drivers. For. Policy Econ. 2024, 161, 103177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, P.; Jamzad, Z.; Pourmajidian, M.; Fallah, A.; Pourhashemi, M.; Sohrabi, H. Taxonomic revision of the Quercus brantii complex (Fagaceae) in Iran with emphasis on leaf and pollen micromorphology. Acta Bot. Hung. 2012, 54, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazirehi, M.; Ebrahimi Rostaghi, M. Silviculture in Zagros; University of Tehran Press: Tehran, Iran, 2003. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, S.; Oehler, F.; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Camia, A.; Pereira, J.M. Modeling spatial patterns of fire occurrence in Mediterranean Europe using Multiple Regression and Random Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 275, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastour, H.; Ahmed, M.R.; Hassan, Q.K. Analysis of forest fire patterns and their relationship with climate variables in Alberta’s natural subregions. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tošić, I.; Mladjan, D.; Gavrilov, M.; Živanović, S.; Radaković, M.; Putniković, S.; Petrović, P.; Mistridželović, I.K.; Marković, S. Potential influence of meteorological variables on forest fire risk in Serbia during the period 2000–2017. Open Geosci. 2019, 11, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai-feng, L. Study on the relationship among forest fire, temperature and precipitation and its spatial–temporal variability in China. Agric. Sci. Technol. Hunan 2011, 12, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Won, M.-S.; Koo, K.-S.; Lee, M.-B. An analysis of forest fire occurrence hazards by changing temperature and humidity of ten-day intervals for 30 years in spring. Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 8, 250–259. [Google Scholar]
- Beygi Heidarlou, H.; Banj Shafiei, A.; Erfanian, M. Forest fire risk mapping using analytical hierarchy process technique and frequency ratio method (Case study: Sardasht Forests, NW Iran). Iran. J. For. Poplar Res. 2014, 22, 559–573. [Google Scholar]
- Daşdemir, İ.; Aydın, F.; Ertuğrul, M. Factors affecting the behavior of large forest fires in Turkey. Environ. Manag. 2021, 67, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, M.A.; Price, O.F.; Fox-Hughes, P. The influence of regional wind patterns on air quality during forest fires near Sydney, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojarov, P.; Nikolova, M. Heat waves and forest fires in Bulgaria. Nat. Hazards 2022, 114, 1879–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Radovanovic, M. Solar activity as a possible cause of large forest fires—A case study: Analysis of the Portuguese forest fires. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NASA POWER Project, N. Prediction of Worldwide Energy Resource (POWER); Climatology Resource for SSE-Renewable Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Gunaratne, M.; De Silva, S.; Amarasinghe, R. Can NASA Power Climatic Data Fill the Gap of Climatic Data Required for Agriculture and Forest Ecosystems Modeling? In Proceedings of the International Forestry and Environment Symposium, Nugegoda, Sri Lanka, 20–21 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrari, A.H. Create Daily Wind Speed. Available online: https://github.com/AmirhosseinAhrari/GoogleEarthEngine (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.P.; Bornstein, R.D.; Soares, J. Annual and diurnal wind patterns in the city of São Paulo. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2003, 3, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. Meteorology for Scientists and Engineers: A Technical Companion Book with Ahrens’ Meteorology Today, 2nd ed.; Brooks/Cole Pacific: Grove, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, S.; Dosio, A.; Graversen, R.G.; Sillmann, J.; Carrao, H.; Dunbar, M.B.; Singleton, A.; Montagna, P.; Barbola, P.; Vogt, J.V. Magnitude of extreme heat waves in present climate and their projection in a warming world. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.T.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Gohlke, J.M. Heat waves in the United States: Definitions, patterns and trends. Clim. Chang. 2013, 118, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.E.; Alexander, L.V. On the measurement of heat waves. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 4500–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A.; Tebaldi, C. More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science 2004, 305, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharvandi, N.; Mojarrad, F.; Masompour, J. Identification of heat waves and analysis of Their temporal-spatial variations in Iran. J. Appl. Res. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 20, 39–58. (In Persian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tranmer, M.; Elliot, M. Multiple linear regression. Cathie Marsh Cent. Census Surv. Res. (CCSR) 2008, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, A.J.; Asner, G.P.; Hughes, R.F. Satellite monitoring of vegetation phenology and fire fuel conditions in Hawaiian drylands. Earth Interact. 2005, 9, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Cohen, P.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kutner, M.H.; Nachtsheim, C.J.; Neter, J.; Li, W. Applied Linear Statistical Models; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, J.; Shevlin, M. Applying Regression and Correlation: A Guide for Students and Researchers; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich, J.O. Using IBM SPSS Statistics: An Interactive Hands-On Approach; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Neter, J.; Kutner, M.H.; Nachtsheim, C.J.; Wasserman, W. Applied Linear Statistical Models, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- IBM Corp. Released 2020. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 27.0; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moritz, M.A.; Batllori, E.; Bradstock, R.A.; Gill, A.M.; Handmer, J.; Hessburg, P.F.; Leonard, J.; McCaffrey, S.; Odion, D.C.; Schoennagel, T. Learning to coexist with wildfire. Nature 2014, 515, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Williams, A.P. Impact of anthropogenic climate change on wildfire across western US forests. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11770–11775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, S.J.; Andrews, P.L.; Laven, R.D. Introduction to Wildland Fire, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Karamat Mirshekrlou, A.; Banj Shafiei, A.; Beygi Heidarlou, H. Modeling Forest Fire Behaviour in Controlled and Accidental Ignitions in Iranian Northern Zagros Forests, with an Emphasis on Fuel Load. Ecol. Iran. For. 2023, 11, 120–137. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Stanturf, J.; Goodrick, S. Trends in global wildfire potential in a changing climate. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, W.M.; Cochrane, M.A.; Freeborn, P.H.; Holden, Z.A.; Brown, T.J.; Williamson, G.J.; Bowman, D.M. Climate-induced variations in global wildfire danger from 1979 to 2013. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Goodrick, S.L.; Stanturf, J.A. Future US wildfire potential trends projected using a dynamically downscaled climate change scenario. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 294, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannigan, M.; Wotton, B.; Marshall, G.; De Groot, W.; Johnston, J.; Jurko, N.; Cantin, A. Fuel moisture sensitivity to temperature and precipitation: Climate change implications. Clim. Chang. 2016, 134, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, T.M.; Bowman, D.M.; Jain, P.; Flannigan, M.D.; Williamson, G.J. Global increase in wildfire risk due to climate-driven declines in fuel moisture. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 1544–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calviño-Cancela, M.; Chas-Amil, M.L.; García-Martínez, E.D.; Touza, J. Interacting effects of topography, vegetation, human activities and wildland-urban interfaces on wildfire ignition risk. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 397, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoennagel, T.; Balch, J.K.; Brenkert-Smith, H.; Dennison, P.E.; Harvey, B.J.; Krawchuk, M.A.; Mietkiewicz, N.; Morgan, P.; Moritz, M.A.; Rasker, R. Adapt to more wildfire in western North American forests as climate changes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4582–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerling, A.L.; Hidalgo, H.G.; Cayan, D.R.; Swetnam, T.W. Warming and earlier spring increase western US forest wildfire activity. Science 2006, 313, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flannigan, M.; Stocks, B.; Turetsky, M.; Wotton, M. Impacts of climate change on fire activity and fire management in the circumboreal forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyser, A.; Westerling, A.L. Climate drives inter-annual variability in probability of high severity fire occurrence in the western United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).