The Impact of Social Capital on Farmers’ Green Production Behavior: Moderation Effects Based on Agricultural Support and Protection Subsidies
Abstract
1. Introduction
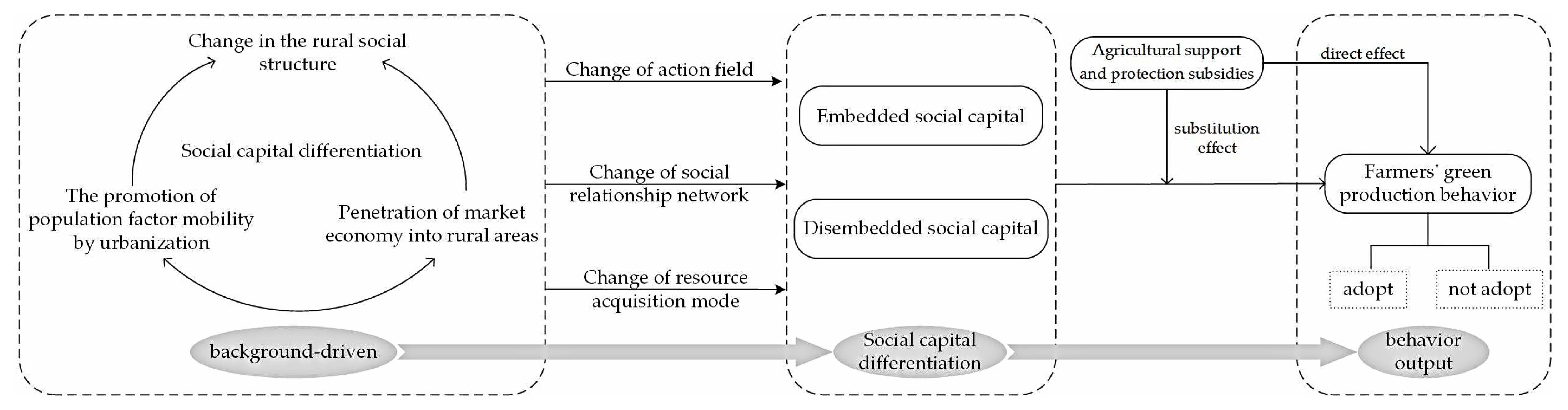
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. The Impact of Social Capital on Farmers’ Green Production Behavior
2.2. The Moderating Effect of Agricultural Support and Protection Subsidies on the Influence of Social Capital on Farmers’ Green Production Behavior
3. Materials and Methods
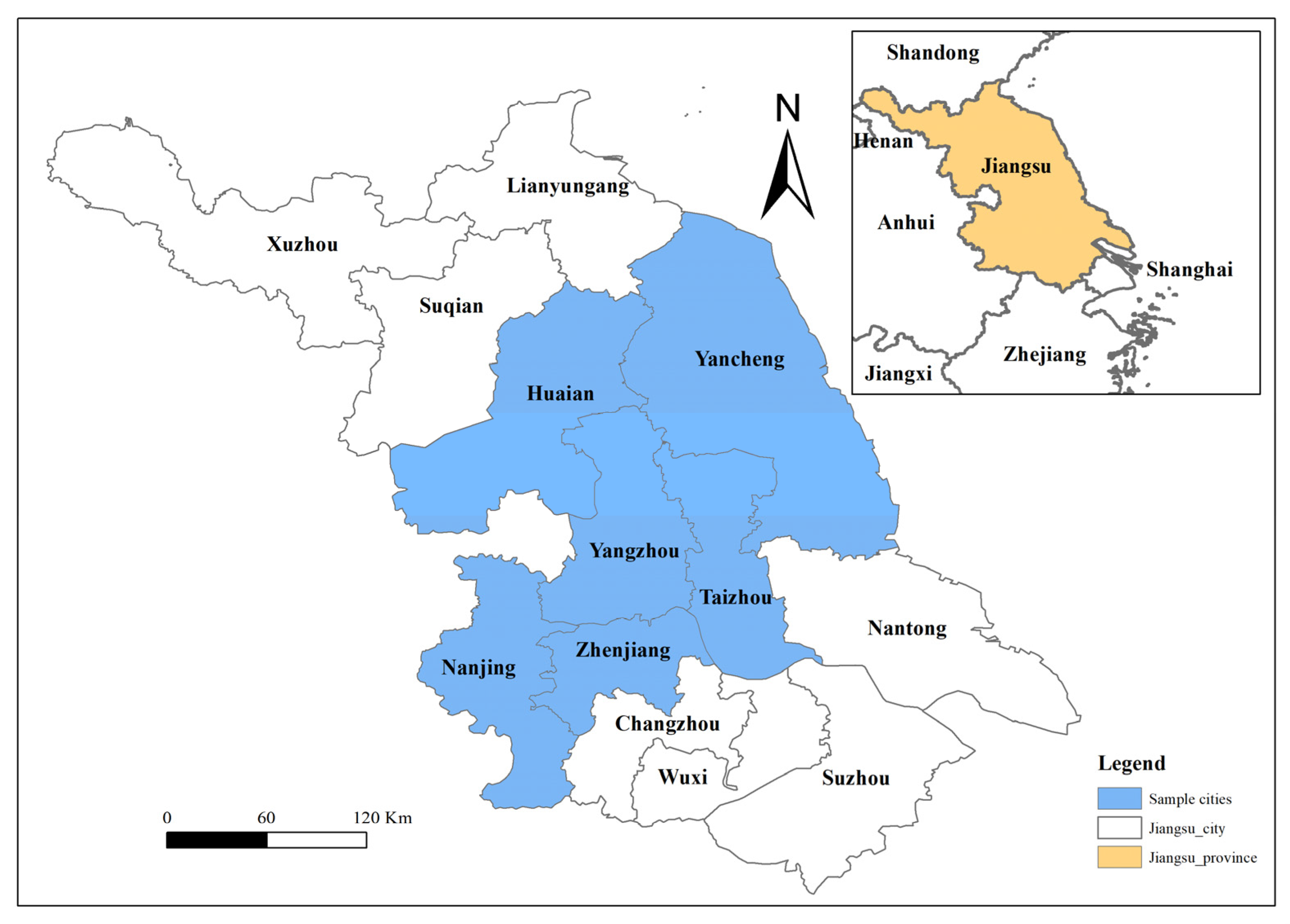
3.1. Data Source
3.2. Variable Selection
3.2.1. Dependent Variable
3.2.2. Core Independent Variable
3.2.3. Moderator Variable
3.2.4. Control Variable
3.3. Methods
3.4. Multicollinearity Test
4. Results
4.1. Benchmark Regression Analysis
4.2. Robustness Test
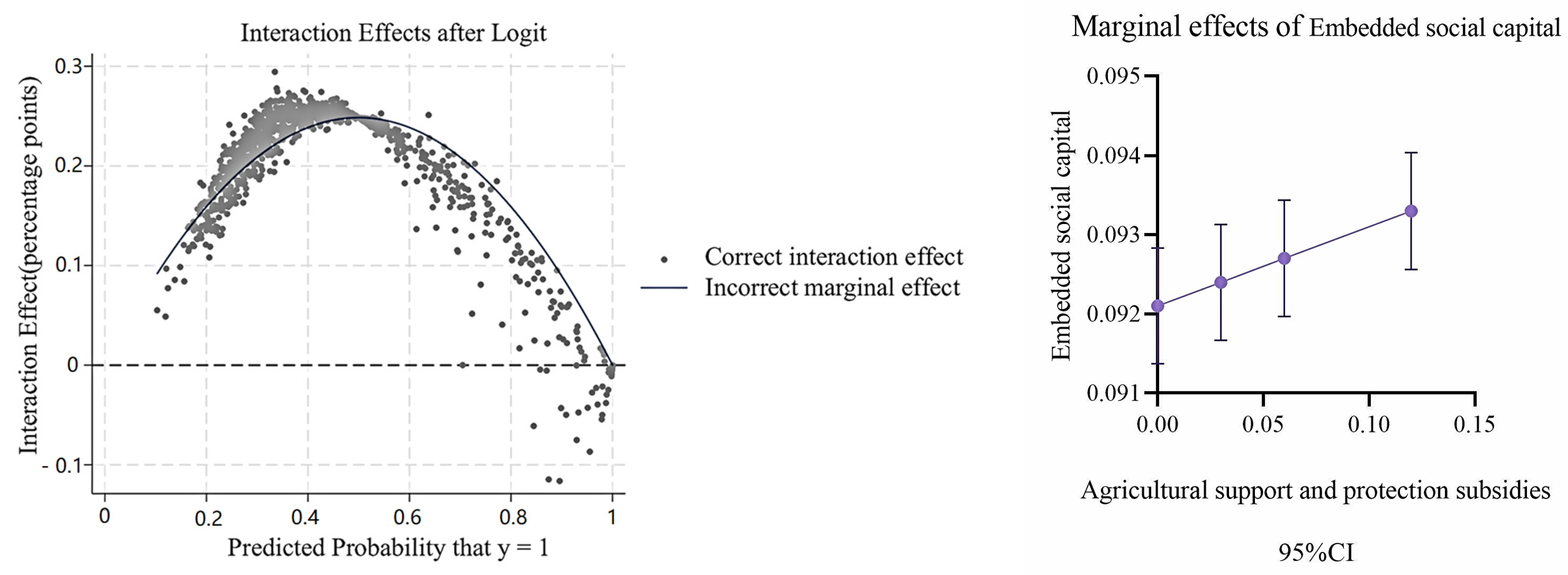
4.3. Moderation Effect Test of Agricultural Support and Protection Subsidies
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kay, M.; Bunning, S.; Burke, J.; Boerger, V.; Bojic, D.; Bosc, P.-M.; Clark, M.; Dale, D.; England, M.; Hoogeveen, J. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture 2021, Systems at Breaking Point; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Towards a Green Economy: Pathways to Sustainable Development and Poverty Eradication; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Crippa, M.; Solazzo, E.; Guizzardi, D.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Tubiello, F.N.; Leip, A. Food Systems Are Responsible for a Third of Global Anthropogenic GHG Emissions. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubiello, F.N.; Rosenzweig, C.; Conchedda, G.; Karl, K.; Gütschow, J.; Xueyao, P.; Obli-Laryea, G.; Wanner, N.; Qiu, S.Y.; De Barros, J. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Food Systems: Building the Evidence Base. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 65007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2022–2031|OECD. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/oecd-fao-agricultural-outlook-2022-2031_f1b0b29c-en.html (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Zhang, D.; Dong, F.; Li, Z.; Xu, S. How Can Farmers’ Green Production Behavior Be Promoted? A Literature Review of Drivers and Incentives for Behavioral Change. Agriculture 2025, 15, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Common Agricultural Policy. Available online: https://agriculture.ec.europa.eu/common-agricultural-policy_en (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Liu, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, G.; Zhao, X. An Evaluation of China’s Agricultural Green Production: 1978–2017. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 243, 118483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Shen, L.; Wang, F.; Tang, H.; Zhou, Z. Dual Carbon Goal and Agriculture in China: Exploring Key Factors Influencing Farmers’ Behavior in Adopting Low Carbon Technologies. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 3215–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, Y. How to Implement the Government Subsidy Policy in Promoting the Green Development of Agriculture in Hebei Province? J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 496, 145141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liang, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xue, Y. Can Government Regulation Weak the Gap between Green Production Intention and Behavior? Based on the Perspective of Farmers’ Perceptions. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity Based on Carbon Emission: An Analysis of Evolution Trend and Influencing Factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Peng, B. The Impact of Digital Financial Inclusion on Green and Low-Carbon Agricultural Development. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, W. The Role of Agricultural Green Production Technologies in Improving Low-Carbon Efficiency in China: Necessary but Not Effective. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ruiz-Menjivar, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Swisher, M.E. Technical Training and Rice Farmers’ Adoption of Low-Carbon Management Practices: The Case of Soil Testing and Formulated Fertilization Technologies in Hubei, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, T.; Khan, S.U. How Does Capital Endowment Impact Farmers’ Green Production Behavior? Perspectives on Ecological Cognition and Environmental Regulation. Land 2023, 12, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart-Getz, A.; Prokopy, L.S.; Floress, K. Why Farmers Adopt Best Management Practice in the United States: A Meta-Analysis of the Adoption Literature. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 96, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, Z.; Jiang, G.; Quan, Z. Addressing the Differences in Farmers’ Willingness and Behavior Regarding Developing Green Agriculture—A Case Study in Xichuan County, China. Land 2021, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Meng, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Driving Factors of Farmers’ Green Agricultural Production Behaviors in the Multi-Ethnic Region in China Based on NAM-TPB Models. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 50, e02812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Yu, L.; Yang, H.; Yin, S. Social Capital, Land Tenure and the Adoption of Green Control Techniques by Family Farms: Evidence from Shandong and Henan Provinces of China. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, G. Effect of Farmland Scale on Agricultural Green Production Technology Adoption: Evidence from Rice Farmers in Jiangsu Province, China. Land Use Policy 2024, 147, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, L.; Ke, X.; Zhang, E.; Zhu, J.; Lin, A. Impact of Agricultural Machinery Purchase Subsidies on the Sustainable and Intensive Utilization of Cultivated Land: A Perspective on Agricultural Machinery Socialization Services. J. Rural Stud. 2025, 119, 103798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qian, Y.; Kong, F. Does Outsourcing Service Reduce the Excessive Use of Chemical Fertilizers in Rural China? The Moderating Effects of Farm Size and Plot Size. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.; Knickel, K.; María Díaz-Puente, J.; Afonso, A. The Role of Social Capital in Agricultural and Rural Development: Lessons Learnt from Case Studies in Seven Countries. Sociol. Rural. 2019, 59, 66–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, F.; Bulte, E.; Adekunle, A. Social Capital and Agricultural Innovation in Sub-Saharan Africa. Agric. Syst. 2012, 108, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, E.A.; Petousi, V. Social Capital, Trust, and Cultivation of Bioenergy Crops: Evidence from Germany and Greece. Agriculture 2024, 14, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbuch, B.; Thorsøe, M.H.; Kjeldsen, C. Using Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping and Social Capital to Explain Differences in Sustainability Perceptions between Farmers in the Northeast US and Denmark. Agric. Hum. Values 2022, 39, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Krom, M.P. Farmer Participation in Agri-Environmental Schemes: Regionalisation and the Role of Bridging Social Capital. Land Use Policy 2017, 60, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, H. How Social Capital Affects Willingness of Farmers to Accept Low-Carbon Agricultural Technology (LAT)? A Case Study of Jiangsu, China. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2021, 13, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofré-Bravo, G.; Klerkx, L.; Engler, A. Combinations of Bonding, Bridging, and Linking Social Capital for Farm Innovation: How Farmers Configure Different Support Networks. J. Rural Stud. 2019, 69, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yuan, L.; Lu, M. Analysis of Influencing Factors of Farmers’ Homestead Revitalization Intention from the Perspective of Social Capital. Land 2023, 12, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N. Social Capital: A Theory of Social Structure and Action; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; Volume 19, ISBN 0-521-52167-X. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; Chen, W.; Zeng, J. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Traditional Villages in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Tou, L. The Impact of Capital Endowment and Green Agricultural Subsidies on Farmers’ Adoption of Green Agricultural Technologies: The Obscuring Effect Based on Perceived Value. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2025, 25, 149–161. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dingyi, S.; Xiaofang, L.; Zhide, J. Influence of Peasant Household Differentiation and Risk Perception on Soil and Water Conservation Tillage Technology Adoption-an Analysis of Moderating Effects Based on Government Subsidies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Long, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. Implications of Land-Use Change in Rural China: A Case Study of Yucheng, Shandong Province. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.Z.; Wang, W.T. Social Structure Change, Social Capital Transition, and Income Inequality in Rural China. China Soft Sci. 2016, 10, 20–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fei, X.; Hamilton, G.G.; Zheng, W. From the Soil: The Foundations of Chinese Society; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 1992; ISBN 0-520-07796-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Gu, X. How Does Urban-Rural Capital Flow Affect Rural Reconstruction near Metropolitan Areas? Evidence from Shanghai, China. Land 2023, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, G. The Consequences of Modernity; Polity Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Granovetter, M.S. The Strength of Weak Ties. Am. J. Sociol. 1973, 78, 1360–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, X. International Comparison of Individual Social Capital: Dual Perspectives on Structural Crossing and Resource Attainment. Sociol. Stud. 2024, 39, 180–203, 230. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.C. The Moral Economy of the Peasant: Rebellion and Subsistence in Southeast Asia; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1977; ISBN 0-300-18555-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y. The Flow of Gifts: Reciprocity and Social Networks in a Chinese Village; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993; ISBN 979-8-6419-3685-7. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, B.E.; Bergtold, J.S.; Featherstone, A.M.; Wilson, C.A. Farmers’ Choice of Credit among the Farm Credit System, Commercial Banks, and Nontraditional Lenders. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2019, 44, 362–379. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X. The Moderating Effect of Training, Subsidies and Propaganda on the Relationship between Psychological Factors and Farmers’ Willingness to Reduce Chemical Fertilizer Application: Evidence from Dryland Farming Areas of China. Agric. Syst. 2025, 224, 104257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; He, K. Impact of informal institutions and environmental regulations on farmers’green production behavior: Based on survey data of 1105 households in Hubei Province. Resour. Sci. 2019, 41, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, K. Does Farmers’ Adoption of Green Production Technologies Help Mitigate Household Livelihood Vulnerability?—Based on China Land Economic Survey. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 491, 144824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Impact of Environmental Regulation Perception on Farmers’ Agricultural Green Production Technology Adoption: A New Perspective of Social Capital. Technol. Soc. 2022, 71, 102085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zissi, A.; Tseloni, A.; Skapinakis, P.; Savvidou, M.; Chiou, M. Exploring Social Capital in Rural Settlements of an Islander Region in Greece. J. Community Appl. Soc. 2010, 20, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axsen, J.; Orlebar, C.; Skippon, S. Social Influence and Consumer Preference Formation for Pro-Environmental Technology: The Case of a UK Workplace Electric-Vehicle Study. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 95, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-J.; Hirano, N.; Takakuwa, S.; Yen, H.-W.; Aso, Y. Physical and Chemical Conditions of the Protostellar Envelope and the Protoplanetary Disk in HL Tau. Astrophys. J. 2018, 869, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Qiao, D.; Tang, J.; Wan, A.; Qiu, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, X. Training of Farmers’ Cooperatives, Value Perception and Members’ Willingness of Green Production. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, H. Post-Assessment in Policy-Based Strategic Environmental Assessment: Taking China’s Agricultural Support and Protection Subsidy Policy as an Example. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 100, 107047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Chen, C.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, K. Peer Effects, Attention Allocation and Farmers’ Adoption of Cleaner Production Technology: Taking Green Control Techniques as an Example. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, J.M. Econometric Analysis of Cross Section and Panel Data; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; ISBN 0-262-29679-9. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ban, A.W. Boer en Landbouwonderwijs: De Landbouwkundige Ontwikkeling van de Nederlandse Boeren; Landbouwhogeschool: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- van den Ban, A.; Hawkins, H.S. Agricultural Extension; Wiley: Blackwell, OK, USA, 1996; ISBN 0-632-04053-X. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, Y.; Parolin, B.; Fan, X. New Professional Farmers’ Training (NPFT): A Multivariate Analysis of Farmers’ Participation in Lifelong Learning in Shaanxi, China. Int. Rev. Educ. 2019, 65, 579–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F. Exploring Mediating Factors between Agricultural Training and Farmers’ Adoption of Drip Fertigation System: Evidence from Banana Farmers in China. Water 2021, 13, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- People’s Daily Online. “New Agricultural Entrepreneurs” Return to Hometowns to Pursue Dreams and Jointly Paint a New Picture of Rural Revitalization. 2024. Available online: http://finance.people.com.cn/n1/2024/0215/c1004-40177784.html (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Oi, J.C. State and Peasant in Contemporary China: The Political Economy of Village Government; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 1989; Volume 30, ISBN 0-520-91189-X. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Li, H.; Cao, X.; Cao, A.; Huang, M. Effect of Agricultural Subsidies on the Use of Chemical Fertilizer. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Wan, J.-Y.; Wang, C. Agricultural Subsidy with Capacity Constraints and Demand Elasticity. Agric. Econ. 2015, 61, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wu, K.-J.; Tseng, M.-L. Exploring a Novel Agricultural Subsidy Model with Sustainable Development: A Chinese Agribusiness in Liaoning Province. Sustainability 2016, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, T.; Zilberman, D.; Gil, J.M. Farms’ Technical Inefficiencies in the Presence of Government Programs. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2008, 52, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Meng, T.; Hou, Y.; Huang, X.; Oenema, O. Which Policy Is Preferred by Crop Farmers When Replacing Synthetic Fertilizers by Manure? A Choice Experiment in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuzhou Municipal Bureau of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (The People’s Government of Anhui Province). Notice on Printing and Issuing the Implementation Plan for One-Time Subsidy Funds for Actual Grain-Planting Farmers in 2022. 2022. Available online: https://nyncj.chuzhou.gov.cn/public/2681513/1110120487.html (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- The Paper (Shanghai United Media Group). Farmer Sentenced for Defrauding Agricultural Special Subsidy Funds by Fabricating Projects. 2022. Available online: https://m.thepaper.cn/baijiahao_21427671 (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Yang, D.; Liu, K.; Zhou, Z. Study on regional economic development disparity and its evolution between southern and northern China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2018, 33, 1083–1092. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, K.A.; Dobson, A.D.M.; Kroschel, J.; Natarajan, B.; Orlandini, S.; Tonnang, H.E.; Valdivia, C. The Effects of Climate Variability and the Color of Weather Time Series on Agricultural Diseases and Pests, and on Decisions for Their Management. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 170, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Descriptions | Mean | S.D. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmers’ green production behavior (GPB) | farmland pollution control and remediation, deep plowing and deep tillage of soil, pest and disease prevention and control, and pesticide packaging recycling: The number of adoptions exceeds the average of the four actions, No = 0; Yes = 1 | 0.473 | 0.496 |
| Embedded social capital (ESC) | Do you volunteer to vote in the village committee election or are you mobilized to participate: 1 = passive participation; 2 = Take the initiative, because there is a gift; 3 = Active participation, even without gifts | 2.554 | 0.774 |
| How many members of your family have worked in agriculture(people) | 1.506 | 1.005 | |
| Your satisfaction with the village-style civilization: 1 = very dissatisfied; 2 = less satisfied; 3 = general; 4 = more satisfied; 5 = Very satisfied | 4.124 | 0.732 | |
| Disembedded social capital (DSC) | Education or training in agricultural technology: No = 0; Yes = 1 | 0.431 | 0.495 |
| How many members of your family have worked outside the farm(people) | 1.352 | 1.112 | |
| Whether you are a business owner: No = 0; Yes = 1 | 0.076 | 0.266 | |
| Agricultural support and protection subsidies (AS) | Planting subsidies (10,000 CNY) | 0.210 | 1.105 |
| Household head’s educational attainment (HHEA) | The number of years of education for the head of household | 7.435 | 3.780 |
| The health condition of the household head (HHHC) | Self-perceived health status of the head of household: 1 = incapacity to work; 2 = difference; 3 = medium; 4 = good; 5 = Excellent | 3.626 | 1.438 |
| Permanent resident population of the household (HHPRP) | How many people live in your family (6 months or more a year) | 3.033 | 1.565 |
| Age of family members (FMA) | Average age of family members | 53.331 | 13.927 |
| Educational attainment of family members (FMEA) | Family members average years of education | 7.196 | 2.893 |
| Annual household income (AHI) | Take logarithm of total annual household income | 1.841 | 4.433 |
| Farmland scale (FS) | Total farmland land operation area (mu) | 15.988 | 75.113 |
| Agricultural socialized services (ASSs) | agricultural socialized machinery operation service fee (yuan) | 87.289 | 327.380 |
| Ecologically livable environment (ELE) | Your satisfaction with the ecological livability of the village: 1 = very dissatisfied; 2 = less satisfied; 3 = general; 4 = more satisfied; 5 = Very satisfied | 3.294 | 1.419 |
| Rural living environment (RLE) | Do you know about the improvement of the rural living environment?: 1 = Never heard of it; 2 = Have heard of it but don’t know much; 3 = Know a little about it; 4 = Know it relatively well; 5 = Know it very well | 2.774 | 1.364 |
| Variables | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| RLE | 4.62 | 0.2166 |
| HHHC | 4.24 | 0.2357 |
| ELE | 4.01 | 0.2493 |
| AS | 1.71 | 0.5846 |
| FS | 1.68 | 0.5953 |
| HHEA | 1.39 | 0.7183 |
| FMEA | 1.38 | 0.7258 |
| HHPRP | 1.32 | 0.7589 |
| DSC | 1.29 | 0.7772 |
| FMA | 1.28 | 0.7789 |
| AHI | 1.14 | 0.8799 |
| ESC | 1.13 | 0.8814 |
| ASSs | 1.04 | 0.9629 |
| Mean VIF | 2.02 |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Marginal Effect | Coefficient | Marginal Effect | |
| ESC | 0.527 *** | 0.121 *** | 0.461 *** | 0.096 *** |
| (0.108) | (0.024) | (0.115) | (0.023) | |
| DSC | 0.633 *** | 0.145 *** | 0.637 *** | 0.132 *** |
| (0.104) | (0.022) | (0.126) | (0.025) | |
| HHEA | 0.056 | 0.012 | ||
| (0.080) | (0.017) | |||
| HHHC | 0.023 | 0.005 | ||
| (0.047) | (0.010) | |||
| HHPRP | −0.130 * | −0.027 * | ||
| (0.075) | (0.016) | |||
| FMA | −0.020 | −0.004 | ||
| (0.074) | (0.015) | |||
| FMEA | −0.111 | −0.023 | ||
| (0.081) | (0.017) | |||
| AHI | 0.027 | 0.006 | ||
| (0.059) | (0.012) | |||
| FS | 0.004 | 0.001 | ||
| (0.003) | (0.001) | |||
| ASSs | 1.551 *** | 0.322 *** | ||
| (0.267) | (0.049) | |||
| ELE | 0.045 | 0.009 | ||
| (0.050) | (0.010) | |||
| RLE | 0.034 | 0.007 | ||
| (0.052) | (0.011) | |||
| Constant | −0.249 *** | −0.538 * | ||
| (0.064) | (0.315) | |||
| N | 1054 | 1054 | ||
| Pseudo R2 | 0.0493 | 0.1232 | ||
| Prob > chi2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | ||
| Variables | Limiting Samples | Replacing Models |
|---|---|---|
| Model 3 | Model 4 | |
| ESC | 0.381 *** | 0.289 *** |
| (0.138) | (0.070) | |
| DSC | 0.627 *** | 0.402 *** |
| (0.148) | (0.076) | |
| Control variable | controlled | controlled |
| Constant | −0.504 | −0.336 * |
| (0.357) | (0.190) | |
| N | 775 | 1054 |
| Pseudo R2 | 0.1148 | 0.1181 |
| Prob > chi2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Variables | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Marginal Effect | Coefficient | Marginal Effect | Coefficient | Marginal Effect | |
| ESC | 0.440 *** | 0.091 *** | 0.353 *** | 0.073 *** | 0.438 *** | 0.090 *** |
| (0.115) | (0.023) | (0.120) | (0.024) | (0.115) | (0.023) | |
| DSC | 0.601 *** | 0.124 *** | 0.598 *** | 0.123 *** | 0.655 *** | 0.135 *** |
| (0.126) | (0.025) | (0.127) | (0.026) | (0.134) | (0.027) | |
| AS | 0.688 ** | 0.142 ** | 0.615 ** | 0.126 ** | 0.911 *** | 0.187 *** |
| (0.315) | (0.064) | (0.295) | (0.060) | (0.348) | (0.071) | |
| ESC×AS | 0.994 ** | 0.204 ** | ||||
| (0.484) | (0.098) | |||||
| DSC×AS | −0.402 | −0.083 | ||||
| (0.336) | (0.069) | |||||
| Control variable | controlled | controlled | controlled | |||
| Constant | −0.583 * | −0.584 * | −0.585 * | |||
| (0.318) | (0.319) | (0.318) | ||||
| N | 1054 | 1054 | 1054 | |||
| Pseudo R2 | 0.1289 | 0.1316 | 0.1299 | |||
| Prob > chi2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Ning, A. The Impact of Social Capital on Farmers’ Green Production Behavior: Moderation Effects Based on Agricultural Support and Protection Subsidies. Land 2025, 14, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112123
Zhou Z, Ning A. The Impact of Social Capital on Farmers’ Green Production Behavior: Moderation Effects Based on Agricultural Support and Protection Subsidies. Land. 2025; 14(11):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112123
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zhuoyi, and Aifeng Ning. 2025. "The Impact of Social Capital on Farmers’ Green Production Behavior: Moderation Effects Based on Agricultural Support and Protection Subsidies" Land 14, no. 11: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112123
APA StyleZhou, Z., & Ning, A. (2025). The Impact of Social Capital on Farmers’ Green Production Behavior: Moderation Effects Based on Agricultural Support and Protection Subsidies. Land, 14(11), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112123







