X-SDD: A New Benchmark for Hot Rolled Steel Strip Surface Defects Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a hot-rolled steel strip defect dataset for strip surface defect classification, which is named Xsteel Surface Defect Dataset (X-SDD) and contains seven typical hot-rolled steel strip defects with 1360 defect images;
- We apply RepVGG algorithms and spatial attention (RepVGG+SA) to classify the defects of X-SDD we proposed. The classification accuracy, Macro-Recall, Macro-Precision, and Macro-F1-score of the testset are 95.10%, 93.92%, 95.16%, 93.25%, respectively;
- We employ a variety of different algorithms such as ResNet, VGG, MobileNet etc. to verify the effectiveness of the dataset X-SDD and algorithm RepVGG+SA. The comparison of test results demonstrate that the RepVGG+SA we proposed achieves the best performance in several metrics.
2. Related Work
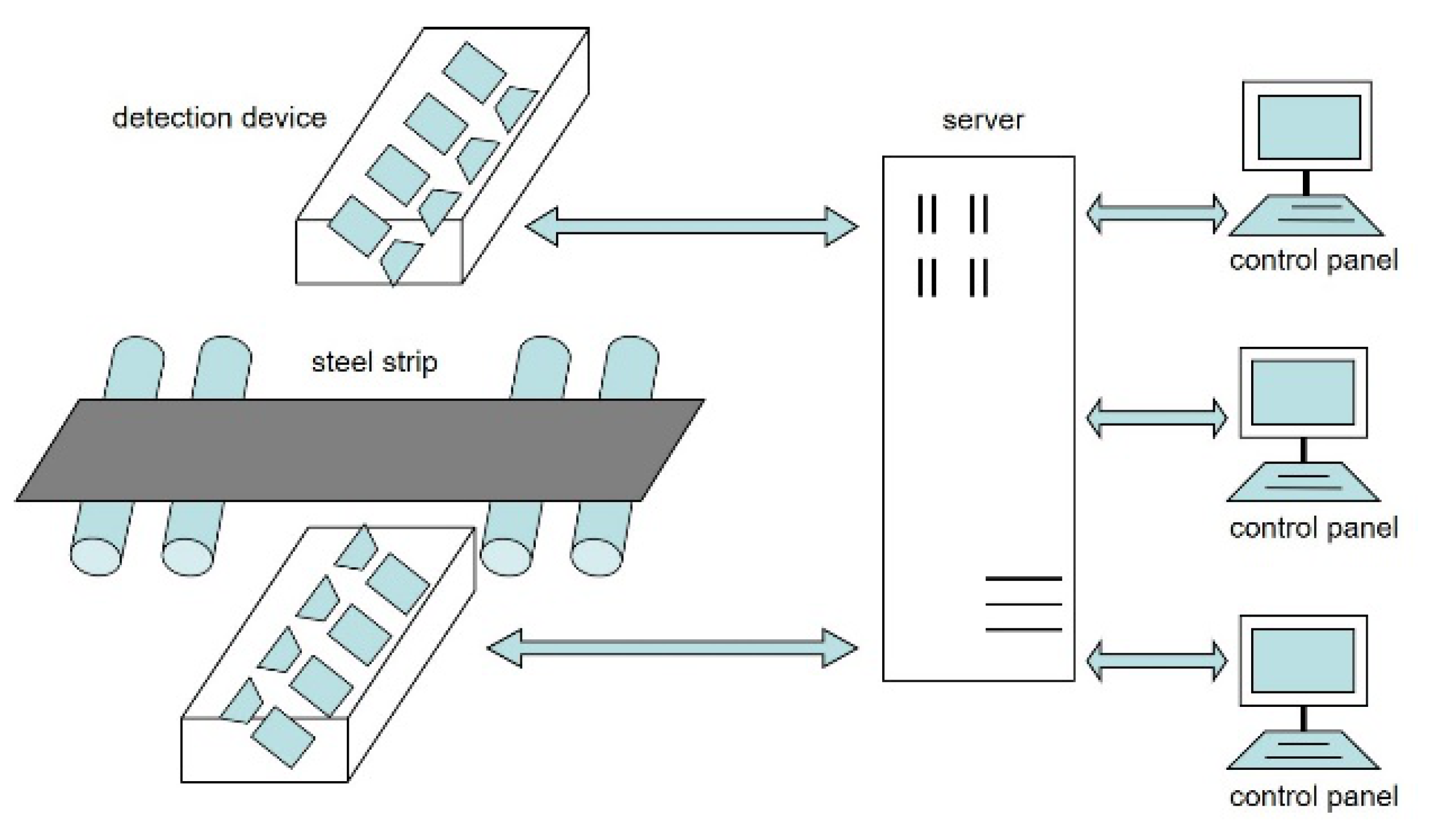
3. Introduction to Datasets
3.1. The Xsteel Surface Defect Dataset
3.2. The Comparison between Xsteel Surface Defect Dataset and NEU Surface Defect Database
4. Methodology
4.1. Introduction of RegVGG Algorithom
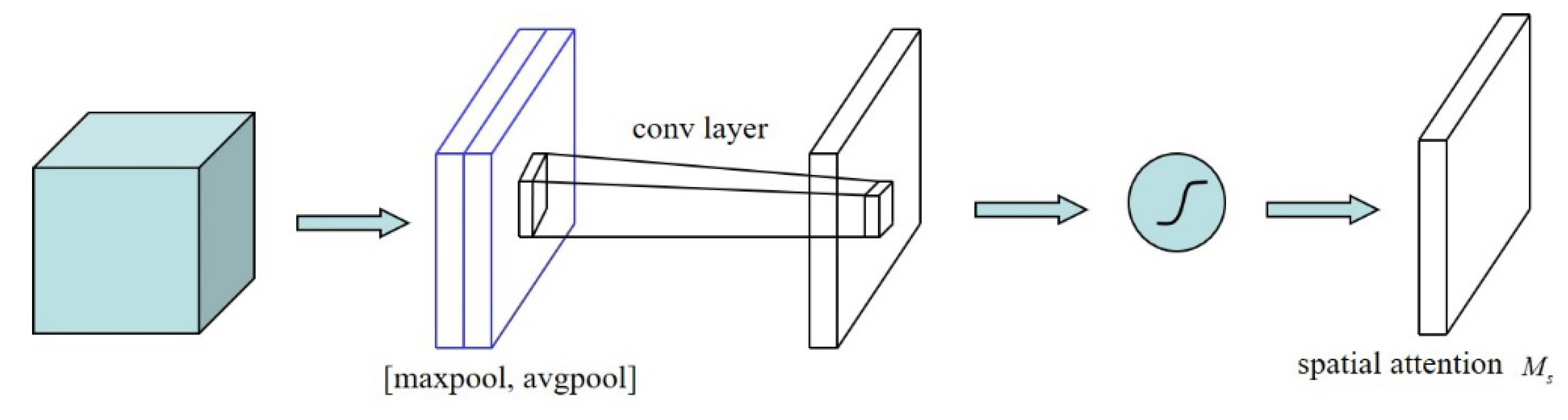
4.2. Introduction of Spatial Attention Mechanism
4.3. Introduction of Spatial Attention Mechanism
5. Experiments
5.1. Experimental Environment
5.2. Experimental Results
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aldunin, A. Development of method for calculation of structure parameters of hot-rolled steel strip for sheet stamping. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2017, 52, 737–740. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, K. Mechanical Properties Prediction for Hot Rolled Alloy Steel Using Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47068–47078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Das, A.K. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of Co-SiC tungsten inert gas cladded coating on 304 stainless steel. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2020, 24, 591–604. [Google Scholar]
- Afanasieva, L.E.; Ratkevich, G.V.; Ivanova, A.I.; Novoselova, M.V.; Zorenko, D.A. On the Surface Micromorphology and Structure of Stainless Steel Obtained via Selective Laser Melting. J. Surf. Investig. X-Ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2018, 12, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromov, V.E.; Gorbunov, S.V.; Ivanov, Y.F.; Vorobiev, S.V.; Konovalov, S.V. Formation of surface gradient structural-phase states under electron-beam treatment of stainless steel. J. Surf. Investigation. X-Ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2011, 5, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Fang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.; Ai, J.; Yang, C.; Simpson, O. Surface Defect Classification for Hot-Rolled Steel Strips by Selectively Dominant Local Binary Patterns. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 23488–23499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.W.; Khalid, F.; Halin, A.A.; Abdullah, L.N.; Darwish, S.H. Surface defects classification of hot-rolled steel strips using multi-directional shearlet features. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youkachen, S.; Ruchanurucks, M.; Phatrapomnant, T.; Kaneko, H. Defect Segmentation of Hot-rolled Steel Strip Surface by using Convolutional Auto-Encoder and Conventional Image processing. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference of Information and Communication Technology for Embedded Systems (IC-ICTES), Bangkok, Thailand, 25–27 March 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenetskiy, P.; Alkapov, R.; Vetoshkin, N.; Chulkevich, R.; Napolskikh, I.; Poponin, O. Real-time system for automatic cold strip surface defect detection. FME Trans. 2019, 47, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, I.; Koinov, T. Quality Control system for a hot-rolled metal surface. Frat. Ed Integrità Strutt. 2016, 10, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severstal is Mastering the Production of Video Inspection Systems for Rolled Surfaces. Available online: https://metallurgprom.org/en/press-releases/4952-severstal-osvaivaet-izgotovlenie-sistem-videoinspekcii-poverhnosti-prokata.html (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Kim, C.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, G.B.; Joo, W.J. Classification of surface defect on steel strip by KNN classifier. J. Korean Soc. Precis. Eng. 2006, 23, 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Pravin, M.C.; Sathyabama, B.; Mareeswari, M. DWT Based LCP Features for the Classification of Steel Surface Defects in SEM Images with KNN Classifier. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 10. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2792637 (accessed on 17 April 2021).
- Zaghdoudi, R.; Seridi, H.; Boudiaf, A. Multiple classifier combination for steel surface inspection. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Informatics and Applied Mathematics, IAM 2019, Guelma, Algeria, 24–25 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, K.; Zhang, X. Classification technology for automatic surface defects detection of steel strip based on improved BP algorithm. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Natural Computation, Tianjian, China, 14–16 August 2009; pp. 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Amid, E.; Aghdam, S.R.; Amindavar, H. Enhanced performance for support vector machines as multi-class classifiers in steel surface defects detection. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 6, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Schleif, F.M.; Tino, P. Indefinite core vector machine. Pattern Recogn. 2017, 71, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Jiang, M.; Li, G.; Xie, L.; Yi, L. An evolutionary classifier for steel surface defects with small sample set. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2017, 2017, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Wu, C.; Chu, M. Steel surface defect classification using multiple hyper-spheres support vector machine with additional information. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2018, 172, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Xu, D. Twin support vector hypersphere (TSVH) classifier for pattern recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikalp, H. Best fitting hyperplanes for classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, K.; Xu, J. An improved MB-LBP defect recognition approach for the surface of steel plates. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classi-fication with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Curran Associates Inc.: Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, LasVegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van, D.M.L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Lin, M.X.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference onComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Wey, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Yan, Y. Micro Surface defect detection method for silicon steel strip based on saliency convex active contour model. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 429094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Song, K.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Yan, Y.; Meng, Q. PGA-Net: Pyramid Feature Fusion and Global Context Attention Network for Automated Surface Defect Detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2020, 16, 7448–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Song, K.; Meng, Q.; Yan, Y. An End-to-end Steel Surface Defect Detection Approach via Fusing Multiple Hierarchical Features. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Song, K.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Yan, Y. Unified Detection Method of Aluminium Profile Surface Defects: Common and Rare Defect Categories. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 126, 105936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, X.; Yan, X. A semi-supervised convolutional neural network-based method for steel surface defect recognition. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Fang, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y. Automated Visual Defect Detection for Flat Steel Surface: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 626–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Analysis the Causes of Scale on Hot Rolled Strips & Its Prevention Measures; Xinjiang Bayi Iron & Steel Stock Co., Ltd.: Ürümqi, China, 2009; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Han, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J. RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets Great Again. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.03697. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Konovalenko, I.; Maruschak, P.; Brezinová, J.; Viňáš, J.; Brezina, J. Steel Surface Defect Classification Using Deep Residual Neural Network. Metals 2020, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]






| Model | Accuary | Macro-Recall | Macro-Precision | Macro-F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EspNet-v2 | 89.95% | 84.19% | 88.28% | 84.28% |
| GhostNet | 88.72% | 87.87% | 86.93% | 87.07% |
| ShuffleNet | 87.50% | 85.84% | 84.83% | 84.68% |
| SqueezeNet | 91.42% | 83.21% | 90.36% | 84.15% |
| Xception | 90.44% | 87.39% | 89.41% | 88.25% |
| VGG16 | 92.65% | 90.46% | 91.70% | 90.92% |
| ResNet50 | 93.87% | 89.41% | 93.45% | 90.02% |
| ResNet101 | 87.01% | 88.30% | 88.18% | 87.05% |
| ResNet152 | 92.16% | 89.41% | 91.41% | 89.92% |
| RepVGG_B1g2 | 88.97% | 82.04% | 90.79% | 81.58% |
| RepVGG_B3g4 | 91.67% | 85.28% | 88.46% | 84.94% |
| RepVGG_B3g4+SA(ours) | 95.10% | 93.92% | 95.16% | 93.25% |
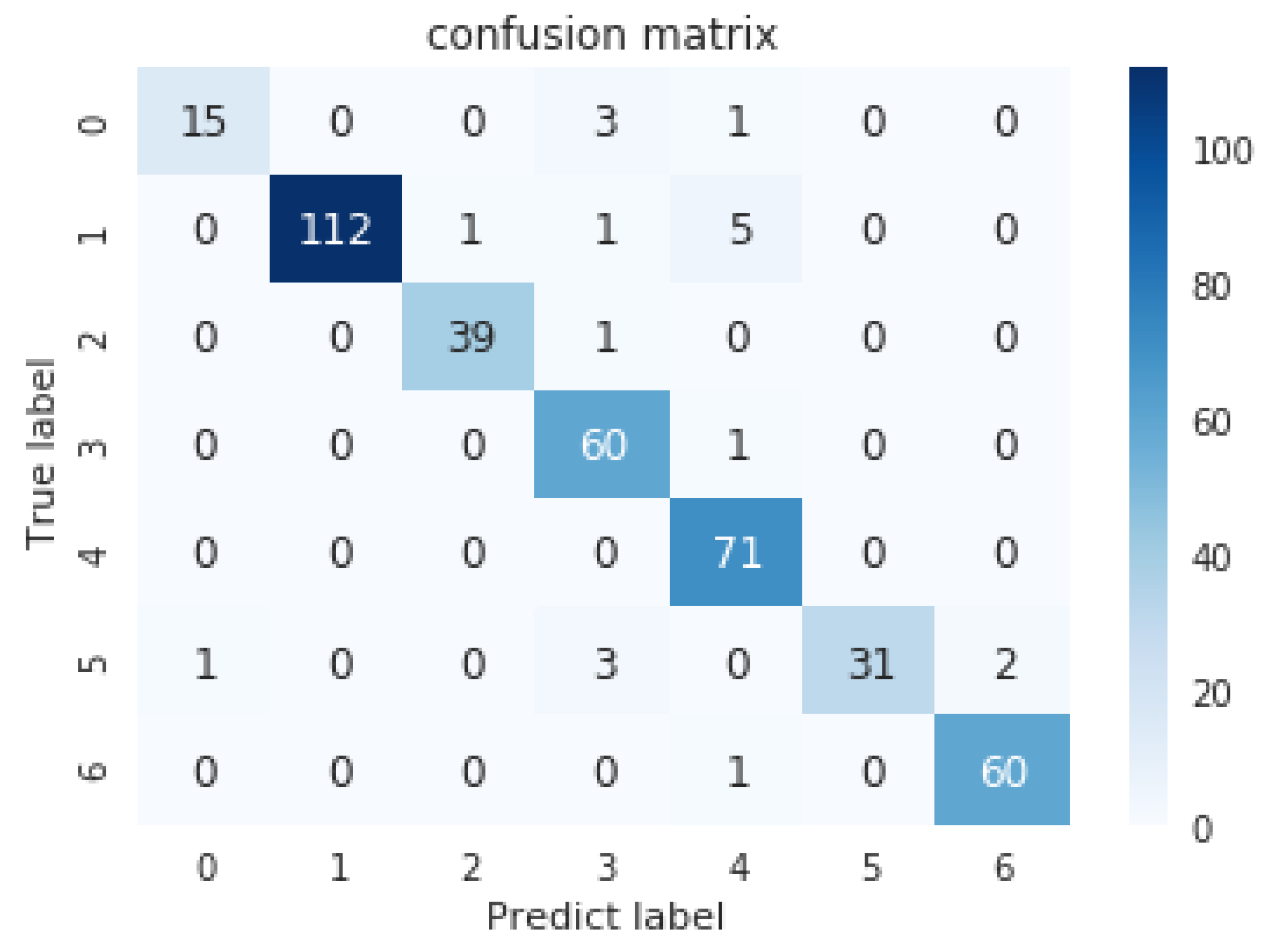
| Defect Category/Indicators | Right | Error | Total Number | Accuary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oxide scale of plate system | 15 | 4 | 19 | 78.95% |
| red iron sheet | 112 | 7 | 119 | 94.12% |
| scratches | 39 | 1 | 40 | 97.50% |
| inclusion | 60 | 1 | 61 | 98.36% |
| finishing roll printing | 71 | 0 | 71 | 100% |
| iron sheet ash | 31 | 6 | 37 | 83.78% |
| oxide scale of temperature system | 60 | 1 | 61 | 98.36% |
| total | 388 | 20 | 408 | 95.10% |
| Model | Params (M) | MACs (G) |
|---|---|---|
| EspNet-v2 | 0.627 | 0.090 |
| GhostNet | 3.127 | 0.208 |
| ShuffleNet | 0.840 | 0.129 |
| SqueezeNet | 0.722 | 0.720 |
| Xception | 20.822 | 4.617 |
| VGG16 | 134.289 | 15.480 |
| ResNet50 | 23.522 | 4.109 |
| ResNet101 | 42.515 | 7.832 |
| ResNet152 | 58.158 | 11.557 |
| RepVGG_B1g2 | 43.748 | 9.815 |
| RepVGG_B3g4 | 81.282 | 17.888 |
| RepVGG_B3g4+SA(ours) | 83.825 | 17.892 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Gao, X.; Luo, L. X-SDD: A New Benchmark for Hot Rolled Steel Strip Surface Defects Detection. Symmetry 2021, 13, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13040706
Feng X, Gao X, Luo L. X-SDD: A New Benchmark for Hot Rolled Steel Strip Surface Defects Detection. Symmetry. 2021; 13(4):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13040706
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xinglong, Xianwen Gao, and Ling Luo. 2021. "X-SDD: A New Benchmark for Hot Rolled Steel Strip Surface Defects Detection" Symmetry 13, no. 4: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13040706
APA StyleFeng, X., Gao, X., & Luo, L. (2021). X-SDD: A New Benchmark for Hot Rolled Steel Strip Surface Defects Detection. Symmetry, 13(4), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13040706






