Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Identification and Search Method
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.2.1. Types of Studies
2.2.2. Participants
2.2.3. Interventions
2.2.4. Outcomes
2.2.5. Data Extractions
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
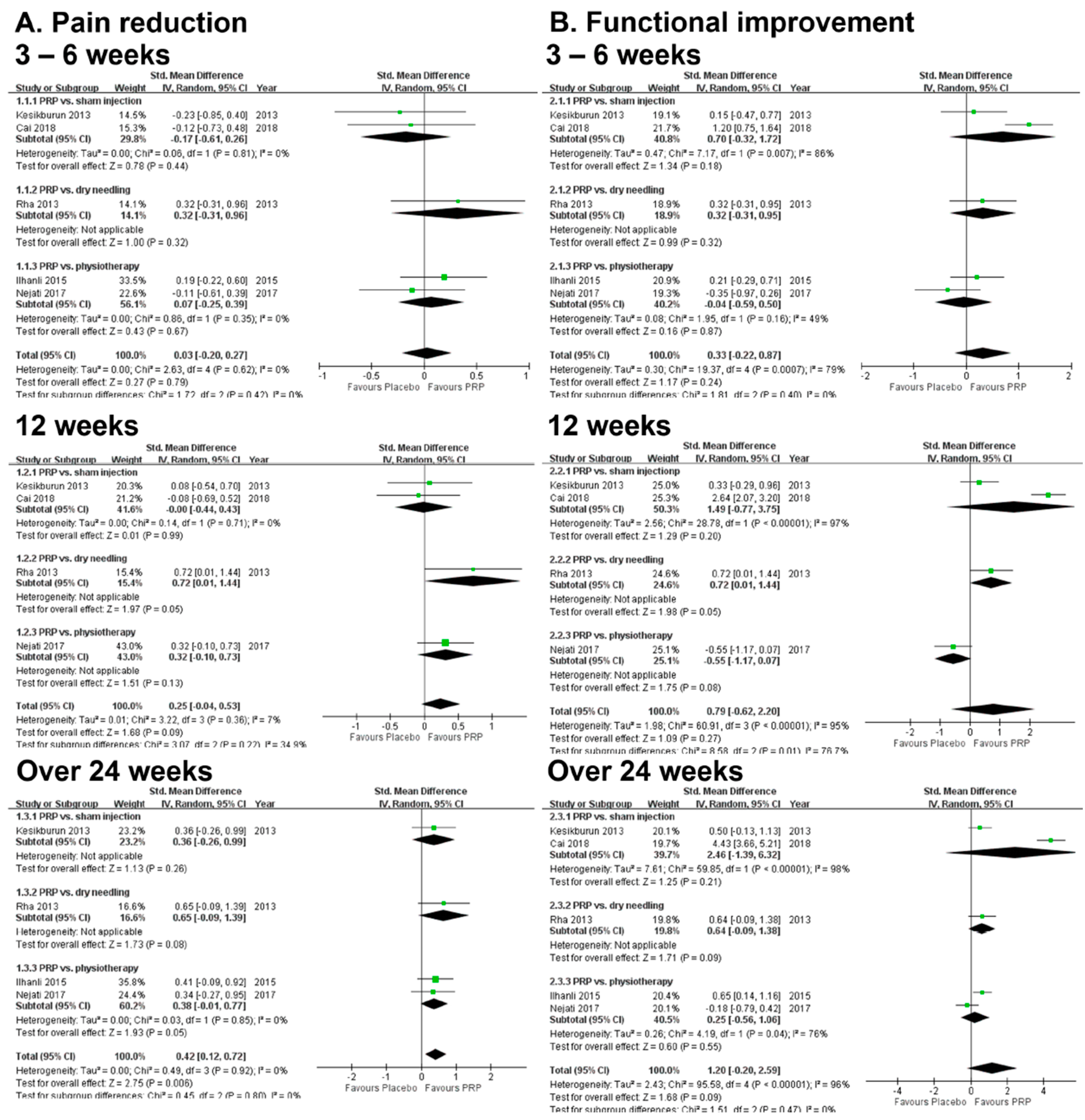
3.3. Results of Meta-Analysis: Primary Outcome (Pain Reduction)
3.4. Results of Meta-Analysis: Secondary Outcome (Functional Improvement)
3.5. Meta-Regression
3.6. Adverse Effect
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PRP | Platelet-rich plasma |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Chard, M.D.; Cawston, T.E.; Riley, G.P.; Gresham, G.A.; Hazleman, B.L. Rotator cuff degeneration and lateralepicondylitis: A comparative histological study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1994, 53, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, E.; Kuhn, M. Exercise in the treatment of rotator cuff impingement: A systematic review and a synthesized evidence-based rehabilitation protocol. J. Shoulder Elbow. Surg. 2009, 18, 138–160. [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood, C.; Ashton, J.; Chance-Larsen, K.; May, S.; Sturrock, B. Exercise for rotator cuff tendinopathy: A systematic review. Physiotherapy 2012, 98, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desjardins-Charbonneau, A.; Roy, J.S.; Dionne, C.E.; Fremont, P.; MacDermid, J.C.; Desmeules, F. The efficacy of manual therapy for rotator cuff tendinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 45, 330–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steuri, R.; Sattelmayer, M.; Elsig, S.; Kolly, C.; Tal, A.; Taeymans, J.; Hilfiker, R. Effectiveness of conservative interventions including exercise, manual therapy and medical management in adults with shoulder impingement: A systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coombes, B.K.; Bisset, L.; Vicenzino, B. Efficacy and safety of corticosteroid injections and other injections for management of tendinopathy: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2010, 376, 1751–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei-Dan, O.; Carmont, M.R. The Role of Platelet-rich Plasma in Rotator Cuff Repair. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2011, 19, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.L.; Zhou, A.G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arthroscopy 2017, 33, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, J.; Bulsara, M.; Zheng, M.H. The Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Tendinopathy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rha, D.W.; Park, G.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, M.T.; Lee, S.C. Comparison of the therapeutic effects of ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injection and dry needling in rotator cuff disease: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2013, 27, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesikburun, S.; Tan, A.K.; Yilmaz, B.; Yasar, E.; Yazicioglu, K. Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: A randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 2609–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhanli, I.; Guder, N.; Gul, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment With Physical Therapy in Chronic Partial Supraspinatus Tears. Iran. Red. Crescent Med. J. 2015, 17, e23732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nejati, P.; Ghahremaninia, A.; Naderi, F.; Gharibzadeh, S.; Mazaherinezhad, A. Treatment of Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: Platelet-Rich Plasma or Exercise Therapy? A Randomized Controlled Trial. Orthop J. Sports Med. 2017, 5, 2325967117702366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liao, B.; Song, Z.; Xiao, T.; Zhu, P. Sodium Hyaluronate and Platelet-Rich Plasma for Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.T.; Chiang, C.F.; Wu, C.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Tu, Y.K.; Wang, T.G. Comparative Effectiveness of Injection Therapies in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review, Pairwise and Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brox, J.I.; Staff, P.H.; Ljunggren, A.E.; Brevik, J.I. Arthroscopic surgery compared with supervised exercises in patients with rotator cuff disease (stage II impingement syndrome). BMJ 1993, 307, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA Extension Statement for Reporting of Systematic Reviews Incorporating Network Meta-analyses of Health Care Interventions: Checklist and Explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis. J.S. Rotator cuff tendinopathy. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [Updated March 2011]; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fleiss, J.L. The statistical basis of meta-analysis. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1993, 2, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, A.; El-Sayed, M.; Gamal, O.; Ewes, W. Subacromial injection of autologous platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid for the treatment of symptomatic partial rotator cuff tears. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2016, 26, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.H.; El-Gzazzar, N.M.; El-Saadany, H.M.; El-Khouly, R.M. Ultrasound-guided injection of platelet rich plasma versus corticosteroidfor treatment of rotator cuff tendinopathy: Effect on shoulder pain, disability, range of motion and ultrasonographic findings. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2019, 41, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffulli, N.; Wong, J.; Almekinders, L.C. Types and epidemiology of tendinopathy. Clin. Sports Med. 2003, 22, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredson, H. Chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy: An update on research and treatment. Clin. Sports Med. 2003, 22, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.H. PRP Treatment Efficacy for Tendinopathy: A Review of Basic Science Studies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Zhang, C.; Lin, X.J. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in arthroscopic repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears: A meta-analysis. J. Shoulder Elbow. Surg. 2015, 24, 1852–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jones, I.A.; Park, C.; Vangsness, C.T., Jr. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Tendon and Ligament Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis With Bias Assessment. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 2020–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spargoli, G. Treatment of Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy as a Contractile Dysfunction. A Clinical Commentary. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2019, 14, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarrel, T.M.; Mall, N.A.; Lee, A.S.; Cole, B.J.; Butty, D.C.; Fortier, L.A. Considerations for the Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Orthopedics. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei-Dan, O.; Carmont, M.R.; Laver, L.; Mann, G.; Maffulli, N.; Nyska, M. Platelet-rich plasma or hyaluronate in the management of osteochondral lesions of the talus. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Reference | Study/LOE | Interventions | Inclusion Criteria | Number | Age | Symptom Duration | Injection/Interval | Rx dose/Guidance Method and Injection Location | Co-Interventions | Outcome Measure | Follow-Up Weeks | Adverse Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rha et al., 2013 [10] | RCT/ level 1 | PRP vs. dry needling | Supraspinatus tendon lesion (tendinosis or a partial tear) | 20/19 | 52.2/53.9 | 9.6/9.2 M | 2/4W | PRP: 3 mL of PRP(Prosys®) extracted from centrifuged 25 mL of patients’ blood Placebo: dry needling / Method: ultrasound guided; supraspinatous tendon | Self-exercise rehabilitation program | SPADI, ROM | 2W, 4W, 6W,12W, 24W | Pain lasting for few days |
| Kesikburun et al., 2013 [11] | RCT/ level 1 | PRP vs. sham injection | Rotator cuff tendinosis or partial tear diagnosed by MRI | 20/20 | 45.5/51.4 | 8.5/10 M | 1/NA | PRP: 5 mL of PRP (GPS III Platelet Separation System) extracted from centrifuged 54 mL of venous blood Placebo: 5 mL of saline / Method: ultrasound guided; subacromial | Exercise program (supervised by PT), then home program | VAS, SPADI, WORC, ROM | 3W, 6W, 12W, 24W, 1Y | Local pain lasting for few days |
| Ilhanli et al. 2015 [12] | RCT/ level 1 | PRP vs. physiotherapy | Supraspinatus partial tear diagnosed with MRI | 35/35 | 59.2/59.7 | 7.3/7.2 M | 3/1W | PRP: 6 mL of PRP extracted from 15 mL of peripheral blood PT: hot packing, ultrasound, TENS, ROM exercise, stretching and strengthening exercise /Method: Intra-articular injection | PT program after end of injections | ROM, VAS, DASH, BECK | End of the treatment, 12M | Pain |
| Nejati et al. 2017 [13] | RCT/ level 1 | PRP vs. physiotherapy | Subacromial impingement syndrome via clinical assessment and MRI | 22/20 | 52.5/53.9 | Not reported | 2/1M | PRP: 4 mL of PRP (Tubex Autotube System) extracted from centrifuged 25 mL of venous blood Exercise therapy: supervised and self ROM exercise and strengthening exercise /Method: ultrasound guided; torn or injured tendon and subacromial space | Nil | VAS, ROM, DASH, WORC, MRI findings | 1M, 3M, 6M | Not reported |
| Cai et al. 2018 [14] | RCT/ level 1 | PRP vs. sham injection | Partial-thickness rotator cuff tears diagnosed clinically and via MRI | 45/47 | 40.6/39.9 | 14.1/13.5W | 4/1W | PRP: 4 mL of PRP extracted from centrifuged 20 mL of autologous venous blood Placebo: 4 mL of saline /Method: ultrasound guided; subacromial injection | Nil | ASES, Constant score, VAS, AP tear size on MRI | 1M, 3M, 6M, 12M | Not reported |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, M.-T.; Wei, K.-C.; Wu, C.-H. Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040189
Lin M-T, Wei K-C, Wu C-H. Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(4):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Meng-Ting, Kuo-Chang Wei, and Chueh-Hung Wu. 2020. "Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Diagnostics 10, no. 4: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040189
APA StyleLin, M.-T., Wei, K.-C., & Wu, C.-H. (2020). Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diagnostics, 10(4), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040189





