The Past, Present, and Future in Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA)
Abstract
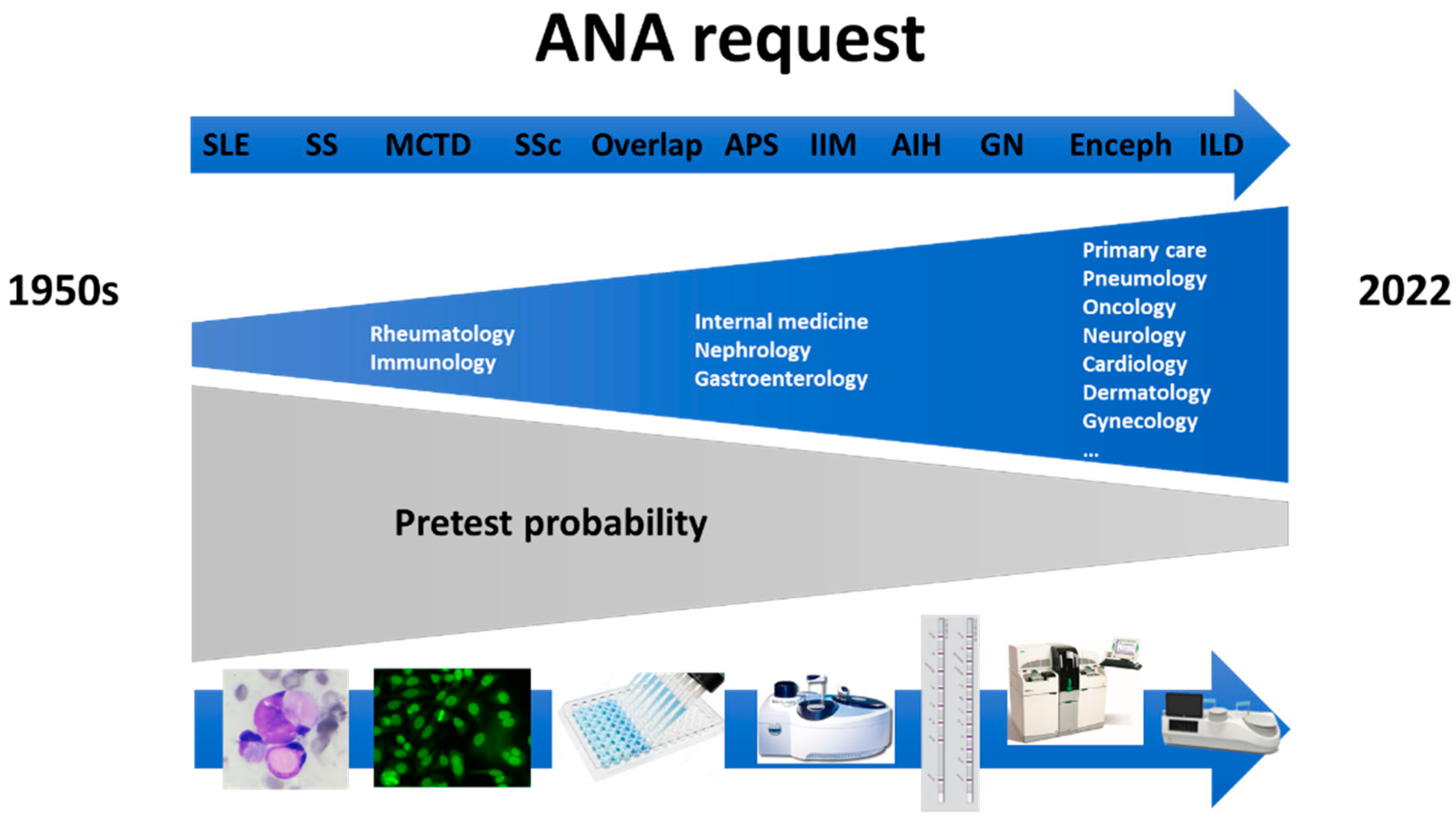
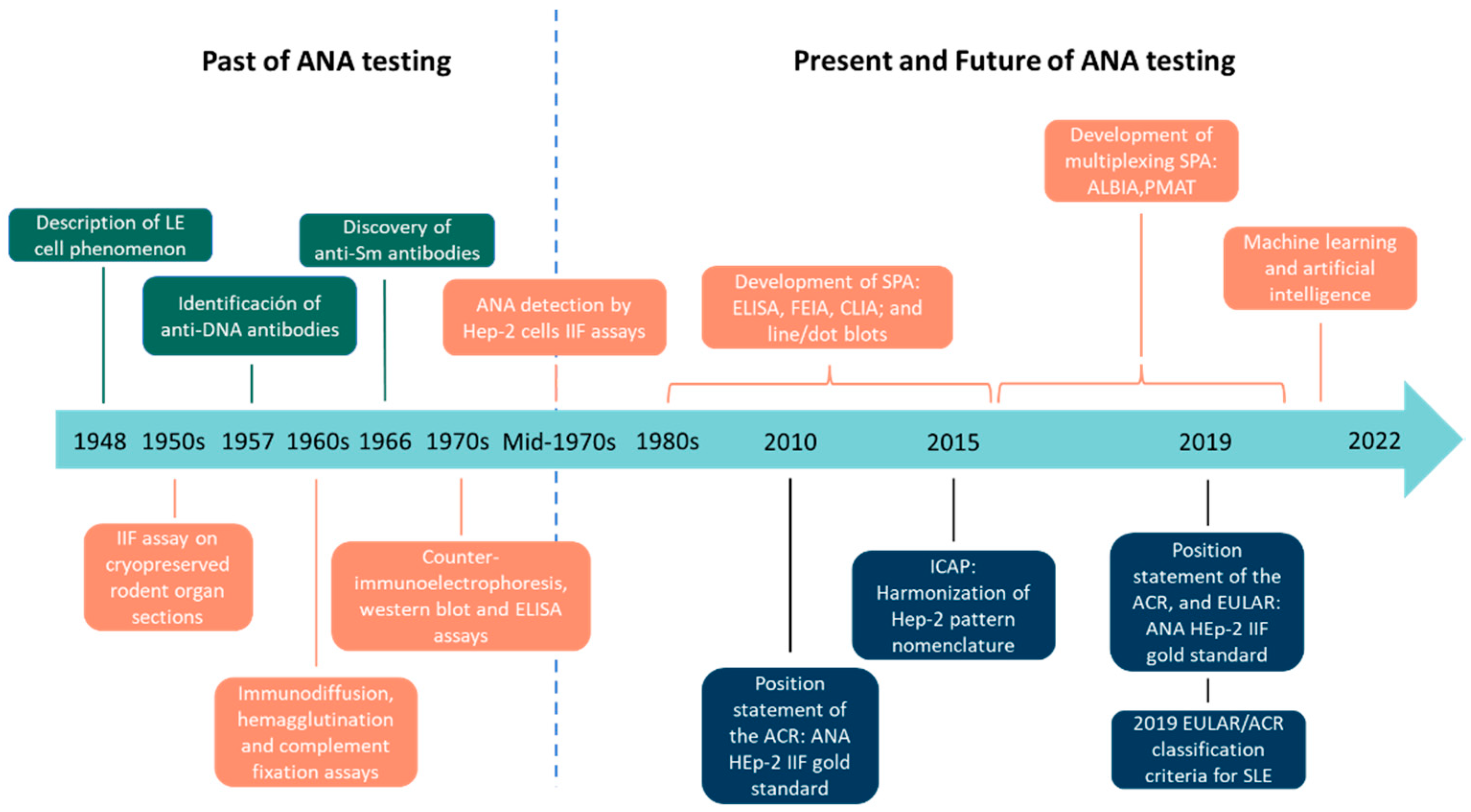
1. Introduction
2. Past of ANA Testing
3. Present of ANA Testing
3.1. Indirect Immunofluorescence (IIF) Assays Using HEp-2 Cells
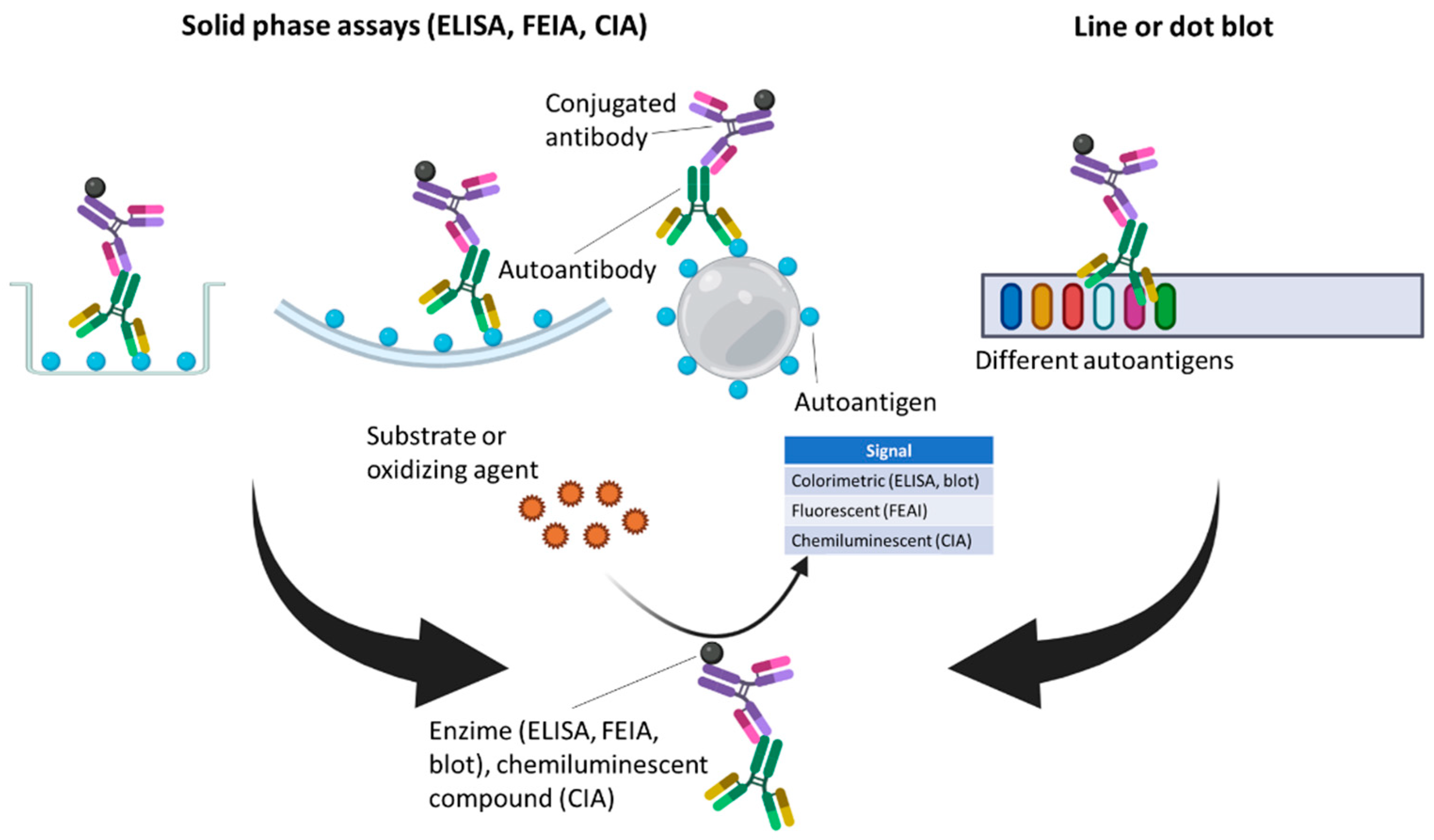
3.2. Solid-Phase Assays (SPAs)
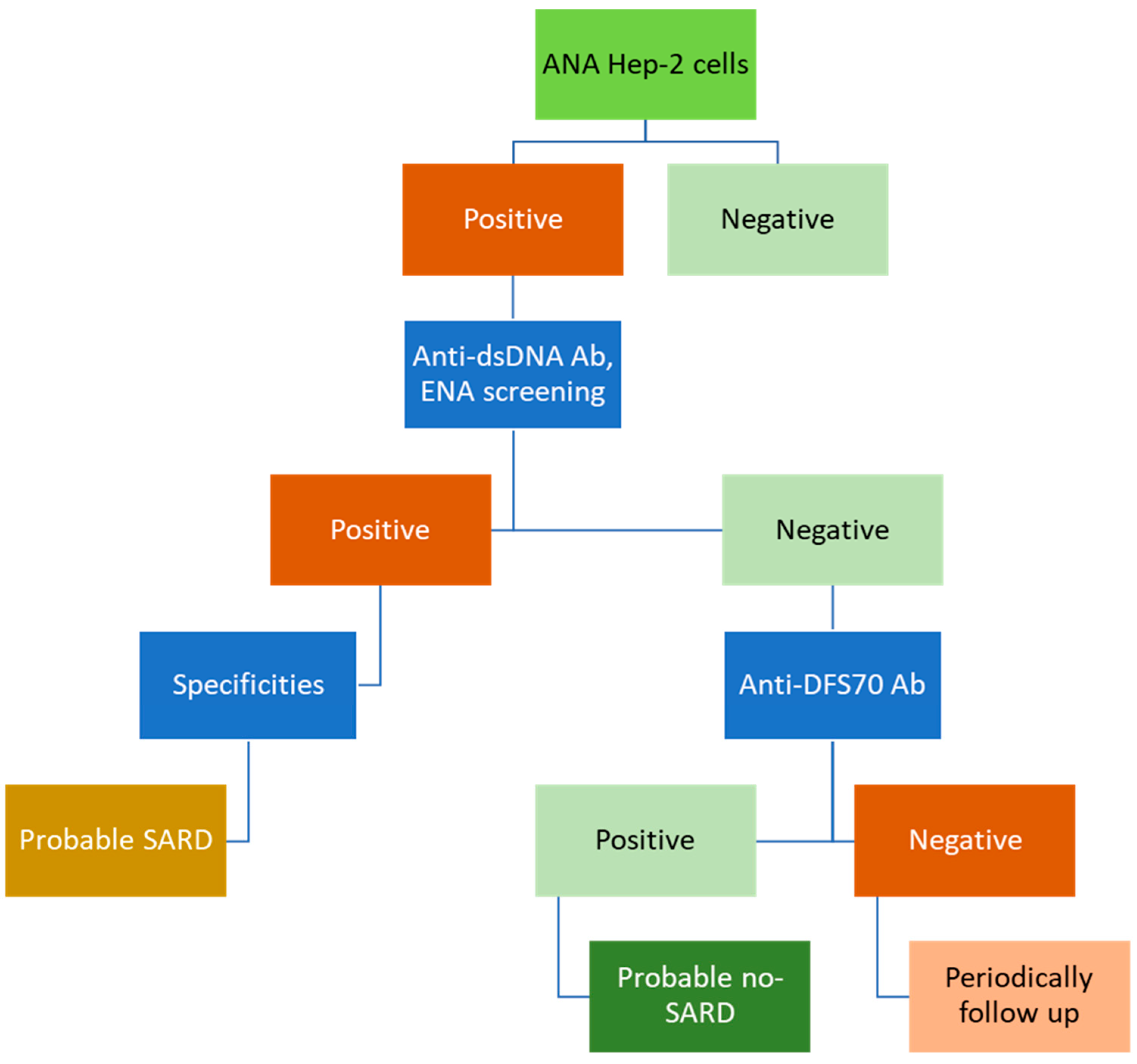
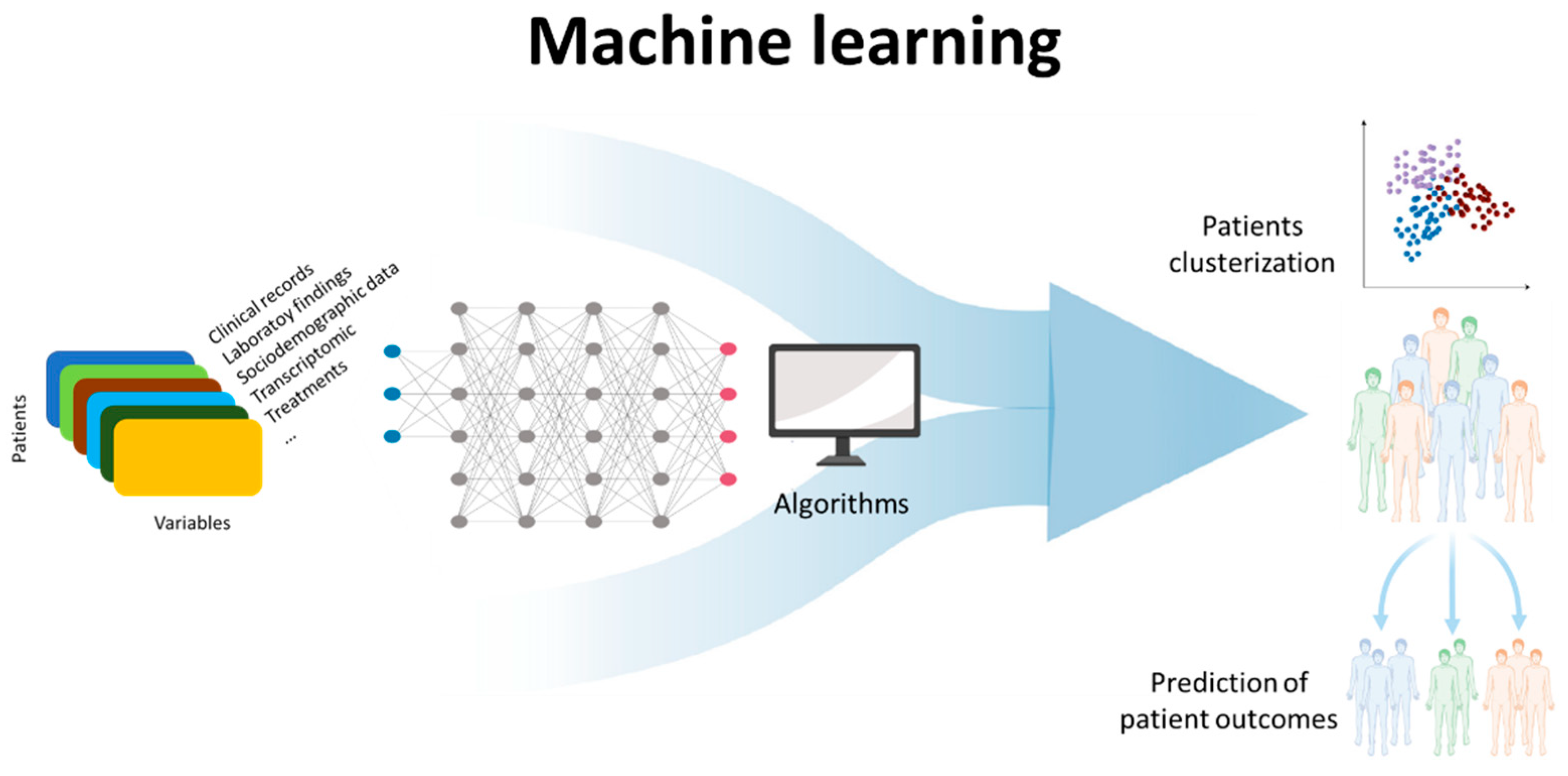
4. Future of ANA Testing
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hargraves, M.M.; Richmond, H.; Morton, R. Presentation of Two Bone Marrow Elements; the Tart Cell and the L.E. Cell. Proc. Staff. Meet. Mayo Clin. 1948, 23, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holborow, E.J.; Weir, D.M.; Johnson, G.D. A Serum Factor in Lupus Erythematosus with Affinity for Tissue Nuclei. Br. Med. J. 1957, 2, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, W.C.; Holman, H.R.; Deicher, H.; Kunkel, H.G. Complement Fixation with Cell Nuclei and DNA in Lupus Erythematosus. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1957, 96, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.M.; Kunkel, H.G. Characteristics of a Soluble Nuclear Antigen Precipitating with Sera of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. 1966, 96, 464–471, Erratum in: J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Fritzler, M.J. Autoantibody Testing: Procedures and Significance in Systemic Rheumatic Diseases. Methods Achiev. Exp. Pathol. 1986, 12, 224–260. [Google Scholar]
- Weller, T.H.; Coons, A.H. Fluorescent Antibody Studies with Agents of Varicella and Herpes Zoster Propagated in Vitro. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1954, 86, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, W.; Schuit, H.R.; Mandema, E.; Nienhuis, R.L.; Feltkamp, T.E.; Holborow, E.J.; Johnson, G.D. Comparative study for the detection of antinuclear factors with the fluorescent antibody technique. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1964, 23, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S. Variations in the Morphological Patterns of “Autoimmune” Nuclear Fluorescence. Lancet 1961, 277, 1203–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, H.G.; Tan, E.M. Autoantibodies and disease. Adv. Immunol. 1964, 4, 351–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.M.; Tan, E.M. Recent Progress in the Study of Autoantibodies to Nuclear Antigens. Hum. Pathol. 1978, 9, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.M.; Tan, E.M. Recent Advances in Laboratory Tests and the Significance of Autoantibodies to Nuclear Antigens in Systemic Rheumatic Diseases-PubMed. Clin. Lab. Med. 1986, 6, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, M.; Meroni, P.L.; Bossuyt, X.; Fritzler, M.J. Current Concepts and Future Directions for the Assessment of Autoantibodies to Cellular Antigens Referred to as Anti-Nuclear Antibodies. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 315179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, J.; Belmondo, T.; de Langhe, E.; Westhovens, R.; Poesen, K.; Hüe, S.; Blockmans, D.; Mahler, M.; Fritzler, M.J.; Bossuyt, X. Solid-phase assays versus Automated Indirect Immunofluorescence for Detection of Antinuclear Antibodies. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, X. Clinical Performance Characteristics of a Laboratory Test. A Practical Approach in the Autoimmune Laboratory. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 8, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Rheumatology Ad Hoc Committee on Immunologic Testing Guidelines. Guidelines for Immunologic Laboratory Testing in the Rheumatic Diseases: An Introduction. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 47, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didier, K.; Bolko, L.; Giusti, D.; Toquet, S.; Robbins, A.; Antonicelli, F.; Servettaz, A. Autoantibodies Associated With Connective Tissue Diseases: What Meaning for Clinicians? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaed, O.S.; Alamlih, L.I.; Al-Radideh, O.; Chandra, P.; Alemadi, S.; Al-Allaf, A.W. Clinical Utility of ANA-ELISA vs ANA-Immunofluorescence in Connective Tissue Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheer, P.; Agarwal, A.; Vishnu, V.Y. Antinuclear Antibodies in Neurology and Their Clinical Application. QJM Mon. J. Assoc. Physicians 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebode, M.; Weiler-Normann, C.; Liwinski, T.; Schramm, C. Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Liver Disease-Clinical and Diagnostic Relevance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Rheumatology. Position Statement Subject: Methodology of Testing for Antinuclear Antibodies. Available online: https://www.rheumatology.org/Practice/Clinical/Position/Position_Statements/ (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Pérez, D.; Gilburd, B.; Azoulay, D.; Shovman, O.; Bizzaro, N.; Shoenfeld, Y. Antinuclear Antibodies: Is the Indirect Immunofluorescence Still the Gold Standard or Should Be Replaced by Solid Phase Assays? Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orme, M.E.; Andalucia, C.; Sjölander, S.; Bossuyt, X. A Hierarchical Bivariate Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy to Provide Direct Comparisons of Immunoassays vs. Indirect Immunofluorescence for Initial Screening of Connective Tissue Diseases. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 59, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, X.; Claessens, J.; de Langhe, E.; Belmondo, T.; Westhovens, R.; Hue, S.; Poesen, K.; Blockmans, D.; Mahler, M.; Fritzler, M.J. Antinuclear Antibodies by Indirect Immunofluorescence and Solid Phase Assays. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, E65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzaro, N. Can Solid-Phase Assays Replace Immunofluorescence for ANA Screening? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.M.; Feltkamp, T.E.W.; Smolen, J.S.; Butcher, B.; Dawkins, R.; Fritzler, M.J.; Gordon, T.; Hardin, J.A.; Kalden, J.R.; Lahita, R.G.; et al. Range of Antinuclear Antibodies in “Healthy” Individuals. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashnina, I.A.; Krivolapova, I.M.; Fedotkina, T.V.; Ryabkova, V.A.; Chereshneva, M.V.; Churilov, L.P.; Chereshnev, V.A. Antinuclear Autoantibodies in Health: Autoimmunity Is Not a Synonym of Autoimmune Disease. Antibodies 2021, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Carballo, O.G.; Conrad, K.; Francescantonio, P.L.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; Garcia De La Torre, I.; Herold, M.; Klotz, W.; Cruvinel, W.D.M.; et al. Clinical Relevance of HEp-2 Indirect Immunofluorescent Patterns: The International Consensus on ANA Patterns (ICAP) Perspective. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mühlen, C.A.; Garcia-De La Torre, I.; Infantino, M.; Damoiseaux, J.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Carballo, O.G.; Conrad, K.; Francescantonio, P.L.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; Herold, M.; et al. How to Report the Antinuclear Antibodies (Anti-Cell Antibodies) Test on HEp-2 Cells: Guidelines from the ICAP Initiative. Immunol. Res. 2021, 69, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.K.L.; Damoiseaux, J.; Carballo, O.G.; Conrad, K.; de Melo Cruvinel, W.; Francescantonio, P.L.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; Garcia-De La Torre, I.; Herold, M.; Mimori, T.; et al. Report of the First International Consensus on Standardized Nomenclature of Antinuclear Antibody HEp-2 Cell Patterns 2014-2015. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.E.C.; Klotz, W.; Herold, M.; Conrad, K.; Rönnelid, J.; Fritzler, M.J.; von Mühlen, C.A.; Satoh, M.; Damoiseaux, J.; de Melo Cruvinel, W.; et al. International Consensus on Antinuclear Antibody Patterns: Definition of the AC-29 Pattern Associated with Antibodies to DNA Topoisomerase I. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irure-Ventura, J.; Rodríguez, C.; Vergara-Prieto, E.; Vargas, M.L.; Quirant, B.; Jurado, A.; Fernández-Pereira, L.; Martínez-Cáceres, E.; San José, M.; López-Hoyos, M. Rare Immunofluorescence Patterns of Autoantibodies on HEp-2 Cells Defined by ICAP Identify Different Autoimmune Diseases in the Absence of Associated Specificities: A Spanish Multicentre Study. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 3904–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.X.; Miller, J.S.; Zheng, S.G. An Updated Advance of Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaniv, G.; Twig, G.; Shor, D.B.A.; Furer, A.; Sherer, Y.; Mozes, O.; Komisar, O.; Slonimsky, E.; Klang, E.; Lotan, E.; et al. A Volcanic Explosion of Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Diversity of 180 Different Antibodies Found in SLE Patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irure-Ventura, J.; López-Hoyos, M. Disease Criteria of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE); the Potential Role of Non-Criteria Autoantibodies. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2022, 5, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stochmal, A.; Czuwara, J.; Trojanowska, M.; Rudnicka, L. Antinuclear Antibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: An Update. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 58, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, C.; Fritzler, M.J. Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: Unanswered Questions. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecoli, C.A.; Casciola-Rosen, L. An Update on Autoantibodies in Scleroderma. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Tanaka, S.; Ceribelli, A.; Calise, S.J.; Chan, E.K.L. A Comprehensive Overview on Myositis-Specific Antibodies: New and Old Biomarkers in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 52, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuhlmüller, B.; Schneider, U.; González-González, J.B.; Feist, E. Disease Specific Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Vulsteke, J.B.; Tseng, C.W.; Platteel, A.C.M.; Piette, Y.; Shovman, O.; Bonroy, C.; Hamann, D.; de Langhe, E.; Musset, L.; et al. Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Clinical Associations and Laboratory Evaluation by Mono- and Multispecific Immunoassays. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Beeck, K.O.; Vermeersch, P.; Verschueren, P.; Westhovens, R.; Mariën, G.; Blockmans, D.; Bossuyt, X. Detection of Antinuclear Antibodies by Indirect Immunofluorescence and by Solid Phase Assay. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, X.; de Langhe, E.; Borghi, M.O.; Meroni, P.L. Understanding and Interpreting Antinuclear Antibody Tests in Systemic Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmon-Levin, N.; Damoiseaux, J.; Kallenberg, C.; Sack, U.; Witte, T.; Herold, M.; Bossuyt, X.; Musset, L.; Cervera, R.; Plaza-Lopez, A.; et al. International Recommendations for the Assessment of Autoantibodies to Cellular Antigens Referred to as Anti-Nuclear Antibodies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Leuchten, N.; Johnson, S.R. New Criteria for Lupus. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuchten, N.; Hoyer, A.; Brinks, R.; Schoels, M.; Schneider, M.; Smolen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Daikh, D.; Dörner, T.; Aringer, M.; et al. Performance of Antinuclear Antibodies for Classifying Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Regression of Diagnostic Data. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, X.; Luyckx, A. Antibodies to Extractable Nuclear Antigens in Antinuclear Antibody-Negative Samples. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2426–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mahler, M.; Kessenbrock, K.; Szmyrka, M.; Takasaki, Y.; Garcia-De La Torre, I.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Hiepe, F.; Shun-Le, C.; von Mühlen, C.A.; Locht, H.; et al. International Multicenter Evaluation of Autoantibodies to Ribosomal P Proteins. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceribelli, A.; Fredi, M.; Taraborelli, M.; Cavazzana, I.; Franceschini, F.; Quinzanini, M.; Tincani, A.; Ross, S.J.; Chan, J.Y.F.; Pauley, B.A.; et al. Anti-MJ/NXP-2 Autoantibody Specificity in a Cohort of Adult Italian Patients with Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzler, M.J.; Choi, M.Y.; Mahler, M. The Antinuclear Antibody Test in the Diagnosis of Antisynthetase Syndrome and Other Autoimmune Myopathies. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.H.; Chung, M.H.; Park, Y.K.; Kwon, H.Y.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.S. Antinuclear Antibodies in Infectious Diseases. Infect. Dis. 2020, 52, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Dotan, A.; Fritzler, M.J.; Bogdanos, D.P.; Meroni, P.L.; Roggenbuck, D.; Goldman, M.; Landegren, N.; Bastard, P.; Shoenfeld, Y.; et al. Autoantibodies and SARS-CoV2 Infection: The Spectrum from Association to Clinical Implication: Report of the 15th Dresden Symposium on Autoantibodies. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 21, 103012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygiel-Górniak, B.; Rogacka, N.; Rogacki, M.; Puszczewicz, M. Antinuclear Antibodies in Autoimmune and Allergic Diseases. Reumatologia 2017, 55, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.C.S.; Sandler, D.P.; Simonsick, E.M.; Weng, N.P.; Parks, C.G. Sex Differences in the Association between Antinuclear Antibody Positivity with Diabetes and Multimorbidity in Older Adults: Results from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 135, 110906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinse, G.E.; Parks, C.G.; Weinberg, C.R.; Co, C.A.; Wilkerson, J.; Zeldin, D.C.; Chan, E.K.L.; Miller, F.W. Increasing Prevalence of Antinuclear Antibodies in the United States. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, K.; Mercer, S.W.; Norbury, M.; Watt, G.; Wyke, S.; Guthrie, B. Epidemiology of Multimorbidity and Implications for Health Care, Research, and Medical Education: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet 2012, 380, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador-Patarroyo, M.J.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, A.; Montoya-Ortiz, G. How Does Age at Onset Influence the Outcome of Autoimmune Diseases? Autoimmune Dis. 2012, 2012, 251730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, W.; Vinet, É.; Somers, E.C. Rheumatic Autoimmune Diseases in Women and Midlife Health. Women’s Midlife Health 2015, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Hwang, H.; Roh, J.; Shim, J.E.; Kim, J.; Kim, G.T.; Tag, H.S.; Kim, H.S. Evaluation of an Automated Screening Assay, Compared to Indirect Immunofluorescence, an Extractable Nuclear Antigen Assay, and a Line Immunoassay in a Large Cohort of Asian Patients with Antinuclear Antibody-Associated Rheumatoid Diseases: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 9094217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, P.; de Langhe, E.; Claessens, J.; Westhovens, R.; van Hoeyveld, E.; Poesen, K.; Vanderschueren, S.; Blockmans, D.; Bossuyt, X. Screening for Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Antibodies by Automated Immunoassay. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Brito, F.; Santos, S.M.E.; Ferreira, G.A.; Pedrosa, W.; Gradisse, J.; Costa, L.C.; Neves, S.P.F. Diagnostic Evaluation of ELISA and Chemiluminescent Assays as Alternative Screening Tests to Indirect Immunofluorescence for the Detection of Antibodies to Cellular Antigens. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 145, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, H.G.; Brummelhuis, W.J.; Fritsch-Stork, R.; Leavis, H.L.; Wisse, B.W.; van Laar, J.M.; Derksen, R.H.W.M. Measurement of Antinuclear Antibodies and Their Fine Specificities: Time for a Change in Strategy? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bentow, C.; Lakos, G.; Rosenblum, R.; Bryant, C.; Seaman, A.; Mahler, M. Clinical Performance Evaluation of a Novel, Automated Chemiluminescent Immunoassay, QUANTA Flash CTD Screen Plus. Immunol. Res. 2015, 61, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzaro, N.; Brusca, I.; Previtali, G.; Alessio, M.G.; Daves, M.; Platzgummer, S.; Cinquanta, L.; Paura, G.; Infantino, M.; Manfredi, M.; et al. The Association of Solid-Phase Assays to Immunofluorescence Increases the Diagnostic Accuracy for ANA Screening in Patients with Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Beéck, K.O.; Vermeersch, P.; Verschueren, P.; Westhovens, R.; Mariën, G.; Blockmans, D.; Bossuyt, X. Antinuclear Antibody Detection by Automated Multiplex Immunoassay in Untreated Patients at the Time of Diagnosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 12, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orme, M.E.; Andalucia, C.; Sjölander, S.; Bossuyt, X. A Comparison of a Fluorescence Enzyme Immunoassay versus Indirect Immunofluorescence for Initial Screening of Connective Tissue Diseases: Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, N.J.; Choi, M.Y.; Fritzler, M.J. Emerging Technologies in Autoantibody Testing for Rheumatic Diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazzana, I.; Richards, M.; Bentow, C.; Seaman, A.; Fredi, M.; Giudizi, M.G.; Palterer, B.; Pratesi, F.; Migliorini, P.; Franceschini, F.; et al. Evaluation of a Novel Particle-Based Assay for Detection of Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. J. Immunol. Methods 2019, 474, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, I.S.; Kellermann, M.; Mossotto, E.; Beattie, R.M.; MacArthur, B.D.; Ennis, S. A Systematic Review of the Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Autoimmune Diseases. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsmore, K.M.; Puglisi, C.E.; Grammer, A.C.; Lipsky, P.E. An Introduction to Machine Learning and Analysis of Its Use in Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 710–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, T.S.; Dondelinger, F.; Wang, D. Looking beyond the Hype: Applied AI and Machine Learning in Translational Medicine. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irure-Ventura, J.; López-Hoyos, M. The Past, Present, and Future in Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA). Diagnostics 2022, 12, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12030647
Irure-Ventura J, López-Hoyos M. The Past, Present, and Future in Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA). Diagnostics. 2022; 12(3):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12030647
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrure-Ventura, Juan, and Marcos López-Hoyos. 2022. "The Past, Present, and Future in Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA)" Diagnostics 12, no. 3: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12030647
APA StyleIrure-Ventura, J., & López-Hoyos, M. (2022). The Past, Present, and Future in Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA). Diagnostics, 12(3), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12030647






