Multidimensional Approach of Heart Failure Diagnosis and Prognostication Utilizing Cardiac Imaging with Biomarkers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
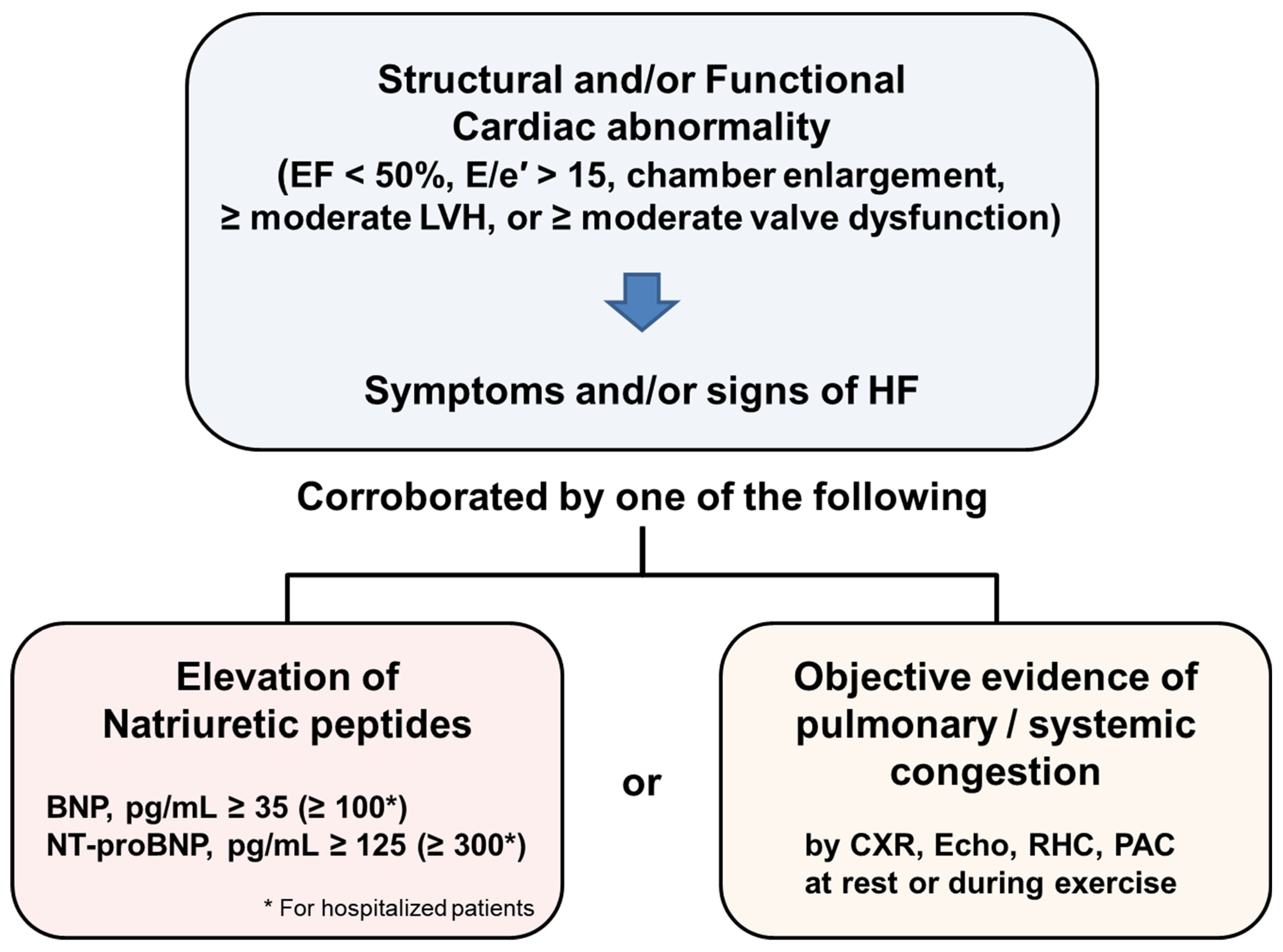
2. Diagnosis of Heart Failure in Recent Guidelines
3. Multimodality Imaging Approaches in Various HF
3.1. Multimodality Imaging in HF
3.2. Echocardiography
3.3. Lung Ultrasound
3.4. Cardiac Computed Tomography
3.5. Nuclear Imaging
3.6. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
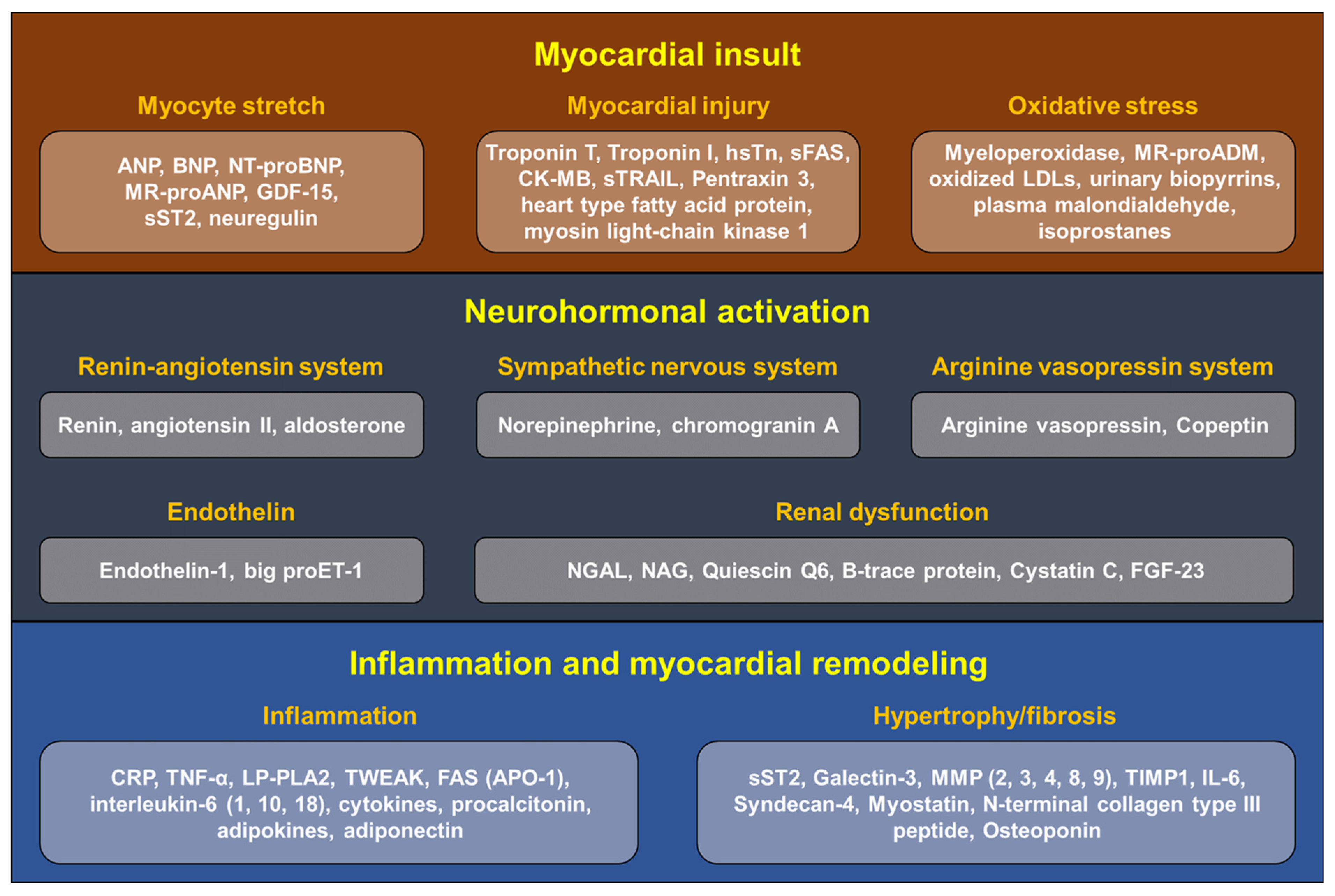
4. Biomarkers in Heart Failure
4.1. Markers for Myocardial Insult
- (1)
- B-type natriuretic peptides
- (2)
- Atrial natriuretic peptide
- (3)
- High-sensitivity troponin
- (4)
- Myeloperoxidase
- (5)
- Uric acid
4.2. Markers for Neurohormonal Activation
- (1)
- Adrenomedullin
- (2)
- Arginine vasopressin
- (3)
- Endothelin-1
4.3. Markers for Inflammation and Myocardial Remodeling
- (1)
- Tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6
- (2)
- Soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2
- (3)
- Galectin-3
- (4)
- Matrix metalloproteinases
- (5)
- Growth/differentiation factor-15
5. Multidimensional Approach in HF with Cardiac Imaging and Biomarkers
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozkurt, B.; Coats, A.J.; Tsutsui, H.; Abdelhamid, M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Albert, N.; Anker, S.D.; Atherton, J.; Böhm, M.; Butler, J.; et al. Universal Definition and Classification of Heart Failure: A Report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition of Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 23, 352–380. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, E.J.; Park, D.G.; Park, S.J.; Park, J.J.; Shin, M.S.; Yoo, B.S.; Youn, J.C.; Lee, S.E.; et al. Korean Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Heart Failure. Korean Circ. J. 2017, 47, 555–643. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Bohm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Celutkiene, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. Corrigendum to: 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsui, H.; Ide, T.; Ito, H.; Kihara, Y.; Kinugawa, K.; Kinugawa, S.; Makaya, M.; Murohara, T.; Node, K.; Saito, Y.; et al. JCS/JHFS 2021 Guideline Focused Update on Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 1404–1444. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, T.M.; Januzzi, J.L.; Jr Allen, L.A.; Breathett, K.; Butler, J.; Davis, L.L.; Fonarow, G.C.; Ibrahim, N.E.; Lindenfeld, J.; Masoudi, F.A.; et al. 2021 Update to the 2017 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway for Optimization of Heart Failure Treatment: Answers to 10 Pivotal Issues About Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 772–810. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoletini, I.; Coats, A.J.S.; Senni, M.; Rosano, G.M.C. Monitoring of biomarkers in heart failure. Eur. Heart. J. Suppl. 2019, 21 (Suppl. SM), M5–M8. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, N.E.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Established and Emerging Roles of Biomarkers in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 614–629. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, S.K.; Shaikh, M.M. Biomarkers in Routine Heart Failure Clinical Care. Card. Fail. Rev. 2019, 5, 50–56. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Januzzi, J.L.; Butler, J.; Fombu, E.; Maisel, A.; McCague, K.; Piña, I.L.; Prescott, M.F.; Riebman, J.B.; Solomon, S. Rationale and methods of the Prospective Study of Biomarkers, Symptom Improvement, and Ventricular Remodeling During Sacubitril/Valsartan Therapy for Heart Failure (PROVE-HF). Am. Heart J. 2018, 199, 130–136. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kimmenade, R.R.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Emerging biomarkers in heart failure. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 127–138. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarhene, M.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Acheampong, E.; Zhengcan, Z.; Xiaoyan, Q.; Yunsheng, X.; et al. Biomarkers in heart failure: The past, current and future. Heart Fail. Rev. 2019, 24867, 867–903. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.E.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Beyond Natriuretic Peptides for Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 211–222. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.C.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, D.; Seo, S.M.; Yang, J.H.; Cha, M.J.; Choi, J.I.; Choi, D.J. Focused Update of 2016 Korean Society of Heart Failure Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Heart Failure. Int. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 1, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ederhy, S.; Mansencal, N.; Réant, P.; Piriou, N.; Barone-Rochette, G. Role of multimodality imaging in the diagnosis and management of cardiomyopathies. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 112, 615–629. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adigopula, S.; Grapsa, J. Advances in Imaging and Heart Failure: Where are we Heading? Card. Fail. Rev. 2018, 4, 73–77. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, J.J.; Di Carli, M.; Narula, J.; Delgado, V. Multimodality imaging in ischaemic heart failure. Lancet 2019, 393, 1056–1070. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.C.; Hong, G.R. Intraventricular Flow: More than Pretty Pictures. Heart Fail. Clin. 2019, 15, 257–265. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.C.; Hong, G.R.; Pedrizzetti, G.; Shim, C.Y.; Kang, S.M.; Chung, N. Usefulness of Left Ventricular Vortex Flow Analysis for Predicting Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Quantitative Vorticity Imaging Study Using Contrast Echocardiography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 1951–1959. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.; Blanke, P.; Bax, J.J.; Leipsic, J. Multimodality imaging in valvular heart disease: How to use state-of-the-art technology in daily practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1912–1925. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, T.R.; Shillcutt, S.K.; Adams, M.S.; Desjardins, G.; Glas, K.E.; Olson, J.J.; Troughton, R.W. Guidelines for the use of echocardiography as a monitor for therapeutic intervention in adults: A report from the American Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 40–56. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudski, L.G.; Lai, W.W.; Afilalo, J.; Hua, L.; Handschumacher, M.D.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Solomon, S.D.; Louie, E.K.; Schiller, N.B. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the right heart in adults: A report from the American Society of Echocardiography endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2010, 23, 685–713. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanspa, M.J.; Grissom, C.K.; Hirshberg, E.L.; Jones, J.P.; Brown, S.M. Applying dynamic parameters to predict hemodynamic response to volume expansion in spontaneously breathing patients with septic shock. Shock 2013, 39, 155–160. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Picano, E.; Scali, M.C.; Ciampi, Q.; Lichtenstein, D. Lung Ultrasound for the Cardiologist. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 1692–1705. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, S.; Platz, E.; Cullen, L.; Tavazzi, G.; Christ, M.; Cowie, M.R.; Maisel, A.S.; Masip, J.; Miro, O.; McMurray, J.J.; et al. Expert consensus document: Echocardiography and lung ultrasonography for the assessment and management of acute heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 427–440. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mezière, G.A. Relevance of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure: The BLUE protocol. Chest 2008, 134, 117–125. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Čelutkienė, J.; Lainscak, M.; Anderson, L.; Gayat, E.; Grapsa, J.; Harjola, V.P.; Manka, R.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.; Filardi, P.P.; Vrettou, R.; et al. Imaging in patients with suspected acute heart failure: Timeline approach position statement on behalf of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 181–195. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwick, T.H.; Raman, S.V.; Carrió, I.; Bax, J.J. Recent developments in heart failure imaging. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 429–439. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, W.; Claridge, S.; Ntalas, I.; Gould, J.; de Vecchi, A.; Razeghi, O.; Toth, D.; Mountney, P.; Preston, R.; Rinaldi, C.A.; et al. Emerging role of cardiac computed tomography in heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2019, 6, 909–920. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, I.-C.; Chang, H.-J.; Cho, I.-J.; Shim, C.Y.; Hong, G.-R.; Heo, J.H.; Nam, H.S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, B.-W.; Chung, N. Benefit of Four-Dimensional Computed Tomography Derived Ejection Fraction of the Left Atrial Appendage to Predict Thromboembolic Risk in the Patients with Valvular Heart Disease. Korean Circ. J. 2019, 49, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, I.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.A.; Han, S. COVID-19-related myocarditis in a 21-year-old female patient. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagueh, S.F.; Chang, S.M.; Nabi, F.; Shah, D.J.; Estep, J.D. Imaging to Diagnose and Manage Patients in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, e005615. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smiseth, O.A.; Morris, D.A.; Cardim, N.; Cikes, M.; Delgado, V.; Donal, E.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Galderisi, M.; Gerber, B.L.; Gimelli, A.; et al. Multimodality imaging in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: An expert consensus document of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 23, e34–e61. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisel, S.R.; Januzzi, J.L.; Medvedovski, M.; Sharist, M.; Shochat, M.; Ashkar, J.; Peschansky, P.; Haim, S.B.; Blondheim, D.S.; Glikson, M.; et al. Pre-admission NT-proBNP improves diagnostic yield and risk stratification-the NT-proBNP for EValuation of dyspnoeic patients in the Emergency Room and hospital (BNP4EVER) study. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2012, 1, 99–108. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Camargo, C.A.; Anwaruddin, S.; Baggish, A.L.; Chen, A.A.; Krauser, D.G.; Tung, R.; Cameron, R.; Nagurney, J.T.; Chae, C.U.; et al. The N-terminal Pro-BNP investigation of dyspnea in the emergency department (PRIDE) study. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 948–954. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggin, H.K.; Chen-Tournoux, A.A.; Christenson, R.H.; Doros, G.; Hollander, J.E.; Levy, P.D.; Nagurney, J.T.; Nowak, R.M.; Pang, P.S.; Patel, D.; et al. Rationale and design of the ICON-RELOADED study: International Collaborative of N-terminal pro-B-type Natriuretic Peptide Re-evaluation of Acute Diagnostic Cut-Offs in the Emergency Department. Am. Heart J. 2017, 192, 26–37. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mueller, C.; Scholer, A.; Laule-Kilian, K.; Martina, B.; Schindler, C.; Buser, P.; Pfisterer, M.; Perruchoud, A.P. Use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the evaluation and management of acute dyspnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 647–654. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, G.W.; Howlett, J.; Januzzi, J.L.; Zowall, H. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide testing improves the management of patients with suspected acute heart failure: Primary results of the Canadian prospective randomized multicenter IMPROVE-CHF study. Circulation 2007, 115, 3103–3110. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, e263–e421. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.; Packer, M.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; Rizkala, A.R.; Rouleau, J.L.; Shi, V.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Swedberg, K.; et al. Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 993–1004. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velazquez, E.J.; Morrow, D.A.; DeVore, A.D.; Duffy, C.I.; Ambrosy, A.P.; McCague, K.; Rocha, R.; Braunwald, E. Angiotensin–Neprilysin Inhibition in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 380, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Prescott, M.F.; Butler, J.; Felker, G.M.; Maisel, A.S.; McCague, K.; Camacho, A.; Piña, I.L.; Rocha, R.A.; Shah, A.M.; et al. Association of Change in N-Terminal Pro–B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Following Initiation of Sacubitril-Valsartan Treatment with Cardiac Structure and Function in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction. JAMA 2019, 322, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonarow, G.C.; Peacock, W.F.; Phillips, C.O.; Givertz, M.M.; Lopatin, M. Admission B-type natriuretic peptide levels and in-hospital mortality in acute decompensated heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1943–1950. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Januzzi, J.L.; Jr Sakhuja, R.; O’Donoghue, M.; Baggish, A.L.; Anwaruddin, S.; Chae, C.U.; Cameron, R.; Krauser, D.G.; Tung, R.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; et al. Utility of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide testing for prediction of 1-year mortality in patients with dyspnea treated in the emergency department. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 315–320. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masson, S.; Latini, R.; Anand, I.S.; Barlera, S.; Angelici, L.; Vago, T.; Tognoni, G.; Cohn, J.N. Prognostic value of changes in N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in Val-HeFT (Valsartan Heart Failure Trial). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 997–1003. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maisel, A.; Mueller, C.; Nowak, R.; Peacock, W.F.; Landsberg, J.W.; Ponikowski, P.; Mockel, M.; Hogan, C.; Wu, A.H.; Richards, M.; et al. Mid-region pro-hormone markers for diagnosis and prognosis in acute dyspnea: Results from the BACH (Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2062–2076. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, R.V.; Truong, Q.A.; Gaggin, H.K.; Pfannkuche, J.; Hartmann, O.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide and pro-adrenomedullin testing for the diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of patients with acute dyspnoea. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2197–2205. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masson, S.; Latini, R.; Carbonieri, E.; Moretti, L.; Rossi, M.G.; Ciricugno, S.; Milani, V.; Marchioli, R.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; et al. The predictive value of stable precursor fragments of vasoactive peptides in patients with chronic heart failure: Data from the GISSI-heart failure (GISSI-HF) trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2010, 12, 338–347. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Vergaro, G.; Ripoli, A.; Latini, R.; Masson, S.; Magnoli, M.; Anand, I.S.; Cohn, J.N.; Tavazzi, L.; et al. Prognostic Value of High-Sensitivity Troponin T in Chronic Heart Failure: An Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. Circulation 2018, 137, 286–297. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Figal, D.A.; Casas, T.; Ordonez-Llanos, J.; Manzano-Fernández, S.; Bonaque, J.C.; Boronat, M.; Muñoz-Esparza, C.; Valdés, M.; Januzzi, J.L. Highly sensitive troponin T for risk stratification of acutely destabilized heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2012, 163, 1002–1010. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parissis, J.T.; Papadakis, J.; Kadoglou, N.P.; Varounis, C.; Psarogiannakopoulos, P.; Rafouli-Stergiou, P.; Ikonomidis, I.; Paraskevaidis, I.; Dimopoulou, I.; Zerva, A.; et al. Prognostic value of high sensitivity troponin T in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure and non-detectable conventional troponin T levels. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3609–3612. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motiwala, S.R.; Gaggin, H.K.; Gandhi, P.U.; Belcher, A.; Weiner, R.B.; Baggish, A.L.; Szymonifka, J.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Concentrations of highly sensitive cardiac troponin-I predict poor cardiovascular outcomes and adverse remodeling in chronic heart failure. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2015, 8, 164–172. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichlin, T.; Socrates, T.; Egli, P.; Potocki, M.; Breidthardt, T.; Arenja, N.; Meissner, J.; Noveanu, M.; Reiter, M.; Twerenbold, R.; et al. Use of myeloperoxidase for risk stratification in acute heart failure. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 944–951. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.H.; Brennan, M.L.; Philip, K.; Tong, W.; Mann, S.; Van Lente, F.; Hazen, S.L. Plasma myeloperoxidase levels in patients with chronic heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 796–799. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, E. Hyperuricemia and incident heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2009, 2, 556–562. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedict, C.R.; Shelton, B.; Johnstone, D.E.; Francis, G.; Greenberg, B.; Konstam, M.; Probstfield, J.L.; Yusuf, S. Prognostic significance of plasma norepinephrine in patients with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. SOLVD Investigators. Circulation 1996, 94, 690–697. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabassi, A.; de Champlain, J.; Maggiore, U.; Parenti, E.; Coghi, P.; Vicini, V.; Tedeschi, S.; Cremaschi, E.; Binno, S.; Rocco, R.; et al. Prealbumin improves death risk prediction of BNP-added Seattle Heart Failure Model: Results from a pilot study in elderly chronic heart failure patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3334–3339. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Haehling, S.; Filippatos, G.S.; Papassotiriou, J.; Cicoira, M.; Jankowska, E.A.; Doehner, W.; Rozentryt, P.; Vassanelli, C.; Struck, J.; Banasiak, W.; et al. Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin as a novel predictor of mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2010, 12, 484–491. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, A.; Xue, Y.; Shah, K.; Mueller, C.; Nowak, R.; Peacock, W.F.; Ponikowski, P.; Mockel, M.; Hogan, C.; Wu, A.H.; et al. Increased 90-day mortality in patients with acute heart failure with elevated copeptin: Secondary results from the Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure (BACH) study. Circ. Heart. Fail. 2011, 4, 613–620. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.H.; Shrestha, K.; Martin, M.G.; Borowski, A.G.; Jasper, S.; Yandle, T.G.; Richards, A.M.; Klein, A.L.; Troughton, R.W. Clinical significance of endogenous vasoactive neurohormones in chronic systolic heart failure. J. Card. Fail. 2010, 16, 635–640. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Penninx, B.W.; Newman, A.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Nicklas, B.J.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; Rubin, S.M.; Ding, J.; Simonsick, E.M.; Harris, T.B.; et al. Inflammatory markers and onset of cardiovascular events: Results from the Health ABC study. Circulation 2003, 108, 2317–2322. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rauchhaus, M.; Doehner, W.; Francis, D.P.; Davos, C.; Kemp, M.; Liebenthal, C.; Niebauer, J.; Hooper, J.; Volk, H.D.; Coats, A.J.; et al. Plasma cytokine parameters and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2000, 102, 3060–3067. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coglianese, E.E.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Ho, J.E.; Ghorbani, A.; McCabe, E.L.; Cheng, S.; Fradley, M.G.; Kretschman, D.; Gao, W.; et al. Distribution and clinical correlates of the interleukin receptor family member soluble ST2 in the Framingham Heart Study. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 1673–1681. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Vergaro, G.; Ripoli, A.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Pascual Figal, D.A.; de Boer, R.A.; Lassus, J.; Mebazaa, A.; Gayat, E.; Breidthardt, T.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Soluble Suppression of Tumorigenicity-2 and Prognosis in Acute Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 287–296. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Vergaro, G.; Passino, C.; Ripoli, A.; Ky, B.; Miller, W.L.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Anand, I.; Januzzi, J.L.; Emdin, M. Prognostic Value of Soluble Suppression of Tumorigenicity-2 in Chronic Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis. JACC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 280–286. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Peacock, W.F.; Maisel, A.S.; Chae, C.U.; Jesse, R.L.; Baggish, A.L.; O’Donoghue, M.; Sakhuja, R.; Chen, A.A.; van Kimmenade, R.R.; et al. Measurement of the interleukin family member ST2 in patients with acute dyspnea: Results from the PRIDE (Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Investigation of Dyspnea in the Emergency Department) study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 607–613. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzano-Fernández, S.; Mueller, T.; Pascual-Figal, D.; Truong, Q.A.; Januzzi, J.L. Usefulness of soluble concentrations of interleukin family member ST2 as predictor of mortality in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure relative to left ventricular ejection fraction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 107, 259–267. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boisot, S.; Beede, J.; Isakson, S.; Chiu, A.; Clopton, P.; Januzzi, J.; Maisel, A.S.; Fitzgerald, R.L. Serial sampling of ST2 predicts 90-day mortality following destabilized heart failure. J. Card. Fail. 2008, 14, 732–738. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggin, H.K.; Motiwala, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Parks, K.A.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Soluble concentrations of the interleukin receptor family member ST2 and β-blocker therapy in chronic heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 1206–1213. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Kimmenade, R.R.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Ellinor, P.T.; Sharma, U.C.; Bakker, J.A.; Low, A.F.; Martinez, A.; Crijns, H.J.; MacRae, C.A.; Menheere, P.P.; et al. Utility of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, galectin-3, and apelin for the evaluation of patients with acute heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1217–1224. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López, B.; Ravassa, S.; González, A.; Zubillaga, E.; Bonavila, C.; Bergés, M.; Echegaray, K.; Beaumont, J.; Moreno, M.U.; San José, G.; et al. Myocardial Collagen Cross-Linking Is Associated with Heart Failure Hospitalization in Patients with Hypertensive Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 251–260. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- George, J.; Patal, S.; Wexler, D.; Roth, A.; Sheps, D.; Keren, G. Circulating matrix metalloproteinase-2 but not matrix metalloproteinase-3, matrix metalloproteinase-9, or tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 predicts outcome in patients with congestive heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2005, 150, 484–487. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buralli, S.; Dini, F.L.; Ballo, P.; Conti, U.; Fontanive, P.; Duranti, E.; Metelli, M.R.; Marzilli, M.; Taddei, S. Circulating matrix metalloproteinase-3 and metalloproteinase-9 and tissue Doppler measures of diastolic dysfunction to risk stratify patients with systolic heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 105, 853–856. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, S.; Störk, S.; Michels, K.; Eigenthaler, M.; Ertl, G.; Bauersachs, J.; Angermann, C.E. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases levels in patients with chronic heart failure: An independent predictor of mortality. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 388–395. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zannad, F.; Alla, F.; Dousset, B.; Perez, A.; Pitt, B. Limitation of excessive extracellular matrix turnover may contribute to survival benefit of spironolactone therapy in patients with congestive heart failure: Insights from the randomized aldactone evaluation study (RALES). Rales Investigators. Circulation 2000, 102, 2700–2706. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zile, M.R.; Desantis, S.M.; Baicu, C.F.; Stroud, R.E.; Thompson, S.B.; McClure, C.D.; Mehurg, S.M.; Spinale, F.G. Plasma biomarkers that reflect determinants of matrix composition identify the presence of left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2011, 4, 246–256. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wollert, K.C.; Kempf, T.; Wallentin, L. Growth Differentiation Factor 15 as a Biomarker in Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 140–151. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, B.F.; Eze, S.M.; Yang, L.; Castellino, R.C.; Nahta, R. Growth differentiation factor 15 mediates epithelial mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancers through IGF-1R-FoxM1 signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 94393–94406. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulogne, M.; Sadoune, M.; Launay, J.M.; Baudet, M.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Logeart, D. Inflammation versus mechanical stretch biomarkers over time in acutely decompensated heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 226, 53–59. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmers, T.A.; Jin, X.; Hsiao, E.C.; Perez, E.A.; Pierce, R.H.; Chavin, K.D.; Koniaris, L.G. Growth differentiation factor-15: Induction in liver injury through p53 and tumor necrosis factor-independent mechanisms. J. Surg. Res. 2006, 130, 45–51. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, T.; Eden, M.; Strelau, J.; Naguib, M.; Willenbockel, C.; Tongers, J.; Heineke, J.; Kotlarz, D.; Xu, J.; Molkentin, J.D.; et al. The transforming growth factor-beta superfamily member growth-differentiation factor-15 protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 351–360. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggin, H.K.; Szymonifka, J.; Bhardwaj, A.; Belcher, A.; De Berardinis, B.; Motiwala, S.; Wang, T.J.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Head-to-head comparison of serial soluble ST2, growth differentiation factor-15, and highly-sensitive troponin T measurements in patients with chronic heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2014, 2, 65–72. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, G.; Voors, A.A.; Prescott, M.F.; Felker, G.M.; Filippatos, G.; Greenberg, B.H.; Pang, P.S.; Ponikowski, P.; Milo, O.; Hua, T.A.; et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) in patients admitted for acute heart failure: Results from the RELAX-AHF study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 1133–1143. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, I.S.; Kempf, T.; Rector, T.S.; Tapken, H.; Allhoff, T.; Jantzen, F.; Kuskowski, M.; Cohn, J.N.; Drexler, H.; Wollert, K.C. Serial measurement of growth-differentiation factor-15 in heart failure: Relation to disease severity and prognosis in the Valsartan Heart Failure Trial. Circulation 2010, 122, 1387–1395. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Echo | Stress Echo | CCT | CMR | SPECT | PET | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chamber size | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | - | - |
| Systolic function | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | - |
| Diastolic function | +++ | +++ | - | - | - | - |
| Valve function | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | - | - |
| Intracardiac pressure | +++ | +++ | - | - | - | - |
| Coronary artery disease | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| Myocardial viability | - | +++ | - | +++ | ++ | +++ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, I.-C.; Yoo, B.-S. Multidimensional Approach of Heart Failure Diagnosis and Prognostication Utilizing Cardiac Imaging with Biomarkers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061366
Kim I-C, Yoo B-S. Multidimensional Approach of Heart Failure Diagnosis and Prognostication Utilizing Cardiac Imaging with Biomarkers. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(6):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061366
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, In-Cheol, and Byung-Su Yoo. 2022. "Multidimensional Approach of Heart Failure Diagnosis and Prognostication Utilizing Cardiac Imaging with Biomarkers" Diagnostics 12, no. 6: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061366
APA StyleKim, I.-C., & Yoo, B.-S. (2022). Multidimensional Approach of Heart Failure Diagnosis and Prognostication Utilizing Cardiac Imaging with Biomarkers. Diagnostics, 12(6), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061366







