High-Resolution Ultrasound of the Forefoot and Common Pathologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. US Techniques and Methods
3. Anatomy and Normal US Images
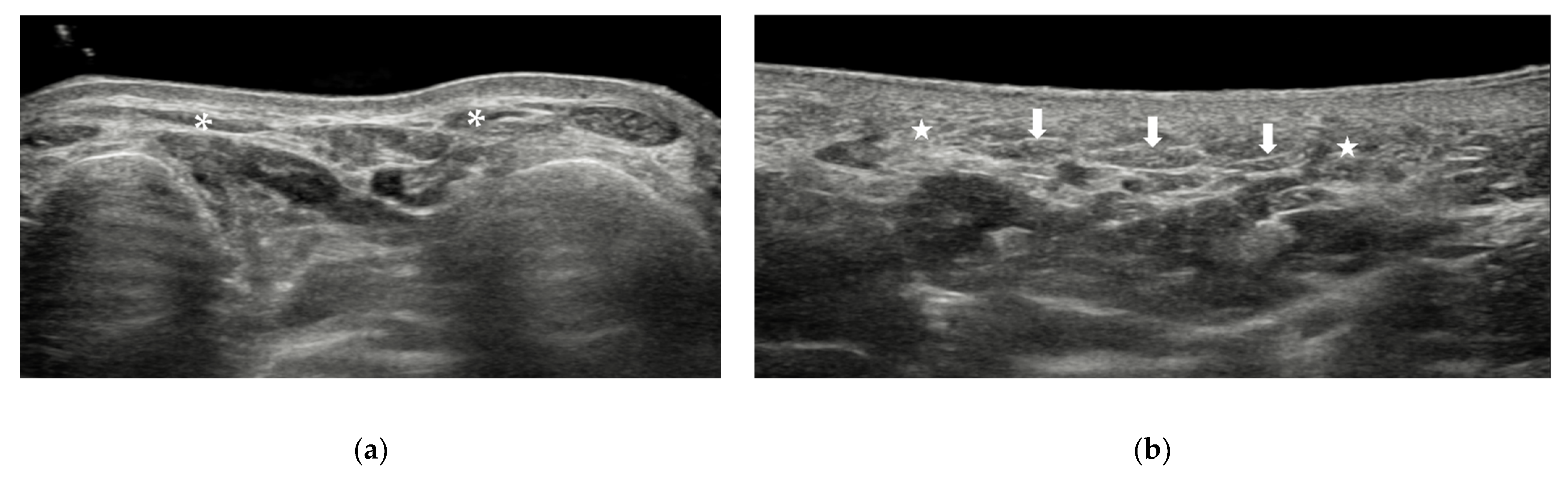
3.1. Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
3.2. Muscles and Tendons
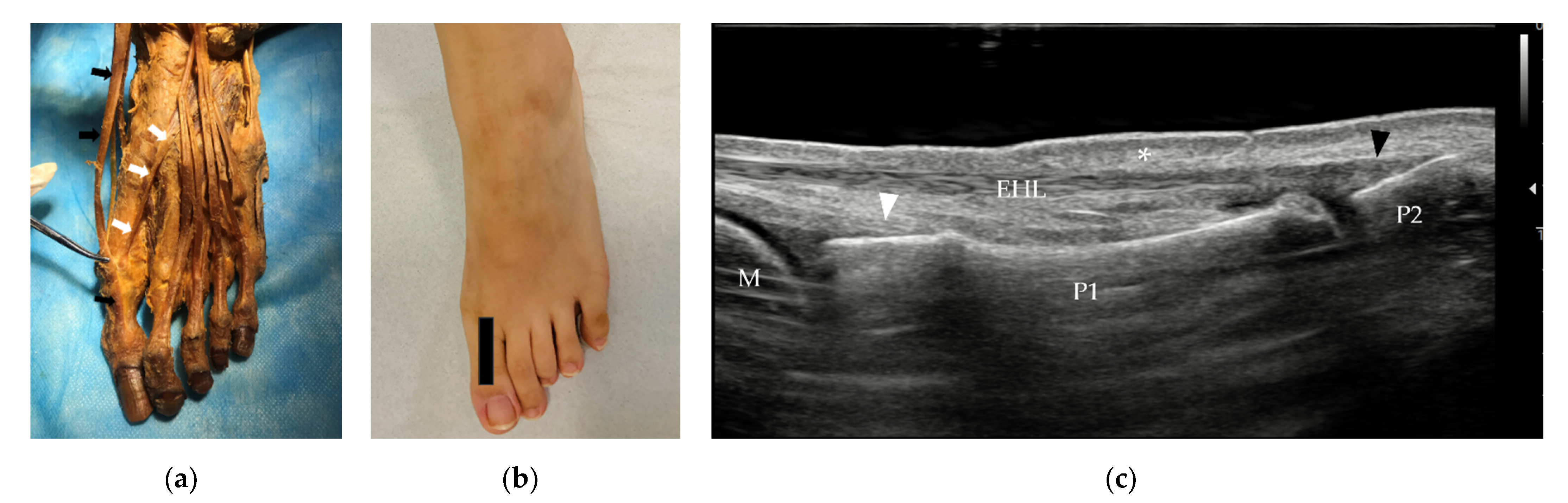
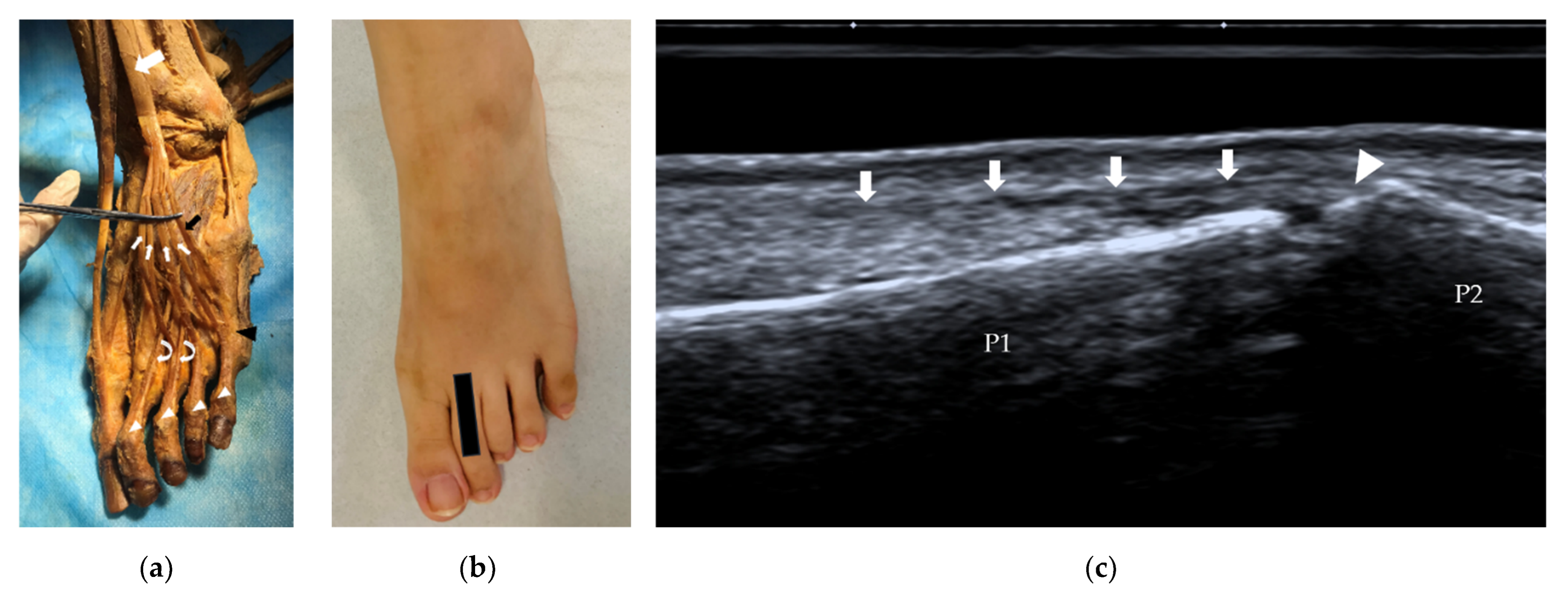
3.2.1. Tendons and Muscles of the Dorsal Foot
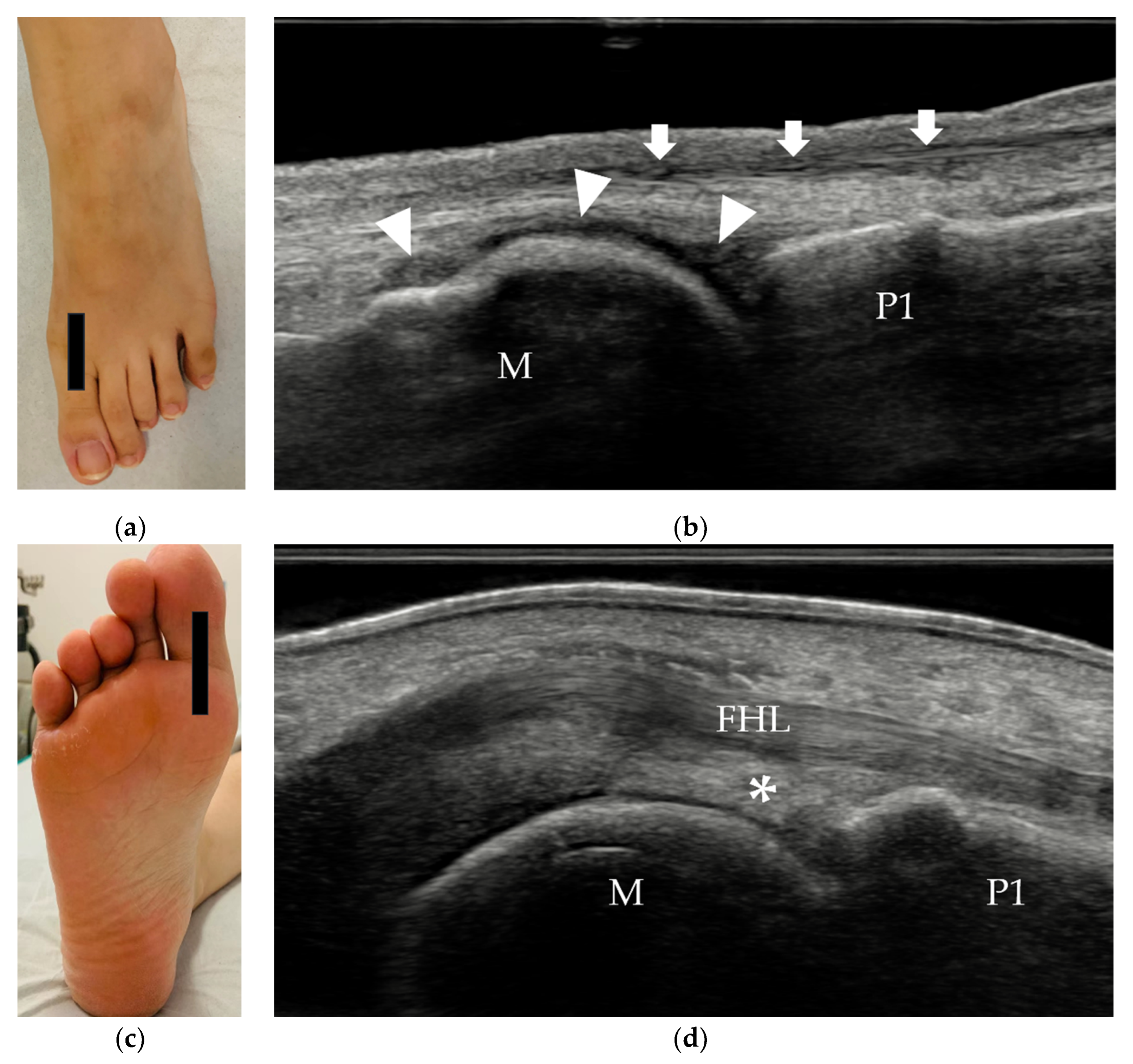
3.2.2. Tendons and Muscles of the Plantar Foot
3.3. Soft Tissues between Metatarsal Bones
3.4. Sesamoids and Osseous Components
3.5. Ligaments and Joint Capsule
4. Common Pathologies of the Forefoot
4.1. Traumatic Disorders of the Forefoot
4.1.1. Plantar Plate Tear
4.1.2. Sesamoiditis
4.1.3. Stress Fracture
4.1.4. Foreign Bodies (FBs)
4.2. Inflammation and Infection of the Forefoot
4.2.1. Synovitis and Tenosynovitis
4.2.2. Adventitial Bursitis
4.2.3. Intermetatarsal Bursitis
4.3. Morton’s Neuroma
4.4. Other Causes of Forefoot Pain
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunn, J.E.; Link, C.L.; Felson, D.T.; Crincoli, M.G.; Keysor, J.J.; McKinlay, J.B. Prevalence of foot and ankle conditions in a multiethnic community sample of older adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 159, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menz, H.B.; Tiedemann, A.; Kwan, M.M.; Plumb, K.; Lord, S.R. Foot pain in community-dwelling older people: An evaluation of the Manchester Foot Pain and Disability Index. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, A.; Warner, J.; Aniq, H. Central Metatarsalgia and Walking on Pebbles: Beyond Morton Neuroma. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, D.S.; Evans, R.; Arbel, Y.; Luria, O.; Hadid, A.; Yanovich, R.; Milgrom, C.; Finestone, A.S. Physical and psychological stressors linked with stress fractures in recruit training. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 23, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welck, M.J.; Hayes, T.; Pastides, P.; Khan, W.; Rudge, B. Stress fractures of the foot and ankle. Injury 2017, 48, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Habibzadeh, S.R.; Ahmadi, S.R.; Khajeh Nasiri, S.; Kaveh, M.M.; Foroughian, M. Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in Diagnosis of Metatarsal Bone Fracture; a Cross Sectional Study. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2019, 7, e49. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, F.; Hariharan, K. The rheumatoid forefoot. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2013, 6, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Dalbeth, N.; Vandal, A.C.; Rome, K. The first metatarsophalangeal joint in gout: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colebatch, A.N.; Edwards, C.J.; Ostergaard, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Balint, P.V.; D’Agostino, M.A.; Forslind, K.; Grassi, W.; Haavardsholm, E.A.; Haugeberg, G.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging of the joints in the clinical management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.; Weishaupt, D. MR imaging of the forefoot: Morton neuroma and differential diagnoses. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2005, 9, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Caprio, F.; Meringolo, R.; Shehab Eddine, M.; Ponziani, L. Morton’s interdigital neuroma of the foot: A literature review. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 24, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olewnik, L. Fibularis Tertius: Anatomical Study and Review of the Literature. Clin. Anat. 2019, 32, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, J.I.; Walker, F.O.; Kwak, S.G. Evaluation of extensor digitorum brevis thickness in healthy subjects: A comparative analysis of nerve conduction studies and ultrasound scans. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 1664–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooding, T.M.; Feger, M.A.; Hart, J.M.; Hertel, J. Intrinsic Foot Muscle Activation During Specific Exercises: A T2 Time Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. J. Athl. Train. 2016, 51, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, B.L.; Jones, C.J. Predicting plantar fasciitis in runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1987, 19, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, A.L.; Kurup, H.V. Painful sesamoid of the great toe. World J. Orthop. 2014, 5, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.M.; Silberstein, M.; Schneider, T.; Kerr, J.B.; Marks, P. Sonography of plantar plates in cadavers: Correlation with MRI and histology. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, C.L.; Thompson, G.V. Ultrasound findings of plantar plate tears of the lesser metatarsophalangeal joints. Skelet. Radiol. 2021, 50, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, R.H.; Brooks, B.M.; Chingre, M.; Klein, E.E.; Weil, L.S., Jr.; Fleischer, A.E. Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) versus dynamic ultrasound for plantar plate injuries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 152, 110315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linklater, J.M.; Bird, S.J. Imaging of Lesser Metatarsophalangeal Joint Plantar Plate Degeneration, Tear, and Repair. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2016, 20, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerstein, C.A.; Weil, L., Jr.; Weil, L.S., Sr.; Klein, E.E.; Fleischer, A.; Argerakis, N.G. Static Versus Dynamic Musculoskeletal Ultrasound for Detection of Plantar Plate Pathology. Foot Ankle Spec. 2014, 7, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallinan, J.; Statum, S.M.; Huang, B.K.; Bezerra, H.G.; Garcia, D.A.L.; Bydder, G.M.; Chung, C.B. High-Resolution MRI of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: Gross Anatomy and Injury Characterization. Radiographics 2020, 40, 1107–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombard, C.; Gillet, R.; Rauch, A.; Germain, E.; Dodin, G.; Blum, A.; Teixeira, P.G. Hallux sesamoid complex imaging: A practical diagnostic approach. Skelet. Radiol. 2020, 49, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedert, R.; Hintermann, B. Stress fractures of the medial great toe sesamoids in athletes. Foot Ankle Int. 2003, 24, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banal, F.; Gandjbakhch, F.; Foltz, V.; Goldcher, A.; Etchepare, F.; Rozenberg, S.; Koeger, A.C.; Bourgeois, P.; Fautrel, B. Sensitivity and specificity of ultrasonography in early diagnosis of metatarsal bone stress fractures: A pilot study of 37 patients. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Habib, M.; Tanwar, Y.S. Neglected foreign body in contralateral limb in a traumatic transfemoral amputee—Radiographs can be misleading. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2013, 16, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Cui, L.G.; Romagnoli, C.; Li, Z.Q.; Lei, Y.T. Ultrasound-guided Removal of Retained Soft Tissue Foreign Body with Late Presentation. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 1753–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, K.; Ogasa, H.; Tokushige, A.; Imagama, T.; Seki, T.; Nakashima, D.; Sakai, T. Ultrasonography-detected synovitis of hand is associated with the presence of synovitis in the forefoot of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Orthop. Sci. 2021, 26, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, O.; Badarinza, M.; Fodor, D. The relevance of ultrasound examination of the foot and ankle in patients with rheumatoid arthritis—A review of the literature. Med. Ultrason. 2019, 21, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riente, L.; Delle Sedie, A.; Scire, C.A.; Filippucci, E.; Meenagh, G.; Iagnocco, A.; Possemato, N.; Valesini, G.; Grassi, W.; Montecucco, C.; et al. Ultrasound imaging for the rheumatologist. XXXI. Sonographic assessment of the foot in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Filippucci, E.; Meenagh, G.; Delle Sedie, A.; Sakellariou, G.; Iagnocco, A.; Riente, L.; Gutierrez, M.; Bombardieri, S.; Valesini, G.; Montecucco, C.; et al. Ultrasound imaging for the rheumatologist XXXVI. Sonographic assessment of the foot in gout patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Beattie, K.A.; Allen, M.; Ioannidis, G.; Larché, M.J. Ultrasonography supplements clinical exam to improve early rheumatoid arthritis disease activity monitoring in metatarsophalangeal joints. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, W.A.; Schicke, B.; Ostendorf, B.; Scherer, A.; Krause, A.; Walther, M. Low-field MRI versus ultrasound: Which is more sensitive in detecting inflammation and bone damage in MCP and MTP joints in mild or moderate rheumatoid arthritis? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2013, 31, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dakkak, Y.J.; Jansen, F.P.; DeRuiter, M.C.; Reijnierse, M.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Tenosynovitis at the Metatarsophalangeal Joints: An Anatomic and MRI Study of the Forefoot Tendon Sheaths. Radiology 2020, 295, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakkak, Y.J.; Wouters, F.; Matthijssen, X.M.E.; Reijnierse, M.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M. Walking disabilities are associated with tenosynovitis at the metatarsophalangeal joints: A longitudinal MRI-study in early arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2022, 74, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studler, U.; Mengiardi, B.; Bode, B.; Schottle, P.B.; Pfirrmann, C.W.; Hodler, J.; Zanetti, M. Fibrosis and adventitious bursae in plantar fat pad of forefoot: MR imaging findings in asymptomatic volunteers and MR imaging-histologic comparison. Radiology 2008, 246, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, J.M. Ultrasound detection of plantar bursitis of the forefoot in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 229–230. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, C.J.; Culliford, D.; Dewbury, K.; Sampson, M.; Burridge, J.; Hooper, L.; Edwards, C.J.; Arden, N.K. The clinical importance of ultrasound detectable forefoot bursae in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Albtoush, O.M.; Xenitidis, T.; Horger, M. Intermetatarsal bursitis as first disease manifestation in different rheumatological disorders and related MR-imaging findings. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Koga, T.; Eguchi, M.; Okamoto, M.; Tsuji, S.; Takatani, A.; Shimizu, T.; Sumiyoshi, R.; Igawa, T.; Kawashiri, S.Y.; et al. Utility of power Doppler ultrasonography for detecting forefoot bursae in early rheumatoid arthritis: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addante, J.B.; Peicott, P.S.; Wong, K.Y.; Brooks, D.L. Interdigital neuromas. Results of surgical excision of 152 neuromas. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 1986, 76, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, T.J.; Jacobson, J.A.; Craig, J.G.; van Holsbeeck, M.T. Sonography of Morton’s neuromas. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 174, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.L.; Miller, T.T.; Ellis, S.J.; Roberts, M.M.; DiCarlo, E.F. Sonography of Morton Neuromas: What Are We Really Looking At? J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 2191–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, J.W.; Noakes, J.B.; Kerr, D.; Crichton, K.J.; Slater, H.K.; Bonar, F. Morton’s metatarsalgia: Sonographic findings and correlated histopathology. Foot Ankle Int. 1999, 20, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.; Pan, S.C.; Shieh, S.J.; Lee, J.W.; Chiu, H.Y.; Ho, C.L. Glomus Tumor: Twenty-Year Experience and Literature Review. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76 (Suppl. S1), S35–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







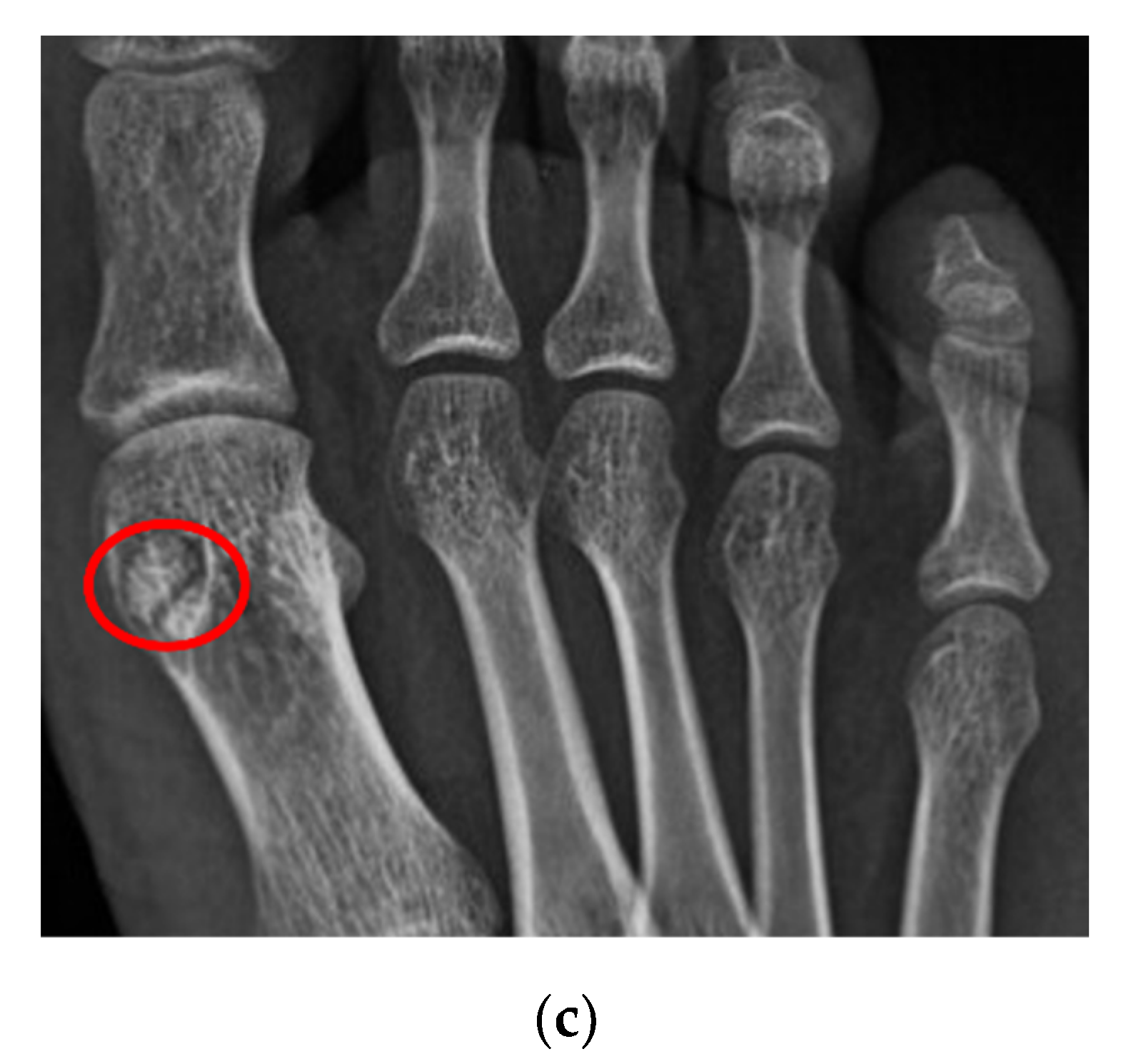

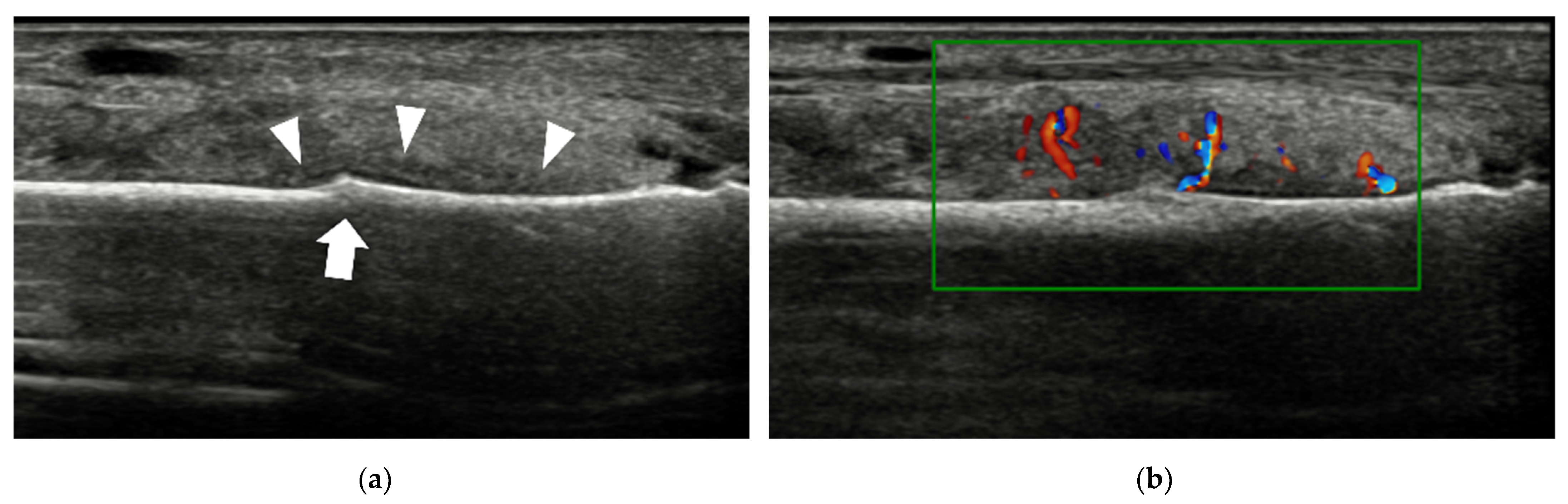








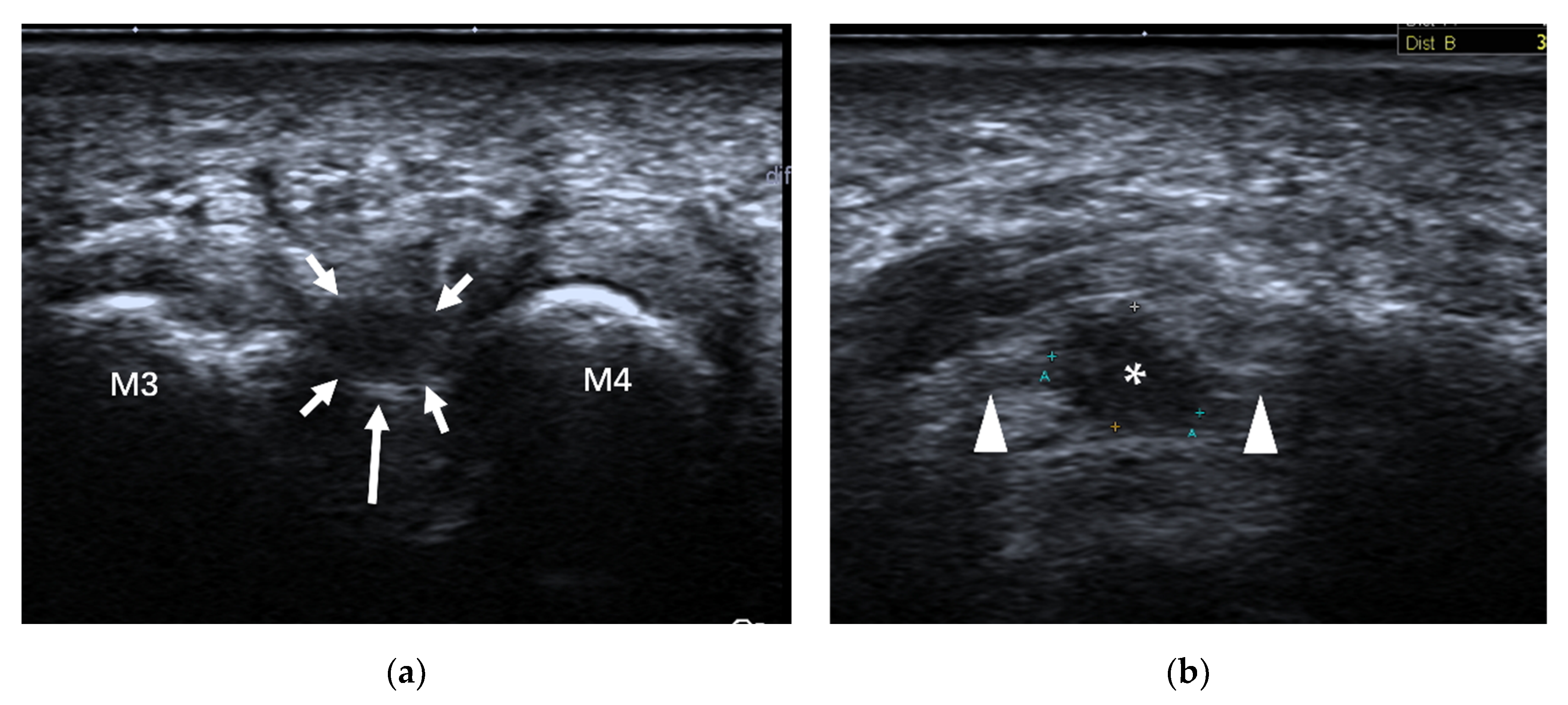

| Disorders | Common Sites | Classical Ultrasound Features |
|---|---|---|
| Plantar plate tear | 2nd MTP joint | discrete anechoic cleft or area of heterogeneous echotexture in the plantar plate |
| Sesamoiditis | / | blurred sesamoid bone cortex, with or without cortical disruption and surrounding soft tissue edema |
| Stress fracture | 2nd and 3rd metatarsals | periosteal lifting or cortical disruption, hypoechoic hematoma above the cortical bone |
| Foreign bodies | / | strong reflector surrounded by hypoechoic tissue |
| Synovitis | 2nd to 4th MTP joints | hypoechoic, poorly compressible, non-displaceable intra-articular tissue, with or without increased vascularity |
| Tenosynovitis | / | tendon sheath distension with surrounding effusion, “target” sign in transverse view |
| Adventitial bursitis | plantar side of the 1st and 5th metatarsal heads | unilocular area with heterogeneous echogenicity, compressible, with or without increased vascularity |
| Intermetatarsal bursitis | intermetatarsal spaces between 2nd and 3rd toes | hypoechoic mass with increased vascularity, compressible |
| Morton’s neuroma | intermetatarsal spaces between the 3rd and 4th metatarsal heads | fusiform, hypoechoic mass with “rat’s tail sign” |
| Glomus tumor | beneath the nails | solid, hypoechoic mass with hypervascularity |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zhou, G.; Xue, H.; Wang, R.; Bird, S.; Sun, D.; Cui, L. High-Resolution Ultrasound of the Forefoot and Common Pathologies. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071541
Chen X, Zhou G, Xue H, Wang R, Bird S, Sun D, Cui L. High-Resolution Ultrasound of the Forefoot and Common Pathologies. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(7):1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071541
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiangmei, Guangjin Zhou, Heng Xue, Run Wang, Stephen Bird, Desheng Sun, and Ligang Cui. 2022. "High-Resolution Ultrasound of the Forefoot and Common Pathologies" Diagnostics 12, no. 7: 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071541
APA StyleChen, X., Zhou, G., Xue, H., Wang, R., Bird, S., Sun, D., & Cui, L. (2022). High-Resolution Ultrasound of the Forefoot and Common Pathologies. Diagnostics, 12(7), 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071541





