Ultrasound Imaging of Facial Vascular Neural Structures and Relevance to Aesthetic Injections: A Pictorial Essay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aesthetic Injections and Relevant Neurovascular Structures
2.1. Upper Face
2.2. Middle Face
2.3. Lower Face
2.4. Submental Region
3. Mechanism of Neurovascular Injury
4. Sonoanatomy of the Neurovascular Structures of the Upper Face
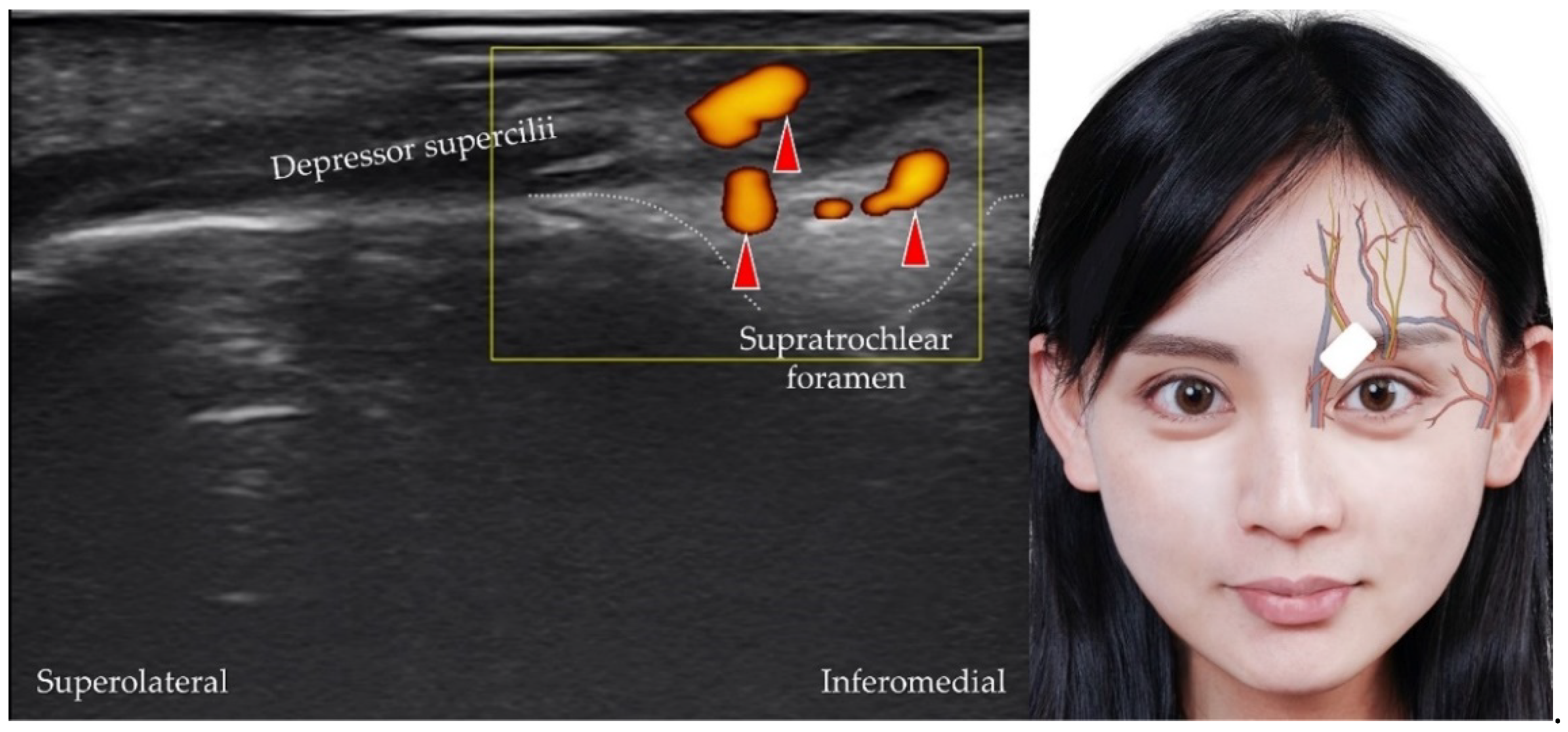
4.1. Supratrochlear Artery, Vein, and Nerve
4.2. Supraorbital Artery, Vein, and Nerve
4.3. Frontal Branch of the Superficial Temporal Artery/Vein
5. Sonoanatomy of the Neurovascular Structures of the Middle Face
5.1. Dorsal Nasal Artery and Vein
5.2. Angular Artery and Vein
5.3. Superior Labial Artery and Vein
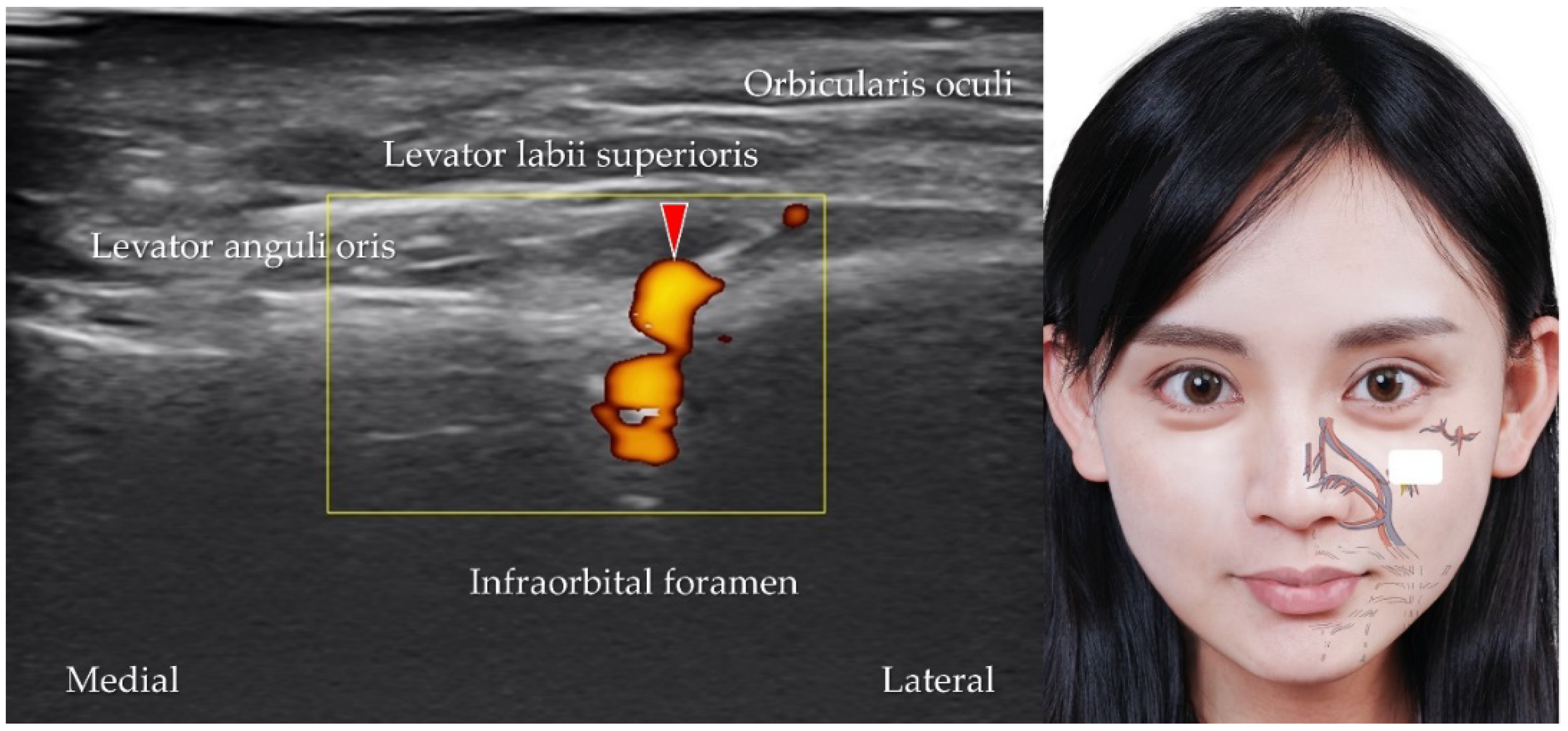
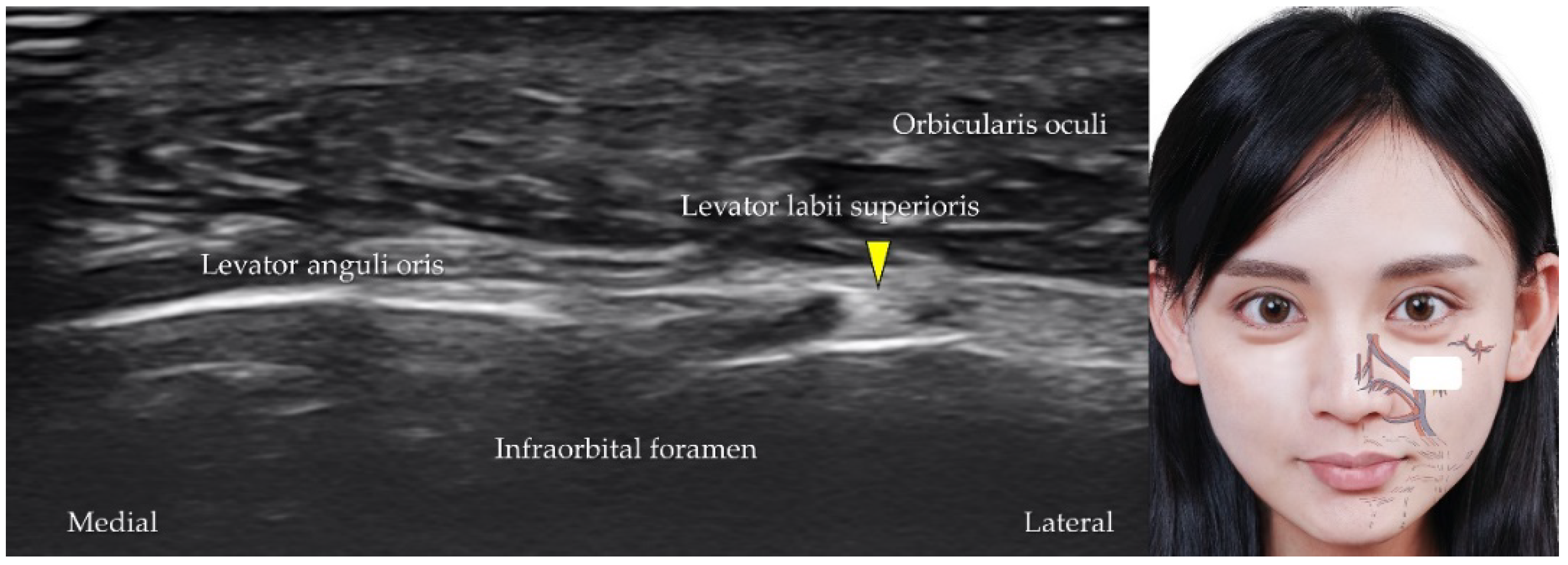
5.4. Infraorbital Artery, Vein, and Nerve
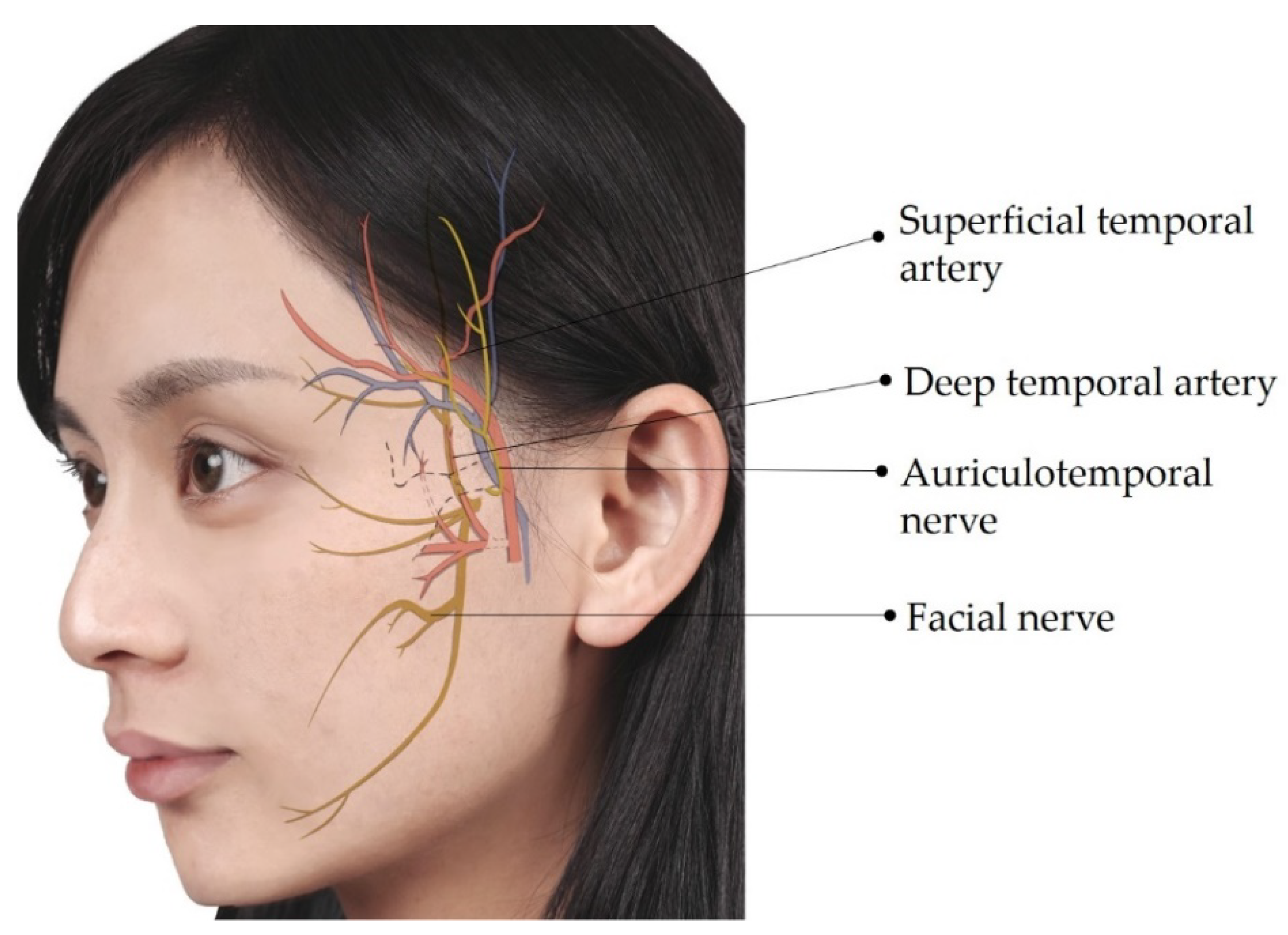
5.5. Superficial Temporal Artery and Vein
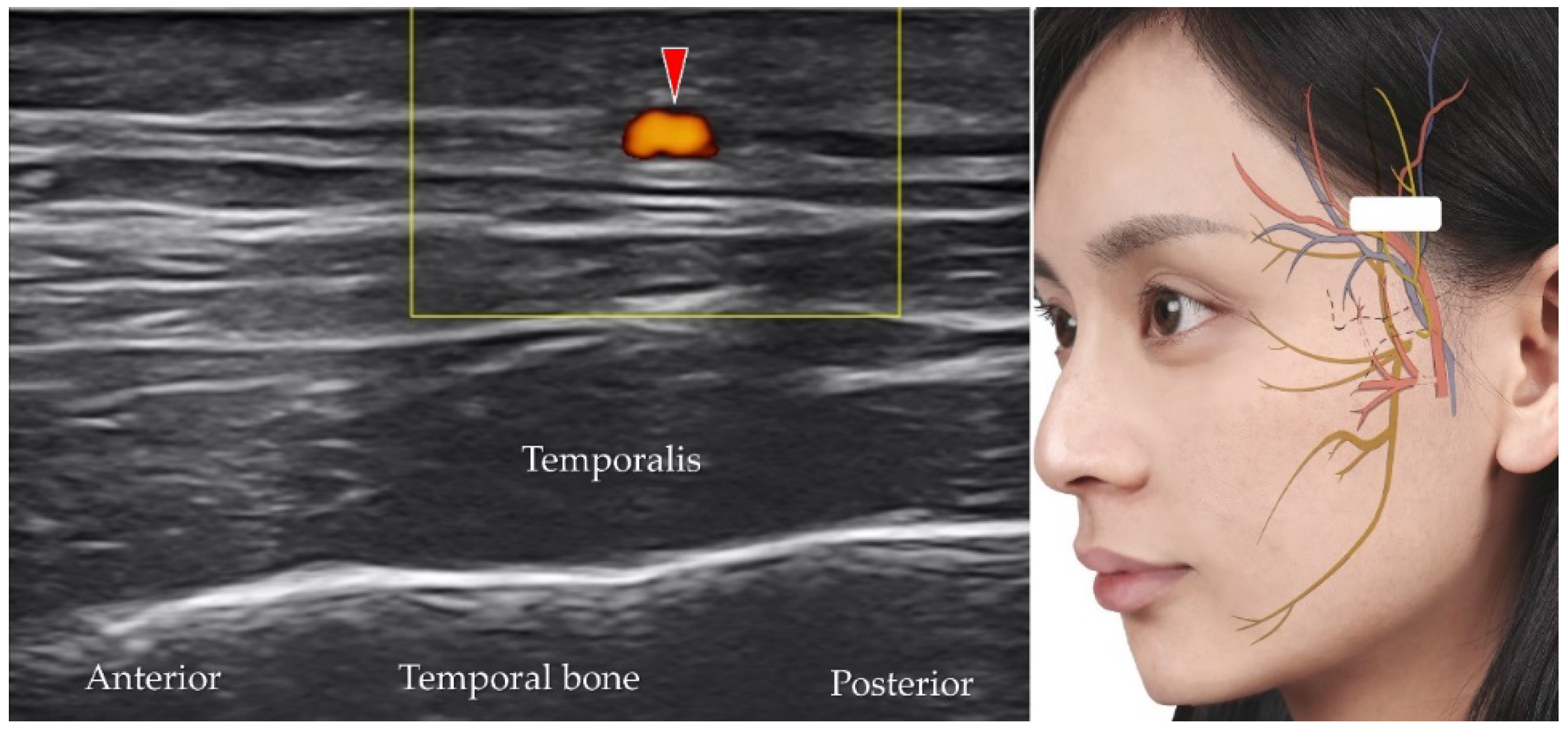
5.6. Deep Temporal Artery and Vein
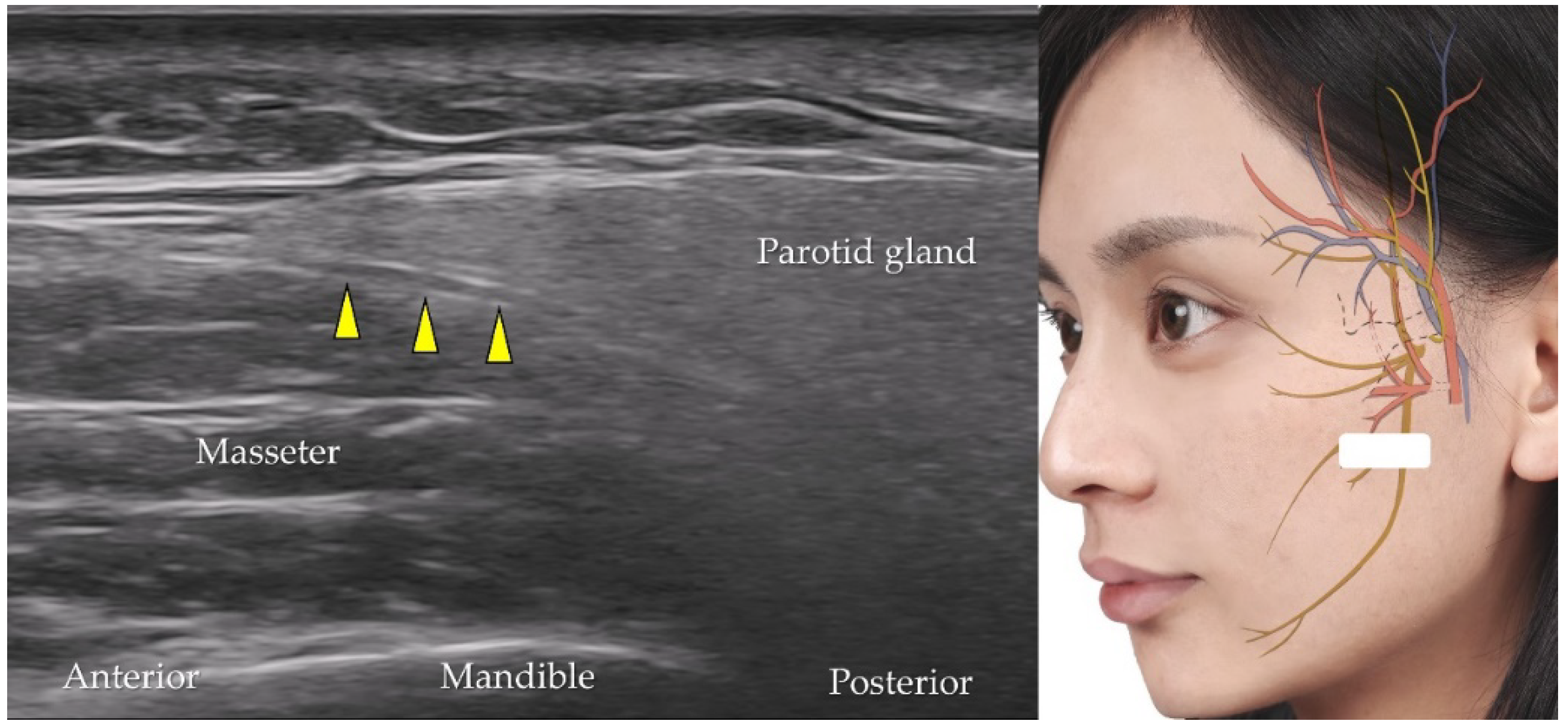
5.7. Auriculotemporal Nerve
5.8. Facial Nerve
6. Sonoanatomy of the Neurovascular Structures of the Lower Face
6.1. Facial Artery and Vein
6.2. Inferior Labial Artery and Vein
6.3. Mental Nerve
7. Sonoanatomy of the Neurovascular Structures of the Submental Region
7.1. Submental Artery
7.2. Hypoglossal Nerve
8. Factors Associated with Ultrasound-Guided Aesthetic Injections into the Facial and Submental Regions
- (i)
- Injectors unfamiliar with real-time guided injections should perform ultrasound imaging using a marking pen to confirm important neurovascular structures. This method facilitates palpation-based injections after removing the transducer and provides a guideline to avoid the marked regions.
- (ii)
- Injectors familiar with ultrasound-guided techniques should prepare an ultrasound machine equipped with a high-frequency (>20 MHz) transducer, which also has a small footprint (<2.5 cm in width). The out-of-plane approach, which allows multiple injections in one scanning plane, is recommended to shorten the needle pathway under the skin.
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nestor, M.; Cohen, J.L.; Landau, M.; Hilton, S.; Nikolis, A.; Haq, S.; Viel, M.; Andriopoulos, B.; Prygova, I.; Foster, K.; et al. Onset and Duration of AbobotulinumtoxinA for Aesthetic Use in the Upper face: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2020, 13, E56–E83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akinbiyi, T.; Othman, S.; Familusi, O.; Calvert, C.; Card, E.B.; Percec, I. Better Results in Facial Rejuvenation with Fillers. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, S.; Femmer, P.; Beleznay, K.; Carruthers, J.D.A. Deoxycholic Acid for Submental Fullness and More: Real-World Experience With 202 Patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, H. Facial Injections and Blindness: A Review on Anatomy. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 88, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Nooreyezdan, S. Nonvascular Complications of Injectable Fillers-Prevention and Management. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2020, 53, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Wang, J.C.; Ozcakar, L. Effects of Ultrasound-Guided Peritendinous and Intrabursal Corticosteroid Injections on Shoulder Tendon Elasticity: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 102, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcakar, L.; Kara, M.; Chang, K.V.; Carl, A.B.; Akkaya, N.; Tok, F.; Chen, W.S.; Wang, T.G.; Tekin, L.; Ulasl, A.M.; et al. Nineteen reasons why physiatrists should do musculoskeletal ultrasound: EURO-MUSCULUS/USPRM recommendations. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 94, e45–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.V.; Wu, S.H.; Lin, S.H.; Shieh, J.Y.; Wang, T.G.; Chen, W.S. Power Doppler presentation of shoulders with biceps disorder. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.T.; Chang, K.V.; Chang, H.C.; Chen, L.R.; Kuan, C.H.; Kao, J.T.; Wei, L.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Han, D.S.; Ozcakar, L. Ultrasound Imaging of the Facial Muscles and Relevance with Botulinum Toxin Injections: A Pictorial Essay and Narrative Review. Toxins 2022, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, R. Botulinum toxin injection for facial wrinkles. Am. Fam. Phys. 2014, 90, 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, J.S.; Kream, E.; Fabi, S.; Cohen, S.R. Facial Rejuvenation with Fat Grafting and Fillers. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2021, 41, S31–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agorgianitis, L.; Panagouli, E.; Tsakotos, G.; Tsoucalas, G.; Filippou, D. The Supratrochlear Artery Revisited: An Anatomic Review in Favor of Modern Cosmetic Applications in the Area. Cureus 2020, 12, e7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, N.; Outi, H. Relation of the supraorbital nerve and vessels to the notch and foramen of the supraorbital margin. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn. 1962, 38, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Allam, A.E.; Khalil, A.A.F.; Eltawab, B.A.; Wu, W.T.; Chang, K.V. Ultrasound-Guided Intervention for Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia: An Updated Review of Anatomy and Techniques. Pain Res. Manag. 2018, 2018, 5480728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, N.; Nakajima, H.; Minabe, T.; Chang, H.; Aiso, S. Venous drainage architecture of the temporal and parietal regions: Anatomy of the superficial temporal artery and vein. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 109, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansatit, T.; Apinuntrum, P.; Phetudom, T. Facing the Worst Risk: Confronting the Dorsal Nasal Artery, Implication for Non-surgical Procedures of Nasal Augmentation. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2017, 41, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombolevskiy, V.; Gelezhe, P.; Morozov, S.; Melnikov, D.V.; Vorontsov, A.; Kulberg, N.; Frank, K.; Gotkin, R.H.; Lachman, N.; Cotofana, S. The Course of the Angular Artery in the Midface: Implications for Surgical and Minimally Invasive Procedures. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2021, 41, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Gil, Y.C.; Choi, Y.J.; Tansatit, T.; Kim, H.J.; Hu, K.S. Topographic anatomy of the superior labial artery for dermal filler injection. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Lee, K.-L.; Gil, Y.-C.; Hu, K.-S.; Tansatit, T.; Kim, H.-J. Topographic Anatomy of the Infraorbital Artery and Its Clinical Implications for Nasolabial Fold Augmentation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 273e–280e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinar, Y.A.; Govsa, F. Anatomy of the superficial temporal artery and its branches: Its importance for surgery. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2006, 28, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Núñez, T.; Amghar-Maach, S.; Gay-Escoda, C. Efficacy of botulinum toxin in the treatment of bruxism: Systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2019, 24, e416–e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotofana, S.; Alfertshofer, M.; Schenck, T.L.; Bertucci, V.; Beleznay, K.; Ascher, B.; Lachmann, N.; Green, J.B.; Swift, A.; Frank, K. Anatomy of the Superior and Inferior Labial Arteries Revised: An Ultrasound Investigation and Implication for Lip Volumization. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2020, 40, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atamaz Pinar, Y.; Govsa, F.; Bilge, O. The anatomical features and surgical usage of the submental artery. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2005, 27, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Reissig, L.F.; Tzou, C.H.; Meng, K.; Grisold, W.; Weninger, W. Ultrasound of the Hypoglossal Nerve in the Neck: Visualization and Initial Clinical Experience with Patients. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.R. Traumatic injury to peripheral nerves. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Chang, K.V.; Mezian, K.; Nanka, O.; Wu, W.T.; Yang, Y.C.; Meng, S.; Ricci, V.; Ozcakar, L. Sonographic Pearls for Imaging the Brachial Plexus and Its Pathologies. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLorenzi, C. Complications of Injectable Fillers, Part 2: Vascular Complications. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2014, 34, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotofana, S.; Velthuis, P.J.; Alfertshofer, M.; Frank, K.; Bertucci, V.; Beleznay, K.; Swift, A.; Gavril, D.L.; Lachman, N.; Schelke, L. The Change of Plane of the Supratrochlear and Supraorbital Arteries in the Forehead-An Ultrasound-Based Investigation. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2021, 41, NP1589–NP1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janis, J.E.; Hatef, D.A.; Hagan, R.; Schaub, T.; Liu, J.H.; Thakar, H.; Bolden, K.M.; Heller, J.B.; Kurkjian, T.J. Anatomy of the Supratrochlear Nerve: Implications for the Surgical Treatment of Migraine Headaches. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napier, A.; De Jesus, O.; Taylor, A. Supraorbital Nerve Block; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Shen, Y.; Luo, F. Treatment of Supraorbital Neuralgia Using Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation of the Supraorbital Nerve: A Retrospective Study. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziej, M.; Wnuk, J.; Polak, J.; Trybus, M.; Pękala, P.; Pękala, J.; Hołda, M.; Antoszewski, B.; Tomaszewski, K. The superficial temporal artery: A meta-analysis of its prevalence and morphology. Clin. Anat. 2020, 33, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansatit, T.; Jitaree, B.; Uruwan, S.; Rungsawang, C. Anatomical Study of the Dorsal Nasal Artery to Prevent Visual Complications during Dorsal Nasal Augmentation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfertshofer, M.G.; Frank, K.; Moellhoff, N.; Helm, S.; Freytag, L.; Mercado-Perez, A.; Hargiss, J.B.; Dumbrava, M.; Green, J.B.; Cotofana, S. Ultrasound Anatomy of the Dorsal Nasal Artery as it Relates to Liquid Rhinoplasty Procedures. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 30, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimatsu, H.; Harima, M.; Iida, T.; Narushima, M.; Karakawa, R.; Nakatsukasa, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Hayashi, A. Use of the Distal Facial Artery (Angular Artery) for Supermicrosurgical Midface Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.L.; Lee, H.J.; Youn, K.H.; Kim, H.J. Positional relationship of superior and inferior labial artery by ultrasonography image analysis for safe lip augmentation procedures. Clin. Anat. 2020, 33, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalek, P.; Donaldson, W.; McAleavey, F.; Johnston, P.; Kiska, R. Ultrasound imaging of the infraorbital foramen and simulation of the ultrasound-guided infraorbital nerve block using a skull model. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2013, 35, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahaliou, M.; Vaiopoulos, G.; Papaspyrou, S.; Kanakis, M.A.; Revenas, K.; Sfikakis, P.P. Colour duplex sonography of temporal arteries before decision for biopsy: A prospective study in 55 patients with suspected giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolis, A.; Enright, K.M.; Troupis, T.; Koutsilieris, M.; Stratigos, A.J.; Rigopoulos, D.; Cotofana, S. Topography of the deep temporal arteries and implications for performing safe aesthetic injections. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xue, Y.; Liu, P. Application of auriculotemporal nerve block and dextrose prolotherapy in exercise therapy of TMJ closed lock in adolescents and young adults. Head Face Med. 2021, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, E.A. Sonographic characteristics of the facial nerve in healthy volunteers. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, E.A.; Walker, F.O.; Cartwright, M.S. Neuromuscular ultrasound of cranial nerves. J. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 11, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Won, S.Y.; O, J.; Hu, K.S.; Mun, S.Y.; Yang, H.M.; Kim, H.J. The facial artery: A Comprehensive Anatomical Review. Clin. Anat. 2018, 31, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















| Vessel/Nerve | Origin/Drain to | Supply | Transducer Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supratrochlear artery | Ophthalmic artery | Medial aspect of the upper eye lid forehead, glabella and frontalis muscle | The transducer is placed over the medial orbital rim in the horizontal plane |
| Supratrochlear vein | Supratrochlear foramen | Anterior forehead and scalp | The transducer is placed over the medial orbital rim in the horizontal plane |
| Supratrochlear nerve | Frontal nerve, branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1) | Cutaneous innervation of the lateral lower forehead and upper eyelid | The transducer is placed over the medial orbital rim in the horizontal plane |
| Supraorbital artery | Ophthalmic artery | Upper eyelid and skin of the forehead and the scalp | The transducer is placed in proximity over the center of the superior orbital rim |
| Supraorbital vein | Angular vein | Forehead, eyebrow, and upper eyelid | The transducer is placed in proximity over the center of the superior orbital rim |
| Supraorbital nerve | Frontal nerve, branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1) | Cutaneous sensation of the lateral forehead and upper eyelid | The transducer is placed in proximity over the center of the superior orbital rim |
| Frontal branch of the superficial temporal artery | Superficial temporal artery | Lateral aspect of the forehead with anastomosis of the supraorbital artery | The transducer is placed over the lateral part of the forehead slightly cranial to the eyebrow |
| Frontal branch of the superficial temporal vein | Superficial temporal vein | Lateral aspect of the forehead | The transducer is placed over the lateral part of the forehead slightly cranial to the eyebrow |
| Vessel/Nerve | Origin/Drain to | Supply | Transducer Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dorsal nasal artery | Ophthalmic artery | Lacrimal sac and tip of the nose | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane near the medial orbital rim |
| Dorsal nasal vein | Angular vein | Lateral side of the nose | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane near the medial orbital rim |
| Angular artery | Facial artery | Lacrimal sac, nose, lower eyelid, and orbicularis oculi muscles | The transducer can be placed in the horizontal plane lateral to the ala of the nose |
| Angular vein | Facial vein | Medial canthus, and nose and upper lip | The transducer can be placed in the horizontal plane lateral to the ala of the nose lateral to the angular artery |
| Superior labial artery | Facial artery | Upper lip | The transducer is placed in the sagittal plane medial to the angle of the mouth |
| Superior labial vein | Facial vein | Upper lip | The transducer is placed in the sagittal plane medial to the angle of the mouth |
| Infraorbital artery | Maxillary artery | Lacrimal sac, upper incisor and canine teeth | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane slightly distal to the inferior eyelid |
| Infraorbital vein | Pterygoid venous plexus | Lacrimal sac, upper incisor and canine teeth | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane slightly distal to the inferior eyelid |
| Infraorbital nerve | Maxillary nerve (CN V2) | Lower eyelid, anterior cheek, and upper lip | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane slightly distal to the inferior eyelid |
| Superficial temporal artery | External carotid artery | Parietal branch for the posterior temporal area and frontal branch for the lateral forehead | The transducer can be placed in the horizontal plane cranial to the zygomatic arch |
| Superficial temporal vein | Retromandibular vein | Posterior temporal area and lateral forehead | The transducer can be placed in the horizontal plane cranial to the zygomatic arch |
| Deep temporal artery | Maxillary artery | Temporalis muscle and temporal fossa | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane cranial to the zygomatic arch to identify the vessels under the temporalis muscle |
| Deep temporal vein | Retromandibular vein | Temporalis muscle and temporal fossa | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane cranial to the zygomatic arch to identify the vessels under the temporalis muscle |
| Auriculotemporal nerve | Mandibular nerve (CN V3) | Auricle, external acoustic meatus, and temporal region | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane slightly anterior to the tragus |
| Facial nerve | Pons of the brain stem | Motor to facial expression muscles, the posterior belly of digastric, stylohyoid; sensory to taste (anterior two-thirds of tongue) | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane at the cranial level of the mandibular ramus |
| Vessel/Nerve | Origin/Drain to | Supply | Transducer Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower face | |||
| Facial artery | External carotid artery | Anterior upper neck and anterior mandible region | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane at the midpoint of the mandibular body |
| Facial vein | Retromandibular or internal jugular vein | Anterior upper neck and anterior mandible region | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane at the midpoint of the mandibular body |
| Inferior labial artery | Facial artery | Lower lip | The transducer is placed in the sagittal plane over the lower lip |
| Inferior labial Vein | Facial vein | Lower lip | The transducer is placed in the sagittal plane over the lower lip |
| Mental nerve | Mandibular nerve (CN V3) | Cutaneous sensation of the anterior chin and lower lip | The transducer is placed in the horizontal plane caudal to the lower lip and lateral to the mental protuberance |
| Submental region | |||
| Submental artery | Facial artery | Submental area | The transducer is placed in the coronal plane over the submental region |
| Hypoglossal nerve | Brain stem | Tongue muscle | The transducer is positioned in the coronal plane over the submental area |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.-T.; Chang, K.-V.; Chang, H.-C.; Kuan, C.-H.; Chen, L.-R.; Mezian, K.; Ricci, V.; Özçakar, L. Ultrasound Imaging of Facial Vascular Neural Structures and Relevance to Aesthetic Injections: A Pictorial Essay. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071766
Wu W-T, Chang K-V, Chang H-C, Kuan C-H, Chen L-R, Mezian K, Ricci V, Özçakar L. Ultrasound Imaging of Facial Vascular Neural Structures and Relevance to Aesthetic Injections: A Pictorial Essay. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(7):1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071766
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wei-Ting, Ke-Vin Chang, Hsiang-Chi Chang, Chen-Hsiang Kuan, Lan-Rong Chen, Kamal Mezian, Vincenzo Ricci, and Levent Özçakar. 2022. "Ultrasound Imaging of Facial Vascular Neural Structures and Relevance to Aesthetic Injections: A Pictorial Essay" Diagnostics 12, no. 7: 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071766
APA StyleWu, W.-T., Chang, K.-V., Chang, H.-C., Kuan, C.-H., Chen, L.-R., Mezian, K., Ricci, V., & Özçakar, L. (2022). Ultrasound Imaging of Facial Vascular Neural Structures and Relevance to Aesthetic Injections: A Pictorial Essay. Diagnostics, 12(7), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071766








