Clinical Presentation and MRI Characteristics of Appendicular Soft Tissue Lymphoma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Quality Assessment of Included Studies
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
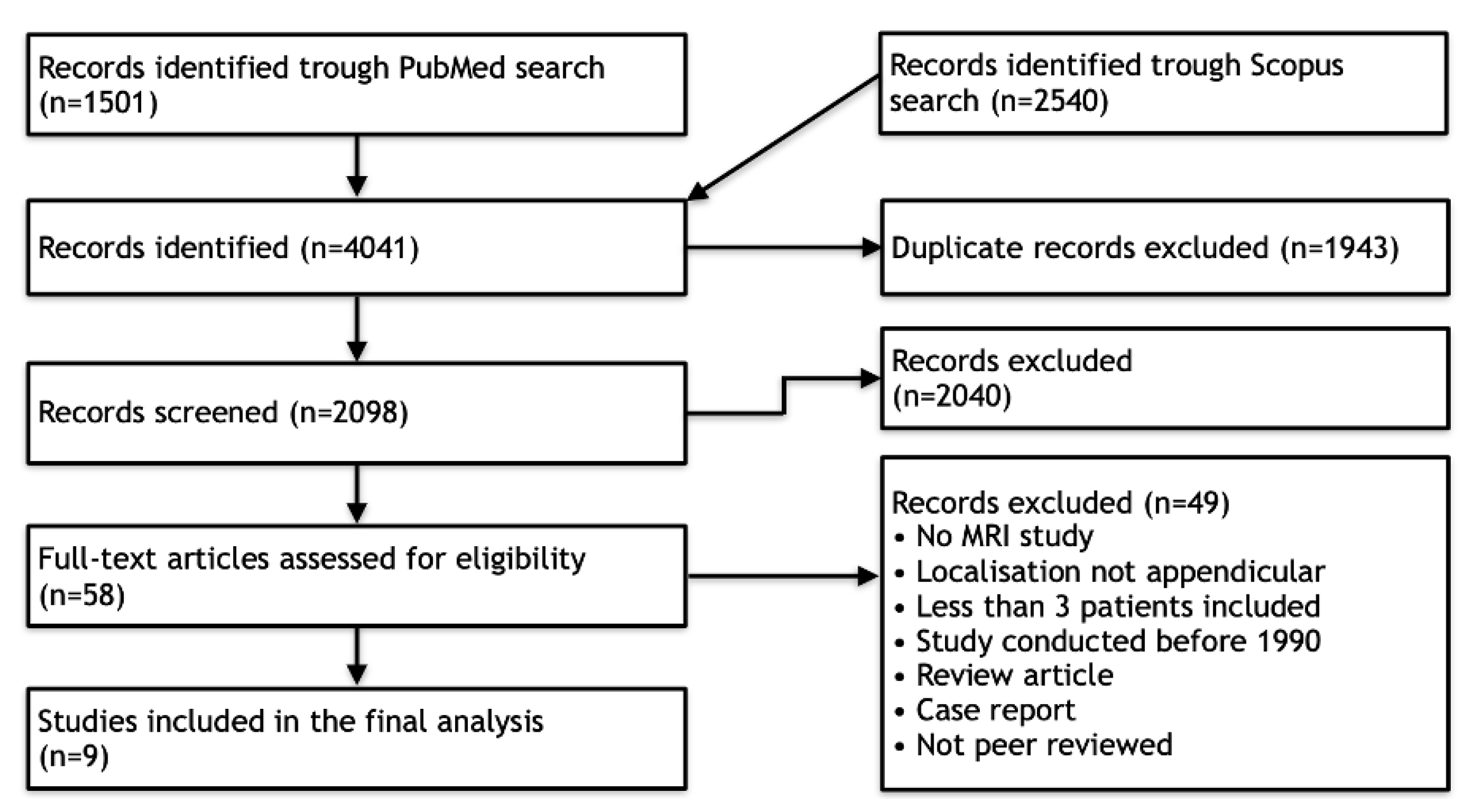
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Quality Assessment
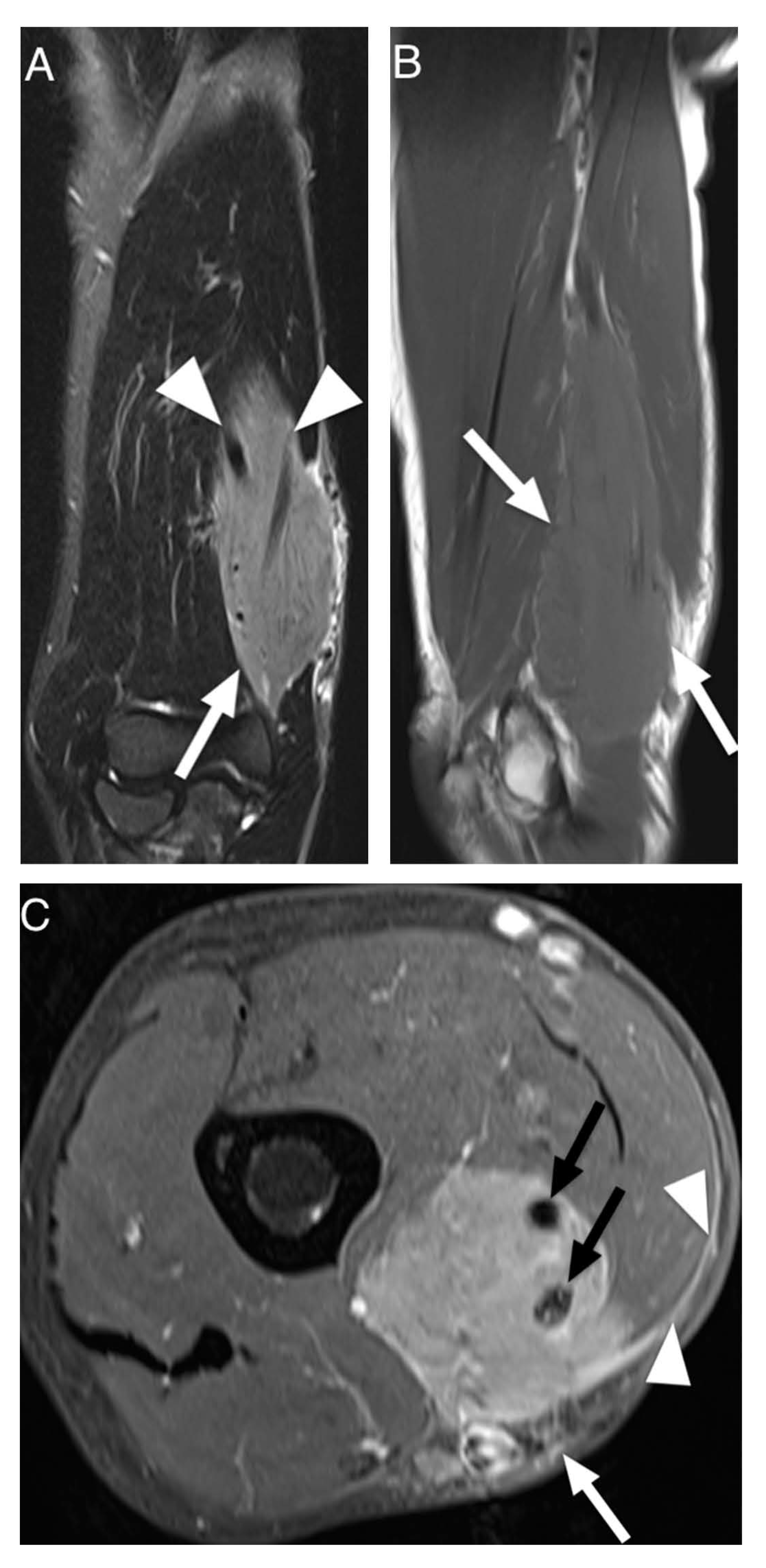
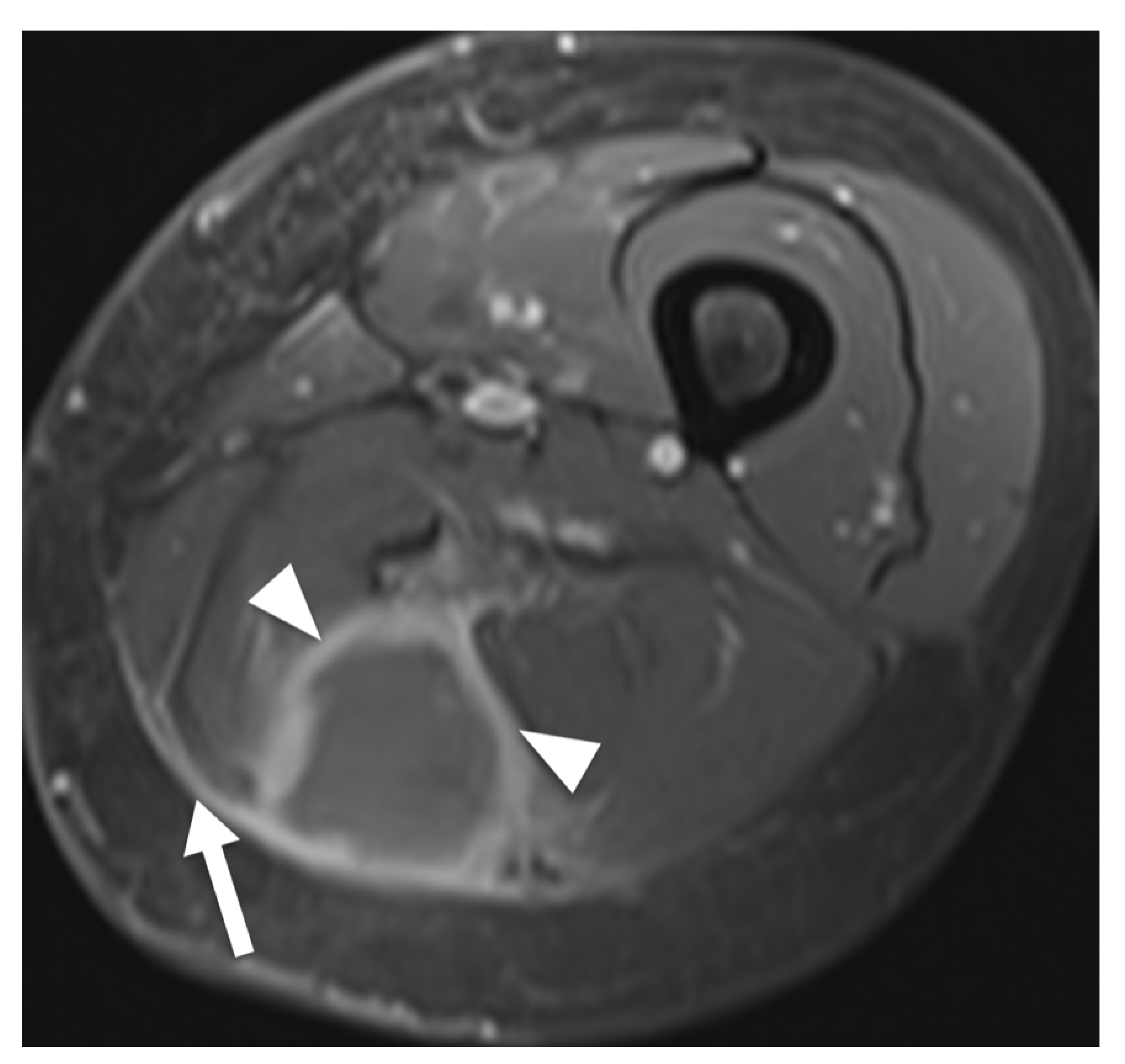
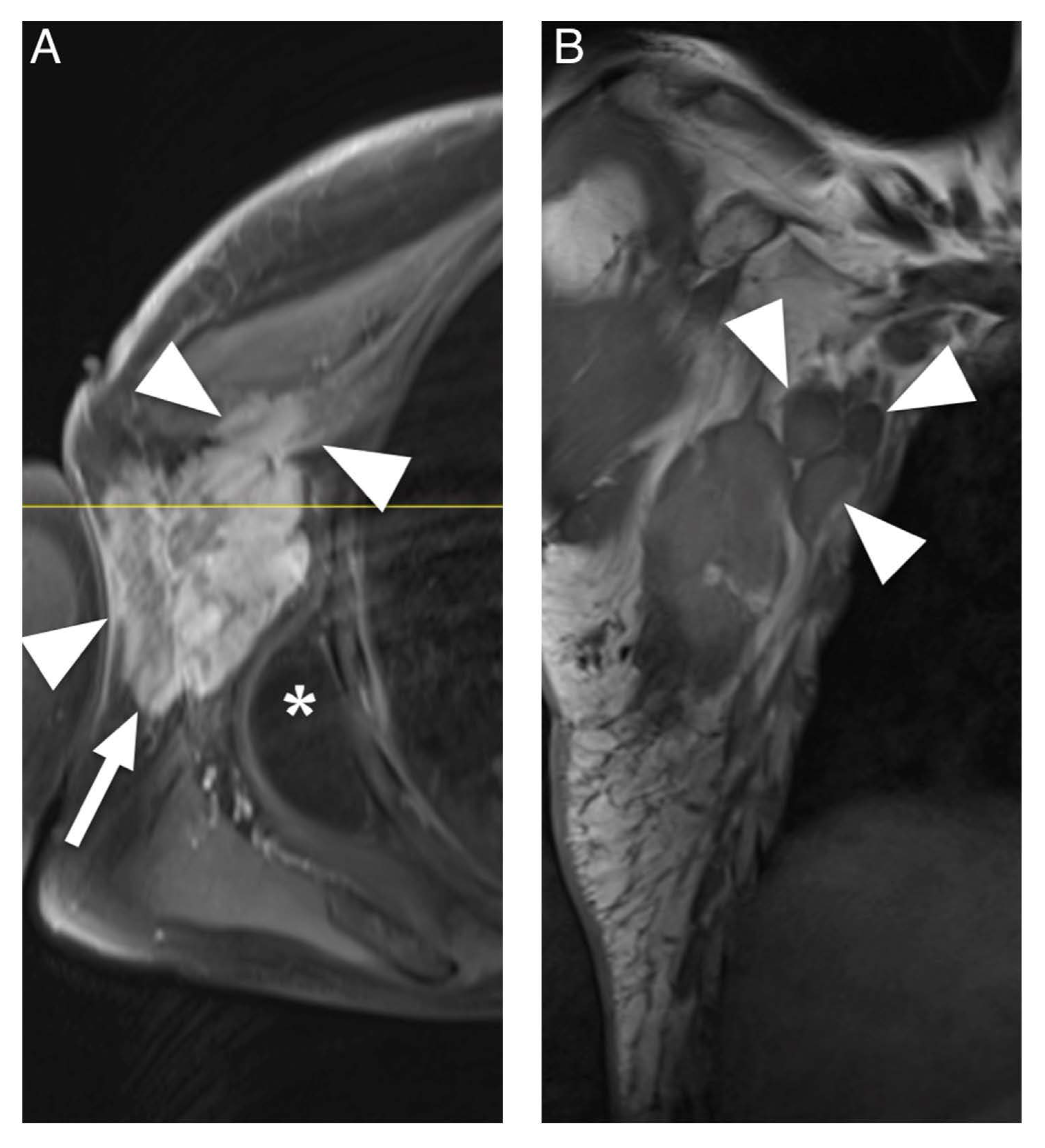
3.3. Data Extraction
| Study Parameters | Demographics | Clinical Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author/Year | AXIS Score | No. of Patients Included | Imaging Modalities | Sex | Age Range (Years) | Regional Lymphadenopathy (Yes/No) | Pain/Discomfort (Yes/No) | Swelling/Enlargement of Muscle (Based on Clinical vs. MRI Examination) (Yes/No) |
| Hosono et al., 1995 [31] | 6 | 4 | MRI/CT | 2F 2M | 58–65 | N/A | 2/4 | 4/4 (via MRI) |
| Beggs et al., 1996 [32] | 5 | 4 | MRI/ CT/ Ultrasound | 2F 2M | 42–68 | 1/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 (clinical) |
| Eustace et al., 1996 [33] | 8 | 2 | MRI | 2F | 67–68 | N/A | 1/2 | 2/2 (via MRI) |
| Lee et al., 1997 [34] | 8 | 3 | MRI/CT/ Radiography/ Scintigraphy | 3F | 15–80 | N/A | 1/3 | 3/3 (clinical) |
| Carroll et al., 2007 [19] | 9 | 7 | MRI | 2F 5M | 56–68 | 6/7 | N/A | N/A |
| Suresh et al., 2008 [18] | 10 | 24 | MRI | 10F 14M | 35–91 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Surov et al., 2010 [11] | 11 | 5 | MRI/CT | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 5/5 (via MRI) |
| Chun et al., 2010 [30] | 10 | 20 | MRI | 6F 14M | 5–90 | 0/20 | N/A | 20/20 (via MRI) |
| Surov et al., 2014 [35] | 9 | 8 | MRI | 5F 3M | 58–73 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Total | 2 Low quality 4 Medium quality 3 High quality | 77 | 4 MRI 5 Multimodal | 32F 40M 5 N/A | Range: 15–91 Mean ± SD: 59 ± 17 | 7 Yes 24 No 46 N/A | 7 Yes 6 No 64 N/A | 37 Yes 1 No 39 N/A |
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dickson, B.C.; Serra, S.; Chetty, R. Primary gastrointestinal tract lymphoma: Diagnosis and management of common neoplasms. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2006, 6, 1609–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauw, M.I.S.; Lucas, C.G.; Ohgami, R.S.; Wen, K.W. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas: A Diagnostic Overview of Key Histomorphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Genetic Features. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.S.; Song, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.M. Imaging analysis of superficial soft tissue lymphomas. Clin. Imaging 2018, 49, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitsoulis, P.; Vlychou, M.; Papoudou-Bai, A.; Karatzias, G.; Charchanti, A.; Agnantis, N.J.; Bai, M. Primary lymphomas of bone. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooksley, N.; Judge, D.J.; Brown, J. Primary pulmonary Hodgkin’s lymphoma and a review of the literature since 2006. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, bcr2014204020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Banks, P.M.; Reiman, H.M. Primary extranodal soft tissue lymphoma of the extremities. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1987, 11, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kransdorf, M.J. Malignant soft-tissue tumors in a large referral population: Distribution of diagnoses by age, sex, and location. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1995, 164, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginelli, A.; Urraro, F.; Sangiovanni, A.; Russo, G.M.; Russo, C.; Grassi, R.; Agostini, A.; Belfiore, M.P.; Cellina, M.; Floridi, C.; et al. Extranodal Lymphomas: A pictorial review for CT and MRI classification. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D.G.; Gokan, T.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Totterman, S.M.; Fultz, P.J.; Judkins, A.R.; Meyers, S.P.; Rubens, D.J.; Sickel, J.Z.; Rosier, R.N. Primary lymphoma of bone. Correlation of magnetic resonance imaging features with cytokine production by tumor cells. Cancer 1995, 75, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzek, K.A.; Wenger, D.E. The multiple faces of lymphoma of the musculoskeletal system. Skelet. Radiol. 2004, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A.; Holzhausen, H.-J.; Arnold, D.; Schmidt, J.; Spielmann, R.-P.; Behrmann, C. Intramuscular manifestation of non-hodgkin lymphoma and myeloma: Prevalence, clinical signs, and computed tomography features. Acta Radiol. 2010, 51, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, J.P.; Fleckenstein, J.L.; Vuitch, F.; Frenkel, E.P. Skeletal muscle lymphoma: MRI evaluation. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1992, 10, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.Y.; Ong, K.O. Imaging of musculoskeletal lymphoma. Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphey, M.D.; Kransdorf, M.J. Primary Musculoskeletal Lymphoma. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 54, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerson, J.L.; Scharschmidt, T.J.; Lewis, V.O.; Morris, C.D. Diagnosis and Management of Soft-tissue Masses. Instr. Course Lect. 2015, 64, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Shu, H.; Yang, H. Imaging features of skeletal muscle lymphoma: A case report and literature review. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damron, T.A.; Le, M.H.; Rooney, M.T.; Vermont, A.; Poiesz, B.J. Lymphoma presenting as a soft tissue mass. A soft tissue sarcoma simulator. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1999, 360, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Saifuddin, A.; O’Donnell, P. Lymphoma presenting as a musculoskeletal soft tissue mass: MRI findings in 24 cases. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 2628–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, G.; Breidahl, W.; Robbins, P. Musculoskeletal lymphoma: MRI of bone or soft tissue presentations. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 57, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, B.; Serpell, J.W. Extra-nodal lymphoma presenting as a mimic of soft-tissue sarcoma. ANZ J. Surg. 2003, 73, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, K.D.; Tandon, A.A.; Ho, B.C.; Chong, B.K. MRI features of soft-tissue lumps and bumps. Clin. Radiol. 2014, 69, e568–e583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nganga, E.C.; Gitau, S. Spectrum of imaging findings in AIDS-related diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, H. The imaging diagnostic criteria of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome associated with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Radiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, T.; Baxter, G. Lymphoma: Pictorial review. II. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.J.; Brennan, M.L.; Williams, H.C.; Dean, R.S. Development of a critical appraisal tool to assess the quality of cross-sectional studies (AXIS). BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.-L.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Yang, Z.-H.; Huang, D.; Weng, H.; Zeng, X.-T. Methodological quality (risk of bias) assessment tools for primary and secondary medical studies: What are they and which is better? Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McArthur, K.; Jorgensen, D.; Climstein, M.; Furness, J. Epidemiology of Acute Injuries in Surfing: Type, Location, Mechanism, Severity, and Incidence: A Systematic Review. Sports 2020, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menolotto, M.; Komaris, D.S.; Tedesco, S.; O’Flynn, B.; Walsh, M. Motion Capture Technology in Industrial Applications: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, C.W.; Jee, W.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.H. MRI features of skeletal muscle lymphoma. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Kotoura, Y.; Tsuboyama, T.; Tsutsui, K.; Konishi, J. Involvement of muscle by malignant lymphoma: MR and CT appearances. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1995, 19, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beggs, I. Primary muscle lymphoma. Clin. Radiol. 1997, 52, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustace, S.; Winalski, C.S.; McGowen, A.; Lan, H.; Dorfman, D. Skeletal muscle lymphoma: Observations at MR imaging. Skeletal Radiol. 1996, 25, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.S.; Martinez, S.; Coleman, R.E. Primary muscle lymphoma: Clinical and imaging findings. Radiology 1997, 203, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A.; Behrmann, C. Diffusion-weighted imaging of skeletal muscle lymphoma. Skeletal Radiol. 2014, 43, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaheb, Z.; Aledavood, A.; Farzad, F. Distributions of major sub-types of lymphoid malignancies among adults in Mashhad, Iran. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011, 35, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, H.J.; Chou, Y.H.; Chiou, S.Y.; Chen, W.M.; Chen, W.; Wang, H.K.; Chang, C.Y. High-resolution ultrasonography of primary peripheral soft tissue lymphoma. J. Ultrasound Med. 2005, 24, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, H.-J.; Chou, Y.-H.; Chiou, S.-Y.; Chen, W.-M.; Chen, W.; Wan, H.-K.; Chao, T.-C.; Chang, C.-Y. Superficial soft-tissue lymphoma: Sonographic appearance and early survival. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A. Imaging findings of skeletal muscle lymphoma. Clin. Imaging 2014, 38, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracke, P.; Vanhoenacker, F.; De Schepper, A.M. Soft Tissue Lymphoma. In Imaging of Soft Tissue Tumors; De Schepper, A.M., Parizel, P.M., De Beuckeleer, L., Vanhoenacker, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, J.K.; Devaraj, V.; Silver, D.A.; Sarsfield, P.; Stone, C.A. Extranodal lymphomas presenting as soft tissue sarcomas to a sarcoma service over a two-year period. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2007, 60, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano-Massiah, S.; Luciani, A.; Itti, E.; Zerbib, P.; Vignaud, A.; Belhadj, K.; Baranes, L.; Haioun, C.; Lin, C.; Rahmouni, A. Whole-Body Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Hodgkin Lymphoma and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Radiographics 2015, 35, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, K.; Duetsch, S.; Fauser, C.; Eiber, M.; Rummeny, E.J.; Gaa, J. Value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the differentiation between benign and malignant cervical lymph nodes. Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 72, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A.; Nagata, S.; Razek, A.A.; Tirumani, S.H.; Wienke, A.; Kahn, T. Comparison of ADC values in different malignancies of the skeletal musculature: A multicentric analysis. Skeletal Radiol. 2015, 44, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudeck, O.; Zeile, M.; Pink, D.; Pech, M.; Tunn, P.U.; Reichardt, P.; Ludwig, W.D.; Hamm, B. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging allows monitoring of anticancer treatment effects in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrizzi, L.; Fiorentino, M.V.; Salvagno, L.; Segati, R.; Pappagallo, G.L.; Fosser, V. Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) as a prognostic index for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Eur. J. Cancer Clin. Oncol. 1982, 18, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, L.M.; White, J.; Lessells, A.M.; Roddie, H.; Matheson, L.M. Primary non-Hodgkins lymphoma of muscle. Clin. Oncol. R. Coll. Radiol. 1999, 11, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Question No. | Introduction |
|---|---|
| Q1 | Were the aims/objectives of the study clear? |
| Methods | |
| Q2 | Was the study design appropriate for the stated aim(s)? |
| Q3 | Was the sample size justified? |
| Q4 | Was the target/reference population clearly defined, did the sample frame represent the defined target/reference population and was the selection process appropriately? |
| Q5 | Were the methods sufficiently described to enable them to be repeated? |
| Results | |
| Q6 | Were the basic data adequately described? |
| Q7 | Were the results internally consistent? |
| Q8 | Were the results presented for all the analyses described in the methods? |
| Discussion | |
| Q9 | Were the authors discussions and conclusions justified by the results? |
| Q10 | Were the limitations of the study discussed? |
| Other | |
| Q11 | Were there any funding sources or conflicts of interest that may affect the authors interpretation of the results? |
| Q12 | Was ethical approval or consent of participants attained? |
| AXIS Score | Risk of Bias | Reporting Quality | Number of Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–6 | High | Low | 2 |
| 7–9 | Medium | Medium | 4 |
| 10–12 | Low | High | 3 |
| Author/Year | T1W 1 | T2W 1 | T2W 2 | PD 1 | STIR 1 | T1W Contrast Enhancement | Margins | No. of Affected Compartments | Long Segmental Involvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hosono et al., 1995 [31] | 2 Slightly hyperintense 2 Isointense | 3 Hyperintense 1 N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2 Homogeneous 2 N/A | N/A | 1 Multiple 3 Single | 2 Yes 2 N/A |
| Beggs et al., 1996 [32] | 3 Slightly hyperintense 1 N/A | 3 Hyperintense 1 N/A | N/A | 3 Hyperintense 1 N/A | 2 Hyperintense 2 N/A | 2 Heterogeneous 2 N/A | 1 Well-defined 3 poorly-defined | 3 Multiple 1 Single | N/A |
| Eustace et al., 1996 [33] | 2 Isointense | 2 Hyperintense | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2 Homogeneous | 1 Well-defined 1 N/A | 1 Multiple 1 Single | N/A |
| Lee et al., 1997 [34] | 3 Isointense | N/A | 3 Hyperintense | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | “Often more than one” | 3 Yes |
| Carroll et al., 2007 [19] | 5 Iso to slightly hyperintense 1 Isointense 1 Hyperintense | 7 Hyperintense | N/A | N/A | N/A | 5 Homogeneous 2 Heterogeneous | 4 Well-defined 3 Poorly-Defined | 5 Multiple 2 Single | N/A |
| Suresh et al., 2008 [18] | 15 slightly hyperintense 8 Isointense 1 N/A | 14 hyperintense 10 N/A | 14 hypointense 10 N/A | N/A | 16 Hyperintense 8 N/A | 4 Homogeneous 9 Heterogeneous 11 N/A | 8 Well-defined 16 Poorly-defined | 12 Multiple 12 Single | N/A |
| Surov et al., 2010 [11] | 5 Isointense | 5 Hyperintense | 5 hypointense | N/A | N/A | 5 Homogeneous | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Chun et al., 2010 [30] | 9 Slightly hyperintense 11 Isointense | N/A | 20 Intermediate (isointense) | N/A | N/A | 13 Diffuse homogeneous 4 Thick peripheral bandlike 2 Marginal-septal 1 N/A | N/A | 14 Multiple 6 Single | 15 Yes 5 No |
| Surov et al., 2014 [35] | 8 Isointense | 8 Hyperintense | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Total | 40 Isointense 29 Slightly hyperintense 5 Iso- to slightly hyperintense 1 Hyperintense 2 N/A | 42 Hyperintense 35 N/A | 20 Intermediate (Isointense) 19 Hypointense 3 Hyperintense 35 N/A | 3 Hyperintense 74 N/A | 18 Hyperintense 59 N/A | 31 Homogeneous 19 Heterogeneous 27 N/A | 22 Poorly-defined 14 Well-defined 41 N/A | 36 Multiple 25 Single 16 N/A | 20 Yes 5 No 52 N/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weiss, S.; Weisse, V.; Korthaus, A.; Bannas, P.; Frosch, K.-H.; Schlickewei, C.; Barg, A.; Priemel, M. Clinical Presentation and MRI Characteristics of Appendicular Soft Tissue Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071623
Weiss S, Weisse V, Korthaus A, Bannas P, Frosch K-H, Schlickewei C, Barg A, Priemel M. Clinical Presentation and MRI Characteristics of Appendicular Soft Tissue Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(7):1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071623
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeiss, Sebastian, Valentin Weisse, Alexander Korthaus, Peter Bannas, Karl-Heinz Frosch, Carsten Schlickewei, Alexej Barg, and Matthias Priemel. 2022. "Clinical Presentation and MRI Characteristics of Appendicular Soft Tissue Lymphoma: A Systematic Review" Diagnostics 12, no. 7: 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071623
APA StyleWeiss, S., Weisse, V., Korthaus, A., Bannas, P., Frosch, K.-H., Schlickewei, C., Barg, A., & Priemel, M. (2022). Clinical Presentation and MRI Characteristics of Appendicular Soft Tissue Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics, 12(7), 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071623






