Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Plasma Level Influences the Effect of n-3 PUFA Supplementation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
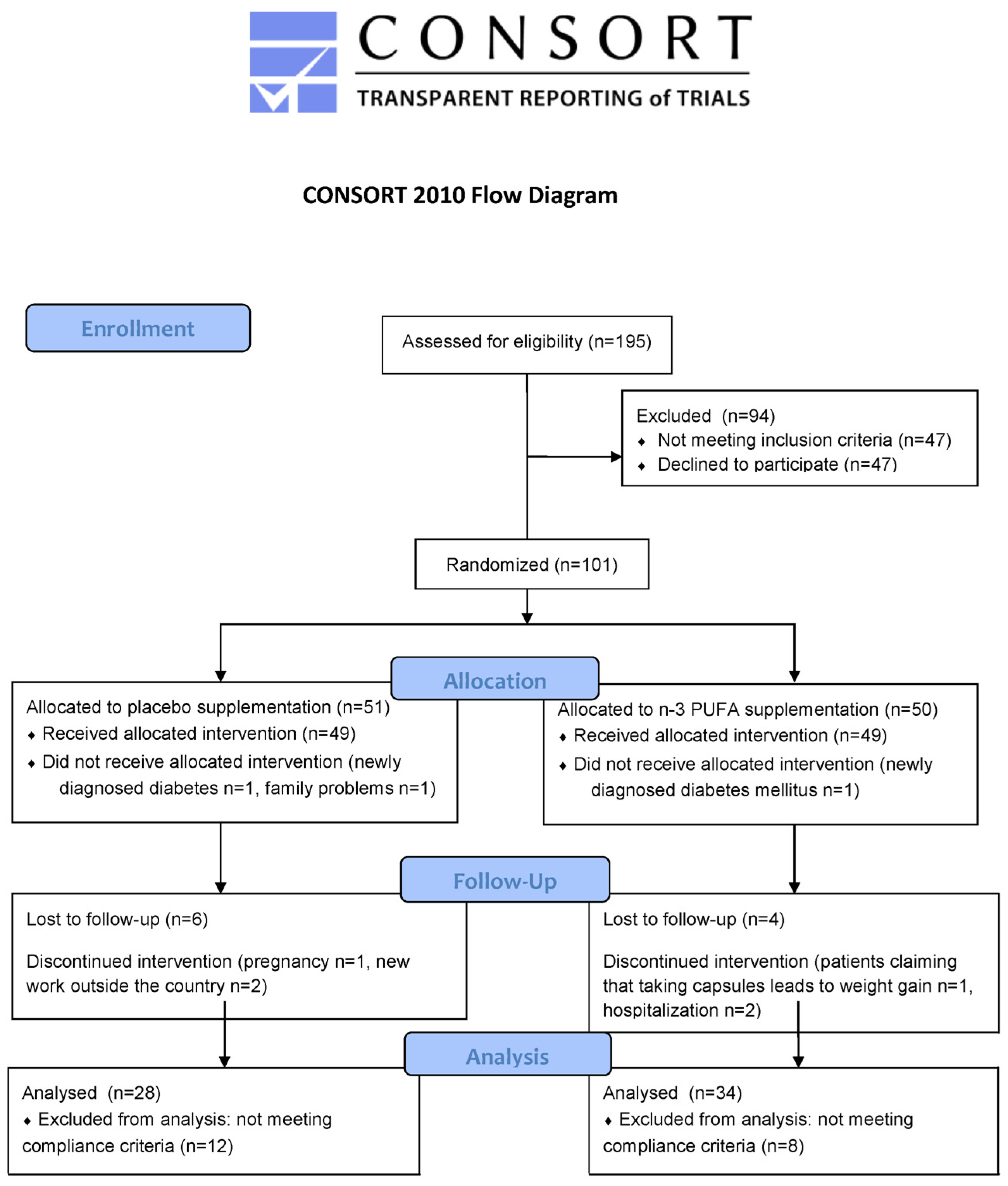
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Anthropometric Measures and Blood Collection
2.3. Blood Analyses
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Effect of n-3 PUFA Supplementation on Markers of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism
3.3. Effect of n-3 PUFA Supplementation on Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism According to GIP Plasma Levels
3.4. Effect of n-3 PUFA supplementation on Plasma Fatty Acid Profile According to Plasma GIP Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samms, R.J.; Coghlan, M.P.; Sloop, K.W. How May GIP Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy of GLP-1? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, N.; Gault, V.A.; O’Harte, F.P.M.; Flatt, P.R. Blockade of Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide (GIP) Action as a Novel Means of Countering Insulin Resistance in the Treatment of Obesity-Diabetes. Peptides 2020, 125, 170203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Delessa, C.T.; Augustin, R.; Bakhti, M.; Colldén, G.; Drucker, D.J.; Feuchtinger, A.; Caceres, C.G.; Grandl, G.; Harger, A.; et al. The Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) Regulates Body Weight and Food Intake via CNS-GIPR Signaling. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 833–844.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thondam, S.K.; Daousi, C.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Holst, J.J.; Ameen, G.I.; Yang, C.; Whitmore, C.; Mora, S.; Cuthbertson, D.J. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Promotes Lipid Deposition in Subcutaneous Adipocytes in Obese Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Maladaptive Response. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 312, E224–E233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsche, L.; Heni, M.; Eckstein, S.S.; Hummel, J.; Schürmann, A.; Häring, H.-U.; Preißl, H.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Peter, A.; Fritsche, A.; et al. Incretin Hypersecretion in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e2425–e2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polus, A.; Zapala, B.; Razny, U.; Gielicz, A.; Kiec-Wilk, B.; Malczewska-Malec, M.; Sanak, M.; Childs, C.E.; Calder, P.C.; Dembinska-Kiec, A. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation Influences the Whole Blood Transcriptome in Women with Obesity, Associated with pro-Resolving Lipid Mediator Production. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 1746–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razny, U.; Goralska, J.; Calder, P.C.; Gruca, A.; Childs, C.E.; Kapusta, M.; Slowinska-Solnica, K.; Dembinska-Kiec, A.; Solnica, B.; Malczewska-Malec, M. The Effect of Caloric Restriction with and without N-3 Pufa Supplementation on Bone Turnover Markers in Blood of Subjects with Abdominal Obesity: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Gobbo, L.C.; Imamura, F.; Aslibekyan, S.; Marklund, M.; Virtanen, J.K.; Wennberg, M.; Yakoob, M.Y.; Chiuve, S.E.; dela Cruz, L.; Frazier-Wood, A.C.; et al. ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Biomarkers and Coronary Heart Disease: Pooling Project of 19 Cohort Studies. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Amar, M.; Sampson, M.; Courville, A.B.; Sorokin, A.V.; Gordon, S.M.; Aponte, A.M.; Stagliano, M.; Playford, M.P.; Fu, Y.P.; et al. Comparison of Omega-3 Eicosapentaenoic Acid versus Docosahexaenoic Acid-Rich Fish Oil Supplementation on Plasma Lipids and Lipoproteins in Normolipidemic Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Venditti, C.; Lee, H.Y.; Darch, M.; Floyd, S.; West, S.; Simon, R. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Intervention Studies on the Effectiveness of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 581–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, L.; Gunn, P.J. The Regulation of Hepatic Fatty Acid Synthesis and Partitioning: The Effect of Nutritional State. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaire, J.; Vors, C.; Harris, W.S.; Jackson, K.H.; Tchernof, A.; Couture, P.; Lamarche, B. Comparing the Serum TAG Response to High-Dose Supplementation of Either DHA or EPA among Individuals with Increased Cardiovascular Risk: The ComparED Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbuMweis, S.; Jew, S.; Tayyem, R.; Agraib, L. Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid Containing Supplements Modulate Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Placebo-Control Human Clinical Trials. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 31, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Metabolic Partitioning of Fatty Acids within the Liver in the Context of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2022, 25, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razny, U.; Kiec-Wilk, B.; Polus, A.; Goralska, J.; Malczewska-Malec, M.; Wnek, D.; Zdzienicka, A.; Gruca, A.; Childs, C.E.; Kapusta, M.; et al. Effect of Caloric Restriction with or without N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Subjects: A Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial. BBA Clin. 2015, 4, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Góralska, J.; Raźny, U.; Polus, A.; Dziewońska, A.; Gruca, A.; Zdzienicka, A.; Dembińska-Kieć, A.; Solnica, B.; Micek, A.; Kapusta, M.; et al. Enhanced GIP Secretion in Obesity Is Associated with Biochemical Alteration and MiRNA Contribution to the Development of Liver Steatosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razny, U.; Goralska, J.; Zdzienicka, A.; Gruca, A.; Zapala, B.; Micek, A.; Dembinska-Kiec, A.; Solnica, B.; Malczewska-Malec, M. High Fat Mixed Meal Tolerance Test Leads to Suppression of Osteocalcin Decrease in Obese Insulin Resistant Subjects Compared to Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandarra, N.M.; Palma, P.; Batista, I.; Nunes, M.L.; Morais, G.; Bruges, M.; Dickson, J.; Barata, J.D.; Silva-Lima, B. Effect of a Supplemented Diet with Canned Sardine on the Lipid Fraction of Human Plasma and Erythrocytes. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2002, 11, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, C.; Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B. High-Throughput Analysis of Total Plasma Fatty Acid Composition with Direct in Situ Transesterification. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e0012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.S. The Omega-3 Index as a Risk Factor for Coronary Heart Disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1997S–2002S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J.K.; Calder, P.C. The Differential Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, V.B.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Nutrient-Induced Cellular Mechanisms of Gut Hormone Secretion. Nutrients 2021, 13, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkin, L.A.; Childs, C.E.; Calder, P.C. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Intestinal Epithelium—A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grevengoed, T.J.; Trammell, S.A.J.; Svenningsen, J.S.; Makarov, M.V.; Nielsen, T.S.; Jacobsen, J.C.B.; Treebak, J.T.; Calder, P.C.; Migaud, M.E.; Cravatt, B.F.; et al. An Abundant Biliary Metabolite Derived from Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Regulates Triglycerides. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e143861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grespan, E.; Giorgino, T.; Natali, A.; Ferrannini, E.; Mari, A. Different Mechanisms of GIP and GLP-1 Action Explain Their Different Therapeutic Efficacy in Type 2 Diabetes. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2021, 114, 154415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskinen, M.-R.; Matikainen, N.; Björnson, E.; Söderlund, S.; Ainola, M.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lundbom, N.; Sihlbom, C.; Thorsell, A.; Andersson, L.; et al. Role of Endogenous Incretins in the Regulation of Postprandial Lipoprotein Metabolism. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 187, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbürger, S.M.; Bergmann, N.C.; Augustin, R.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Christensen, M.B.; Knop, F.K. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and Cardiovascular Disease. Peptides 2020, 125, 170174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimburger, S.M.N.; Nielsen, C.N.; Calanna, S.; Holst, J.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K.; Christensen, M.B. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Induces Lipolysis during Stable Basal Insulin Substitution and Hyperglycaemia in Men with Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Clinical Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Na, K. Lipid Photosensitizers for Suppression of Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide in Obese with Type 2 Diabetes. Biomaterials 2020, 246, 119977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakane, N.; Osaki, N.; Takase, H.; Suzuki, J.; Suzukamo, C.; Nirengi, S.; Suganuma, A.; Shimotoyodome, A. The Study of Metabolic Improvement by Nutritional Intervention Controlling Endogenous GIP (Mini Egg Study): A Randomized, Cross-over Study. Nutr. J. 2019, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killion, E.A.; Chen, M.; Falsey, J.R.; Sivits, G.; Hager, T.; Atangan, L.; Helmering, J.; Lee, J.; Li, H.; Wu, B.; et al. Chronic Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor (GIPR) Agonism Desensitizes Adipocyte GIPR Activity Mimicking Functional GIPR Antagonism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.-J.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.K.; Byun, J.; Kim, I.; Ha, J.-H. Lowering N-6/n-3 Ratio as an Important Dietary Intervention to Prevent LPS-Inducible Dyslipidemia and Hepatic Abnormalities in Ob/Ob Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Moriguchi, R.; Yamada, Y.; Fujita, M.; Yamato, T.; Oumi, M.; Holst, J.J.; Seino, Y. High Saturated Fatty Acid Intake Induces Insulin Secretion by Elevating Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide Levels in Healthy Individuals. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, M. The Role of GIP Receptor in the CNS for the Pathogenesis of Obesity. Diabetes 2021, 70, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H. The Evolving Story of Incretins (GIP and GLP-1) in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Disease: A Pathophysiological Update. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirro, V.; Roth, K.D.; Lin, Y.; Willency, J.A.; Milligan, P.L.; Wilson, J.M.; Ruotolo, G.; Haupt, A.; Newgard, C.B.; Duffin, K.L. Effects of Tirzepatide, a Dual GIP and GLP-1 RA, on Lipid and Metabolite Profiles in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Chai, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Zhan, S. Effect of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Lipid Profiles among Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 225–241.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjørne, A.P.; Modvig, I.M.; Holst, J.J. The Sensory Mechanisms of Nutrient-Induced GLP-1 Secretion. Metabolites 2022, 12, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CR + PLACEBO n = 28 | CR + n-3 PUFAs n = 34 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| Age [years] | 47.7 (12.9) | 47.4 (10.7) | ns |
| Sex [women] | 24 (86%) | 22 (65%) | ns |
| Weight [kg] | 93.47 (13.23) | 94.19 (16.83) | ns |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 34.35 (4.18) | 32.98 (4.35) | ns |
| Body fat [%] | 40.61 (5.14) | 37.29 (6.04) | ns |
| Glucose [mmol/L] | 5.18 (0.72) | 5.32 (0.61) | ns |
| Insulin [µIU/mL] | 16.19 (9.27) | 14.89 (9.26) | ns |
| GIP [pg/mL] | 32.21 (20.57) | 30.47 (15.15) | ns |
| NEFAs [mmol/L] | 0.78 (0.27) | 0.78 (0.32) | ns |
| TGs [mmol/L] | 1.41 (0.66) | 1.89 (1.12) | ns |
| Total-cholesterol [mmol/L] | 5.37 (1.08) | 5.67 (0.92) | ns |
| HDL-cholesterol [mmol/L] | 1.34 (0.25) | 1.25 (0.23) | ns |
| LDL-cholesterol [mmol/L] | 3.39 (0.90) | 3.65 (0.92) | ns |
| CR + PLACEBO (n = 28) | CR + n-3 PUFAs (n = 34) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 3-Months | Baseline | 3-Months | Time * Suppl. Interaction | |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p | |
| Weight [kg] | 93.47 | 86.30 ** | 94.19 | 88.24 ** | 0.244 |
| (13.23) | (13.77) | (16.83) | (15.69) | ||
| BMI [kg/m2] | 34.35 | 31.73 * | 32.98 | 30.81 ** | 0.222 |
| (4.18) | (4.66) | (4.35) | (4.07) | ||
| Body fat [%] | 40.61 | 37.60 * | 37.29 | 34.05 ** | 0.806 |
| (5.14) | (6.14) | (6.04) | (7.62) | ||
| EPA in plasma | 42.67 | 32.16 * | 41.63 | 67.36 ** | <0.001 |
| [µg/mL] | (24.97) | (12.80) | (21.83) | (32.18) | |
| DHA in plasma | 68.09 | 62.24 | 67.06 | 119.33 ** | <0.001 |
| [µg/mL] | (27.99) | (19.14) | (23.58) | (30.75) | |
| EPA in RBCs | 1.16 | 0.98 * | 1.06 | 1.97 ** | <0.001 |
| [%] | (0.46) | (0.36) | (0.37) | (0.84) | |
| DHA in RBC m. | 4.45 | 4.44 | 4.31 | 7.53 ** | <0.001 |
| [%] | (1.17) | (1.18) | (0.95) | (1.10) | |
| Omega-3 index | 5.61 | 5.42 | 5.37 | 9.49 ** | <0.001 |
| [%] | (1.51) | (1.47) | (1.22) | (1.71) | |
| Glucose fasting | 5.18 | 5.15 | 5.32 | 5.24 | 0.348 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.72) | (0.51) | (0.61) | (0.55) | |
| Insulin fasting | 16.19 | 14.62 | 14.89 | 13.60 | 0.584 |
| [µIU/mL] | (9.27) | (8.76) | (9.26) | (5.33) | |
| GIP fasting | 32.21 | 30.65 | 30.47 | 26.61 # | 0.226 |
| [pg/mL] | (20.57) | (18.05) | (15.15) | (26.05) | |
| GIP AUC-OGTT [pg/mL*min] | 76,586 (34,902) | 70,425 (33,541) | 42,152 (38,120) | 68,783 (36,920) | 0.702 |
| GIP AUC-HFMTT [pg/mL*min] | 399,913 (145,822) | 429,312 (182,117) | 420,605 (202,863) | 427,395 (185,684) | 0.676 |
| NEFA fasting | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.384 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.27) | (0.37) | (0.32) | (0.27) | |
| TG fasting | 1.41 | 1.26 | 1.89 | 1.44 * | 0.134 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.66) | (0.48) | (1.12) | (0.66) | |
| TG AUC-OGTT [mmol/L*min] | 612.97 (350.62) | 606.06 (353.74) | 674.44 (394.90) | 596.40 * (312.69) | 0.393 |
| TG AUC-HFMTT [mmol/L*min] | 3546.62 (1843.27) | 3214.71 (1448.03) | 4823.93 (2460.67) | 3520.14 * (1428.75) | 0.023 |
| Total-cholesterol | 5.37 | 5.15 | 5.67 | 5.37 | 0.779 |
| [mmol/L] | (1.08) | (1.24) | (0.92) | (1.03) | |
| HDL-cholesterol | 1.34 | 1.35 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 0.739 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.25) | (0.27) | (0.23) | (0.18) | |
| LDL-cholesterol | 3.39 | 3.23 | 3.65 | 3.47 | 0.619 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.90) | (1.05) | (0.92) | (1.01) | |
| LOW GIP n = 32 | HIGH GIP n = 30 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p | |
| Weight [kg] | 94.28 (14.18) | 93.75 (16.71) | n.s. |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 33.91 (4.08) | 33.42 (4.64) | n.s. |
| Body fat [%] | 39.21 (6.06) | 38.30 (5.77) | n.s. |
| Glucose [mmol/L] | 5.07 (0.49) | 5.8 (0.67) | 0.039 |
| Insulin [µIU/mL] | 13.80 (7.84) | 17.31 (10.30) | n.s. |
| GIP [pg/mL] | 17.97 (7.23) | 44.75 (19.06) | <0.001 |
| NEFAs [mmol/L] | 0.83 (0.33) | 0.72 (0.26) | n.s. |
| TGs [mmol/L] | 1.67 (1.05) | 1.64 (0.89) | n.s. |
| Total-cholesterol [mmol/L] | 5.51 (0.96) | 5.61 (1.05) | n.s. |
| HDL-cholesterol [mmol/L] | 1.34 (0.24) | 1.25 (0.23) | n.s. |
| LDL-cholesterol [mmol/L] | 3.48 (0.93) | 3.64 (0.89) | n.s. |
| CR + PLACEBO (n = 28) | CR + n-3 PUFA (n = 34) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOW GIP (n = 13) | HIGH GIP (n = 15) | Time * GIP Group Interaction | LOW GIP (19) | HIGH GIP (n = 15) | Time * GIP Group Interaction | Time * Supplementation Interaction | Time * GIP Group * Supplementation Interaction | |||||
| Baseline | 3-Months | Baseline | 3-Months | Baseline | 3-Months | Baseline | 3-Months | |||||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p | p | p | |
| Weight [kg] | 93.28 | 86.10 ** | 94.29 | 86.59 ** | 0.771 | 94.96 | 89.25 ** | 93.21 | 86.96 ** | 0.691 | 0.180 | 0.994 |
| (11.61) | (12.25) | (15.49) | (16.14) | (15.97) | (14.84) | (18.39) | (17.14) | |||||
| BMI [kg/m2] | 34.34 | 31.69 ** | 34.67 | 31.89 ** | 0.819 | 33.62 | 31.61 ** | 32.17 | 29.79 ** | 0.426 | 0.165 | 0.757 |
| (3.47) | (3.89) | (4.92) | (5.57) | (4.51) | (4.30) | (4.14) | (3.66) | |||||
| EPA in RBC membrane | 1.26 | 1.06 | 1.09 | 0.93 | 0.804 | 1.03 | 1.94 ** | 1.10 | 2.01 ** | 0.982 | <0.001 | 0.913 |
| [%] | (0.52) | (0.46) | (0.41) | (0.29) | (0.37) | (0.86) | (0.39) | (0.83) | ||||
| DHA in RBC membrane | 4.74 | 4.69 | 4.43 | 4.34 | 0.919 | 4.47 | 7.56 ** | 4.12 | 7.48 ** | 0.531 | <0.001 | 0.598 |
| [%] | (1.20) | (1.39) | (1.06) | (1.03) | (0.97) | (1.08) | (0.90) | (1.17) | ||||
| Omega-3 index | 5.99 | 5.75 | 5.52 | 5.27 | 0.979 | 5.50 | 9.50 ** | 5.22 | 9.48 ** | 0.662 | <0.001 | 0.717 |
| [%] | (1.61) | (1.73) | (1.34) | (1.27) | (1.29) | (1.76) | (1.14) | (1.70) | ||||
| Glucose fasting | 4.93 | 4.95 | 5.23 | 5.32 | 0.739 | 5.16 | 5.18 | 5.53 | 5.33 | 0.294 | 0.315 | 0.322 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.48) | (0.45) | (0.65) | (0.52) | (0.50) | (0.57) | (0.68) | (0.53) | ||||
| Glucose OGTT AUC | 3767 | 3273 * | 3388 | 3636 | 0.005 | 3288 | 3250 | 3821 | 3491 * | 0.207 | 0.716 | 0.003 |
| [mmol/L * min] | (716) | (647) | (503) | (951) | (800) | (828) | (916) | (869) | ||||
| Insulin fasting | 14.34 | 12.49 | 17.79 | 16.47 | 0.811 | 13.42 | 13.30 | 16.79 | 13.96 | 0.848 | 0.597 | 0.760 |
| [µIU/mL] | (9.93) | (8.51) | (8.68) | (8.83) | (6.22) | (4.58) | (12.12) | (6.29) | ||||
| Insulin OGTT AUC | 45,312 | 32,581 | 48,570 | 50,271 | 0.119 | 42,748 | 36,063 | 45,070 | 31,547 | 0.942 | 0.579 | 0.246 |
| [µIU/mL * min] | (31,114) | (21,955) | (25,845) | (34,038) | (22,599) | (21,120) | (41,210) | (16,544) | ||||
| GIP fasting | 18.25 | 18.72 | 42.59 | 35.69 | 0.364 | 17.77 | 18.73 | 46.90 | 35.82 # | 0.094 | 0.728 | 0.659 |
| [pg/mL] | (7.76) | (10.89) | (13.40) | (21.40) | (7.05) | (11.07) | (23.72) | (22.42) | ||||
| GIP 30′ OGTT | 150.1 | 134.2 | 154.9 | 141.0 | 0.942 | 153.2 | 122.5 | 215.7 | 166.7 # | 0.432 | 0.148 | 0.558 |
| [pg/mL] | (62.2) | (68.3) | (77.1) | (73.7) | (58.9) | (58.8) | (145.4) | (131.2) | ||||
| GIP OGTT AUC | 59,660 | 60,106 | 71,837 | 72,937 | 0.947 | 65,736 | 58,639 | 89,320 | 76,606 | 0.514 | 0.123 | 0.453 |
| [pg/mL * min] | (19,250) | (29,132) | 26,553) | (39,108) | (22,474) | (27,020) | (43,708) | (34,523) | ||||
| TG fasting | 1.26 | 1.04 | 1.48 | 1.48 | 0.171 | 1.96 | 1.42 | 1.80 | 1.46 | 0.412 | 0.096 | 0.735 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.63) | (0.29) | (0.71) | (0.56) | (1.20) | (0.60) | (1.04) | (0.75) | ||||
| TG OGTT AUC | 3353 | 2796 | 3842 | 3544 | 0.451 | 4919 | 3448 | 4703 | 3608 | 0.381 | 0.069 | 0.924 |
| [mmol/L *min] | (1552) | (1081) | (2246) | (1738) | (2673) | (1434) | (22,490) | (1476) | ||||
| NEFAs fasting | 0.670 | 0.663 | 0.767 | 0.744 | 0.959 | 0.732 | 0.733 | 0.750 | 0.615 * | 0.028 | 0.681 | 0.179 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.253) | (0.266) | (0.424) | (0.399) | (0.251) | (0.280) | (0.352) | (0.229) | ||||
| NEFAs OGTT AUC | 1411 | 1386 | 1618 | 1492 | 0.519 | 1665 | 1514 | 1565 | 1286 * | 0.111 | 0.409 | 0.670 |
| [mmol/L * min] | (445) | (389) | (735) | (504) | (317) | (372) | (646) | (510) | ||||
| Total-cholesterol | 5.45 | 5.00 * | 5.40 | 5.35 | 0.091 | 5.55 | 5.32 | 5.82 | 5.43 | 0.938 | 0.906 | 0.211 |
| [mmol/L] | (1.06) | (1.19) | (1.14) | (1.35) | (0.92) | (1.14) | (0.93) | (0.92) | ||||
| HDL-cholesterol | 1.44 | 1.39 | 1.26 | 1.35 | 0.087 | 1.27 | 1.26 | 1.23 | 1.23 | 0.999 | 0.646 | 0.194 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.26) | (0.22) | (0.23) | (0.31) | (0.22) | (0.21) | (0.24) | (0.15) | ||||
| LDL-cholesterol | 3.44 | 3.14 * | 3.46 | 3.32 | 0.297 | 3.50 | 3.42 | 3.84 | 3.53 | 0.942 | 0.4312 | 0.437 |
| [mmol/L] | (0.90) | (1.02) | (0.93) | (1.14) | (0.98) | (1.13) | (0.83) | (0.89) | ||||
| CR + PLACEBO (n = 28) | CR + n-3 PUFA (n = 34) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOW GIP (n = 13) | HIGH GIP (n = 15) | Time * GIP Group Interaction | LOW GIP (19) | HIGH GIP (n = 15) | Time * GIP Group Interaction | Time * Supplementation Interaction | Time * GIP Group * Supplementation Interaction | |||||
| Baseline | 3-Months | Baseline | 3-Months | Baseline | 3-Months | Baseline | 3-Months | |||||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p | p | p | |
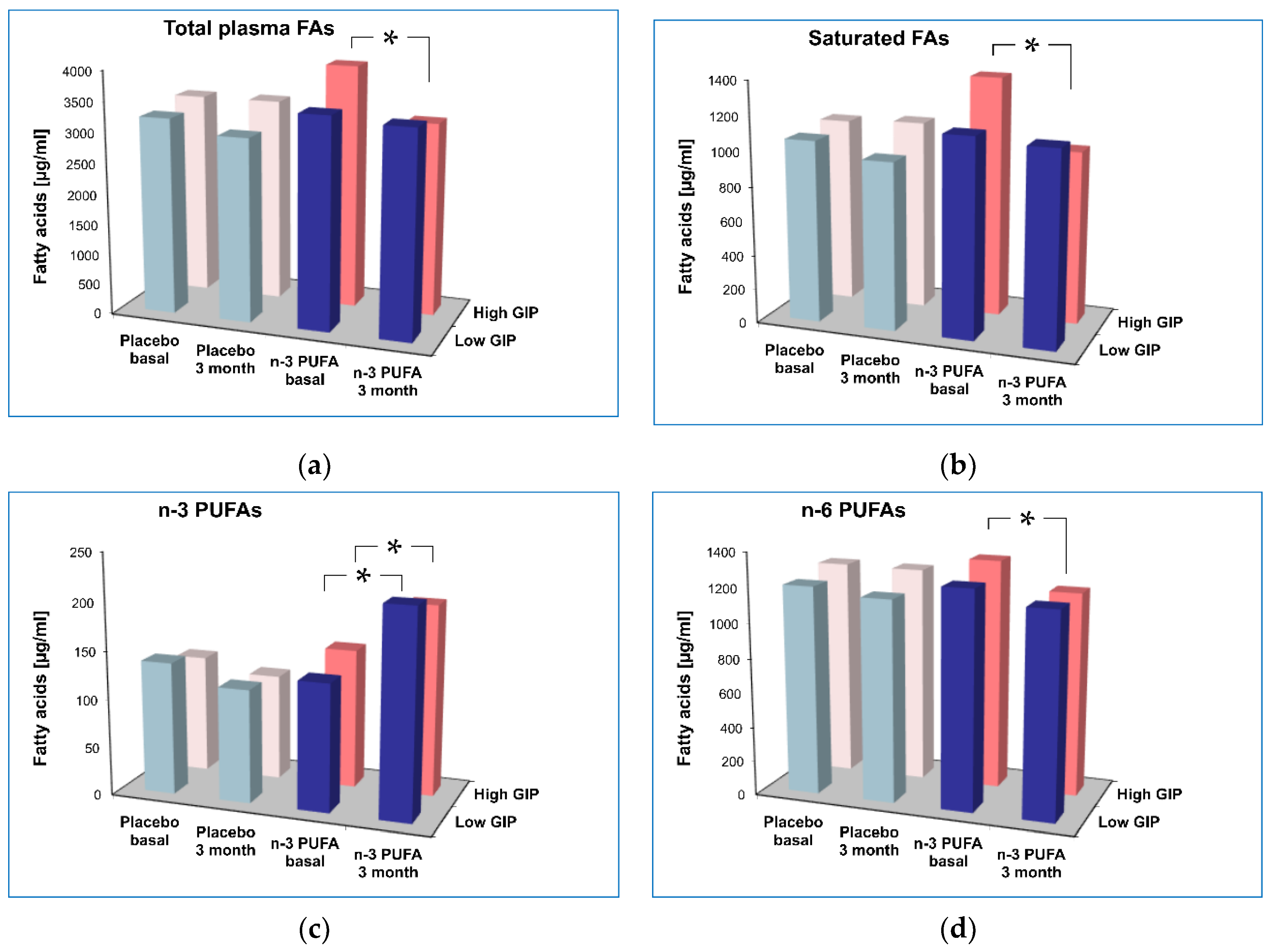
| Total FAs | 3223 | 3007 | 3342 | 3344 | 0.191 | 3453 | 3364 | 3996 | 3162 ** | 0.006 | 0.027 | 0.003 |
| [µg/mL] | (507) | (490) | (817) | (828) | (519) | (579) | (1194) | (637) | ||||
| Saturated FAs | 1057 | 972 * | 1083 | 1102 | 0.079 | 1150 | 1119 | 1390 | 1001 ** | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.001 |
| [µg/mL] | (176) | (159) | (279) | (287) | (225) | (239) | (520) | (217) | ||||
| Myristic acid (14:0) | 36.50 | 29.37 | 35.21 | 40.66 | 0.005 | 44.91 | 38.95 | 65.46 | 29.32 ** | 0.018 | 0.004 | 0.003 |
| [µg/mL] | (13.78) | (12.03) | (16.08) | (18.52) | (17.22) | (18.68) | (49.78) | (9.77) | ||||
| Palmitic acid (16:0) | 729.3 | 678.5 | 763.6 | 775.1 | 0.177 | 805.8 | 791.8 | 985.2 | 706.8 ** | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.002 |
| [µg/mL] | (118.0) | (107.2) | (205.3) | (199.0) | (164.1) | (171.7) | (384.6) | (163.1) | ||||
| Stearic acid (18:0) | 239.5 | 219.1 | 235.8 | 238.2 | 0.055 | 249.96 | 240.46 | 286.92 | 217.00 ** | 0.008 | 0.021 | 0.002 |
| [µg/mL] | (42.7) | (39.3) | (57.0) | (65.4) | (46.45) | (51.01) | (91.26) | (42.86) | ||||
| Unsaturated FAs | 2167 | 2035 | 2259 | 2243 | 0.298 | 2304 | 2245 | 2606 | 2161 ** | 0.012 | 0.061 | 0.009 |
| [µg/mL] | (345) | (338) | (547) | (547) | (319) | (361) | (684) | (423) | ||||
| Saturated /unsaturated | 0.489 | 0.479 | 0.479 | 0.491 | 0.016 | 0.498 | 0.497 | 0.521 | 0.462 ** | 0.011 | 0.015 | 0.002 |
| FAs [µg/mL] | (0.037) | (0.029) | (0.034) | (0.028) | (0.051) | (0.056) | (0.068) | (0.021) | ||||
| MUFAs | 825.2 | 754.2 | 882.6 | 885.5 | 0.257 | 918.9 | 857.1 | 1135.0 | 789.8 ** | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.006 |
| [µg/mL] | (144) | (128) | (294) | (292) | (220.6) | (222.6) | (466.1) | (209.0) | ||||
| Palmitoleic acid (16:1n-7) | 108.2 | 91.1 | 103.3 | 102.9 | 0.136 | 108.1 | 98.9 | 126.0 | 78.4 ** | 0.024 | 0.057 | 0.009 |
| [µg/mL] | (31.8) | (25.6) | (41.4) | (39.1) | (33.5) | (47.0) | (59.0) | (36.1) | ||||
| Oleic acid (18:1n-9) | 671.8 | 616.8 | 734.8 | 740.1 | 0.265 | 770.1 | 713.4 | 966.7 | 664.9 ** | 0.012 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
| [µg/mL] | (117.7) | (108.7) | (250.6) | (256.3) | (196.1) | (184.5) | (428.1) | (181.3) | ||||
| Nervonic acid (24:1) | 45.20 | 46.40 | 44.60 | 42.5 | 0.286 | 40.66 | 44.73 | 42.32 | 46.42 | 0.993 | 0.021 | 0.391 |
| [µg/mL] | (7.3) | (7.2) | (16.3) | (9.5) | (6.04) | (7.97) | (8.85) | (9.19) | ||||
| PUFAs | 1341 | 1280 | 1376 | 1357 | 0.491 | 1385 | 1388 | 1471 | 1371 | 0.082 | 0.834 | 0.086 |
| [µg/mL] | (227) | (228) | (277) | (291) | (180) | (211) | (240) | (239) | ||||
| n-3 PUFAs | 137.2 | 117.3 | 123.3 | 110.4 | 0.633 | 131.7 | 213.2 ** | 144.8 | 197.6 * | 0.208 | <0.001 | 0.202 |
| [µg/mL] | (50.4) | (46.2) | (45.2) | (21.4) | (45.8) | (73.9) | (54.6) | (33.2) | ||||
| n-6 PUFAs | 1204 | 1163 | 1253 | 1247 | 0.509 | 1253 | 1175 | 1326 | 1173 ** | 0.162 | 0.015 | 0.145 |
| [µg/mL] | (220) | (200) | (246) | (277) | (174) | (194) | (200) | (222) | ||||
| n-3/n-6 ratio | 0.117 | 0.100 | 0.097 | 0.090 | 0.404 | 0.107 | 0.186 ** | 0.107 | 0.172 ** | 0.495 | <0.001 | 0.329 |
| [µg/mL] | (0.046) | (0.033) | (0.027) | (0.015) | (0.042) | (0.069) | (0.033) | (0.033) | ||||
| Essential FAs | 946 | 902 | 993 | 1003 | 0.245 | 999 | 932 | 1061 | 930 * | 0.204 | 0.018 | 0.087 |
| [µg/mL] | (199) | (194) | (190) | (226) | (144) | (179) | (173) | (201) | ||||
| Linolenic acid (18:3n-3) | 22.02 | 17.70 | 22.46 | 22.08 | 0.263 | 25.21 | 20.01 | 33.34 | 19.30 * | 0.104 | 0.030 | 0.056 |
| [µg/mL] | (11.43) | (7.65) | (10.00) | (9.18) | (11.01) | (7.27) | (23.87) | (7.68) | ||||
| Eicosapentaenoic acid | 43.54 | 33.66 | 37.56 | 29.81 | 0.774 | 38.56 | 70.05 ** | 45.58 | 63.90 * | 0.263 | <0.001 | 0.287 |
| (20:5n-3) [µg/mL] | (23.08) | (17.92) | (18.14) | (6.43) | (18.86) | (41.43) | (25.33) | (14.21) | ||||
| Docosahexaenoic acid | 71.62 | 65.92 | 63.27 | 58.46 | 0.899 | 67.98 | 123.17 ** | 65.89 | 114.41 ** | 0.562 | <0.001 | 0.589 |
| (22:6n-6) [µg/mL] | (25.22) | (24.04) | (26.44) | (12.37) | (22.61) | (34.91) | (25.59) | (24.79) | ||||
| Linoleic acid (18:2n-6) | 924.4 | 884.6 | 970.3 | 981.4 | 0.262 | 973.8 | 911.5 | 1027.4 | 910.8 ** | 0.246 | 0.024 | 0.108 |
| [µg/mL] | (193.6) | (188.5) | (183.6) | (220.5) | (143.8) | (176.1) | (156.1) | (197.6) | ||||
| Arachidonic acid | 279.7 | 278.8 | 282.7 | 265.4 | 0.378 | 279.4 | 263.2 | 299.1 | 262.5 * | 0.186 | 0.075 | 0.365 |
| (20:4n-6) [µg/mL] | (41.2) | (33.5) | (102.4) | (69.0) | (48.3) | (49.5) | (81.9) | (56.7) | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goralska, J.; Razny, U.; Calder, P.C.; Gruca, A.; Childs, C.E.; Zabielski, P.; Dembinska-Kiec, A.; Banach, M.; Solnica, B.; Malczewska-Malec, M. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Plasma Level Influences the Effect of n-3 PUFA Supplementation. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081984
Goralska J, Razny U, Calder PC, Gruca A, Childs CE, Zabielski P, Dembinska-Kiec A, Banach M, Solnica B, Malczewska-Malec M. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Plasma Level Influences the Effect of n-3 PUFA Supplementation. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(8):1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081984
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoralska, Joanna, Urszula Razny, Philip C. Calder, Anna Gruca, Caroline E. Childs, Piotr Zabielski, Aldona Dembinska-Kiec, Maciej Banach, Bogdan Solnica, and Malgorzata Malczewska-Malec. 2022. "Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Plasma Level Influences the Effect of n-3 PUFA Supplementation" Diagnostics 12, no. 8: 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081984
APA StyleGoralska, J., Razny, U., Calder, P. C., Gruca, A., Childs, C. E., Zabielski, P., Dembinska-Kiec, A., Banach, M., Solnica, B., & Malczewska-Malec, M. (2022). Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Plasma Level Influences the Effect of n-3 PUFA Supplementation. Diagnostics, 12(8), 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081984







