Comparison of Ki67 Proliferation Index in Gastrointestinal Non-Hodgkin Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Conventional Method of Evaluation or AI Evaluation?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
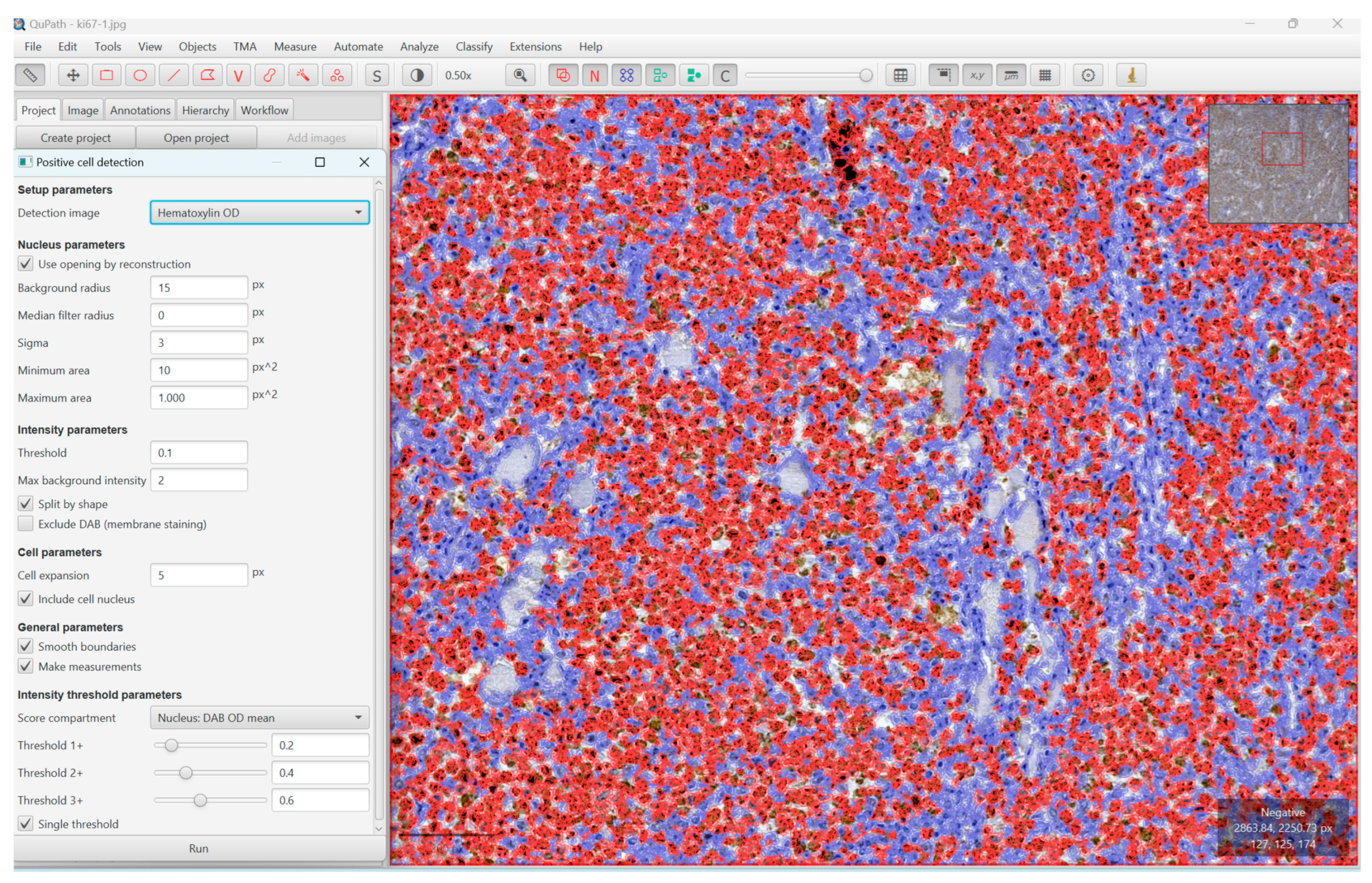
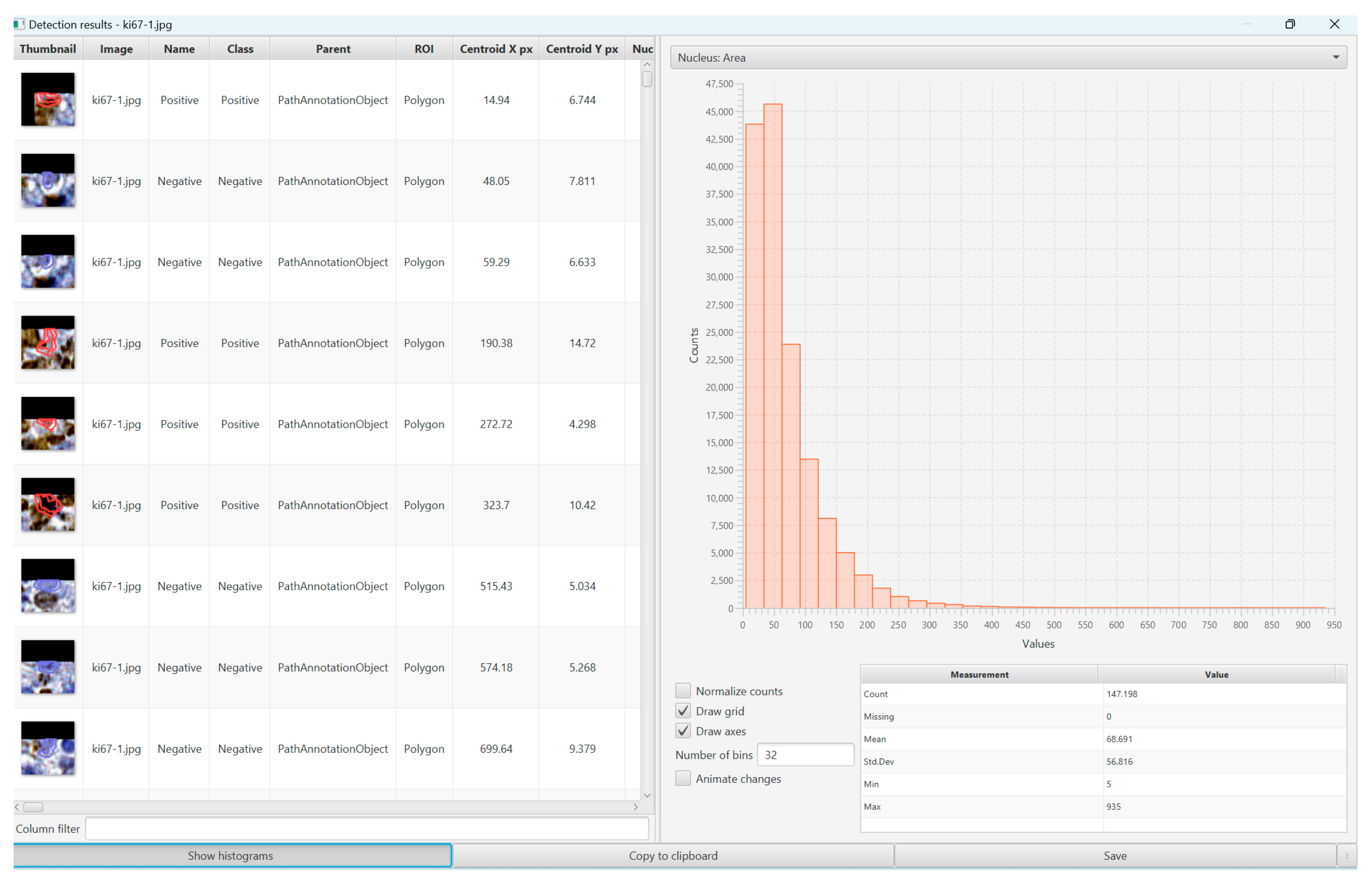
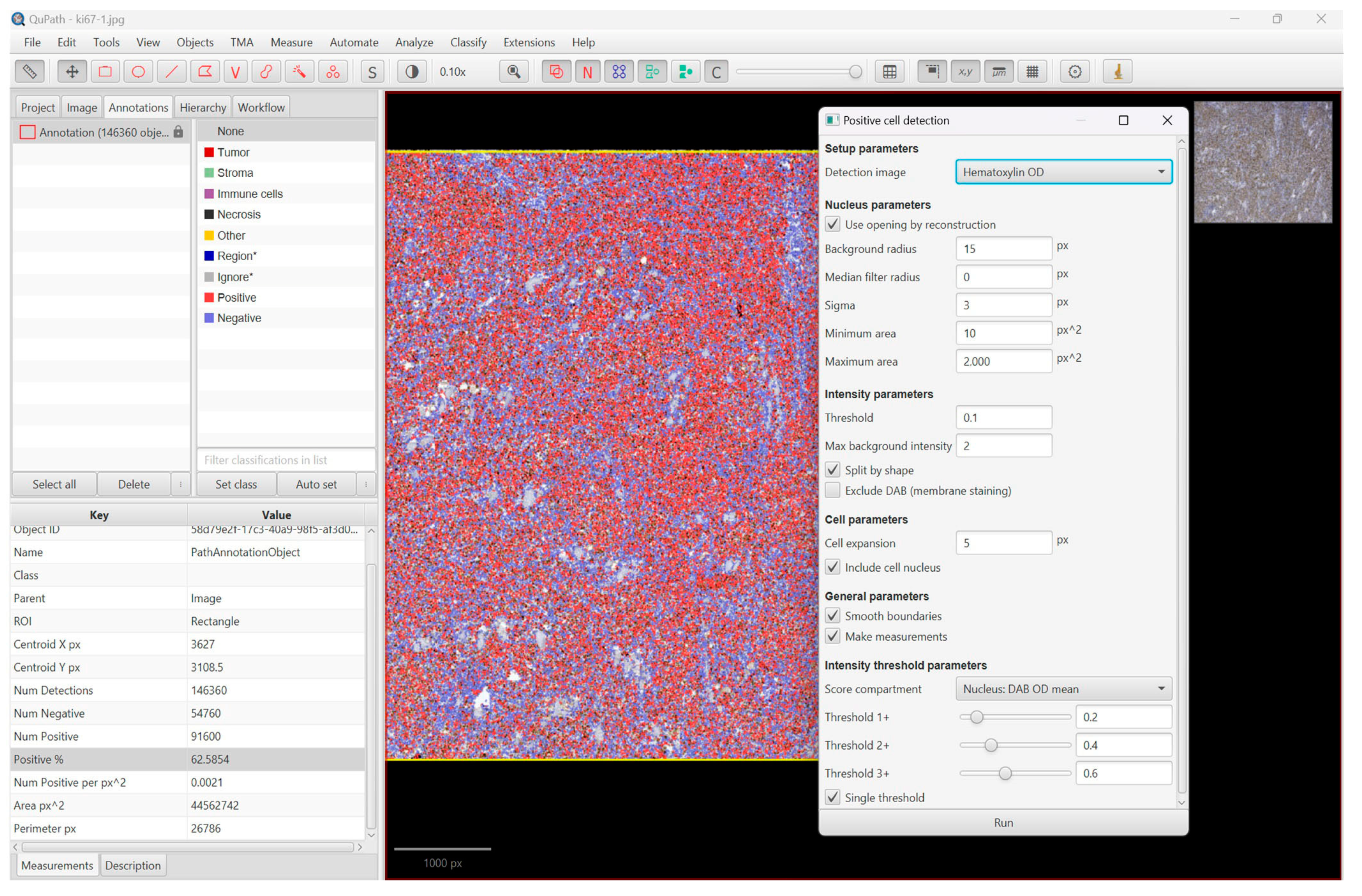
2. Materials and Methods
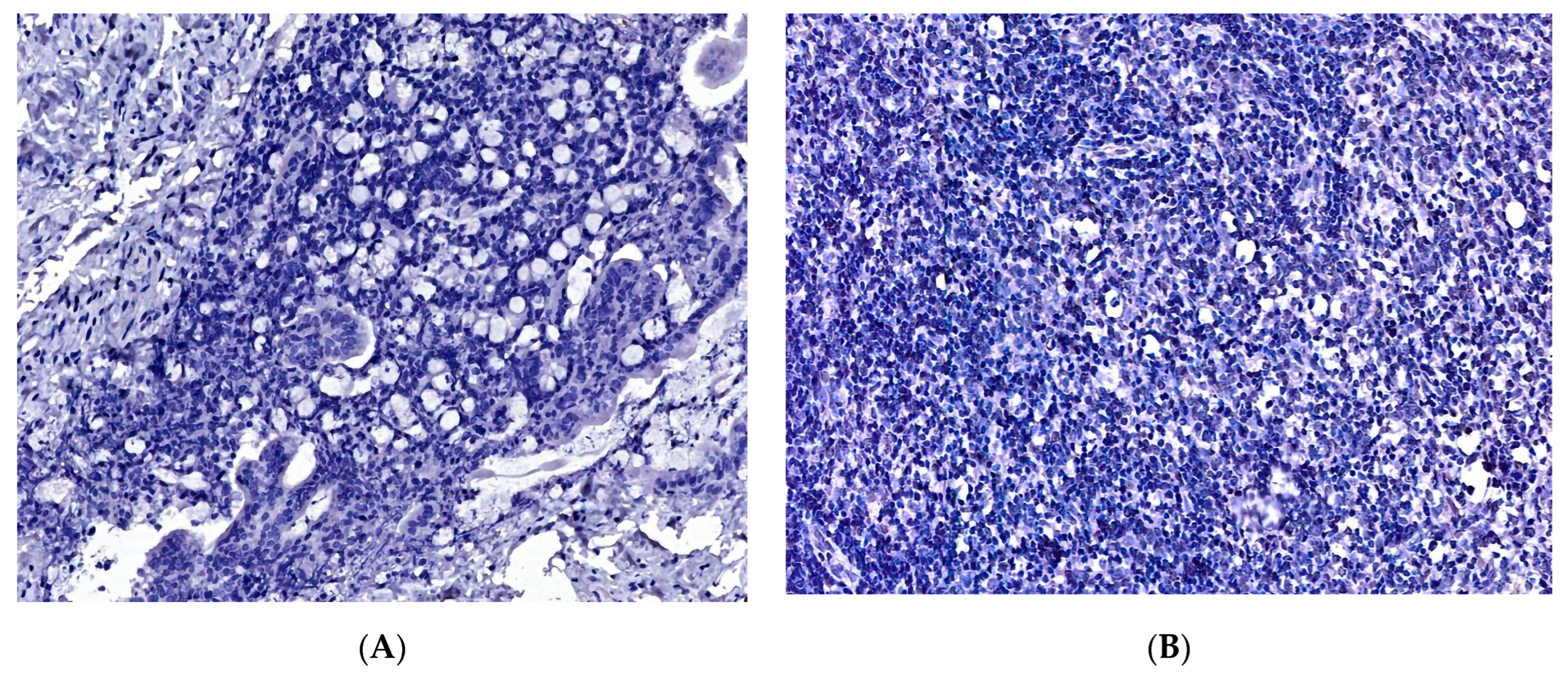
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. The Proliferation Index, Treatment, and Survival Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | activated-B-cell-like |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| COO | cell of origin |
| CHOP | cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, oncovin (vincristine), prednisone, or prednisolone |
| CI | confidence interval |
| DLBCL, NOS | diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified |
| DP | digital pathology |
| EFS | event-free survival |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FL | follicular lymphoma |
| GCB | germinal center B-cell-like |
| GI | gastrointestinal |
| GEP | gene expression profiling |
| HGBL | high-grade B-cell lymphoma |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| LPD | lymphoproliferative disorders |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| MALT | marginal zone lymphoma |
| NA | North America |
| NON-GCB | non-germinal center B-cell-like |
| NHL | non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| OS | overall survival |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| R-CHOP | rituximab, cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, oncovin (vincristine), prednisone, or prednisolone |
| SEEU | South-Eastern Europe |
| WEU | Western Europe |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WSI | whole slide imaging |
References
- Li, S.; Young, K.H.; Medeiros, L.J. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Pathology 2018, 50, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotlic, S.; Perry, A.M.; Petrusevska, G.; Fetica, B.; Diebold, J.; MacLennan, K.A.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Nathwani, B.N.; Boilesen, E.; Bast, M.; et al. Classification of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in South-eastern Europe: Review of 632 cases from the international non-Hodgkin lymphoma classification project. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 171, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, E.C.; Ott, G.; Siebert, R.; Alaggio, R.; de Jong, D.; Kikkeri, N.N.; Sandeep, S.D. WHO Haematolymphoid Tumours (5th ed.), Chapter 4, B-Cell Lymphoid Proliferations and Lymphomas—Large B Cell Lymphomas, WHO Classification of Tumours Online. 2022. Available online: https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/chapters/63 (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Neff, N.V. Whole slide imaging for primary diagnosis: ‘Now it is happening’. CAP Today, May 2017; 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Gurcan, M.N.; Boucheron, L.E.; Can, A.; Madabhushi, A.; Rajpoot, N.M.; Yener, B. Histopathological Image Analysis: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 2, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Allows Marketing of First Whole Slide Imaging System for Digital Pathology. Office of the Commissioner. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm552742.html (accessed on 16 March 2019).
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernández, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, M.F.A.; Pennell, M.; Sahiner, B.; Chen, W.; Shana’ah, A.; Hemminger, J.; Gru, A.; Kurt, H.; Losos, M.; Joehlin-Price, A.; et al. Classification of follicular lymphoma: The effect of computer aid on pathologists grading. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2015, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.S.; Lee, S.; Jordan, J.; Jaye, D.L.; Flowers, C.; Cooper, L. Utilizing Digital Pathology Informatics Algorithms for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Subtyping. Blood 2017, 130, 4147. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Lesmes, J.; Chapman, J.R.; Cassidy, D.; Zhou, Y.; Garcia-Buitrago, M.; Montgomery, E.A.; Lossos, I.S.; Sussman, D.; Poveda, J. Gastrointestinal Tract Lymphomas. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2021, 145, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, T.A.; Crowther, D.; Sutcliffe, S.B.; Glatstein, E.; Canellos, G.P.; Young, R.C.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Coltman, C.A.; Tubiana, M. Report of a committee convened to discuss the evaluation and staging of patients with Hodgkin’s disease: Cotswolds meeting. J. Clin. Oncol. 1989, 7, 1630–1636, Erratum in J. Clin. Oncol. 1990, 8, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipp, M.A. International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. A Predictive Model for Aggressive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Zwickl-Traxler, E.; Pecherstorfer, M.; Singer, J. Evaluation of Ki-67 as a Prognostic Marker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma—A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4521–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Chen, Z.; Fu, T.; Jin, X.; Yu, T.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Huang, L. Ki-67 is a valuable prognostic predictor of lymphoma but its utility varies in lymphoma subtypes: Evidence from a systematic meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, M.K.; Torri, V.; Stewart, L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 2815–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, L.H.; Salles, G. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 842–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Quach, M.A.; Ake, C.D.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. Gastrointestinal lymphomas: Morphology, immunophenotype and molecular features. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2012, 3, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, P.; Wu, G.Y.; Zhu, L. Primary gastrointestinal lymphoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska-Szopa, M.; Wróbel, T. Gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; Bosman, F.T., Ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, P.N.; Fu, K.; Greiner, T.C.; Smith, L.M.; Delabie, J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Ott, G.; Rosenwald, A.; Braziel, R.M.; Campo, E.; et al. Immunohistochemical Methods for Predicting Cell of Origin and Survival in Patients With Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated With Rituximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.W.L.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Piris, M.A.; Banham, A.H.; Delabie, J.; Braziel, R.M.; Geng, H.; Iqbal, J.; Lenz, G.; et al. A New Immunostain Algorithm Classifies Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma into Molecular Subtypes with High Accuracy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5494–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, C.; Li, Y.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Miranda, R.N.; Green, T.M.; Li, Y.; Tzankov, A.; Wen, W.; Liu, W.-M.; Kahl, B.S.; et al. Comprehensive gene expression profiling and immunohistochemical studies support application of immunophenotypic algorithm for molecular subtype classification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A report from the International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2103–2113, Erratum in Leukemia 2014, 28, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanas, G.; Ge, W.; Quek, R.G.W.; Keeven, K.; Nersesyan, K.; Arnason, J.E. Epidemiology of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL) in the United States and Western Europe: Population-level projections for 2020–2025. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 63, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilly, H.; da Silva, M.G.; Vitolo, U.; Jack, A.; Meignan, M.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Walewski, J.; André, M.; Johnson, P.W.; Pfreundschuh, M.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, v116–v125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdum, A.; Tieu, R.; Reddy, S.R.; Broder, M.S. Direct Costs Associated with Relapsed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Therapies. Oncologist 2019, 24, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyling, M.; Ghielmini, M.; Rule, S.; Salles, G.; Ladetto, M.; Tonino, S.; Herfarth, K.; Seymour, J.; Jerkeman, M.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Newly diagnosed and relapsed follicular lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 32, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halwani, A.S.; Chien, H.-C.; Morreall, D.K.; Patil, V.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Li, C.; Burningham, Z.R.; Masaquel, A.S.; Halloran, M.; Delong-Sieg, E.; et al. Survival Patterns in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: Treatment Trajectories and Responses after the First Relapse. Blood 2019, 134, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.C.; Postow, M.A.; Orlowski, R.J.; Mick, R.; Bengsch, B.; Manne, S.; Xu, W.; Harmon, S.; Giles, J.R.; Wenz, B.; et al. T-cell invigoration to tumour burden ratio associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2017, 545, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, F.; Kurtz, D.M.; Newman, A.M.; Stehr, H.; Craig, A.F.M.; Esfahani, M.S.; Lovejoy, A.F.; Chabon, J.J.; Klass, D.M.; Liu, C.L.; et al. Distinct biological subtypes and patterns of genome evolution in lymphoma revealed by circulating tumor DNA. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 364ra155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.M.; Green, M.R.; Bratman, S.V.; Scherer, F.; Liu, C.L.; Kunder, C.A.; Takahashi, K.; Glover, C.; Keane, C.; Kihira, S.; et al. Noninvasive monitoring of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunoglobulin high-throughput sequencing. Blood 2015, 125, 3679–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochazka, K.T.; Melchardt, T.; Posch, F.; Schlick, K.; Deutsch, A.; Beham-Schmid, C.; Weiss, L.; Gary, T.; Neureiter, D.; Klieser, E.; et al. NCCN-IPI score-independent prognostic potential of pretreatment uric acid levels for clinical outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.-K.; Chung, J.-S.; Lee, J.-J.; Yang, D.-H.; Kim, I.-S.; Shin, D.-H.; Shin, H.-J. High Ki-67 expression in involved bone marrow predicts worse clinical outcome in diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP therapy. Int. J. Hematol. 2014, 101, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-M.; Huang, J.-J.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Zhao, W.; Wei, W.-X.; Jiang, W.-Q.; Lin, T.-Y.; Huang, H.-Q.; Guan, Z.-Z. High Ki-67 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients with non-germinal center subtype indicates limited survival benefit from R-CHOP therapy. Eur. J. Haematol. 2012, 88, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudio, F.; Giordano, A.; Perrone, T.; Pastore, D.; Curci, P.; Delia, M.; Napoli, A.; Risi, C.D.; Spina, A.; Ricco, R.; et al. High Ki67 Index and Bulky Disease Remain Significant Adverse Prognostic Factors in Patients with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma before and after the Introduction of Rituximab. Acta Haematol. 2011, 126, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, D.H.; Choi, D.R.; Ahn, H.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, B.H.; Yoon, S.O.; Huh, J.; Lee, S.-W.; et al. Ki-67 expression as a prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with rituximab plus CHOP. Eur. J. Haematol. 2010, 85, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pătraşcu, A.M.; Rotaru, I.; Olar, L.; Pătraşcu, Ş.; Ghiluşi, M.C.; Neamţu, S.D.; Nacea, J.G.; Gluhovschi, A. The prognostic role of Bcl-2, Ki67, c-MYC and p53 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. Rev. Roum. Morphol. Embryol. 2017, 58, 837–843. [Google Scholar]
- Llanos, M.; Alvarez-Argüelles, H.; Alemán, R.; Oramas, J.; Díaz-Flores, L.; Batista, N. Prognostic Significance of Ki-67 Nuclear Proliferative Antigen, bcl-2 Protein, and p53 Expression in Follicular and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Med. Oncol. 2001, 18, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broyde, A.; Boycov, O.; Strenov, Y.; Okon, E.; Shpilberg, O.; Bairey, O. Role and prognostic significance of the Ki-67 index in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2009, 84, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orasanu, C.I.; Aschie, M.; Deacu, M.; Bosoteanu, M.; Vamesu, S.; Enciu, M.; Bălţătescu, G.I.; Cozaru, G.C.; Mitroi, A.F.; Voda, R.I. Implications of Cellular Immaturity in Necrosis and Microvascularization in Glioblastomas IDH-Wild-Type. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowsett, M.; Nielsen, T.O.; A’hern, R.; Bartlett, J.; Coombes, R.C.; Cuzick, J.; Ellis, M.; Henry, N.L.; Hugh, J.C.; Lively, T.; et al. Assessment of Ki67 in breast cancer: Recommendations from the International Ki67 in breast cancer working group. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ki67 Evaluation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Case | Conventional Method (Controls) Low (≤70%)/High (>70%) | QuPath Software Evaluation | ||
| Pathologist 1 N (%) | Pathologist 2 N (%) | Positive Cells (%) | The Mean Value of Positive Cells | |
| 1 | 70% | 75% | 73.69% | 79.870 |
| 2 | 70% | 75% | 72.96% | 78.960 |
| 3 | 40% | 45% | 37.13% | 58.440 |
| 4 | 85% | 80% | 88.99% | 85.876 |
| 5 | 20% | 20% | 22.67% | 19.978 |
| 6 | 75% | 80% | 79.97% | 89.258 |
| 7 | 80% | 75% | 71.78% | 75.786 |
| 8 | 50% | 60% | 62.58% | 68.691 |
| 9 | 75% | 75% | 67.70% | 71.637 |
| 10 | 50% | 50% | 49.67% | 53.667 |
| 11 | 80% | 85% | 83.80% | 86.356 |
| 12 | 40% | 45% | 42.05% | 58.015 |
| 13 | 30% | 25% | 35.52% | 65.037 |
| 14 | 65% | 70% | 61.29% | 58.184 |
| 15 | 30% | 30% | 33.03% | 64.716 |
| ICC | 95% Confidence Interval | F Test with True Value 0 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Value | df1 | df2 | Sig | ||
| Single Measures | 0.970 | 0.932 | 0.989 | 100.251 | 14 | 28 | 0.000 |
| Average Measures | 0.990 | 0.976 | 0.996 | 100.251 | 14 | 28 | 0.000 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | CI95 | P | HR | CI95 | p | |
| IPI score | 5.406 | 0.945–30.932 | 0.058 | 10.597 | 1.211–92.717 | 0.033 |
| Ki67 Low/High | 1.122 | 0.278–4.528 | 0.871 | 2.888 | 0.479–17.424 | 0.248 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cristian, M.; Așchie, M.; Deacu, M.; Boșoteanu, M.; Bălțătescu, G.I.; Stoica, A.G.; Nicolau, A.A.; Poinăreanu, I.; Orășanu, C.I. Comparison of Ki67 Proliferation Index in Gastrointestinal Non-Hodgkin Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Conventional Method of Evaluation or AI Evaluation? Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2775. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172775
Cristian M, Așchie M, Deacu M, Boșoteanu M, Bălțătescu GI, Stoica AG, Nicolau AA, Poinăreanu I, Orășanu CI. Comparison of Ki67 Proliferation Index in Gastrointestinal Non-Hodgkin Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Conventional Method of Evaluation or AI Evaluation? Diagnostics. 2023; 13(17):2775. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172775
Chicago/Turabian StyleCristian, Miruna, Mariana Așchie, Mariana Deacu, Mădălina Boșoteanu, Gabriela Izabela Bălțătescu, Andreea Georgiana Stoica, Anca Antonela Nicolau, Ionuț Poinăreanu, and Cristian Ionuț Orășanu. 2023. "Comparison of Ki67 Proliferation Index in Gastrointestinal Non-Hodgkin Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Conventional Method of Evaluation or AI Evaluation?" Diagnostics 13, no. 17: 2775. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172775
APA StyleCristian, M., Așchie, M., Deacu, M., Boșoteanu, M., Bălțătescu, G. I., Stoica, A. G., Nicolau, A. A., Poinăreanu, I., & Orășanu, C. I. (2023). Comparison of Ki67 Proliferation Index in Gastrointestinal Non-Hodgkin Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Conventional Method of Evaluation or AI Evaluation? Diagnostics, 13(17), 2775. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172775






