Comparing Outcomes of Single-Incision Laparoscopic Herniorrhaphy in Newborns and Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
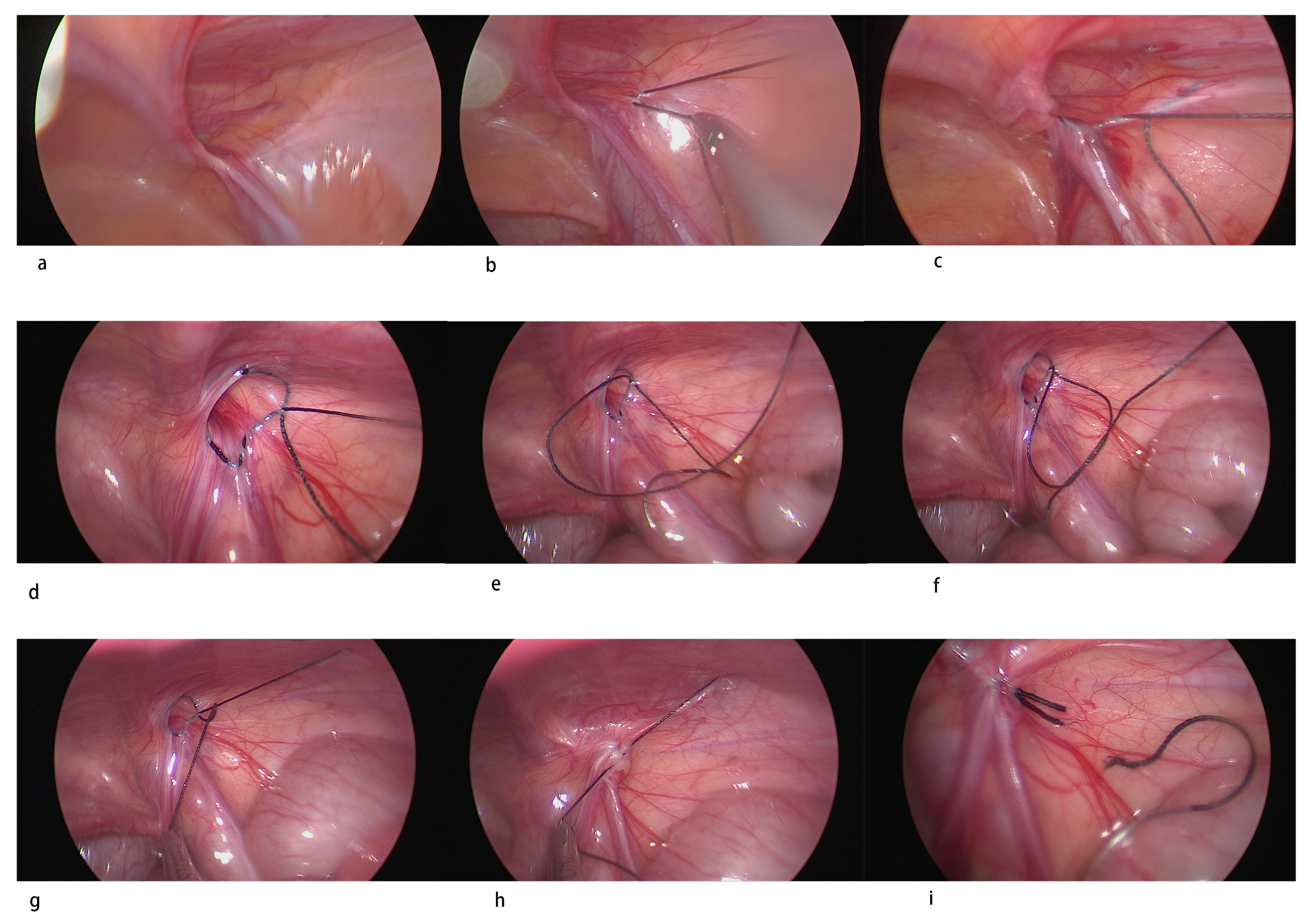
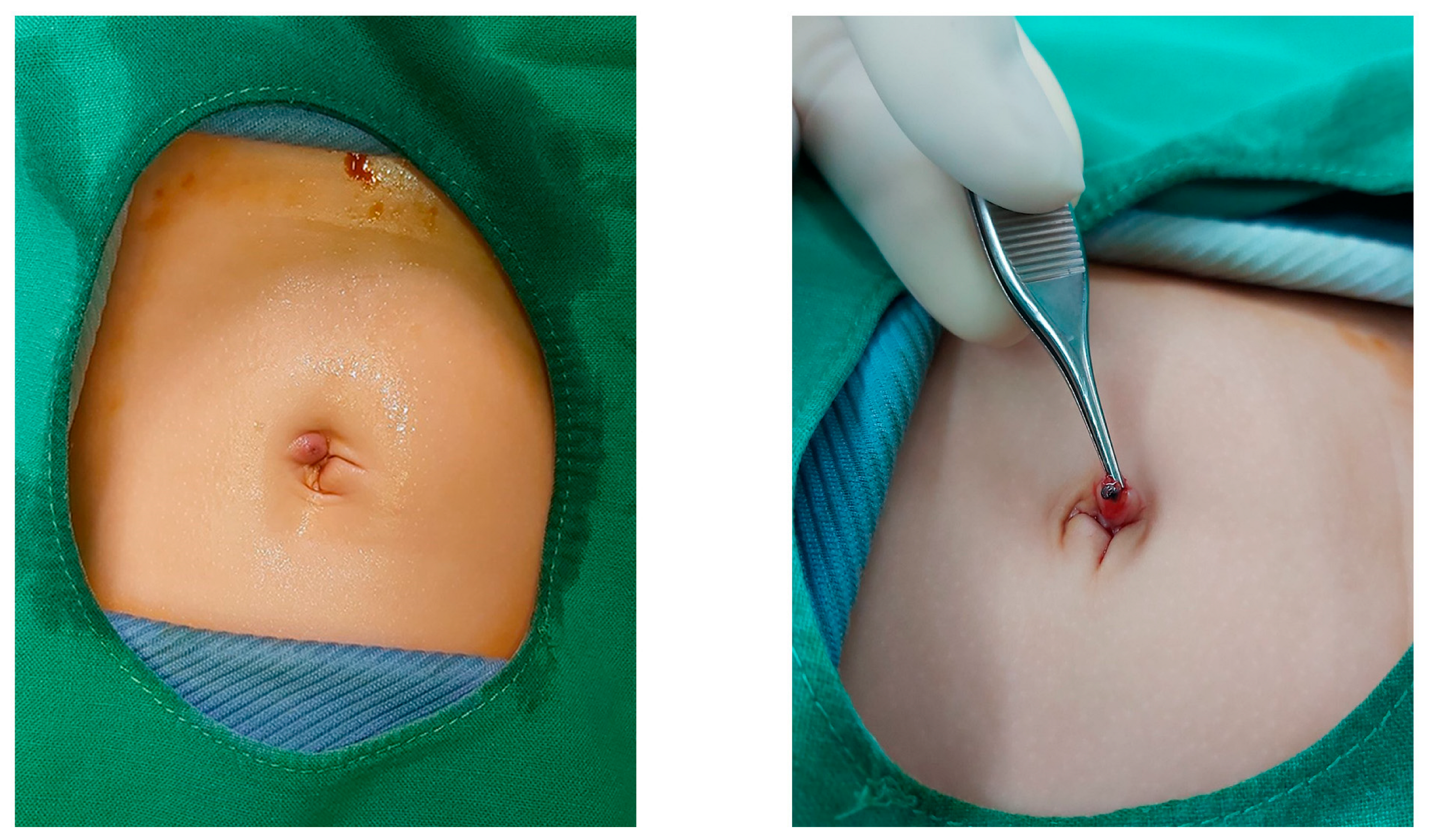
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Underlying Diseases
3.1.1. Primary Outcome
Recurrence
3.1.2. Secondary Outcome
Anesthetic Time
3.2. Peri-Operative Complications
3.3. cPPV
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schier, F. Laparoscopic herniorrhaphy in girls. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1998, 33, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.L.; Hui, W.C.; Tam, P.K. Prospective randomized single-center, single-blind comparison of laparoscopic vs open repair of pediatric inguinal hernia. Surg. Endosc. 2005, 19, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.J.; Swanson, T.; Ansermino, M.; Milner, R. The frequency of apneas in premature infants after inguinal hernia repair: Do they need overnight monitoring in the intensive care unit? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2008, 43, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patkowski, D.; Czernik, J.; Chrzan, R.; Jaworski, W.; Apoznański, W. Percutaneous internal ring suturing: A simple minimally invasive technique for inguinal hernia repair in children. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2006, 16, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Huskić, D.; Čohadžić, T.; Jukić, M.; Šušnjar, T. Learning Curve for Laparoscopic Repair of Pediatric Inguinal Hernia Using Percutaneous Internal Ring Suturing. Children 2021, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.C.H.; Chan, I.H.Y.; Wong, K.K.Y. Outcome and learning curve for laparoscopic intra-corporeal inguinal hernia repair in children. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, I.H.; Lau, C.T.; Chung, P.H.; Chan, K.L.; Lan, L.C.; Wong, K.K.; Tam, P.K. Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair in premature neonates: Is it safe? Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2013, 29, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.; Turial, S.; Escolino, M.; Giurin, I.; Alicchio, F.; Enders, J.; Krause, K.; Settimi, A.; Schier, F. Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair in premature babies weighing 3 kg or less. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2012, 28, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.; Horwood, J.F.; Clements, C.; Leyland, D.; Corbett, H.J. Complications of inguinal herniotomy are comparable in term and premature infants. Hernia 2016, 20, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J. Pediatric inguinal hernia repair-a critical appraisal. Hernia 2008, 12, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Toki, F.; Yamamoto, H.; Otake, S.; Oki, Y.; Kuwano, H. Outcomes of herniotomy in premature infants: Recent 10 year experience. Pediatr. Int. 2012, 54, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schier, F. Laparoscopic surgery of inguinal hernias in children--initial experience. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2000, 35, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schier, F.; Montupet, P.; Esposito, C. Laparoscopic inguinal herniorrhaphy in children: A three-center experience with 933 repairs. J. Pediar. Surg. 2002, 37, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turial, S.; Enders, J.; Krause, K.; Schier, F. Laparoscopic inguinal herniorrhaphy in babies weighing 5 kg or less. Surg. Endosc. 2011, 25, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turial, S.; Enders, J.; Krause, K.; Schier, F. Laparoscopic inguinal herniorrhaphy in premature infants. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2010, 20, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.M.; Chang, H.K.; Park, S.J. Laparoscopic Pediatric Inguinal Hernia Repair; Intracorporeal Purse-String Suture Using Needlescopic 2-mm Instruments. J. Minim. Invasive Surg. 2020, 23, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Cao, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, S.; Cao, G.; Chi, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; et al. Re-evaluation of jumping purse-string suturing in pediatric laparoscopic hernia repair. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 3277–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimsby, G.M.; Keays, M.A.; Villanueva, C.; Bush, N.C.; Snodgrass, W.T.; Gargollo, P.C.; Jacobs, M.A. Non-absorbable sutures are associated with lower recurrence rates in laparoscopic percutaneous inguinal hernia ligation. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2015, 11, e271–e274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laparoscopic Ligation of Inguinal Hernia in Girls. Pediatr. Endosurgery Innov. Tech. 1997, 1, 185–188. [CrossRef]
- Montupet, P.; Esposito, C. Laparoscopic treatment of congenital inguinal hernia in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1999, 34, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, M.R.; Lee, H.; Albanese, C.T.; Farmer, D.L. Subcutaneous endoscopically assisted ligation (SEAL) of the internal ring for repair of inguinal hernias in children: A novel technique. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2005, 40, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oue, T.; Kubota, A.; Okuyama, H.; Kawahara, H. Laparoscopic percutaneous extraperitoneal closure (LPEC) method for the exploration and treatment of inguinal hernia in girls. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2005, 21, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzoni, M.; Jaramillo, J.D.; Kastenberg, Z.J.; Wall, J.K.; Wright, R.; Dutta, S. Long-term follow-up of laparoscopic transcuta-neous inguinal herniorraphy with high transfixation suture ligature of the hernia sac. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotny, N.M.; Puentes, M.C.; Leopold, R.; Ortega, M.; Godoy-Lenz, J. The Burnia: Laparoscopic Sutureless Inguinal Hernia Repair in Girls. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2017, 27, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z. A systematic review and meta-analysis concerning single-site laparo-scopic percutaneous extraperitoneal closure for pediatric inguinal hernia and hydrocele. Surg. Endosc. 2017, 31, 4888–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.A.; Novillo, I.C.; Vázquez, A.G.; de Miguel Moya, M. Is the Laparoscopic Approach Safe for Inguinal Hernia Repair in Preterms? J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2019, 29, 1302–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergün, E.; Yağız, B.; Kara, Y.A.; Abay, A.N.; Balcı, Ö.; Eryılmaz, S.; Özgüner, İ.F.; Karaman, A.; Karaman, İ. Comparison of laparoscopic percutaneous internal ring suturing method and open inguinal hernia repair in children under 3 months of age. Turk. J. Surg. 2021, 37, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.M.; Ng, J.; Saxena, A.K. Comparative Analysis of Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair in Neonates and Infants. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan. Tech. 2020, 30, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Baik, Y.H.; Kwak, B.S.; Oh, M.G.; Choi, W.Y. A purse-string suture at the level of internal inguinal ring, taking only the peritoneum leaving the distal sac: Is it enough for inguinal hernia in pediatric patients? Hernia 2015, 19, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, T.N.; Bao, H.V. Long-term absorbable versus non-absorbable suture in laparoscopic percutaneous extraperitoneal closure of internal ring for inguinal hernia in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 56, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.I.; Copelson, L.W.; Clatworthy, H.W. The patent processus vaginalis and the inguinal hernia. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1969, 4, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, S.; Mansson, J.; Saad, A.; Goldfarb, M.A. Ten-year review of groin laparoscopy in 1001 pediatric patients with clinical unilateral inguinal hernia: An improved technique with transhernia multiple-channel scope. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinxiang, L.; Qingwei, C.; Shenghua, Q.; Yunqiang, X.; Haiyang, L.; Chengliang, L.; Meng, X. Contralateral patent processus vaginalis repair in boys: A single-center retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgmeier, C.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Schier, F. Gender-related differences of inguinal hernia and asymptomatic patent processus vaginalis in term and preterm infants. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgmeier, C.; Schier, F. Cardiorespiratory complications after laparoscopic hernia repair in term and preterm babies. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 48, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevešćanin, A.; Vickov, J.; Elezović Baloević, S.; Pogorelić, Z. Laryngeal Mask Airway Versus Tracheal Intubation for Laparo-scopic Hernia Repair in Children: Analysis of Respiratory Complications. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2020, 30, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, P.; Whyte, S.D.; Baird, R.; Malherbe, S. Caudal and Intravenous Anesthesia Without Airway Instrumentation for Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair in Infants: A Case Series. A A Pract 2020, 14, e01251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulkowski, J.P.; Cooper, J.N.; Duggan, E.M.; Balci, O.; Anandalwar, S.P.; Blakely, M.L.; Heiss, K.; Rangel, S.; Minneci, P.C.; Deans, K.J. Does timing of neonatal inguinal hernia repair affect outcomes? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawazir, O.A. Delaying surgery for inguinal hernia in neonates: Is it worthwhile? J. Taibah. Univ. Med. Sci. 2019, 14, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Huh, Y.J.; Han, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, C.; Jo, A.H.; Park, K.W.; Jung, S.E. Inguinal hernia in preterms in neonatal intensive care units: Optimal timing of herniorrhaphy and necessity of contralateral exploration in unilateral presentation. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno-Wolf, N.; Mircea, L.; Sanchez, O.; Genin, B.; Lironi, A.; Chardot, C.; Birraux, J.; Wildhaber, B.E. Long-term outcome of children with patent processus vaginalis incidentally diagnosed by laparoscopy. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 1898–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, D.I.; Baker, C.; Patel, S.; Hebra, A.V.; Cina, R.A.; Streck, C.J.; Lesher, A.P. Long-term outcomes of pediatric laparoscopic needled-assisted inguinal hernia repair: A 10-year experience. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 56, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Anand, S.; Križanac, Z.; Singh, A. Comparison of Recurrence and Complication Rates Following Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair among Preterm versus Full-Term Newborns: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Children 2021, 8, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.A.; Briggs, K.B.; Svetanoff, W.J.; Rentea, R.M.; Aguayo, P.; Juang, D.; Fraser, J.D.; Snyder, C.L.; Hendrickson, R.J.; St Peter, S.D.; et al. Umbilical access in laparoscopic surgery in infants less than 3 months: A single institution retrospective review. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2022, 57, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Watanabe, T.; Nakano, M.; Yoshida, F.; Ukiyama, E. Laparoscopic completely extraperitoneal repair of inguinal hernia in children: A single-institute experience with 1257 repairs compared with cut-down herniorrhaphy. Surg. Endosc. 2009, 23, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Group 1 (Age ≤ 2 mo) | Group 2 (Age > 2 mo) | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients (n) | 114 | 83 | |||||||
| Age (weeks) | 4.9 ± 1.8 | 23.1 ± 15.9 | <0.01 * | ||||||
| Gender (male) | 88 (77.2%) | 69 (89.1%) | 0.31 | ||||||
| Weight (kg) | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 6.7 ± 2.1 | <0.01 * | ||||||
| Laterality | Preoperative | Postoperative | Preoperative | Postoperative | |||||
| Right: | 51 | Right: | 14 | Right: | 48 | Right: | 19 | ||
| Left: | 36 | Left: | 9 | Left: | 27 | Left: | 8 | ||
| Bilateral: | 27 | Bilateral: | 91 | Bilateral: | 8 | Bilateral: | 54 | ||
| Umbilical hernia (n) | 13 (11.4%) | 12 (14.5%) | 0.53 | ||||||
| Pre-OP Hb (g/dL) | 10.6 ± 1.7 | 11.4 ± 1.3 | 0.1 | ||||||
| Underlying disease (n) | |||||||||
| Cardiac | 14 (12.3%) | 10 (12.0%) | 0.1 | ||||||
| Pulmonary | 0 | 2 (2.4%) | |||||||
| Characteristics | Group 1 (Age ≤ 2 mo) | Group 2 (Age > 2 mo) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intraoperative complication | None | None | |
| Operative time (min) | 34.1 ± 10.8 | 32.3 ± 11.0 | 0.26 |
| Unilateral | 28.8 ± 9.4 | 25.9 ± 8.5 | |
| Bilateral | 35.4 ± 10.8 | 35.4 ± 10.7 | |
| Anesthetic time (min) | 80.0 ± 14.5 | 76.3 ± 12.9 | 0.07 |
| Unilateral | 78.1 ± 16.5 | 72.2 ± 12.6 | |
| Bilateral | 80.4 ± 14.0 | 78.2 ± 12.7 | |
| cPPV (n) | 64 (56.1%) | 48 (34.1%) | <0.01 * |
| cPPV-L | 27(23.7%) | 19(23.2%) | 0.78 |
| cPPV-R | 37(32.5%) | 29(35.4%) | 0.21 |
| Conversion | 0 | 0 | |
| Comorbidity (n) | |||
| Pulmonary | 2 (1.8%) | 1 (1.2%) | |
| UTI | 1 (0.7%) | 0 | |
| LOS (days) | 2.3 ± 1.6 | 2.4 ± 9.3 | 0.88 |
| Postoperative complication | |||
| Omphalitis | 6 (5.3%) | 1 (1.2%) | 0.13 |
| Surgical site infection | 1 (0.9%) | 1 (1.2%) | 0.81 |
| Transient hydrocele | 4 (3.5%) | 7 (8.4%) | 0.14 |
| Resolution day | 1.2 ± 9.0 | 13.5 ± 63.3 | 0.04 |
| Recurrence (n) | 0 | 0 | |
| Testicular acent/atrophy | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, T.-J.; Lin, C.-M.; Cheang, I.N.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Wei, C.-H.; Chin, T.-W.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chang, W.-Y.; Fu, Y.-W. Comparing Outcomes of Single-Incision Laparoscopic Herniorrhaphy in Newborns and Infants. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030529
Tsai T-J, Lin C-M, Cheang IN, Hsu Y-J, Wei C-H, Chin T-W, Wu C-Y, Chang W-Y, Fu Y-W. Comparing Outcomes of Single-Incision Laparoscopic Herniorrhaphy in Newborns and Infants. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(3):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030529
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Tsung-Jung, Ching-Min Lin, I Nok Cheang, Yao-Jen Hsu, Chin-Hun Wei, Tai-Wai Chin, Chin-Yen Wu, Wen-Yuan Chang, and Yu-Wei Fu. 2023. "Comparing Outcomes of Single-Incision Laparoscopic Herniorrhaphy in Newborns and Infants" Diagnostics 13, no. 3: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030529
APA StyleTsai, T.-J., Lin, C.-M., Cheang, I. N., Hsu, Y.-J., Wei, C.-H., Chin, T.-W., Wu, C.-Y., Chang, W.-Y., & Fu, Y.-W. (2023). Comparing Outcomes of Single-Incision Laparoscopic Herniorrhaphy in Newborns and Infants. Diagnostics, 13(3), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030529





