Machine Learning Approach with Harmonized Multinational Datasets for Enhanced Prediction of Hypothyroidism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
Related Work
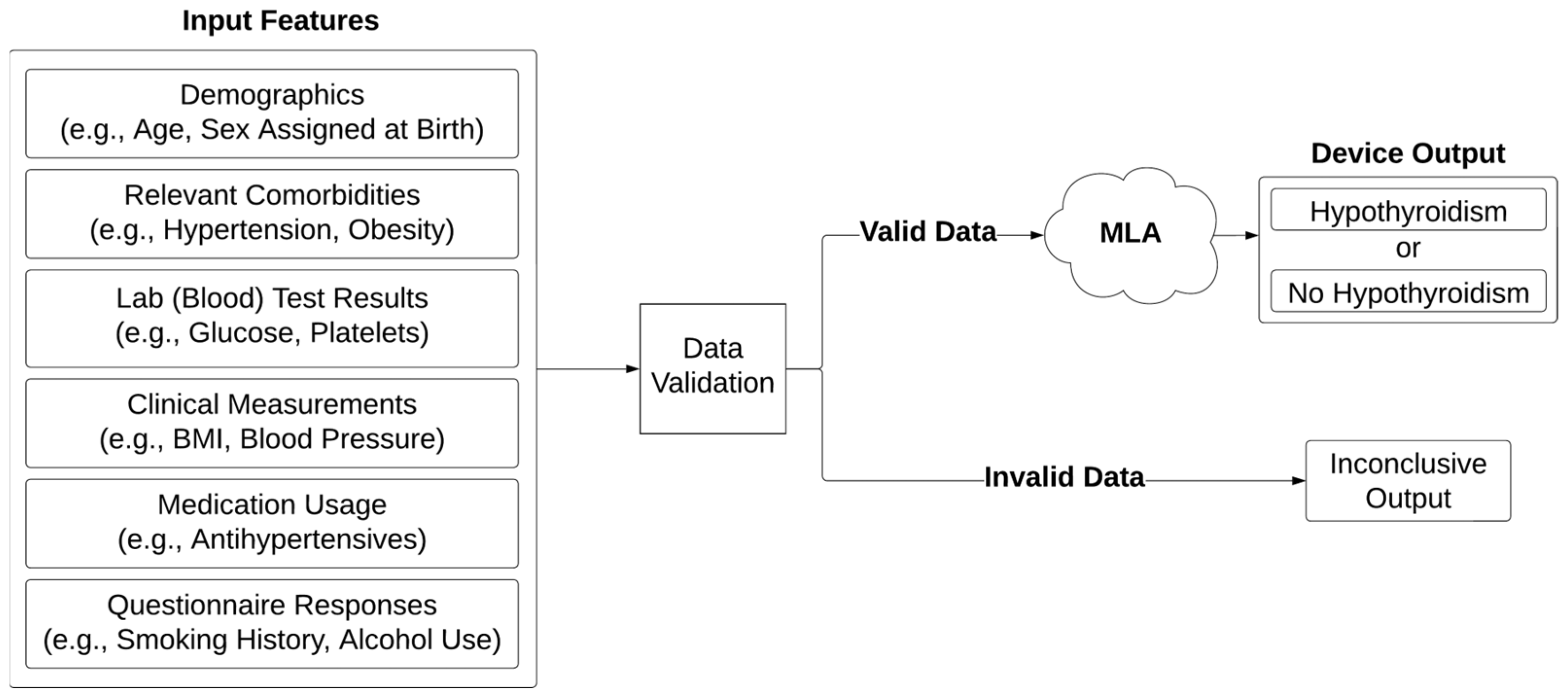
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Data Processing and Feature Selection
2.2.1. Data Processing and Feature Selection for the UKBB Dataset
2.2.2. Data Processing and Feature Selection for the AoU Dataset
2.2.3. Data Harmonization to Create the Multinational Combined Dataset
2.3. Model Training
2.3.1. Algorithm Selection
2.3.2. UKBB MLA Training
2.3.3. AoU MLA Training
2.3.4. Combined MLA Training
2.4. Model Performance Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. System Requirements
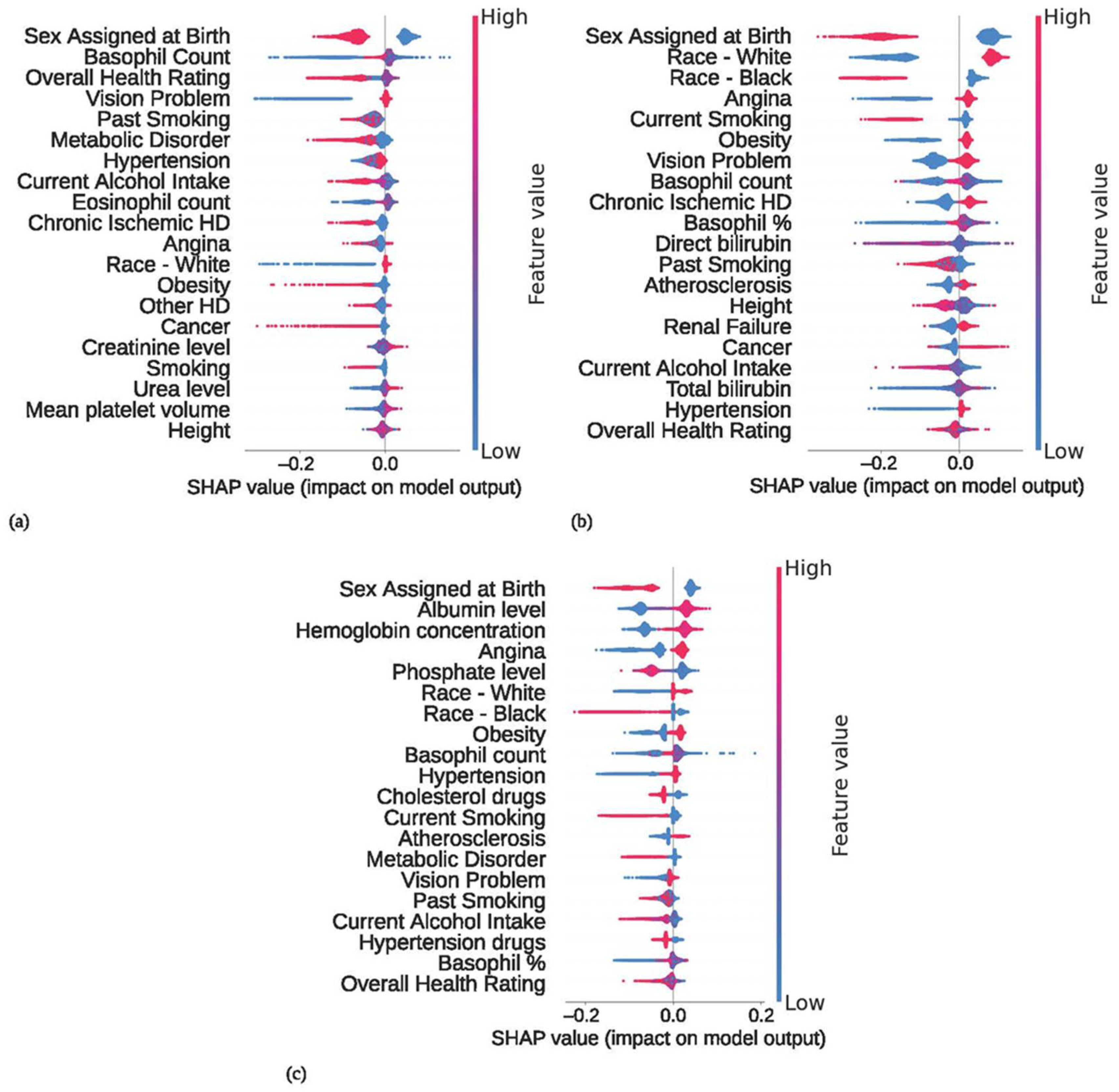
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Current Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bullard, K.M.; Cowie, C.C.; Lessem, S.E.; Saydah, S.H.; Menke, A.; Geiss, L.S.; Orchard, T.J.; Rolka, D.B.; Imperatore, G. Prevalence of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults by Diabetes Type—United States, 2016. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC National Diabetes Statistics Report Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Lin, J.; Thompson, T.J.; Cheng, Y.J.; Zhuo, X.; Zhang, P.; Gregg, E.; Rolka, D.B. Projection of the future diabetes burden in the United States through 2060. Popul. Health Metrics 2018, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. Home, Resources, diabetes wL, Acknowledgement, Faqs, Contact, Policy P. In IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- International Diabetes Federation. Facts & Figures 2023. Available online: https://idf.org/about-diabetes/diabetes-facts-figures/ (accessed on 4 October 2023).
- Lin, P.J.; Pope, E.; Zhou, F.L. Comorbidity Type and Health Care Costs in Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Claims Database Analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.; Aggarwal, S.; Khandelwal, D. Thyroid Dysfunction and Dysmetabolic Syndrome: The Need for Enhanced Thyrovigilance Strategies. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 2021, 9641846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Links, T.P.; Gans, R.O.B.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R. Thyroid Function Is Associated with Components of the Metabolic Syndrome in Euthyroid Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raval, A.D.; Sambamoorthi, U. Incremental Healthcare Expenditures Associated with Thyroid Disorders among Individuals with Diabetes. J. Thyroid. Res. 2012, 2012, 418345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, J.R.; Cobin, R.H.; Gharib, H.; Hennessey, J.V.; Klein, I.; Mechanick, J.I.; Pessah-Pollack, R.; Singer, P.A.; Kenneth A. Woeber for the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American Thyroid Association Taskforce on Hypothyroidism in Adults. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: Cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Thyroid. Off. J. Am. Thyroid. Assoc. 2012, 22, 1200–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottwald-Hostalek, U.; Schulte, B. Low awareness and under-diagnosis of hypothyroidism. Curr. Med Res. Opin. 2022, 38, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyne, K.L.; Nair, L.; Schneiderman, C.P.; Pinsky, B.; Antunez Flores, O.; Guo, D.; Barger, B.; Tessnow, A.H. Hypothyroidism Prevalence in the United States: A Retrospective Study Combining National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and Claims Data, 2009–2019. J. Endocr. Soc. 2022, 7, bvac172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demitrost, L.; Ranabir, S. Thyroid dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective study. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16 (Suppl. 2), S334–S335. [Google Scholar]
- Jali, M.V.; Kambar, S.; Jali, S.; Pawar, N.; Nalawade, P. Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2017, 11 (Suppl. 1), S105–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; He, X.; Xia, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Shan, Z.; Teng, W. Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, S.A.; Mahmood, N. Subclinical hypothyroidism: Controversies to consensus. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17 (Suppl. 3), S636–S642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magri, F.; Chiovato, L.; Croce, L.; Rotondi, M. Thyroid hormone therapy for subclinical hypothyroidism. Endocrine 2019, 66, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maratou, E.; Hadjidakis, D.J.; Kollias, A.; Tsegka, K.; Peppa, M.; Alevizaki, M.; Mitrou, P.; Lambadiari, V.; Boutati, E.; Nikzas, D.; et al. Studies of insulin resistance in patients with clinical and subclinical hypothyroidism. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Singh, R.; Kumar Singh, S.; Iquebal, M.A.; Jaiswal, S.; Kumar Rai, P. Risk of progression to overt hypothyroidism in Indian patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: A prospective observational study. Int. J. Adv. Med. 2022, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhou, L.; Wu, K.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiang, D.; Gao, L. Abnormal Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Resistance Are Induced via the IRE1alpha/XBP-1 Pathway in Subclinical Hypothyroidism. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.J.; Heald, A.H.; Ogunmekan, S.; Fryer, A.A.; Duff, C.J. Should we be screening for thyroid dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2018, 68, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, B.; Kahaly, G.J.; Robertson, R.P. Thyroid Dysfunction and Diabetes Mellitus: Two Closely Associated Disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 789–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadi, A.; Dabaghi, P.; Hosseini, Y.; Gholampourdehaki, M.; Solouki, S.; Gholamhosseini, L.; Eshtiaghi, R. Identifying depressive symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: The role of glucose variability and concomitant hypothyroidism. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2023, 43, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Song, J. Hypothyroidism and Diabetes-Related Dementia: Focused on Neuronal Dysfunction, Insulin Resistance, and Dyslipidemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winocour, P.H. Diabetes and chronic kidney disease: An increasingly common multi-morbid disease in need of a paradigm shift in care. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Hussein, S.M.; AbdElmageed, R.M. The Relationship Between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Related Thyroid Diseases. Cureus 2021, 13, e20697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duntas, L.H.; Orgiazzi, J.; Brabant, G. The interface between thyroid and diabetes mellitus. Clin. Endocrinol. 2011, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.L. Diabetes Control in Thyroid Disease. Diabetes Spectr. 2006, 19, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladenson, P.W.; Singer, P.A.; Ain, K.B.; Bagchi, N.; Bigos, S.T.; Levy, E.G.; Smith, S.A.; Daniels, G.H. American Thyroid Association guidelines for detection of thyroid dysfunction. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 1573–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdick, H.; Pino, E.; Gabel-Comeau, D.; Gu, C.; Roberts, J.; Le, S.; Slote, J.; Saber, N.; Pellegrini, E.; Green-Saxena, A.; et al. Validation of a machine learning algorithm for early severe sepsis prediction: A retrospective study predicting severe sepsis up to 48 h in advance using a diverse dataset from 461 US hospitals. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, C.K.; Smith, A.M.; Walsh, J.R. Machine learning for comprehensive forecasting of Alzheimer’s Disease progression. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Software as a Medical Device; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Le, S.; Allen, A.; Calvert, J.; Palevsky, P.M.; Braden, G.; Patel, S.; Pellegrini, E.; Green-Saxena, A.; Hoffman, J.; Das, R. Convolutional Neural Network Model for Intensive Care Unit Acute Kidney Injury Prediction. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, K.; Garikipati, A.; Barnes, G.; Hoffman, J.; Calvert, J.; Mao, Q.; Das, R. Early prediction of central line associated bloodstream infection using machine learning. Am. J. Infect. Control 2022, 50, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, L.; Maharjan, J.; Mataraso, S.; Barnes, G.; Hoffman, J.; Mao, Q.; Calvert, J.; Das, R. Predicting pulmonary embolism among hospitalized patients with machine learning algorithms. Pulm. Circ. 2022, 12, e12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, R.; Garikipati, A.; Ciobanu, M.; Singh, N.P.; Browning, E.; DeCurzio, J.; Barnes, G.; Dinenno, F.; Mao, Q.; Das, R. Machine Learning Differentiation of Autism Spectrum Sub-Classifications. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, R.; Garikipati, A.; Shokouhi, S.; Hurtado, M.; Barnes, G.; Hoffman, J.; Calvert, J.; Katzmann, L.; Mao, Q.; Das, R. Predicting Falls in Long-term Care Facilities: Machine Learning Study. JMIR Aging 2022, 5, e35373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Iqbal, Z.; Garikipati, A.; Siefkas, A.; Hoffman, J.; Mao, Q.; Das, R. Early prediction of severe acute pancreatitis using machine learning. Pancreatology 2022, 22, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsopra, R.; Fernandez, X.; Luchinat, C.; Alberghina, L.; Lehrach, H.; Vanoni, M.; Dreher, F.; Sezerman, O.; Cuggia, M.; de Tayrac, M.; et al. A framework for validating AI in precision medicine: Considerations from the European ITFoC consortium. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, J.; Garikipati, A.; Dinenno, F.A.; Ciobanu, M.; Barnes, G.; Browning, E.; DeCurzio, J.; Mao, Q.; Das, R. Machine learning determination of applied behavioral analysis treatment plan type. Brain Inform. 2023, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellahham, S. Artificial Intelligence: The Future for Diabetes Care. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, U.M.; Letchmunan, S.; Ali, M.; Hassan, F.H.; Baqir, A.; Sherazi, H.H.R. Machine Learning Based Diabetes Classification and Prediction for Healthcare Applications. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9930985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modak, S.K.S.; Jha, V.K. Diabetes prediction model using machine learning techniques. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 83, 38523–38549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuppad, A.; Patil, S.D. Machine learning for diabetes clinical decision support: A review. Adv. Comput. Intell. 2022, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, B.F.; Sivakumar, S.; Lim, K.H.; Wong, W.K.; Juwono, F.H. Diabetes detection based on machine learning and deep learning approaches. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 83, 4153–24185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-F.; Lee, S.-H.; Tseng, C.-D.; Lin, C.-H.; Chiu, C.-M.; Lin, G.-Z.; Yang, J.; Chang, L.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Su, C.-T.; et al. Using machine learning algorithm to analyse the hypothyroidism complications caused by radiotherapy in patients with head and neck cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, A.; Senapati, B.; Chauhan, A.S.; Makhija, M.; Singh, A.; Gupta, M.; Tiwari, P.K.; Abdel-Rehim, W. Hypothyroidism Disease Diagnosis by Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2023, 11, 368–373. [Google Scholar]
- Rad, S.R.; Mohammadi, Z.H.; Zadeh, M.J.; Mosleh-Shirazi, M.A.; Dehesh, T. Identification of important symptoms and diagnostic hypothyroidism patients using machine learning algorithms. Ann. Med. Surg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubb, S.A.P.; Peters, K.E.; Bruce, D.G.; Davis, W.A.; Davis, T.M.E. The relationship between thyroid dysfunction, cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in type 2 diabetes: The Fremantle Diabetes Study Phase II. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, R.; Peter, R.; Okosieme, O.E. Thyroid dysfunction in patients with diabetes: Clinical implications and screening strategies. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2010, 64, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK Biobank: An Open Access Resource for Identifying the Causes of a Wide Range of Complex Diseases of Middle and Old Age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Investigators TAoURP. The “All of Us” Research Program. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamti, H.; Alharthi, R.; Anizi, A.A.; Alhebshi, R.M.; Eshmawi, A.A.; Alsubai, S.; Umer, M. Improving Prediction of Cervical Cancer Using KNN Imputed SMOTE Features and Multi-Model Ensemble Learning Approach. Cancers 2023, 15, 4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elreedy, D.; Atiya, A.F. A Comprehensive Analysis of Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) for handling class imbalance. Inf. Sci. 2019, 505, 32–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, M.; Jauhiainen, S. Comparison of feature importance measures as explanations for classification models. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonlau, M.; Zou, R.Y. The random forest algorithm for statistical learning. Stata J. Promot. Commun. Stat. Stata 2020, 20, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Hajian-Tilaki, K. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Analysis for Medical Diagnostic Test Evaluation. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 4, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Lyness, J.M.; McDermott, M.P. Direct estimation of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve in the presence of verification bias. Stat. Med. 2009, 28, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. (Eds.) A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30, p. 20172017. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail Fawaz, H.; Forestier, G.; Weber, J.; Idoumghar, L.; Muller, P.-A. Deep learning for time series classification: A review. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 33, 917–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.; Haque, I.; Lu, H.; Moni, M.A.; Gide, E. Comparative performance analysis of K-nearest neighbour (KNN) algorithm and its different variants for disease prediction. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Singh Rawat, A.; Bijalwan, A.; Bahuguna, H. (Eds.) Application of Multi Layer (Perceptron) Artificial Neural Network in the Diagnosis System: A Systematic Review. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Research in Intelligent and Computing in Engineering (RICE), San Salvador, El Salvador, 22–24 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Trevethan, R. Sensitivity, Specificity, and Predictive Values: Foundations, Pliabilities, and Pitfalls in Research and Practice. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, A.J.; Cronin, A.M.; Begg, C.B. One statistical test is sufficient for assessing new predictive markers. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2011, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Bao, C.; Deng, M.; Xu, H.; Fan, M.; Paillard-Borg, S.; Xu, W.; Qi, X. The prevalence and determinants of hypothyroidism in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 2017, 55, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A. Screening for Thyroid Disease. In Guide to Clinical Preventive Services: Report of the US Preventive Services Task Force; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Amjad, A.; Kordel, P.; Fernandes, G. A Review on Innovation in Healthcare Sector (Telehealth) through Artificial Intelligence. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, M.T. Biochemical Testing of the Thyroid: TSH is the Best and, Oftentimes, Only Test Needed—A Review for Primary Care. Clin Med. Res. 2016, 14, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, C.D.; Arao, R.F.; Sprague, B.L.; Lee, J.M.; Buist, D.S.M.; Kerlikowske, K.; Henderson, L.M.; Onega, T.; Tosteson, A.N.A.; Rauscher, G.H.; et al. National Performance Benchmarks for Modern Screening Digital Mammography: Update from the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium. Radiology 2017, 283, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boadu, R.; Darko, G.; Nortey, P.; Akweongo, P.; Sarfo, B. Assessing the sensitivity and specificity of First Response HIV-1-2 test kit with whole blood and serum samples: A cross-sectional study. AIDS Res. Ther. 2016, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CIA. HIV/AIDS—Adult Prevalence Rate CIA: CIA; 2022 [HIV/AIDS—Adult Prevalence Rate Compares the Percentage of Adults (Aged 15-49) Living with HIV/AIDS.]. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/about/archives/2022/field/hiv-aids-adult-prevalence-rate/country-comparison (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Burt, T.; Button, K.S.; Thom, H.; Noveck, R.J.; Munafò, M.R. The Burden of the “False-Negatives” in Clinical Development: Analyses of Current and Alternative Scenarios and Corrective Measures. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 10, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonathan, P.; Dominic, W.; Julian, S. Sense and sensitivity: Can an inaccurate test be better than no test at all? J. Med. Ethics 2022, 48, 329. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, S.; Horiguchi, K.; Akuzawa, M.; Sakamaki, K.; Yamada, E.; Ozawa, A.; Kobayashi, I.; Shimomura, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Andou, T.; et al. The Impact of Age- and Sex-Specific Reference Ranges for Serum Thyrotropin and Free Thyroxine on the Diagnosis of Subclinical Thyroid Dysfunction: A Multicenter Study from Japan. Thyroid 2023, 33, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljabri, K.S.; Bokhari, S.A.; Alshareef, M.A.; Khan, P.M.; Mallosho, A.M.; Jalal, M.M.; Safwat, R.F.; El Boraie, R.; Aljabri, N.K.; Aljabri, B.K. The Prevalence of Hypothyroidism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Community based Hospital a Retrospective Single Centre Study. Arch. Diabetes Obes. 2019, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profiles OfHIaDPh. Diabetes—Data—OHID Office for Health Improvement and Disparitie 2024. Available online: https://fingertips.phe.org.uk/profile/diabetes-ft/data (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- US Department of Health and Human Services Office of Minority Health. Diabetes and African Americans. 2024. Available online: https://minorityhealth.hhs.gov/diabetes-and-african-americans (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Olmos, R.D.; Figueiredo, R.C.; Aquino, E.M.; Lotufo, P.A.; Bensenor, I.M. Gender, race and socioeconomic influence on diagnosis and treatment of thyroid disorders in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MERCK Basophilic Disorders—Blood Disorders: MERCK. 2023. Available online: https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/blood-disorders/white-blood-cell-disorders/basophilic-disorders (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Pizzolo, F.; Castagna, A.; Olivieri, O.; Girelli, D.; Friso, S.; Stefanoni, F.; Udali, S.; Munerotto, V.; Baroni, M.; Cetera, V.; et al. Basophil Blood Cell Count Is Associated With Enhanced Factor II Plasma Coagulant Activity and Increased Risk of Mortality in Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease: Not Only Neutrophils as Prognostic Marker in Ischemic Heart Disease. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2021, 10, e018243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asvold, B.O.; Bjoro, T.; Nilsen, T.I.; Vatten, L.J. Tobacco smoking and thyroid function: A population-based study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordo, M.; Zeng, Q. (Eds.) On Sample Size and Classification Accuracy: A Performance Comparison. In Biological and Medical Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tsangaratos, P.; Ilia, I. Comparison of a logistic regression and Naïve Bayes classifier in landslide susceptibility assessments: The influence of models complexity and training dataset size. Catena 2016, 145, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Kwon, H.S.; Baek, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, W.C.; Sohn, H.S.; Lee, K.-W.; Song, K.-H. Effects of thyroid hormone on A1C and glycated albumin levels in nondiabetic subjects with overt hypothyroidism. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2546–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vliet, N.A.; Kamphuis, A.E.P.; den Elzen, W.P.J.; Blauw, G.J.; Gussekloo, J.; Noordam, R.; van Heemst, D. Thyroid Function and Risk of Anemia: A Multivariable-Adjusted and Mendelian Randomization Analysis in the UK Biobank. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e643–e652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wopereis, D.M.; Du Puy, R.S.; van Heemst, D.; Walsh, J.P.; Bremner, A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Bauer, D.C.; Cappola, A.R.; Ceresini, G.; Degryse, J.; et al. The Relation Between Thyroid Function and Anemia: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Participant Data. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3658–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Government Accountability Office. Artificial Intelligence in Health Care: Benefits and Challenges of Technologies to Augment Patient Care 2020; United States Government Accountability Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tasin, I.; Nabil, T.U.; Islam, S.; Khan, R. Diabetes prediction using machine learning and explainable AI techniques. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Rustam, F.; Kanwal, K.; Aljedaani, W.; Alfarhood, S.; Safran, M.; Ashraf, I. Detecting Thyroid Disease Using Optimized Machine Learning Model Based on Differential Evolution. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2024, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Asami, C.; Iwakura, H.; Nakajima, Y.; Sema, R.; Kikuchi, T.; Miyata, T.; Sakamaki, K.; Kudo, T.; Yamada, M.; et al. Development and preliminary validation of a machine learning system for thyroid dysfunction diagnosis based on routine laboratory tests. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
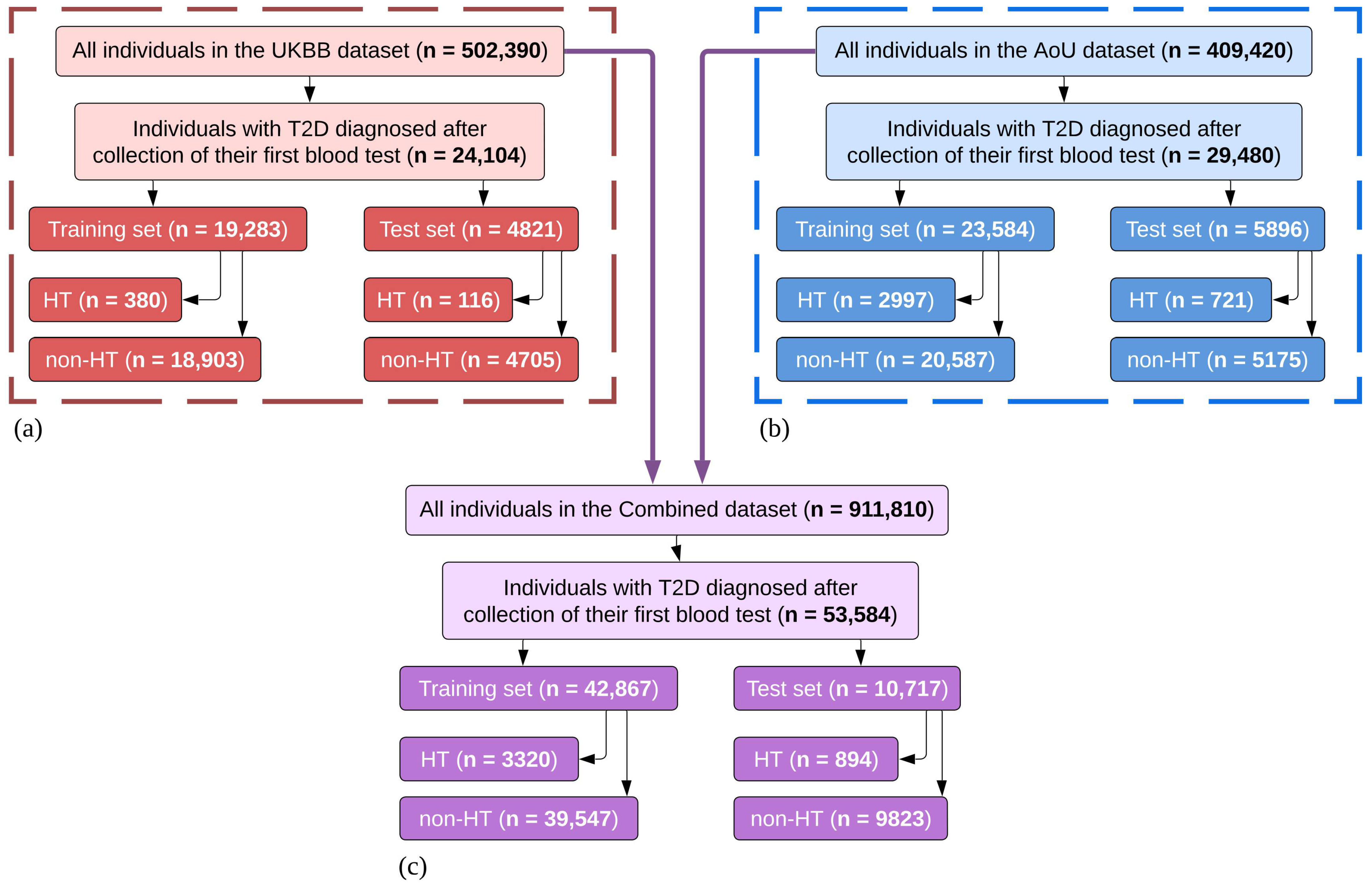

| Demographics (Training Set) | UKBB Dataset | AoU Dataset | Combined Dataset | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT (n = 380) | non-HT (n = 18,903) | HT (n = 2997) | non-HT (n = 20,587) | HT (n = 3320) | non-HT (n = 39,547) | ||
| Age (years) | 22–40 | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 377 (12.6%) | 2810 (13.6%) | 365 (11.0%) | 2789 (7.1%) |
| 41–50 | 0 (0.0%) | 125 (0.7%) | 619 (20.7%) | 4331 (21.0%) | 580 (17.5%) | 4451 (11.3%) | |
| 51–60 | 39 (10.3%) | 2291 (12.1%) | 985 (32.9%) | 6564 (31.9%) | 1005 (30.3%) | 8956 (22.6%) | |
| 61–70 | 143 (37.6%) | 6409 (33.9%) | 752 (25.1%) | 5020 (24.4%) | 921 (27.7%) | 11,473 (29.0%) | |
| 71–80 | 198 (52.1%) | 10,048 (53.2%) | 238 (7.9%) | 1635 (7.9%) | 423 (12.7%) | 11,631 (29.4%) | |
| >80 | 0 (0.0%) | 30 (0.2%) | 26 (0.9%) | 227 (1.1%) | 26 (0.8%) | 247 (0.6%) | |
| Sex assigned at birth | Female | 213 (56.1%) | 6724 (35.6%) | 2060 (68.7%) | 11,094 (53.9%) | 2222 (66.9%) | 17,804 (45.0%) |
| Male | 167 (43.9%) | 12,179 (64.4%) | 866 (28.9%) | 9058 (44.0%) | 1029 (31.0%) | 21,297 (53.9%) | |
| Unknown | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 71 (2.4%) | 435 (2.1%) | 69 (2.1%) | 446 (1.1%) | |
| Racial identity | White | 333 (87.6%) | 16,569 (87.7%) | 1756 (58.6%) | 8812 (42.8%) | 2033 (61.2%) | 25,315 (64.0%) |
| Black | 10 (2.6%) | 624 (3.3%) | 528 (17.6%) | 6175 (30.0%) | 519 (15.6%) | 6890 (17.4%) | |
| Asian | 25 (6.6%) | 980 (5.2%) | 66 (2.2%) | 413 (2.0%) | 96 (2.9%) | 1398 (3.5%) | |
| More than one race | 0 (0.0%) | 78 (0.4%) | 32 (1.1%) | 251 (1.2%) | 33 (1.0%) | 325 (0.8%) | |
| Other | 9 (2.4%) | 285 (1.5%) | 42 (1.4%) | 369 (1.8%) | 55 (1.7%) | 676 (1.7%) | |
| Unknown | 3 (0.8%) | 367 (1.9%) | 573 (19.1%) | 4567 (22.2%) | 584 (17.6%) | 4943 (12.5%) | |
| Substance use (Yes/No) | Current smoker | 44 (11.6%) | 2446 (12.9%) | 312 (10.4%) | 3191 (15.5%) | 342 (10.3%) | 5648 (14.3%) |
| Unknown smoking status | 0 (0.0%) | 81 (0.4%) | 1671 (55.8%) | 11,372 (55.2%) | 1635 (49.2%) | 11,524 (29.1%) | |
| Ever smoked | 176 (46.2%) | 8798 (46.5%) | 1332 (44.4%) | 9254 (45.0%) | 1480 (44.6%) | 17,985 (45.5%) | |
| Unknown smoking history | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 72 (2.4%) | 508 (2.5%) | 79 (2.4%) | 519 (1.3%) | |
| Currently frequently use alcohol | 87 (22.9%) | 5860 (31.0%) | 159 (5.3%) | 1268 (6.2%) | 244 (7.3%) | 7105 (18.0%) | |
| Unknown alcohol status | 0 (0.0%) | 100 (0.5%) | 456 (15.2%) | 3512 (17.1%) | 452 (13.6%) | 3668 (9.3%) | |
| Medications | Cholesterol | 259 (68.2%) | 12,208 (64.6%) | 847 (28.3%) | 5470 (26.6%) | 1121 (33.8%) | 17,716 (44.8%) |
| Hypertension | 227 (59.7%) | 11,449 (60.6%) | 1062 (35.4%) | 6415 (31.2%) | 1281 (38.6%) | 17,952 (45.4%) | |
| Comorbidities | Obesity | 67 (17.6%) | 3211 (17.0%) | 2108 (70.3%) | 12,887 (62.6%) | 2129 (64.1%) | 16,048 (40.6%) |
| Angina | 84 (22.1%) | 3738 (19.8%) | 2112 (70.5%) | 12,480 (60.6%) | 2166 (65.2%) | 16,261 (41.1%) | |
| Chronic ischemic HD | 101 (26.6%) | 5192 (27.5%) | 1321 (44.1%) | 6814 (33.1%) | 1374 (41.4%) | 12,058 (30.5%) | |
| Pulmonary HD | 10 (2.6%) | 647 (3.4%) | 192 (6.4%) | 765 (3.7%) | 197 (5.9%) | 1392 (3.5%) | |
| Atherosclerosis | 4 (1.1%) | 181 (1.0%) | 1417 (47.3%) | 7608 (37.0%) | 1369 (41.2%) | 7864 (19.9%) | |
| Vision problem | 310 (81.6%) | 14,847 (78.5%) | 1405 (46.9%) | 7889 (38.3%) | 1658 (50.0%) | 22,827 (57.7%) | |
| Performance Metrics | UKBB MLA | AoU MLA | Combined MLA |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUROC (95% CI) | 0.622 (0.573–0.671) | 0.666 (0.646–0.687) | 0.762 (0.747–0.778) |
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | 0.655 (0.577–0.733) | 0.997 (0.995–1.000) | 0.965 (0.955–0.976) |
| Specificity (95% CI) | 0.489 (0.476–0.502) | 0.035 (0.032–0.038) | 0.238 (0.230–0.245) |
| PPV (95% CI) | 0.031 (0.025–0.037) | 0.126 (0.120–0.131) | 0.103 (0.097–0.109) |
| NPV (95% CI) | 0.983 (0.978–0.988) | 0.989 (0.979–0.999) | 0.987 (0.983–0.991) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adelson, R.P.; Garikipati, A.; Zhou, Y.; Ciobanu, M.; Tawara, K.; Barnes, G.; Singh, N.P.; Mao, Q.; Das, R. Machine Learning Approach with Harmonized Multinational Datasets for Enhanced Prediction of Hypothyroidism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111152
Adelson RP, Garikipati A, Zhou Y, Ciobanu M, Tawara K, Barnes G, Singh NP, Mao Q, Das R. Machine Learning Approach with Harmonized Multinational Datasets for Enhanced Prediction of Hypothyroidism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(11):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111152
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdelson, Robert P., Anurag Garikipati, Yunfan Zhou, Madalina Ciobanu, Ken Tawara, Gina Barnes, Navan Preet Singh, Qingqing Mao, and Ritankar Das. 2024. "Machine Learning Approach with Harmonized Multinational Datasets for Enhanced Prediction of Hypothyroidism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes" Diagnostics 14, no. 11: 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111152
APA StyleAdelson, R. P., Garikipati, A., Zhou, Y., Ciobanu, M., Tawara, K., Barnes, G., Singh, N. P., Mao, Q., & Das, R. (2024). Machine Learning Approach with Harmonized Multinational Datasets for Enhanced Prediction of Hypothyroidism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diagnostics, 14(11), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111152







