Vitamin D in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome (pSS) and the Identification of Novel Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Involved in the Development of pSS-Associated Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Immunomodulatory Function of Vitamin D
The Role of Vitamin D in pSS
3. SNPs Associated with Sjögren’s Syndrome
3.1. Overview of Genetic Findings in Sjögren’s Syndrome
3.2. Key Genetic Pathways and Variants
3.3. Ethnic Differences and Genetic Associations
4. Interaction with Other Diseases
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mariette, X.; Criswell, L.A. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Chen, S.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xuan, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G. Early Diagnosis and Treatment for Sjögren’s Syndrome: Current Challenges, Redefined Disease Stages and Future Prospects. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 117, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, N.; Salesi, M. The Association between Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome and Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Kostov, B.; Solans, R.; Fraile, G.; Suárez-Cuervo, C.; Casanovas, A.; Rascón, F.J.; Qanneta, R.; Pérez-Alvarez, R.; Ripoll, M.; et al. Systemic Activity and Mortality in Primary Sjögren Syndrome: Predicting Survival Using the EULAR-SS Disease Activity Index (ESSDAI) in 1045 Patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehrfeld, N.; Abelmann, M.; Benz, S.; Zippel, C.L.; Beider, S.; Kramer, E.; Seeliger, T.; Sogkas, G.; Gödecke, V.; Ahrenstorf, G.; et al. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Independently Promotes Premature Subclinical Atherosclerosis. RMD Open 2024, 10, e003559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yao, P.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Feng, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Causal Associations of Sjögren’s Syndrome with Cancers: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alani, H.; Henty, J.; Thompson, N.; Jury, E.; Ciurtin, C. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Epidemiology of Polyautoimmunity in Sjögren’s Syndrome (Secondary Sjögren’s Syndrome) Focusing on Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 47, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, M.; Ma, N.; Huang, F.; Zhong, R. Epidemiology of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1983–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvarnström, M.; Ottosson, V.; Nordmark, B.; Wahren-Herlenius, M. Incident Cases of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome during a 5-Year Period in Stockholm County: A Descriptive Study of the Patients and Their Characteristics. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 44, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dézsi, A.J.; Erdei, C.; Demeter, T.; Kovács, A.; Nagy, G.; Mensch, K.; Németh, O.; Hermann, P.; Tóth, G.; Füst, Á.; et al. Prevalence of Sjögren’s Syndrome in Patients with Dry Mouth in the Region of Central Hungary. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 2756–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Acar-Denizli, N.; Zeher, M.; Rasmussen, A.; Seror, R.; Theander, E.; Li, X.; Baldini, C.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Danda, D.; et al. Influence of Geolocation and Ethnicity on the Phenotypic Expression of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome at Diagnosis in 8310 Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study from the Big Data Sjögren Project Consortium. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, V.M.; Sharma, R.; Cavett, J.; Kurien, B.T.; Liu, K.; Koelsch, K.A.; Rasmussen, A.; Radfar, L.; Lewis, D.; Stone, D.U.; et al. Klinefelter’s Syndrome (47,XXY) Is in Excess among Men with Sjögren’s Syndrome. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 168, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Kurien, B.T.; Zimmerman, S.L.; Kaufman, K.M.; Taft, D.H.; Kottyan, L.C.; Lazaro, S.; Weaver, C.A.; Ice, J.A.; Adler, A.J.; et al. X Chromosome Dose and Sex Bias in Autoimmune Diseases: Increased Prevalence of 47,XXX in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Harris, V.M.; Cavett, J.; Kurien, B.T.; Liu, K.; Koelsch, K.A.; Fayaaz, A.; Chaudhari, K.S.; Radfar, L.; Lewis, D.; et al. Brief Report: Rare X Chromosome Abnormalities in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 2187–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrel, L.; Willard, H.F. X-Inactivation Profile Reveals Extensive Variability in X-Linked Gene Expression in Females. Nature 2005, 434, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukurba, K.R.; Parsana, P.; Balliu, B.; Smith, K.S.; Zappala, Z.; Knowles, D.A.; Favé, M.-J.; Davis, J.R.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; et al. Impact of the X Chromosome and Sex on Regulatory Variation. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairfax, B.P.; Makino, S.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Plant, K.; Leslie, S.; Dilthey, A.; Ellis, P.; Langford, C.; Vannberg, F.O.; Knight, J.C. Genetics of Gene Expression in Primary Immune Cells Identifies Cell Type–Specific Master Regulators and Roles of HLA Alleles. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodewes, I.L.A.; Al-Ali, S.; Van Helden-Meeuwsen, C.G.; Maria, N.I.; Tarn, J.; Lendrem, D.W.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; Steenwijk, E.C.; Van Daele, P.L.A.; Both, T.; et al. Systemic Interferon Type I and Type II Signatures in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Reveal Differences in Biological Disease Activity. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carapito, R.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Kotova, I.; Untrau, M.; Michel, S.; Naegely, L.; Aouadi, I.; Kwemou, M.; Paul, N.; Pichot, A.; et al. A New MHC-Linked Susceptibility Locus for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: MICA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2565–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teos, L.Y.; Alevizos, I. Genetics of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 182, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortíz-Fernández, L.; Martín, J.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E. A Summary on the Genetics of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Sclerosis, and Sjögren’s Syndrome. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 64, 392–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imgenberg-Kreuz, J.; Rasmussen, A.; Sivils, K.; Nordmark, G. Genetics and Epigenetics in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2085–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstappen, G.M.; Pringle, S.; Bootsma, H.; Kroese, F.G.M. Epithelial–Immune Cell Interplay in Primary Sjögren Syndrome Salivary Gland Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontarini, E.; Lucchesi, D.; Bombardieri, M. Current Views on the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Han, M.; Zhu, X.; Xiao, F.; Huang, E.; Che, N.; Tang, X.; Zou, H.; Jiang, Q.; Lu, L. The Multiple Roles of B Cells in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 684999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiripolsky, J.; McCabe, L.G.; Kramer, J.M. Innate Immunity in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 182, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horai, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Umeda, M.; Nishihata, S.-Y.; Nakamura, H.; Kawakami, A. Current Views on Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Review from the Perspective of Viral Infections, Toll-like Receptors, and Long-Noncoding RNAs. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, A.; Mofors, J.; Wahren-Herlenius, M. Environmental Factors in the Pathogenesis of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslinska, M.; Kostyra-Grabczak, K. The Role of Virus Infections in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 823659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.-C.; Seo, Y.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, S.J.; Ji, J.D.; Song, G.G. Association between FCGR3B Copy Number Variations and Susceptibility to Autoimmune Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Li, X. Association of FAM167A-BLK Rs2736340 Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Autoimmune Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Immunol. Investig. 2016, 45, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Mu, L.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wu, H. Associations between TNFSF4 Gene Polymorphisms (Rs2205960 G > A, Rs704840 T > G and Rs844648 G > A) and Susceptibility to Autoimmune Diseases in Asians: A Meta-Analysis. Immunol. Investig. 2021, 50, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wax, J.; Huang, R.; Petersen, F.; Yu, X. Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of the Association between a Hypoactive NCF1 Variant and Various Autoimmune Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Dai, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, B. Risk Factors for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Hu, N.; Xu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Bai, Y.; Sun, H. Associations between TNFSF13B Polymorphisms and Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Susceptibility in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Patients: A Meta-analysis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2023, 11, e1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorlacius, G.E.; Björk, A.; Wahren-Herlenius, M. Genetics and Epigenetics of Primary Sjögren Syndrome: Implications for Future Therapies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 288–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavragani, C.P. Mechanisms and New Strategies for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.; Sarkar, I.; Hammenfors, D.; Bergum, B.; Vogelsang, P.; Solberg, S.M.; Gavasso, S.; Brun, J.G.; Jonsson, R.; Appel, S. Single Cell Based Phosphorylation Profiling Identifies Alterations in Toll-Like Receptor 7 and 9 Signaling in Patients With Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, J.A.; Guthridge, J.M.; Chen, H.; Lu, R.; Bourn, R.L.; Bean, K.; Munroe, M.E.; Smith, M.; Chakravarty, E.; Baer, A.N.; et al. Unique Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient Subsets Defined by Molecular Features. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorlacius, G.E.; Hultin-Rosenberg, L.; Sandling, J.K.; Bianchi, M.; Imgenberg-Kreuz, J.; Pucholt, P.; Theander, E.; Kvarnström, M.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H.; Bucher, S.M.; et al. Genetic and Clinical Basis for Two Distinct Subtypes of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soret, P.; Le Dantec, C.; Desvaux, E.; Foulquier, N.; Chassagnol, B.; Hubert, S.; Jamin, C.; Barturen, G.; Desachy, G.; Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; et al. A New Molecular Classification to Drive Precision Treatment Strategies in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassi, F.; Tamone, C.; D’Amelio, P. Vitamin D: Nutrient, Hormone, and Immunomodulator. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakos, S.; Li, S.; De La Cruz, J.; Bikle, D.D. New Developments in Our Understanding of Vitamin D Metabolism, Action and Treatment. Metabolism 2019, 98, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.L.G.D.; Chaves, A.T.; Menezes, C.A.S.; Guimarães, N.S.; Bueno, L.L.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Rocha, M.O.D.C. Vitamin D Receptor Expression and Hepcidin Levels in the Protection or Severity of Leprosy: A Systematic Review. Microbes Infect. 2017, 19, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeharto, D.A.; Rifai, D.A.; Marsudidjadja, S.; Roekman, A.E.; Assegaf, C.K.; Louisa, M. Vitamin D as an Adjunctive Treatment to Standard Drugs in Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients: An Evidence-Based Case Report. Adv. Prev. Med. 2019, 2019, 5181847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismailova, A.; White, J.H. Vitamin D, Infections and Immunity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, A.; Wierzbicka, J.; Żmijewski, M.A. Vitamin D in the Skin Physiology and Pathology. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranow, C. Vitamin D and the Immune System. J. Investig. Med. 2011, 59, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D Regulation of Immune Function. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2022, 20, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, S. Taking Regulatory T Cells into Medicine. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20210831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantorna, M.; Snyder, L.; Lin, Y.-D.; Yang, L. Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T Cells. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3011–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, D.V.; Al-Jaberi, F.A.H.; Woetmann, A.; Ødum, N.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Kongsbak-Wismann, M.; Geisler, C. Macrophages Control the Bioavailability of Vitamin D and Vitamin D-Regulated T Cell Responses. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 722806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, T.; Kikuta, J.; Ishii, M. The Effects of Vitamin D on Immune System and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, A.; Rejnmark, L.; Heickendorff, L.; Møller, H.J. 25(OH)D3 and 1.25(OH)2D3 Inhibits TNF-α Expression in Human Monocyte Derived Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Cook, N.R.; Lee, I.; Hahn, J.; Walter, J.; Bubes, V.; Kotler, G.; Yang, N.; Friedman, S.; Alexander, E.K.; et al. Vitamin D and Marine N-3 Fatty Acids for Autoimmune Disease Prevention: Outcomes Two Years After Completion of a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.R.; Li, D.; Jeffery, L.E.; Raza, K.; Hewison, M. Vitamin D, Autoimmune Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 106, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.-C. Vitamin D Level in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Correlation with the Disease Activity: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 827–833. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-L.; Lee, F.-K.; Wang, P.-H. Vitamin D and Systemic Lupus Erythematous. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2022, 85, 811–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny, C.; Souberbielle, J.-C. Vitamin D and Multiple Sclerosis: An Update. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2017, 14, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, A.C.; Smith, V.; Gotelli, E.; Ghio, M.; Paolino, S.; Pizzorni, C.; Vanhaecke, A.; Ruaro, B.; Sulli, A.; Cutolo, M. Vitamin D Deficiency and Clinical Correlations in Systemic Sclerosis Patients: A Retrospective Analysis for Possible Future Developments. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernia, F.; Valvano, M.; Longo, S.; Cesaro, N.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Vitamin D in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Implications. Nutrients 2022, 14, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illescas-Montes, R.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Ruiz, C.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J. Vitamin D and Autoimmune Diseases. Life Sci. 2019, 233, 116744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanassiou, L.; Kostoglou-Athanassiou, I.; Koutsilieris, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Vitamin D and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.-C.; Lee, Y.H. Association between Vitamin D Level and/or Deficiency, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, L.L.W.; Colavite, P.M.; Fraga-Silva, T.F.D.C.; Mimura, L.A.N.; França, T.G.D.; Zorzella-Pezavento, S.F.G.; Chiuso-Minicucci, F.; Marcolino, L.D.; Penitenti, M.; Ikoma, M.R.V.; et al. Vitamin D Deficiency and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 52, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, A.; Carvalho, C.; Boleixa, D.; Bettencourt, A.; Leal, B.; Guimarães, J.; Neves, E.; Oliveira, J.C.; Almeida, I.; Farinha, F.; et al. Vitamin D Supplementation Effects on FoxP3 Expression in T Cells and FoxP3+/IL-17A Ratio and Clinical Course in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Study in a Portuguese Cohort. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, R.; Saliba, C.; Camilleri, L.; Scerri, C.; Borg, A.A. Vitamin D Supplementation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Relationship to Disease Activity, Fatigue and the Interferon Signature Gene Expression. BMC Rheumatol. 2021, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, H.; Shirzadi, M.; Karimifar, M. The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation in Disease Activity of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients with Vitamin D Deficiency: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 22, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kushi, A.; Azzeh, F.; Header, E.; ElSawy, N.; Hijazi, H.; Jazar, A.; Ghaith, M.; Alarjah, M. Effect of Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lin, K.-J.; Tsai, T.-Y. Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated with Severity of Dry Eye Symptoms and Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2020, 66, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, M.; Kolak, E.; Đogaš, H.; Gelemanović, A.; Bučan Nenadić, D.; Vučković, M.; Radić, J. Vitamin D and Sjögren’s Disease: Revealing the Connections—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y. The Association between Vitamin D Level and Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Meta-analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Byun, Y.-S.; Lee, J.; Park, S.-H.; Chung, S.-H. The Association of Serum Vitamin D Level with the Severity of Dry Eye Parameters in Primary Sjögren Syndrome. Cornea 2020, 39, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Oh, H.J.; Choi, B.Y.; Jang, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.K.; Song, Y.W. Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 and BAFF Levels Are Associated with Disease Activity in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 5781070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, P. Vitamin D Levels and Associations in Indian Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2017, 11, OC33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wei, F.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Fei, G.; Ge, Y.; Wei, P. Serum Vitamin D Levels and Sjogren’s Syndrome: Bi-Directional Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, M.C.; Herman, H.; Balta, C.; Rosu, M.; Ciceu, A.; Mladin, B.; Gesualdo, C.; Lepre, C.C.; Russo, M.; Petrillo, F.; et al. Oral Administration of Vitamin D3 Prevents Corneal Damage in a Knock-Out Mouse Model of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, D.; Sezer Kürkçü, M.; Günaydin, B.; Tarhan, E.F. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Regulates t Helper and b Lymphocyte Responses Substantially in Drug-Naive Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Patients’ Mononuclear Cells. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latini, A.; De Benedittis, G.; Perricone, C.; Colafrancesco, S.; Conigliaro, P.; Ceccarelli, F.; Chimenti, M.S.; Novelli, L.; Priori, R.; Conti, F.; et al. VDR Polymorphisms in Autoimmune Connective Tissue Diseases: Focus on Italian Population. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 5812136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilahi, E.; Chen, J.-Q.; Papp, G.; Szántó, A.; Zeher, M. Lack of Association of Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphisms/Haplotypes in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, C.J.; Li, H.; Adrianto, I.; Ice, J.A.; Rasmussen, A.; Grundahl, K.M.; Kelly, J.A.; Dozmorov, M.G.; Miceli-Richard, C.; Bowman, S.; et al. Variants at Multiple Loci Implicated in Both Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses Are Associated with Sjögren’s Syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, B.; Tessneer, K.L.; Rasmussen, A.; Aghakhanian, F.; Reksten, T.R.; Adler, A.; Alevizos, I.; Anaya, J.-M.; Aqrawi, L.A.; Baecklund, E.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Sjögren’s Risk Loci with Functional Implications in Immune and Glandular Cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simula, E.R.; Jasemi, S.; Cossu, D.; Manca, P.C.; Sanna, D.; Scarpa, F.; Meloni, G.; Cusano, R.; Sechi, L.A. The Genetic Landscape of Systemic Rheumatic Diseases: A Comprehensive Multigene-Panel Study Identifying Key Gene Polymorphisms. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colafrancesco, S.; Ciccacci, C.; Priori, R.; Latini, A.; Picarelli, G.; Arienzo, F.; Novelli, G.; Valesini, G.; Perricone, C.; Borgiani, P. STAT4, TRAF3IP2, IL10, and HCP5 Polymorphisms in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Association with Disease Susceptibility and Clinical Aspects. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7682827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Sun, F.; Xu, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Luan, H.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study in Han Chinese Identifies a Susceptibility Locus for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome at 7q11.23. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Xie, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Mai, R.; Lin, Q.; et al. Germline Genetic Patterns Underlying Familial Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Highlight T Cell-Initiated Autoimmunity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Lee, K.; Han, S.K.; Ahn, H.-J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.H. Variants at Potential Loci Associated with Sjogren’s Syndrome in Koreans: A Genetic Association Study. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 207, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E.; Wong, Q.; Levine, D.M.; McHugh, C.; Laurie, C.; Doheny, K.; Lam, M.Y.; Baer, A.N.; Challacombe, S.; Lanfranchi, H.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Reveals Genetic Heterogeneity of Sjögren’s Syndrome According to Ancestry. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Xin, D.E.; Wang, Z.; Peng, W.; Zeng, Y.; Liang, J.; Xu, M.; Chen, N.; Zhang, J.; Yue, J.; et al. Acetylation Licenses Th1 Cell Polarization to Constrain Listeria Monocytogenes Infection. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 2303–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madera-Salcedo, I.K.; Ramírez-Sánchez, A.L.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, N.; García-Quintero, R.; Rubio, R.M.; Morales-Montes De Oca, G.; Dávalos, E.; Cuervo, R.; Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Alcocer-Varela, J.; et al. Down-Regulation–Resistant STAT4 Risk Haplotype Contributes to Lupus Nephritis Through CD4+ T Cell Interferon-γ Production. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; Vieira, P.; O’Garra, A. Biology and Therapeutic Potential of Interleukin-10. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabiyik, A.; Peck, A.B.; Nguyen, C.Q. The Important Role of T Cells and Receptor Expression in S Jögren’s Syndrome. Scand. J. Immunol. 2013, 78, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersone, L.; Edner, N.M.; Ovcinnikovs, V.; Heuts, F.; Ross, E.M.; Ntavli, E.; Wang, C.J.; Walker, L.S.K. T Cell/B Cell Collaboration and Autoimmunity: An Intimate Relationship. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Li, Q. Primary Biliary Cholangitis and Sjogren’s Syndrome: Bi-Directional Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 3556–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, F.; Lan, T. Sjögren’s Syndrome and Parkinson’s Disease: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xing, H.; Gao, W.; Yu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, K.; Li, P.; Yu, J.; Xu, W.; et al. A Functional Variant in the OAS1 Gene Is Associated with Sjögren’s Syndrome Complicated with HBV Infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Shu, Q.; Hua, B.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Ge, W.; Fang, Y. NUDT15 R139C Variation Increases the Risk of Azathioprine-Induced Toxicity in Chinese Subjects: Case Report and Literature Review. Medicine 2018, 97, e0301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Lang, Y.; Kong, L.; Lin, X.; Du, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H. The Causal Relationship between Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder and Other Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 959469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norheim, K.B.; Imgenberg-Kreuz, J.; Alexsson, A.; Johnsen, S.J.A.; Bårdsen, K.; Brun, J.G.; Dehkordi, R.K.; Theander, E.; Mandl, T.; Jonsson, R.; et al. Genetic Variants at the RTP4/MASP1 Locus Are Associated with Fatigue in Scandinavian Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flessa, C.-M.; Zampeli, E.; Evangelopoulos, M.-E.; Natsis, V.; Bodewes, I.L.A.; Huijser, E.; Versnel, M.A.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Mavragani, C.P. Genetic Variants of the BAFF Gene and Risk of Fatigue Among Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 836824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocturne, G.; Tarn, J.; Boudaoud, S.; Locke, J.; Miceli-Richard, C.; Hachulla, E.; Dubost, J.-J.; Bowman, S.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Criswell, L.A.; et al. Germline Variation of TNFAIP3 in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome-Associated Lymphoma. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccacci, C.; Latini, A.; Perricone, C.; Conigliaro, P.; Colafrancesco, S.; Ceccarelli, F.; Priori, R.; Conti, F.; Perricone, R.; Novelli, G.; et al. TNFAIP3 Gene Polymorphisms in Three Common Autoimmune Diseases: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Primary Sjogren Syndrome—Association with Disease Susceptibility and Clinical Phenotypes in Italian Patients. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 6728694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyriou, E.; Nezos, A.; Roussos, P.; Venetsanopoulou, A.; Voulgarelis, M.; Boki, K.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Mavragani, C.P. Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor A3 (LILRA3): A Novel Marker for Lymphoma Development among Patients with Young Onset Sjogren’s Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragkioudaki, S.; Nezos, A.; Souliotis, V.L.; Chatziandreou, I.; Saetta, A.A.; Drakoulis, N.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Voulgarelis, M.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Koutsilieris, M.; et al. MTHFR Gene Variants and Non-MALT Lymphoma Development in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezos, A.; Makri, P.; Gandolfo, S.; De Vita, S.; Voulgarelis, M.; Crow, M.K.; Mavragani, C.P. TREX1 Variants in Sjogren’s Syndrome Related Lymphomagenesis. Cytokine 2020, 132, 154781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safonova, T.N.; Surnina, Z.V.; Zaitseva, G.V.; Burdennyi, A.M.; Loginov, V.I. The Role of Polymorphic Markers Rs1478604, Rs2292305, and Rs2228262 in THBS1 Gene in the Development of Autoimmune Dry Eye Syndrome. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 169, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-S.; Hudgins, A.D.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Tu, Z.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; DiLorenzo, T.P.; Suh, Y. A Comprehensive Integrated Post-GWAS Analysis of Type 1 Diabetes Reveals Enhancer-Based Immune Dysregulation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadegesin, R.A.; Brophy, P.D.; Adeyemo, A.; Hall, G.; Gupta, I.R.; Hains, D.; Bartkowiak, B.; Rabinovich, C.E.; Chandrasekharappa, S.; Homstad, A.; et al. TNXB Mutations Can Cause Vesicoureteral Reflux. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, S.; Meiners, P.M.; Moerman, R.V.; Kroese, F.G.M.; Brouwer, E.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Vissink, A.; Bootsma, H. Physical Fatigue Characterises Patient Experience of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, W. The Possible Role of MOPr-DOPr Heteromers and Its Regulatory Protein RTP4 at Sensory Neurons in Relation to Pain Perception. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 609362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyo-Becerra, C.; Liu, Z.; Yao, J.; Kaltwasser, B.; Gerken, G.; Hermann, D.M.; Schlaak, J.F. Rapid Regulation of Depression-Associated Genes in a New Mouse Model Mimicking Interferon-α-Related Depression in Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, R.; Furze, C.M.; Wright, D.W.; Gor, J.; Wallis, R.; Perkins, S.J. Flexibility in Mannan-Binding Lectin-Associated Serine Proteases-1 and -2 Provides Insight on Lectin Pathway Activation. Structure 2017, 25, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.A.; Liu, B. Navigating the Landscape of the Unfolded Protein Response in CD8+ T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1427859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassan, S.S. Increased Risk of Lymphoma in Sicca Syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 1978, 89, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ordoñez, I.; Piedrahita, J.-M.; Arévalo, J.-A.; Agualimpia, A.; Tobón, G.J. Lymphomagenesis Predictors and Related Pathogenesis. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wallach, J.D.; Ma, X.; Rogne, T. Autoimmune Diseases and Risk of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Mendelian Randomisation Study. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alunno, A.; Leone, M.C.; Giacomelli, R.; Gerli, R.; Carubbi, F. Lymphoma and Lymphomagenesis in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourou, K.D.; Pezoulas, V.C.; Georga, E.I.; Exarchos, T.; Papaloukas, C.; Voulgarelis, M.; Goules, A.; Nezos, A.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Moutsopoulos, E.M.; et al. Predicting Lymphoma Development by Exploiting Genetic Variants and Clinical Findings in a Machine Learning-Based Methodology with Ensemble Classifiers in a Cohort of Sjögren’s Syndrome Patients. IEEE Open J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2020, 1, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.G.; Singh, S.; Matteson, E.L. Rate, Risk Factors and Causes of Mortality in Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Rheumatology 2015, 55, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undas, A.; Chojnowski, K.; Klukowska, A.; Łętowska, M.; Mital, A.; Młynarski, W.; Musiał, J.; Podolak-Dawidziak, M.; Sąsiadek, M.; Treliński, J.; et al. Determination and Interpretation of MTHFR Gene Mutations in Gynecology and Internal Medicine. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2019, 129, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanulla, M.; Seidemann, K.; Schnakenberg, E.; Book, M.; Mehles, A.; Welte, K.; Schrappe, M.; Reiter, A. Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) 677C> T Polymorphism and Risk of Pediatric Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in a German Study Population. Blood 2005, 105, 906–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavragani, C.P.; Patronas, N.; Dalakas, M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Ill-Defined Neurological Syndromes with Autoimmune Background: A Diagnostic Challenge. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Günther, C.; Berndt, N.; Wolf, C.; Lee-Kirsch, M.A. Familial Chilblain Lupus Due to a Novel Mutation in the Exonuclease III Domain of 3′ Repair Exonuclease 1 (TREX1). JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellyard, J.I.; Jerjen, R.; Martin, J.L.; Lee, A.Y.S.; Field, M.A.; Jiang, S.H.; Cappello, J.; Naumann, S.K.; Andrews, T.D.; Scott, H.S.; et al. Brief Report: Identification of a Pathogenic Variant in TREX1 in Early-Onset Cerebral Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Whole-Exome Sequencing. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3382–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalak, G.; Dobberstein, S.B.; Matthias, T.; Reuter, S.; The, Y.-H.; Dörner, T.; Schmidt, R.E.; Witte, T. Association of Immunoglobulin-like Transcript 6 Deficiency with Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2923–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, H.Z.; Reuter, S.; Topperwien, M.; Dankenbrink, N.; Peest, D.; Kabalak, G.; Stripecke, R.; Schmidt, R.E.; Matthias, T.; Witte, T. Association of the LILRA3 Deletion with B-NHL and Functional Characterization of the Immunostimulatory Molecule. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Su, Y.; He, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Y.; Luo, C.; Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, F.; et al. Impact of the Leucocyte Immunoglobulin-like Receptor A3 (LILRA3) on Susceptibility and Subphenotypes of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Sjögren’s Syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

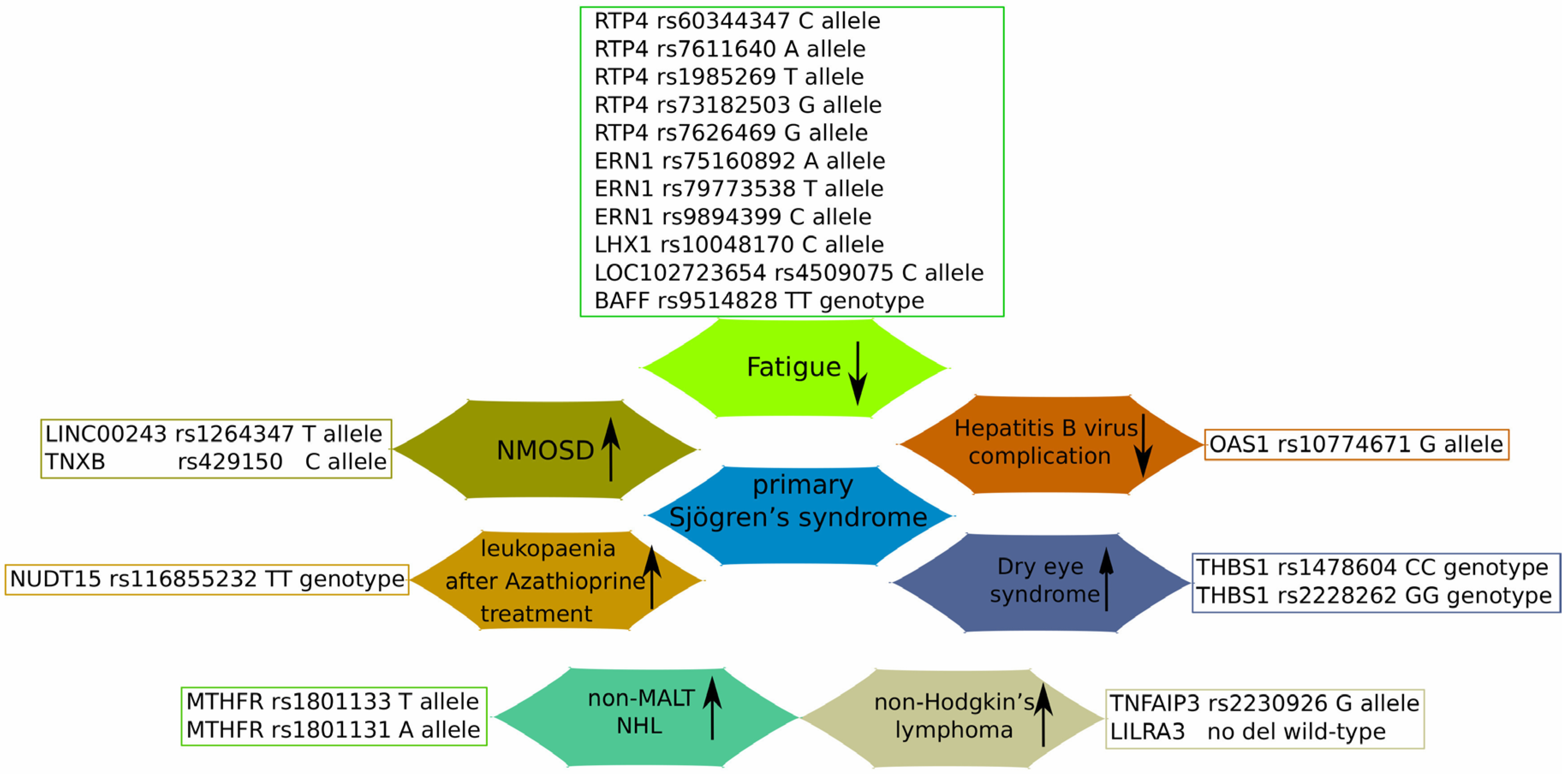
| Gene | SNP | Associated Disease/Mechanism | Patients Notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OAS1 | rs10774671 A>G | G allele decreased the risk of pSS, anti-SSA-positive SS, and anti-SSA-positive pSS complicated with HBV infection, but not the risk of anti-SSA-negative pSS | Chinese Han pSS patients | [96] |
| NUDT15 | rs116855232 C>T | TT genotype was associated with poor enzyme performance, and, subsequently, severe leukopenia after Azathioprine administration | A case study of Chinese pSS patients | [97] |
| LINC00243 | rs1264347 C>T | T allele (for rs1264347) and C allele (for rs429150) may facilitate NMOSD pathology | Multiple GWASs’ data | [98] |
| TNXB | rs429150 T>C | |||
| RTP4/MASP1 | rs60344347 CCTCT>C rs7611640 G>A rs1985269 C>T rs73182503 A>G rs7626469 C>G | Minor allele of these SNPs associated with less fatigue | Swedish and Norwegian cohorts; | [99] |
| ERN1 | rs75160892 G>A | |||
| rs79773538 C>T | ||||
| rs9894399 A>C | ||||
| LHX1 | rs10048170 C>T | C allele associated with less fatigue | Meta-analysis of USA, UK, Swedish and Norwegian cohorts | |
| LOC102723654 | rs4509075 T>C | C allele associated with less fatigue | ||
| BAFF | rs9514828 C>T | TT genotype associated with lower fatigue levels | Greek and Dutch pSS patients | [100] |
| TNFAIP3 | rs2230926 T>G | G allele carriers have more than double the risk of pSS-associated NHL | French and UK cohorts; meta-analysis | [101] |
| Of Italian pSS and lymphoma patients | [102] | |||
| LILRA3 | 1-7 exon deletion | A functional variant was prevalent in the young pSS patients with NHL; LILRA3 protein serum levels were higher in young pSS patients with NHL | Greek pSS and lymphoma patients | [103] |
| MTHFR | rs1801133 C>T | rs1801133 TT genotype and T allele and rs1801131 AA genotype and A allele were more frequent in the pSS non-MALT NHL group; rs1801133 TT genotype was associated with reduced levels of DNA methylation, while rs1801131 AC genotype with reduced levels of double-strand breaks | Greek pSS and lymphoma patients | [104] |
| rs1801131 A>C | ||||
| TREX1 | rs11797 A>G | decreased the prevalence of A allele in pSS patients with non-MALT; pSS patients who were AA genotype carriers showed increased expression of type I IFN-related genes in minor salivary gland tissues | Greek pSS and lymphoma patients | [105] |
| THBS1 | rs1478604 C>T | rs1478604 CC and rs2228262 GG carriers showed a higher risk of severe DES development | Russian DES and pSS patients | [106] |
| rs2228262 A>G |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dabravolski, S.A.; Churov, A.V.; Starodubtseva, I.A.; Beloyartsev, D.F.; Kovyanova, T.I.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Orekhov, N.A. Vitamin D in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome (pSS) and the Identification of Novel Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Involved in the Development of pSS-Associated Diseases. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14182035
Dabravolski SA, Churov AV, Starodubtseva IA, Beloyartsev DF, Kovyanova TI, Sukhorukov VN, Orekhov NA. Vitamin D in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome (pSS) and the Identification of Novel Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Involved in the Development of pSS-Associated Diseases. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(18):2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14182035
Chicago/Turabian StyleDabravolski, Siarhei A., Alexey V. Churov, Irina A. Starodubtseva, Dmitry F. Beloyartsev, Tatiana I. Kovyanova, Vasily N. Sukhorukov, and Nikolay A. Orekhov. 2024. "Vitamin D in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome (pSS) and the Identification of Novel Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Involved in the Development of pSS-Associated Diseases" Diagnostics 14, no. 18: 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14182035
APA StyleDabravolski, S. A., Churov, A. V., Starodubtseva, I. A., Beloyartsev, D. F., Kovyanova, T. I., Sukhorukov, V. N., & Orekhov, N. A. (2024). Vitamin D in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome (pSS) and the Identification of Novel Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Involved in the Development of pSS-Associated Diseases. Diagnostics, 14(18), 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14182035







