Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Humans: A Comprehensive Approach Involving the General Population, HIV-Infected Patients and Intermediate-Duration Fever in the Canary Islands, Spain
Abstract
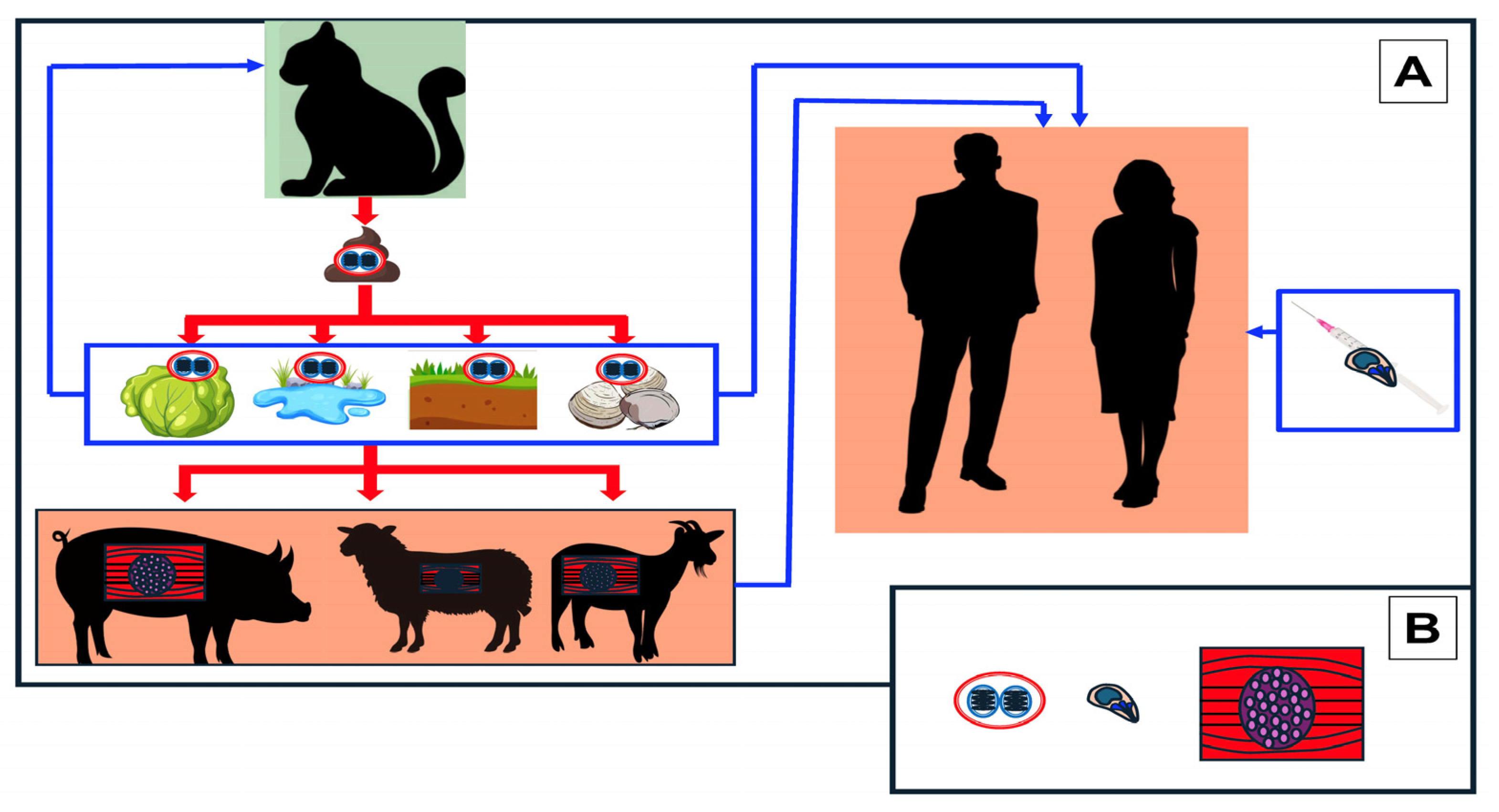
1. Introduction
2. Population and Methods
2.1. Population-Based Survey
2.2. HIV-Infected Patients
2.3. Fever of Intermediate Duration (FDI)
2.4. Serological Study
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, J.L.; Harkness, J.; Marriott, D.; Ellis, J.T.; Stark, D. Importance of nonenteric protozoan infections in immunocompromised people. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 795–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Jones, J.L. Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans and animals in the United States. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Outbreaks of clinical toxoplasmosis in humans: Five decades of personal experience, perspectives and lessons learned. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López Ureña, N.M.; Chaudhry, U.; Calero Bernal, R.; Cano Alsua, S.; Messina, D.; Evangelista, F.; Betson, M.; Lalle, M.; Jokelainen, P.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; et al. Contamination of Soil, Water, Fresh Produce, and Bivalve Mollusks with Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barge-Caballero, E.; Barbeito-Caamaño, C.; Barge-Caballero, G.; Couto-Mallón, D.; Paniagua-Martín, M.J.; Marzoa-Rivas, R.; Solla-Buceta, M.; Estévez-Cid, F.; Herrera-Noreña, J.M.; Cuenca-Castillo, J.J.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii serostatus in heart transplant recipients: Is it an independent prognostic factor? Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2016, 69, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Asensi Cantó, P.; Mayordomo, E.; Dorado, A.; Villalba, M.; Mañez, R.B.; González, E.; Salavert, M.; Facal, A.; Chorão, P.; Balaguer, A.; et al. Disseminated toxoplasma infection after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with myositis and encephalitis. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2023, 25, e14067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, G.; Roussos, N.; Falagas, M.E. Toxoplasmosis snapshots: Global status of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and implications for pregnancy and congenital toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, N.M.; Ismail, K.A.; Badawy, A.F.; Elhasanein, K.F. In vivo effect of anti-TNF agent (etanercept) in reactivation of latent toxoplasmosis. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.B.; Sande, M.A. Toxoplasmosis of the central nervous system in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.M.; Clifford, S.; Nsutebu, E. Toxoplasmosis in immunosuppressed patients. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1939–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, J.M.; Smith, J.R.; Belfort, R., Jr.; Gattey, D.; Winthrop, K.L. Toxoplasmosis: A global threat. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2011, 3, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, R.E.; Stanford, M.R. Is ocular toxoplasmosis caused by prenatal or postnatal infection? Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 84, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.; Fernandes, M.; Correia da Costa, J.M. Serotyping, a challenging approach for Toxoplasma gondii typing. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1111509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegr, J.; Prandota, J.; Sovičková, M.; Israili, Z.H. Toxoplasmosis—A global threat. Correlation of latent toxoplasmosis with specific disease burden in a set of 88 countries. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thebault, A.; Kooha, P.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Villena, I. Risk Factors for Sporadic Toxoplasmosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microb. Risk Anal. 2021, 17, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Ferreira, F.; Caldart, E.T.; Pasquali, A.K.S.; Mitsuka-Breganó, R.; Freire, R.L.; Navarro, I.T. Patterns of Transmission and Sources of Infection in Outbreaks of Human Toxoplasmosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, A.; Zambrana, J.L.; Pachón, J. Fever of intermediate duration. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2003, 21, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteo, J.A. Fever of intermediate duration: New times, new tools and change of spectrum. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2010, 28, 407–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños-Rivero, M.; Carranza-Rodríguez, C.; Hernández-Cabrera, M.; Pisos-Álamo, E.; Jaén-Sánchez, N.; Pérez-Arellano, J.L. Usefulness of the early molecular diagnosis of Q fever and rickettsial diseases in patients with fever of intermediate duration. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux-Buisson, N.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Foussadier, A.; Rolland, D.; Suchel-Jambon, A.S.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Pelloux, H. Comparative analysis of the VIDAS Toxo IgG IV assay in the detection of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 53, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, M.E.; da Silva, S.M.; Leser, P.G.; Granato, C.H. Avidity of specific IgG antibodies as markers of recent primary infection caused by Toxoplasma gondii. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1991, 33, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, L.A.; Rocha, R.J.; Rossi, C.L. Evaluation of serological markers for the immunodiagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hedman, K.; Seppälä, I. Recent rubella virus infection indicated by a low avidity of specific IgG. J. Clin. Immunol. 1988, 8, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, K.; Lappalainen, M.; Seppäiä, I.; Mäkelä, O. Recent primary toxoplasma infection indicated by a low avidity of specific IgG. J. Infect. Dis. 1989, 159, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Center for Disease Control, Atlanta, USA. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/toxoplasmosis/index.html (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Milne, G.C.; Webster, J.P.; Walker, M. Is the incidence of congenital toxoplasmosis declining? Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, J.Q.; Chissel, S.; Jones, J.; Warburton, F.; Verlander, N.Q. Risk factors for toxoplasmosis in pregnant women in Kent, United Kingdom. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 133, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagel, U.; Krämer, A.; Mikolajczyk, R.T. Incidence of maternal Toxoplasma infections in pregnancy in Upper Austria, 2000–2007. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, B.; Janson, M.; Viltrop, A.; Neare, K.; Hütt, P.; Golovljova, I.; Tummeleht, L.; Jokelainen, P. Serological Evidence of Exposure to Globally Relevant Zoonotic Parasites in the Estonian Population. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Congenital Toxoplasmosis. In ECDC Annual Epidemiological Report for 2015; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018; Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/documents/AER_for_2015-toxoplasmosis.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Luft, B.J.; Remington, J.S. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in AIDS. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 15, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meireles, L.R.; Ekman, C.C.; Andrade, H.F., Jr.; Luna, E.J. Human toxoplasmosis outbreaks and the agent infecting form. Findings from a systematic review. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2015, 57, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, O.A.; Koshy, A.A. Toxoplasma gondii: Entry, association, and physiological influence on the central nervous system. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero-Bernal, R.; Gennari, S.M.; Cano, S.; Salas-Fajardo, M.Y.; Ríos, A.; Álvarez-García, G.; Ortega-Mora, L.M. Anti Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in European Residents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Published between 2000 and 2020. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, I.; Rubio, J.M.; Ramírez, C.; Alvar, J. Genotypic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strains associated with human toxoplasmosis in Spain: Direct analysis from clinical samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz Batet, C.; Guardià Llobet, C.; Juncosa Morros, T.; Viñas Domenech, L.; Sierra Soler, M.; Sanfeliu Sala, I.; Bosch Mestres, J.; Dopico Ponte, E.; Lite Lite, J.; Matas Andreu, L.; et al. Toxoplasmosis and pregnancy. Multicenter study of 16,362 pregnant women in Barcelona. Med. Clin. 2004, 123, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.M.; Milla, A.; Rodríguez, J.C.; Gutiérrez, F. Seroprevalence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii, rubella virus, hepatitis B virus, HIV and Treponema pallidum in foreign pregnant women in Elche (Spain). Med. Clin. 2007, 129, 677–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomé Alvarez, J.; Martínez Serrano, M.; Moreno Parrado, L.; Lorente Ortuño, S.; Crespo Sánchez, M.D. Prevalence and incidence in Albacete, Spain, of Toxoplasma gondii infection in women of childbearing age: Differences between immigrant and non-immigrant (2001–2007). Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2008, 82, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro, A.; Mazuelas, P.; Rodríguez-Granger, J.; Torres, E.; Puertas, A.; Navarro, J.M. Serological markers in immigrant and Spanish pregnant women in Granada. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2010, 28, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.M.; Milla, A.; Rodríguez, J.C.; Padilla, S.; Masiá, M.; Gutiérrez, F. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection among immigrant and native pregnant women in Eastern Spain. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fabal, F.; Gómez-Garcés, J.L. Serological markers of Spanish and immigrant pregnant women in the south of Madrid during the period 2007–2010. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2013, 26, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guarch-Ibáñez, B.; Carreras-Abad, C.; Frick, M.A.; Blázquez-Gamero, D.; Baquero-Artigao, F.; Fuentes-Corripio, I.; Soler-Palacin, P. The Spanish REIV-TOXO Group. Results of the REIV-TOXO national survey on prenatal screening for toxoplasmosis in Spain. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchi-Elanzi, M.; Mayoral, A.M.; Morales, J.; Pinargote-Celorio, H.; González-Alcaide, G.; Ramos-Rincón, J.M. Toxoplasma gondii infection in hospitalized people living with HIV in Spain, 1997 to 2015. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estévez Reboredo, R.M.; de Fuentes Corripio, I.; Carmona, R.; Cano Portero, R. Toxoplasmosis in Spain, analysis of hospitalizations during the period 1997–2018. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2021, 95, e202112194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ponce, E.; Molina, J.M.; Hernandez, S. Seroprevalence of human toxoplasmosis in Grand Canary (Canary Islands). Acta Parasitol. Portuguesa 1993, 332. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Ponce, E.; Conde, M.; Corbera, J.A.; Jaber, J.R.; Ventura, M.R.; Gutiérrez, C. Serological survey of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninium in goat population in Canary Islands (Macaronesia Archipelago, Spain). Small Rum. Res. 2017, 147, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; Kruszon-Moran, D.; Elder, S.; Rivera, H.N.; Press, C.; Montoya, J.G.; McQuillan, G.M. Toxoplasma gondii Infection in the United States, 2011–2014. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, L.N.; Wang, P.; Lv, T.T.; Fan, Y.G.; Pan, H.F. Elevated seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in AIDS/HIV patients: A meta-analysis. Acta Trop. 2017, 176, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolaños, M.; Santana, E.; Carranza, C.; Anda, P.; Jado, I.; Hernández-Cabrera, M.; Martín-Sánchez, A.M.; Pérez-Arellano, J.L. Anaplasma phagocytophilum is not an aetiological agent of fever of intermediate duration in Gran Canaria (Spain). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15 (Suppl. 2), 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra Ruiz, J.; Peña Monje, A.; Tomás Jiménez, C.; Parejo Sánchez, M.I.; Vinuesa García, D.; Muñoz Medina, L.; Martínez Pérez, M.A.; Garcia, F.; Hernández Quero, J. Clinical spectrum of fever of intermediate duration in the south of Spain. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangdi, K.; Kasturiaratchi, K.; Nery, S.V.; Lau, C.L.; Gray, D.J.; Clements, A.C.A. Diversity of infectious aetiologies of acute undifferentiated febrile illnesses in south and Southeast Asia: A systematic review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Island | N | Pos (%) | OR * | 95% CI * | RR * | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| El Hierro | 31 | 13 (42) | 1.2639 | 0.5911–2.7024 | 1.1532 | 0.273 |
| La Palma | 31 | 17 (54.8) | 2.2840 | 1.0732–4.8608 | 1.5799 | 0.017 |
| La Gomera | 31 | 13 (42) | 1.2639 | 0.5911–2.7024 | 1.1532 | 0.273 |
| Tenerife | 60 | 29 (48) | 1.8320 | 1.0252–3.2737 | 1.4299 | 0.021 |
| Gran Canaria | 60 | 19 (31.7) | 0.7403 | 0.4023–1.3625 | 0.8226 | 0.169 |
| Fuerteventura | 30 | 6 (20) | 0.3895 | 0.1535–0.9881 | 0.5116 | 0.019 |
| Lanzarote | 30 | 4 (13.3) | 0.2316 | 0.0784–0.6843 | 0.3340 | 0.001 |
| Variable | n | Pos (%) | OR * | 95% CI * | RR * | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||||
| Young | 97 | 10 (10.3) | 0.1074 | 0.0524–0.2202 | 0.1994 | 0.001 |
| Adult | 114 | 44 (38.6) | 1.1248 | 0.6841–1.8494 | 1.0766 | 0.322 |
| Elder | 62 | 47 (75.8) | 9.1099 | 4.7161–1,705,970 | 2.9621 | 0.001 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | 147 | 51 (34.7) | 0.8075 | 0.4934–1.3216 | 0.8743 | 0.199 |
| Male | 126 | 50 (39.7) | 1.2384 | 0.7566–2.0268 | 1.1438 |
| IgG +Toxoplasma HIV-Infected Patients n = 46 | IgG -Toxoplasma HIV-Infected Patients n = 278 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (n,%) | |||
| Male | 36 (80) | 253 (91) | 0.026 |
| Female | 9 (20) | 25 (9) | |
| Age (years) median ± DS * | 40 ± 11.9 | 31 ± 11.4 | 0.001 |
| Age groups (years) (n,%) | |||
| ≤30 | 9 (20) | 120 (45.8) | 0.03 |
| 31–50 | 30 (66.7) | 126 (48.1) | |
| >50 | 6 (13.3) | 16 (6.1) |
| Sex (n,%) | |
| Male | 12 (80) |
| Female | 3 (20) |
| Age (years), median ± DS * | 40 ± 11.7 |
| Age groups (years), (n,%) | |
| ≤30 | 3 (20) |
| 31–50 | 9 (60) |
| >50 | 3 (20) |
| Diagnosis of HIV infection after current admission (n,%) | 8 (53.3) |
| CD4+ count (cells/mm3) median (IQR *) | 45 (10–112) |
| <50 | 8 (53.3) |
| 50–200 | 5 (33.3) |
| >200 | 1 (6.7) |
| Viral load (copies/µL) median (IQR *) | 152,000 (114,720–512,500) |
| On ART (n,%) | 6 (40%) |
| Hospital stay (days) median (IQR *) | 18 (14–42) |
| Mortality per year | 3 (20%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carranza-Rodríguez, C.; Bolaños-Rivero, M.; Pérez-Arellano, J.-L. Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Humans: A Comprehensive Approach Involving the General Population, HIV-Infected Patients and Intermediate-Duration Fever in the Canary Islands, Spain. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14080809
Carranza-Rodríguez C, Bolaños-Rivero M, Pérez-Arellano J-L. Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Humans: A Comprehensive Approach Involving the General Population, HIV-Infected Patients and Intermediate-Duration Fever in the Canary Islands, Spain. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(8):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14080809
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarranza-Rodríguez, Cristina, Margarita Bolaños-Rivero, and José-Luis Pérez-Arellano. 2024. "Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Humans: A Comprehensive Approach Involving the General Population, HIV-Infected Patients and Intermediate-Duration Fever in the Canary Islands, Spain" Diagnostics 14, no. 8: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14080809
APA StyleCarranza-Rodríguez, C., Bolaños-Rivero, M., & Pérez-Arellano, J.-L. (2024). Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Humans: A Comprehensive Approach Involving the General Population, HIV-Infected Patients and Intermediate-Duration Fever in the Canary Islands, Spain. Diagnostics, 14(8), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14080809






