A Multimodal Deep Learning Model for the Classification of Breast Cancer Subtypes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
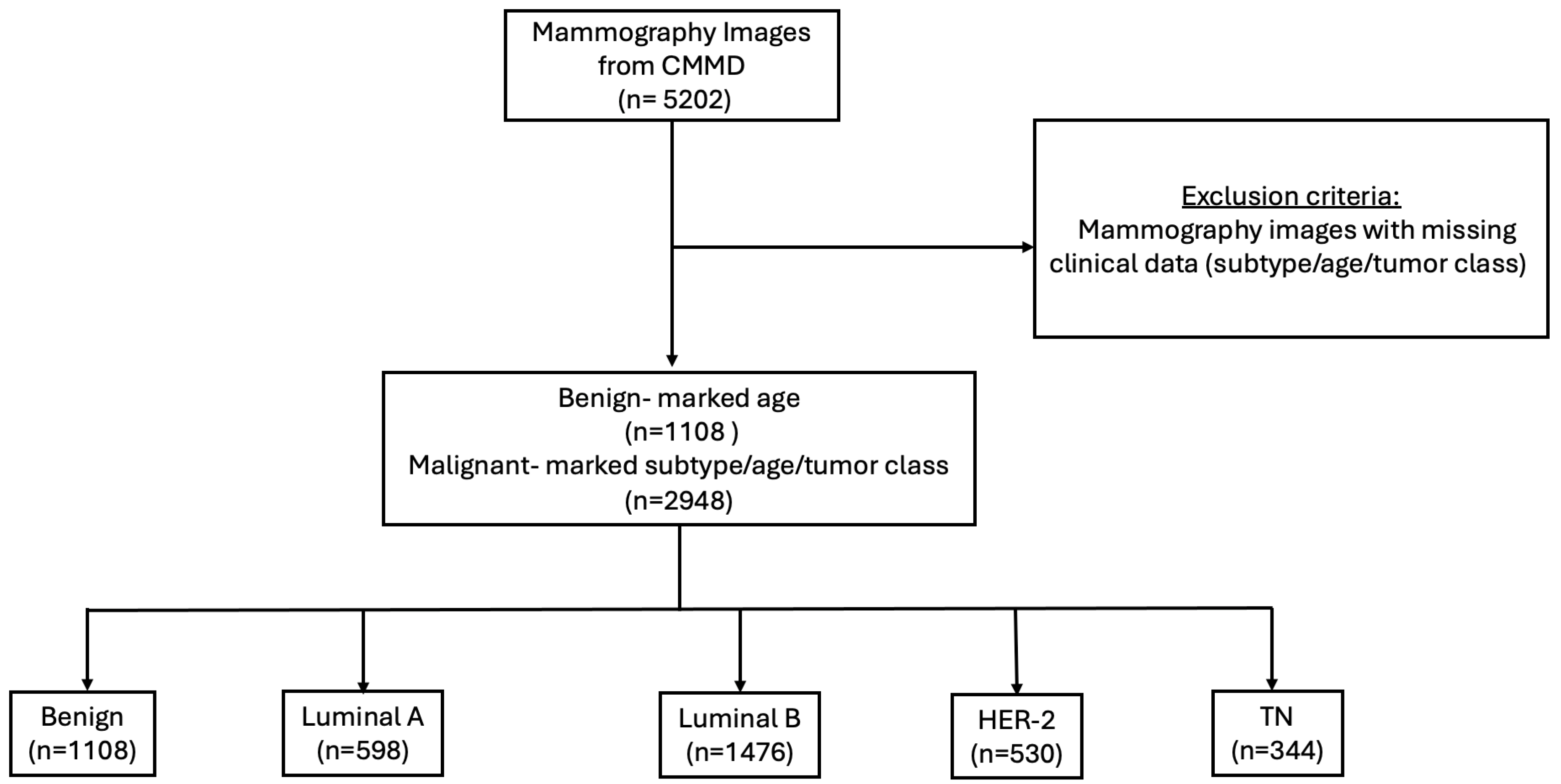
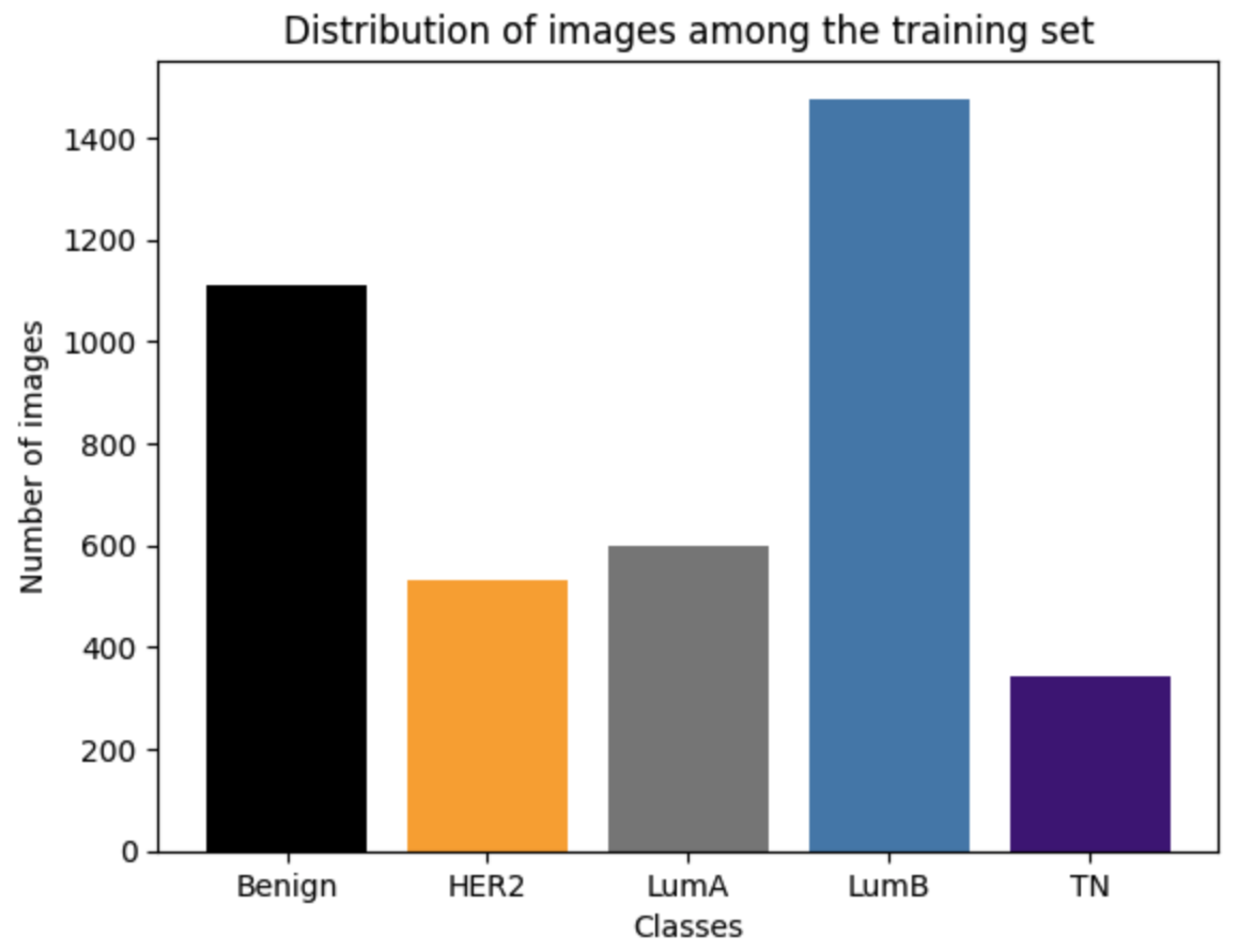
2.1. Dataset
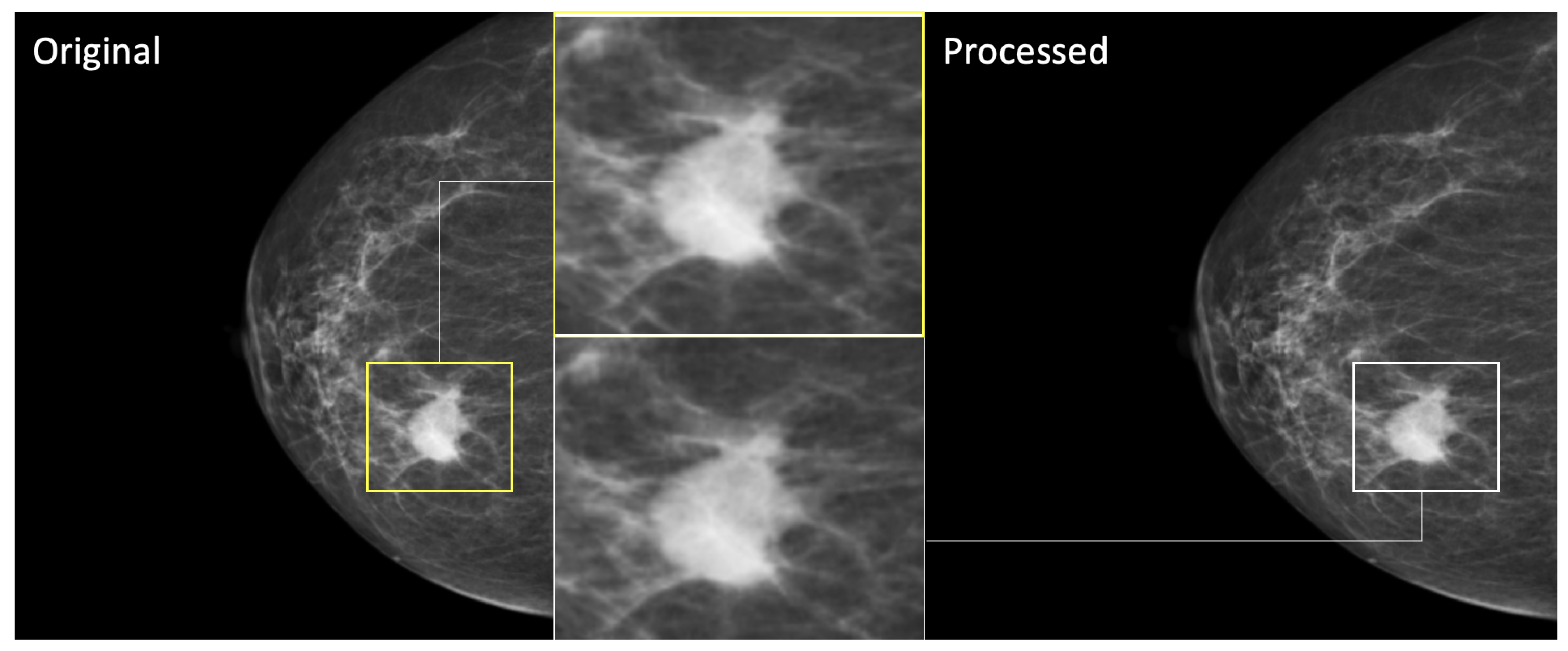
2.2. Data Preprocessing
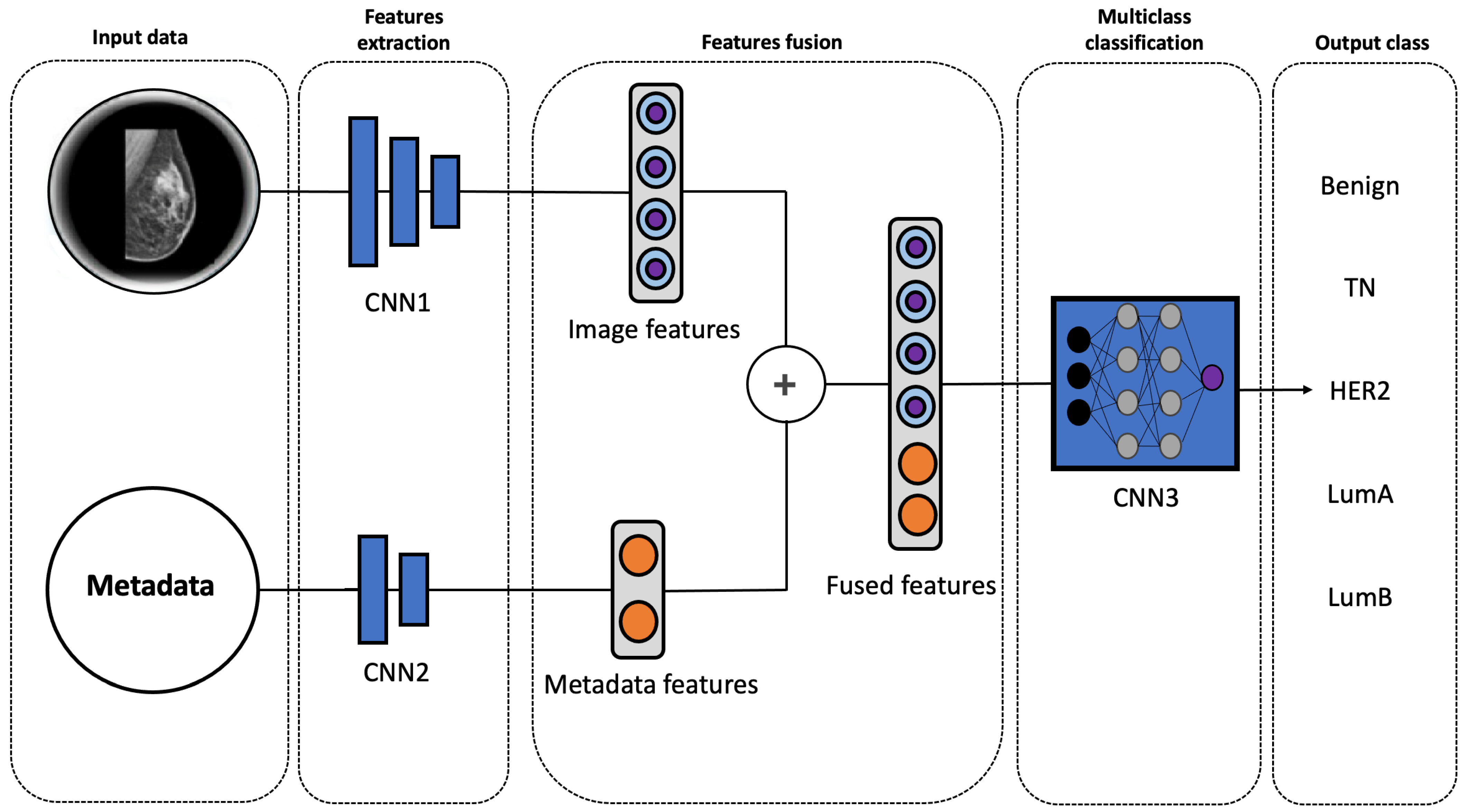
2.3. Multimodal Model
2.4. Implementation Details
2.5. Evaluation Metrics
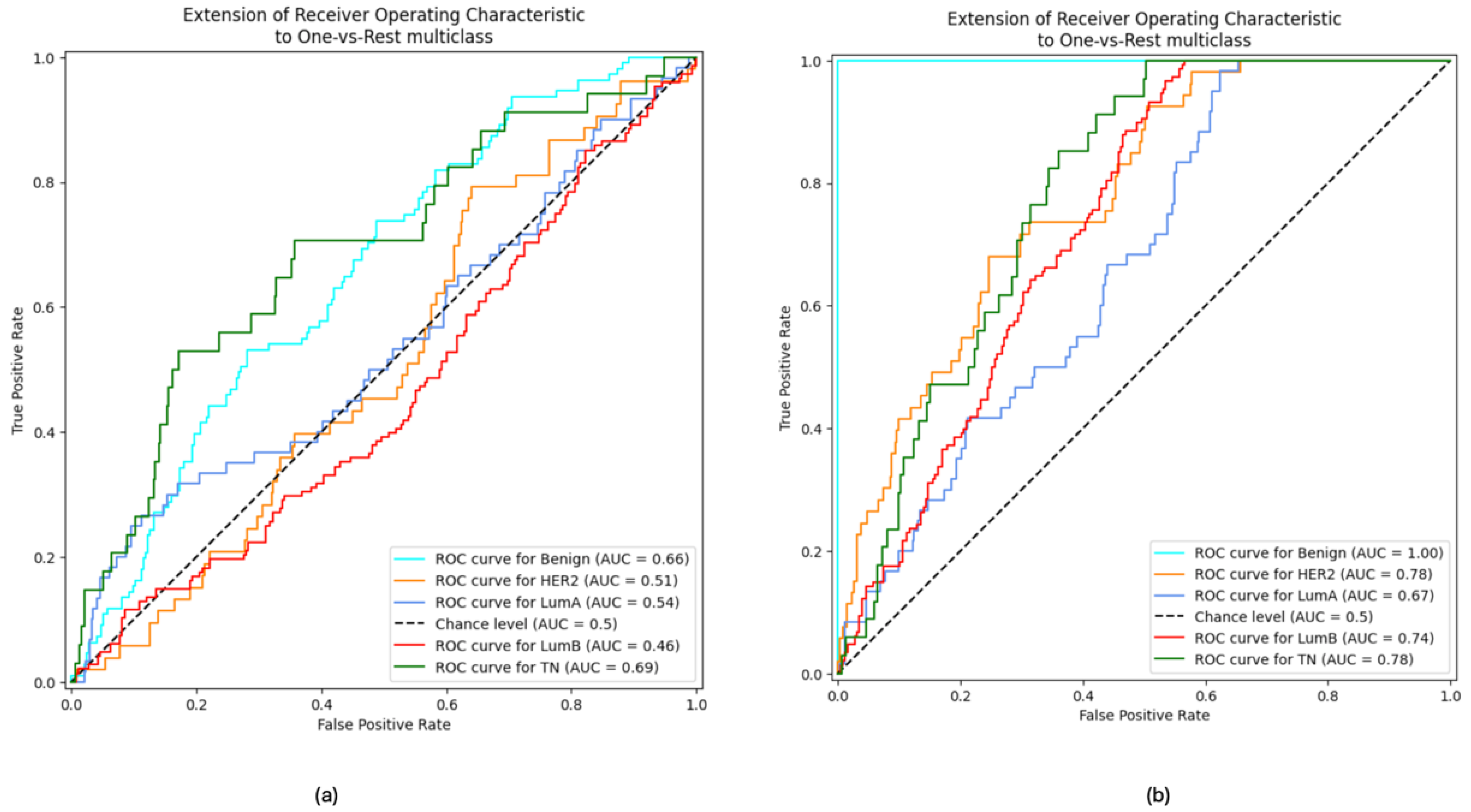
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ACC | ACCuracy |
| AUC | Area Under the ROC Curve |
| CNN | Convolutional neural networks |
| CMMd | Chinese Mammography Database |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| ER | Estrogen Receptor |
| HER2 | Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2 |
| IHC | ImmunoHistoChemistry |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PR | Progesterone Receptor |
| PRE | PREcision |
| REC | RECall |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| TCIA | The Cancer Imaging Archive |
| TN | Triple Negative |
References
- Testa, U.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Breast cancer: A molecularly heterogenous disease needing subtype-specific treatments. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, J.; Gary, M. Molecular classification of breast cancer. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2020, 27, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Filho, J.; Pusztai, L. Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: Classification and prognostication and and prediction. Lancet 2011, 378, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creighton, C.J. Gene expression profiles in cancers and their therapeutic implications. Cancer J. 2023, 29, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horr, C.; Buechler, S.A. Breast Cancer Consensus Subtypes: A system for subtyping breast cancer tumors based on gene expression. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørlie, T.; Perou, C.M.; Tibshirani, R.; Aas, T.; Geisler, S.; Johnsen, H.; Hastie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; Van De Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10869–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.S.; Mullins, M.; Cheang, M.C.; Leung, S.; Voduc, D.; Vickery, T.; Davies, S.; Fauron, C.; He, X.; Hu, Z.; et al. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A. The clinical behavior of different molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2021, 29, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, A.; Adamo, B.; Cheang, M.C.; Anders, C.K.; Carey, L.A.; Perou, C.M. Molecular characterization of basal-like and non-basal-like triple-negative breast cancer. Oncologist 2013, 18, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somal, P.K.; Sancheti, S.; Sharma, A.; Sali, A.P.; Chaudhary, D.; Goel, A.; Dora, T.K.; Brar, R.; Gulia, A.; Divatia, J. A Clinicopathological Analysis of Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer using Immunohistochemical Surrogates: A 6-Year Institutional Experience from a Tertiary Cancer Center in North India. South Asian J. Cancer 2023, 12, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoras, E.; Zerdes, I.; Tsiknakis, N.; Manikis, G.C.; Mezheyeuski, A.; Bergh, J.; Matikas, A.; Foukakis, T. Dissecting tumor-immune microenvironment in breast cancer at a spatial and multiplex resolution. Cancers 2022, 14, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.J.; Su, G.H.; You, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Shao, Z.M. Radiomics in breast cancer: Current advances and future directions. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.M.; Han, K.; Seo, M. Immunohistochemical subtypes of breast cancer: Correlation with clinicopathological and radiological factors. Iran. J. Radiol. 2016, 13, e31386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhir, R.; Koppula, V.C.; Rao, T.S.; Sannapareddy, K.; Rajappa, S.J.; Murthy, S.S. Accuracy of digital mammography, ultrasound and MRI in predicting the pathological complete response and residual tumor size of breast cancer after completion of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Indian J. Cancer 2022, 59, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayarathna, S.; Islam, K.T.; Uribe, S.; Yang, G.; Hayat, M.; Chen, Z. Deep learning based synthesis of MRI, CT and PET: Review and analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 92, 103046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumbharkar, P.; Vanam, S.; Sharma, S. Medical images classification using deep learning: A survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 19683–19728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adla, D.; Reddy, G.; Nayak, P.; Karuna, G. Deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis model for skin cancer detection and classification. Distrib. Parallel Databases 2022, 40, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Rabah, C.; Petropoulos, I.; Malik, R.; Serag, A. Vision Transformers for Automated Detection of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Corneal Confocal Microscopy Images. Front. Imaging 2025, 4, 1542128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, C.; Zhang, M.; Shan, J. Improving knee osteoarthritis classification using multimodal intermediate fusion of X-ray, MRI, and clinical information. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 9763–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, A.; Mendes, J.; Matela, N. Breast Cancer Molecular Subtype Prediction: A Mammography-Based AI Approach. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, J.; Dan, T.; Li, J.; Fan, Z.; Yi, W.; Cui, C.; Jiang, X.; Li, L. An online mammography database with biopsy-confirmed types. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical Image Database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F, C. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, B.M.; Green, A.R.; Rakha, E.A.; Morgan, D.A.; Ellis, I.O.; Cheung, K.L. Age-related biology of early-stage operable breast cancer and its impact on clinical outcome. Cancers 2021, 13, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.W.; Vulkan, D.; Cuckle, H.; Parmar, D.; Sheikh, S.; Smith, R.A.; Evans, A.; Blyuss, O.; Johns, L.; Ellis, I.O.; et al. Effect of mammographic screening from age 40 years on breast cancer mortality (UK Age trial): Final results of a randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.; Freedman, R.A.; Partridge, A.H. The impact of young age at diagnosis (age < 40 years) on prognosis varies by breast cancer subtype: A US SEER database analysis. Breast 2022, 61, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Newman, L.A.; Freedman, R.A.; Smith, R.A.; Star, J.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast cancer statistics 2024. CA 2024, 74, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Zhou, P.; Lv, X.; Chen, C. MDFNet: Application of multimodal fusion method based on skin image and clinical data to skin cancer classification. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 3287–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolarz, B.; Nowak, A.Z.; Romanowicz, H. Breast cancer—epidemiology, classification, pathogenesis and treatment (review of literature). Cancers 2022, 14, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J.; Yu, N.Y.L.; Johansson, A.; Ploner, A.; Hall, P.; Lindström, L.S.; Czene, K. Concordance of immunohistochemistry-based and gene expression-based subtyping in breast cancer. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2021, 5, pkaa087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couture, H.D.; Williams, L.A.; Geradts, J.; Nyante, S.J.; Butler, E.N.; Marron, J.; Perou, C.M.; Troester, M.A.; Niethammer, M. Image analysis with deep learning to predict breast cancer grade, ER status, histologic subtype, and intrinsic subtype. NPJ Breast Cancer 2018, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Asad, Z.; Coburn, L.A.; Wilson, K.T.; Landman, B.A.; Huo, Y. Deep multimodal fusion of image and non-image data in disease diagnosis and prognosis: A review. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 5, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiliger, L.; Sekuboyina, A.; Menze, B.; Egger, J.; Kleesiek, J. Beyond medical imaging—A review of multimodal deep learning in radiology. TechRxiv 2022. TechRxiv:19103432. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Xiong, J.; Li, Y.; Ding, W. Deep learning based multimodal biomedical data fusion: An overview and comparative review. Inf. Fusion 2024, 112, 102536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checka, C.M.; Chun, J.E.; Schnabel, F.R.; Lee, J.; Toth, H. The relationship of mammographic density and age: Implications for breast cancer screening. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 198, W292–W295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelson, M.T.; Oestreicher, N.; Porter, P.L.; White, D.; Finder, C.A.; Taplin, S.H.; White, E. Breast density as a predictor of mammographic detection: Comparison of interval-and screen-detected cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, J.D.; Davidson, N.E. Estrogen carcinogenesis in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, L.A.; Perou, C.M.; Livasy, C.A.; Dressler, L.G.; Cowan, D.; Conway, K.; Karaca, G.; Troester, M.A.; Tse, C.K.; Edmiston, S.; et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. Jama 2006, 295, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Altekruse, S.F.; Li, C.I.; Chen, V.W.; Clarke, C.A.; Ries, L.A.; Cronin, K.A. US incidence of breast cancer subtypes defined by joint hormone receptor and HER2 status. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N. Molecular subtypes and imaging phenotypes of breast cancer. Ultrasonography 2016, 35, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.S.; Ali, M.A.; Eriksson, M.; Hall, P.; Humphreys, K.; Czene, K. Mammography features for early markers of aggressive breast cancer subtypes and tumor characteristics: A population-based cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, D.; Xu, L.; Li, N.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.; Xu, B.; Liu, C.L.; Liu, Z.; Luo, T. BI-RADS 3–5 microcalcifications can preoperatively predict breast cancer HER2 and Luminal a molecular subtype. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunzunegui, R.G.; Chung, M.A.; Oruwari, J.; Golding, D.; Marchant, D.J.; Cady, B. Casting-type calcifications with invasion and high-grade ductal carcinoma in situ: A more aggressive disease? Arch. Surg. 2003, 138, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, J.N.; Falcone, G.J.; Rajpurkar, P.; Topol, E.J. Multimodal biomedical AI. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.z.; Li, X.h.; Wen, X.l.; Wang, N.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, X.; Fu, S.h.; Xiong, F.f.; Bai, J.; Gao, X.l.; et al. Integration of multi-omics data reveals a novel hybrid breast cancer subtype and its biomarkers. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1130092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.S.; Sahoo, C.R.; Padhy, R.N. Role of hormone receptors and HER2 as prospective molecular markers for breast cancer: An update. Genes Dis. 2022, 9, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beňačka, R.; Szabóová, D.; Gul’ašová, Z.; Hertelyová, Z.; Radoňák, J. Classic and new markers in diagnostics and classification of breast cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodewes, F.; Van Asselt, A.; Dorrius, M.; Greuter, M.; De Bock, G. Mammographic breast density and the risk of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast 2022, 66, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covington, M.F.; Parent, E.E.; Dibble, E.H.; Rauch, G.M.; Fowler, A.M. Advances and future directions in molecular breast imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, G.G.; Mendelson, E.B. Automated breast ultrasound: Supplemental screening for average-risk women with dense breasts. Clin. Imaging 2021, 76, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littrup, P.J.; Duric, N.; Sak, M.; Li, C.; Roy, O.; Brem, R.F.; Larsen, L.H.; Yamashita, M. Multicenter study of whole breast stiffness imaging by ultrasound tomography (SoftVue) for characterization of breast tissues and masses. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinker, K.; Chin, J.; Melsaether, A.N.; Morris, E.A.; Moy, L. Precision medicine and radiogenomics in breast cancer: New approaches toward diagnosis and treatment. Radiology 2018, 287, 732–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheller, M.J.; Edwards, B.; Reina, G.A.; Martin, J.; Pati, S.; Kotrotsou, A.; Milchenko, M.; Xu, W.; Marcus, D.; Colen, R.R.; et al. Federated learning in medicine: Facilitating multi-institutional collaborations without sharing patient data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briant, P.; Bischoff, J.E.; Dharia, M.A.; Le Navéaux, F.; Li, X.; Kulkarni, S.; Levine, D.; Ramos, D.O.; Afshari, P. Use of real-world data for enhancing model credibility: Applications to medical device development. J. Med. Devices 2022, 16, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| ACC | AUC | F1 Score | PRE | REC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 45.07% | 84.45% | 33% | 29% | 49% |
| ResNet50 | 46.31% | 83.63% | 38% | 33% | 49% |
| EfficientNetB7 | 45.07% | 84.57% | 33% | 29% | 49% |
| InceptionV3 | 47.78% | 85.87% | 38% | 42% | 46% |
| Xception (proposed) | 63.79% | 88.87% | 52% | 46% | 64% |
| ACC | AUC | F1 Score | PRE | REC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mammography Images Only | 31.78% | 61.3% | 26% | 26% | 29% |
| Mammography Images + Metadata | 63.79% | 88.87% | 52% | 46% | 64% |
| Proposed Multimodal Approach | Mota et al. [23] | |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset | CMMD | OPTIMAM |
| Number of images | 4101 | 1397 |
| Number of patients | 1750 | 660 |
| Patients’ age | 17–87 | 50–90 |
| Clinical metadata | ✓ | X |
| Benign class | ✓ | X |
| AUC | 88.87% | 60.62% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Rabah, C.; Sattar, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Serag, A. A Multimodal Deep Learning Model for the Classification of Breast Cancer Subtypes. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080995
Ben Rabah C, Sattar A, Ibrahim A, Serag A. A Multimodal Deep Learning Model for the Classification of Breast Cancer Subtypes. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(8):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080995
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Rabah, Chaima, Aamenah Sattar, Ahmed Ibrahim, and Ahmed Serag. 2025. "A Multimodal Deep Learning Model for the Classification of Breast Cancer Subtypes" Diagnostics 15, no. 8: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080995
APA StyleBen Rabah, C., Sattar, A., Ibrahim, A., & Serag, A. (2025). A Multimodal Deep Learning Model for the Classification of Breast Cancer Subtypes. Diagnostics, 15(8), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080995







