Deciphering the Olfactory Mechanisms of Sitotroga cerealella Olivier (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae): Insights from Transcriptome Analysis and Molecular Docking
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing and Tissue Collection
2.2. RNA-Seq Library Construction and Illumina Sequencing
2.3. De Novo Assembly and Sequence Annotation
2.4. Identification of Olfactory Genes and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Expression Analysis of Olfactory Genes
2.6. Structure Modeling and Molecular Docking of Ligands
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptome Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
3.2. Olfactory-Related Genes in S. cerealella
3.2.1. Identification and Analysis of Putative OBPs
3.2.2. Identification and Analysis of Putative CSPs
3.2.3. Identification and Analysis of Putative ORs
3.2.4. Identification and Analysis of Putative IRs
3.2.5. Identification and Analysis of Putative GRs
3.2.6. Identification and Analysis of Putative SNMPs
3.3. Identification of Sex-Bias Expression Genes Based on Transcriptome
3.4. Protein Structure and Interaction Analysis by 3-Dimensional Docking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OBPs | Odorant-binding proteins |
| GOBPs | General odorant-binding proteins |
| PBPs | Pheromone-binding proteins |
| CSPs | Chemosensory proteins |
| ORs | Odorant receptors |
| IRs | Ionotropic receptors |
| GRs | Gustatory receptors |
| SNMPs | Sensory neuron membrane proteins |
| ODEs | Odorant-degrading enzymes |
| ORNs | Olfactory receptor neurons |
| ORFs | Open-reading frames |
| BLASTx | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SOAPnuke | RSOAPaligner nuke |
| FPKM | Fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped fragments |
| KOG | Eukaryotic Ortholog Groups |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
References
- Zhang, T.; Coates, B.S.; Ge, X.; Bai, S.; He, K.; Wang, Z. Male-and female-biased gene expression of olfactory-related genes in the antennae of Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jing, D.; Zhang, T.; Bai, S.; He, K.; Prabu, S.; Luan, J.; Wang, Z. Sexual-biased gene expression of olfactory-related genes in the antennae of Conogethes pinicolalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhou, C.; Mu, W. Sex-and tissue-specific expression profiles of odorant binding protein and chemosensory protein genes in Bradysia odoriphaga (Diptera: Sciaridae). Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Dani, F.R. Beyond chemoreception: Diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Bacteriol. Rev. 2018, 93, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Zhou, J.J.; Ban, L.P.; Calvello, M. Soluble protein in insect chemical communication. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.N.; He, M. Identification of odorant-binding and chemosensory protein genes and the ligand affinity of two of the encoded proteins suggest a complex olfactory perception system in Periplaneta americana. Insect Mol. Biol. 2017, 26, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.G.; Riddiford, L.M. Pheromone binding and inactivation by moth antennae. Nature 1981, 293, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.Q.; Nie, X.P.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, F.F.; Lv, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.Q. De novo analysis of the oriental armyworm Mythimna separata antennal transcriptome and expression patterns of odorant-binding proteins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2017, 22, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Chen, H.C.; Yan, M.W.; Wang, J.; Shao, Z.M.; Wu, F.A.; Sheng, S.; Wang, J. Identification of chemosensory genes by antennal transcriptome analysis and expression profiles of odorant-binding proteins in parasitoid wasp Aulacocentrum confusum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, F.; Johny, J.; Walker, W.B.; Guan, Q.; Mfarrej, S.; Jakše, J.; Montagné, N.; Jacquin-Joly, E.; Alqarni, A.S.; Al-Saleh, M.A.; et al. Antennal transcriptome sequencing and identification of candidate chemoreceptor proteins from an invasive pest, the American palm weevil, Rhynchophorus palmarum. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.C.; Liu, S.; Jiang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Xiao, J.J.; Gao, Q.; Sheng, C.W.; Shi, T.F.; Zeng, H.R.; Yu, L.S.; et al. Identification of olfactory genes from the greater wax moth by antennal transcriptome analysis. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 663040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Meng, R.; Liu, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, T. Identification of chemosensory genes from the antennal transcriptome of Semiothisa cinerearia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.S.; Li, K.B.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Y.Z.; Yin, J. Identification of candidate chemosensory genes by transcriptome analysis in Loxostege sticticalis Linnaeus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, V.; Jiménez, H.; Palma-Millanao, R.; González-González, A.; Machuca, J.; Godoy, R.; Ceballos, R.; Mutis, A.; Venthur, H. Analysis of the grapevine moth Lobesia botrana antennal transcriptome and expression of odorant-binding and chemosensory proteins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2018, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Tao, J.; Zong, S. Antennal transcriptome analyses and olfactory protein identification in an important wood-boring moth pest, Streltzoviella insularis (Lepidoptera: Cossidae). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, P.J.; Warr, C.G.; Freeman, M.R.; Lessing, D.; Kim, J.; Carlson, J.R. A novel family of divergent seven-transmembrane proteins: Candidate odorant receptors in Drosophila. Neuron 1999, 22, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Pellegrino, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Vosshall, L.B.; Touhara, K. Insect olfactory receptors are heteromeric ligand-gated ion channels. Nature 2008, 452, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trible, W.; Olivos-Cisneros, L.; McKenzie, S.K.; Saragosti, J.; Chang, N.C.; Matthews, B.J.; Oxley, P.R.; Kronauer, D.J. Orco mutagenesis causes loss of antennal lobe glomeruli and impaired social behavior in ants. Cell 2017, 170, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, R.; Vannice, K.S.; Gomez-Diaz, C.; Vosshall, L.B. Variant ionotropic glutamate receptors as chemosensory receptors in Drosophila. Cell 2009, 136, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Liao, X.; Walker, W.B.; Li, J.; Wang, G. Identification of candidate olfactory genes in Chilo suppressalis by antennal transcriptome analysis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, J.I.; Melo, N.; Castillo, J.S.; Gonzalez, S.; Saldana, V.; Stensmyr, M.C.; DeGennaro, M. Aedes aegypti mosquitoes detect acidic volatiles found in human odor using the IR8a pathway. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuin, L.; Bargeton, B.; Ulbrich, M.H.; Isacoff, E.Y.; Kellenberger, S.; Benton, R. Functional architecture of olfactory ionotropic glutamate receptors. Neuron 2011, 69, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Diaz, C.; Martin, F.; Garcia-Fernandez, J.M.; Alcorta, E. The two main olfactory receptor families in Drosophila, ORs and IRs: A comparative approach. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montell, C. A taste of the Drosophila gustatory receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2009, 19, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, E.G.; Wisotsky, Z.; Dahanukar, A. Detection of sweet tastants by a conserved group of insect gustatory receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1598–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, A.R.; Roy, A.A.; Joshi, R.S. Gustatory receptors in Lepidoptera: Chemosensation and beyond. Insect Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, R. Identification of olfactory genes in Monochamus saltuarius and effects of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus infestation on their expression. Forests 2022, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, R.; Vannice, K.S.; Vosshall, L.B. An essential role for a CD36-related receptor in pheromone detection in Drosophila. Nature 2007, 450, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstner, M.; Gohl, T.; Gondesen, I.; Raming, K.; Breer, H.; Krieger, J. Differential expression of SNMP-1 and SNMP-2 proteins in pheromone-sensitive hairs of moths. Chem. Senses 2008, 33, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassau, S.; Krieger, J. The role of SNMPs in insect olfaction. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 383, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devillers, J. 2D and 3D structure–activity modelling of mosquito repellents: A review. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2018, 29, 693–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggri, P.G.; Pérez-Garrido, A.; Tsitsanou, K.E.; Dileep, K.V.; Michaelakis, A.; Papachristos, D.P.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; Zographos, S.E. 2D finger-printing and molecular docking studies identified potent mosquito repellents targeting odorant binding protein 1. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 157, 103961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling by iterative alignment, model building and model assessment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3982–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, N.F.; Moreira, M.F.; Melo, A.C.A. A look inside odorant-binding proteins in insect chemoreception. J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 95, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Qi, X.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z. Crystal structure of the Locusta migratoria odorant binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venthur, H.; Mutis, A.; Zhou, J.J.; Quiroz, A. Ligand binding and homology modelling of insect odorant-binding proteins. Physiol. Entomol. 2014, 39, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wen, X.; Lu, Y.; Wen, J. Comparison and functional analysis of chemosensory protein genes from Eucryptorrhynchus scrobiculatus Motschulsky and Eucryptorrhynchus brandti Harold. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 661310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Qian, K.; He, L.; Zhang, Z. iORandLigandDB: A Website for Three-Dimensional Structure Prediction of Insect Odorant Receptors and Docking with Odorants. Insects 2023, 14, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimoto, N.; Futatsugi, N.; Fuji, H.; Suenaga, A.; Morimoto, G.; Yanai, R.; Ohno, Y.; Narumi, T.; Taiji, M. High-performance drug discovery: Computational screening by combining docking and molecular dynamics simulations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chang, M.M.; Lei, C.L.; Yang, F.L. A garlic substance disrupts odorant-binding protein recognition of insect pheromones released from adults of the angoumois grain moth, Sitotroga cerealella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Chang, H.; Zhao, L.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y. Sex-and tissue-specific transcriptome analyses and expression profiling of olfactory-related genes in Ceracris nigricornis Walker (Orthoptera: Acrididae). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Fedorova, N.D.; Jackson, J.D.; Jacobs, A.R.; Kiryutin, B.; Koonin, E.V.; Krylov, D.M.; Mazumder, R.; Mekhedov, S.L.; Nikolskaya, A.N.; et al. The COG database: An updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; Van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, J.U.; Lüthy, R.; Eisenberg, D. A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure. Science 1991, 253, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthy, R.; Bowie, J.U.; Eisenberg, D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature 1992, 356, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2. 0: New docking methods, expanded force field, and python bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An Open-Source Molecular Graphics Tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Adasme, M.F.; Linnemann, K.L.; Bolz, S.N.; Kaiser, F.; Salentin, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Schroeder, M. PLIP 2021: Expanding the scope of the protein-ligand interaction profiler to DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W530–W534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Kang, C.; Wu, Z.; Lin, J. Identification and expression analyses of olfactory gene families in the rice grasshopper, Oxya chinensis, from antennal transcriptomes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Du, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. Identification and sex-biased profiles of candidate olfactory genes in the antennal transcriptome of the parasitoid wasp Cotesia vestalis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 34, 100657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Xia, Y.; Keyhani, N.O. Sex-specific variation in the antennal proteome of the migratory locust. J. Proteomics 2020, 216, 103681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, K.; Mei, R.; Li, W.; Tang, F. Analysis of the Antennal Transcriptome and Identification of Tissue-specific Expression of Olfactory-related Genes in Micromelalopha troglodyta (Lepidoptera: Notodontidae). J. Insect Sci. 2022, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.X.; Li, L.; Li, F.Q.; Zang, L.S. Identification and Comparative Expression Profiles of Candidate Olfactory Receptors in the Transcriptomes of the Important Egg Parasitoid Wasp Anastatus japonicus Ashmead (Hymenoptera: Eupelmidae). Plants 2023, 12, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, A.; Rubio-Meléndez, M.E.; Ballesteros, G.I.; Ramírez, C.C.; Palma-Millanao, R. Sex-and tissue-specific expression of odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in adults of the scarab beetle Hylamorpha elegans (Burmeister) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). PeerJ 2019, 7, e7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, D.; Zhang, T.; Prabu, S.; Bai, S.; He, K.; Luan, J.; Wang, Z. PBP genes regulated by the development of the ovaries, sex pheromone release, mating and oviposition behavior in Conogethes punctiferalis (Guenée). Chemoecology 2021, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihani, K.; Ferveur, J.F.; Briand, L. The 40-year mystery of insect odorant-binding proteins. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Xu, B.Q.; Li, C.Q.; Li, B.L.; Chen, X.L.; Li, G.W. Different Binding Affinities of Three General Odorant-Binding Proteins in Grapholita funebrana (Treitscheke)(Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) to Sex Pheromones, Host Plant Volatiles, and Insecticides. J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 1129–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Hao, E.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Sun, P.; Lu, P.; Qiao, H. Antennal transcriptome analysis of olfactory genes and tissue expression profiling of odorant binding proteins in Semanotus bifasciatus (cerambycidae: Coleoptera). BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Iovinella, I.; Dani, F.R.; Pelosi, P.; Wang, G. Chemosensory proteins: A versatile binding family. Olfactory Concepts Insect Control 2019, 2, 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; He, L.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; He, H.; Ding, W.; Li, Y. Identification and phylogenetics of Spodoptera frugiperda chemosensory proteins based on antennal transcriptome data. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 34, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picimbon, J.F. Evolution of protein physical structures in insect chemosensory systems. Olfactory Concepts Insect Control 2019, 2, 231–263. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Q. Identification and functional analysis of a chemosensory protein from Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Tephritidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 3479–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabayashi, A.N.; Arai, T.; Kubo, T.; Natori, S. Molecular cloning of cDNA for p10, a novel protein that increases in the regenerating legs of Periplaneta americana (American cockroach). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 28, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Cui, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Gao, X.; Tian, Z.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Z. OcomCSP12, a chemosensory protein expressed specifically by ovary, mediates reproduction in Ophraella communa (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleszka, J.; Forêt, S.; Saint, R.; Maleszka, R. RNAi-induced phenotypes suggest a novel role for a chemosensory protein CSP5 in the development of embryonic integument in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). Dev. Genes Evol. 2007, 217, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liang, G.; He, X. Si-CSP9 regulates the integument and moulting process of larvae in the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.F.; Zhao, Z.F.; Yan, M.J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Lu, Z.X.; Wang, M.Q. Identification and comparative expression profiles of chemoreception genes revealed from major chemoreception organs of the rice leaf folder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.X.; Xiao, W.Y.; Ji, C.H.; Ren, Q.; Xia, X.S.; Zhang, X.F.; Huang, W.Z. Candidate chemosensory genes identified from the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella, through a transcriptomic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Huang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S. Identification of candidate olfactory genes in the antennal transcriptome of the stink bug Halyomorpha halys. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Klein, M.; Svec, K.V.; Budelli, G.; Chang, E.C.; Ferrer, A.J.; Benton, R.; Samuel, A.D.; Garrity, P.A. The ionotropic receptors IR21a and IR25a mediate cool sensing in Drosophila. eLife 2016, 5, e13254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, J.J.; Wilbourne, J.T.; Omelchenko, A.A.; Yoon, J.; Ni, L. Ionotropic Receptor-dependent cool cells control the transition of temperature preference in Drosophila larvae. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Zhang, M.; Üçpunar, H.K.; Svensson, T.; Quillery, E.; Gompel, N.; Ignell, R.; Grunwald Kadow, I.C. Ionotropic chemosensory receptors mediate the taste and smell of polyamines. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Blais, S.; Park, J.Y.; Min, S.; Neubert, T.A.; Suh, G.S. Ionotropic glutamate receptors IR64a and IR8a form a functional odorant receptor complex in vivo in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 10741–10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, C.; Hirsh, A.; Bucks, S.; Klinner, C.; Vogel, H.; Shukla, A.; Mansfield, J.H.; Morton, B.; Hansson, B.S.; Grosse-Wilde, E. A reference gene set for chemosensory receptor genes of Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 66, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, K.W.; Robertson, H.M. The gustatory receptor family in the silkworm moth Bombyx mori is characterized by a large expansion of a single lineage of putative bitter receptors. Insect Mol. Biol. 2008, 17, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Du, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Identification of putative olfactory genes from the oriental fruit moth Grapholita molesta via an antennal transcriptome analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Qin, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, K.; Zhou, J.J.; Wang, S.; Yin, J. Evidence of the involvement of a Plus-C odorant-binding protein HparOBP14 in host plant selection and oviposition of the Scarab Beetle Holotrichia parallela. Insects 2021, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.L.; Lin, J.H.; Lin, J.T.; Wu, Z.Z. Odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins potentially involved in host plant recognition in the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Yang, H.H.; Gu, N.; Li, J.Q.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.N. Identification of attractants for adult Spodoptera litura based on the interaction between odorant-binding protein 34 and host volatiles. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 203, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.L.; Huang, J.R.; Xu, J.W.; Yao, W.C.; Yang, H.H.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H.R.; Dewer, Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.N. Ligand-binding properties of odorant-binding protein 6 in Athetis lepigone to sex pheromones and maize volatiles. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.F.; Wang, K.; Sun, Y.L.; Tian, C.H.; Wang, S.L. Antennal transcriptome analysis of odorant-binding proteins and characterization of GOBP2 in the variegated cutworm Peridroma saucia. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1241324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.Q.; Wu, F.; Wen, P.; Qing, J.; Song, X.M.; Li, H.L. Eastern honeybee Apis cerana sense cold flowering plants by increasing the static binding affinity of odorant-binding protein to cold floral volatiles from loquats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



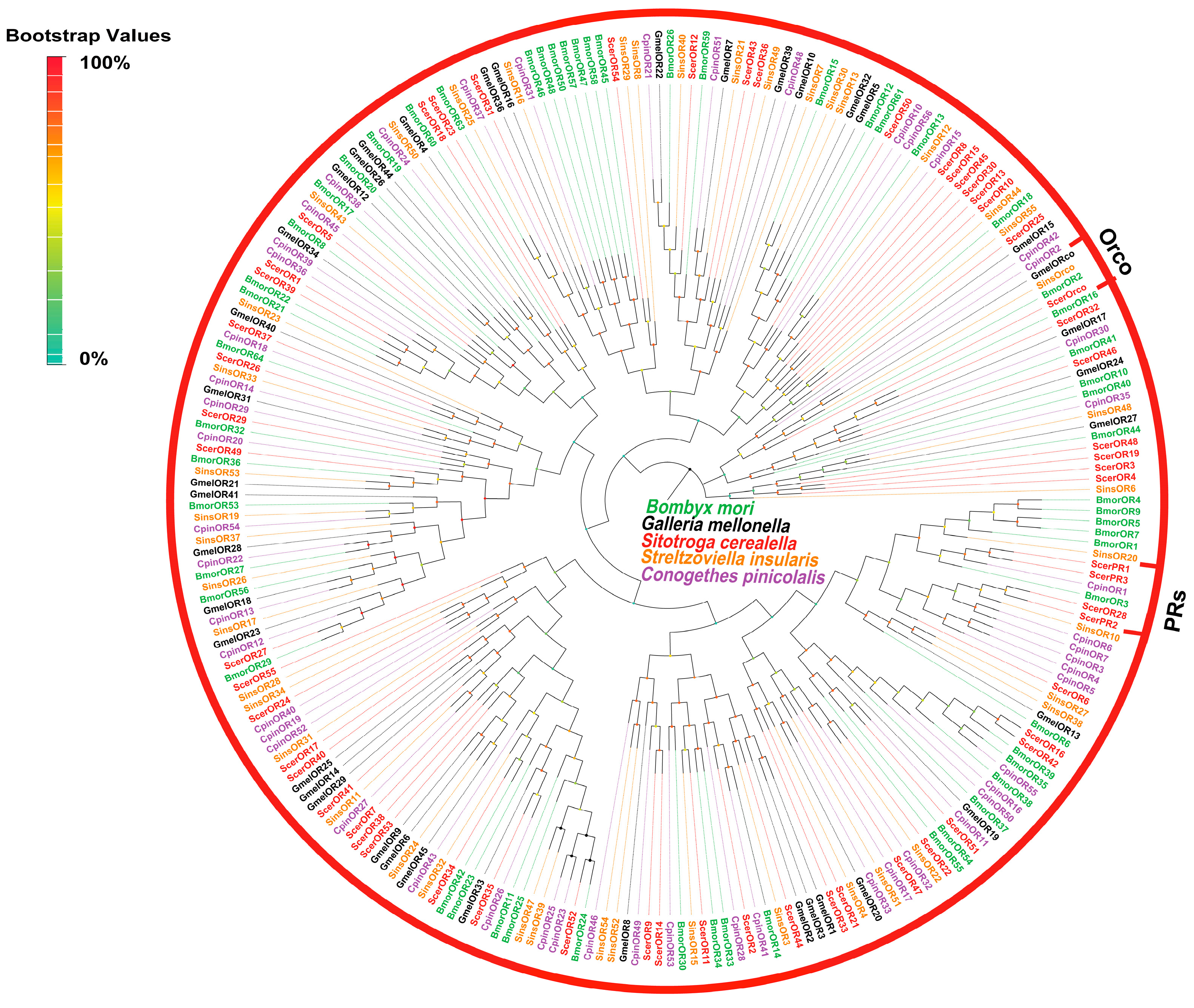




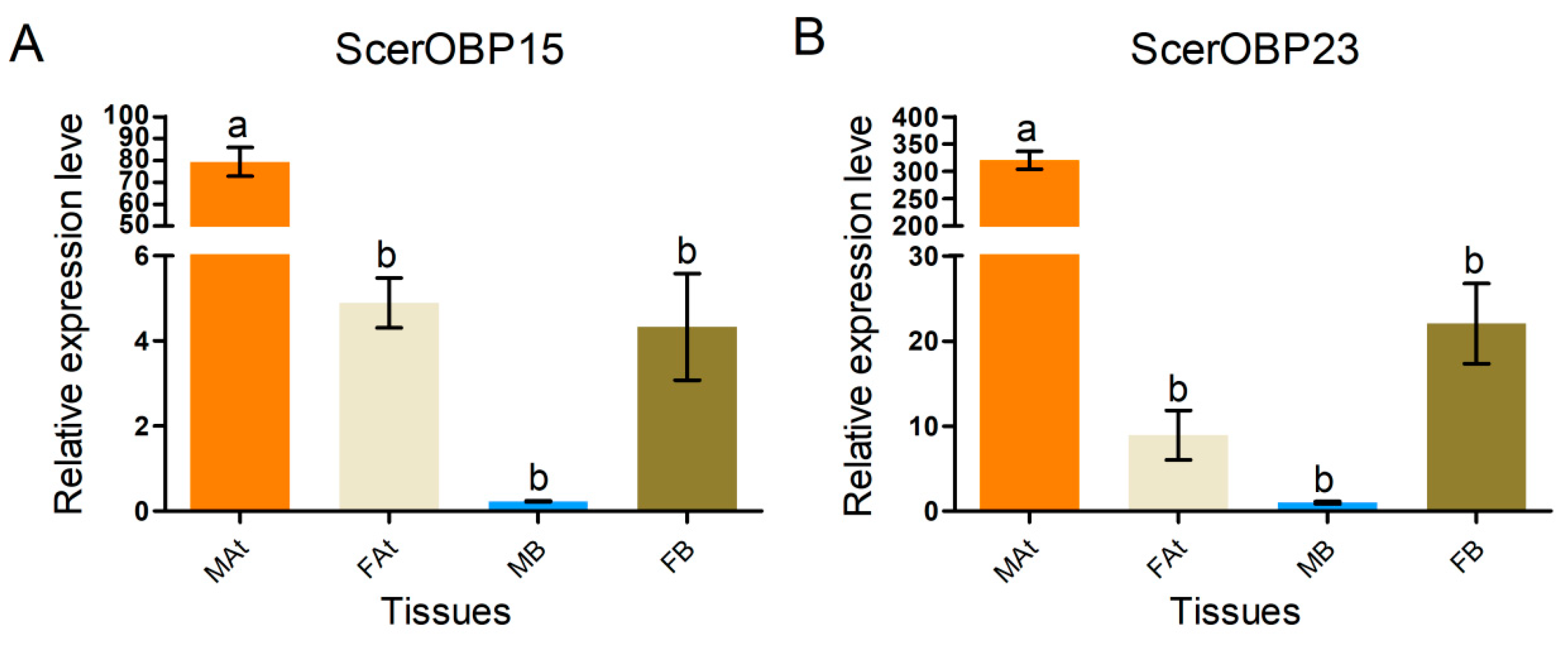


| Category | Unmated Male | Unmated Female | Mated Male | Mated Female |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean reads (million) | 25.33 ± 4.61 | 26.65 ± 1.95 | 23.75 ± 1.36 | 26.64 ± 1.27 |
| Average length (bp) | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Q20 (%) | 98.23 ± 0.16 | 98.13 ± 0.16 | 98.23 ± 0.06 | 98.20 ± 0.20 |
| Q30 (%) | 92.60 ± 0.44 | 92.17 ± 0.23 | 92.53 ± 0.06 | 92.53 ± 0.75 |
| GC (%) | 45.07 ± 0.38 | 44.73 ± 1.89 | 44.70 ± 0.46 | 45.63 ± 0.70 |
| Transcript length interval | Number of Transcripts | Percentage (%) | ||
| <500 bp | 47,663 | 33.48 | ||
| 500–1k bp | 30,599 | 21.49 | ||
| 1k–2k bp | 30,716 | 21.57 | ||
| >2k bp | 33,404 | 23.46 | ||
| Total Transcripts | 142,382 | 100.00 | ||
| Annotated Transcript | Number of Transcripts | Percentage (%) | ||
| Annotated in NR | 67,529 | 47.43 | ||
| Annotated in KEGG | 34,591 | 24.29 | ||
| Annotated in SwissProt | 45,867 | 32.21 | ||
| Annotated in GO | 17,666 | 12.41 | ||
| Annotated in KOG | 30,849 | 21.67 | ||
| Unknown | 74,629 | 52.41 | ||
| Total Transcripts | 142,382 | 100 | ||
| Name | Template | Species/Protein Name | Seq Identify | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ScerOBP15 | 2erb.1.A | Anopheles gambiae/AgamOBP1 | 40.37% | 0.95 |
| ScerOBP23 | 3ogn.1.A | Culex quinquefasciatus/OBP | 31.93% | 0.90 |
| Compounds | Molecular Formula | CAS Number | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ScerOBP15 | ScerOBP23 | |||
| tetradecane | C14H30 | 629-59-4 | −5.402 | −5.392 |
| 1-pentadecene | C15H30 | 13360-61-7 | −5.308 | −5.349 |
| hexadecane | C16H34 | 544-76-3 | −5.386 | −5.293 |
| n-heptadecane | C17H36 | 629-78-7 | −5.685 | −5.938 |
| 1-iododecane | C10H21I | 2050-77-3 | −4.406 | −4.901 |
| nonylaldehyde | C9H18O | 124-19-6 | −4.468 | −4.595 |
| capric aldehyde | C10H20O | 112-31-2 | −4.384 | −4.608 |
| palmitic acid | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | −5.509 | −5.37 |
| oleic acid | C18H34O2 | 112-79-8 | −6.016 | −5.907 |
| pentadecanoic acid | C15H30O2 | 1002-84-2 | −5.721 | −5.632 |
| methylheptenone | C8H14O | 110-90-3 | −4.638 | −4.755 |
| geranyl acetone | C13H22O | 689-67-8 | −6.201 | −5.811 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Qiao, S.; Hong, X.; Wei, Y. Deciphering the Olfactory Mechanisms of Sitotroga cerealella Olivier (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae): Insights from Transcriptome Analysis and Molecular Docking. Insects 2025, 16, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050461
Li H, Qiao S, Hong X, Wei Y. Deciphering the Olfactory Mechanisms of Sitotroga cerealella Olivier (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae): Insights from Transcriptome Analysis and Molecular Docking. Insects. 2025; 16(5):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050461
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hui, Sheng Qiao, Xiwen Hong, and Yangyang Wei. 2025. "Deciphering the Olfactory Mechanisms of Sitotroga cerealella Olivier (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae): Insights from Transcriptome Analysis and Molecular Docking" Insects 16, no. 5: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050461
APA StyleLi, H., Qiao, S., Hong, X., & Wei, Y. (2025). Deciphering the Olfactory Mechanisms of Sitotroga cerealella Olivier (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae): Insights from Transcriptome Analysis and Molecular Docking. Insects, 16(5), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050461






