Abstract
As the grade of the copper concentrate decreases and its composition becomes increasingly complex, the silver content in anode plates cast after fire refining increases, leading to a higher silver content in the copper cathode during electrorefining and a substantial loss of precious metals. This study investigates the impact of 5-amino-1H tetrazole (5-AT) on reducing silver in copper cathodes during electrorefining with high silver content anode plates. 5-AT forms an “adsorption layer” on the anode surface, reacting with Ag+ released by the anode to form a precipitate and prevent Ag+ from entering the electrolyte. This process agglomerates fine Ag-Se compounds and AgCl particles, creating larger anode slime particles that settle quickly, thus inhibiting fine silver-containing particles from adhering to the cathode. Furthermore, 5-AT adsorbs on the cathode, binding with Cu+ and promoting the Cu2+ electrodeposition process while inhibiting Ag+ electrodeposition. This facilitates uniform copper cathode grain growth and reduces inclusions in the copper cathode. The grain size of the copper cathode initially decreases and then increases as the concentration of 5-AT increases. At an optimal 5-AT concentration of 15 mg/L, the Ag content in the copper cathode decreased from 6.9 ppm to 4.7 ppm, indicating the potential efficacy of 5-AT in improving the quality of electrorefined copper.
1. Introduction
Copper electrorefining typically involves using a fire-refined casting copper plate as the anode and a stainless-steel plate as the cathode., Copper and metals with a negative potential relative to copper in the anode dissolve into the electrolyte in electrorefining process, while precious metals with a positive potential relative to copper (such as gold, silver, and platinum) and insoluble non-metallic impurities form anode slime that sinks to the bottom of the electrolytic cell. Copper ions are preferentially deposited at the cathode, resulting in high purity copper. Currently, gold concentrate is often mixed with copper ore for matting and gold smelting due to the pollution concerns of the traditional cyaniding method of gold extraction. Integrating gold and silver enrichment into the copper production process supports cleaner gold and silver extraction, aligning with the green development trend in copper electrolysis. The availability of high-grade copper concentrates has decreased, leading to the increased use of low-grade copper concentrates with complex compositions in copper smelting enterprises. This shift has led to an increase in the gold and silver contents of crude copper [1,2]. Consequently, using high silver content anode plates as a raw material for electrorefining has become a trend in the copper industry. However, the electrorefining of high silver content anode plates poses challenges, including increased impurity ion concentrations, such as gold and silver, in the electrolyte and suspended anode slime. Electrochemical reduction and deposition and mechanical adhesion of anode slimes can increase the content of impurities, such as gold and silver, in the copper cathode [3], which not only improves product quality but also results in the loss of precious metals [4,5].
Researchers worldwide use additives and optimise process parameters to control impurity elements such as gold and silver during the copper electrorefining process. Traditional additives, including gum, thiourea (TU), chloride, polyacrylamide (PAM), and polyethylene glycol (PEG), improve the surface quality and reduce the Cu cathode impurity content [6,7]. Nonetheless, these additives have limitations such as hydrolysis in acidic electrolytes [8] and the introduction of undesirable elements (e.g., S) into the copper cathode under industrial conditions [9]. Although PAM can purify copper electrorefining solutions as a common flocculant, its silver reduction effects are not significant [10]. The copper cathode surface can be flattened due to the synergistic effect of PEG and Cl−, but the impact of silver reduction is minimal. According to Zeng [11] and Patcharawit [12], the discharge reduction of free Ag+ in the electrolyte and the inclusion of fine AgCl and Ag granules in the cathode are the main reasons for high copper/Ag content in the cathode. Nkuna et al. [13] reduced the Ag content in the copper cathode to 7.3 ppm by adding NaCl to the electrolyte, which improved Ag precipitation and recovery in the anode slime, but the addition of Cl− made it difficult to further reduce the Ag content in the copper cathode. Feng et al. [14] adopted electrolytes with low concentrations of As, Sb, and Bi, adding Cl− or Br− at optimal levels to yield a copper cathode with an Ag content of less than 8 ppm. This study indicates that traditional additives can only reduce silver content in copper cathodes to 7–8 ppm, making it challenging to achieve lower levels of silver content. Considering the limitations of the aforementioned traditional additives in the control of copper and silver content, some domestic and foreign scholars have developed new tetrazole additives. The Mitsubishi Company in Japan used tetrazoles as silver-reducing agents, reducing the silver content of copper cathodes to under 0.5 ppm [15]. Zhang and Cotton et al. [16,17] demonstrated tetrazoles’ ability to form complexes with N atoms, Cu2+, and Cu+ ions, influencing copper deposition and reducing the silver concentration. Sherif et al. [18] explored the enhanced adsorption capability of amino and phenyl groups in 5-(3-aminophenyl)-tetrazole (APT) on copper surfaces, forming Cu-APT complexes on the electrode surface that create a protective film composed of APT. Medici et al. [19,20] studied the coordination-dependent binding potential of tetrazoles with Ag and confirmed the possibility of coordination-dependent binding of tetrazoles with Ag+. In summary, tetrazole compounds can improve Cu cathode surface quality and reduce Ag+ concentration in electrolytes. However, the effect of tetrazole compounds in high silver anode plate electrorefining has not been reported.
The silver reduction effect of 5-amino-1H tetrazole in electrorefining of high silver content anode plates was studied in this paper. The effect of 5-AT on the deposition of copper and silver in copper electrorefining was studied using electrochemical measurement. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray energy spectrometry (SEM-EDS), electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD), spark discharge atomic emission spectrometry (SPSE), Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), inverted metallographic microscopy (IMM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were utilized to characterize and analyse the anode slime and the copper cathode. The impacts of 5-AT concentration on the silver content, grain growth, and surface quality of copper cathodes and the occurrence and distribution of silver in anode slime were studied. This study provides theoretical guidance for electrorefining of high silver content anode plates and has certain significance for improving the economic benefit of copper electrorefining enterprises.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
The high silver anode plates and electrolyte used in the experiments were provided by a factory in China. The results of the analyses are presented in Table 1 and Table 2. The reagents used in the experiment were 5-amino-1H tetrazole (5-AT, ≥98%, Shanghai Aladin Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl, 37.5%, Luoyang Haohua Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Luoyang, China), copper sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O, ≥99.0%, Tianjin Zhiyuan Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China), concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4, ≥98%, Tianjin Yaohua Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China), and silver nitrate (AgNO3, ≥99.8%, Tianjin Chemical Technology Development Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China).

Table 1.
Elemental analysis of high silver anode platess.

Table 2.
Analysis of industrial electrolyte.
2.2. Electrochemical Testing
The electrochemical measurements were performed at room temperature using a three-electrode battery. A pure titanium electrode with an area of 1.5 cm2 was used as the working electrode. A saturated mercury sulfate electrode (MSE) served as the reference electrode. A platinum electrode was used as the opposing electrode.
Electrochemical measurements were conducted on an electrochemical workstation (Model 660E, Shanghai Chenhua Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The electrolyte used in the experiments was composed of CuSO4·5H2O, concentrated H2SO4, AgNO3, analytically pure concentrated HCl, and 5-AT. The concentrations of Cu2+, H2SO4, Ag+, and HCl were consistent with those used in the electrorefining experiment.
The electrochemical methods include cyclic voltammetry (CV), chronoamperometry (CA), and linear sweep voltammetry (LSV). The cathodic peak current density as a function of the square root of the scan rate was obtained from cyclic voltammetry curves of the electrolyte at different scan rates.
For electrochemically reversible electron transfer processes involving freely diffusing redox species, the Randles−Sevcik equation (Equation (1)) describes how the peak current ip a increases linearly with the square root of the scan rate υ (V s−1).
For an electrode-adsorbed species, the current response is described as follows:
where n is the number of electrons transferred in the redox event, A (cm2) is the electrode surface area, D0 (cm2 s−1) is the diffusion coefficient of the oxidized analyte, C0 (mol cm−3) is the bulk concentration of the analyte, and is the surface coverage of the adsorbed species in mol cm−2. The current response for an adsorbed species is expected to vary linearly with v [21,22].
Additionally, the change in cathodic peak potential was determined as a function of the logarithm of the scan rate, where the slope of the line is −2.3 R T/α nαF, and the value of α nα was estimated using the cathodic peak expression [23]. For an irreversible system at 298 K, Equation (3) can be applied to calculate the diffusion coefficient of copper ions in the electrolyte [21]:
where α is the transfer coefficient; n is the number of electrons involved in the rate determining step; D is the diffusion coefficient, cm2 s−1; Co is the volume concentration, mol cm−3; and v corresponds to the scan rate, V s−1.
The effects of different 5-AT at −0.74 V (activation region) on the deposition kinetics of copper ions were analysed using CA. Two limit models of three-dimensional instantaneous and progressive nucleation proposed by Scharifker and Hills [24] were evaluated. These two models describe instantaneous and progressive nucleation and can be expressed using the following equations:
where iinst (iprog) and t are the real-time current density and corresponding time, respectively; and im and tm are the peak current density and corresponding time, respectively.
Additionally, the declining part of the CA curve (initial stage) was evaluated as the relationship diagram of i~t1/2, and the diffusion coefficients of copper ion electrodeposition at different concentrations of 5-AT were calculated using the Cottrell equation (Equation (6)) [25].
Here, A represents the electrode area (A/cm2); n and F are the number of electrons and Faraday’s constant, respectively; and c is the volume concentration of metal ions (mol/cm3).
The nucleation density of Cu2+ electrodeposition in the electrolyte was calculated using Equation (7) [26].
Here, N is the density of nucleus formation (dm−2), and Vm is the molar volume (mol/L).
2.3. Electrorefining Experiment
The electrorefining process utilised a high silver anode plate and a pure titanium plate as the anode and cathode, respectively. The size of the electrolytic cell was 241 mm (L) × 64 mm (W) × 125 mm (H). The high silver anode plate was 58 mm (L) × 50 mm (W) × 4 mm (H) in size, and the cathode plate was 58 mm (L) × 50 mm (W) × 2 mm (H) in size. The back of the titanium cathode plate was coated with insulating paint. The anode and cathode plates were fixed in the middle of the electrolytic cell, maintaining a distance of 50 mm between the anode and cathode. The electrolyte was prepared according to Table 2, with varying concentrations of 5-AT (0 mg/L, 5 mg/L, 15 mg/L, 25 mg/L, and 35 mg/L). During the electrolysis process, the electrolytic cell was placed in a constant-temperature water bath maintained at 63 °C, and the current density was set at 300 A m−2. Electrorefining was carried out for 48 h, after which the samples were analysed.
2.4. Characterisation Analysis
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, FlexSEM 1000, Hitachi High Technology Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was employed to examine the surface microstructures of copper cathode samples and the adhesive anode slime on the anode plate surface. The elemental distribution and composition of the surface microstructures of the adhesive anode slime and anode plate were analysed using an X-ray energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS, Hitachi SU8100, Tokyo, Japan). Electron backscattering diffraction (EBSD) at a voltage of 20 kV and 70° inclination angle was used to analyse the copper cathode. Data processing was conducted using AZtecCrystal software (version number: 5.1.7829.1). Spark discharge atomic emission spectrometry (SPSE, SPECTRO LAB S02, Speck Analytical Instruments, Kleve, Germany) was used to analyse the chemical compositions of the copper cathode samples. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (IRTracer-100, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Thermo Fisher Technologies Ltd., Waltham, MA, USA) were utilised to examine the functional groups and valences of materials in the copper cathode and anode plate attached to the anode slime. An inverted metallographic microscope (OM, Zeiss Axio Vert A1, Oberkochen, Germany) was used to analyse the settling anode slime at the bottom of the cell, and Image-Pro software (version number: 6.00.0000) was employed to calculate and analyse particle size. An X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Bruker D8, Saarbrucken, Germany) was utilised to analyse the copper texture of the cathode and the phase of the anode slime with a CuK radiation source (λ = 1.5046 A) and a scanning speed of 5°/min. The texture coefficient (Tc) of the copper cathode surface was calculated based on the texture analysis results using the following formula:
where Tc(hkl) is the texture coefficient of the (hkl) crystal surface; I0(hkl) is the diffraction intensity of the (hkl) standard peak; I(hkl) is the diffraction intensity of the (hkl) measured peak; and n is the number of diffraction peaks [27].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Analysis
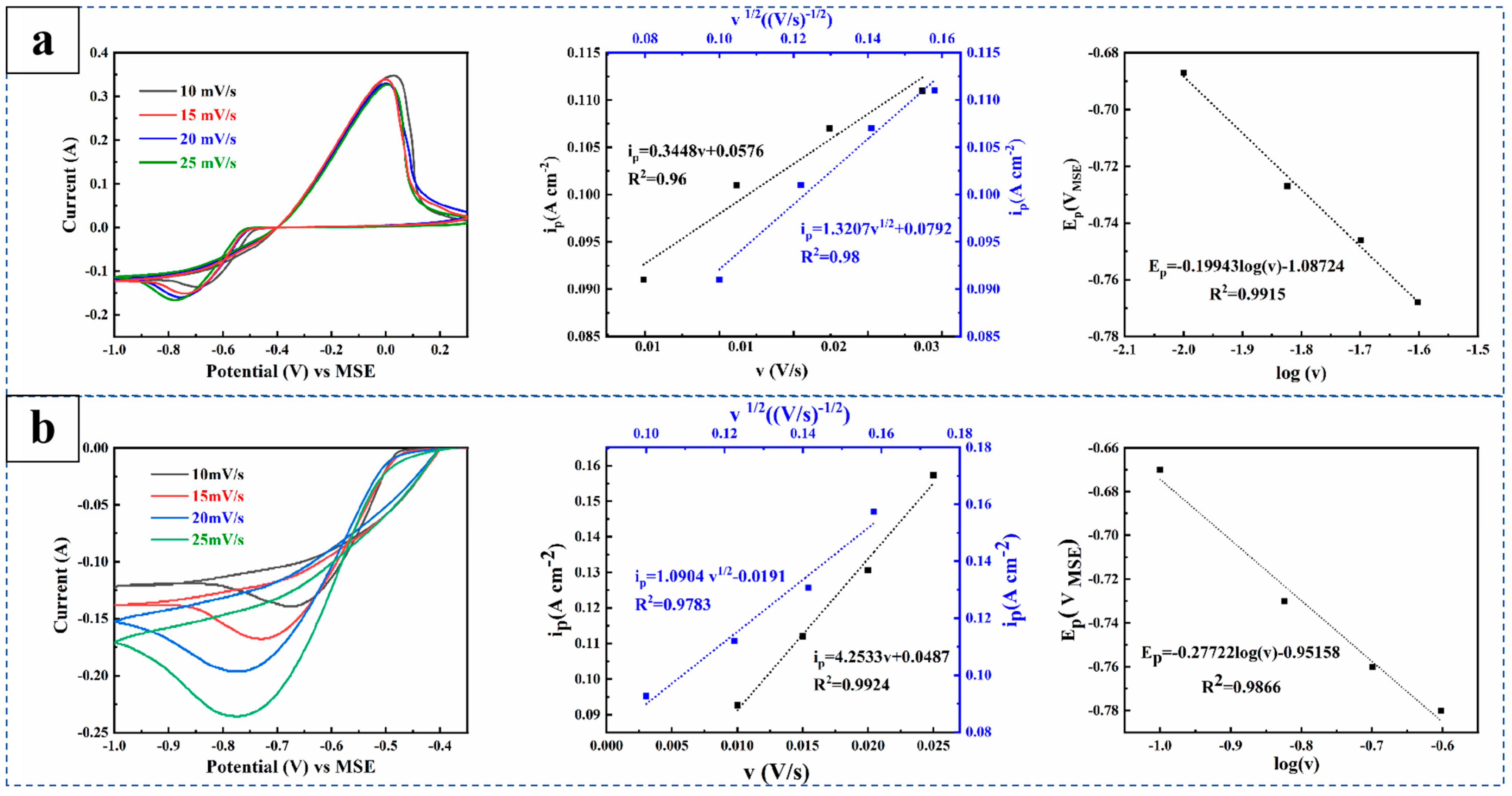
Figure 1 presents the CV diagrams of the different electrolytes, along with derived ip vs. v or v1/2 curves and the cathode peak potential vs. logV curves. As shown in the CV diagram of the electrolyte in Figure 1a, increasing the scan rate results in a negative shift in the cathodic peak potential, an increase in the peak current, indicating the decrease in the thickness of the copper ion deposition layer on the cathode surface. The decline in peak current of the oxidation peak suggests that the copper deposit formed at higher scan rates is thinner, leading to a shorter dissolution during anode scanning. Additionally, a potential difference between the reduction and oxidation peaks (ΔEp = Epa − Epc) that exceeds 59/n mV indicates poor electrochemical reversibility of the Cu(II)/Cu system in the electrolyte [28]. As can be seen from the curves of ip and v or v1/2 in Figure 1a, the relationship between ip and v1/2 suggests that the cathodic peak follows a linear regression, confirming that the Cu2+ reduction reaction is diffusion controlled. As shown in the CV diagram of the electrolyte in Figure 1b, adding 5-AT to the electrolyte enhances copper deposition at the cathode. As shown in the curves of ip and v or v1/2 in Figure 1b, the relationship between ip and v of the cathode peak is more consistent with a linear regression, indicating that ion adsorption occurs during the electrochemical reaction of copper ion deposition. As can be seen from the slope of the Ep and logV curves of the cathode peak potential in Equation (3) and Figure 1, the diffusion coefficients of copper ions before and after adding 5-AT to the electrolyte are 0.31 × 10−5 cm2 s−1 and 2.11 × 10−5 cm2 s−1, respectively. The substantial increase in the diffusion coefficient suggests that 5-AT adsorption on the cathode surface accelerates electron transfer and promotes the Cu2+ electrodeposition process.
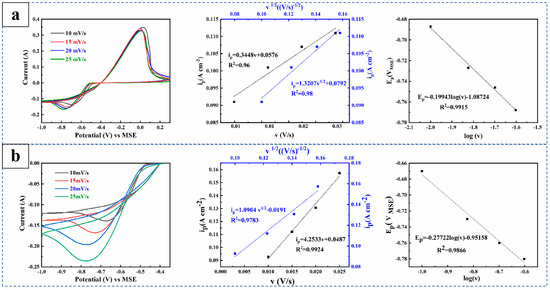
Figure 1.
CV diagram of the electrolyte at different concentrations of 5-AT, ip and v or v1/2 curves, and cathode peak potential Ep and logV curves: (a) 0 mg/L, (b) 15 mg/L 5-AT.
The effect of 5-AT addition to the electrolyte on nucleation dynamics during copper electrodeposition was analysed using chronoamperometry (CA). The CA curves under different conditions and a dimensionless diagram of the nucleation/growth model are shown in Figure S1. The CA curve in Figure S1 shows that immediately after the potential step, the current rapidly increases due to the charging of the double electric layer and the formation and growth of crystal nuclei. Subsequently, the current decreases and peaks, indicating that the Cu2+ nucleation process is typically diffusion controlled. The CA curve in Figure S1a demonstrates that the maximum current value of all the CA curves increases with a greater negative step potential. These results indicate that in the absence of 5-AT, Cu2+ electrodeposition follows a typical three-dimensional nucleation and growth process [29]. In contrast, the CA curve in Figure S1b shows that the maximum current im increases with increasing 5-AT concentrations, suggesting that 5-AT adsorption on the substrate surface facilitates the mass transfer process on the copper cathode surface.
To investigate the effect of 5-AT on the nucleation and growth of copper ions on the cathode surface during copper electrorefining, the (i/im)2 and t/tm curves of Cu2+ electrodeposition were plotted and compared with the models of instantaneous and progressive nucleation. Figure S1a,b shows that 5-AT does not change the nucleation mechanism of Cu2+ electrodeposition, and the three-dimensional nucleation model of Cu2+ electrodeposition still indicates instantaneous nucleation. The declining part of the CA curve in Figure S1b was interpreted as a Cottrel diagram of i~t1/2, and the diffusion coefficients at different 5-AT concentrations were obtained according to Equation (6), as shown in Figure S2. As observed in Figure S2, the diffusion coefficient of Cu2+ electrodeposition increased with increasing 5-AT concentration, indicating that 5-AT promotes Cu2+ deposition. This finding is mainly due to the process being controlled by the conversion of Cu+ electrons to Cu [30]. The N atom in 5-AT’s aromatic ring can form complexes with multiple Cu+, and the amino group (-NH2) renders tetrazole electron-donating, forming an internal salt that accelerates electron transfer. Ye et al. [31] confirmed the complexation of tetrazole compounds with Cu(I) by characterising coordination films formed by different tetrazole compounds on the copper surface. Thus, the coordination between 5-AT and Cu+ to form 5AT-Cu+ accelerates electron transport and Cu electrodeposition [32]. Although Cl− in the electrolyte adsorbs and covers the copper cathode surface, forming CuCl and increasing the energy required for copper deposition while inhibiting the conversion of Cu+ electrons into Cu [33], the promotion of 5AT-Cu+ still plays a dominant role.
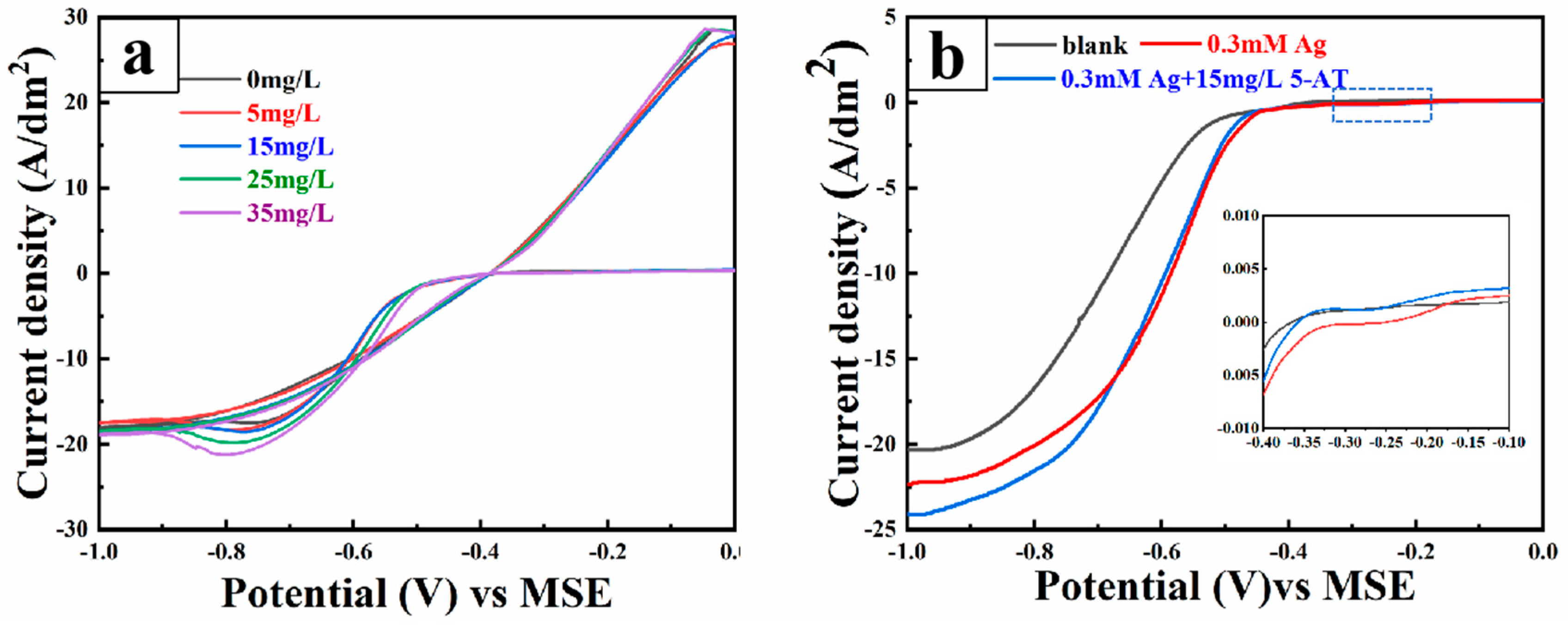
Figure 2 presents the electrochemical test diagrams of different electrolytes. In Figure 2a, the cyclic voltametric diagram starts from −0.05 V vs. MSE, scanning negatively to −1.0 V vs. MSE in the negative direction and then reversing positively. Around −0.5 V, the cathode current sharply increases, indicating Cu2+ reduction on the cathode surface. A relatively stable current platform around −1.0 V indicates mass transfer control. The reverse scan starts at −1.0 (vs. MSE) and completes the cycle by returning to the starting point, forming a loop typical of overpotential-driven nucleation/growth processes of electrodeposition, indicating that copper electrodeposition on the electrode requires an overpotential for nucleation and growth. With increasing 5-AT concentration, the Cu2+ reduction peak current density continuously rises, and the initial deposition potential shifts positively. This shows that 5-AT addition promotes Cu2+ deposition, consistent with the CA curve current peak and copper ion electrodeposition diffusion coefficient shown in Figure S2.
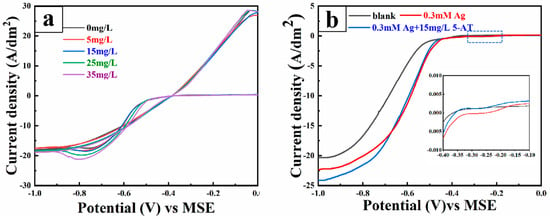
Figure 2.
Electrochemical test diagram of different electrolytes: (a) CV diagram of different concentrations of 5-AT, (b) LSV diagram under different conditions.
To examine the effect of 5-AT on the electrochemical behaviour of Ag+ in the electrolyte, LSV curves of 15 mg/L 5-AT and 0.3 mM Ag+ electrolyte were generated, as shown in Figure 2b. The comparative analysis reveals that when Ag+ is absent in the electrolyte, the initial deposition potential of copper is −0.52 V. When 0.3 mM Ag+ is present, the initial deposition potential of copper shifts forward to −0.48 V, indicating that Ag+ in solution favours copper ion deposition. The initial deposition potential of silver is −0.18 V. When 5-AT is added to the electrolyte, the Ag+ peak current decreases, and the peak and initial deposition potentials shift to negative cathode potentials, demonstrating that 5-AT in the electrolyte hinders Ag+ deposition.
3.2. Characterization and Analysis of Copper Cathodes
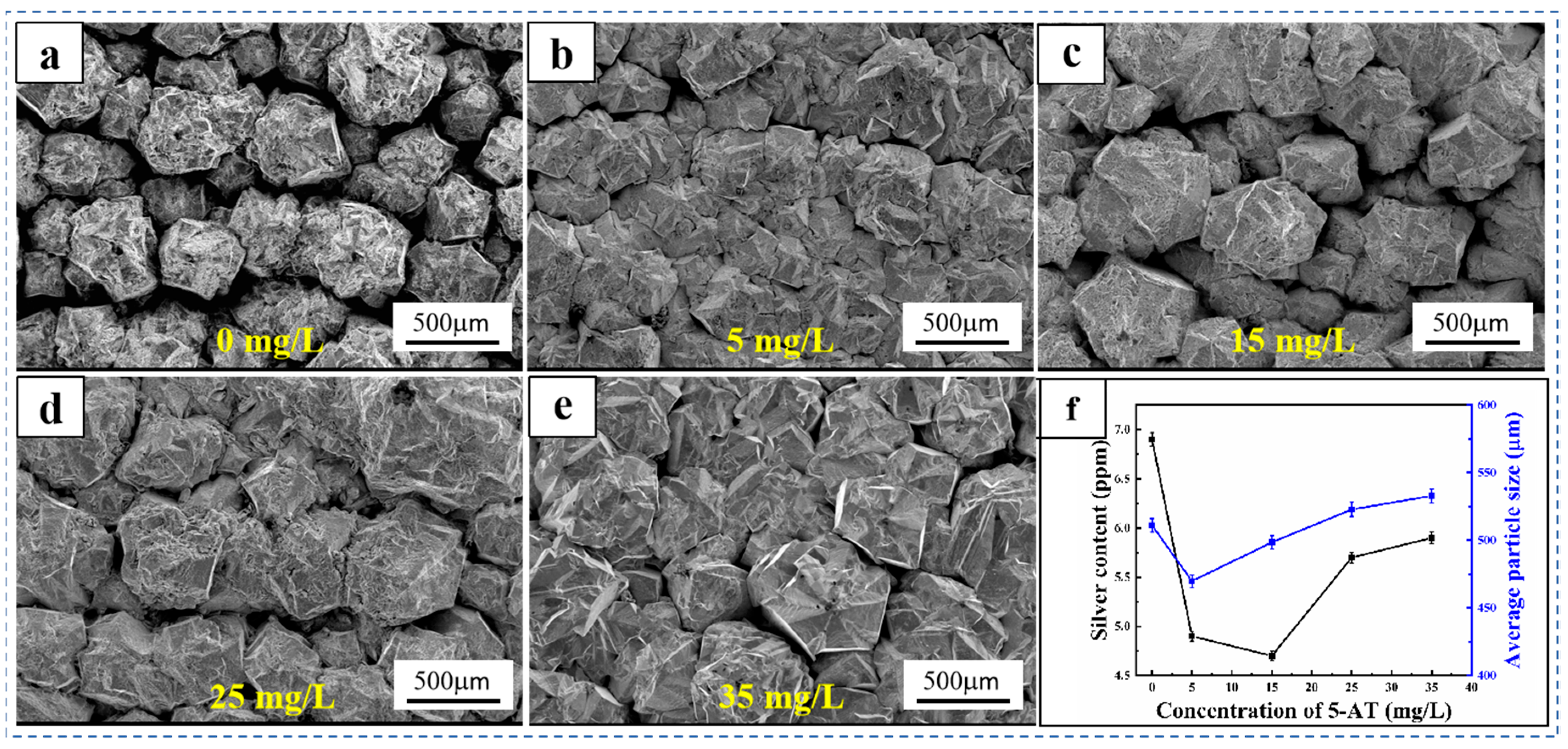
Table 3 lists the compositions of the copper cathodes prepared by adding different concentrations of 5-AT. As shown in Table 3, the Ag content in the copper cathode initially decreases and then increases with an increasing 5-AT concentration. When the additive is not added, the Ag content in the copper cathode is 7.0 ppm. At 15 mg/L 5-AT, the Ag content reaches its lowest level at 4.7 ppm, representing a reduction of 31.88%. The Cu content in the copper cathode is 99.9910% without the additive, increasing to 99.994% when 5-AT is added, indicating improved copper cathode quality due to 5-AT.

Table 3.
Chemical composition of copper cathodes prepared with different concentrations of 5-AT.
Figure S3 provides macroscopic images of the copper cathode surface with varying 5-AT concentrations. As shown in Figure S3, the surface copper particles on the copper cathode prepared without 5-AT were larger, and the particles on the copper cathode were significantly smaller when 5 mg/L 5-AT was added. However, when the concentration of 5-AT exceeds 15 mg/L, the number of copper particles on the cathode surface increases, and their size also increases. Thus, the size of the Cu particles initially decreases and then increases as the 5-AT concentration increases.
Figure 3 displays SEM images of the copper cathode surface and average copper particle size after adding different 5-AT concentrations. As shown in Figure 3, the surface of the copper cathode is composed of regular polyhedral copper particles at different 5-AT concentrations. The copper particles on the surface of the cathode were large and loosely arranged in the absence of 5-AT, whereas copper particles on the surface of the cathode were smaller and more tightly arranged when 5 mg/L 5-AT was added. However, when the concentration of 5-AT increased to more than 15 mg/L, copper particles on the surface of the cathode gradually increased, but the spacing between the copper particles gradually decreased. Therefore, as the 5-AT concentration increased, the size of the copper particles first decreased and then increased. Image-Pro software was used to analyse the surface particle size of copper, as shown in Figure 3f, indicating that as the 5-AT concentration increases, the average size of the copper particles initially decreases and then increases, consistent with the change in the silver content in the copper cathode. One of the main factors influencing the Ag content in the copper cathode is the size of the copper particles on the surface. The large copper particles and gaps are conducive to the adhesion of fine anode slime particles suspended in the electrolyte to the cathode surface. As these particles settle on the cathode, they can penetrate the interior of the copper during deposition, leading to an increase in Ag impurity content.
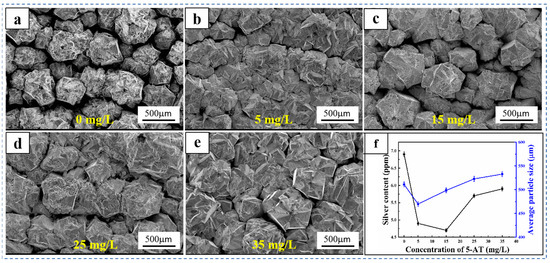
Figure 3.
SEM images of the copper cathode surface (a–e) and the average size of copper particles and sliver content of cathode copper (f) under conditions with different concentrations of 5-AT.
Figure S4 presents the XPS and FT-IR spectra of the copper cathode with and without 15 mg/L of 5-AT. In Figure S4a, the surface of the copper cathode prepared without 5-AT consists of five elements: C, O, Cu, Cl, and S. However, with the addition of 5-AT, the cathode surface was mainly composed of six elements: C, N, O, Cu, Cl, and S. The presence of N indicates that 5-AT was successfully attached to the surface of the copper cathode. Figure S4b,c display the N 1s and Cl 2p spectra, respectively, of the copper cathode with 15 mg/L 5-AT. As can be seen from Figure S4b, two different peaks detected at 397.9 eV and 399.8 eV, which correspond to C-N and N-H, respectively, confirmed the successful adsorption of 5-AT on the copper cathode surface, consistent with the electrochemical experimental results in Figure 1. In Figure S4c, two different peaks are observed at 197.9 eV and 199.8 eV, corresponding to H-Cl and C-Cl bonds, respectively. The presence of Cl− on the copper cathode surface, as well as the complexation between 5-AT and Cl−, is indicated. FT-IR spectroscopy was employed to analyse the surface states and functional groups of the copper cathode (Figure S4d). Comparative analysis shows the presence of a N-H tensile vibration on the 5-AT ring at 807.2 cm−1, along with 5-AT ring tensile vibrations at 904.6 cm−1 and 1043.5 cm−1. A C-N tensile vibration is observed at 1263.1 cm−1 [34]. Both FT-IR and XPS analyses confirm the adsorption of 5-AT and Cl− on the copper cathode surface, affecting the electrodeposition of Cu2+.
Figure S5 illustrates a longitudinal section analysis of the copper cathode with different 5-AT concentrations. The metallographic image in Figure S5a reveals that the copper cathode is composed of columnar crystals under various concentrations of 5-AT. Adding 5 mg/L 5-AT results in a smaller grain size of copper in the longitudinal section of the cathode, tighter grain arrangement, and fewer defects in the cathode. However, at 15 mg/L or greater 5-AT, the copper grain size in the longitudinal section of the copper cathode gradually increases, and the number of defects also rises. The SEM image in Figure S5b demonstrates the presence of cracks, pits, and inclusions in the copper cathode without 5-AT, and these features are significantly reduced after 5-AT addition but reappear at higher concentrations of 5-AT (25 mg/L). The elemental distributions in Figure S5c,d indicate the concentration of elements such as O, S, Pb, As, Sb, Bi, Te, and other elements in the gaps of the cathode’s longitudinal section, suggesting the presence of anode slime. The analysis of the longitudinal section of the copper cathode with different concentrations of 5-AT shows that 5-AT reduces defects and anode slime inclusion in the copper cathode. However, the increased copper cathode grain size promotes the adhesion of fine suspended anode slime particles, which eventually integrate into the copper cathode during copper deposition.
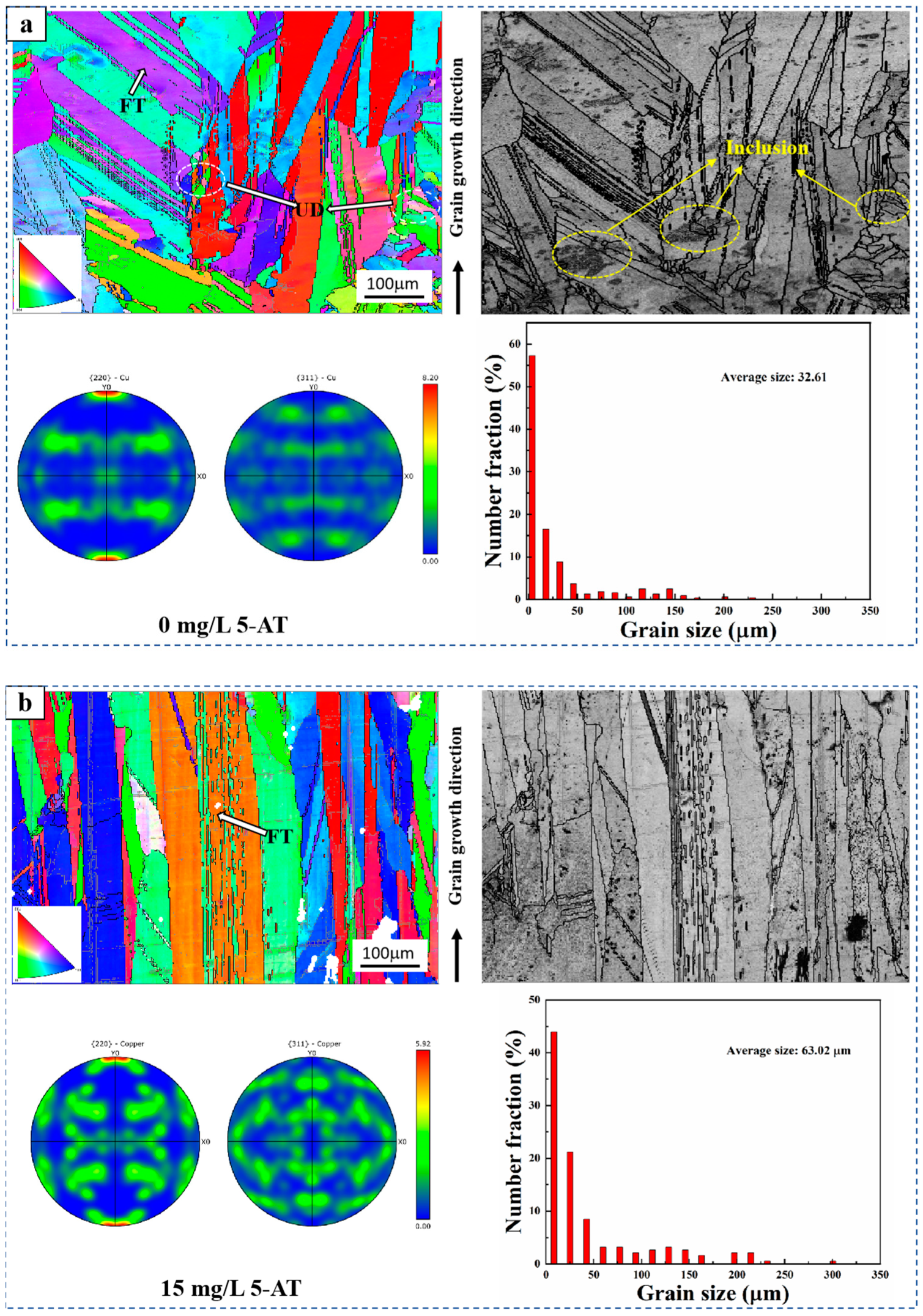
Figure 4 illustrates the inverse pole figure (IPF) distribution, grain boundary distribution, pole diagram, and grain size distribution of the longitudinal section of copper cathode grain growth direction with and without the addition of 15 mg/L 5-AT. The IPF diagram in Figure 4a shows that the copper cathode grain growth presents a field-oriented texture (FT) and a non-oriented dispersion (UD) structure with different growth directions when 5-AT is not added. The grain boundary distribution diagram indicates that inclusions in the copper cathode impede the growth of FT structure grains, leading to the formation of UD structure nodules [35]. The IPF diagram and grain boundary distribution diagram in Figure 4b indicate that with the addition of 5-AT, the copper cathode grains grow predominantly in a single FT structure in the same growth direction without any UD structures or inclusion regions. Comparative analysis shows that 5-AT promotes FT growth of copper cathode grains, reduces inclusions in the copper cathode, and helps lower the silver content. According to the polar diagram in Figure 4, the copper cathodes with and without 5-AT show optimal growth on the (220) crystal surface. However, the maximum state density in the Cu<220> direction decreases from 8.20 to 5.92 when 5-AT is added, while it increases in the Cu<311> direction. The results showed that 5-AT inhibits optimal growth on the (220) crystal planes and promotes growth on the (311) crystal planes. The grain size statistics in Figure 4 demonstrate a significant increase in average grain size from 32.61 μm without 5-AT to 63.02 μm with 5-AT addition, indicating that 5-AT promotes copper grain growth.
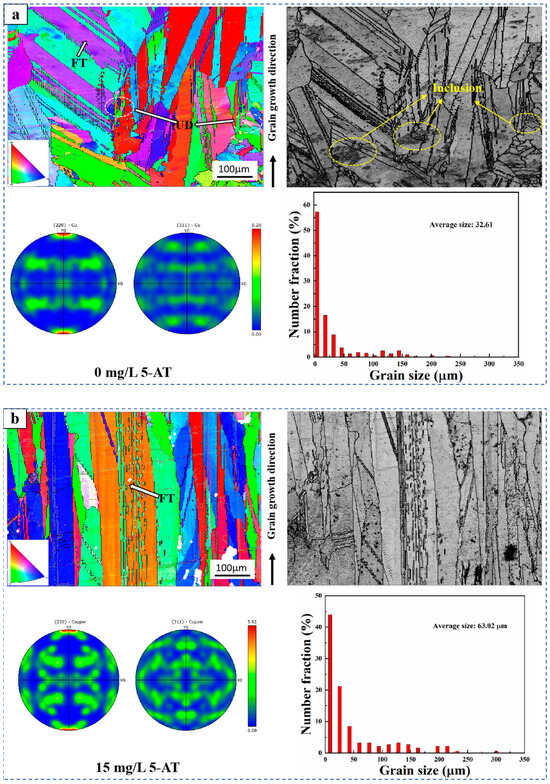
Figure 4.
IPF distribution, grain boundary distribution, pole diagram, and grain size distribution of the longitudinal section of copper cathode grain growth direction at different concentration of 5-AT: (a) 0 mg/L 5-AT, (b) 15 mg/L 5-AT.
Figure S6 presents the XRD patterns and texture coefficients of copper cathodes prepared with different 5-AT concentrations. Figure S6a shows that the copper cathode diffraction peak at the 74° Cu (220) crystal plane was dominant under different concentrations of 5-AT, and the trend of Cu (220) crystal plane dominance decreased with increasing 5-AT concentration. Figure S6b shows that as the 5-AT concentration increases, Tc(220) initially decreases and then increases, while Tc(311) initially increases and then decreases. Tc(111) and Tc(200) remain unchanged. This indicates that the increased 5-AT concentration promotes mutual transformation between Cu (220) and Cu (311) crystal planes. In addition, when the concentration of 5-At was 5 mg/L, Tc(220) was 2.25, and Tc(311) was 0.5, with the smallest difference noted between them. However, at concentrations above 5 mg/L, Tc(220) increased, Tc(311) decreased, and the difference between them gradually increased. SEM analysis of the copper cathode surface in Figure 3 shows fine, closely arranged copper particles when 5 mg/L 5-AT is added. However, when the 5-AT concentration exceeds 15 mg/L, the copper particles on the copper cathode surface increase. The difference between Tc(220) and Tc(311) is consistent with the change in the copper particles on the surface of the copper cathode, suggesting that Cu (311) growth facilitates the reduction and compact arrangement of copper particles on the cathode surface.
3.3. Analysis and Characterization of Anode Slime
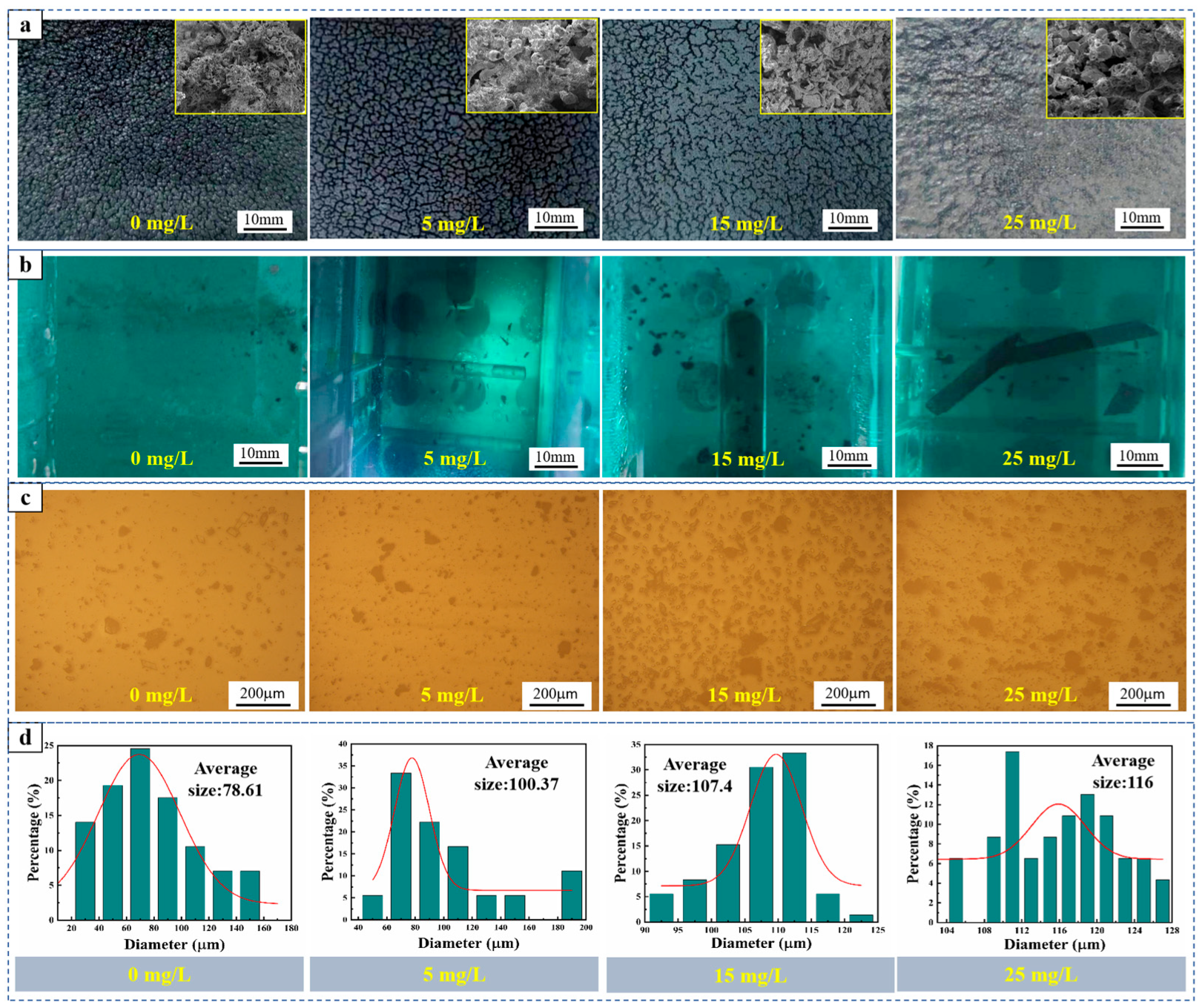
Figure 5 illustrates the analysis diagram of the anode slime agglomeration. Figure 5a demonstrates that 5-AT facilitates the formation of dense, massive anode slime on the surface of the anode as the 5-AT concentration increases. SEM images in Figure 5a indicate that the adhesive anode slime without 5-AT is composed of numerous hollow spherical and hemispherical particles. However, with increased 5-AT concentrations, the hollow spherical particles gradually decrease, while granular, spherical, and semilunar particles increase. The tighter bonding between the anode slime further supports the notion that 5-AT promotes the aggregation of fine anode slime on the anode plate surface. Figure 5b shows that when 5-AT is not added, the anode slime at the bottom of the cell is relatively small. When the concentration of 5-AT increases to >5 mg/L, the size of the anode slime at the bottom of the cell gradually grows. When 25 mg/L 5-AT is added, a dense massive anode slime forms at the bottom of the cell, suggesting that an increased concentration of 5-AT promotes the agglomeration of fine anode slime particles and the formation of massive anode slime, which can easily fall off, preventing anode passivation. Figure 5c shows a gradual increase in the number of large-sized anode slime particles with increasing 5-AT concentration. Image-Pro software was used to analyse the particle size distribution of the anode slime at the bottom of the cell, as shown in Figure 5d. The average particle size in the anode slime at the bottom of the cell was 78.61 µm without adding 5-AT, and 100.37 µm, 107.40 µm, and 116 µm when adding 5 mg/L, 15 mg/L, and 25 mg/L of 5-At, respectively. These results suggest that the average particle size of the anode slime at the bottom of the cell increases with the addition of 5-AT, indicating that 5-AT promotes the agglomeration of fine anode slime into large particles.
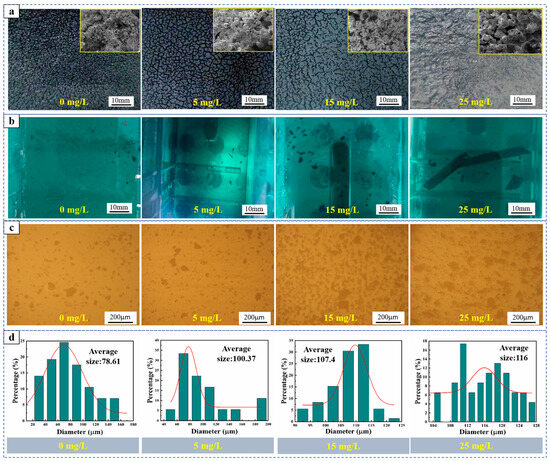
Figure 5.
Analysis of anode slime agglomeration: (a) Macroscopic photos of the anode plate surface and SEM images of anode slime; (b) Macroscopic photos of anode slime at the bottom of the cell; (c) Gold phase diagram of the bottom anode slime; (d) Histogram of particle size distribution of anode slime at the bottom of the cell.
Figure S7 presents the SEM image, elemental distribution, and EDS analysis of typical 5-AT agglomerated anode slime on the surface of the anode plate. In Figure S7a, the microstructure of the anode slime is primarily composed of near-spherical particles, irregular small particles, and loose spongy material, with near-spherical and irregular small particles clustered around the loose spongy material. Elemental distribution in Figure S7b–l reveals that C, O, N, Cl, As, and Cu are concentrated in the loose spongy materials. The EDS analysis of Figure S7m suggests that these loose spongy materials are formed by the complexation of 5-AT with Cl, As, and Cu. Meanwhile, near-spherical particles are rich in Ag, Cl, Se, S, O, Pb, and Bi. According to EDS analysis of the anode slime phase and P1 point (Figure S7n), these near-spherical particles comprise silver selenium compounds, PbSO4, Bi oxides, and AgCl particles. Cl, Ag, and Se are concentrated in random small particles. EDS analysis at P2 point (Figure S7o) indicates that these random small particles are formed by the combination of AgCl and Ag–Se compounds. Comprehensive analysis reveals that 5-AT agglomerated anode slime on the anode plate surface primarily consists of 5-AT and Cl, As, and Cu complexes; silver selenium compounds; PbSO4; Bi-containing oxides; and AgCl particles. This suggests that 5-AT forms adsorption films with Cu, Cl, As, and other elements, while AgCl particles agglomerate with silver selenium compounds, PbSO4, Bi oxides, and AgCl particles.
Figure S8 depicts an analysis diagram of anode slime adhesion on the anode plate. Figure S8a shows that the main phases of anode slime adhered to the anode plates are CuSO4·(H2O)5, PbSO4, silver copper selenium compound, Bi2O3, As2O4, and silver chloride. Without the addition of 5-AT, diffraction peaks of Ag2Se and Ag were not observed. The diffraction peaks of AgCl were weak, while those of CuAgSe and AgCuSe were strong. When the concentration of 5-AT was increased to 5 mg/L, the diffraction peaks of Ag2Se, Ag, and AgCl gradually increased, while those of CuAgSe and AgCuSe gradually decreased. In conclusion, 5-AT promotes the formation of Ag2Se, Ag, and AgCl in the anode slime. As the 5-AT concentration increases, the silver copper selenium compounds in the anode slime gradually convert to Ag2Se, Ag, and AgCl. Figure S8b presents the Fourier infrared spectra of 5-AT with the addition of 15 mg/L of adhesive anode slime. After adding 15 mg/L 5-AT to the anode slime, the N-H tensile vibration of the azole rings is observed at 3100–3200 cm−1, and the N=N double bond tensile vibration is detected at 1410–1460 cm−1, indicating that 5-AT enters the anode plate adhesion slime during the electrolysis process. Comparative analysis of bands at 1160–900 cm−1 after adding 5-AT shows four peaks at 908 cm−1, 1001 cm−1, 1068 cm−1, and 1145 cm−1. The anode slime after adding 5-AT presents four peaks at 962 cm−1, 1001 cm−1, 1093 cm−1, and 1150 cm−1. The presence of these four bands forming two double peaks indicates azole ring vibration in the anode slime. The peak shifts suggest that 5-AT is complexing with copper or silver ions [36].
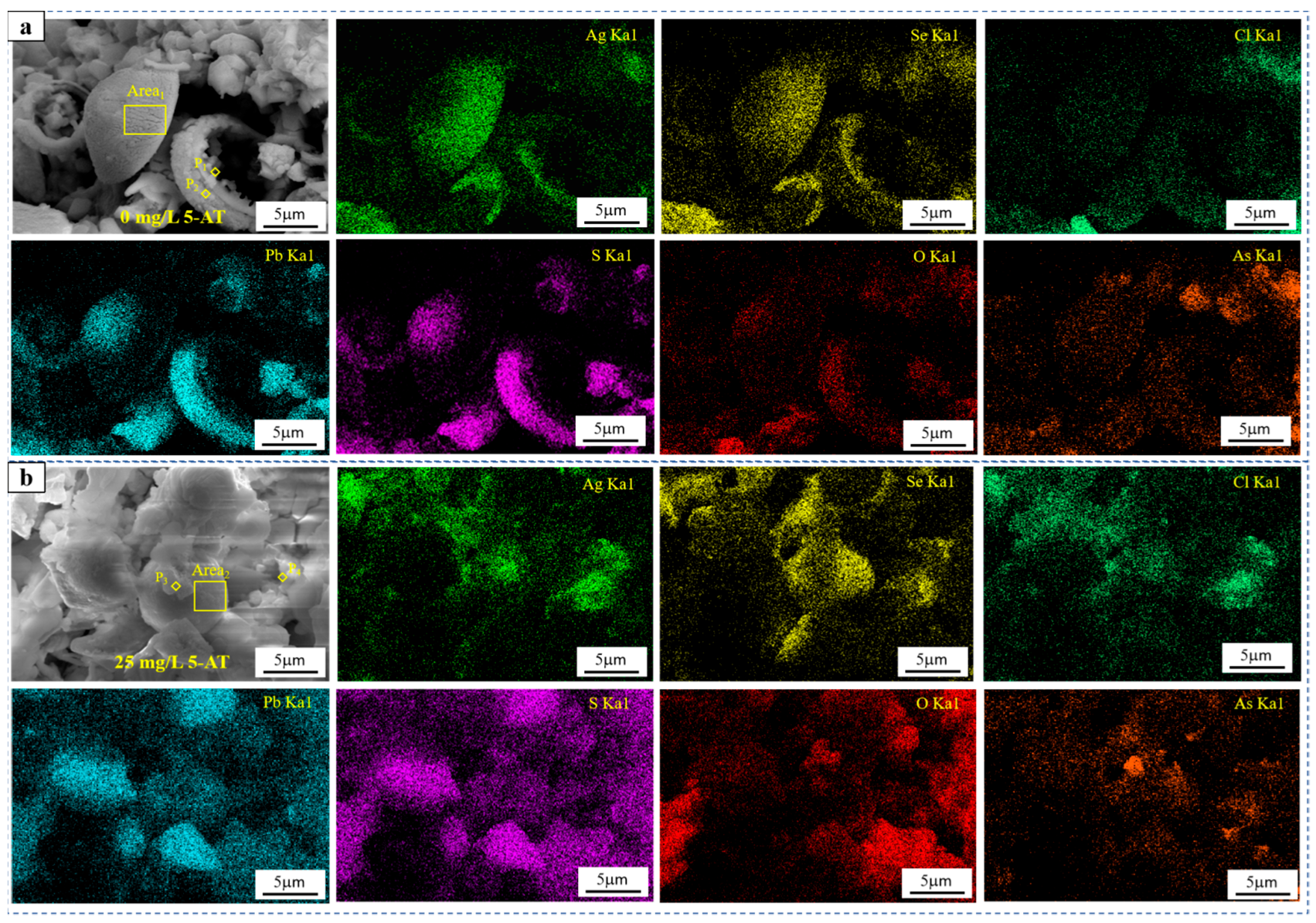
Figure 6 presents the SEM images and elemental distributions of the anode slime attached to the anode plates with and without the addition of 15 mg/L 5-AT. In the SEM image in Figure 6a, the structure of the adhesive anode slime contains numerous helmet-like hollow hemispheres and irregular particles without 5-AT. The hollow hemispheres are composed of inner and outer layers, while the irregular particles are closely connected with the hollow hemispheres. Element distribution analysis shows that Pb, O, and S were mainly distributed on the top and outer layers of the hemispheres, while Cu, Ag, Se, and Te are mainly distributed on the outer surface and inner hemispheres, except for the top hemispheres. Small amounts of Cl are distributed within the hemispherical particles, while some Cl and other elements (Ag, Se, Cu, Pb, O, S, and As) are concentrated in the irregular particles. O and As are concentrated in the centre of the irregular particles, while Cl, Ag, Se, Cu, Pb, and S are concentrated in the periphery. The combined EDS analysis in Table 4 and anodic slime phase indicate that the hollow hemisphere is composed mainly of PbSO4 and AgCu(Se,Te) compounds, while the irregular particles primarily consist of PbSO4, AgCu(Se,Te) compounds, As-O compounds, and AgCl. In Figure 6b, with the addition of 15 mg/L 5-AT, the microstructure of the adhesive anode slime consists mainly of numerous spherical particles and irregular particles. Most of the irregular particles are closely connected to the spherical particles, while some irregular particles are located on the surface of the spherical particles. The distribution diagram shows that Pb and S are primarily distributed on spherical particles, while some Pb, S, and O are concentrated on irregular particles. Ag, Se, Cl, and Te are concentrated on spherical particles, while Ag and Cl are clearly concentrated on the irregular particles on the surface of the spherical particles. In addition, O and As were also concentrated on the irregular particles located on the surface of spherical particles.
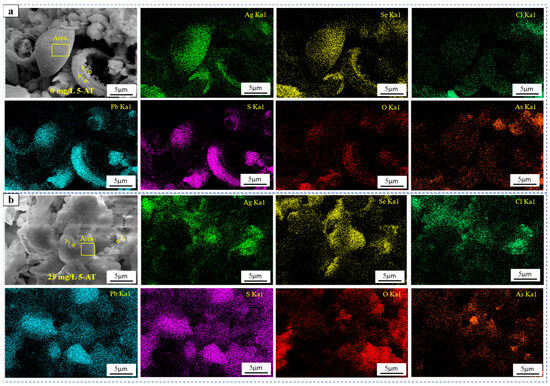
Figure 6.
SEM and element distribution of anode slime attached to anode plate without or with 15 mg/L 5-AT: (a) 0 mg/L 5-AT, (b) 15 mg/L 5-AT.

Table 4.
EDS analysis results of P1–P4 and Area 1–Area 2 in Figure 6, Wt %.
The anodic slime phase and EDS analyses presented in Figure 6b and Table 4 indicate that the spherical particles are mainly composed of PbSO4, Ag(Se,Te) compounds, and AgCl. The irregular particles primarily contain PbSO4, As-O, and AgCl. The SEM images and elemental distributions of the anode slime, both with and without 15 mg/L 5-AT, showed that the helmet-like hollow hemispheres disappeared and spherical particles appeared in the microstructure of the anode slime after the addition of 15 mg/L 5-AT. The bonding between the anode slime particles becomes closer. The concentrated distribution of Se, Ag, and Cl in the microstructure was more evident, indicating that 5-AT had a clear aggregation effect on Ag and Cl in the adhesive anode slime. The composition of P1–P4 and Area 1–Area 2 in Table 4 demonstrates that the enrichment of silver and silver-containing phases in the anode slime was continuously enhanced after the addition of 5-AT. This can be explained by the coordination with Cl− and Cu+ to form an adsorption layer on the surface of the anode, and Cl− and Cu+ in the adsorption layer can react with Ag+ released in the anode to effectively enrich the Ag content in the anode slime. In addition, the Ag content is closely related to the formation of spherical silver selenium compounds, and an increase in the Ag content of the anode slime is conducive to the formation of spherical selenide particles.
Figure S9 presents the SEM and EDS analyses of the anode plate surface after the removal of adhesive anode slime. Figure S9a–c reveals that the anode surface has multifaceted and concave/convex textures on a microscopic scale, including some corrosion holes when 5-AT is not added. However, when 15 mg/L of 5-AT is added, the anode plate surface remains convex, but with more corrosion holes. A comparative analysis showed that 5-AT contributed to the formation of corrosion holes on the surface of the anode plate. EDS analysis in Figure S9b–d indicates that the main components of P1 are O, Cu, Te, S, Ag, and As, and no Cl was detected. In contrast, there was a Cl spectral peak at P2, with an atomic ratio of Cl to Ag close to 1:1, indicating the presence of AgCl in the holes on the anode plate surface after the addition of 5-AT. This can be explained as follows. Most of the silver in the copper anode exists as a solid solution. As the anode undergoes electrolytic corrosion, the silver is released, forming holes on the anode surface. The 5AT-Cu+-Cl− adsorption layer formed by 5-AT and HCl on the anode surface intensifies the release of Ag+ from the anode, resulting in an increase in pore formation. At the same time, Cl− in the adsorbed layer reacts with the released Ag+ in the anode to form AgCl in the holes.
3.4. Mechanism of 5-AT and HCl on Electrorefining of Copper
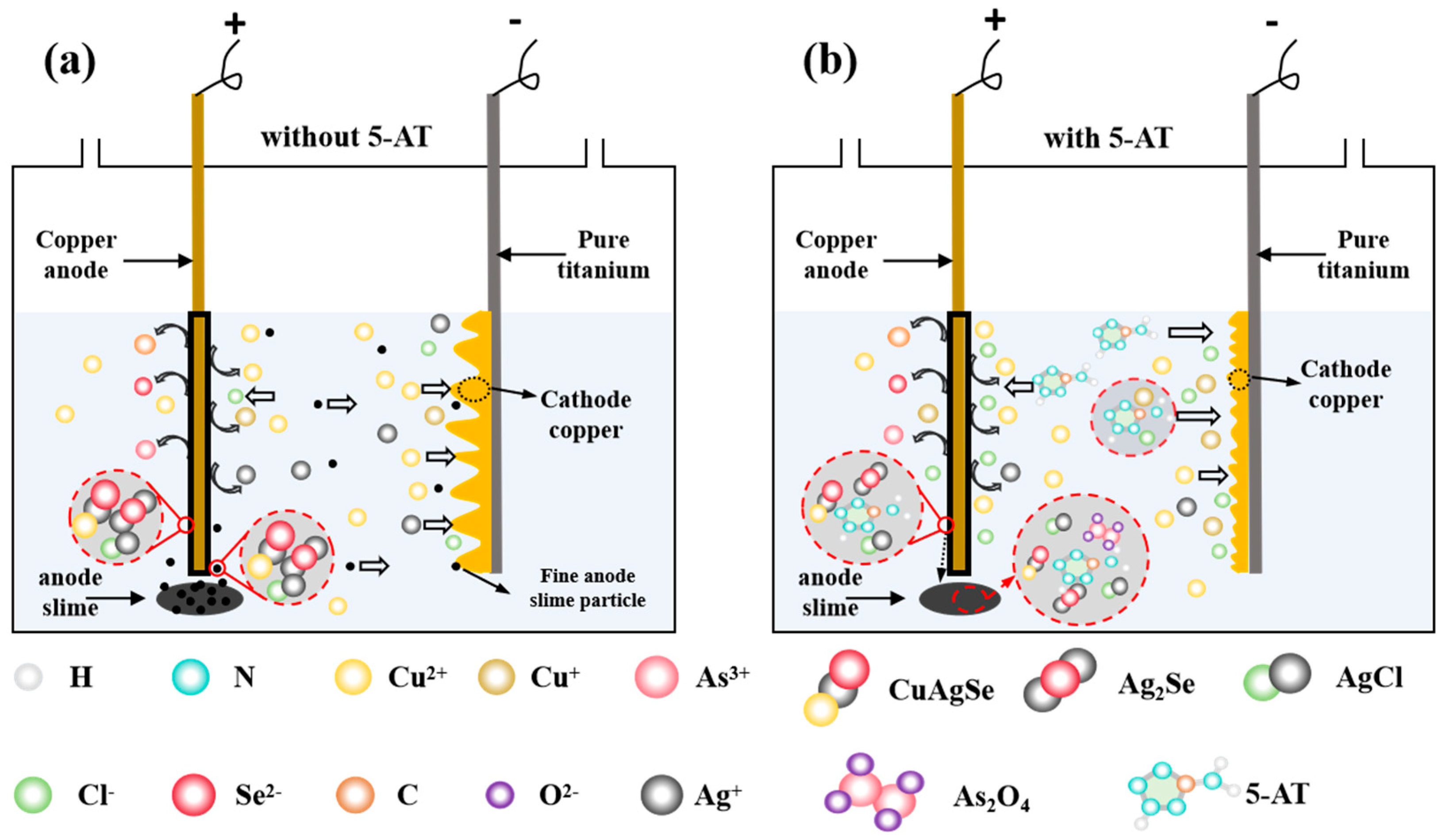
Based on the above experimental results and related discussions, a proposed mechanism of HCl and 5-AT composite additives for silver reduction in copper electrorefining process is illustrated in Figure 7.
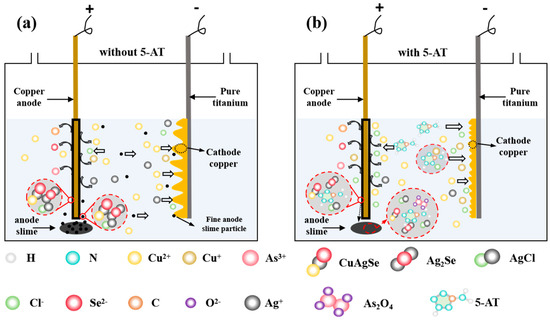
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of the silver reduction mechanism of HCl and 5-AT in copper electrorefining process: (a) without 5-AT; (b) with 5-AT.
As shown in Figure 7a, Cu and Ag in the anode lose electrons and release Ag+, Cu2+, and Cu+ when no 5-AT additive is added. The phases of Cu2(Se,Te), CuO, Cu-Pb-AS-Sb-Bi oxide, and Cu-Pb-As oxide in the anode react chemically with acidic copper sulfate electrolyte to produce Se2−, Cu2+, and As3+. These ions chemically react to form Ag2Se, AgCuSe, and other compounds into the anode slime attached to the anode plate. The adhesive anode slime falls off the anode plate and enters the bottom of the cell with the extension of electrolysis time. A large number of fine anode slime particles are produced and are suspended in the electrolyte when the anode slime falls off. At the same time, Cl− existing in the electrolyte can react with Ag+ to form AgCl. Most of the AgCl particles settle into the bottom of the cell during the electrolytic process, but some small AgCl particles will still be suspended in the electrolyte and combine with the fine anode slime particles. The fine anode slime particles enter the copper cathode under the action of the electric field. Moreover, there are bumps on the copper cathode surface and even copper nodules are formed due to the existence of “tip discharge” on the copper cathode surface during electrochemical deposition.
As shown in Figure 7b, when 5-AT is added to the electrolyte, the adsorption of 5-AT and HCl on the anode surface forms a 5AT-Cu+-Cl− adsorption layer. This layer aggregates fine anode slime on the anode plate surface, tightening the bonding between anode slime particles. The formation of the complex between 5-AT and Cl− is conducive to the agglomeration of fine anode slime particles, preventing the fine anode slime from entering the copper cathode. Meanwhile, the reaction between the adsorption layer and Ag+ released from the anode plate intensifies the release of Ag+, leading to an increase in silver-containing phases, such as Cu-Ag-Se compounds and AgCl. This results in an increase in the silver content in the silver-containing phase. On the cathode surface, 5-AT affects the electrodeposition of Cu2+ ions via adsorption on the cathode surface. The nucleation/growth model shows that while 5-AT does not alter the nucleation mechanism of copper ions, the coordination bond between 5-AT and Cu+ facilitates copper electrodeposition. This reduces the active sites of Ag+ electrodeposition on the cathode surface. Moreover, the FT-type growth of cathode copper grains is promoted by 5-AT. The growth pattern and surface morphology of cathode copper are changed by 5-AT and reduce the risk of fine anode slime and electrolyte alterations in the cathode. In summary, 5-AT serves as a new and effective additive for reducing the silver content in electrolytically refined copper cathodes using a high silver anode plate.
4. Conclusions
In this study, impact of 5-amino-1H tetrazole on reducing silver in copper cathodes during electrorefining with high silver content anode plates was investigated. The following conclusions were drawn.
The content of silver in the copper cathode initially decreases and then increases as the 5-AT concentration in the electrolyte increases. When the 5-AT concentration was 15 mg/L, the Ag content in the copper cathode decreased from 7.0 ppm to 4.7 ppm, and the silver content was decreased by 32.86%. The 5-AT adsorbs and binds with Cu+ on the cathode surface, promoting Cu2+ electrodeposition and inhibiting Ag+ electrodeposition. However, 5-AT does not change the nucleation mechanism of Cu2+ electrodeposition. In addition, 5-AT supports uniform FT growth of copper cathode grains and reduces inclusions in the copper cathode. The surface particles of cathode copper initial decrease and then increase with the increase of 5-AT concentration. The large size of copper particles leads to an increase in silver content in the copper cathode. In the acidic electrolyte, 5-AT forms an “adsorption layer” on the surface of the anode This layer reacts with Ag+ released from the anode, creating silver precipitate, and preventing silver from entering the electrolyte in the form of Ag+. Additionally, the “adsorption layer” aggregates fine Ag-Se compounds, bismuth oxide, PbSO4, and AgCl particles, forming larger anode slime particles that settle quickly to the cell bottom. The agglomeration effect significantly reduces the fine anode slime particles in the electrolyte and the adhesion of silver-containing particles into the cathode copper. The results of our work provide theoretical guidance for the use of tetrazole additives in the reduction of silver content in high silver content anode plates.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/met14070799/s1, Figure S1: CA curve of electrolyte under different conditions, dimensionless diagram of nucleation/growth model; Figure S2: Cottrell Figure and Cu2+ electrodeposition diffusion coefficient at different concentrations of 5-AT; Figure S3: Macroscopic photos of cathode copper surface with different concentrations of 5-AT; Figure S4: The XPS and FT-IR spectra of the cathode copper without and with 15 mg/L 5-AT; Figure S5: Analysis of the longitudinal section of cathode copper with different concentrations of 5-AT; Figure S6: XRD patterns and texture coefficients of cathode copper prepared at different concentrations of 5-AT; Figure S7: SEM, EDS analysis and element distribution of typical 5-AT agglomerated anode slime on the anode plate surface; Figure S8: Analysis of anode slime adhesion to anode plate of XRD patterns and FT-IR diagram; Figure S9: SEM and EDS analysis of the anode plate surface after removing the adhesive anode slime.
Author Contributions
C.C. (Chen Chen), C.C. (Chu Cheng), M.W., H.L., X.L. and K.S. made a significant contribution to the conception or design of the work. C.C. (Chen Chen), C.C. (Chu Cheng), M.W., H.L., X.L. and K.S. were responsible for the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of the data. C.C. (Chen Chen) and C.C. (Chu Cheng) wrote the original draft. Furthermore, X.L. provided great contributions in resource provision. All of the authors played an important role in drafting the paper or in critically examining important intellectual content. All authors have received final approval for the pending edition and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Henan Key Research and Development Project (No. 221111230600), the Zhongyuan Scholar Workstation Funded Project (No. 224400510025), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52071133), the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52204359), the Foundation for Key Teachers of Henan University of Science and Technology (No. 13450026), and Graduate Student Innovation Fund of Henan University of Science and Technology (2023-N49).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Xiaoheng Li was employed by the company Hennan Zhongyuan Gold Smelter LLC. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Anggara, S.; Bevan, F.; Harris, R.C. Direct extraction of copper from copper sulfide minerals using deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 6502–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Lyu, X. Extraction and separation of copper and iron from copper smelting slag: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Free, M.L.; Werner, J. Simulation and validation studies of impurity particle behavior in copper electrorefining. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, E338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butrymowicz, D.B.; Manning, J.R.; Read, M.E. Diffusion in copper and copper alloys, Part II. Copper-silver and copper-gold systems. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1974, 3, 527–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Cheng, J.; Wang, T. Continuous electrorefining process of cathode copper with non-dissolving anode. Miner. Eng. 2019, 135, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, T.; Hallemans, N.; Wouters, B. An operando ORP-EIS study of the copper reduction reaction supported by thiourea and chlorides as electrorefining additives. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 389, 138762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, C.; Tadie, M.; Dorfling, C. Evaluating the effect of molecular properties of polyacrylamide reagents on deposit growth in copper electrowinning. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 195, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Oue, S.; Fujimoto, A. Evaluation of Degradation of Polymer Additives during Long-Term Cu Electrorefining. J. MMIJ 2008, 124, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shize, J.; Edward, G. Effect of thiourea on the copper cathode polarization behavior in acidic copper sulfate at 65 °C. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2001, 32, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshimwanga, N.; Maweja, K.; Tshula, K. Efficacy of polyacrylamide and protein flocculants in preventing anode depassivation induced Pb-contamination of copper electrowinning cathodes. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 105, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.Z.; Wang, S.J.; Free, M.L. Experimental and simulation studies of electrolyte flow and slime particle transport in a pilot scale copper electrorefining cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, E111–E122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patcharawit, T.; Kansomket, C.; Kritsarikun, W. Recovery of pure silver from spent silver electroplating solutions via electrochemical process and zinc cementation. JOM J. 2023, 33, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkuna, E.H.; Popoola, A.P. Effect of Chloride Electrolyte Additive on the Quality of Electrorefined Copper Cathode. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 35, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Cao, H.; Shen, Y. Migration regularity and control of silver inclusions during copper electrorefining process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2023, 33, 2853–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenji, K.; Yoshie, T.; Kiyotaka, N. Additives for Electrorefining of High Purity Copper and Method for Manufacturing High Purity Copper. U.S. Patent 20170058412 Al, 15 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.P.; Lin, Y.; Huang, X.C. Copper (I) 1, 2, 4-triazolates and related complexes: Studies of the solvothermal ligand reactions, network topologies, and photoluminescence properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5495–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotton, F.A.; Murillo, C.A.; Wang, X. Trinuclear complexes of copper, cobalt and iron with N, N′-di (2-pyridyl) formamidinate ligands, [M3(DPyF)4][PF6]2. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 1998, 1, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, E.S.; Erasmus, R.M.; Comins, J.D. Inhibition of corrosion processes on copper in aerated sodium chloride solutions by 5-(3-aminophenyl)-tetrazole. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Crisponi, G. Silver coordination compounds: A new horizon in medicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, A.; Mahjani, M.G.; Moshrefi, R. Electrochemical and DFT study on the inhibition of 316L stainless steel corrosion in acidic medium by 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-amino-1 H-tetrazole. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 20031–20037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Elgrishi, N.; Rountree, K.J.; McCarthy, B.D. A practical beginner’s guide to cyclic voltammetry. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 95, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviron, E. General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1979, 101, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharifker, B.R.; Hills, G. Theoretical and experimental studies of multiple nucleation. Electrochim. Acta 1983, 28, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Hua, Y. The effect of quaternary ammonium-based ionic liquids on copper electrodeposition from acidic sulfate electrolyte. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2015, 45, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Lu, W.; Song, K. Preparation of electrodeposited copper foils with ultrahigh tensile strength and elongation: A functionalized ionic liquid as the unique additive. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, A.; Abhyankar, A. Influence of texture coefficient on surface morphology and sensing properties of w-doped nanocrystalline tin oxide thin films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3571–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savéant, J.M. Elements of molecular and biomolecular electrochemistry: An electrochemical approach to electron transfer chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Liu, H.; Li, Z. Electrochemical deposition of silver in room-temperature ionic liquids and its surface-enhanced Raman scattering effect. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10260–10267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianat, A.; Yang, H.; Bobeth, M. DFT study of interaction of additives with Cu (111) surface relevant to Cu electrodeposition. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2018, 48, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.R.; Xin, X.Q.; Zhu, J.J. Coordination compound films of 1-phenyl-5-mercaptotetrazole on copper surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 135, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonijević, M.M.; Milić, S.M.; Petrović, M.B. Films formed on copper surface in chloride media in the presence of azoles. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Feng, W.; Zhang, H. Chlorine inclusion mechanism in high purity copper electrorefining from nitric acid system. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassen, H.B.; Paukert, T.; Henry, R.A. Infrared spectra of some 5-aminotetrazoles and their deuterated derivatives. Appl. Spectrosc. 1967, 21, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, M.; Mitsuno, S.; Kitada, A. Mechanism of nodular growth in copper electrorefining with the inclusion of impurity particles under natural convection. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 216, 106013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, N.D.; Glišić, B.Đ.; Wadepohl, H. Silver (I) complexes with quinazoline and phthalazine: Synthesis, structural characterization and evaluation of biological activities. Med. Chem. Commun. 2016, 7, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).