Reoxidation Behavior of the Direct Reduced Iron and Hot Briquetted Iron during Handling and Their Integration into Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Direct Reduction of Iron Ore
2.1. Main Principles of DR
2.2. Main Routes and Reactors for the DR Processes
2.3. DRI Characteristics
3. Carburization
4. Passivation of DRI
4.1. Reoxidation Issue of DRI
4.2. Creating the Oxide Layer
4.3. Hot Briquetted Iron
4.4. Other Methods
5. Storage, Handling, and Transportation
6. Application of DRI/HBI in an EAF Steelmaking
7. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dall’Osto, G.; Mombelli, D.; Mapelli, C. Consequences of the Direct Reduction and Electric Steelmaking Grid Creation on the Italian Steel Sector. Metals 2024, 14, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, A. Evaluation of the Smelting Behaviour of Direct Reduced Iron. Ph.D. thesis, Montanuniversitaet Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Béchara, R.; Hamadeh, H.; Mirgaux, O.; Patisson, F. Optimization of the Iron Ore Direct Reduction Process through Multiscale Process Modeling. Materials 2018, 11, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Guan, X.; Kuang, S.; Yu, A.; Yang, N. A Review on the Modeling and Simulation of Shaft Furnace Hydrogen Metallurgy: A Chemical Engineering Perspective. ACS Eng. Au 2023, 4, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, M.A.; Centeno, T.A.; Amado-Fierro, Á. Coal Use for Iron and Steel Production in Low-Carbon Transition Scenarios. In The Coal Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 493–546. ISBN 978-0-12-824327-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hammam, A.; Cao, Y.; El-Geassy, A.-H.A.; El-Sadek, M.H.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.; Omran, M.; Yu, Y. Non-Isothermal Reduction Kinetics of Iron Ore Fines with Carbon-Bearing Materials. Metals 2021, 11, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boretti, A. The Perspective of Hydrogen Direct Reduction of Iron. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 429, 139585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, A.; Kossen, J.; Goldie-Jones, H.; Yang, A. Global Green Hydrogen-Based Steel Opportunities Surrounding High Quality Renewable Energy and Iron Ore Deposits. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Yang, H.; Tian, G.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, X. Direct Reduction of Iron to Facilitate Net Zero Emissions in the Steel Industry: A Review of Research Progress at Different Scales. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 441, 140933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechberger, K.; Spanlang, A.; Sasiain Conde, A.; Wolfmeir, H.; Harris, C. Green Hydrogen-Based Direct Reduction for Low-Carbon Steelmaking. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 2000110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DRI Production. Available online: https://www.metallics.org/dri-production.html (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- 2022 World Direct Reduction Statistics. Available online: https://www.midrex.com/wp-content/uploads/MidrexSTATSBook2022.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Guo, D.; Li, Y.; Cui, B.; Chen, Z.; Luo, S.; Xiao, B.; Zhu, H.; Hu, M. Direct Reduction of Iron Ore/Biomass Composite Pellets Using Simulated Biomass-Derived Syngas: Experimental Analysis and Kinetic Modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.C.; Cang, D. A Brief Overview of Low CO2 Emission Technologies for Iron and Steel Making. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2010, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakgala, C.; Danha, G. A Review of Ironmaking by Direct Reduction Processes: Quality Requirements and Sustainability. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 35, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschen, M.; Badr, K.; Pfeifer, H. Influence of Direct Reduced Iron on the Energy Balance of the Electric Arc Furnace in Steel Industry. Energy 2011, 36, 6146–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.D.; Conejo, A.N.; Rodriguez, H.H. Process Dynamics of Electric Arc Furnace during Direct Reduced Iron Melting. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2002, 33, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Steel Association, Sustainability Indicators. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/steeltopics/sustainability/sustainability-indicators/ (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Kirschen, M.; Hay, T.; Echterhof, T. Process Improvements for Direct Reduced Iron Melting in the Electric Arc Furnace with Emphasis on Slag Operation. Processes 2021, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolpour, B.; Afsahi, M.M.; Azizkarimi, M. Hydrogen Reduction of Magnetite Concentrate Particles. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2021, 130, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.L.G. Power Delivery from the Arc in AC Electric Arc Furnaces with Different Gas Atmospheres. Steel Res. Int. 2009, 80, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.L.; Fradet, Q.; Riedel, U. Kinetic Mechanism Development for the Direct Reduction of Single Hematite Pellets in H2/CO Atmospheres. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2200043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ei-Geassy, A.A.; Shehata, K.A.; Ezz, S.Y. Mechanism of Iron Oxide Reduction with Hydrogen/Carbon Monoxide Mixtures. ISIJ Int. 1977, 17, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharm, C.; Küster, F.; Laabs, M.; Huang, Q.; Volkova, O.; Reinmöller, M.; Guhl, S.; Meyer, B. Direct Reduction of Iron Ore Pellets by H2 and CO: In-Situ Investigation of the Structural Transformation and Reduction Progression Caused by Atmosphere and Temperature. Miner. Eng. 2022, 180, 107459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Pang, K.; Barati, M.; Meng, X. Hydrogen-Based Reduction Technologies in Low-Carbon Sustainable Ironmaking and Steelmaking: A Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 10, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zuo, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, Q.; Ren, B.; Yang, F. The Production and Application of Hydrogen in Steel Industry. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 10548–10569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Tahari, M.N.; Salleh, F.; Tengku Saharuddin, T.S.; Samsuri, A.; Samidin, S.; Yarmo, M.A. Influence of Hydrogen and Carbon Monoxide on Reduction Behavior of Iron Oxide at High Temperature: Effect on Reduction Gas Concentrations. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 24791–24805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Narita, K.; Kaneko, D. Mathematical Model of Direct Reduction Shaft Furnace and Its Application to Actual Operations of a Model Plant. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1986, 10, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y.; Sakawa, M.; Kondo, S. Mathematical Model of the Shaft Furnace for Reduction of Iron-Ore Pellet. Tetsu-to-Hagane 1976, 62, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Z.; Li, Z.; Wei, R.; Liu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Chun, T.; Long, H.; Li, J.; Wang, P. Sticking Behaviour and Mechanism of Iron Ore Pellets in COREX Pre-Reduction Shaft Furnace. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2019, 46, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.; Niknahad, N.; Iljana, M.; Fabritius, T. A Review on the Kinetics of Iron Ore Reduction by Hydrogen. Materials 2021, 14, 7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza Filho, I.R.; Springer, H.; Ma, Y.; Mahajan, A.; Da Silva, C.C.; Kulse, M.; Raabe, D. Green Steel at Its Crossroads: Hybrid Hydrogen-Based Reduction of Iron Ores. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patisson, F.; Mirgaux, O. Hydrogen Ironmaking: How It Works. Metals 2020, 10, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P.; Perrone, A.; Marsano, D. Effect of Reducing Atmosphere on the Direct Reduction of Iron Oxides Pellets. Powder Technol. 2023, 426, 118650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anameric, B.; Kawatra, S.K. Properties and features of direct reduced iron. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2007, 28, 59–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lei, C.; Zhu, Q. Reduction of Fine Iron Ore via a Two-Step Fluidized Bed Direct Reduction Process. Powder Technol. 2014, 254, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhu, G.; Xu, Q. Numerical Simulation of the Operating Conditions for the Reduction of Iron Ore Powder in a Fluidized Bed Based on the CPFD Method. Processes 2022, 10, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Roy, G.G. Effect of Amount of Carbon on the Reduction Efficiency of Iron Ore-Coal Composite Pellets in Multi-Layer Bed Rotary Hearth Furnace (RHF). Met. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Yi, L.; Huang, Z.; Lu, B.; Jiang, X.; Cai, W.; Tian, B.; Jin, Y. Insight of Iron Ore-Coal Composite Reduction in a Pilot Scale Rotary Kiln: A Post-Mortem Study. Powder Technol. 2019, 356, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.G. Flexibility in Using Iron Ores for Direct Reduction. In Proceedings of the Metal Bulletin-2nd Latin American Steel & Iron Ore Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, April 2000; Available online: https://www.market-ing.com.mx/images/descargas/esp/MB_Paper.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- Lu, Q.; Jiang, W.F.; Lu, C.X.; Zhao, L.G.; Yin, H.S.; Lang, J.F. Carbonising Mechanism and Carbon Distribution Behaviour during Direct Reduction in Shaft Furnace. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1999, 26, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, J.C.; Dippenaar, R.J. Fluidized-Bed Reduction of Fine Iron Ore by the in Situ Combustion of Coal. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 1989, 89, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Komatina, M.; Gudenau, H.W. The Sticking Problem during Direct Reduction of Fine Iron Ore in the Fluidized Bed. Metall. Mater. Eng. 2004, 10, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, I.; Fruehan, R.J. The Reduction of Iron Oxides by Volatiles in a Rotary Hearth Furnace Process: Part I. The Role and Kinetics of Volatile Reduction. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2005, 36, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakudya, R.Y.; Ayomoh, M. Sustainability Enhancement of the Coal Based Direct Reduction of Iron Premised on a Rotary Kiln. In Manufacturing Driving Circular Economy; Kohl, H., Seliger, G., Dietrich, F., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 211–218. ISBN 978-3-031-28838-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Mendes, V.; Chun, T.; Pan, J.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Qiu, G. Direct Reduction Behaviors of Composite Binder Magnetite Pellets in Coal-Based Grate-Rotary Kiln Process. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfinger, T.; Spreitzer, D.; Schenk, J. Analysis of the Usability of Iron Ore Ultra-Fines for Hydrogen-Based Fluidized Bed Direct Reduction—A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, K.; Kaneko, D.; Kimura, Y.; Takenaka, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Inada, Y. Production of Reduced Iron by Model Plant of Shaft Furnace. Tetsu-to-Hagane 1981, 67, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.-Y.; Song, J.; Lee, J.-S. Reaction Kinetics and Phase Transformation during Hydrogen Reduction of Spherical Fe2O3 Nanopowder Agglomerates. Powder Technol. 2016, 302, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe Kinaci, M.; Lichtenegger, T.; Schneiderbauer, S. Direct Reduction of Iron-Ore in Fluidized Beds. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 43, pp. 217–222. ISBN 978-0-444-64235-6. [Google Scholar]
- Battle, T.; Srivastava, U.; Kopfle, J.; Hunter, R.; McClelland, J. The Direct Reduction of Iron. In Treatise on Process Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 89–176. ISBN 978-0-08-096988-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Raipala, K.; Holappa, L. Ironmaking. In Treatise on Process Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 2–88. ISBN 978-0-08-096988-6. [Google Scholar]
- Baig, S. Cost Effectiveness Analysis of HYL and Midrex DRI Technologies for the Iron and Steel-Making Industry. Master’s Thesis, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nduagu, E.I.; Yadav, D.; Bhardwaj, N.; Elango, S.; Biswas, T.; Banerjee, R.; Rajagopalan, S. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Natural Gas and Coal-Based Directly Reduced Iron (DRI) Production: A Case Study for India. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Mishra, S.; Roy, G.G.; Sen, P.K. Estimation of Carbon Dioxide Emissions in Rotary Hearth Furnace Using a Thermodynamic Model. Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1600265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Raipala, K.; Holappa, L. Future of Process Metallurgy. In Treatise on Process Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1563–1726. ISBN 978-0-08-096988-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, H.; Kopfle, J.; McClelland, J.; Ripke, J. Rotary Hearth Furnace Technologies for Iron Ore and Recycling Applications. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2008, 53, 541–545. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, A.E. Iron Resources and Direct Iron Production. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 4302–4310. ISBN 978-0-08-043152-9. [Google Scholar]
- Soeparto, A.B. The Effect of Oxy-Carbon Injection on EAF Efficiency. Master’s Thesis, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Sohn, I. Critical Challenges Facing Low Carbon Steelmaking Technology Using Hydrogen Direct Reduced Iron. Joule 2022, 6, 2228–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsen, B.; Thomassen, E.; Bragstad, I.; Ringdalen, E.; Hoegaas, P. Characterization of DR Pellets for DRI Applications. In Proceedings of the AISTech 2015 Proceedings; Association for Iron and Steel Technology: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- International Iron Metallics Association. Available online: https://www.metallics.org/ (accessed on 14 April 2024).
- Small, M. Direct Reduction of Iron Ore. JOM 1981, 33, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paknahad, P.; Askari, M.; Shahahmadi, S.A. Cold-Briquetted Iron and Carbon (CBIC), Investigation of Steelmaking Behavior. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 6655–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direct Reduced Iron (DRI). Available online: https://www.metallics.org/dri.html (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Abd Elkader, M.; Fathy, A.; Eissa, M.; Shama, S. Effect of Direct Reduced Iron Proportion in Metallic Charge on Technological Parameters of EAF Steelmaking Process. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 5, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tappeiner, T. Ganzheitliche Betrachtung Des Einsatzes von LRI (Low Reduced Iron) Im Hochofen Zur CO2-Minimierung. Ph.D. Thesis, Montanuniversität Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.; Sandeep Kumar, T.K.; Alatalo, J.; Björkman, B. Effect of Carbon Concentration and Carbon Bonding Type on the Melting Characteristics of Hydrogen-Reduced Iron Ore Pellets. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon Hurtado, F.A.; Govro, J.; Emdadi, A.; O’Malley, R.J. The Melting Behavior of Hydrogen Direct Reduced Iron in Molten Steel and Slag: An Integrated Computational and Experimental Study. Metals 2024, 14, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linklater, J. Adapting to Raw Materials Challenges: Part 1—Operating MIDREX Plants with Lower Grade Pellets & Lump Ores. Available online: https://www.midrex.com/tech-article/adapting-to-raw-materials-challenges-part-1-operating-midrex-plants-with-lower-grade-pellets-lump-ores/ (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Barati, M. Application of Slag Engineering Fundamentals to Continuous Steelmaking. In Treatise on Process Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 305–357. ISBN 978-0-08-096984-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Souza Filho, I.R.; Bai, Y.; Schenk, J.; Patisson, F.; Beck, A.; Van Bokhoven, J.A.; Willinger, M.G.; Li, K.; Xie, D.; et al. Hierarchical Nature of Hydrogen-Based Direct Reduction of Iron Oxides. Scr. Mater. 2022, 213, 114571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyllenram, R.; Sikstrom, P.; Hahne, R.; Tottie, M. Classification of DRI/HBI Based on the Performance in the EAF A Help for Steelmaker’s Procurement of Metallics, METEC ESTAD: Düsseldorf, Germany,, 2015.
- Tokuda, M.; Yoshikoshi, H.; Ohtani, M. Kinetics of the Reduction of Iron Ore. ISIJ Int. 1973, 13, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Geassy, A.A. Influence of Doping with CaO and/or MgO on Stepwise Reduction of Pure Hematite Compacts. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1999, 26, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.L.; Acosta, F.L.; Lowry, M.; Kundrat, D.; Wyatt, A.; Kuntze, J.; Fuchs, H. Improvements in Yield in an All-DRI-Fed EAF from Minimization of FeO Generation during Melting as Well as Post-Reduction of FeO from Residual Slag; Iron and Steel Technology: Nashville, TN, USA, 2018; pp. 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, C.P.; Chevrier, V.F. Maximizing Iron Unit Yield from Ore to Liquid Steel (Part 2—DRI Physical Properties and DRI Handling and Storage). Available online: https://www.midrex.com/tech-article/maximizing-iron-unit-yield-from-ore-to-liquid-steel-part-2-dri-physical-properties-and-dri-handling-and-storage/ (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Sane, A.; Buragino, G.; Makwana, A.; He, X. Enhancing Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) for Use in Electric Steelmaking. Available online: https://www.airproducts.com/-/media/files/en/335/335-20-002-us-enhancing-direct-reduced-iron-43251.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Heo, J.H.; Park, J.H. Effect of Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) on Dephosphorization of Molten Steel by Electric Arc Furnace Slag. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 3381–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-S.; Chung, U.-C.; Chung, W.-S.; Cho, Y.-R.; Jung, B.-H.; Martin, G.P. Carburization of Iron Using CO−H2 Gas Mixture. Met. Mater. Int. 2004, 10, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Pistorius, P.C. Laboratory Carburization of Direct-Reduced Iron in CH4-H2-N2 Gas Mixtures, and Comparison with Industrial Samples. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 1538–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longbottom, R.J.; Ostrovski, O.; Zhang, J.; Young, D. Stability of Cementite Formed from Hematite and Titanomagnetite Ore. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2007, 38, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, T.K.S.; Alatalo, J.; Ahmed, H.; Björkman, B. Effect of Temperature and Gas Mixtures on Cementite Formation During the Carburization of Hydrogen-Reduced DRI. J. Sustain. Metall. 2022, 8, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, R.G.; Turkdogan, E.T. Catalitic Effect of Iron on Decomposition of Carbon Monoxide: II. Effect of Additions of H2, H2O, CO2, SO2 and H2S. Metall. Trans. 1974, 5, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruehan, R.J. The Rate of Carburization of Iron in CO-H2 Atmospheres: Part I. Effect of Temperature and CO and H2-Pressures. Met. Trans. 1973, 4, 2123–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, Y.; Endo, S. Carburized Carbon Content of Reduced Iron and Direct Carburization in Carbon Composite Iron Ore Pellets Heated at Elevated Temperature. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabke, H.J.; Müller-Lorenz, E.M.; Schneider, A. Carburization and Metal Dusting on Iron. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, S.; Iguchi, Y. Production of Iron Carbide from Iron Ores in a Fluidized Bed. ISIJ Int. 1998, 38, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, G. Carbon Concentration and the Use of Direct-Reduced Iron in Ironmaking and Steelmaking. Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Kacar, Y.; Pistorius, P.C. Carbon Bonding State Has a Small Effect on Melting of Direct-Reduced Iron. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 2508–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jess, A.; Grabke, H.; Steffen, R. Reoxidation and Ignition Behaviour of DRI to Improve Safety; European Commission, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation: Luxemburg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Majhi, T.R. Modeling of Rotary Kiln for Sponge Iron Processing. Master’s Thesis, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pietsch, N. The Influence of Raw Material and Reduction Temperature on the Structure and Characteristics of DRI. SME-AIME 1978, 264, 1784. [Google Scholar]
- AbdElmomen, S.S. Reoxidation of Direct Reduced Iron in Ambient Air. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2014, 41, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P.; Dijon, L.; Laska, A.; Koszelow, D. Hydrogen Direct Reduction and Reoxidation Behaviour of High-Grade Pellets. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 49, 1235–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paknahad, P.; Askari, M. Modeling, kinetics investigation and determining the controlling mechanisms of atmospheric oxidation of “cold” briquetted iron and carbon (CBIC). Met. Eng. 2021, 23, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazir, D.; Sahin, B.; Alkac, M. Selection of an Inert Gas System for the Transportation of Direct Reduced Iron. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8529724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towhidi, N. Influence of Direct Reduction Condition of Hematite Pellets with H2/CO on the Oxidation Behaviour of DRI in Air. Steel Res. Int. 2003, 74, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Geassy, A.A.; El-Kashif, F.O.; Nasr, M.I.; Omar, A.A. Kinetics and Mechanisms of Re-Oxiation of Freshly Reduced Iron Compacts. ISIJ Int. 1994, 34, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abd Elmomen, S.S. Reoxidation of Direct Reduced Iron in Stagnant Air in The Temperature Range between 150 and 450°C. Bull. Tabbin Inst. Metall. Stud. (TIMS) 2021, 109, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhya, K. The Kinetics and Mechanism(s) of Oxidation of Direct Reduced Iron. JOM 1984, 36, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.O. Studies of the Re-Oxidation Behavior of DRI in Air at Moderate Temperatures. Master’s Thesis, Michigan Tech. University, Houghton, MI, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Bandopadhyay, A.; Ganguly, A.; Gupta, K.N.; Ray, H.S. Investigations on the Anomalous Oxidation Behaviour of High-Carbon Gas-Based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI). Thermochim. Acta 1996, 276, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, A.; Ganguly, A.; Prasad, K.K.; Sarkar, S.B.; Ray, H.S. Determination of Kinetic Parameters for the Reoxidation of Direct Reduced Iron under Rising Temperature Conditions. Thermochim. Acta 1993, 228, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.L. Direct Reduced Iron: Technology and Economics of Production and Use; ISS-AIME: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Merki, A.; Rothberger, J.; Millner, R.; Sterrer, W. The New Age of HBI. Available online: https://magazine.primetals.com/2023/02/28/the-new-age-of-hbi/ (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Understanding the Different Direct Reduced Iron Products. Available online: https://gard.no/articles/understanding-the-different-direct-reduced-iron-products/ (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- Hot Briquetted Iron (HBI). Available online: https://www.metallics.org/hbi.html (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Daghagheleh, O.; Schenk, J.; Zheng, H.; Taferner, B.; Forstner, A.; Rosenfellner, G. Long-Term Reoxidation of Hot Briquetted Iron in Various Prepared Climatic Conditions. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 94, 2200535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, H. Die Oxydation Des Eisenschwamms, Die Fakultät Für Bergbau Und Hüttenwesen Der Rheinisch. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Hendry, M.J. Application of Raman Spectroscopy to Identify Iron Minerals Commonly Found in Mine Wastes. Chem. Geol. 2011, 290, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrington, C. Safe Shipment of HBI—HBI C-FLEX Project & IMO Regulatory Update. Available online: https://www.midrex.com/tech-article/safe-shipment-of-hbi-hbi-c-flex-project-imo-regulatory-update/ (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Barrington, C. Hot Briquetted Iron-c-Flex Project: Addressing a Challenge to the HBI Value Chain. Available online: https://www.midrex.com/tech-article/hot-briquetted-iron-c-flex-project-addressing-a-challenge-to-the-hbi-value-chain/ (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Gray, J.; Saha-Chaudhury, N.; Sahajwalla, V. Characterisation and Corrosion of Laboratory Scale Briquettes of Reduced Iron. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HBI C-Flex. Available online: https://hbi-c-flex.eu/ (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- DRI Products and Applications. Providing Flexibility for Steelmaking. Available online: https://www.midrex.com/wp-content/uploads/MIdrexDRI_ProductsBrochure_4-12-18-1.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Ravenscroft, C.; Hunter, R.; Griscom, F. The Versatile OBM (Ore-Based Metallic): Part 2—How to Get What You Paid for: A Guide to Maintaining the Value of DRI. Available online: https://www.midrex.com/tech-article/the-versatile-obm-ore-based-metallic-part-2-how-to-get-what-you-paid-for-a-guide-to-maintaining-the-value-of-dri/ (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Ahmad, J.K. Inhibition of Reoxidation of Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) or sponge iron. Int. J. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2015, 4, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.A. Inhibition of Reoxidation of Direct Reduced Iron. ISIJ Int. 1984, 24, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, I.; Kurniawan, A.; Hasegawa, H.; Kashiwaya, Y.; Nomura, T.; Akiyama, T. Reduction Behaviors and Generated Phases of Iron Ores Using Ammonia as Reducing Agent. ISIJ Int. 2022, 62, 2483–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Bae, J.W.; Kim, S.; Jovičević-Klug, M.; Li, K.; Vogel, D.; Ponge, D.; Rohwerder, M.; Gault, B.; Raabe, D. Reducing Iron Oxide with Ammonia: A Sustainable Path to Green Steel. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2300111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCafferty, E. Effect of Ion Implantation on the Corrosion Behavior of Iron, Stainless Steels, and Aluminum—A Review. Corrosion 2001, 57, 1011–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokai, S.; Kasiwaya, Y.; Matsui, K.; Okinaka, N.; Akiyama, T. Ironmaking with Ammonia at Low Temperature. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, N.; Mochizuki, Y.; Tsubouchi, N.; Akiyama, T. Reduction and Nitriding Behavior of Hematite with Ammonia. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durnovich, D.; Miller, T. The Basics of DRI Plant Safety. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/69da5c8a7bbaf3345542e09e2cf683de/1.pdf?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=1056347#:~:text=Any%20DRI%20at%20a%20temperature,more%20than%20one%20metre%20high.&text=Bins%20and%20silos%20should%20be,inert%20gas%20from%20the%20bottom.&text=Top%20slide%20gates%20should%20be%20closed%20except%20when%20DRI%20is%20being%20delivered (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Djadjev, I. The Evolving Law and Regulation of the Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Sea The IMDG Code and the IMSBC Code. SSRN J. 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.K.; Sah, R. Worldwide Direct Reduced Iron Scenario and Hazards Associated with Their Storage and Shipments. Iron Steel Rev. 2014, 58, 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Direct Reduced Iron (DRI). Available online: https://www.cargohandbook.com/Direct_Reduced_Iron_(DRI) (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Durinck, D.; Gurlit, W.; Muller, F.; van Albada, B. Closing Europe’s Green-Metallics Gap. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/metals-and-mining/our-insights/closing-europes-green-metallics-gap (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Sanjal, S. The Value of DRI—Using the Product for Optimum Steelmaking. Available online: https://www.midrex.com/tech-article/the-value-of-dri-using-the-product-for-optimum-steelmaking/#:~:text=versus%20Charge%20Material-,USING%20DRI,)%2C%20and%20less%20back%20charging (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Voelker, B. Getting the Most from Direct Reduced Iron—Operational Results of MIDREX® Hot Transport-Hot Charging. Available online: https://www.midrex.com/tech-article/getting-the-most-from-direct-reduced-iron-operational-results-of-midrex-hot-transport-hot-charging/ (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Li, J.; Barati, M. Kinetics and Mechanism of Decarburization and Melting of Direct-Reduced Iron Pellets in Slag. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2009, 40, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millner, R.; Rothberger, J.; Rammer, B.; Boehm, C.; Sterrer, W.; Hanspeter, O.; Chevrier, V. MIDREX H2—The Road to CO2-Free Direct Reduction. Available online: https://www.primetals.com/fileadmin/user_upload/landing_pages/2021/Green_Steel/Publications/downloads/AISTech_2021_MIDREX_H2_Final.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- González, O.J.P.; Ramírez-Argáez, M.A.; Conejo, A.N. Mathematical Modeling of the Melting Rate of Metallic Particles in the Electric Arc Furnace. ISIJ Int. 2010, 50, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gyllenram, R.; Arzpeyma, N.; Wei, W.; Jönsson, P.G. Driving Investments in Ore Beneficiation and Scrap Upgrading to Meet an Increased Demand from the Direct Reduction-EAF Route. Min. Econ. 2022, 35, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, A.; Ernst, D.; Zheng, H.; Wimmer, G.; Schenk, J. The Behavior of Direct Reduced Iron in the Electric Arc Furnace Hotspot. Metals 2023, 13, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.D.; Rubén, L.G.; López, F.; Camacho, J.; Romero, J.A. The Slag Foaming Practice in EAF and Its Influence on the Steelmaking Shop Productivity. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birley, R.I. Decarbonising the DRI Feed for EAF Using H2; Materials Processing Institute: Sheffield, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte, S.; Marquis, H.; Dancy, T. The Use of Direct Reduced Iron in the Electric Arc Furnace. In Electric Furnace Steelmaking; AIME, Iron Steel Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1985; pp. 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kieush, L.; Schenk, J.; Koveria, A.; Hrubiak, A.; Hopfinger, H.; Zheng, H. Evaluation of Slag Foaming Behavior Using Renewable Carbon Sources in Electric Arc Furnace-Based Steel Production. Energies 2023, 16, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieush, L.; Schenk, J. Influence of Carbon Material Properties on Slag-Foaming Dynamics in Electric Arc Furnaces: A Review. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 2400235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieush, L. Coal Pyrolysis Products Utilisation for Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes. Pet. Coal 2019, 61, 461–463. [Google Scholar]
- Kurecki, M.; Meena, N.; Shyrokykh, T.; Korobeinikov, Y.; Jarnerud Örell, T.; Voss, Z.; Pretorius, E.; Jones, J.; Sridhar, S. Recycling Perspectives of Electric Arc Furnace Slag in the United States: A Review. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 2300854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memoli, F. Behavior and Benefits of High Fe3C-DRI in the EAF. Iron Steel Technol. 2019, 2, 1928–1945. [Google Scholar]
- Lule, R.; Lopez, F.; Espinoza, J.; Torres, R.; Molares, R.D. The Production of Steels Applying 100% DRI for Nitrogen Removal, the Experience of ArcelorMittal Lazaro Cardenas Flat Carbon. In Proceedings of the AISTech 2009—Iron and Steel Technology Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 4 May 2009; Volume 1, pp. 489–498. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, S.K.; Lele, A.B.; Pancholi, N.K. Studies on Direct Reduced Iron Melting in Induction Furnace. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2004, 57, 467–473. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.; Kotelnikov, G.; Abdelwahed, H. Melting Characteristics of Alternative Charging Materials in an Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhao, J.; Pistorius, P.C. MgO Refractory Attack by Transient Non-Saturated EAF Slag. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Park, J.H. Interfacial Reactions between Magnesia Refractory and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Slag with Use of Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) as Raw Material. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 4526–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Park, J.H. Effect of Temperature on the Slag/Refractory Interfacial Reaction with Directed Reduced Iron (DRI) Addition in an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Process: Diffusional Growth of Magnesiowüstite Layer by Boltzmann-Matano Analysis. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 17217–17224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, E.W.; Hazeldean, G.S.F.; Davies, M.W. Visualization of Slag-Metal Reactions by X-RAY Fluoroscopy: Decarburization in Basic Oxygen Steelmaking. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1973, 211, 632–639. [Google Scholar]
- Min, D.-J.; Fruehan, R.J. Rate of Reduction of FeO in Slag by Fe-C Drops. Met. Trans. B 1992, 23, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.A.; Fruehan, R.J.; Oztruk, B. The Behaviour of DRI in Slag-Metal Systems and Its Effect on the Nitrogen Content of Steel. Iron Steelmak. 1999, 26, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, E.; Barati, M. The Reaction Behavior of Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) in Steelmaking Slags: Effect of DRI Carbon and Preheating Temperature. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2010, 41, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiasaraei, E.S. Decarburization and Melting Behavior of Direct-Reduced Iron Pellets in Steelmaking Slag. Master’s Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, G.G.K.; Sawada, Y.; Elliott, J.F. Reduction of FeO Dissolved in CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 Slags by Fe—C Droplets. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1993, 20, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Sadrnezhaad, K. Direct Reduced Iron: An Advantageous Charge Material for Induction Furnaces. J. Eng. 1990, 3, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
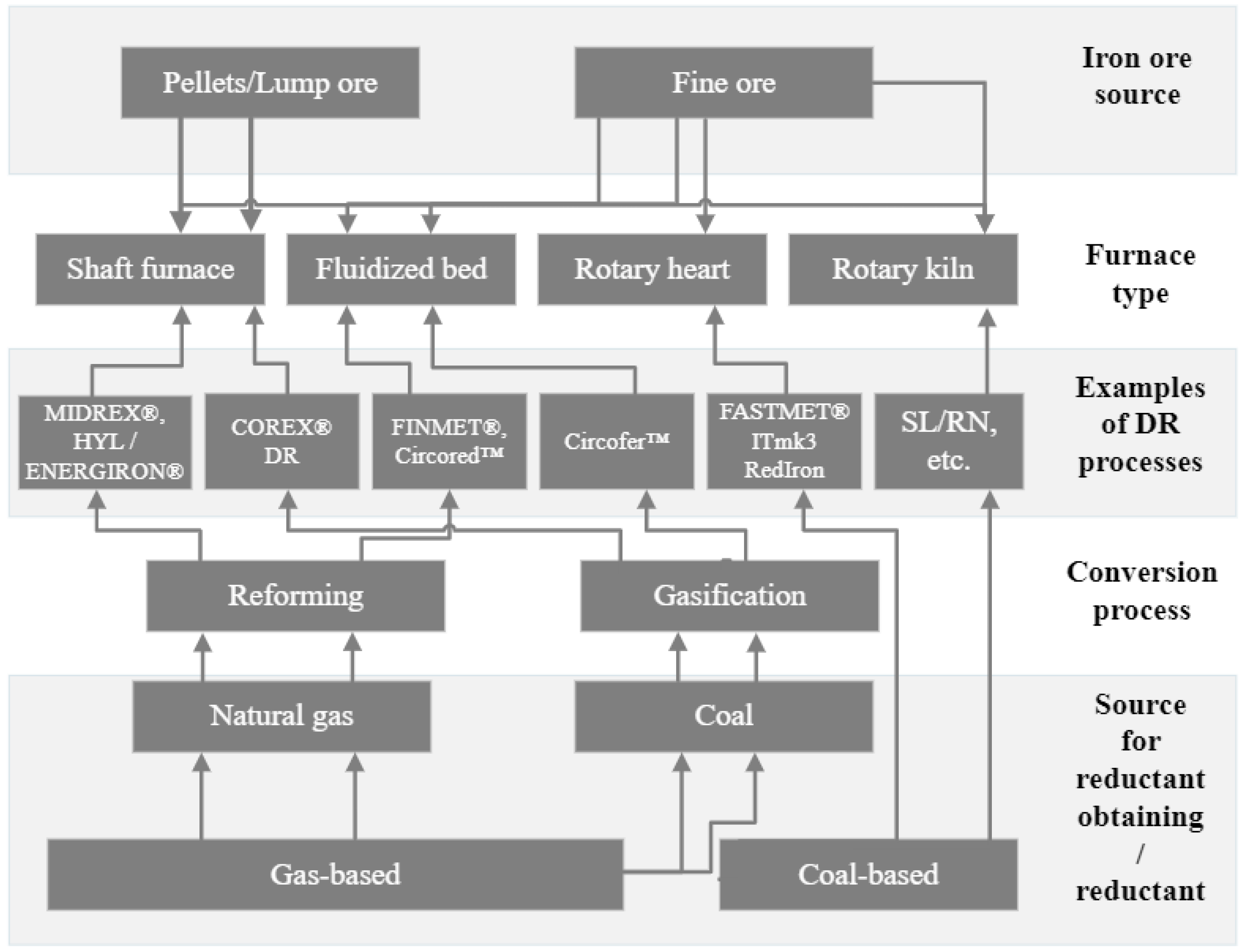









| Furnace Type | Form of Reactant (Iron Ore) | Reductant | Short Description of the Process | Advantages | Disadvantages | Metallization Degree of the Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaft furnace | Lump, pellets | Converted NG, syngas, H2 | A vertical furnace in which iron ore pellets or lumps are charged at the top, and reducing gas flows upward, reducing the iron oxides to iron. It relies on solid-gas reactions at high temperatures. | Large production capacity. High product quality. | Ore in pellet form should have a minimum of 67% Fe content. High cost of reducing gas. | ≥92% |
| Fluidized bed | Fines | Converted NG, syngas, H2 | Iron ore particles are suspended in an upward-flowing stream of reducing gas, promoting high mass and heat transfer. Using a fluidizing medium enhances the reaction kinetics by increasing the contact surface area between the reducing gas and the iron ore particles. | Iron ore fines can be used without pelletizing and agglomeration. Fast reaction rate. | Complex structure of reactors. Particle sticking tendency. | ≥92% |
| Rotary kiln | Lump, pellets | Coal (5–20 mm) and recycled char | A kiln is a rotating cylindrical vessel through which lumps or pellets, along with coal or gas as a reductant, are passing. The kiln is slightly inclined to assist material flow. Reduction occurs in solid and gaseous phases; the rotating action promotes mixing and contact between ore and reducing agents, enhancing the reduction process. | Various types of coal can be used. Processing low-grade ores. Flexible structure of the reactor. | Significant levels of impurities, including sulfur. Slow reaction rate. Significant energy usage. Problems with kiln lining agglomeration. | ≥90% |
| Char, coal | ||||||
| Rotary hearth furnace | Composite pellets (16–22 mm) | Coal (70% below 45 µm) | A flat, refractory-lined furnace that rotates, carrying the iron ore and carbon mixture through different temperature zones for reduction. Direct reduction occurs in a solid state, with heat supplied predominantly by radiation from overhead burners, facilitating rapid heating and reduction. | Processing low-grade ores or iron-containing by-products. Simple structure of furnace. | Significant levels of impurities, including sulfur. High CO2 emissions. | ≥93% |
| Composite pellets | Coal |
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Fetot, wt.% | ≥67.0 |
| SiO2, wt.% | 1.0–3.0 |
| Al2O3, wt.% | 0.2–3.0 |
| MgO, wt.% | 0.2–0.9 |
| CaO, wt.% | 0.4–1.2 |
| Sulfur, wt.% | ≤0.008 |
| Phosphorus, wt.% | ≤0.03 |
| Pellet size, mm | 9.0–16.0 |
| Porosity, % | ~50.0 |
| Compression strength, N | 2500–3000 |
| Tumble index, % + 6.15 mm | 92.0–95.0 |
| Reducibility index, % | 92.0–95.0 |
| m−3 | |
| bulk | 1.6–1.9 |
| apparent | ~3.5 |
| Characteristics | Range, wt.% |
|---|---|
| Metallization degree | 92.0–96.0 |
| Fetot | 86.1–94.0 |
| Femetal | 81.0–89.0 |
| Carbon content | 0.02 *–4.5 |
| Sulfur content | 0.001–0.03 |
| Phosphorus content | 0.001–0.09 |
| Gangue | |
| Acid | 2.5–7.6 |
| Basic | 0.5–2.7 |
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Bulk density, t∙m−3 | 1.5–1.9 |
| Apparent density, t∙m−3 | 3.2–3.6 |
| Specific surface area, m2∙g−1 | 0.5–4.0 |
| Volumetric porosity, vol.% | ~47.0 |
| Average size, mm | 4.0–20.0 |
| Weight, g | 3.0–4.0 |
| Water absorption (saturated), % | 12.0–15.0 |
| Fines (−4 mm), % | ~5.0 |
| Characteristics | HBI |
|---|---|
| Bulk density, t∙m−3 | 2.4–3.3 |
| Apparent density, t∙m−3 | 5.0–5.5 |
| Specific surface area, m2∙g−1 | ~0.75 |
| Volumetric porosity, % | ~21.0 |
| Weight, g | 500.0–700.0 |
| Water absorption (saturated), % | ~3.0 |
| Fines (−4 mm), % | 1.0–3.0 |
| Production Parameters | 100% Scrap | 80–95% DRI |
|---|---|---|
| Share of DRI/HBI, % procedures | 0–5 (HBI) | 60–95 (DRI) |
| Electric energy demand, kWh∙t−1 | 310–460 | 530–680 |
| Natural gas, m3∙t−1 | 3–10 | 0–2 |
| Oxygen, m3∙t−1 | 25–40 | 20–35 |
| Coal and carbon fines, kg∙t−1 | 2–9 | 8–17 |
| Slag former, kg∙t−1 | 23–35 | 27–60 |
| Tap temperature, °C | 1600–1635 | 1600–1635 |
| Tap-to-tap time, min | 50–60 | 60–100 |
| Metal yield, % | 90–94 | 87–92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kieush, L.; Lesiak, S.; Rieger, J.; Leitner, M.; Schmidt, L.; Daghagheleh, O. Reoxidation Behavior of the Direct Reduced Iron and Hot Briquetted Iron during Handling and Their Integration into Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking: A Review. Metals 2024, 14, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14080873
Kieush L, Lesiak S, Rieger J, Leitner M, Schmidt L, Daghagheleh O. Reoxidation Behavior of the Direct Reduced Iron and Hot Briquetted Iron during Handling and Their Integration into Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking: A Review. Metals. 2024; 14(8):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14080873
Chicago/Turabian StyleKieush, Lina, Stefanie Lesiak, Johannes Rieger, Melanie Leitner, Lukas Schmidt, and Oday Daghagheleh. 2024. "Reoxidation Behavior of the Direct Reduced Iron and Hot Briquetted Iron during Handling and Their Integration into Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking: A Review" Metals 14, no. 8: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14080873
APA StyleKieush, L., Lesiak, S., Rieger, J., Leitner, M., Schmidt, L., & Daghagheleh, O. (2024). Reoxidation Behavior of the Direct Reduced Iron and Hot Briquetted Iron during Handling and Their Integration into Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking: A Review. Metals, 14(8), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14080873








