Abstract
An increasing focus has been placed on clean energy, carbon neutrality, carbon footprint monitoring, and adaptation of building information modeling (BIM)-based facility management (FM). Hence, there is also a growing demand to evaluate and prioritize which BIM applications are the most relevant to FM and are the most beneficial in the asset lifecycle, particularly in the operations stage. To inform BIM-FM application on smart hospital management, this research introduces a one-systems method through an interpretive structural model (ISM) to establish a structural contextual interrelationship between BIM uses in the operations stages of the asset. Through a literature review, this research first summarizes facility management functionalities achievable by BIM-FM and establishes their pairwise contextual relationship. A structural self-interaction matrix (SSIM) is then established, followed by partitioning these functionalities into separate levels to form the ISM model, while using driving power and dependence to form a MICMAC analysis matrix. The finding that the BIM uses “Environmental Monitoring and Building Performance” is the foundation that enables the other functionalities whilst validating that ad-hoc operations and maintenance activities enablement has the highest driving power, and automation and robotics have the highest dependency. Among the applications, energy monitoring plays a pivotal and transitional role with a strong dependency between airflow monitoring and solar monitoring, while its performance would directly impact emergency responses.
1. Introduction
Recent trends in energy monitoring toward carbon neutrality necessitate further investigation into energy optimization goal adoption, as well as digital innovative tools that can aid in measuring and achieving such goals. In the healthcare sector, with the increasing complexity of medical facilities, there is increased interest in using tools, such as building information modeling (BIM), to aid energy use and energy cost monitoring [1]. As energy use drives other building systems, their intertwining relationships are worth investigating and clarifying via a structural and relational approach.
A further complication that can be perceived as an opportunity is the digital twinning trend in the context of digital transformation in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. Digital twinning, as a concept, has been widely adopted by various industries in an attempt to optimize the design and simulate performance in a time- and cost-effective way, among other benefits, by adopting the virtual tool prior to, or in parallel with, physicalizing a construct [2]. The adoption of building information modeling (BIM) technology to aid digital twinning has resulted in its rapid adoption and incentives for further technological inputs and developments [3,4,5]. An increasing and expanding set of advantages has been harvested in academia and research beyond serving individual parties or technical practitioners; innovators, decision-makers, and thought leaders have all started to realize measurable benefits from optimizing and extending their BIM use regarding practicability [6]. With further technological developments, there is a trend to expand BIM uses beyond its originally conceived uses in the design and construction stages. There is increasing BIM application in the lifecycle, namely the preparatory planning stage and operations stage subsequent to construction completion. In the operations stage, BIM largely embodies asset management (AM) and facility management (FM). This trend covers multiple industries, such as manufacturing and technology; in the medical field, hospitals have seen a rapid rise in this application of BIM-enabled and IoT-linked digital twinning [7,8,9].
The COVID-19 pandemic, among other unexpected outbreaks, including Ebola and monkeypox, necessitated more aggressive application of digital twin-based technologies. These technological advancements for the built environment aim to prevent, contain, and mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic caused by a transmissive virus. Expediency to deploy solutions has become ever more pressing to combat the airborne nature of this pathogen that targets the human respiratory system. While the pandemic subsided as of mid-2022, its confirmed cases and the death toll have seemingly reached a plateau; faster solutions have yet to be discovered and implemented, irrespective of past warnings from those studying trends to forecast the future [10]. The uncertainties associated with future mutations and the capability of systematically monitoring the disease, infected individuals, and environment have led to a call for more systematic asset management (AM) and facility management (FM) strategies in the smart hospital’s lifecycle.
Prior research has established that BIM can facilitate the IoT and CPS among the top smart hospital management constructs. The current application of BIM beyond building-IoT mainly focuses on mapping sensors to building systems in a 3D visualized and interactive environment [11]. BIM’s ability to support digital twinning within CPS makes it a primary tool. With the ability to sense, record, monitor, and act, the interdisciplinary applications are linked through the equipment, platform, and management functions [12]. The complexities involve calls for further research in the specific context of COVID-19, where the three major demands of IoT exist. First, the need to monitor and improve indoor air quality, as related to the airborne nature of COVID-19, through air pressure and flow. Second, the control and prevention of proximity and touch between humans, who are the primary carriers of the pathogen, as related to patient traffic control and inhabitant identification and sorting. Third, the gathering and processing of spatial information related to medical staff’s other functional needs that may directly or indirectly relate to patient treatment and research.
In addition to the gaps in literature focused on holistic smart hospital management, other research gaps exist. Some research and reviews are from the perspective of users (hospital/patient) instead of exploring the latest available technologies. The majority of research is heavily focused on the equipment aspects. Most importantly, there is a lack of focused research on the integration of BIM-enabled digital twinning with IoT management platforms for smart hospitals that can specifically address COVID-related needs. Overall, there is a lack of comprehensive instructions on the most critical functionalities for a graphical and cloud-based system that could utilize BIM as the backbone technology.
This research focuses on establishing causal relationships between BIM uses and AM and FM. The research questions are as follows:
- Based on current literature, what are the BIM-FM applications, and how should they be categorized?
- How do these BIM-FM applications relate to each other? How do they enable or depend upon each other in a structural, layered matrix, and what are the levels of dependencies?
The research is structured as follows. After introducing the research in Section 1, Section 2 contains literature reviews pertaining to smart buildings and hospitals, BIM-based facility management (FM), and information management systems/platforms. In Section 3, the interpretive structural model (ISM) research methodology is introduced. Two steps of the quantitative studies are conducted: first, ISM was used to synthesize the relationship between BIM applications for smart hospital design. Then, the MICMAC analysis was conducted to further clarify the relationships between applications and factors. Section 4 discusses the results from previous chapters, followed by Section 5, which concludes the research.
2. State of the Art Review and Background
Prior to applying any methodology, a literature review is key to establishing factors, criteria, or applications. In the context of this research, a comprehensive list of applications in building information modeling-aided facility management (BIM-FM) was compiled through a literature review. Prior research publications that were SCOPUS-indexed, in particular papers from higher-impact journals, were included in the built environment. A few book chapters were referenced to support the BIM trends in the industry. In order to first understand the overall context and applications, keywords were used that combined BIM, facility management (FM), asset management (AM), building operations and maintenance, and smart building. Further focus was placed on AM over FM because the literature review revealed that the former encompasses the latter. Hence, prior research on FM and AM was reviewed and considered. In order to cover healthcare, in particular hospital facility management, smart building was first used as the search keyword, while smart hospital, clinic, and healthcare facility were added in the next step. To stay up-to-date and relevant to the BIM-FM focus of this research, the results were then filtered to prioritize the literature within the last five years while considering key literature from the past ten years.
2.1. Building Information Management in Facility and Asset Contexts
Building information modeling (BIM) is defined internationally as a shared digital representation; BIM is founded on open standards that support interoperability [13]. BIM is widely used in the construction industry for design, construction, and asset management, with 75% of construction firms in North America using BIM for project design and construction, while 50% use BIM for facility management [14].
In recent years, BIM has been increasingly utilized beyond the design and construction stage for which the technology was first developed. There is an increasing realization that the design and construction stages are only a short timeframe within the lifecycle of the built structure. The research focus has therefore shifted toward extending BIM’s application for facility management (FM) practices on services of lifecycle asset management (AM) [6,15,16]. It is important to distinguish facility management (FM) and asset management (AM) as two related yet distinct disciplines: the former is a subset of asset management, focusing on the physical facilities and infrastructure of an organization, while the latter encompasses a broader range of assets which include two types (i.e., physical and intangible) and focuses on maximizing their financial and operational performance over time [17,18,19]. Facility management refers to the management of physical assets and the infrastructure of a facility, such as buildings, equipment, and utilities, to ensure their proper functioning and maintenance, with tasks such as managing building operations and maintenance, ensuring compliance with safety and environmental regulations, managing energy and utility consumption, and overseeing the use of space within a facility. Meanwhile, asset management focuses on managing the financial and operational performance of an organization’s assets, including physical assets such as facilities and equipment, as well as intangible assets such as intellectual property and brand reputation, from acquisition and maintenance to eventual disposal or replacement, to ensure that they provide maximum value to the organization.
BIM is becoming more common in manufacturing as more companies adopt digital technologies for plant design and operations. According to an article in Control Engineering, “Using BIM for Manufacturing Plant Design,” BIM can help manufacturers optimize their space use, reduce energy usage, and improve overall asset performance. In educational contexts, BIM is used in education for asset and space management, as well as sustainability initiatives. According to an article in EdTech Magazine, “How BIM is Making College Campuses Smarter,” BIM can help educational institutions track and manage their assets, optimize their use of space, and reduce their energy usage.
BIM is also increasingly used in healthcare facilities for asset, space, and compliance management. According to a case study by the National Institute of Building Sciences, “BIM for Healthcare Facility Management,” BIM can help healthcare facilities track and manage their equipment and supplies, optimize their use of space, and ensure compliance with regulations and standards [20]. Overall, BIM-FM offers a range of applications that can support more efficient and effective management of buildings and infrastructure throughout their lifecycle, from design and construction to operation and maintenance.
2.2. BIM, CPS, and IoT Applications in Smart Buildings and Hospitals
As BIM contains geometric information and non-geometric capabilities, the former contributes to the ability to visualize the designed and built conditions predictably, while the latter allows further categorizing and measuring using embedded attributes [21,22]. In the United Kingdom, for example, the National BIM Society has designated BIM applications on physical asset management as a major component and focus of the continually guiding UK BIM Framework [23]. The Singapore government has also provisioned a grant to further research and implementation of integrated facilities management (IFM) and aggregated facilities management (AFM) to acknowledge the trend and transformation shift in how buildings are maintained [24].
Upon construction completion, in a real estate context, BIM has been recognized as an effective tool for asset and space management to optimize their use of space, track occupancy trends, and manage energy usage [25]. There are virtually limitless numbers and types of attributes that can be incorporated (including numbers/counts and measurements). Recent research on BIM applications for smart hospitals has ranked the internet of things (IoT) and cyber-physical system (CPS) as more important constructs, and BIM is a valid alternative vetted by industry experts to address smart hospital management under COVID-19 [26]. Various types, forms, and complexities of BIM-integrated IoT platforms exist with varying capabilities to serve data repository, security/monitoring, and communication functions [27]. IoT-based wearable devices can monitor patient status even outside the smart hospital premises [28]. Based on the principles of CPS, there is increasing research on BIM-FM (building information modeling for facility management)—a process that involves the use of BIM software and related technologies to support the management and operation of buildings and infrastructure throughout their lifecycle. The CPS technology can be seen as the backbone for digital twinning, which is a virtual replica of a physical asset or system, such as a building, machine, or entire manufacturing process, which simulates the behavior and performance of physical assets and systems, such as predictive maintenance, performance optimization, and simulation testing [29].
2.3. BIM-FM Information Management Functionalities
For asset and facility management during the operations stage, BIM-FM can be used to create a comprehensive database of all assets within a building or infrastructure, inclusive of each asset’s specifications, location, and maintenance history. This information can be used to track and manage assets throughout their lifecycle, enabling more effective maintenance and replacement planning. Recent key research has demonstrated the potential benefits of BIM for asset management in buildings and infrastructure, including improved asset tracking, reduced maintenance costs, and extended asset lifespan. Wong et al. (2014) demonstrated the benefits of using BIM for asset management in public buildings; the study found that BIM can help beyond client satisfaction and achieve end user-oriented sustainability key performance indicators (KPIs) for flexibility and integration [30]. Guillén et al. (2016) explored the use of BIM for asset management in the operation phase of construction projects. They found that BIM can help improve asset identification and tracking, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall asset performance [31]. Sacks (2018) also provides guidance on using BIM for asset management in buildings and infrastructure by highlighting the benefits of BIM for more accurate and less time-consuming asset tracking, maintenance planning, and sustainability [16].
2.3.1. Operations and Maintenance Activities
In current facility management trends, trigger event-based methodology is prevalent in today’s operations framework. BIM-FM can be used to track the maintenance history of individual assets within a building and to schedule and plan routine maintenance tasks. This information can improve maintenance efficiency, reduce downtime, and extend the assets’ lifespans [16,32].
In addition to scheduled activities, there are oftentimes ad-hoc operations and maintenance stemming from natural disasters (earthquakes, hurricanes, typhoons), accidents (fires, flooding, gas leaks, building system failures), and similar unforeseeable and unplannable incidents. BIM-FM, which is object-based and visualizable, can enable such activities [33]. These activities, whether planned (scheduled) or triggered (ad-hoc), can be recorded and paired to objects or spaces within a BIM-based FM database to enable a spatial relationship [34,35].
2.3.2. Environment and Resources
For space management and to monitor the built environment and building performance, BIM can be used to create a detailed 3D model of a building, including its internal spaces and their uses. This information can be used to optimize space utilization, track occupancy and occupancy trends, and plan for future changes to the building layout. By connecting with IoT sensors and a building management system (BMS), the information collected by sensors can be centrally stored and matched with BIM objects or space planning (e.g., rooms) [34].
Regarding energy monitoring and management, BIM-FM can be used to model and simulate energy usage within a building and to identify potential areas for energy savings. This information can be used to optimize energy usage, reduce costs, and improve building sustainability. By extension, the energy usage in the building, in particular electricity and sometimes natural gas pipeline, can be consolidated and tracked [36,37,38]. Furthermore, solar energy is a sustainable energy source, and evaluation is critical in the ESG context and carbon neutrality. It has become a key energy use category to keep track of, while lighting, air, and water are the three main elements of building wellness. The monitoring of airflow and water through heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems and water meters are also mainstream applications in environmental monitoring within buildings [34,39].
2.3.3. Static Equipment and Documents
In addition to activities and environmental conditions that continue to occur within a facility, recent trends show an increasing desire to optimize the potential of BIM-FM. The BIM-AM’s function is focused on asset data and associated documents [17]. Equipment and document management have been mandatory facility management applications, and building into the BIM-FM context, they are more prevalent and interconnected as BIM is object-based, and unique codes can connect BIM objects/spaces, equipment, and documents, whether directly into BIM models or through database mapping [40].
2.3.4. Medical Services, Automation, and Robotics Management
In the smart hospital context, medical services management is mandatory. Different literature shows various findings as to how interconnected medical services management and facility management should be. Yang et al. (2021), while researching environmental monitoring and building performance in the BIM-FM context, posited that medical services management integration should be comprehensively considered, as both can leverage BIM–IoT integration in the smart hospital context based on the example of particulate matter monitoring [41]. Dadhich et al. (2022) found that an IoT-based e-health management system boasts co-managing medical services and the physical space of healthcare facilities [42].
Automation and robotic development are also emerging topics of investigation in the smart hospital or healthcare facility context. Dong et al. (2020) and Tang et al. (2019) mentioned but did not prioritize automation and robotics [37,39]. Zhang and Navimipour (2022) more specifically investigated the applications’ relationships with other applications [35]. Chen et al. (2023) further established a strong relationship between robotics’ role in knowledge accumulation and dissemination in the BIM-aided facility management context [43].
2.3.5. Security and Emergency
For compliance and security management, BIM-FM can be used to track and manage compliance with relevant regulations and standards, including health and safety, environmental, and accessibility requirements. This information can be used to reduce compliance risks and ensure that buildings and infrastructure are safe and accessible for all users [35,37].
Previous research has aimed to establish the relationship between emergency response and building performance monitoring. Bi et al. (2022) presented a more comprehensive system to aggregate data on the flow of pedestrians, energy, and information to enhance the performance of an emergency response system that can assist in emergency evacuation [44]. Kang et al. (2023) also pointed out that monitoring infrastructures has a measurable impact on emergency responses [45]. However, insufficient literature has directly investigated the healthcare sectors’ adoption of monitoring systems directly related to dealing with emergencies. The current research, therefore, aims to seize the opportunity to investigate further and discover whether and how a relationship may exist.
2.3.6. Cost Management
One of the key points of facility or asset management lies with the cost implications [32]. The operational costs involved with smart hospitals’ facility management includes cost of human resources (employees), natural resources (energy, water, etc.), and other costs. In sum, operational costs are related to facility management of the hospital beyond the physical building and assets [46].
Meanwhile, the maintenance costs are closely associated with asset management in the context of the overall facility management. As each asset has its expected life, sooner or later they must be replaced. According to the S-P-I-D-F safety reliability theory, an asset goes through a curve by connecting the following key points: specify, design, installation, potential failure, and failure [47]. Within the potential failure to failure periods, repair (or eventually replacement) of said asset is imminent, resulting in cost implication to the asset owner or asset operator.
2.4. Interpretive Structural Model
First introduced by Warfield in 1976, the interpretive structural model (ISM) is an agile and widely used approach used by researchers in supplier selection, knowledge management, green supply chain management, and energy conservation fields. ISM is a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) method used by strategic decision-makers in various organizations [48]. Interpretive structural modeling (ISM) is a tool used to analyze complex relationships among factors and variables in a system or organization. ISM involves a group of experts who identify and analyze the relationships among the factors or variables and then construct a hierarchical model that represents the relationships among them. The model can be used to identify the most important factors or variables and their impact on the system and to develop strategies for improving the system’s performance. ISM seeks to identify/construct relationships between factors that affect decision-making when a particular problem arises. It solves the problem by considering the driving and dependent forces of each factor. The interrelationships among the factors are determined by experts and thereafter define the ISM framework [49].
ISM is used to analyze complex relationships among factors or variables in a system, while the Delphi method is used to synthesize expert opinions on a particular topic or research issue. Compared to structural equation modeling or the Delphi method, fewer experts are required. As ISM is used to create models for dealing with decision-making problems, the selection of experts is important to ensure research integrity. The Delphi method is a structured process for gathering and synthesizing expert opinions, which involves a group of experts who are asked to provide their opinions on a series of questions, often through a series of iterative rounds of questioning and feedback. The results of each round are summarized and fed back to the experts in the subsequent round to reach a consensus or convergence of opinions on the topic. In sum, ISM and the Delphi method differ in terms of the level of detail and complexity of the analysis. They involve different levels of interactions among the experts’ opinions [50].
ISM is also seen as more appropriate than another widely-used method—DEMATEL. While the DEMATEL method focuses on causality—the comparison of cause-and-effect relationship between various decision criteria in large numbers—ISM focuses on clarifying the multi-level hierarchy by breaking down the previously entangled and unclear elements of a complex problem into smaller and more manageable parts, with a focus on the hierarchy levels after clarification. This is evident in recent research that combines ISM with other MCDM methods, such as DEMATEL, to enhance the latter [51,52].
In recent years, ISM has been used in research on BIM and related technologies. Despite current advancements in BIM, as summarized in Section 2.1, BIM has only become a mainstream tool in the U.S.A. and European countries in the past ten years and has not fully matured around the world. There has been increased research using ISM to investigate prohibitive factors of BIM implementation, with few studies enabling aspects of BIM. Tan (2019), Farooq et al. (2020), and Saka (2020) investigated barriers to BIM implementation in organization and industry; these studies have been region- and industry-specific, focused on China, Pakistan, and SMEs, respectively [53,54,55]. Shore and Chileshe (2021) used ISM-MICMAC to analyze the AEC industry’s design and construction changes and impacts related to BIM [56]. Sun et al. (2020) studied the risk factors surrounding BIM implementation, in which BIM was viewed as the cause rather than the result [57]. On more optimistic notes, other contemporary research has focused on interrelationships between enabling factors of BIM implementation. Abbasnejad (2021), Likhitruangsilp et al. (2019), and Ma et al. (2019) endeavored to map enabling relationships between factors contributing to BIM proliferation [58,59,60].
This research takes on a novel approach. Rather than focusing on the much-discussed barriers or enablers, this research aims to fill the research gap relating BIM uses to each other and facility management (FM).
3. Methodology
In reviewing recent research on BIM-FM applications, six categories and more than ten applications were deduced. The wide number of these individual applications lacks a structural correlation in a holistic hierarchical relationship. This gap is in theory and practice, and the lack of indication of priority calls for a quantitative and structural approach. Further to the literature review in Section 2.4 on ISM methodology, when addressing interdisciplinary and wide-ranged topics, ISM is superior to the Delphi method and DEMATEL when dealing with the specific multi-factor hierarchy problem.
Based on the conventional and unmodified ISM approach, this research follows six major steps, as shown in Figure 1 below.

Figure 1.
ISM methodology process (drawn by this research).
3.1. Summary of FM Applications
Summarizing literature review results from Section 2, fifteen (15) major applications are shown in Table 1 below. The black bullets indicate the IoT-based BIM-FM application(s) applicable to each prior research.

Table 1.
IoT-based BIM-FM applications: summary of literature.
3.2. Expert Congregation
Fifteen expert interviews were conducted, followed by desktop analysis where necessary to identify the most critical factors and their interrelationships. Table 2 below provides demographic information for the experts. The experts all currently hold BIM-related positions in the industry, have cross-discipline experience with at least two discipline involvements, and have at least five years of BIM experience. To minimize misunderstanding of interview questions, which are in English, through currently working in different parts of the world, all experts use English as their daily working language. All experts have worked on at least one medical project, so they have a basic understanding of the design and construction requirements for a healthcare facility.

Table 2.
Interviewee demographics.
Each interview lasted approximately one hour; each interviewee was given a brief description and overview of the research beforehand. Interviewees were first asked about their understanding of each of the fifteen factors to ensure an aligned baseline. Follow up questions served to ensure completeness of responses to the interview questions.
3.3. Reachability Matrix and Conical Matrix
From the interviews, an enabling relationship matrix was established as the structural self-interacted matrix (SSIM) in Table 3 below. The leftmost column (i) and the top row (j) each contain the fifteen applications distilled from the literature review. The following four abbreviations indicate one relationship between the two applications:

Table 3.
Structural Self Interaction Matrix (SSIM).
- V—application i enables application j
- A—application j enables application i
- X—applications i and j enable each other
- O—applications i and j are unrelated
The reachability matrix was calculated by evolving the matrix into binary (0 and 1) terms for calculation. To arrive at the conical matrix, the driving power of each application was calculated by summing the numbers in each row and dependence power by summing the numbers in each column. The results are shown in Table 4 below.

Table 4.
Reachability Binary Matrix and Conical Matrix.
Various manual and computer-aided methods exist to analyze the results from the two matrices (i.e., reachability binary and conical) with respect to the academic lineage from Warfield and the subsequent custodians, Broom and Hogan, who authored and made available the Windows ISM software (WINISM) for researchers wishing to conduct ISM analysis in accordance with Warfield’s method [61]. Considering the popularity of the Windows operating system (OS) over other desktop and laptop OSs, WINISM was selected over its predecessor operating on Microsoft Disk Operating System (MS-DOS). After running WINISM, the level partitions of the reachability matrix is shown in Table 5 below.

Table 5.
Reachability Matrix–Level Partitions.
3.4. Forming the ISM Model
The reliability matrix stemming from WINISM analysis can be further simplified into seven hierarchical levels, each with one (1) to four (4) applications. This summarizes the complicated interrelationship between each application into clear top-down levels in preparation for the second-to-final step of graphically illustrating the hierarchy as indicated in Table 6 below.

Table 6.
Hierarchal levels and applications at each level.
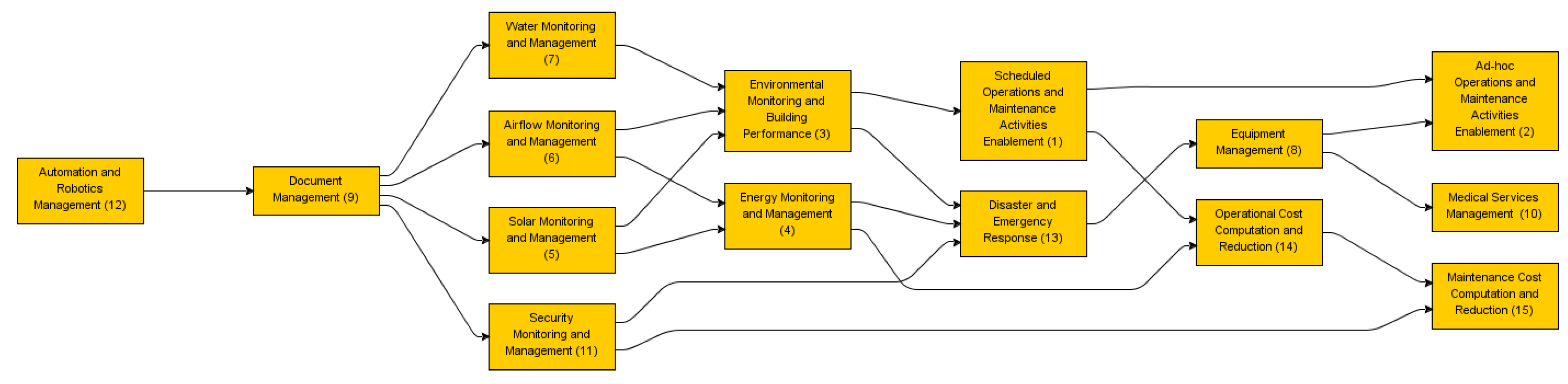
Upon preliminary analysis assisted by the WINISM software and its graphical output, further elaboration was conducted to clarify the root enablers. This diagrammatic analysis serves to distinguish the six level as well as the indirect relationships between the applications. The resulting ISM model is presented in Figure 2 below.
Figure 2.
Preliminary ISM model (generated by this research using WINISM).
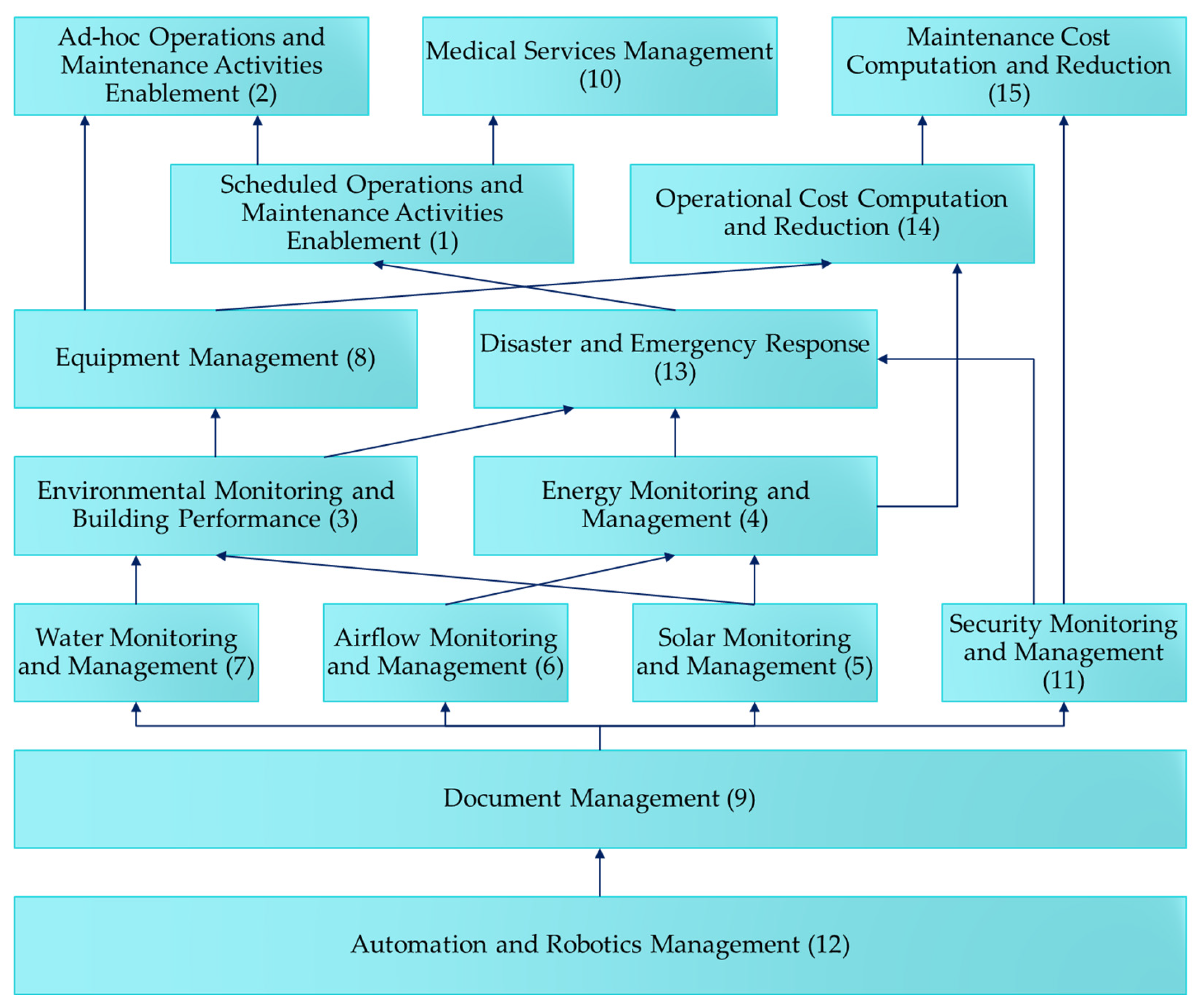
Alternative to the horizontal left-to-right expression, the preliminary model was deduced to visualize the driving and dependency relationship from the bottom up. The drivers, i.e., automation and robotics management (12), are of the highest driving power on level seven, whereas ad-hoc operations and maintenance activity enablement (2), medical services management (10), and maintenance cost computation and reduction (15), are of the highest dependency power on level one. Figure 3 below provides a further consolidated illustration of the elaborated ISM model.
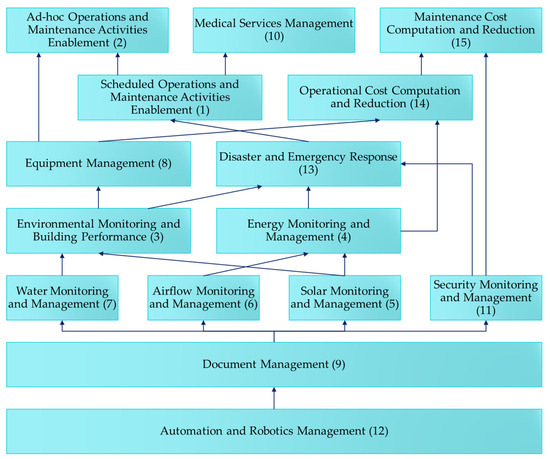
Figure 3.
Elaborated ISM Model (drawn by this research).
4. Results and Discussion
This research utilizes the ISM methodology, which aims to inform causal and enabling relationships between factors in a complex, non-linear situation. In the context of BIM-FM applications for smart hospitals, fifteen factors summarized from the literature review were analyzed to form the research matrix; a few findings regarding structural relationships, causality, and priority have surfaced.
4.1. MICMAC Analysis Matrix
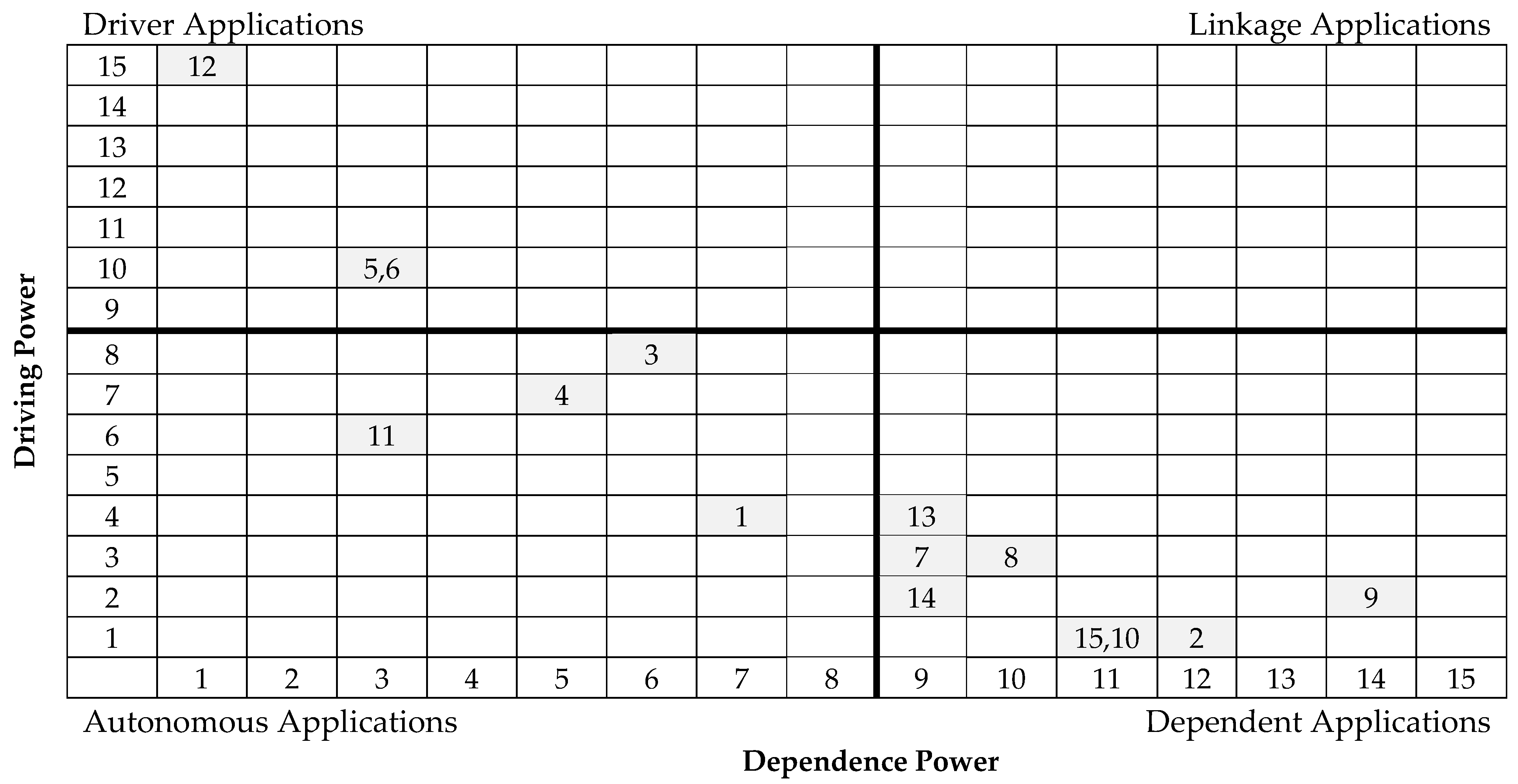
The purpose of the MICMAC analysis (in French: Matrice d’Impacts croises-multiplication appliqúe an classment; meaning cross-impact matrix multiplication applied to classification) is to analyze the drive power and dependence power of constructs or factors (and in this research enabling applications). Commonly accompanying the ISM methodology as its last step, the MICMAC principle is based on the multiplication properties of matrices used to identify the key factors that drive the system in various categories [56,62]. While ISM focuses on organizing various factors/applications into a single and relatively pyramidal hierarchy, the results are expanded back into the two-dimensional matrix of the driving-dependent and linking-autonomous dichotomies through MICMAC analysis. Based on their drive power and dependence power, the factors were classified into four categories (i.e., autonomous, linkage, dependent, and independent factors).
Graphically and in a two-by-two matrix, the resulting ISM model is presented in Figure 4 below.
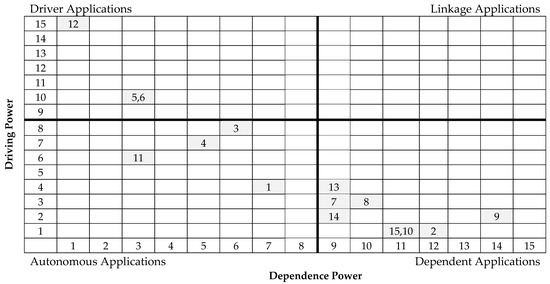
Figure 4.
MICMAC Analysis of BIM-FM Applications (drawn by this research).
4.2. Overall Structure of Dependencies
Within IoT-based monitoring and management, while the practical methodologies are similar, the causal relationship indicates that two major tiers exist. The upper tier contains water, airflow, and solar power monitoring, all of which feed into environment and energy monitoring. More importantly, consistent with prior literature, this dependency demonstrates the importance of monitoring the energy consumption of various building systems and renewable energy generation as a way of offsetting the energy costs as mentioned in previous studies [1,38,44,63].
The monitoring of security systems, which could involve IoT integration of CCTV, infra-red scanning, and alert systems, is seemingly parallel to the monitoring of first-tier environmental factors (water, airflow and solar). However, rather than contributing to environmental and energy monitoring, security system monitoring directly informs disaster and emergency responses in tier 5 and directly enables maintenance cost computation and reduction in tier 7. This outcome supports the previous research by Tang et al. (2019) and further clarifies the causality relationship between these applications [36].
The applications with lower dependent power can be carried out relatively independently. For example, corresponding to the graphical position of energy management (4) with a relatively balanced driving power and dependence power and slightly lower dependency (higher automation) suggests that energy monitoring can be easily conducted irrespective of whether other BIM-FM functions are adopted. In addition to energy, monitoring of environment (3), solar (5), airflow (6), and security (11) may have the flexibility to be provisioned individually based on each healthcare facility’s needs without concerns of their dependencies on other monitoring functions.
4.3. Driving BIM-FM Applications for Smart Hospital Management
From the research diagram and MICMAC matrix, automation and robotics management (12) is the fundamental BIM-FM application with the strongest driving power, on which all other applications depend. Automation and robotics management is, therefore, at the 1st tier in the ISM diagram. This corresponds to the nearly unanimous opinion expressed by the experts that systematic implementation of automatic mechanisms and the employment of machine intelligence are pivotal to accurately organizing other facility management functions. Not only does this finding vet previous research of Dong et al. (2020) [39], Zhang et al. (2021) [5] and Zhang & Navimipour (2022) [35], recent research such as Javaid et al. (2020) [64] linked automated medical robotics to response solution to unforeseen and rapidly developing events such as COVID-19, which is consistent with this research’s conclusion that automatic and robotics would be the key fundamental driver against the other fourteen applications [43].
In the 2nd tier, document management appeared to be directly driven by automation and robotics and then drives four dependent monitoring functions, including water, airflow, solar, and security. When shared with the interviewed experts, the results were unexpected by a few experts and warranted further clarification through in-depth interviews. Upon cross-checking with previous research and recent literature, it became more apparent that a sound document management system is not only for passive quality control and quality assurance compliance. As Nunhes et al. (2019) [65] previously pointed out, the principles of an electronic document management system would go beyond systematic management and standardization, which are more reactive; the proactive goals would include strategic, tactical, and operational integration, organizational learning, de-bureaucratization, and continuous improvement. In the context of smart hospital BIM-FM applications, this finding directly echoes recent review articles and further bolsters the conclusion that document management intermediates standard-based automation and key building monitoring functions, as it collects data and, through defined standards adopted by the specific smart hospital, documents and organizes data into information and eventually into intelligence through automation in tier 1.
It is also worth noting that there are subtle causality and dependency relationships between tier 3 and tier 4 monitoring and management options. It was vetted logically by experts that environmental monitoring would also encompass water and solar monitoring as the two key data aggregates, while airflow and solar monitoring would feed data into energy monitoring. For airflow, it is worth noting that the relationship with energy is perhaps due to smart hospitals’ heavy dependency on HVAC systems. For solar monitoring, its effect on energy is two-fold based on additional literature; according to Izadi et al. (2023) [61], solar PV panels can provide electrical energy for key building systems, while solar exposure, in combination with building orientation, affects hospital buildings’ heating and cooling needs. As the experts interviewed are based in lower altitude and lower latitude regions in Eastern Asia, it is clearly observed in the interview process that they were experienced and aware of solar impacts on building systems and assigned more driving importance to this application when relating it to environmental and energy monitoring.
4.4. Dependent BIM-FM Applications for Smart Hospital Management
Above tier 4, the applications are related to operation actions and responses, which demonstrates the rationality of the overall ISM structure. Tier 5′s scheduled operations and maintenance activities are directly driven by the monitoring of environmental aspects of the smart hospital. These activities, together with security monitoring results, also drive disaster and emergency responses. From expert opinions, it is worth noting that, similar to that reported previously by Tang et al. (2019), the disaster and emergency responses would refer to enacting specific established SOPs in the event of disasters rather than purely reactive and unplanned measures when triggering disastrous event strikes [36].
Moving to tiers 6 and 7, the ISM structure supports the scheduling of operation activities and operation cost allotment and optimization (applications 1 and 14, respectively), which are common baseline reporting items in FM operations, depend directly and indirectly on ten other BIM-FM applications. Only after these applications are robust and resilient will the interdependent applications be able to drive the two key applications and, in turn, enable them to further solidify ad-hoc activities (2), medical services management (10), and maintenance cost computation and reduction (15).
4.5. Lack of Linkage Variables and Few Autonomous Variables
The MICMAC analysis found that while some applications are drivers or dependents, few are slightly autonomous, and none fall within or near the linkage quadrants. This leads one to question the nature of the applications’ relationships with each other. For example, from the expert interview, it was found that tier 1 automation and robotics management could inform medical services management only through document management and various building-related monitoring, combined with operations and maintenance activities and cost-related computation and reduction. This shows the importance of comprehensive structuring and intentionally planned implementation of these functions, especially leveraging BIM’s unique geometric (models and objects) and non-geometric (parameters) toolkits in an integrated fashion throughout the tiers.
5. Conclusions
The digital twinning trend combining the technological strength of BIM with FM is increasingly prioritized and well aligned with advancements in present-day technologies, including IoT, robotics, and cloud-based platform technologies. With individual factions of these technologies and applications maturing, including various monitoring of building systems involving energies and other building performance factors, there is increasing demand to interrelate the functionalities of BIM-FM. More importantly, unique challenges faced by smart hospital management during the COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 eras, such as increasing precision in spatial definition, segregation, monitoring, and control, calls for quantitative analysis and clear prioritization of BIM-FM applications that were previously analyzed separately in depth but not comparatively side-by-side. With limited time and monetary and human capital resources to operate each facility, systematic decision-making on prioritization has historically been a managerial challenge. This research has therefore adopted an interpretive structural modeling approach toward smart hospitals, which highly demand energy while having similarly high energy generation and reuse potential.
When reviewing the conclusion, an unexpected finding was that two seemingly unrelated managerial tools (i.e., automation and robotics (12) and document management (9)) with direct relationships drive other applications. The former is perceived as the most cutting-edge, while the latter has historically been present and made available early since the start of technology employment toward facility management. However, deeper consideration would reveal that AI applications, such as robotics, heavily rely on the wealth of a fundamental knowledge base, which can be well-served by good document management practice. In today’s world, with document management increasingly taken over by automated and cloud-based tools, the boundary between the two may be narrowing. As previous literature on these applications’ interrelationships is scarce, this research is among the first to directly call out their interdependency and joint power to impact downstream BIM-FM applications.
The theoretical implication of this research centers on applying a well-vetted structural approach—interpretive structural modeling—toward relating dependencies of past independent research results. Not only was the conclusive preliminary ISM model drawn from detailed expert interviews, but this model also went through three iterations to create the hierarchy diagram, elaborated model, and ultimately MICMAC analysis. Overcoming challenges presented by the initial software-analyzed representation, the outcome of the ISM model would, in a matrix, represent the gradient degrees of driver-dependent autonomous linkage for each application. With all applications extracted from recent literature, the findings are highly relatable and can be used as the foundation for future research. Through the lens of easy-to-understand and well-defined BIM-FM applications, the established relationship structure sheds light on refreshing the definition of driving and dependency characteristics.
Aiming to provide decision-making frameworks for selecting and implementing BIM-FM applications for smart hospitals, this research also achieved measurable, practical contributions. By engaging industry experts well-versed in healthcare BIM-FM and lifecycle building information management rather than subjective opinions, the structural framework ensures a hierarchical and easy-to-understand priority and interrelationship matrix between common applications. Hence, if there are budgetary constraints, hospital management may focus on interconnected routes of applications to ensure the highly dependent applications can function properly. It is best to start from the driving applications and move toward dependent applications by phase. Alternatively, vertically connected applications with dependencies can also be implemented simultaneously to achieve compounding effectiveness.
This research has a few limitations that can be addressed by future research. This paper is focused on the smart hospital aspect of BIM-FM applications with varying degrees of relevance to non-medical contexts. As BIM-FM is still predominantly used in construction, real estate, and manufacturing, studies on the structural relationship of applications in these industries could enhance the overall BIM-FM research. Finally, the lack of dominant linkage application and over five tiers could be further reviewed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-H.H.; methodology, H.-H.H.; software, H.-H.H.; validation, J.K.C.C.; formal analysis, H.-H.H.; investigation, H.-H.H.; resources, H.-H.H.; data curation, J.K.C.C.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-H.H.; writing—review and editing, J.K.C.C.; visualization, H.-H.H.; supervision, J.K.C.C.; project administration, H.-H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data shared are in accordance with consent provided by participants on the use of confidential data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Khahro, S.H.; Kumar, D.; Siddiqui, F.H.; Ali, T.H.; Raza, M.S.; Khoso, A.R. Optimizing energy use, cost and carbon emission through building information modelling and a sustainability approach: A case-study of a hospital building. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fang, S.; Dong, H.; Xu, C. Review of digital twin about concepts, technologies, and industrial applications. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayici, Y.; Aouad, G. Building information modelling (BIM) for construction lifecycle management. In Construction and Building: Design, Materials, and Techniques; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 99–118. [Google Scholar]
- Olawumi, T.O.; Chan, D.W.M. Identifying and prioritizing the benefits of integrating BIM and sustainability practices in construction projects: A Delphi survey of international experts. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, H.; Xu, J. Towards fully BIM-enabled building automation and robotics: A perspective of lifecycle information flow. Comput. Ind. 2022, 135, 103570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarieh, A.; Jayasinghe, L.B.; Waldmann, D.; Teferle, F.N. BIM-based end-of-lifecycle decision making and digital deconstruction: Literature review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adere, E.M. Blockchain in healthcare and IoT: A systematic literature review. Array 2022, 14, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Lian, W.; Tian, J. Building the hospital intelligent twins for all-scenario intelligence health care. Digit. Health 2022, 8, 20552076221107894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woll, A.; Tørresen, J. What is a Smart Hospital? A Review of the Literature. In Human-Automation Interaction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 145–165. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, B. The Next Outbreak? We’re Not Ready. TED Talks. 3 April 2015. Available online: https://www.ted.com/talks/bill_gates_the_next_outbreak_we_re_not_ready (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Lin, C.L.; Chen, J.K.; Ho, H.H. BIM for smart hospital management during COVID-19 Using MCDM. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargnoli, M.; Lleshaj, A.; Lombardi, M.; Sciarretta, N.; Di Gravio, G. A BIM-based PSS approach for the management of maintenance operations of building equipment. Buildings 2019, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIBS (National Institute of Building Science). National Building Information Modeling Standard—United States Version 3 (NBIMS-US V3); NIBS: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cassino, K.E. (Ed.) The Business Value of BIM for Construction in Major Global Markets: How Contractors Around the World Are Driving Innovation with Building Information Modeling; Dodge Data & Analytics: Hamilton Township, NJ, USA, 2014; Available online: https://www.construction.com (accessed on 26 November 2023).
- Eadie, R.; Browne, M.; Odeyinka, H.; McKeown, C.; McNiff, S. BIM implementation throughout the UK construction project lifecycle: An analysis. Autom. Constr. 2013, 36, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, R.; Eastman, C.; Lee, G.; Teicholz, P. BIM Handbook: A Guide to Building Information Modeling for Owners, Designers, Engineers, Contractors, and Facility Managers, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Farghaly, K.; Abanda, F.H.; Vidalakis, C.; Wood, G. Taxonomy for BIM and asset management semantic interoperability. J. Manag. Eng. 2018, 34, 04018012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, B.; Brooks, A. Total Facility Management; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Eom, S. Case Study of the Asset Monitoring Focused on Facility Management. In Advances in Greener Energy Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 219–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, H. BIM standards in Hong Kong: Development, impact and future. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Architecture and Civil Engineering, London, UK, 3–4 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fitz, D.V.; Saleeb, N. Examining the quality and management of non-geometric building information modelling data at project hand-over. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2019, 15, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikdag, U. Design patterns for BIM-based service-oriented architectures. Autom. Constr. 2012, 25, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBS Enterprises Ltd. 10th Annual BIM Report 2020; NBS Enterprises Ltd.: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Facilities Management (FM). BCA Corp. Available online: https://www1.bca.gov.sg/buildsg/facilities-management-fm (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Evans, D.; Teague, W. BIM and Facilities Management. Built Environ. J. 2019.
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.P.; Hu, H.T.; Su, Y.C. Developing final as-built BIM model management system for owners during project closeout: A case study. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 36, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babun, L.; Denney, K.; Celik, Z.B.; McDaniel, P.; Uluagac, A.S. A survey on IoT platforms: Communication, security, and privacy perspectives. Comput. Netw. 2021, 192, 108040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassam, N.A.; Hussain, S.A.; Qaraghuli, A.A.; Khan, J.; Sumesh, E.P.; Lavanya, V. IoT based wearable device to monitor the signs of quarantined remote patients of COVID-19. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 24, 100588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.M.; El Saddik, A. C2PS: A digital twin architecture reference model for the cloud-based cyber-physical systems. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.; Kumaraswamy, M.; Mahesh, G.; Ling, Y.Y.F. Building integrated project and asset management teams for sustainable built infrastructure development. J. Facil. Manag. 2014, 12, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, A.; Crespo, A.; Gómez, J.L.; González-Prida, V.; Kobbacy, K.a.H.; Shariff, S.M. Building Information Modeling as Assest Management Tool. IFAC PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar Kshirsagar, A.; El-Gafy, M.A.; Sami Abdelhamid, T. Suitability of life cycle cost analysis (LCCA) as asset management tools for institutional buildings. J. Facil. Manag. 2010, 8, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, J.; Parlikad, A.K.; Schooling, J. A Building Information Modelling approach to the alignment of organisational objectives to Asset Information Requirements. Autom. Constr. 2019, 104, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmo, R.; Polverino, F.; Nicolella, M.; Tibaut, A. Building performance and maintenance information model based on IFC schema. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Navimipour, N.J. A comprehensive and systematic review of the IoT-based medical management systems: Applications, techniques, trends and open issues. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Shelden, D.R.; Eastman, C.M.; Pishdad-Bozorgi, P.; Gao, X. A review of building information modeling (BIM) and the internet of things (IoT) devices integration: Present status and future trends. Autom. Constr. 2019, 101, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Shelden, D.R.; Eastman, C.M.; Pishdad-Bozorgi, P.; Gao, X. BIM assisted Building Automation System information exchange using BACnet and IFC. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 103049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Khan, A.M.; Eldin, S.M.; Aslam, F.; Rehman, S.K.U.; Jameel, M. BIM adoption in sustainability, energy modelling and implementing using ISO 19650: A review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 15, 102252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Shi, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, C. Technology evolution from self-powered sensors to AIoT enabled smart homes. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, I.J.; García Valldecabres, J.L.; Tzortzopoulos, P.; Pellicer, E. An online platform to unify and synchronise heritage architecture information. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 103008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.T.; Chen, H.W.; Chang, E.J.; Kristiani, E.; Nguyen, K.L.P.; Chang, J.S. Current advances and future challenges of AIoT applications in particulate matters (PM) monitoring and control. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadhich, M.; Poddar, S.; Hiran, K.K. Antecedents and consequences of patients’ adoption of the IoT 4.0 for e-health management system: A novel PLS-SEM approach. Smart Health 1003, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, W.; Fu, Y.; Dong, Z. Automated facility inspection using robotics and BIM: A knowledge-driven approach. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 55, 101838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Shang, W.L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, K. Joint optimization for pedestrian, information and energy flows in emergency response systems with energy harvesting and energy sharing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 22421–22435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Dai, H. Improving the emergency management of energy infrastructure using scenario construction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 8731–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Akbarnezhad, A.; Arashpour, M. A neural network approach to predicting the net costs associated with BIM adoption. Autom. Constr. 2020, 119, 103306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hanlon, T.; The Introduction of the SDIPF Safety Reliability Curve. Reliabilityweb. 6 July 2022. Available online: https://reliabilityweb.com/pf-curve (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Warfield, J.N. Societal systems Planning, Policy and Complexity. J. Cybern. 1976, 8, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushil, S. Interpreting the Interpretive Structural Model. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2012, 13, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, R. Interpretive structural modelling: A comprehensive literature review on applications. Int. J. Six Sigma Compet. Advant. 2017, 10, 258–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Chen, K.; Xue, F.; Lu, W. Barriers to Building Information Modeling (BIM) implementation in China’s prefabricated construction: An interpretive structural modeling (ISM) approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Rehman, S.K.U.; Javed, M.F.; Jameel, M.; Aslam, F.; Alyousef, R. Investigating BIM implementation barriers and issues in Pakistan using ISM approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Bhanot, N. An integrated DEMATEL-MMDE-ISM based approach for analysing the barriers of IoT implementation in the manufacturing industry. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 2454–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dixit, G. An analysis of barriers affecting the implementation of e-waste management practices in India: A novel ISM-DEMATEL approach. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2018, 14, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, A.B.; Chan, D.W. Profound barriers to building information modelling (BIM) adoption in construction small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs): An interpretive structural modelling approach. Constr. Innov. 2020, 20, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoar, S.; Chileshe, N. Exploring the causes of design changes in building construction projects: An interpretive structural modeling approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xu, H.; Jiang, S. Understanding the risk factors of BIM technology implementation in the construction industry: An interpretive structural modeling (ISM) approach. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2020, 27, 3289–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasnejad, B.; Nepal, M.P.; Mirhosseini, S.A.; Moud, H.I.; Ahankoob, A. Modelling the key enablers of organizational building information modelling (BIM) implementation: An interpretive structural modelling (ISM) approach. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2021, 26, 974–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhitruangsilp, V.; Kiet, T.T. Key Knowledge Enabler Factors for Effective BIM Implementation in Construction Organizations. In Interdependence between Structural Engineering and Construction Management; ISEC Press: Fargo, ND, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Jia, J.; Ding, J.; Shang, S.; Jiang, S. Interpretive structural model based factor analysis of BIM adoption in Chinese construction organizations. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warfield, T. Interpretive Structural Modeling Software. Available online: https://www.jnwarfield.com/ism-software.html (accessed on 26 November 2023).
- Hussain, K.; He, Z.; Ahmad, N.; Iqbal, M.; Saeed, M.Z. Establishing a Green, Lean and Six Sigma implementation model for sustainable construction industry: An analysis of driving forces through ISM-MICMAC approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 30462–30492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, A.; Shahafve, M.; Ahmadi, P.; Hanafizadeh, P. Design, and optimization of COVID-19 hospital wards to produce Oxygen and electricity through solar PV panels with hydrogen storage systems by neural network-genetic algorithm. Energy 2023, 263, 125578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Vaish, A.; Vaishya, R.; Iyengar, K.P. Robotics applications in COVID-19: A review. J. Ind. Integr. Manag. 2020, 5, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunhes, T.V.; Bernardo, M.; Oliveira, O.J. Guiding principles of integrated management systems: Towards unifying a starting point for researchers and practitioners. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).