Building Information Modeling and Geographic Information System: Integrated Framework in Support of Facility Management (FM)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Facility Management and BIM
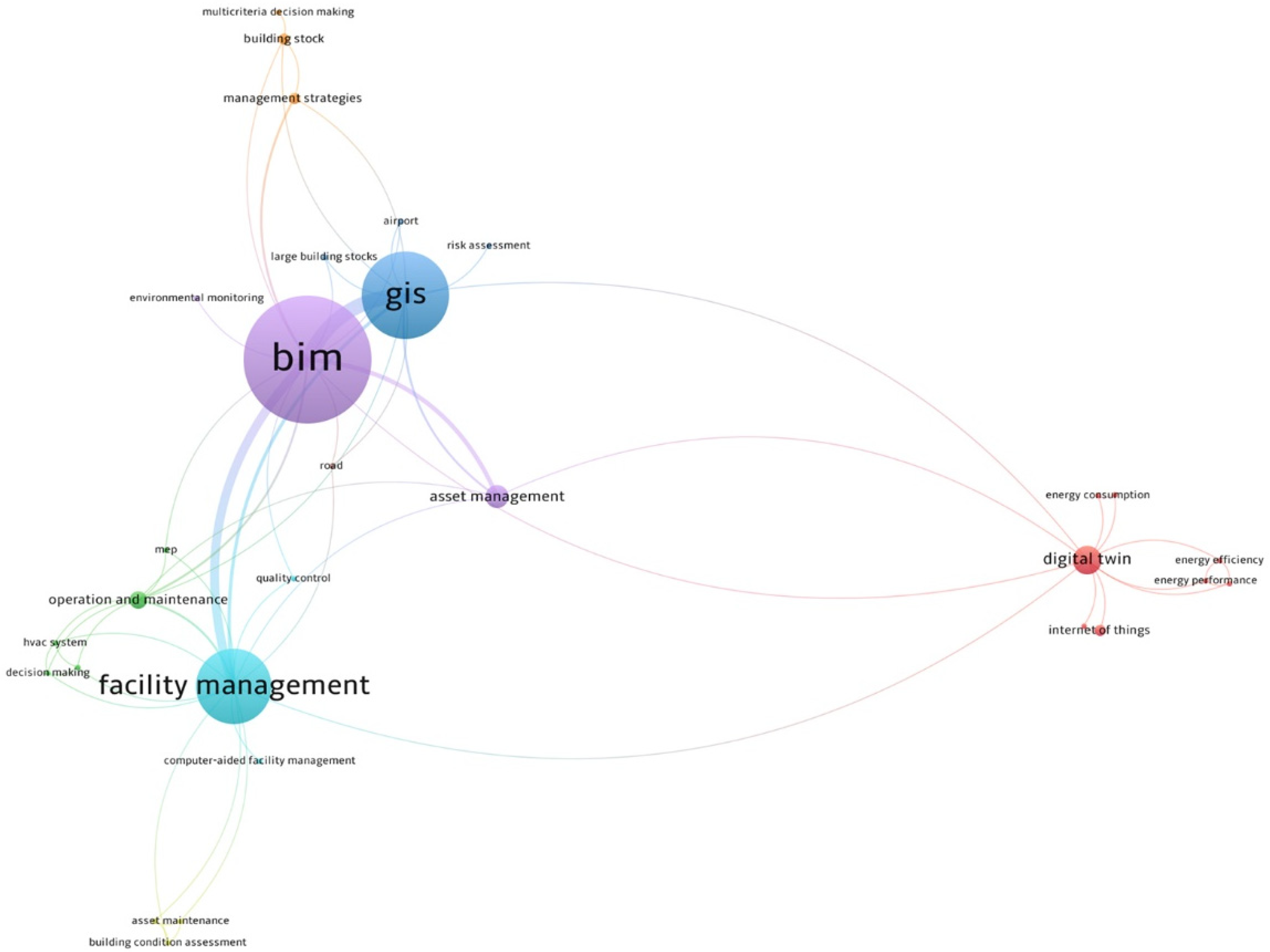
2.2. BIM–GIS Integrated Systems
- -
- Spatial (geographic coordinates, primitive type: point, polyline, polygon);
- -
- Alphanumeric (descriptive type such as acquisition date, object type, thickness, temperature, etc.);
- -
- Temporal (dates of a particular activity, etc.).
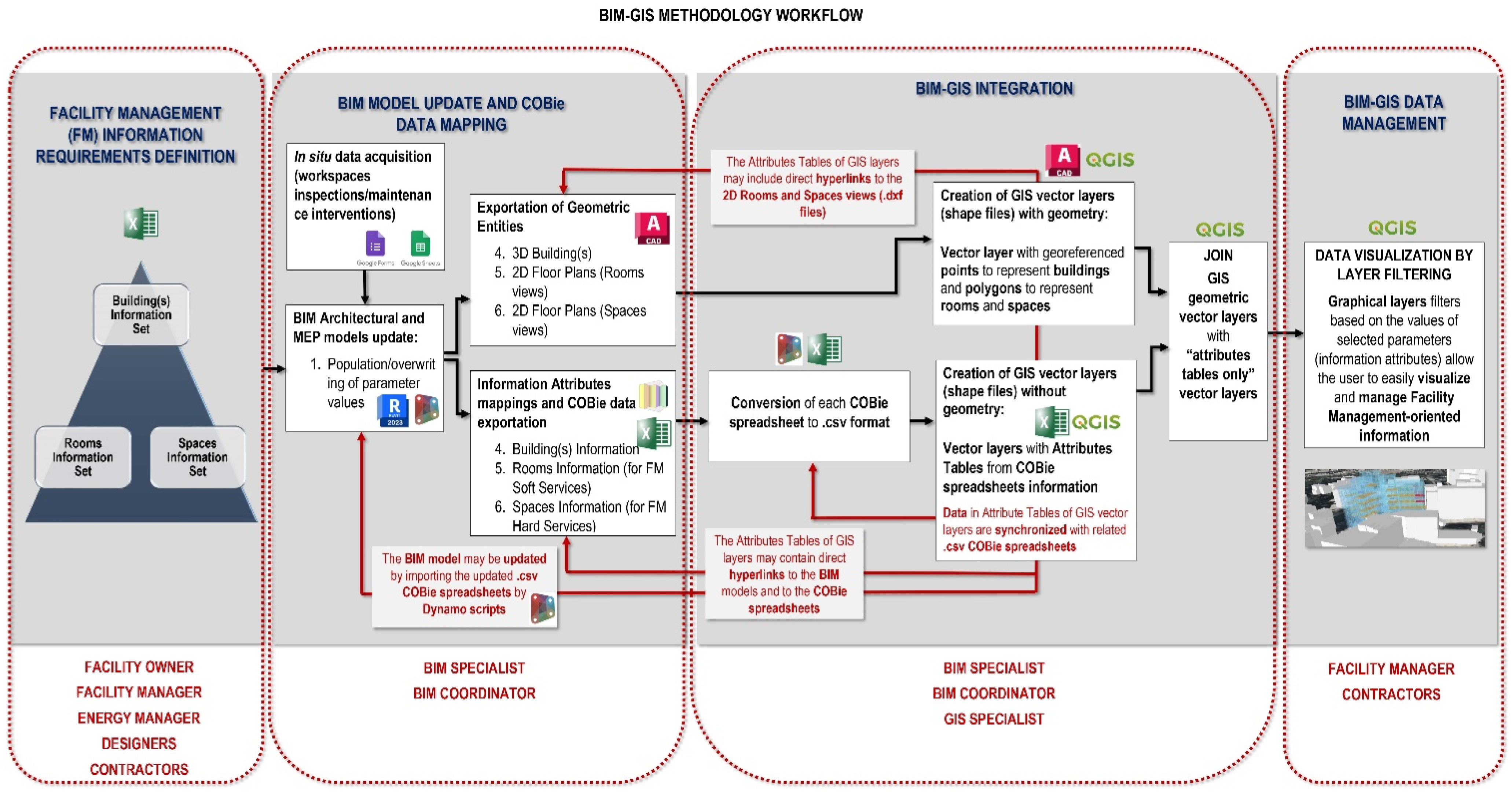
3. Methods and Tools
3.1. Information Requirements Definition for FM
3.2. Building Information Model (BIM) Update
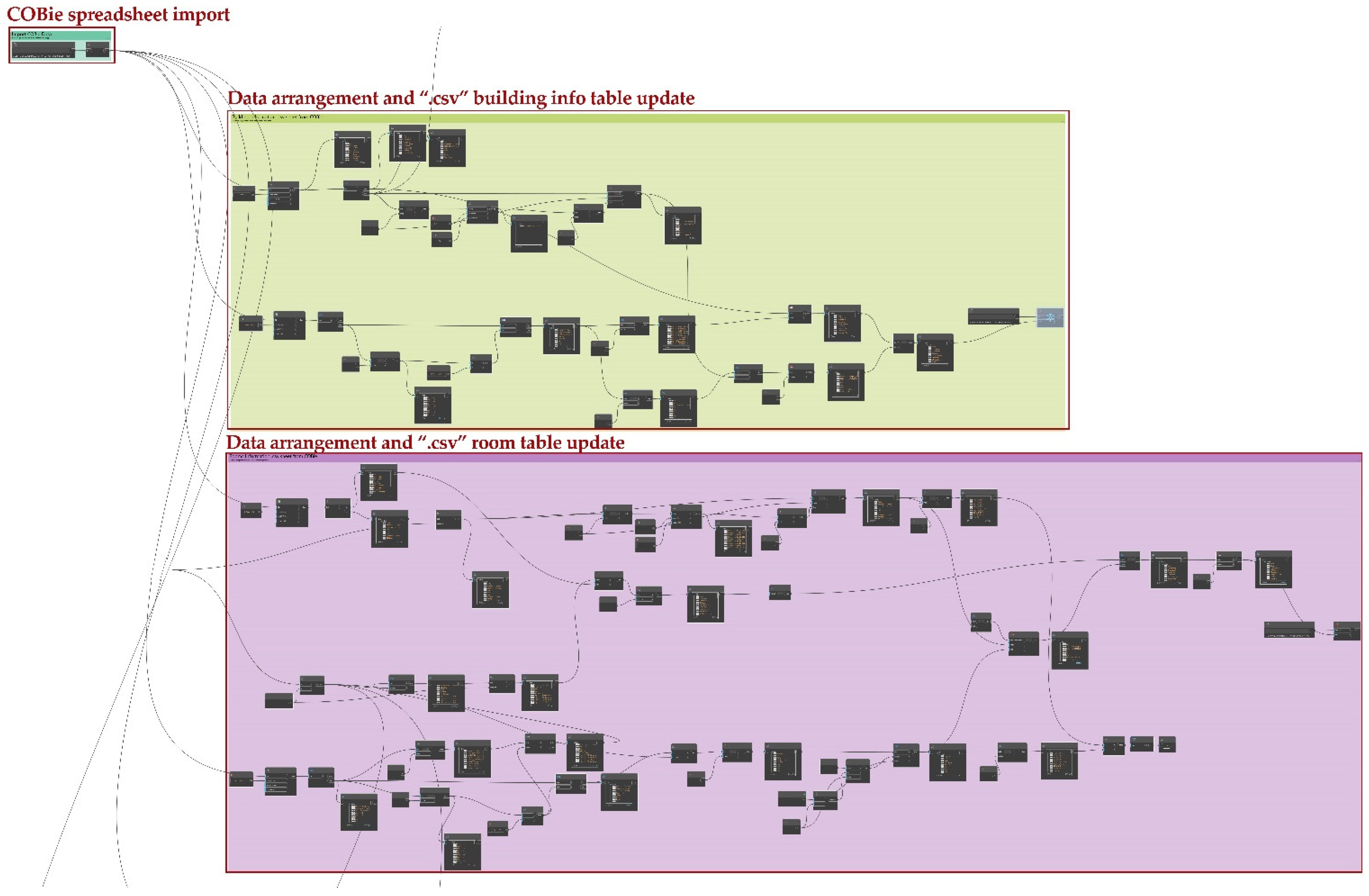
3.3. COBie Data Mapping and Management
3.4. BIM–GIS Integration
- DTM (Digital Terrain Model) raster layer adopted as DEM (Digital Elevation Model) source for the terrain elevation (freely available for Sardinia Italian region [70]);
- Orthophoto of the area (GSD 20 cm, freely available for Sardinia Italian region [71]);
- Vector shape file of volumetric units of buildings from a geo-topographic database 1:2000 (freely available for Sardinia Italian region [72]).
3.5. BIM–GIS Data Visualization and Management
4. Experimental Phase
4.1. The Case Study: The Former Macciotta Pediatric Hospital
4.2. Applications of the Proposed BIM–GIS Workflow to Workspace Management Case Studies
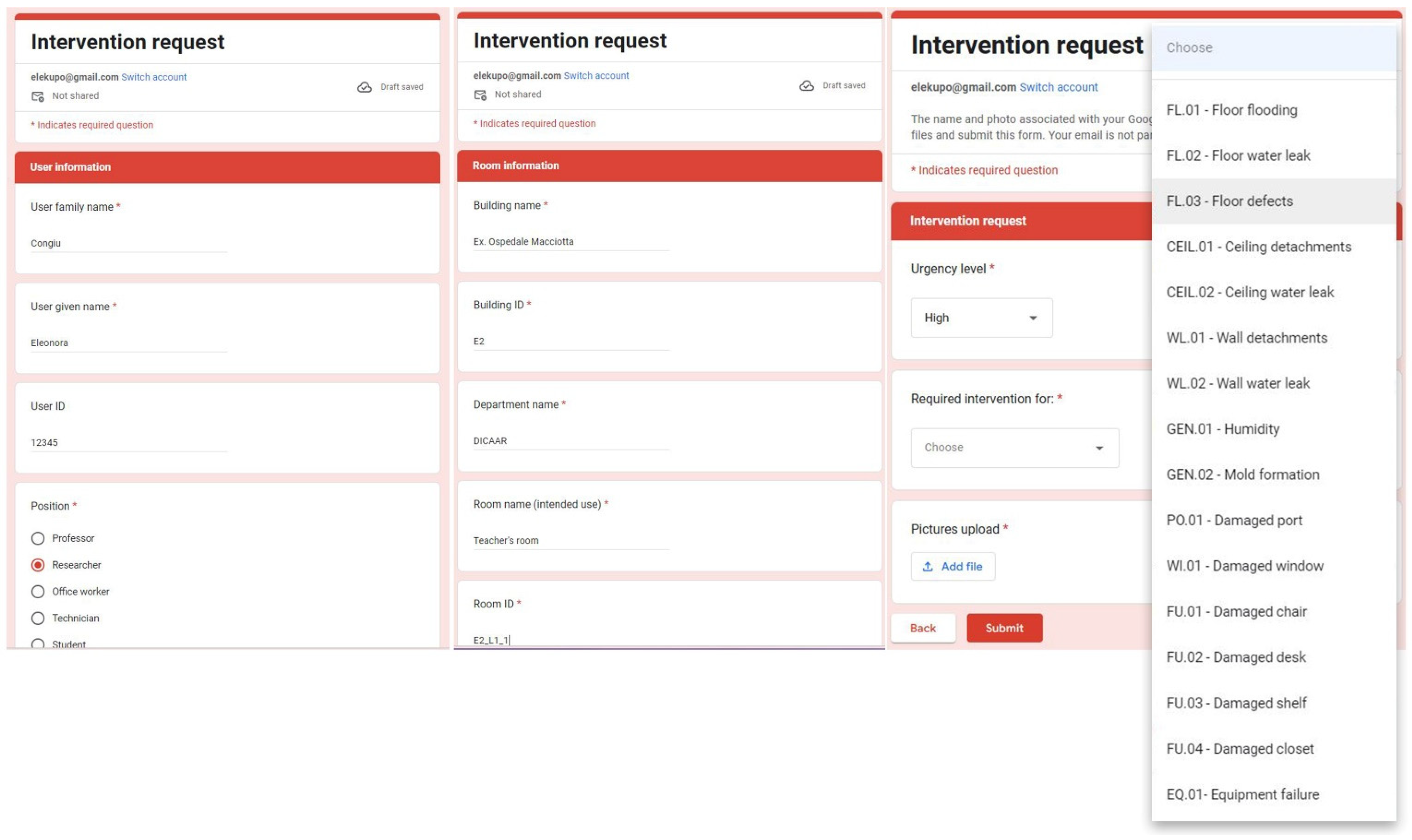
- An urgent intervention request sent by a generic user (e.g., a student, a professor, a researcher, or an office worker) to solve critical issues that make a workspace uncomfortable and/or unusable (e.g., floor flooding, water leaks, humidity and/or mold formation, equipment failures, etc.);
- Scheduled mandatory inspections carried out by a qualified physician (or by another responsible person designated by the facility manager) to regularly assess workspaces healthiness, compliance with safety standards, ergonomics, and functionality.
- Most of the parameters have been conceived to be populated and updated with values acquired during user-required or scheduled inspections (e.g., CI parameters and quantitative parameters related to equipment and furniture);
- The values of some crucial parameters are constrained by some specific conditions and/or mathematical functions. These parameters therefore should not be manually edited, but rather they have to be automatically overwritten by executing specific Dynamo scripts (see Figures S2 and S3 in Supplementary Materials) that take into account constraint conditions and functions (e.g., room available workspace parameter, inspection delay, and new intervention request parameters).
4.3. Use Case 1: Intervention Request from Users
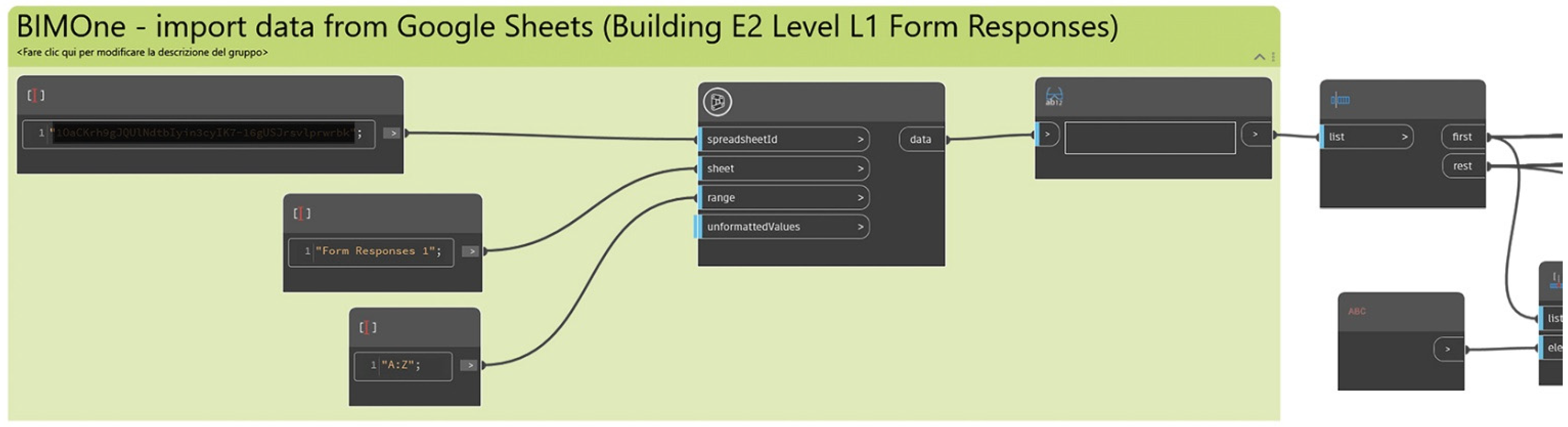
4.3.1. Intervention Request by Google Form
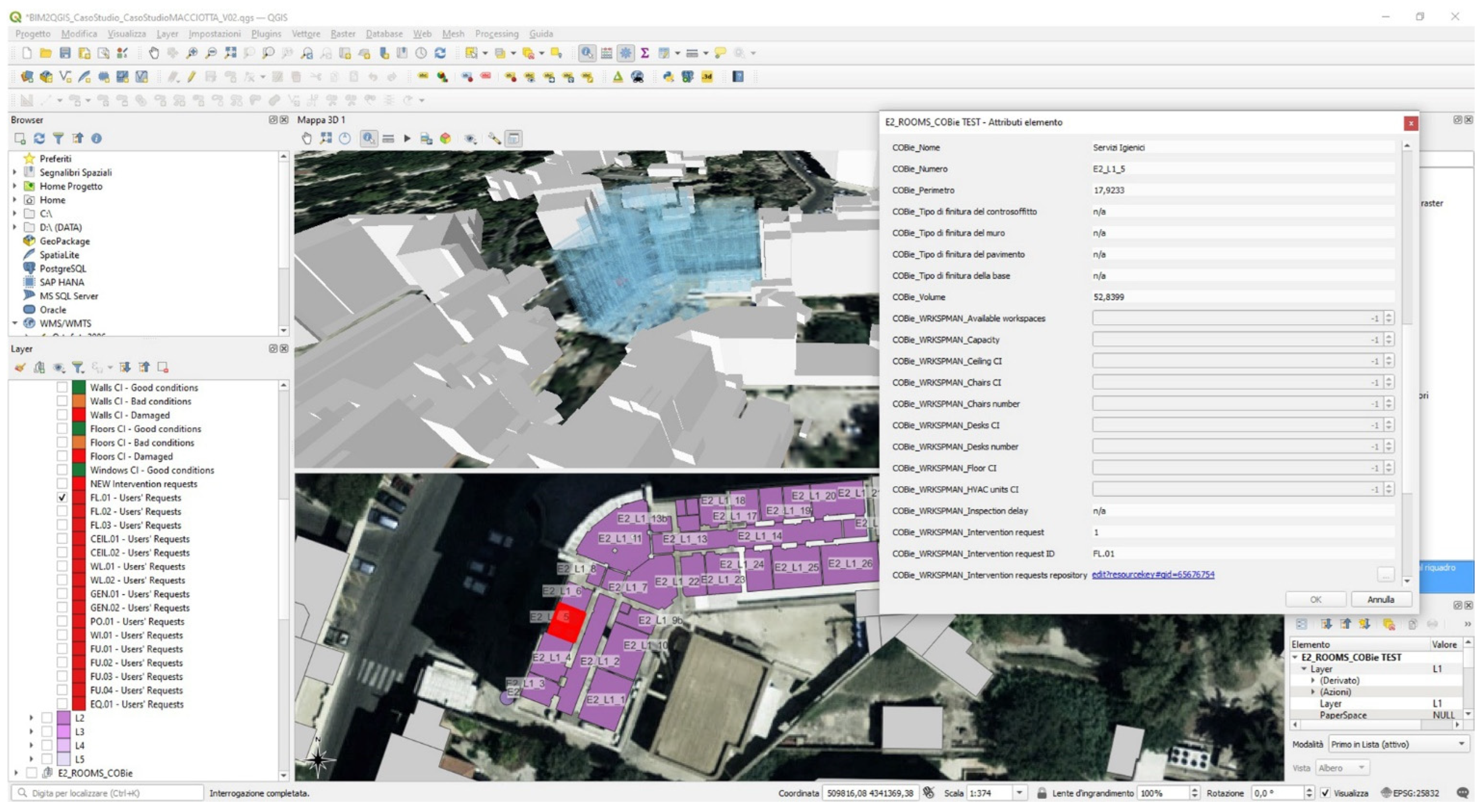
4.3.2. Data Storage: BIM and GIS Models Update through COBie
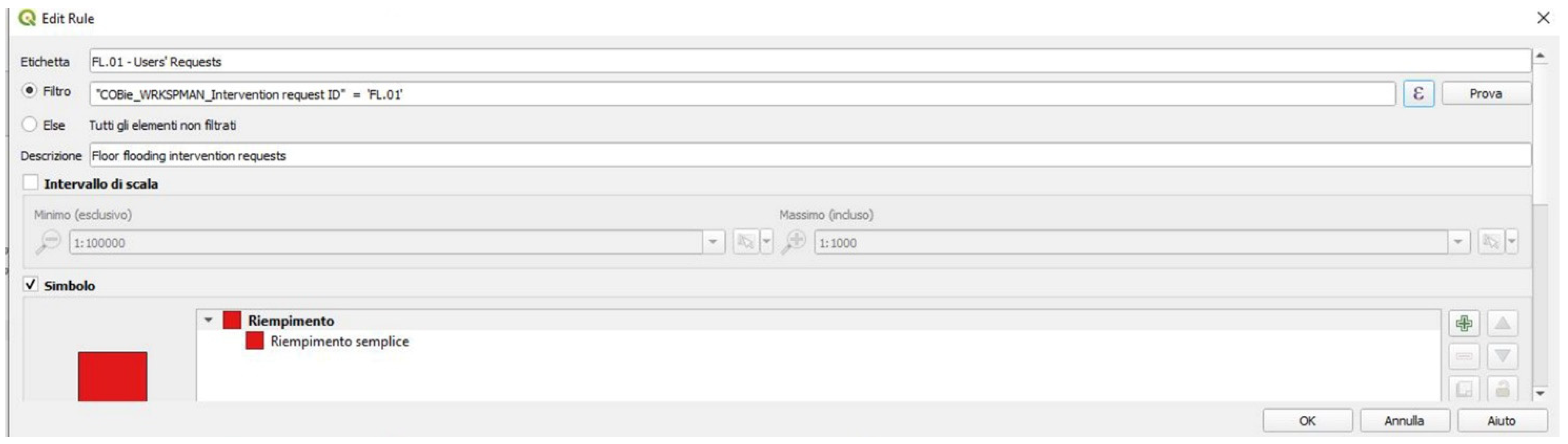
4.3.3. Data Visualization and Management Based on Graphical Alerts
4.3.4. Issue Solution and Informative Systems Update
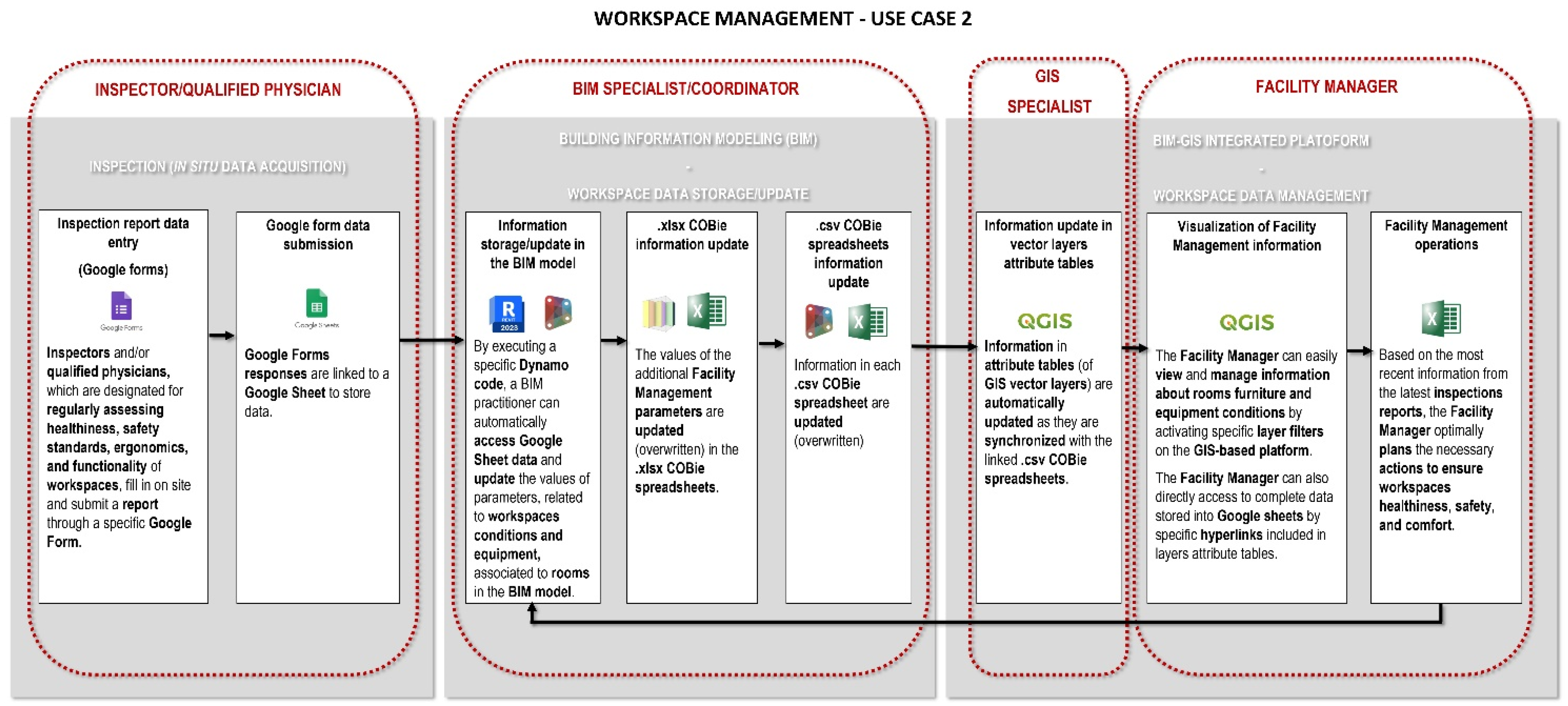
4.4. Use Case 2: Scheduled Annual Inspections by a Qualified Physician
4.4.1. In Situ Data Acquisition by Google Form
4.4.2. Data Storage: BIM and GIS Models Update through COBie
4.4.3. Data Visualization and Management Based on Graphical Alerts
4.4.4. Issue Solution and Informative Systems Update
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salzano, A.; Parisi, C.M.; Acampa, G.; Nicolella, M. Existing Assets Maintenance Management: Optimizing Maintenance Procedures and Costs through BIM Tools. Autom. Constr. 2023, 149, 104788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 41011-2017; Facility Management-Vocabulary. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/68167.html (accessed on 22 July 2023).
- van Sprang, H.; Drion, B. What Is Facility Management? Available online: https://www.ifma.org/about/what-is-fm/ (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Celeste, G.; Lazoi, M.; Mangia, M.; Mangialardi, G. Innovating the Construction Life Cycle through BIM/GIS Integration: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirdöğen, G.; Işık, Z.; Arayici, Y. BIM-Based Big Data Analytic System for Healthcare Facility Management. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 64, 105713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.; Kelly, G.; Dawood, N.; Serginson, M.; Lockley, S. BIM in Facilities Management Applications: A Case Study of a Large University Complex. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2015, 5, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarneh, S.T.; Danso-Amoako, M.; Al-Bizri, S.; Gaterell, M.; Matarneh, R.T. BIM for FM: Developing Information Requirements to Support Facilities Management Systems. Facilities 2020, 38, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, R.; Stengel, J.; Schultmann, F. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Existing Buildings-Literature Review and Future Needs. Autom. Constr. 2014, 38, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teicholz, P.M. IFMA Foundation. BIM for Facility Managers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 19650-3; Organization and Digitization of Information about Buildings and Civil Engineering Works, Including Building Information Modelling (BIM)—Information Management Using Building Information Modelling Part 3: Operational Phase of the Assets. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–46.
- Panteli, C.; Kylili, A.; Fokaides, P.A. Building Information Modelling Applications in Smart Buildings: From Design to Commissioning and beyond A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.; Kelly, G.; Serginson, M.; Lockley, S.; Dawood, N. BIM for Facility Management: A Review and a Case Study Investigating the Value and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Construction Applications of Virtual Reality, London, UK, 31 October 2013; pp. 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Becerik-Gerber, B.; Jazizadeh, F.; Li, N.; Calis, G. Application Areas and Data Requirements for BIM-Enabled Facilities Management. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2012, 138, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonari, A.; Corneli, A.; Di Giuda, G.; Ridolfi, L.; Villa, V. Bim-Based Decision Support System for the Management of Large Building Stocks. In Proceedings of the ISARC 2018-35th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction and International AEC/FM Hackathon: The Future of Building Things, Berlin, Germany, 20–25 July 2018; Curran Associates, Inc.: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 340–347. [Google Scholar]
- Alavi, H.; Forcada, N. User-Centric BIM-Based Framework for HVAC Root-Cause Detection. Energies 2022, 15, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, B.C.; Codinhoto, R.; Fabricio, M.M.; Estrella, J.C.; Neves Ribeiro, C.M.; Dos Santos Bueno, J.M.; Doimo Torrezan, J.P. Development of a BIM and IoT-Based Smart Lighting Maintenance System Prototype for Universities’ FM Sector. Buildings 2022, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arowoiya, V.A.; Moehler, R.C.; Fang, Y. Digital Twin Technology for Thermal Comfort and Energy Efficiency in Buildings: A State-of-the-Art and Future Directions. Energy Built Environ. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaballos, A.; Briones, A.; Massa, A.; Centelles, P.; Caballero, V. A Smart Campus’ Digital Twin for Sustainable Comfort Monitoring. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, R.; Rodrigues, R.; Alavi, H.; Vecchia, L.F.D.; Forcada, N. Digital Twins’ Applications for Building Energy Efficiency: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdyev, S.; Ashour, M.; Connelly, S.; Mahdiyar, A. Barriers to the Implementation of Building Information Modelling (BIM) for Facility Management. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leygonie, R.; Motamedi, A.; Iordanova, I. Development of Quality Improvement Procedures and Tools for Facility Management BIM. Dev. Built Environ. 2022, 11, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarneh, S.T.; Danso-Amoako, M.; Al-Bizri, S.; Gaterell, M.; Matarneh, R. Building Information Modeling for Facilities Management: A Literature Review and Future Research Directions. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 24, 100755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisinghe, R.; London, K.A.; Kalutara, P.; Aranda-Mena, G. Building Information Modelling for Facility Management: Are We There Yet? Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2017, 24, 1119–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishdad-Bozorgi, P. Future Smart Facilities: State-of-the-Art BIM-Enabled Facility Management. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, O.I.; Kineber, A.F.; Chileshe, N.; Edwards, D.J. Modelling the Impact of Building Information Modelling (BIM) Implementation Drivers and Awareness on Project Lifecycle. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pärn, E.A.; Edwards, D.J. Conceptualising the FinDD API Plug-in: A Study of BIM-FM Integration. Autom. Constr. 2017, 80, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patacas, J.; Dawood, N.; Kassem, M. BIM for Facilities Management: A Framework and a Common Data Environment Using Open Standards. Autom. Constr. 2020, 120, 103366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN ISO 19650-2:2018; Organization of Information about Construction Works—Information Management Using Building Information Modelling—Part 2: Delivery Phase of the Assets. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2021.
- Hamil, S. What Is COBie?|NBS. Available online: https://www.thenbs.com/knowledge/what-is-cobie (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- East, B. Using COBie. BIM Facil. Manag. 2018, 107–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Lin, E.T.A. Conceptualizing “COBieEvaluator”: A Rule Based System for Tracking Asset Changes Using COBie Datasheets. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2020, 27, 1093–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBIMS National BIM Standard Purpose. Available online: http://www.nibs.org/BIM/NBIMS_Purpose.pdf%5Cnhttp://www.wbdg.org/pdfs/NBIMSv1_p1.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Khosrowshahi, F.; Arayici, Y. Roadmap for Implementation of BIM in the UK Construction Industry. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2012, 19, 610–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. BIM Handbook: A Guide to Building Information Modeling for Owners, Managers, Designers, Engineers and Contractors; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 12, ISBN 9780470185285. [Google Scholar]
- Béjar, R.; Latre, M.Á.; Nogueras-Iso, J.; Muro-Medrano, P.R.; Zarazaga-Soria, F.J. An RM-ODP Enterprise View for Spatial Data Infrastructures. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2012, 34, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satria, R.; Castro, M. GIS Tools for Analyzing Accidents and Road Design: A Review. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Procedia; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 18, pp. 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, S.S. Determining Wind Energy Potential Using Geographic Information System Functions: A Case Study in Balıkesir, Turkey. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniatis, Y.; Doganis, A.; Chatzigeorgiadis, M. Fire Risk Probability Mapping Using Machine Learning Tools and Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis in the GIS Environment: A Case Study in the National Park Forest Dadia-Lefkimi-Soufli, Greece. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacu, J.G.; Monjardin, C.E.F.; de Jesus, K.L.M.; Senoro, D.B. GIS-Based Risk Assessment of Structure Attributes in Flood Zones of Odiongan, Romblon, Philippines. Buildings 2023, 13, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignard, C.; Nicolle, C. Merging BIM and GIS Using Ontologies Application to Urban Facility Management in ACTIVe3D. Comput. Ind. 2014, 65, 1276–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Arayici, Y.; Wu, S.; Abbott, C.; Aouad, G. Integrating Building Information Modelling and Geographic Information Systems for Large-Scale Facilities Asset Management: A Critical Review. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Civil, Structural and Environmental Engineering Computing, Funchal, Madeira, Portugal, 1–4 September 2009; Topping, B.H.V., Costa Neves, L.F., Barros, R.C., Eds.; Civil-Comp Press: Stirlingshire, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hijazi, I.; Zurich, E.; Ehlers, M.; Zlatanova, S. IFC to CityGML Transformation Framework for Geo-Analysis: A Water Utility Network Case. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on 3D Geo-Information, (3DGeoInfo), Ghent, Belgium, 4–5 November 2009; Ghent University: Ghent, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wright, G.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Li, X.; Liu, R. A State-of-the-Art Review on the Integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Geographic Information System (GIS). ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2017, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, E.P.; Irizarry, J.; Haymaker, J. BIM and GIS Integration and Interoperability Based on Semantic Web Technology. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2016, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.W.; Hong, C.H. A Study on Software Architecture for Effective BIM/GIS-Based Facility Management Data Integration. Autom. Constr. 2015, 54, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, N.; Ellul, C.; Re Cecconi, F.; Papapesios, N.; Dejaco, M.C. GeoBIM for Built Environment Condition Assessment Supporting Asset Management Decision Making. Autom. Constr. 2021, 130, 103859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartano, G.; Avena, M.; Cappellazzo, M.; Spanò, A. Hybrid GIS-BIM Approach for the Torino Digital-Twin: The Implementation of a Floor-Level 3D City Geodatabase. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.-ISPRS Arch. 2021, 43, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankova, L.; Krejza, Z.; Kocourkova, G.; Laciga, J. Geographic Information System Usage Options in Facility Management. In Proceedings of the Procedia Computer Science; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 196, pp. 708–716. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gamily, H.I.; Al-Rasheed, K. Deploying an Interactive GIS System for Facility and Asset Management: Case Study-Ministry of Education, Kuwait. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2015, 7, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Z.; Tian, P.L.; Li, S.W.; Zhang, J.P. BIM-Based Integrated Delivery Technologies for Intelligent MEP Management in the Operation and Maintenance Phase. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018, 115, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vach, K.; Holubec, P.; Dlesk, A. New Trends in GIS and BIM for Facility Management in the Czech Republic. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.-ISPRS Arch. 2018, 42, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, G.; Quaquero, E.; Pili, D.; Brandolini, M. Integrating BIM and GIS Data to Support the Management of Large Building Stocks. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.-ISPRS Arch. 2018, 42, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangia, M.; Lazoi, M.; Mangialardi, G. Digital Management of Large Building Stocks: BIM and GIS Integration-Based Systems. In IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology; Canciglieri Junior, O., Noël, F., Rivest, L., Bouras, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 639, pp. 133–150. ISBN 9783030943349. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Mbachu, J. Highway Alignment Optimization: An Integrated BIM and GIS Approach. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2019, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, F.; Calvi, A.; Schiattarella, E.; Di Prete, M.; Veraldi, V. BIM and GIS Data Integration: A Novel Approach of Technical/Environmental Decision-Making Process in Transport Infrastructure Design. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Procedia; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 45, pp. 803–810. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafat, A.; Khan, M.S.; Latif, K.; Tanoli, W.A.; Park, W.; Seo, J. BIM-GIS-Based Integrated Framework for Underground Utility Management System for Earthwork Operations. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hou, D.; Wang, C.; Pan, F.; Yan, L. Integrating and Managing BIM in 3D Web-Based GIS for Hydraulic and Hydropower Engineering Projects. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, Z.; Riaz, Z.; Arslan, M. Leveraging BIM and Big Data to Deliver Well Maintained Highways. Facilities 2017, 35, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepa, J.J.; Pavón, R.M.; Alberti, M.G.; Caramés, P. Towards BIM-GIS Integration for Road Intelligent Management System. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2023, 29, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzoli, S.; Bonazza, M.; Villa, W.S. Revit 2021 per l’Architettura. Guida Completa per La Progettazione BIM; Tecniche Nuove, Ed.; Autodesk Authorized Publisher: Milano, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- AIA (American Institute of Architects). AIA Document G202-2013. Project Building Information Modeling Protocol Form. 2013. Available online: https://www.aiacontracts.org/contract-documents/19016-project-bim-protocol (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Dynamo. Available online: https://dynamobim.org/ (accessed on 11 July 2023).
- Autodesk Autodesk COBie Extension for Revit. Available online: https://interoperability.autodesk.com/cobieextensionrevit.php (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS). COBie v3 Construction to Operations Building Information Exchange Standard; National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS): Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS); Whole Building Design Guide (WBDG). Construction-Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie). Available online: https://www.wbdg.org/bim/cobie (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- Zhu, J.; Tan, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, P. BIM/GIS Integration for Web GIS-Based Bridge Management. Ann. GIS 2021, 27, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschini, S.; Pellegrini, L.; Locatelli, M.; Accardo, D.; Tagliabue, L.C.; Di Giuda, G.M.; Avena, M. Toward Cognitive Digital Twins Using a BIM-GIS Asset Management System for a Diffused University. Front. Built Environ. 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschini, S.; Accardo, D.; Avena, M.; Seghezzi, E.; Tagliabue, L.C.; Di Giuda, G.M. Data Integration through a Bim-Gis Web Platform for the Management of Diffused University Assets. In Proceedings of the 2022 European Conference on Computing in Construction, Rhodes, Greece, 24–26 July 2022; Tagliabue, L.C., Chassiakos, A., Hall, D.M., Nikolic, D., Eds.; University of Turin: Rhodes, Greece, 2022; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- QGIS. Available online: https://www.qgis.org/it/site/ (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- SardegnaGeoportale-Modelli Digitali Del Tereno e Delle Superfici. Available online: https://www.sardegnageoportale.it/areetematiche/modellidigitalidielevazione/ (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- SardegnaGeoportale-Web Map Service. Available online: https://webgis.regione.sardegna.it/geoserverraster/ows?service=WMS&request=GetCapabilities (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- SardegnaGeoportale-Database Geotopografico (DBGT). Available online: https://www.sardegnageoportale.it/areetematiche/databasegeotopografico/ (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- BSI. Specification for Collaborative Sharing and Use of Structured Health and Safety Information Using BIM; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]













| Parameter Name | Parameter Description | Type | Exported to GIS |
|---|---|---|---|
| WRKSPMAN_Capacity | Room capacity (workspace/workstation number) | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Occupants | Room occupants: occupied workspaces (number) | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Available workspaces | Room available workspaces (number) | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Desks number | Number of desks in the room | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Chais number | Number of chairs in the room | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Monitors number | Number of computer displays in the room | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Printers number | Number of printers in the room | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Sockets number | Number of sockets in the room | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Floor CI | Floor Condition Index (CI) between 0 and 5 | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Ceiling CI | Ceiling Condition Index (CI) between 0 and 5 | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Walls CI | Wall Condition Index (CI) between 0 and 5 | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Windows CI | Window Condition Index (CI) between 0 and 5 | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Desks CI | Desk Condition Index (CI) between 0 and 5 | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Chairs CI | Chair Condition Index (CI) between 0 and 5 | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_HVAC units CI | HVAC unit Condition Index (CI) between 0 and 5 | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Lighting and switches CI | Lighting and switches Condition Index (CI) between 0 and 5 | Integer | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Last inspection (date) | Date and time of the latest room inspection | Text | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Last inspection (pictures) | Link to pictures about the latest room inspection | URL | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Next inspection (date) | Date and time of the next scheduled room inspection | Text | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Inspection delay | Alert for delay in scheduled inspections | Yes/No | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Intervention request | Alert for a new intervention request | Yes/No | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Intervention request ID | ID of the intervention request | Text | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Intervention requests repository | Link to the repository of intervention request | URL | Yes |
| WRKSPMAN_Reports repository | Link to the repository of inspection reports | URL | No |
| WRKSPMAN_Ticket open | Alert for open tickets about user requests | Yes/No | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Congiu, E.; Quaquero, E.; Rubiu, G.; Vacca, G. Building Information Modeling and Geographic Information System: Integrated Framework in Support of Facility Management (FM). Buildings 2024, 14, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14030610
Congiu E, Quaquero E, Rubiu G, Vacca G. Building Information Modeling and Geographic Information System: Integrated Framework in Support of Facility Management (FM). Buildings. 2024; 14(3):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14030610
Chicago/Turabian StyleCongiu, Eleonora, Emanuela Quaquero, Giulia Rubiu, and Giuseppina Vacca. 2024. "Building Information Modeling and Geographic Information System: Integrated Framework in Support of Facility Management (FM)" Buildings 14, no. 3: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14030610
APA StyleCongiu, E., Quaquero, E., Rubiu, G., & Vacca, G. (2024). Building Information Modeling and Geographic Information System: Integrated Framework in Support of Facility Management (FM). Buildings, 14(3), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14030610










