A Literature Review of Green Building Policies: Perspectives from Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bibliometric Analysis
2.1. Methodology
2.2. Data Collection
- Citation indexes
- Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) 1975–present
- Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) 1975–present
- Arts & Humanities Citation Index (AHCI) 1975–present
- Conference Proceedings Citation Index—Science (CPCI-S) 2002–present
- Conference Proceedings Citation Index—Social Science & Humanities (CPCI-SSH) 2002–present
- Book Citation Index—Science (BKCI-S) 2005–present
- Book Citation Index—Social Sciences & Humanities (BKCI-SSH) 2005–present
- Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI) 2019–present
- Chemical indexes
- Current Chemical Reactions (CCR-EXPANDED) 1985–present
- Index Chemicus (IC) 1993–present
2.3. Distribution of Core Authors, Institutions and Journals
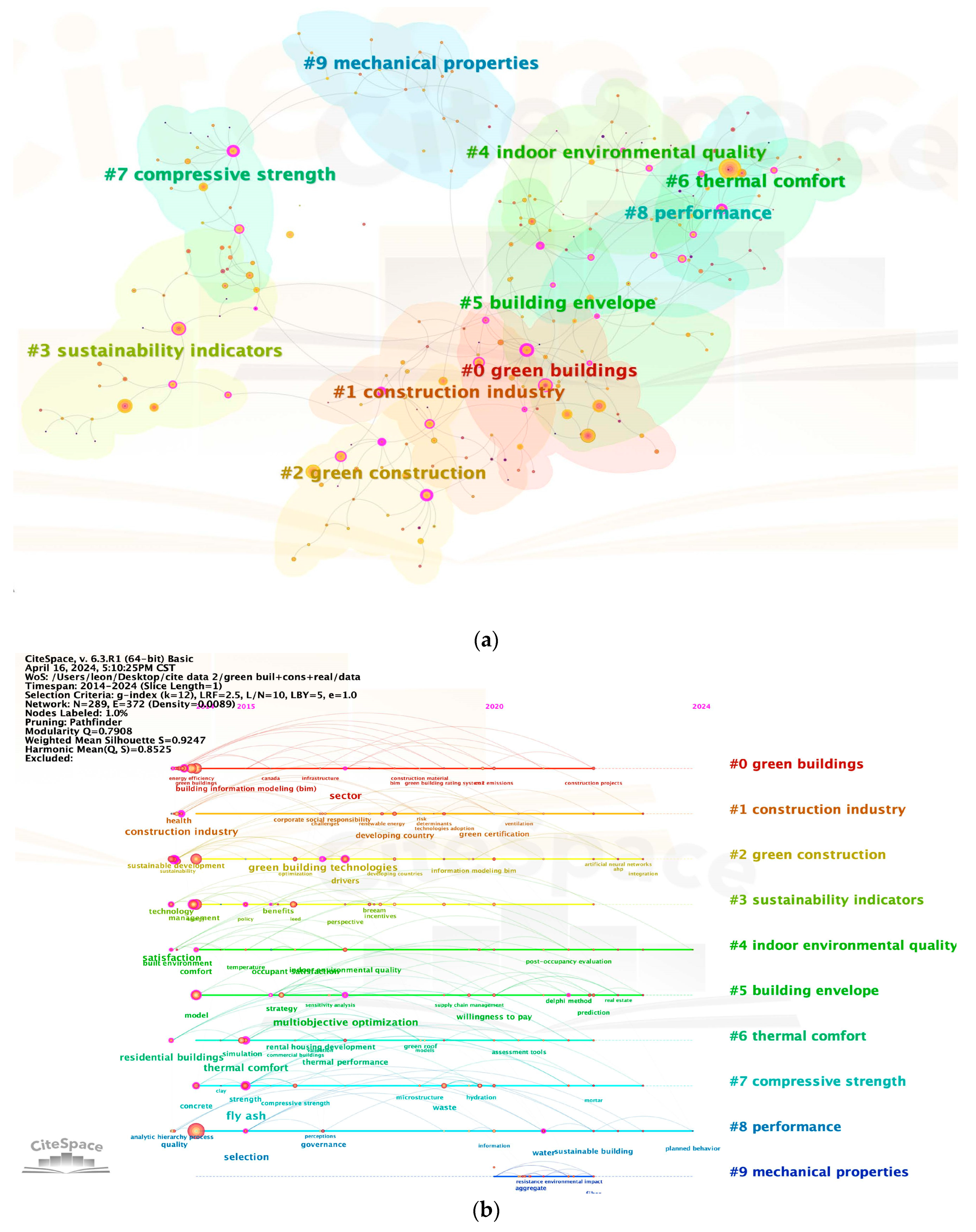
2.4. Research Hotspot Analysis
2.4.1. Keyword Cluster Analysis
- Field 1: overall governance——#0.1.2
- Field 2: use of materials and technology——#5.7.9
- Field 3: objective effects and subjective feelings——#3.4.6.8
2.4.2. Keyword Burst Analysis
3. Evaluating Green Building Policies
3.1. The Nature of Building: From a Life-Cycle Perspective
- Material Production and Supply Stage
- Design and Construction Stage
- Operation and Maintenance Stage
- Demolition and Recycling Phase
3.2. The Impact of Policy: From a Mechanism Perspective
4. Discussion: Integration of Green Building Policy Mechanisms and Regional Differences
4.1. Synergy of Policy Mechanisms
4.2. Factors Influencing Policy Effectiveness
5. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evro, S.; Oni, B.A.; Tomomewo, O.S. Global Strategies for a Low-Carbon Future: Lessons from the US, China, and EU’s Pursuit of Carbon Neutrality. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 461, 142635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Su, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Guo, S. Have Those Countries Declaring “Zero Carbon” or “Carbon Neutral” Climate Goals Achieved Carbon Emissions-Economic Growth Decoupling? J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Msigwa, G.; Yang, M.; Osman, A.I.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.-S. Strategies to Achieve a Carbon Neutral Society: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2277–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia, M.; Reckien, D.; Pietrapesartosa, F.; Eckersley, P.; Spyridaki, N.-A.; Krook-Riekkola, A.; Olazabal, M.; De Gregorio Hurtado, S.; Simoes, S.G.; Geneletti, D.; et al. Will Climate Mitigation Ambitions Lead to Carbon Neutrality? An Analysis of the Local-Level Plans of 327 Cities in the EU. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Environment. Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction|UNEP—UN Environment Programme; UN Environment: Nairobi, Kenya, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Green Buildings. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/land-revitalization/green-buildings (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Matisoff, D.C.; Noonan, D.S.; Flowers, M.E. Policy Monitor—Green Buildings: Economics and Policies. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 2016, 10, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Zhao, Z.-Y. Green Building Research–Current Status and Future Agenda: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press: Benefits of Green Building|U.S. Green Building Council. Available online: https://www.usgbc.org/press/benefits-of-green-building (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Eichholtz, P.; Kok, N.; Quigley, J.M. Doing Well by Doing Good? Green Office Buildings. Am. Econ. Rev. 2010, 100, 2492–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Xue, J.; Liu, R.; Qiping Shen, G.; Xiong, F. Green Building Policies in China: A Policy Review and Analysis. Energy Build. 2023, 278, 112641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberalesso, T.; Cruz, C.O.; Silva, C.M.; Manso, M. Green Infrastructure and Public Policies: An International Review of Green Roofs and Green Walls Incentives. Land Use Pol. 2020, 96, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olubunmi, O.A.; Xia, P.B.; Skitmore, M. Green Building Incentives: A Review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 59, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozingo, L.; Arens, E. Quantifying the Comprehensive Greenhouse Gas Co-Benefits of Green Buildings. 2014. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/935461rm (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Darko, A.; Zhang, C.; Chan, A.P.C. Drivers for Green Building: A Review of Empirical Studies. Habitat Int. 2017, 60, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C. Strategies to Promote Green Building Technologies Adoption in Developing Countries: The Case of Ghana. Build. Environ. 2018, 130, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhan, C.; Wang, X.; Li, G. Asian Green Building Rating Tools: A Comparative Study on Scoring Methods of Quantitative Evaluation Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; He, L. Impacts of Supply-Sided and Demand-Sided Policies on Innovation in Green Building Technologies: A Case Study of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Zuo, J. Assessing Green-Building Policies with Structural Consistency and Behavioral Coherence: A Framework of Effectiveness and Efficiency. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 04021149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Lai, X.; Xie, X.; Zuo, J. Assessment of Green Building Policies—A Fuzzy Impact Matrix Approach. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 36, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to Conduct a Bibliometric Analysis: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Goodell, J.W.; Hassan, M.K.; Paltrinieri, A. A Bibliometric Review of Finance Bibliometric Papers. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 47, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegaard, O.; Wallin, J.A. The Bibliometric Analysis of Scholarly Production: How Great Is the Impact? Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, W. A Review of Emerging Trends in Global PPP Research: Analysis and Visualization. Scientometrics 2016, 107, 1111–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace: A Practical Guide for Mapping Scientific Literature; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. The Data Source of This Study Is Web of Science Core Collection? Not Enough. Scientometrics 2019, 121, 1815–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A Tale of Two Databases: The Use of Web of Science and Scopus in Academic Papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Pitsouni, E.I.; Malietzis, G.A.; Pappas, G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: Strengths and Weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbas, M.; Isik, Z. An Overarching Review on Delay Analyses in Construction Projects. Buildings 2021, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Rollins, J.; Yan, E. Web of Science Use in Published Research and Review Papers 1997–2017: A Selective, Dynamic, Cross-Domain, Content-Based Analysis. Scientometrics 2018, 115, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkle, C.; Pendlebury, D.A.; Schnell, J.; Adams, J. Web of Science as a Data Source for Research on Scientific and Scholarly Activity. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2020, 1, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Retrieval Strategy and Possible Explanations for the Abnormal Growth of Research Publications: Re-Evaluating a Bibliometric Analysis of Climate Change. Scientometrics 2023, 128, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Glänzel, W.; Schubert, A. A Hirsch-Type Index for Journals. Scientometrics 2006, 69, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, F.; Maisano, D.; Mastrogiacomo, L. The Effect of Database Dirty Data on H-Index Calculation. Scientometrics 2013, 95, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihari, A.; Tripathi, S.; Deepak, A. A Review on H-Index and Its Alternative Indices. J. Inf. Sci. 2023, 49, 624–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.E. An Index to Quantify an Individual’s Scientific Research Output. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16569–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cidell, J.; Cope, M.A. Factors Explaining the Adoption and Impact of LEED-Based Green Building Policies at the Municipal Level. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2014, 57, 1763–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H. Governance for Green Urbanisation: Lessons from Singapore’s Green Building Certification Scheme. Environ. Plan. C-Polit. Space 2019, 37, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, L.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Factors Affecting Green Building Development at the Municipal Level: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Energy Build. 2021, 231, 110560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrevik, M.; Wangen, H.F.; Fet, A.M.; De Boer, L. Green Public Procurement—A Case Study of an Innovative Building Project in Norway. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 188, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, M.; Ade, R. Construction Costs Comparison between "green’ and Conventional Office Buildings. Build. Res. Informat. 2013, 41, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Peng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y. Coevolution Mechanisms of Stakeholder Strategies in the Green Building Technologies Innovation Ecosystem: An Evolutionary Game Theory Perspective. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 105, 107418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lin, B. Incorporating Energy Rebound Effect in Technological Advancement and Green Building Construction: A Case Study of China. Energy Build. 2016, 129, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.W.; Zhou, J. Enhancing Environmental Sustainability over Building Life Cycles through Green BIM: A Review. Autom. Constr. 2015, 57, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chiang, P.-C.; Cai, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.-L.; Wei, S.; Huang, Q. Application of Wall and Insulation Materials on Green Building: A Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaei, F.; Jrade, A. Integrating Building Information Modeling (BIM) and LEED System at the Conceptual Design Stage of Sustainable Buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 18, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-Y. Analyzing the Effects of Green Building on Housing Prices: Case Study of Kaohsiung, Taiwan. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 1205–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek, S.; Portnov, B.A. Differential Effect of Knowledge on Stakeholders’ Willingness to Pay Green Building Price Premium: Implications for Cleaner Production. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 251, 119575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T50378-2019; Green Building Evaluation Standard. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Zheng, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Duan, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; Dong, B.; Liu, G.; Zuo, J.; Song, Q. Characterizing the Generation and Flows of Construction and Demolition Waste in China. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierer, A.; Götze, U.; Meynerts, L.; Sygulla, R. Integrating Life Cycle Costing and Life Cycle Assessment Using Extended Material Flow Cost Accounting. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boute, A. Off-Grid Renewable Energy in Remote Arctic Areas: An Analysis of the Russian Far East. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotchen, M. Green Markets and Private Provision of Public Goods. J. Political Econ. 2006, 114, 816–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Sandanayake, M.; Muthukumaran, S.; Navaratna, D. Review on Sustainable Construction and Demolition Waste Management—Challenges and Research Prospects. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, J.A.; Fúquene, C.; Maury-Ramirez, A. Life Cycle Assessment on Construction and Demolition Waste: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H. Promoting Energy Performance Contracting for Achieving Urban Sustainability: What Is the Research Trend? Energies 2019, 12, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.T. Review of The Green Building Revolution. J. Real Estate Lit. 2008, 16, 253–255. [Google Scholar]
- Arisanti, K.; Latief, Y.; Machfudiyanto, R.A. Development Information System for Building Maintenance for Structural Components of Government Green Building Using Building Information Modelling (BIM). IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 830, 022060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.; Reed, J.; Sunderland, T. Bridging Funding Gaps for Climate and Sustainable Development: Pitfalls, Progress and Potential of Private Finance. Land Use Policy 2018, 71, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcoe, T.; Toffel, M.W. Government Green Procurement Spillovers: Evidence from Municipal Building Policies in California. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 68, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanathan, S.; Ramanujan, D.; Bernstein, W.Z.; Zhao, F.; Ramani, K. Integration of Sustainability into Early Design through the Function Impact Matrix. J. Mech. Des. 2010, 132, 081004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, S.; Christensen, T.H.; Astrup, T.F. Life Cycle Assessment of Construction and Demolition Waste Management. Waste Manag. 2015, 44, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuoha, I.J.; Aliagha, G.U.; Rahman, M.S.A. Modelling the Effects of Green Building Incentives and Green Building Skills on Supply Factors Affecting Green Commercial Property Investment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupido, A.F.; Baetz, B.W.; Pujari, A.; Chidiac, S. Evaluating Institutional Green Building Policies: A Mixed-Methods Approach. J. Green Build. 2010, 5, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.-G.; Shan, M.; Phuah, S.L. Safety in Green Building Construction Projects in Singapore: Performance, Critical Issues, and Improvement Solutions. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Lin, C.R.; Ho, M.C. Report on the State of Sustainable Building in Taiwan. Prepared for SB08 Melbourne. 2008. Available online: https://www.iisbe.org/sbconferences/Taiwan_SB_Report_SB08.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, W.; Wang, F.; Zhou, N.; Kammen, D.; Ying, X. A Survey of the Status and Challenges of Green Building Development in Various Countries. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prum, D.A.; Aalberts, R.J.; Del Percio, S. In Third Parties We Trust—The Growing Antitrust Impact of Third-Party Green Building Certification Systems for State and Local Governments. J. Envtl. L. Litig. 2012, 27, 191. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Li, S.; Yin, S.; Xing, Z. How Does the Government Promote the Collaborative Innovation of Green Building Projects? An Evolutionary Game Perspective. Buildings 2022, 12, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E. The Effects of Municipal Policy on Green Building Designations in the United States. Korean J. Policy Stud. 2010, 25, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentman, S.D.; Del Percio, S.T.; Koerner, P. A Climate for Change: Green Building Policies, Programs, and Incentives. J. Green Build. 2008, 3, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-F.J.; Lin, C.-H.; Hsu, M.-W.; Li, M.-H. Evaluation of Intelligent Green Building Policies in Taiwan—Using Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchical Process and Fuzzy Transformation Matrix. Energy Build. 2017, 139, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBose, J.R.; Bosch, S.J.; Pearce, A.R. Analysis of State-Wide Green Building Policies. J. Green Build. 2007, 2, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, D.T.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Naismith, N.; Zhang, T.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Tookey, J. A Critical Comparison of Green Building Rating Systems. Build. Environ. 2017, 123, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X. Literature Review on the Incentive Policies to Promote the Development of Green Building. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 357, 2785–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Hua, J.; Chen, Z.; Wei, L.; Osman, A.I.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D.W.; Dong, L.; Yap, P.-S. Green Construction for Low-Carbon Cities: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 1627–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S. Research on Green Building Materials in Civil Engineering Management System. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 769, 032035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, D.T.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Naismith, N.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Zhang, T.; Tookey, J. Examining Green Star Certification Uptake and Its Relationship with Building Information Modelling (BIM) Adoption in New Zealand. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Faure, M. Green Building in China. Int. Environ. Agreem. 2021, 21, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economidou, M.; Labanca, N.; Castellazzi, L.; Serrenho, T.; Zancanella, P.; Paci, D.; Panev, S.; Gabrielaitiene, I. Assessment of the First National Energy Efficiency Action Plans under the Energy Efficiency Directive; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Landgren, M.; Jensen, L.B. How Does Sustainability Certification Affect the Design Process? Mapping Final Design Projects at an Architectural Office. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2018, 14, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economidou, M.; Todeschi, V.; Bertoldi, P.; D’Agostino, D.; Zangheri, P.; Castellazzi, L. Review of 50 years of EU Energy Efficiency Policies for Buildings. Energy Build. 2020, 225, 110322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, C.; Kamaruzzaman, S.N.; Aziz, N.M. A Systematic Review of Green Building Development in China: Advantages, Challenges and Future Directions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhong, R. The Spatial Distribution of Green Buildings in China: Regional Imbalance, Economic Fundamentals, and Policy Incentives. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 88, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindkvist, C.; Karlsson, A.; Sørnes, K.; Wyckmans, A. Barriers and Challenges in nZEB Projects in Sweden and Norway. Energy Procedia 2014, 58, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, M.K.; Fernández-Solís, J.L.; Lavy, S.; Culp, C.H. Need for an Embodied Energy Measurement Protocol for Buildings: A Review Paper. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3730–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, O.; Puppim de Oliveira, J.A. Sustainable Buildings for Healthier Cities: Assessing the Co-Benefits of Green Buildings in Japan. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S68–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, G.S.; Jha, K.N. What Does It Cost to Convert a Non-Rated Building into a Green Building? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 36, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Rank | Author | Number | H-Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gou, Zhonghua | 8 | 36 |
| 2 | Durdyev, Serdar | 8 | 25 |
| 3 | Mohandes, Saeed Reza | 7 | 9 |
| 4 | Ismail, Syuhaida | 5 | 20 |
| 5 | Simpeh, Eric Kwame | 5 | 5 |
| 6 | Agyekum, Kofi | 5 | 15 |
| 7 | Aigbavboa, Clinton | 4 | 25 |
| 8 | Mahdiyar, Amir | 4 | 21 |
| 9 | Sadeghi, Haleh | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | Ebekozien, Andrew | 4 | 15 |
| Publication Titles | Number | Journal Impact Factor (Five Year) |
|---|---|---|
| SUSTAINABILITY | 242 | 3.6 |
| JOURNAL OF CLEANER PRODUCTION | 154 | 10.2 |
| BUILDINGS | 113 | 3.2 |
| ENERGY AND BUILDINGS | 87 | 6.7 |
| BUILDING AND ENVIRONMENT | 83 | 7.2 |
| JOURNAL OF BUILDING ENGINEERING | 75 | 6.8 |
| JOURNAL OF GREEN BUILDING | 74 | 1 |
| CONSTRUCTION AND BUILDING MATERIALS | 71 | 8 |
| SUSTAINABLE CITIES AND SOCIETY | 51 | 10 |
| ENGINEERING CONSTRUCTION AND ARCHITECTURAL MANAGEMENT | 32 | 4.2 |
| Research Field | Related Research Topics | Size |
|---|---|---|
| overall governance | green buildings | 26 |
| construction industry | 26 | |
| green construction | 25 | |
| use of materials and technology | building envelope | 24 |
| compressive strength | 20 | |
| mechanical properties | 17 | |
| objective effects and subjective feelings | sustainability indicators | 25 |
| indoor environmental quality | 24 | |
| thermal comfort | 22 | |
| performance | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Fanyang, Y.; Wang, J.; Meng, S.; Tang, D. A Literature Review of Green Building Policies: Perspectives from Bibliometric Analysis. Buildings 2024, 14, 2607. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14092607
Ye J, Fanyang Y, Wang J, Meng S, Tang D. A Literature Review of Green Building Policies: Perspectives from Bibliometric Analysis. Buildings. 2024; 14(9):2607. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14092607
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Junyang, Yunlong Fanyang, Jingyi Wang, Shibo Meng, and Daizhong Tang. 2024. "A Literature Review of Green Building Policies: Perspectives from Bibliometric Analysis" Buildings 14, no. 9: 2607. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14092607
APA StyleYe, J., Fanyang, Y., Wang, J., Meng, S., & Tang, D. (2024). A Literature Review of Green Building Policies: Perspectives from Bibliometric Analysis. Buildings, 14(9), 2607. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14092607







