Valorization of Gold Mining Tailings Sludge from Vetas, Colombia as Partial Cement Replacement in Concrete Mixes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material: Mining Tailings Sludge (REMI)
2.1.1. Binder: Type III Portland Cement
2.1.2. Aggregates
2.2. Mix Design and Formulation
2.2.1. Mix Design Methodology
2.2.2. Selection of the Cement Replacement Percentage with REMI
2.3. Manufacturing and Strength Testing
2.3.1. Sample Preparation and Curing
2.3.2. Compressive Strength Tests
2.4. Chemical and Mineralogical Characterization
2.4.1. Chemical Analysis
2.4.2. Mineralogical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. REMI Material Characterization
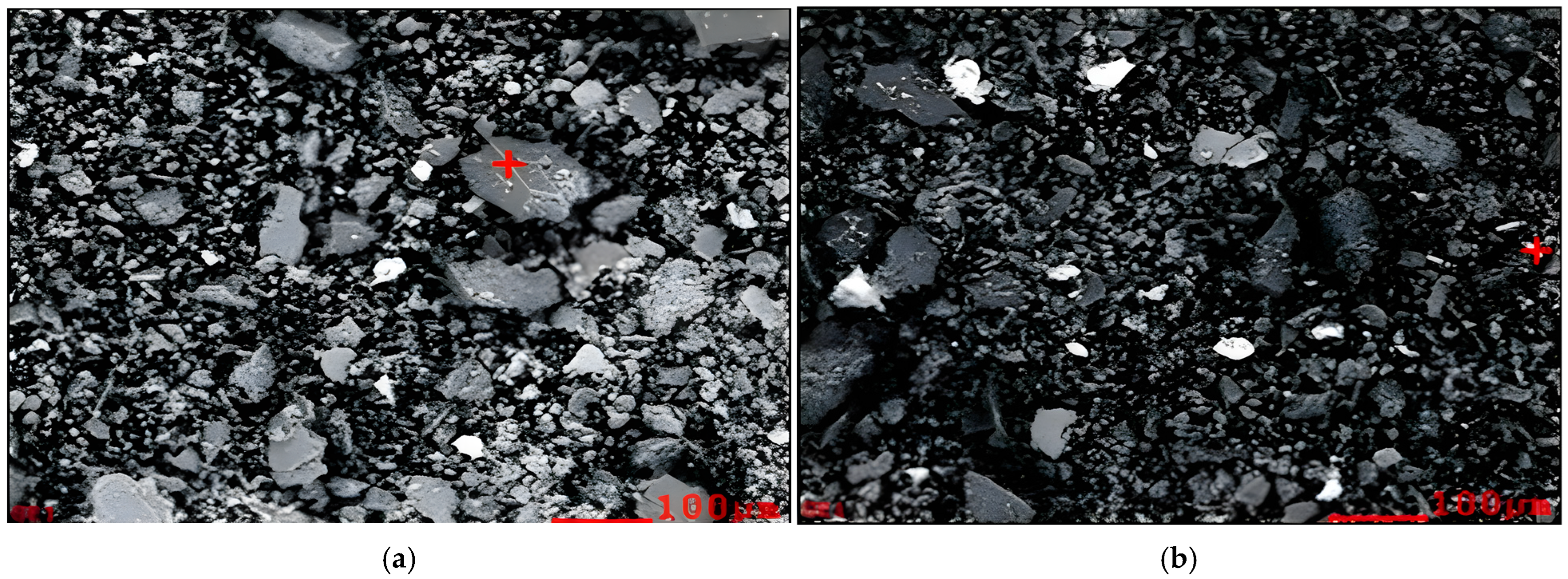
3.1.1. Physical and Morphological Characterization
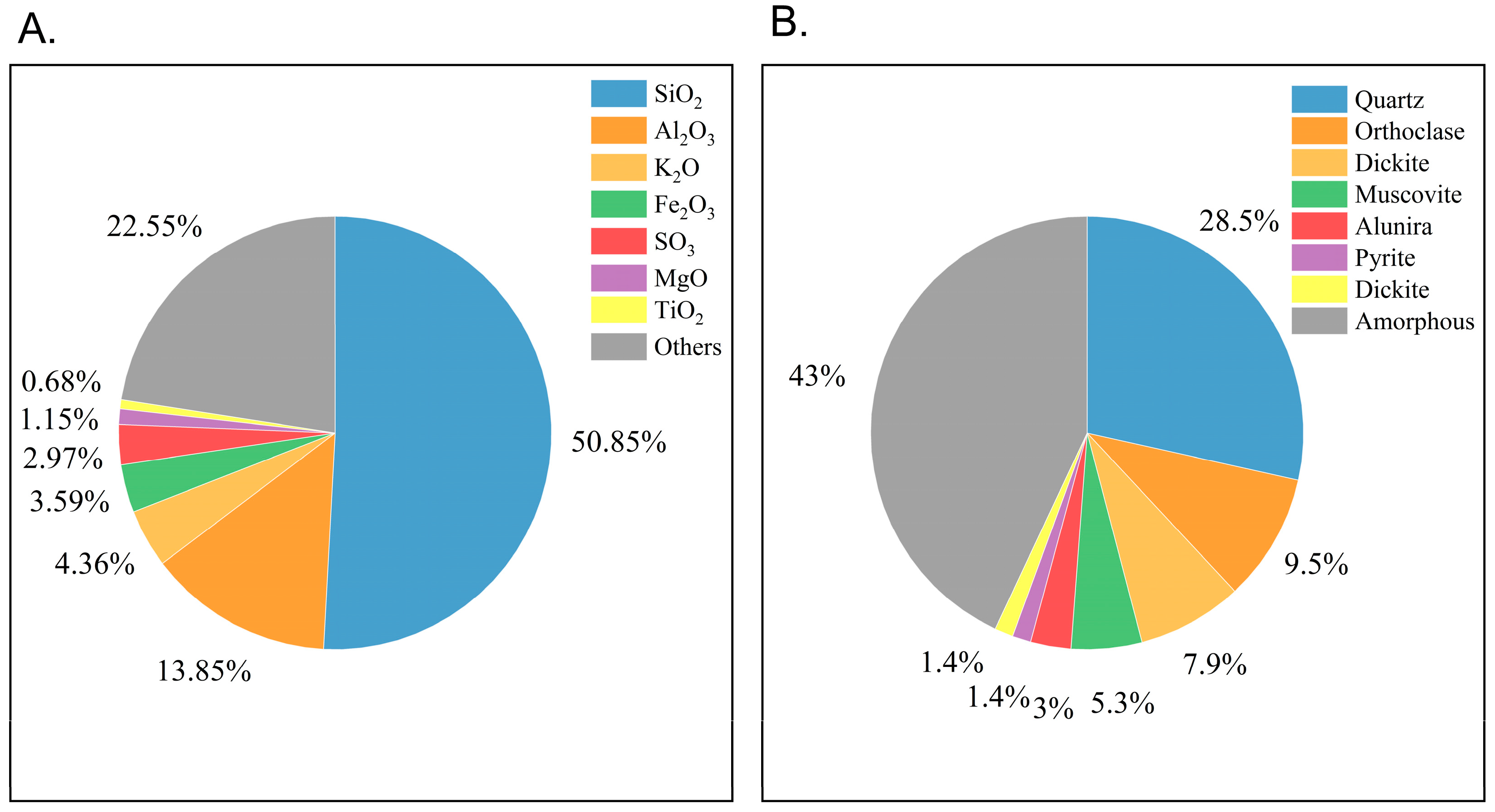
3.1.2. Chemical and Mineralogical Characterization
3.2. Evaluation of the Performance of the Modified Concrete
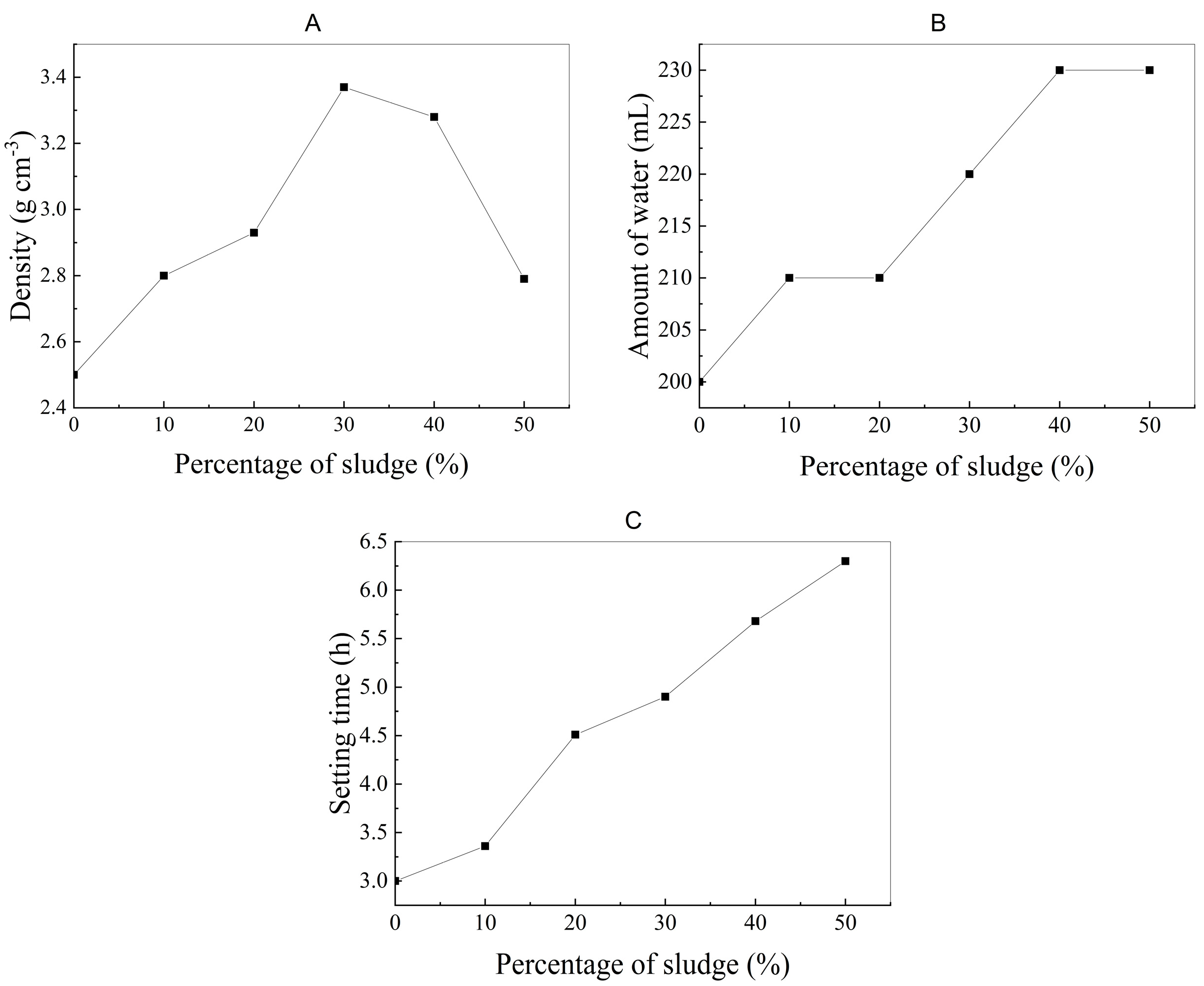
3.2.1. Physical Behavior of the Materials
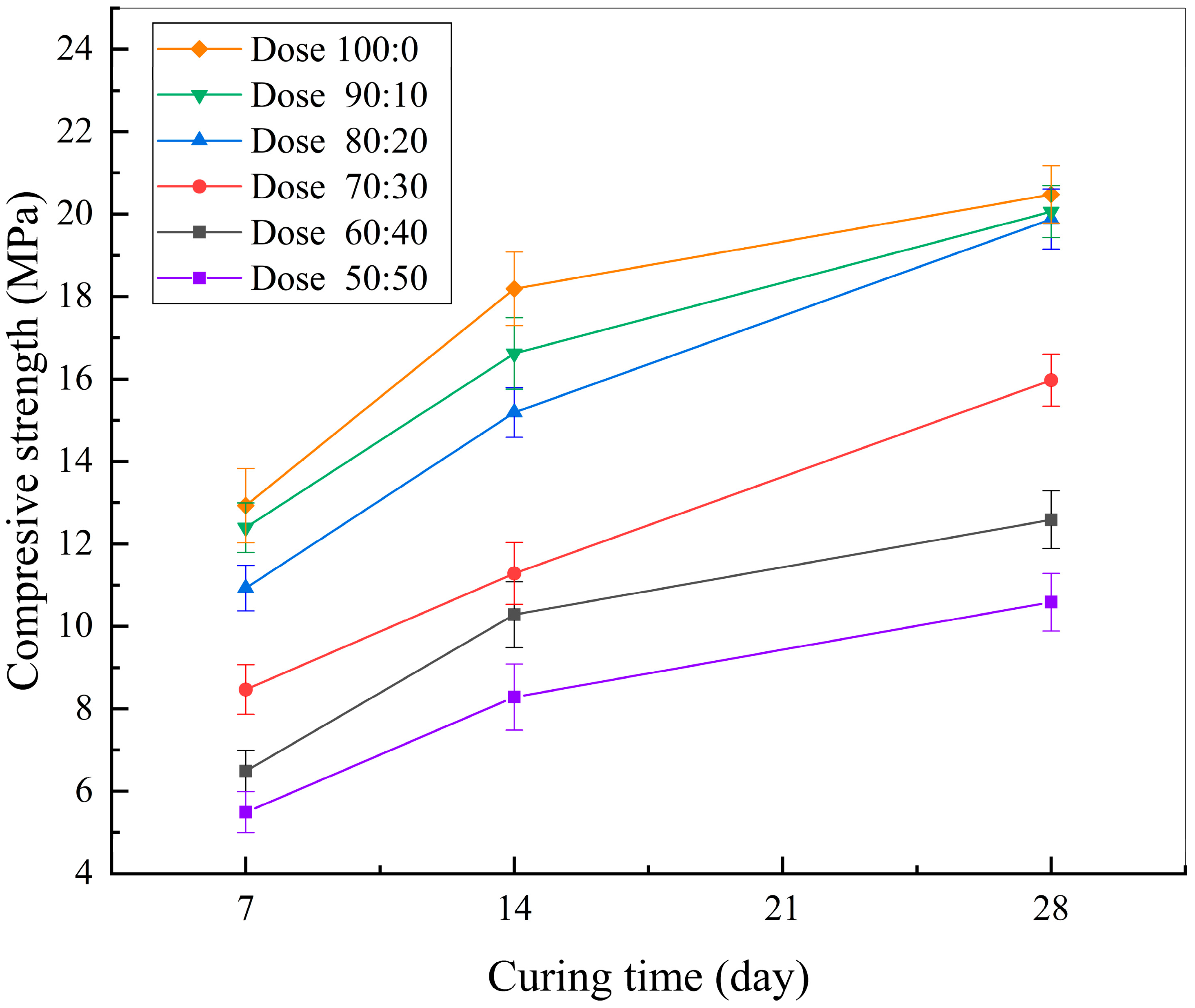
3.2.2. Mechanical Performance and Comparison with Conventional Concrete
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barcelos, D.A.; Pontes, F.V.M.; da Silva, F.A.N.G.; Castro, D.C.; dos Anjos, N.O.A.; Castilhos, Z.C. Gold mining tailing: Environmental availability of metals and human health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belle, G.; Fossey, A.; Esterhuizen, L.; Moodley, R. Contamination of groundwater by potential harmful elements from gold mine tailings and the implications to human health: A case study in Welkom and Virginia, Free State Province, South Africa. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayan, G.; Sakoyan, A.; Sahakyan, G. Drinking water quality and health risk analysis in the mining impact zone, Armenia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombert, P.; Sracek, O.; Koukouzas, N.; Gzyl, G.; Valladares, S.T.; Frączek, R.; Klinger, C.; Bauerek, A.; Areces, J.E.Á.; Chamberlain, S.; et al. An Overview of Priority Pollutants in Selected Coal Mine Discharges in Europe. Mine Water Environ. 2019, 38, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Lei, K.; Wang, W.; Guan, Y. Trace metal element pollution of soil and water resources caused by small-scale metallic ore mining activities: A case study from a sphalerite mine in North China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 24630–24644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, M.J.; Chételat, J.; Richardson, M.; Jamieson, H.E.; Galloway, J.M. Seasonal variation of arsenic and antimony in surface waters of small subarctic lakes impacted by legacy mining pollution near Yellowknife, NT, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, D.D.; Flores Jiménez, P.; Hernández, K.; Peres, F.; Maldonado, A.K.; Klarián, J.; Cáceres, D.A. Health risk due to heavy metal(Loid)s exposure through fine particulate matter and sedimented dust in people living next to a beach contaminated by mine tailings. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2021, 37, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusengemungu, L.; Mubemba, B.; Gwanama, C. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in copper mine tailing soils of Kitwe and Mufulira, Zambia, for reclamation prospects. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.G.; Valente, T.M.; Marinho Reis, A.P.; Ferreira Fonseca, R.M.; Guabiroba, F.; da Mata Filho, J.G.; Magalhães, M.F.; Delbem, I.D.; Rebelo Diório, G. Adding Value to Mine Waste through Recovery Au, Sb, and As: The Case of Auriferous Tailings in the Iron Quadrangle, Brazil. Minerals 2023, 13, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabón, S.E.; Benítez, R.; Sarria-Villa, R.A.; Gallo, J.A. Water contamination by heavy metals, analysis methods and removal technologies. A review. Entre Cienc. Ing. 2020, 14, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.G.; Faz, A.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Gabarrón, M.; Beltrá, J.C.; Martínez, J.; Acosta, J.A. Spatial distribution and pollution evaluation in dry riverbeds affected by mine tailings. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 9157–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadística (DANE)—Colombia. Boletín técnico Producto Interno Bruto (PIB) II Trimestre; Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadística (DANE)—Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff-Carreño, E.; Pinzón-Angel, J.M.; Contreras-Moreno, R.; Bernardy, C. Geological setting, mining and reduction of mercury vapor contamination in the gold-silver district of Vetas-Calofornia (Santander, Colombia). Episodes 2005, 28, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadística (DANE)—Colombia. Análisis Económico y Social de la Minería en Colombia: Retos y Oportunidades; Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadística (DANE)—Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, A.; Silvana, F. Reuse of mining tailing as raw crude for the elaboration of aggregates of contruction for the making of bricks and tile. Ind. Data Investig. J. 2010, 13, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, D.; Guzmán-Martínez, F.; Acosta, M.; Collahuazo, L.; Ibarra, D.; Lalangui, L.; Jiménez-Oyola, S. Use of Tailings as a Substitute for Sand in Concrete Blocks Production: Gravimetric Mining Wastes as a Case Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, N.; Penagos, G.; Correa, M.; López, E. Development of low environmental impact mortars from alkaliny activated silical-aluminum waste from the mining sector. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidr. 2021, 62, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Zhou, L.; Then, N.W.Y. Utilization of tailings in cement and concrete: A review. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2019, 26, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco de Carvalho, J.M.; Fontes, W.C.; de Azevedo, C.F.; Brigolini, G.J.; Schmidt, W.; Peixoto, R.A.F. Enhancing the eco-efficiency of concrete using engineered recycled mineral admixtures and recycled aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Hernández, M.; Pérez-Rea, M.d.l.L. Characterization of mine tailings in their natural state and stabilized with cement, focused on construction Caracterización de residuos mineros en estado natural y estabilizados con cemento, enfocada a construcción. Ing. Investig. Tecnol. 2021, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, I.B.C.; Cavalcante, L.C.D.; Fabris, J.D.; Prat, B.V.; Reis, A.B. Use of mining tailings or their sedimentation and flotation fractions in a mixture with soil to produce structural ceramics. Sustainability 2021, 13, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solismaa, S.; Torppa, A.; Kuva, J.; Heikkilä, P.; Hyvönen, S.; Juntunen, P.; Benzaazoua, M.; Kauppila, T. Substitution of cement with granulated blast furnace slag in cemented paste backfill: Evaluation of technical and chemical properties. Minerals 2021, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Troncoso, N.; Baykara, H.; Cornejo, M.H.; Riofrio, A.; Tinoco-Hidalgo, M.; Flores-Rada, J. Comparative mechanical properties of conventional concrete mixture and concrete incorporating mining tailings sands. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Perdomo, F.; Carvajalino-Umaña, J.D.; López-González, M.; Ardila, N.; González-Curbelo, M.Á. The private sector’s role in Colombia to achieving the circular economy and the Sustainable Development Goals El rol del sector privado en Colombia para alcanzar la economía circular y los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible. DYNA 2023, 90, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTC 454; Standard Test Method for Sampling Freshly MIixed Concrete. Instituto Colombiano de Normas Técnicas y Certificación—ICONTEC: Bogotá, Colombia, 2022.
- NTC 550:2020; Standard Test for Making and Curing of Concrete Test Specimens in the Field. Instituto Colombiano de Normas Técnicas y Certificación—ICONTEC: Bogotá, Colombia, 2020.
- Saedi, A.; Jamshidi-Zanjani, A.; Darban, A.K. A review on different methods of activating tailings to improve their cementitious property as cemented paste and reusability. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Yanful, E.K. A review of binders used in cemented paste tailings for underground and surface disposal practices. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, C.; Marchevsky, N.; Chiacchiarini, P.; Giaveno, M. Caracterización física, química y mineralógica de un antiguo relave, en busca de alternativas de reutilización. Minería Geol. 2022, 38, 70–82. [Google Scholar]
- Casadiego Quintero, E.; Gómez Ríos, W.R.; Monroy, E.L.; Sánchez Londoño, J. Sustainable gold mining: Implications of the use of waste as an aggregate for concrete. Inventum 2021, 16, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagüe, S.; Sánchez, I.; De La Villa, R.V.; García-Giménez, R.; Zapardiel, A.; Frías, M. Coal-mining tailings as a pozzolanic material in cements industry. Minerals 2018, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, F.; Xue, B.; Cao, X. Pore Structure Control of Expanded Dickite and Its Application as a Clay Coating Layer on Cross-Linked Nonwoven Fabrics for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, H.E.; Walker, S.R.; Parsons, M.B. Mineralogical characterization of mine waste. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INGEOMINAS. Geología de la Plancha 110 Pamplona; INGEOMINAS: Bogotá, Colombia, 1977.
- Ramírez-Morales, D.; Rodríguez-Artavia, B.; Sáenz-Vargas, W.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, R.; Villalobos-González, W.; Mora-Barrantes, J.C. Artisanal mining for the extraction of gold through the use of mercury: State of the art of environmental impact in water, air and soil media. Rev. Tecnol. En Marcha 2019, 32, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, K.P.; Avudaiappan, S.; Maureira, N.; Da Costa Garcia Filho, F.; Monteiro, S.N.; Batista, I.D.; de Azevedo, A.R. Innovative use of copper mine tailing as an additive in cement mortar. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 2261–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, C. Reusing gold-mine tailings in cement mortars: Mechanical properties and socio-economic developments for the Lefke-Xeros area of Cyprus. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhit, D.; Kaliyeva, Z.; Bazarbayev, D. Effect of glass waste on ceramics and concrete production. Technobius 2025, 5, 0075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.R.; Hong, Z.Q.; Yin, Y.H.; Kou, S.C. Mechanical activated waste magnetite tailing as pozzolanic material substitute for cement in the preparation of cement products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkaddour, M.; Kenai, S.; Yahiaoui, W.; Bensaci, H.; Khatib, J. Rheological, mechanical and durability performance of some North African commercial binary and ternary cements. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Cordoba, O.; Castro-Herrera, F.; Paez-Melo, M. Mercury Bioaccumulation on Tadpoles of a Gold Mining Zone in Dagua River, Buenaventura, Valle del Cauca, Colombia. Acta Biol. Colomb. 2013, 18, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Odero, B.J.; Mutuku, R.N.; Nyomboi, T.; Gariy, Z.A. Contribution of Surface Treatment on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, Y.; Ren, T.; Horton, R. Quartz contents derived from particle density measurements improve the accuracy of soil thermal conductivity estimates. Geoderma 2023, 436, 116526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, A.M.T.; Solismaa, S.; Hansen, H.K.; Jensen, P.E. Evaluation of mine tailings’ potential as supplementary cementitious materials based on chemical, mineralogical and physical characteristics. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Yilmaz, E.; Song, W.; Cao, S. Mechanical, flexural and microstructural properties of cement-tailings matrix composites: Effects of fiber type and dosage. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 172, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.S.; Bezerra, A.C.d.S.; Costa, L.C.B.; Resende, D.M.; Kuster, L.D.; Peixoto, R.A.F. Sand Mining Tailings as Supplementary Cementitious Material. Buildings 2024, 14, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Prakash, S.; Reddy, P.S.R.; Misra, V.N. An overview of utilization of slag and sludge from steel industries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 50, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.; Chaudhary, S. Performance based evaluation of ISF slag as a substitute of natural sand in concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Jiaqi, F.; Ran, T.; Yuanrui, Z. Study on strength formation and frost resistance of concrete modified by molybdenum tailings. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, R.G.; Moreno, E.I.; Arjona, E. Resistencia de concreto con agregado de alta absorción y baja relación a/c. Rev. Alconpat 2012, 2, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, S.; Tafesse, M.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, H.K. Effects of quartz-based mine tailings on characteristics and leaching behavior of ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argane, R.; El Adnani, M.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bouzahzah, H.; Khalil, A.; Hakkou, R.; Taha, Y. Geochemical behavior and environmental risks related to the use of abandoned base-metal tailings as construction material in the upper-Moulouya district, Morocco. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Song, W. Evaluation of viscosity, strength and microstructural properties of cemented tailings backfill. Minerals 2018, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, L. Utilization of limestone powder as an activator for early-age strength improvement of slag concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C. Evaluación de Mezclas Proyectadas: Comportamiento y Durabilidad; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, Y.; Benzaazoua, M.; Edahbi, M.; Mansori, M.; Hakkou, R. Leaching and geochemical behavior of fired bricks containing coal wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 209, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseldeen Fakhri, R.; Thanon Dawood, E. Limestone powder, calcined clay and slag as quaternary blended cement used for green concrete production. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 79, 107644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Ng, P.L.; Kwan, A.K.H.; Li, L.G. Lowering cement content in mortar by adding superfine zeolite as cement replacement and optimizing mixture proportions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
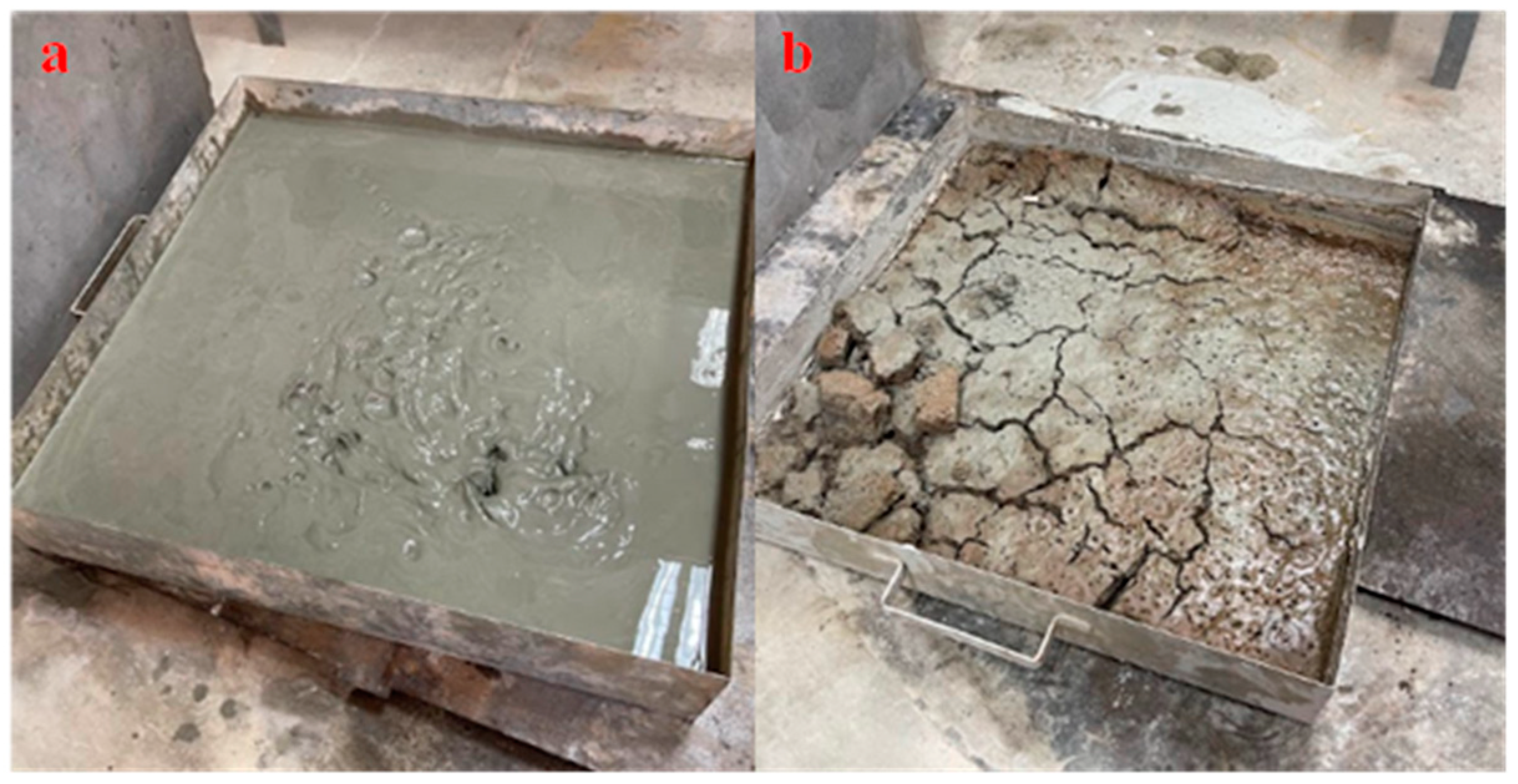



| Sample | Binders | Sand | Gravel | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | REMI | |||
| Dose 100:0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Dose 90:10 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 2 | 3 |
| Dose 80:20 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 2 | 3 |
| Dose 70:30 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 2 | 3 |
| Dose 60:40 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 2 | 3 |
| Dose 50:50 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Crystalline Phases Identified by XRD | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Tailings Slurry Mine: La Elsy LTDA | ||
| Name | Formula | Quantity | |
| Crystalline | Quartz | SiO2 | 28.49% |
| Orthoclase | (K0.931Na0.055Ca0.009Ba0.005) (Al0.97SI3.03O8) | 9.54% | |
| Dickite | Al2Si2O5 (OH)4 (HCONH2) | 7.85% | |
| Muscovite | (K0.99Na0.02) (Al1.42Mg0.33Fe0.24Ti0.04) ((Si3.45Al0.55) O10) (OH)2 | 5.27% | |
| Alunira | (K0.805Na0.132(H2O)0.063) Al3(SO4)2(OH)6 | 3.02% | |
| Pyrite | FeS1.92 | 1.39% | |
| Dickite | Al2Si2O5 (OH)4 | 1.38% | |
| Amorphous | 43.06% | ||
| Sample | Au g Ton−1 | Ag g Ton−1 | Hg mg kg−1 | Cyanide mg kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REMI | 2.55 | 32.11 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bueno-Gómez, T.; López-Bernier, Y.; Caycedo-García, M.S.; Ardila-Rey, J.D.; Rodríguez-Caicedo, J.P.; Joya-Cárdenas, D.R. Valorization of Gold Mining Tailings Sludge from Vetas, Colombia as Partial Cement Replacement in Concrete Mixes. Buildings 2025, 15, 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091419
Bueno-Gómez T, López-Bernier Y, Caycedo-García MS, Ardila-Rey JD, Rodríguez-Caicedo JP, Joya-Cárdenas DR. Valorization of Gold Mining Tailings Sludge from Vetas, Colombia as Partial Cement Replacement in Concrete Mixes. Buildings. 2025; 15(9):1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091419
Chicago/Turabian StyleBueno-Gómez, Thailin, Yariagna López-Bernier, Maya S. Caycedo-García, José Daniel Ardila-Rey, Juliana P. Rodríguez-Caicedo, and Diego R. Joya-Cárdenas. 2025. "Valorization of Gold Mining Tailings Sludge from Vetas, Colombia as Partial Cement Replacement in Concrete Mixes" Buildings 15, no. 9: 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091419
APA StyleBueno-Gómez, T., López-Bernier, Y., Caycedo-García, M. S., Ardila-Rey, J. D., Rodríguez-Caicedo, J. P., & Joya-Cárdenas, D. R. (2025). Valorization of Gold Mining Tailings Sludge from Vetas, Colombia as Partial Cement Replacement in Concrete Mixes. Buildings, 15(9), 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091419






