Effects of Phycosphere Bacteria on Their Algal Host Are Host Species-Specific and Not Phylogenetically Conserved
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
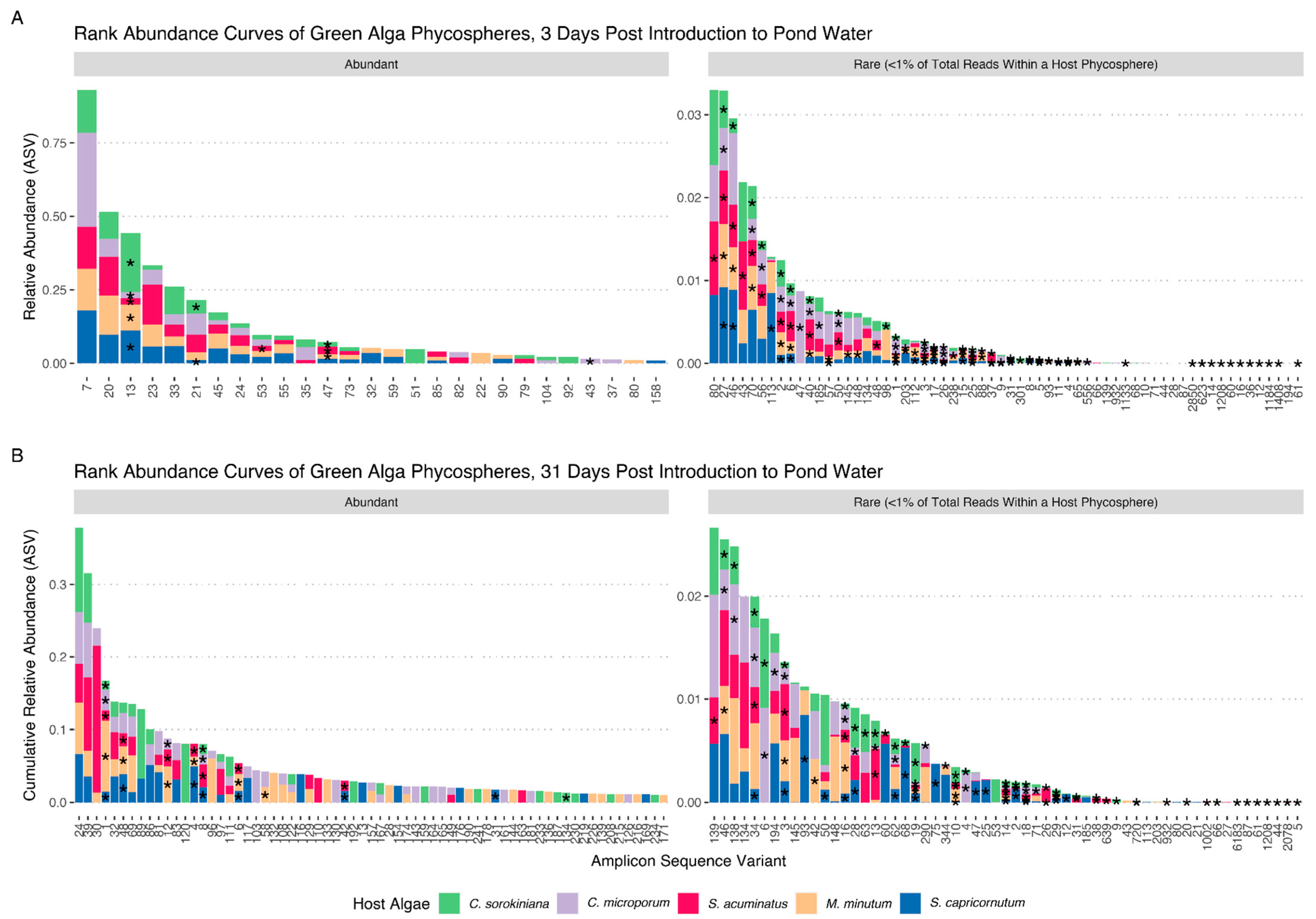
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guiry, M.D. How Many Species of Algae Are There? J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Randerson, J.T.; Falkowski, P. Primary Production of the Biosphere: Integrating Terrestrial and Oceanic Components. Science 1998, 281, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, R.K.; Finlayson, C.M.; Humphries, P.; Sims, N.C.; Hladyz, S. Anthropocene Baselines: Assessing Change and Managing Biodiversity in Human-Dominated Aquatic Ecosystems. BioScience 2015, 65, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R.; Paulsen, I.T. Microbiology of the Anthropocene. Anthropocene 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.; Rost, B.; Rynearson, T.A. Evolutionary Potential of Marine Phytoplankton under Ocean Acidification. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohbeck, K.T.; Riebesell, U.; Reusch, T.B.H. Adaptive Evolution of a Key Phytoplankton Species to Ocean Acidification. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Howard, M.D.A.; Johnson, M.-V.V.; Morton, S.L.; Perkins, D.A.K.; Reavie, E.D.; Scott, G.I.; Smith, S.A.; Steevens, J.A. Are Harmful Algal Blooms Becoming the Greatest Inland Water Quality Threat to Public Health and Aquatic Ecosystems?: Harmful Algal Blooms: The Greatest Water Quality Threat? Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.; Burkholder, J.; Anderson, D.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.; Gobler, C.; Dortch, Q.; Heil, C.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and Harmful Algal Blooms: A Scientific Consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgianna, D.R.; Mayfield, S.P. Exploiting Diversity and Synthetic Biology for the Production of Algal Biofuels. Nature 2012, 488, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghifard, R. Algal Biofuels. Photosynth. Res. 2013, 117, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Aden, A.; Pienkos, P.T. Techno-Economic Analysis of Autotrophic Microalgae for Fuel Production. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, J.W.; McGinty, C.M.; Quinn, J.C. Global Evaluation of Biofuel Potential from Microalgae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8691–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, D.N.; Godwin, C.M.; Hietala, D.C.; Cardinale, B.J.; Lin, X.N.; Savage, P.E. Biodiversity Improves Life Cycle Sustainability Metrics in Algal Biofuel Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9279–9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D.; Kilham, S.S.; Kilham, P. Phytoplankton Community Ecology: The Role of Limiting Nutrients. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1982, 13, 349–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.R.; Amin, S.A.; Raina, J.-B.; Stocker, R. Zooming in on the Phycosphere: The Ecological Interface for Phytoplankton–Bacteria Relationships. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, R.; Kim, B.-H.; Cho, D.-H.; Oh, H.-M.; Kim, H.-S. Algae–Bacteria Interactions: Evolution, Ecology and Emerging Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, W.; Mitchell, R. Chemotactic and Growth Responses of Marine Bacteria to Algal Extracellular Products. Biol. Bull. 1972, 143, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackrel, S.L.; White, J.D.; Evans, J.T.; Buffin, K.; Hayden, K.; Sarnelle, O.; Denef, V.J. Genome Evolution and Host-Microbiome Shifts Correspond with Intraspecific Niche Divergence within Harmful Algal Bloom-Forming Microcystis aeruginosa. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 3994–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.C.; Jackrel, S.L.; Smith, D.J.; Dick, G.J.; Denef, V.J. Genotype and Host Microbiome Alter Competitive Interactions between Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella sorokiniana. Harmful Algae 2020, 99, 101939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, M.T.; Lawrence, A.D.; Raux-Deery, E.; Warren, M.J.; Smith, A.G. Algae Acquire Vitamin B 12 through a Symbiotic Relationship with Bacteria. Nature 2005, 438, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.A.A.; Kazamia, E.; Cicuta, P.; Smith, A.G. Direct Exchange of Vitamin B12 Is Demonstrated by Modelling the Growth Dynamics of Algal-Bacterial Cocultures. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazamia, E.; Czesnick, H.; Nguyen, T.T.V.; Croft, M.T.; Sherwood, E.; Sasso, S.; Hodson, S.J.; Warren, M.J.; Smith, A.G. Mutualistic Interactions between Vitamin B12-Dependent Algae and Heterotrophic Bacteria Exhibit Regulation. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirri, E.; Pohnert, G. Algae–bacteria Interactions That Balance the Planktonic Microbiome. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, F.; Malfatti, F. Microbial Structuring of Marine Ecosystems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.A.; Parker, M.S.; Armbrust, E.V. Interactions between Diatoms and Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratbak, G.; Thingstad, T.F. Phytoplankton-Bacteria Interactions: An Apparent Paradox? Analysis of a Model System with Both Competition and Commensalism. Deep Sea Res. B Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1986, 33, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.; Pohnert, G. Interactions of the Algicidal Bacterium Kordia algicida with Diatoms: Regulated Protease Excretion for Specific Algal Lysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedsayamdost, M.R.; Case, R.J.; Kolter, R.; Clardy, J. The Jekyll-and-Hyde Chemistry of Phaeobacter Gallaeciensis. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tomasch, J.; Michael, V.; Bhuju, S.; Jarek, M.; Petersen, J.; Wagner-Döbler, I. Identification of Genetic Modules Mediating the Jekyll and Hyde Interaction of Dinoroseobacter shibae with the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackrel, S.L.; Schmidt, K.C.; Cardinale, B.J.; Denef, V.J. Microbiomes Reduce Their Host’s Sensitivity to Interspecific Interactions. mBio 2020, 11, e02657-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackrel, S.L.; Yang, J.W.; Schmidt, K.C.; Denef, V.J. Host Specificity of Microbiome Assembly and Its Fitness Effects in Phytoplankton. ISME J. 2021, 15, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigemann, F.; Hilt, S.; Salka, I.; Grossart, H.-P. Bacterial Community Composition Associated with Freshwater Algae: Species Specificity vs. Dependency on Environmental Conditions and Source Community. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Levold, F.; Allgaier, M.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Marine Diatom Species Harbour Distinct Bacterial Communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mönnich, J.; Tebben, J.; Bergemann, J.; Case, R.; Wohlrab, S.; Harder, T. Niche-Based Assembly of Bacterial Consortia on the Diatom Thalassiosira Rotula Is Stable and Reproducible. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1614–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sison-Mangus, M.P.; Jiang, S.; Tran, K.N.; Kudela, R.M. Host-Specific Adaptation Governs the Interaction of the Marine Diatom, Pseudo-Nitzschia and Their Microbiota. ISME J. 2014, 8, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilham, S.S.; Kreeger, D.A.; Lynn, S.G.; Goulden, C.E.; Herrera, L. COMBO: A Defined Freshwater Culture Medium for Algae and Zooplankton. Hydrobiologia 1998, 377, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genolini, C.; Ecochard, R.; Benghezal, M.; Driss, T.; Andrieu, S.; Subtil, F. KmlShape: An Efficient Method to Cluster Longitudinal Data (Time-Series) According to Their Shapes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syakur, M.A.; Khotimah, B.K.; Rochman, E.M.S.; Satoto, B.D. Integration K-Means Clustering Method and Elbow Method For Identification of The Best Customer Profile Cluster. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 336, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketchen, D.J.; Shook, C.L. The Application of Cluster Analysis in Strategic Management Research: An Analysis and Critique. Strateg. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S Ribosomal DNA Amplification for Phylogenetic Study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, P.; Conklin, D. NanoDrop Microvolume Quantitation of Nucleic Acids. J. Vis. Exp.—JoVE 2010, 45, e2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a Dual-Index Sequencing Strategy and Curation Pipeline for Analyzing Amplicon Sequence Data on the MiSeq Illumina Sequencing Platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing Mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-Species Living Tree Project (LTP)” Taxonomic Frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. RStudio, PBC, Boston, MA, USA. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Silge, J. Tidytext: Text Mining Using Dplyr, Ggplot2, and Other Tidy Tools. 2022. Available online: https://juliasilge.github.io/tidytext/ (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Neuwirth, E. RColorBrewer: ColorBrewer Palettes. 2022. Available online: https://r-graph-gallery.com/38-rcolorbrewers-palettes.html (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Kassambara, A. Ggpubr: Ggplot2 Based Publication Ready Plots. 2022. Available online: https://rpkgs.datanovia.com/ggpubr/ (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Campitelli, E. Ggnewscale: Multiple Fill and Colour Scales in Ggplot2. 2022. Available online: https://eliocamp.github.io/ggnewscale/ (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Petzoldt, T. Growthrates: Estimate Growth Rates from Experimental Data. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/growthrates/index.html (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Signorell, A. DescTools: Tools for Descriptive Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/DescTools/index.html (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.-Y. Ggtree: An R Package for Visualization and Annotation of Phylogenetic Trees with Their Covariates and Other Associated Data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Dai, Z.; Guo, P.; Fu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Feng, T.; Chen, M.; Zhan, L.; et al. GgtreeExtra: Compact Visualization of Richly Annotated Phylogenetic Data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 4039–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. Ape 5.0: An Environment for Modern Phylogenetics and Evolutionary Analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassambara, A. Rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests. 2022. Available online: https://mran.microsoft.com/web/packages/rstatix/index.html (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Steen, A.D.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Carini, P.; DeAngelis, K.M.; Fierer, N.; Lloyd, K.G.; Cameron Thrash, J. High Proportions of Bacteria and Archaea across Most Biomes Remain Uncultured. ISME J. 2019, 13, 3126–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henson, M.W.; Lanclos, V.C.; Pitre, D.M.; Weckhorst, J.L.; Lucchesi, A.M.; Cheng, C.; Temperton, B.; Thrash, J.C. Expanding the Diversity of Bacterioplankton Isolates and Modeling Isolation Efficacy with Large-Scale Dilution-to-Extinction Cultivation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00943-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauro, F.M.; McDougald, D.; Thomas, T.; Williams, T.J.; Egan, S.; Rice, S.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Ting, L.; Ertan, H.; Johnson, J.; et al. The Genomic Basis of Trophic Strategy in Marine Bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15527–15533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smriga, S.; Fernandez, V.I.; Mitchell, J.G.; Stocker, R. Chemotaxis toward Phytoplankton Drives Organic Matter Partitioning among Marine Bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1576–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.L.; Kallstrom, G.; Faith, J.J.; Reyes, A.; Moore, A.; Dantas, G.; Gordon, J.I. Extensive Personal Human Gut Microbiota Culture Collections Characterized and Manipulated in Gnotobiotic Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6252–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, P.; Yan, X. Succession of Bacterioplankton Communities over Complete Gymnodinium-Diatom Bloom Cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 135951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paver, S.F.; Hayek, K.R.; Gano, K.A.; Fagen, J.R.; Brown, C.T.; Davis-Richardson, A.G.; Crabb, D.B.; Rosario-Passapera, R.; Giongo, A.; Triplett, E.W.; et al. Interactions between Specific Phytoplankton and Bacteria Affect Lake Bacterial Community Succession: Phytoplankton Affect Bacterial Community Dynamics. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2489–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paver, S.F.; Youngblut, N.D.; Whitaker, R.J.; Kent, A.D. Phytoplankton Succession Affects the Composition of Polynucleobacter Subtypes in Humic Lakes: Phytoplankton Affect Polynucleobacter Composition. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Cai, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z.; Kong, L.; Yu, Y.; Kong, F. Molecular Identification of the Colony-Associated Cultivable Bacteria of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa and Their Effects on Algal Growth. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2009, 24, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, K.; Nishijima, T.; Murata, H.; Doi, S.; Hata, Y. Distribution of Bacteria Influential on the Development and the Decay of Gymnodinium nagasakiense Red Tide and Their Effects on Algal Growth. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1991, 57, 2321–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, K.; Nishijima, T.; Hata, Y. Availability of Deep Seawater and Effects of Bacteria Isolated from Deep Seawater on the Mass Culture of Food Microalga Chaetoceros ceratosporum. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1992, 58, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, K.; Nishijima, T.; Ishida, Y. Stimulative and Inhibitory Effects of Bacteria on the Growth of Microalgae. Hydrobiologia 1997, 358, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Takihana, N.; Aoyagi, H.; Hanada, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Ohmura, N.; Saiki, H.; Tanaka, H. Symbiotic Association in Chlorella Culture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 51, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.A.; Green, D.H.; Hart, M.C.; Küpper, F.C.; Sunda, W.G.; Carrano, C.J. Photolysis of Iron–Siderophore Chelates Promotes Bacterial–Algal Mutualism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17071–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.A.; Hmelo, L.R.; van Tol, H.M.; Durham, B.P.; Carlson, L.T.; Heal, K.R.; Morales, R.L.; Berthiaume, C.T.; Parker, M.S.; Djunaedi, B.; et al. Interaction and Signalling between a Cosmopolitan Phytoplankton and Associated Bacteria. Nature 2015, 522, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, A.; LeCleir, G.R.; Gulvik, C.A.; González, J.M. Master Recyclers: Features and Functions of Bacteria Associated with Phytoplankton Blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koedooder, C.; Stock, W.; Willems, A.; Mangelinckx, S.; De Troch, M.; Vyverman, W.; Sabbe, K. Diatom-Bacteria Interactions Modulate the Composition and Productivity of Benthic Diatom Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, W.; Blommaert, L.; De Troch, M.; Mangelinckx, S.; Willems, A.; Vyverman, W.; Sabbe, K. Host Specificity in Diatom–Bacteria Interactions Alleviates Antagonistic Effects. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, H.; Abbas, B.; Witte, H.; Muyzer, G. Genetic Diversity of “satellite” Bacteria Present in Cultures of Marine Diatoms. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 42, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapp, M.; Schwaderer, A.S.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Hoppe, H.-G.; Gerdts, G.; Wichels, A. Species-Specific Bacterial Communities in the Phycosphere of Microalgae? Microb. Ecol. 2007, 53, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasti, S.; Sieracki, M.E.; Poulton, N.J.; Giewat, M.W.; Rooney-Varga, J.N. Phylogenetic Diversity and Specificity of Bacteria Closely Associated with Alexandrium Spp. and Other Phytoplankton. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3483–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiny, A.C.; Treseder, K.; Pusch, G. Phylogenetic Conservatism of Functional Traits in Microorganisms. ISME J. 2013, 7, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lladó Fernández, S.; Větrovský, T.; Baldrian, P. The Concept of Operational Taxonomic Units Revisited: Genomes of Bacteria That Are Regarded as Closely Related Are Often Highly Dissimilar. Folia Microbiol. 2019, 64, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.L.; White, J.D.; Denef, V.J. Phylogenetic Conservation of Freshwater Lake Habitat Preference Varies between Abundant Bacterioplankton Phyla. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, G.; Cornejo-Castillo, F.M.; Borrull, E.; Díez-Vives, C.; Lara, E.; Vaqué, D.; Arrieta, J.M.; Duarte, C.M.; Gasol, J.M.; Acinas, S.G. Particle-Association Lifestyle Is a Phylogenetically Conserved Trait in Bathypelagic Prokaryotes. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 5692–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baker, D.; Lauer, J.; Ortega, A.; Jackrel, S.L.; Denef, V.J. Effects of Phycosphere Bacteria on Their Algal Host Are Host Species-Specific and Not Phylogenetically Conserved. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010062
Baker D, Lauer J, Ortega A, Jackrel SL, Denef VJ. Effects of Phycosphere Bacteria on Their Algal Host Are Host Species-Specific and Not Phylogenetically Conserved. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010062
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaker, Dylan, James Lauer, Anna Ortega, Sara L. Jackrel, and Vincent J. Denef. 2023. "Effects of Phycosphere Bacteria on Their Algal Host Are Host Species-Specific and Not Phylogenetically Conserved" Microorganisms 11, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010062
APA StyleBaker, D., Lauer, J., Ortega, A., Jackrel, S. L., & Denef, V. J. (2023). Effects of Phycosphere Bacteria on Their Algal Host Are Host Species-Specific and Not Phylogenetically Conserved. Microorganisms, 11(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010062




