Antibiofilm Potential of Coelomic Fluid and Paste of Earthworm Pheretima posthuma (Clitellata, Megascolecidae) against Pathogenic Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Earthworm Collection
2.2. Coelomic Fluid Extraction
2.3. Body Paste Formation
2.4. Pathogenic Bacteria Collection
2.5. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
2.6. Biofilm Formation Time Kinetics
2.7. Antibiofilm Assay of PCF and PBP
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wojcik, G.; Ring, N.; McCulloch, C.; Willis, D.S.; Williams, B.; Kydonaki, K. Understanding the complexities of antibiotic prescribing behaviour in acute hospitals: A systematic review and meta-ethnography. Arch. Public Health 2021, 79, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reygaert, W.C. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwole, O.M. Biofilm: Formation and natural products’ approach to control—A review. Afr. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 16, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.; Mitterer, F.; Pombo, J.P.; Schild, S. Biofilms by bacterial human pathogens: Clinical relevance—Development, composition and regulation-therapeutical strategies. Microb. Cell 2021, 8, 28–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anju, V.T.; Busi, S.; Imchen, M.; Kumavath, R.; Mohan, M.S.; Salim, S.A.; Subhaswaraj, P.; Dyavaiah, M. Polymicrobial infections and biofilms: Clinical significance and eradication strategies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asma, S.T.; Imre, K.; Morar, A.; Herman, V.; Acaroz, U.; Mukhtar, H.; Arslan-Acaroz, D.; Shah, S.R.A.; Gerlach, R. An overview of biofilm formation-combating strategies and mechanisms of action of antibiofilm agents. Life 2022, 12, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Liaqat, I.; Hanif, U.; Sultan, A.; Ara, C.; Aftab, N.; Butt, A. Medicinal perspective of antibacterial bioactive agents in earthworms (Clitellata, Annelida): A comprehensive review. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Yadav, S. Immuno-defense strategy in earthworms: A review article. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Z.H.; Yin, J.J.; Luo, W.; Kotian, R.N.; Gao, S.S.; Yi, Z.Q.; Xiao, W.F.; Li, W.P.; Li, Y.S. The effect of earthworm extract on promoting skin wound healing. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilej, M.; Procházková, P.; Šilerová, M.; Josková, R. Earthworm immunity. Invertebr. Immun. 2010, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubalová, R.; Procházková, P.; Dvořák, J.; Škanta, F.; Bilej, M. The role of earthworm defense mechanisms in ecotoxicity studies. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2015, 12, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, E.L.; Hirabayashi, K.; Balamurugan, M. Dilong: Food for thought and medicine. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2012, 2, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prakash, M.; Gunasekaran, G. Antibacterial activity of the indigenous earthworms Lampito mauritii (Kinberg) and Perionyx excavatus (Perrier). J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2011, 17, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, B.; Niu, B. An extract from the earthworm Eisenia fetida non-specifically inhibits the activity of influenza and adenoviruses. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012, 32, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popoviæ, M.; Enjak, T.M.H.; Babiæ, T.; Kos, J.; Mira, G.A. Effect of earthworm (G-90) extract on formation and lysis of clots originated from venous blood of dogs with cardiopathies and with malignant tumors. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2001, 7, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ečimović, S.; Vrandečić, K.; Kujavec, M.; Žulj, M.; Ćosić, J.; Velki, M. Antifungal Activity of Earthworm Coelomic Fluid Obtained from Eisenia andrei, Dendrobaena veneta and Allolobophora chlorotica on Six Species of Phytopathogenic Fungi. Environments 2021, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Liaqat, I.; Ali, N.M.; Arshad, N.; Hanif, U.; Sajjad, S.; Sardar, A.A.; Awan, U.F.; Khan, F.S.; Slahuddin. Antibacterial and bacteriostatic potential of coelomic fluid and body paste of Pheretima posthuma (Vaillant, 1868) (Clitellata, Megascolecidae) against ampicillin resistant clinical bacterial isolates. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 83, e247016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, M.; Parthasarathi, K.; Cooper, E.L.; Ranganathan, L.S. Anti-inflammatory and anti-pyretic activities of earthworm extract—Lampito mauritii (Kinberg). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 121, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiołka, M.J.; Rzymowska, J.; Bilska, S.; Lewtak, K.; Dmoszyńska-Graniczka, M.; Grzywnowicz, K.; Kaźmierski, W.; Urbanik-Sypniewska, T. Antitumor activity and apoptotic action of coelomic fluid from the earthworm Dendrobaena veneta against A549 human lung cancer cells. Apmis 2019, 127, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waluyo, J.; Wahyuni, D.; Nuri, N. Antipyretic effects of dried earthworm (Pheretima javanica k.) in male white rat (Rattus norvegicus) with typhoid fever. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 8, 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Deng, Z.H.; Li, R.; Cheng, G.; Kotian, R.N.; Li, Y.S.; Li, W.P. Study of analgesic effect of earthworm extract. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Augustine, D.; Rao, R.S.; Anbu, J.; Murthy, K.C. In vitro cytotoxic and apoptotic induction effect of earthworm coelomic fluid of Eudrilus eugeniae, Eisenia foetida, and Perionyx excavatus on human oral squamous cell carcinoma-9 cell line. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramnarain, Y.I.; Ansari, A.A.; Ori, L. Research report on one local earthworm species in surname. J. Biol. Nat. 2016, 5, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore, R.J. Amynthas carnosus (Goto & Hatai, 1899) redescribed on its neotype (Oligochaeta: Megadrilacea: Megascole- 361 cidae). J. Species Res. 2012, 1, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.R.; Biradar, P.M. Earthworm’s coelomic fluid: Extraction and importance. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2017, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Endharti, A.T.; Purnamasari, Y.; Primasari, R.; Poeranto, S.; Permana, S. Coelomic fluid of Lumbricus rubellus synergistically enhances cytotoxic effect of 5-Fluorouracil through modulation of focal adhesion kinase and P21 in HT-29 cancer cell line. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 5632859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esaivani, C.; Vasanthi, K.; Singh, A. An investigation on antimicrobial potency of coelomic fluid of earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae. Br. J. Med. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Vasanthi, K.; Chairman, K.; Singh, A.R. Antimicrobial activity of earthworm (Eudrilus eugeniae) paste. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 783–789. [Google Scholar]
- Liaqat, I.; Mirza, S.A.; Iqbal, R.; Ali, N.M.; Saleem, G.; Majid, S.; Shahid, M. Flagellar motility plays important role in Biofilm formation of Bacillus cereus and Yersinia enterocolitica. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Olawuwo, O.S.; Famuyide, I.M.; McGaw, L.J. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of selected medicinal plant leaf extracts against pathogens implicated in poultry diseases. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, A.; Esfandiari, Z.; Shoaei, P.; Ataei, B. Evaluation of virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, and biofilm formation of Escherichia coli isolated from milk and dairy products in Isfahan, Iran. Foods 2022, 11, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drame, I.; Lafforgue, C.; Formosa-Dague, C.; Chapot-Chartier, M.P.; Piard, J.C.; Castelain, M.; Dague, E. Pili and other surface proteins influence the structure and the nanomechanical properties of Lactococcus lactis biofilms. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Panda, A.K.; De Mandal, S.; Shakeel, M.; Bisht, S.S.; Khan, J. Natural anti-biofilm agents: Strategies to control biofilm-forming pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 566325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, I.; Bachmann, R.T.; Sabri, A.N.; Edyvean, R.G. Isolate-specific effects of patulin, penicillic Acid and EDTA on biofilm formation and growth of dental unit water line biofilm isolates. Curr. Microbial. 2010, 61, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, S.S.; Katas, H.; Azmi, F.; Busra, M.F.M. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm biosynthesised silver and gold nanoparticles for medical applications: Mechanism of action, toxicity and current status. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, C.; Tuchscherr, L.; Unger, N.; Pöllath, C.; Gladigau, F.; Popp, J.; Löffler, B.; Neugebauer, U. Correlation of crystal violet biofilm test results of Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates with Raman spectroscopic read-out. J. Ram. Spectrosc. 2021, 52, 2660–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, I.; Liaqat, M.; Tahir, H.M.; Ali, N.M.; Arshad, M.; Arshad, N. Motility effects biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter cloacae. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 32, 927–932. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlich, G.A.; Chen, C.Y.; Cottrell, B.J.; Nguyen, L.H. Growth media and temperature effects on biofilm formation by serotype O157: H7 and non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 354, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yulinery, T.; Triana, E.; Suharna, N.; Nurhidayat, N. Isolation and anti-Escherichia coli biofilm activity of lytic bacteriophages isolated from water environment in vitro. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 308, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.M.; Gomes, M.; Gomes, L.C.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Mergulhão, F.J. Performance of Graphene/Polydimethylsiloxane Surfaces against S. aureus and P. aeruginosa Single- and Dual-Species Biofilms. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, S.; Harjai, K.; Chhibber, S. Susceptibility of different phases of biofilm of Klebsiella pneumoniae to three different antibiotics. J Antibiot. 2013, 66, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaqat, I.; Gulab, B.; Hanif, U.; Sultan, A.; Sadiqa, A.; Zafar, U.; Afzaal, M.; Naseem, S.; Akram, S.; Saleem, G. Honey Potential as Antibiofilm, Antiquorum Sensing and Dispersal Agent against Multispecies Bacterial Biofilm. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 71, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyofuku, M.; Inaba, T.; Kiyokawa, T.; Obana, N.; Yawata, Y.; Nomura, N. Environmental factors that shape biofilm formation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, R.G.; Saiqa, A.; Domínguez, J.; Jamil, M.; Manzoor, S.; Wazir, S.; Shaheen, B.; Parveen, A.; Khan, R.; Ali, S.; et al. Therapeutic values of earthworm species extract from Azad Kashmir as Anticoagulant, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Agents. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 6949117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bais, D.J.D.; Hiwatig, M.A.R.; Jardin, A.R.; Lacsamana, M.S.L.; Manalo, P.M.; Magbojos-Magtibay, C.R. Antibiofilm Activity of Coelomic Fluid from Holothuria Scabra (Sandfish) Against Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Escherichia Coli. STETH 2018, 12, 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Cusimano, M.G.; Spinello, A.; Barone, G.; Schillaci, D.; Cascioferro, S.; Magistrato, A.; Parrino, B.; Arizza, V.; Vitale, M.A. Synthetic Derivative of Antimicrobial Peptide Holothuroidin 2 from Mediterranean Sea Cucumber (Holothuria tubulosa) in the Control of Listeria monocytogenes. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajani, M.; Hosseini, S.F.; Rezaei, M.; Schillaci, D. Evaluation of antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of phases extracted from coelomic fluid of burrowing urchin (Echinometra mathaei). Aquat. Physiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 145–174. [Google Scholar]
| Methods | Weight of P. posthuma Earthworms (gram) | Volume of PCF (mL) | T (°C) | Time (minutes) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat shock method | 30 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 45 ± 1 °C | 25 | 3 g of earthworms died the while others remained alive and active; produced concentrated fluid. |
| Cold shock method | 30 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 15 ± 1 °C | 25 | All earthworms were active and alive throughout the shock; excreted concentrated fluid. |
| Concentrations (µg/mL) | Pathogenic Bacterial Strains | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | P. aeruginosa | K. pneumoniae | E. coli | |||||
| PBP | PCF | PBP | PCF | PBP | PCF | PBP | PCF | |
| 400 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 200 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 100 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 50 | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | − |
| 25 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 12.5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 6.25 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3.13 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1.56 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 0.781 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| MICs (µg/mL) | 50 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 50 | 100 | 50 | 50 |
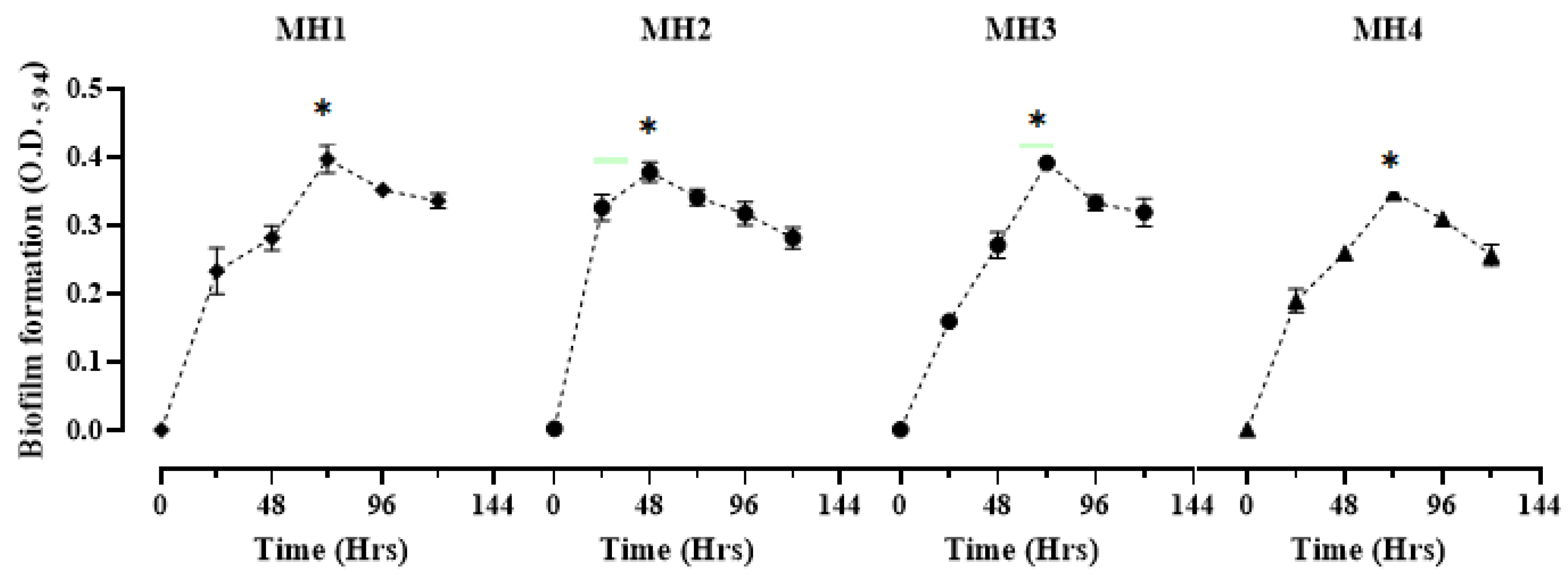
| Bacterial Isolates | Biofilm Formation with Time Kinetics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (h) | 24 (h) | 48 (h) | 72 (h) | 96 (h) | 120 (h) | p Value | |
| MH1 | 0.001 ± 0.0 e | 0.233 ± 0.01 d | 0.282 ± 0.0 cd | 0.397 ± 0.02 a | 0.352 ± 0.03 ab | 0.336 ± 0.01 bc | <0.005 |
| MH2 | 0.003 ± 0.0 d | 0.327 ± 0.01 b | 0.378 ± 0.02 a | 0.342 ± 0.01 ab | 0.318 ± 0.02 bc | 0.282 ± 0.01 c | <0.004 |
| MH3 | 0.005 ± 0.0 e | 0.160 ± 0.02 d | 0.272 ± 0.05 c | 0.392 ± 0.02 a | 0.333 ± 0.05 b | 0.320 ± 0.02 b | <0.008 |
| MH4 | 0.002 ± 0.0 e | 0.190 ± 0.01 d | 0.259 ± 0.02 c | 0.348 ± 0.03 a | 0.310 ± 0.04 b | 0.257 ± 0.01 c | <0.006 |
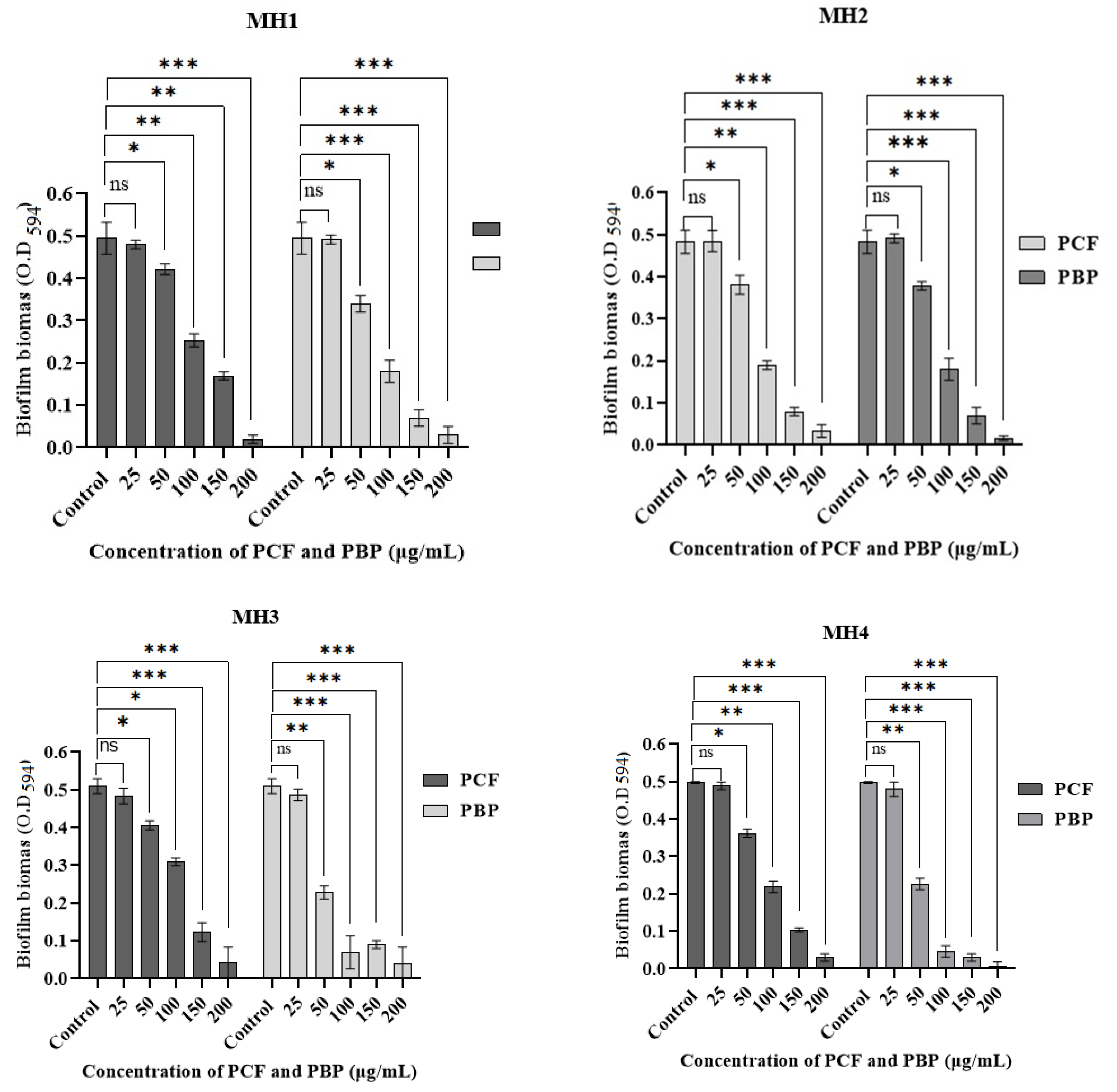
| Bacterial Strains | % of Biofilm Inhibition | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentrations of PCF (µg/mL) | Concentrations of PBP (µg/mL) | |||||||||
| 25 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |
| MH1 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 22.08 ± 2.6 | 61.15 ± 1.0 | 83.64 ± 2.6 | 93.25 ± 2.5 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 22.69 ± 1.3 | 63.19 ± 3.3 | 85.68 ± 2.5 | 93.86 ± 2 |
| MH2 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 23.9 ± 3.5 | 50.87 ± 3.5 | 65.63 ± 2.5 | 95.91 ± 1.3 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 30.47 ± 2.6 | 63.19 ± 0.5 | 85.5 ± 3.0 | 93.86 ± 2 |
| MH3 | 5.23 ± 1 | 20.1 ± 0.5 | 54.68 ± 2.5 | 75.88 ± 1.5 | 92.74 ± 3.5 | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 55.29 ± 1.6 | 72.94 ± 3.3 | 82.35 ± 1.0 | 93.34 ± 2 |
| MH4 | 1.6 ± 1.0 | 27.71 ± 2.5 | 56.22 ± 1.5 | 79.71 ± 0.3 | 94.97 ± 2.5 | 5.61 ± 1 | 54.81 ± 1.6 | 90.96 ± 1.6 | 94.98 ± 2.0 | 99.8 ± 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, M.; Liaqat, I.; Zafar, U.; Saleem, S.; Aftab, M.N.; Khalid, A.; Modafer, Y.; Alshammari, F.A.; Mashraqi, A.; El-Mansi, A.A. Antibiofilm Potential of Coelomic Fluid and Paste of Earthworm Pheretima posthuma (Clitellata, Megascolecidae) against Pathogenic Bacteria. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020342
Hussain M, Liaqat I, Zafar U, Saleem S, Aftab MN, Khalid A, Modafer Y, Alshammari FA, Mashraqi A, El-Mansi AA. Antibiofilm Potential of Coelomic Fluid and Paste of Earthworm Pheretima posthuma (Clitellata, Megascolecidae) against Pathogenic Bacteria. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(2):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020342
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Mudassar, Iram Liaqat, Urooj Zafar, Sadiah Saleem, Muhammad Nauman Aftab, Awais Khalid, Yosra Modafer, Fahdah Ayed Alshammari, Abdullah Mashraqi, and Ahmed A. El-Mansi. 2023. "Antibiofilm Potential of Coelomic Fluid and Paste of Earthworm Pheretima posthuma (Clitellata, Megascolecidae) against Pathogenic Bacteria" Microorganisms 11, no. 2: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020342
APA StyleHussain, M., Liaqat, I., Zafar, U., Saleem, S., Aftab, M. N., Khalid, A., Modafer, Y., Alshammari, F. A., Mashraqi, A., & El-Mansi, A. A. (2023). Antibiofilm Potential of Coelomic Fluid and Paste of Earthworm Pheretima posthuma (Clitellata, Megascolecidae) against Pathogenic Bacteria. Microorganisms, 11(2), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020342








