The Distribution and Influencing Factors of Hypolithic Microbial Communities in the Hexi Corridor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction and Gene Sequencing
2.3. Measurements of Colonization, Soil Physicochemical Characteristic Analyses, and Environmental Data Collection
2.4. Keystone Species Analysis and Function Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Factors and Colonization Rates
3.2. The Physico-Chemical Properties of the Soil Samples
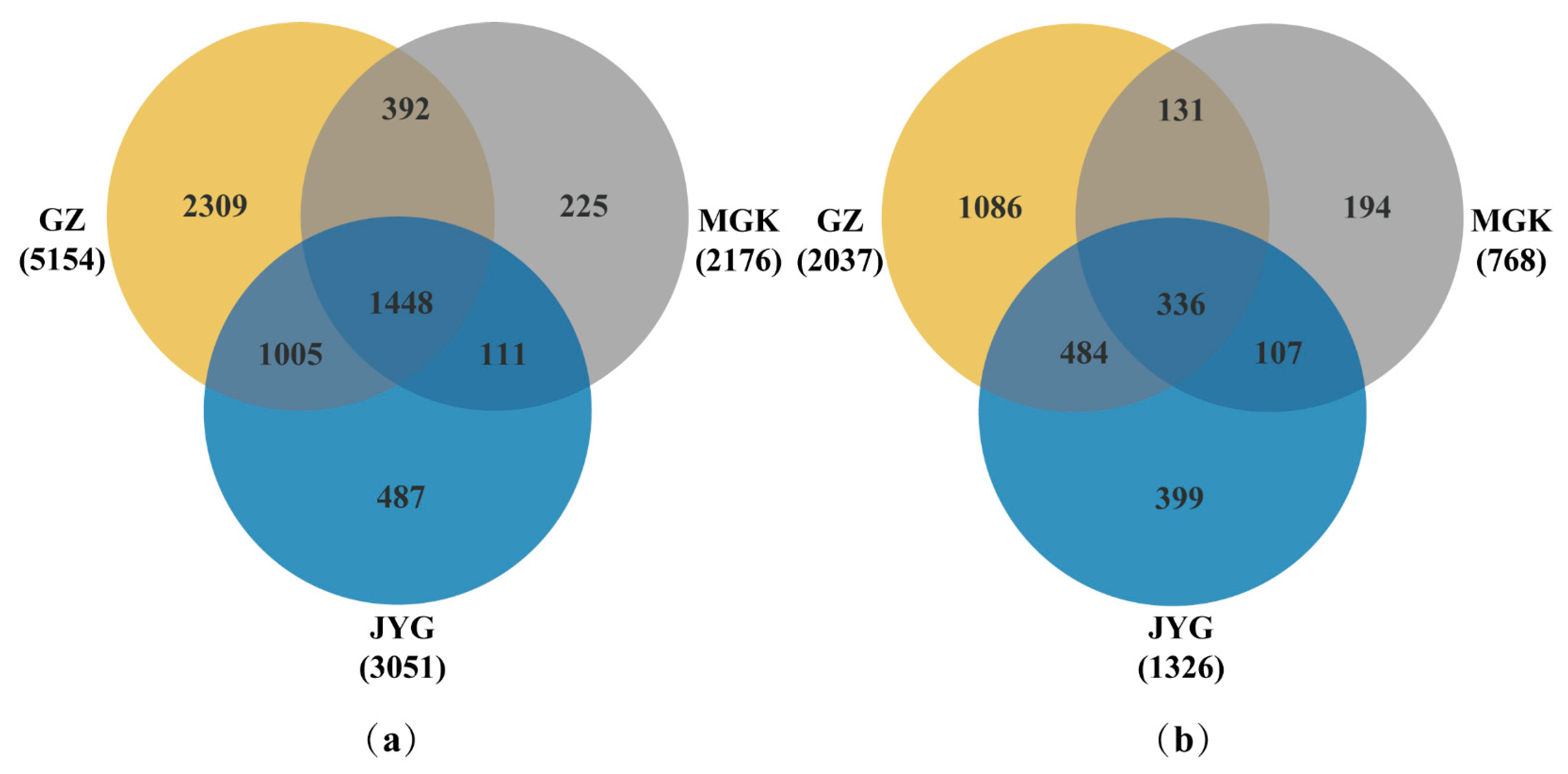
3.3. Hypolithic Microbial Community
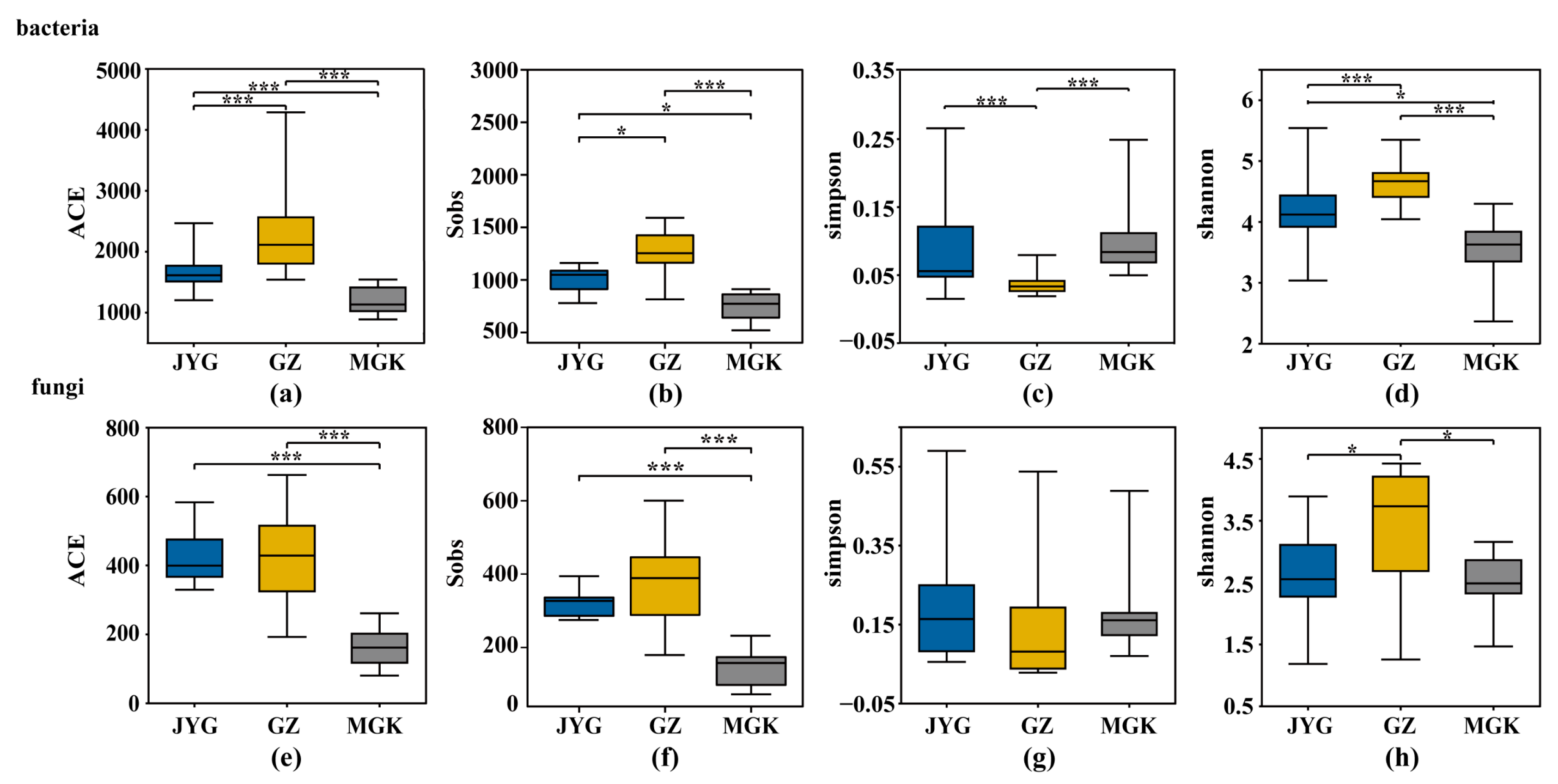
3.4. Alpha Diversity Index of the Hypolithic Microbial Community
3.5. Beta Diversity of the Hypolithic Microbial Community and Functional Predictions
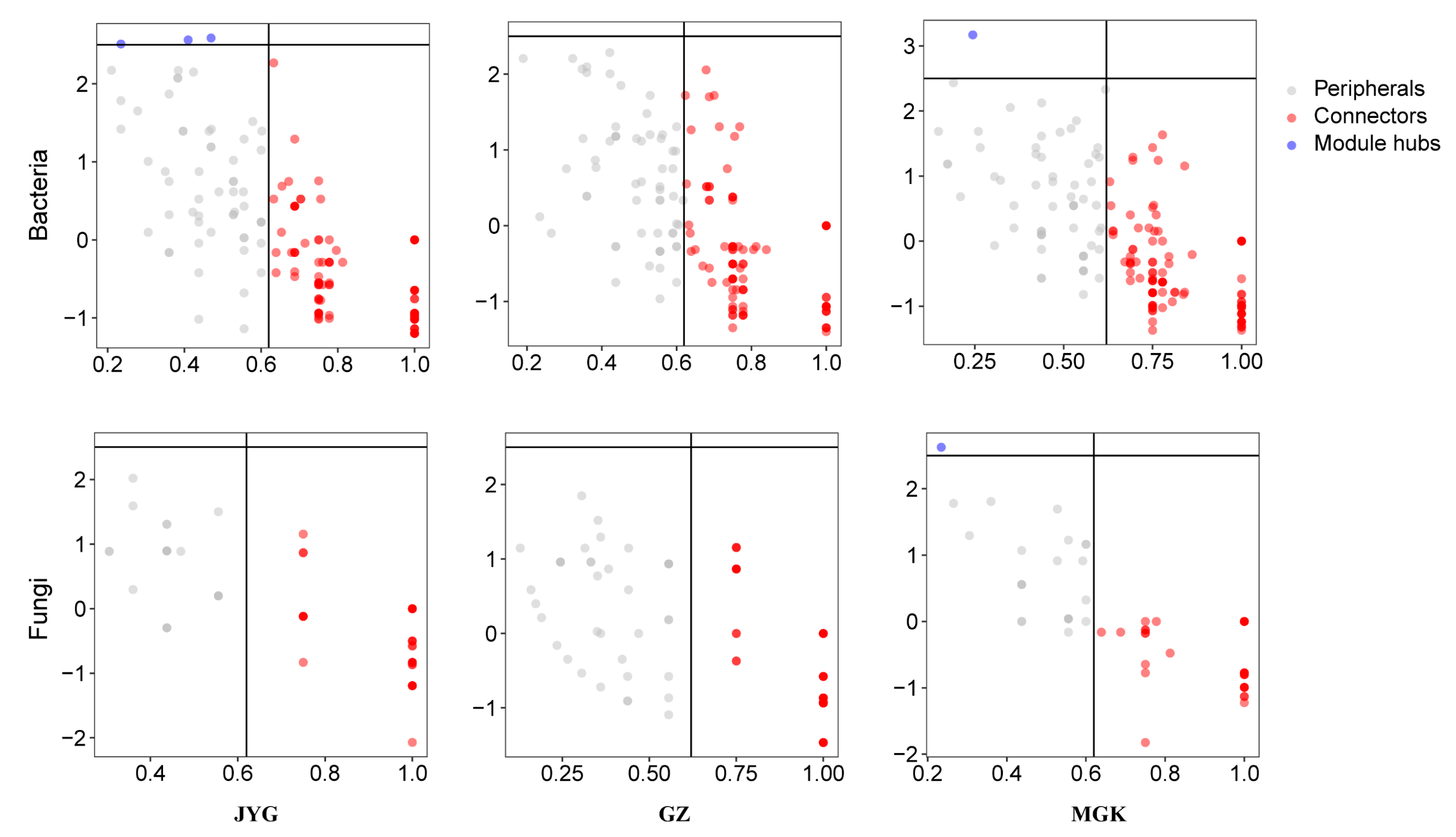
3.6. Keystone Species Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, F.; Lacap-Bugler, D.; Lau, M.; Aitchison, J.; Cowan, D.; Pointing, S. Hypolithic Microbial Community of Quartz Pavement in the High-Altitude Tundra of Central Tibet. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacap-Bugler, D.; Lee, K.; Archer, S.; Gillman, L.; Lau, M.; Leuzinger, S.; Lee, C.; Maki, T.; McKay, C.; Perrott, J.; et al. Global Diversity of Desert Hypolithic Cyanobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren-Rhodes, K.; Rhodes, K.; Pointing, S.; Ewing, S.; Lacap-Bugler, D.; Gomez-Silva, B.; Amundson, R.; Friedmann, E.; McKay, C. Hypolithic Cyanobacteria, Dry Limit of Photosynthesis, and Microbial Ecology in the Hyperarid Atacama Desert. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebre, P.; Bottos, E.; Makhalanyane, T.; Hogg, I.; Cowan, D. Islands in the sand: Are all hypolithic microbial communities the same? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 97, fiaa216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointing, S. Hypolithic Communities. In Biological Soil Crusts: An Organizing Principle in Drylands; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, Y.; Lacap-Bugler, D.; Lau, M.; Ha, K.; Warren-Rhodes, K.; Cockell, C.; Cowan, D.; McKay, C.; Pointing, S. Hypolithic microbial communities: Between a rock and a hard place. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2272–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebre, P.; De Maayer, P.; Cowan, D. Xerotolerant bacteria: Surviving through a dry spell. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointing, S.; Belnap, J. Microbial colonization and controls in dryland systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.; Pippen, J.; Wallenstein, M.; Hofmockel, K.; Klepeis, D.; Mahall, B. Community composition and photosynthesis by photoautotrophs under quartz pebbles, Southern Mojave Desert. Ecology 2003, 84, 3222–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Rhodes, K.; Rhodes, K.; Boyle, L.; Pointing, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhuo, P.; McKay, C. Cyanobacterial ecology across environmental gradients and spatial scales in China’s hot and cold deserts. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 61, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.; Rueckert, A.; Cowan, D.; Cary, S.; Wood, S.A.; Rueckert, A.; Cowan, D.A.; Cary, S.C. Sources of edaphic cyanobacterial diversity in the Dry Valleys of Eastern Antarctica. ISME J. 2008, 2, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Makhalanyane, T.; Seely, M.; Cowan, D. Cyanobacteria drive community composition and functionality in rock-soil interface communities. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacap-Bugler, D.; Warren-Rhodes, K.; McKay, C.; Pointing, S. Cyanobacteria and chloroflexi-dominated hypolithic colonization of quartz at the hyper-arid core of the Atacama Desert, Chile. Extrem. Life Under Extrem. Cond. 2010, 15, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, S.; Gibb, K.; Rose, A.; Kaestli, M.; Christian, K. Differences in structure of northern Australian hypolithic communities according to location, rock type, and gross morphology. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Rhodes, K.; McKay, C.; Boyle, L.; Wing, M.; Cowan, D.; Stomeo, F.; Pointing, S.; Kaseke, K.F.; Eckardt, F.; Henschel, J.; et al. Physical Ecology of Hypolithic Communities in the Central Namib Desert: The Role of Fog, Rain, Rock Habitat and Light. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azua, A.; González-Silva, C.; Villalobos, R.; Salas, L.; Gomez-Silva, B.; McKay, C.; Vicuña, R. Hypolithic Cyanobacteria Supported Mainly by Fog in the Coastal Range of the Atacama Desert. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 61, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scola, V.; Ramond, J.-B.; Frossard, A.; Zablocki, O.; Adriaenssens, E.; Johnson, R.; Seely, M.; Cowan, D. Namib Desert Soil Microbial Community Diversity, Assembly, and Function Along a Natural Xeric Gradient. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stomeo, F.; Valverde, A.; Pointing, S.; McKay, C.; Warren-Rhodes, K.; Tuffin, M.; Seely, M.; Cowan, D. Hypolithic and soil microbial community assembly along an aridity gradient in the Namib Desert. Extrem. Life Under Extrem. Cond. 2013, 17, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointing, S.; Warren-Rhodes, K.; Lacap-Bugler, D.; Rhodes, K.; McKay, C. Hypolithic community shifts occur as a result of liquid water availability along environmental gradients in China’s hot and cold hyperarid deserts. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Kang, E.; Rensheng, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, B. The impact of the development of water resources on environment in Arid Inland River basins of Hexi region, Northwestern China. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Du, W.; Jizu, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, W.; Chai, X.; Ma, L.; Xu, Z. Climatic and Topographical Effects on the Spatiotemporal Variations of Vegetation in Hexi Corridor, Northwestern China. Diversity 2022, 14, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-H.; Li, T.; Zhang, G.-S.; Wu, F.-S.; Chen, T.; Zhang, B.-L.; Wu, X.-K.; Liu, G.-X.; Zhang, K.-C.; Zhang, W. Seasonal Variation of Hypolithic Microbiomes in the Gobi Desert. Microb. Ecol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q. Water Resources in the Hexi Corridor and Its Cycle. In Sustainability in Food and Water; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 299–310. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Ma, C. Effect of Intrinsic Tannins on the Fermentation Quality and Associated with the Bacterial and Fungal Community of Sainfoin Silage. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.; Miletto, M.; Taylor, J.; Bruns, T. Dispersal in microbes: Fungi in indoor air are dominated by outdoor air and show dispersal limitation at short distances. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.-H.; Taylor, A.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Jeppesen, T.; Schigel, D.; Kennedy, P.; Picard, K.; Glöckner, F.; Tedersoo, L.; et al. The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi: Handling dark taxa and parallel taxonomic classifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.R. Soil sampling and methods of analysis. In Cadmium Chromium Lead Nickel; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sadewi, L.; Nugraha, M.; Akhrianti, I. Konsentrasi Dan Distribusi Karbon Organik Total (TOC), Total Nitrogen (TN) Dan Rasio C/N Pada Sedimen Di Perairan Kawasan Pelabuhan Pangkal Balam, Bangka. J. Trop. Mar. Sci. 2022, 5, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvé, S.; Parker, D.R. Chemical Speciation of Trace Elements in Soil Solution. In Chemical Processes in Soils; Science Society of America Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2005; pp. 655–688. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Peñuelas, J.; Chu, H. Abundance of kinless hubs within soil microbial networks are associated with high functional potential in agricultural ecosystems. Env. Int. 2020, 142, 105869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. Fast R Functions For Robust Correlations And Hierarchical Clustering. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 46, i11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimerà, R.; Nunes Amaral, L.A. Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature 2005, 433, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.; Flyvbjerg, H. Octave plots for visualizing diversity of microbial OTUs. Biorxiv 2018, 389833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eb, S. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar]
- Purahong, W.; Hossen, S.; Nawaz, A.; Sadubsarn, D.; Tanunchai, B.; Dommert, S.; Noll, M.; Ampornpan, L.-A.; Werukamkul, P.; Wubet, T. Life on the Rocks: First Insights Into the Microbiota of the Threatened Aquatic Rheophyte Hanseniella heterophylla. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 634960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R. Cryptoendolithic algae of hot semiarid lands and deserts. J. Phycol. 2004, 29, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietkerk, M.; Dekker, S.; Ruiter, P.; van de Koppel, J. Self-Organized Patchiness and Catastrophic Shifts in Ecosystems. Science 2004, 305, 1926–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Dean, J.; Maza, F.; Morel, I.; Pulgar, R.; González, M. Microbial communities from arid environments on a global scale. A systematic review. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, K.; Kaestli, M.; Gibb, K. Spatial patterns of hypolithic cyanobacterial diversity in Northern Australia. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 7023–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zongxiao, Z.; Han, P.; Zheng, Y.; Jiao, S.; Dong, H.; Liang, X.; Gao, D.; Yuhui, N.; Yin, G.; Liu, M.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Bacterial Taxonomic and Functional Profiles in Estuarine Intertidal Soils of China Coastal Zone. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 85, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenet, B.; Lenhart, K.; Leloup, J.; Giusti-Miller, S.; Pouteau, V.P.M.; Nunan, N.; Abbadie, L. The impact of long-term CO2 enrichment and moisture levels on soil microbial community structure and enzyme activities. Geoderma 2012, 170, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Bauersachs, T.; Schwark, L.; Proemse, B.; Eberhard, R.; Coolen, M.; Grice, K. Salinity-driven ecology and diversity changes of heterocytous cyanobacteria in Australian freshwater and coastal-marine microbial mats. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 6493–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, J.; Nouioui, I.; Asenjo, J.; Andrews, B.; Bull, A.; Goodfellow, M. New genus-specific primers for PCR identification of Rubrobacter strains. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 1863–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.; Hemp, J.; Shih, P.; McGlynn, S.; Fischer, W. Evolution of Phototrophy in the Chloroflexi Phylum Driven by Horizontal Gene Transfer. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterflinger, K.; Pinar, G. Microbial deterioration of cultural heritage and works of art—Tilting at windmills? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9637–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Hanada, S.; Philip, H.; Kim, H.; Kamagata, Y.; Nakamura, K. Gemmatimonas aurantiaca gen. nov., sp. nov., a Gram-negative, aerobic, polyphosphate-accumulating micro-organism, the first cultured representative of the new bacterial phylum Gemmatimonadetes phyl. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garritano, A.; Song, W.; Thomas, T. Carbon fixation pathways across the bacterial and archaeal tree of life. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienow, J. Extremophiles: Dry Environments (Including Cryptoendoliths); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gaysina, L.A.; Saraf, A.; Singh, P. Cyanobacteria in Diverse Habitats. In Cyanobacteria; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, T.J. Fungi. In Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Levin, S.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 624–640. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.-Q.; Zhao, R.-L.; Liu, D.-M.; Denchev, T.; Begerow, D.; Yurkov, A.; Kemler, M.; Millanes, A.; Wedin, M.; McTaggart, A.; et al. Species diversity of Basidiomycota. Fungal Divers. 2022, 114, 281–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, A.; Zhang, Z.; Sajjad, W.; Nasir, F.; Zia, A.; Liu, G.; Chen, T. Bacterial community structure and functions in microhabitats associated with black stones in Black Gobi Desert, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Environment | Bacteria | Fungi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE | Shannon | ACE | Shannon | |
| pH | −0.380 ** | −0.422 ** | −0.691 ** | −0.152 |
| EC | −0.535 ** | −0.564 ** | −0.731 ** | −0.279 * |
| SOC | −0.145 | −0.09 | 0.315 * | −0.217 |
| TN | 0.658 ** | 0.669 ** | 0.694 ** | 0.401 ** |
| TP | 0.691 ** | 0.679 ** | 0.530 ** | 0.476 ** |
| MAP | −0.098 | −0.043 | 0.359 ** | −0.188 |
| K+ | −0.637 ** | −0.653 ** | −0.711 ** | −0.377 ** |
| Na+ | −0.608 ** | −0.628 ** | −0.724 ** | −0.347 ** |
| Ca2+ | 0.025 | −0.029 | −0.424 ** | 0.14 |
| Mg2+ | 0.112 | 0.057 | −0.346 ** | 0.197 |
| Cl− | −0.486 ** | −0.442 ** | −0.087 | −0.414 ** |
| HCO3− | 0.669 ** | 0.648 ** | 0.438 ** | 0.482 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, S.; Sun, H.J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, W.; et al. The Distribution and Influencing Factors of Hypolithic Microbial Communities in the Hexi Corridor. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051212
Zhao Y, Wu F, Liu Y, Wu M, Wang S, Sun HJ, Liu G, Zhang Y, Cui X, Zhang W, et al. The Distribution and Influencing Factors of Hypolithic Microbial Communities in the Hexi Corridor. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(5):1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051212
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yidan, Fasi Wu, Yang Liu, Minghui Wu, Shengjie Wang, Henry J. Sun, Guangxiu Liu, Yiyang Zhang, Xiaowen Cui, Wei Zhang, and et al. 2023. "The Distribution and Influencing Factors of Hypolithic Microbial Communities in the Hexi Corridor" Microorganisms 11, no. 5: 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051212
APA StyleZhao, Y., Wu, F., Liu, Y., Wu, M., Wang, S., Sun, H. J., Liu, G., Zhang, Y., Cui, X., Zhang, W., Chen, T., & Zhang, G. (2023). The Distribution and Influencing Factors of Hypolithic Microbial Communities in the Hexi Corridor. Microorganisms, 11(5), 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051212





