Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Frontline of the Greatest Challenge of Biofilm Infection—Its Tolerance to Antibiotics
Abstract
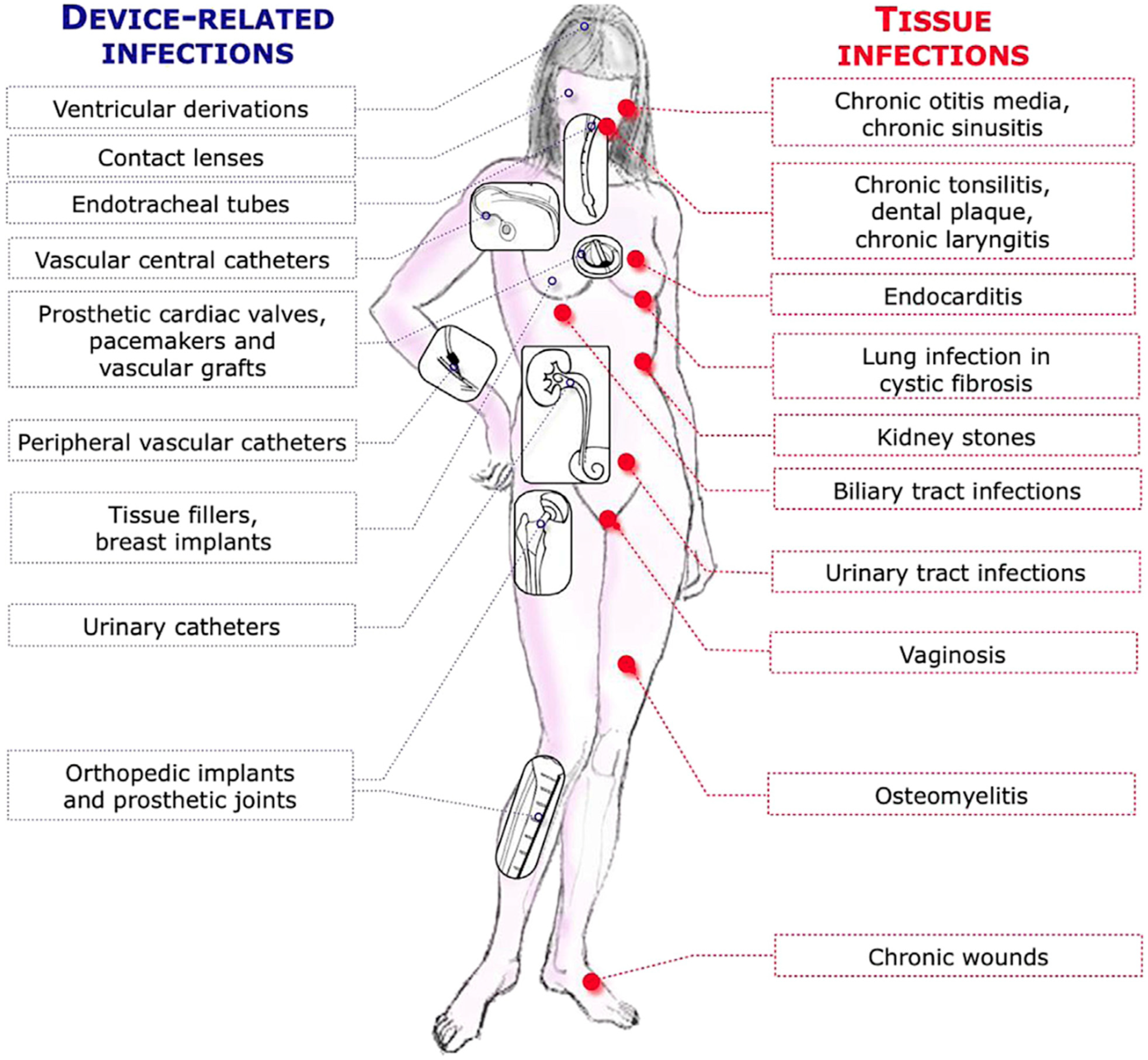
1. Introduction
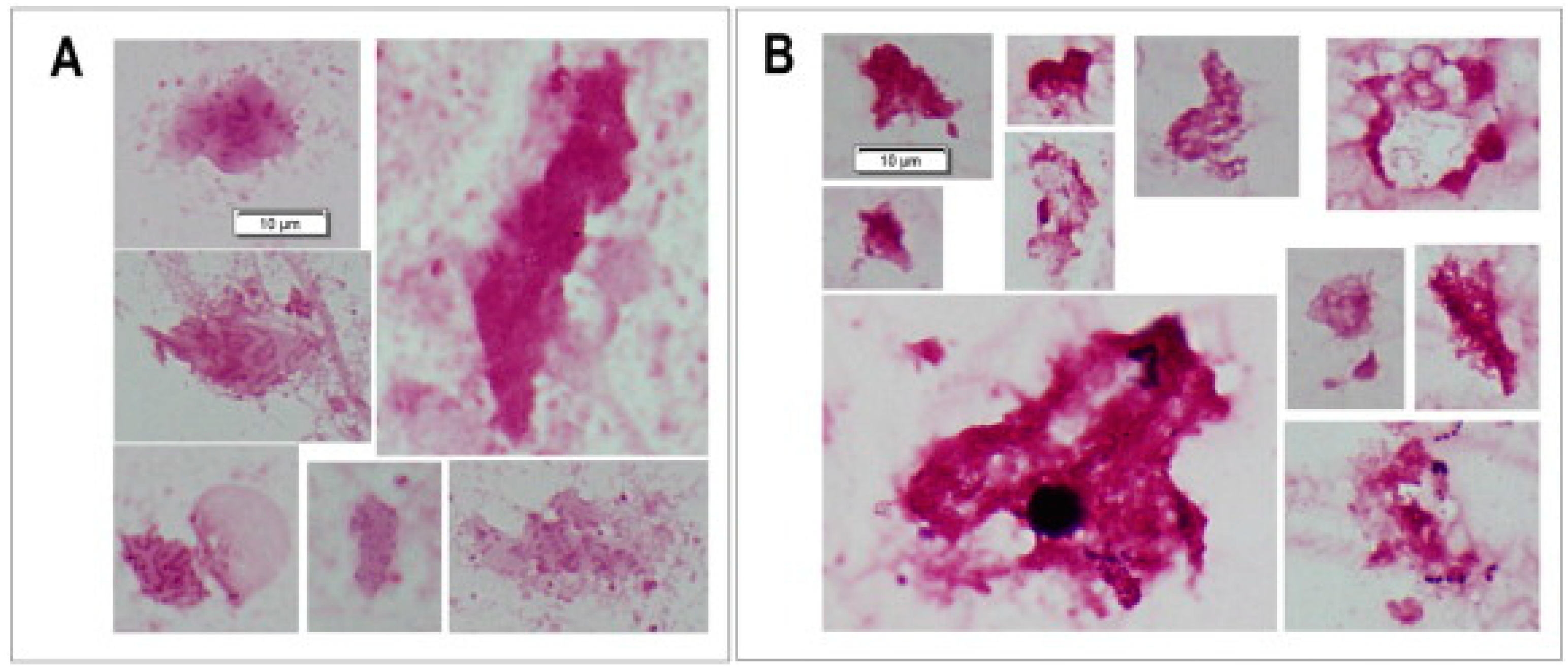
2. The Biofilm Growth of Bacteria
3. Tolerance Mechanisms of P. aeruginosa Biofilms
3.1. The Biofilm Matrix
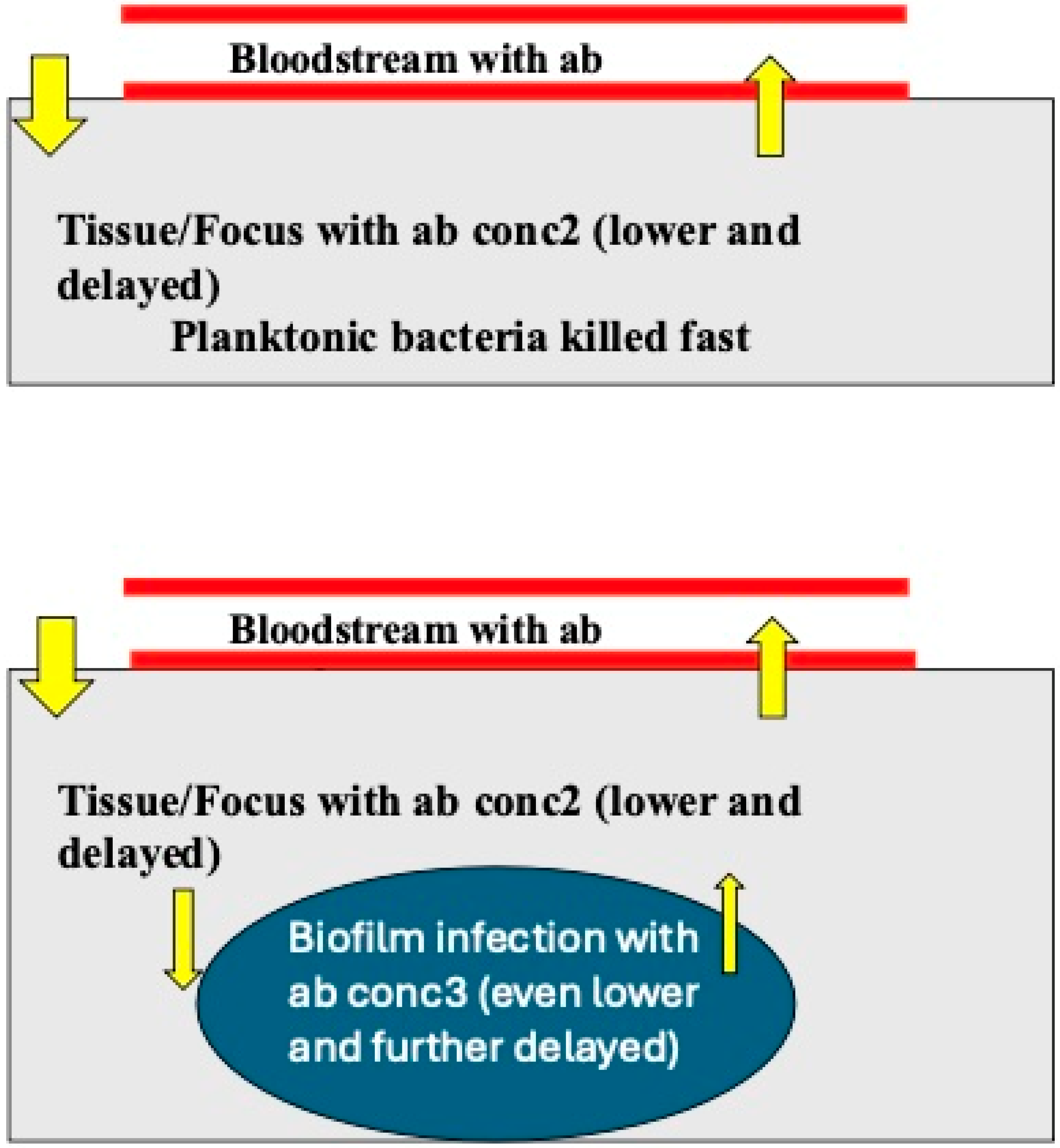
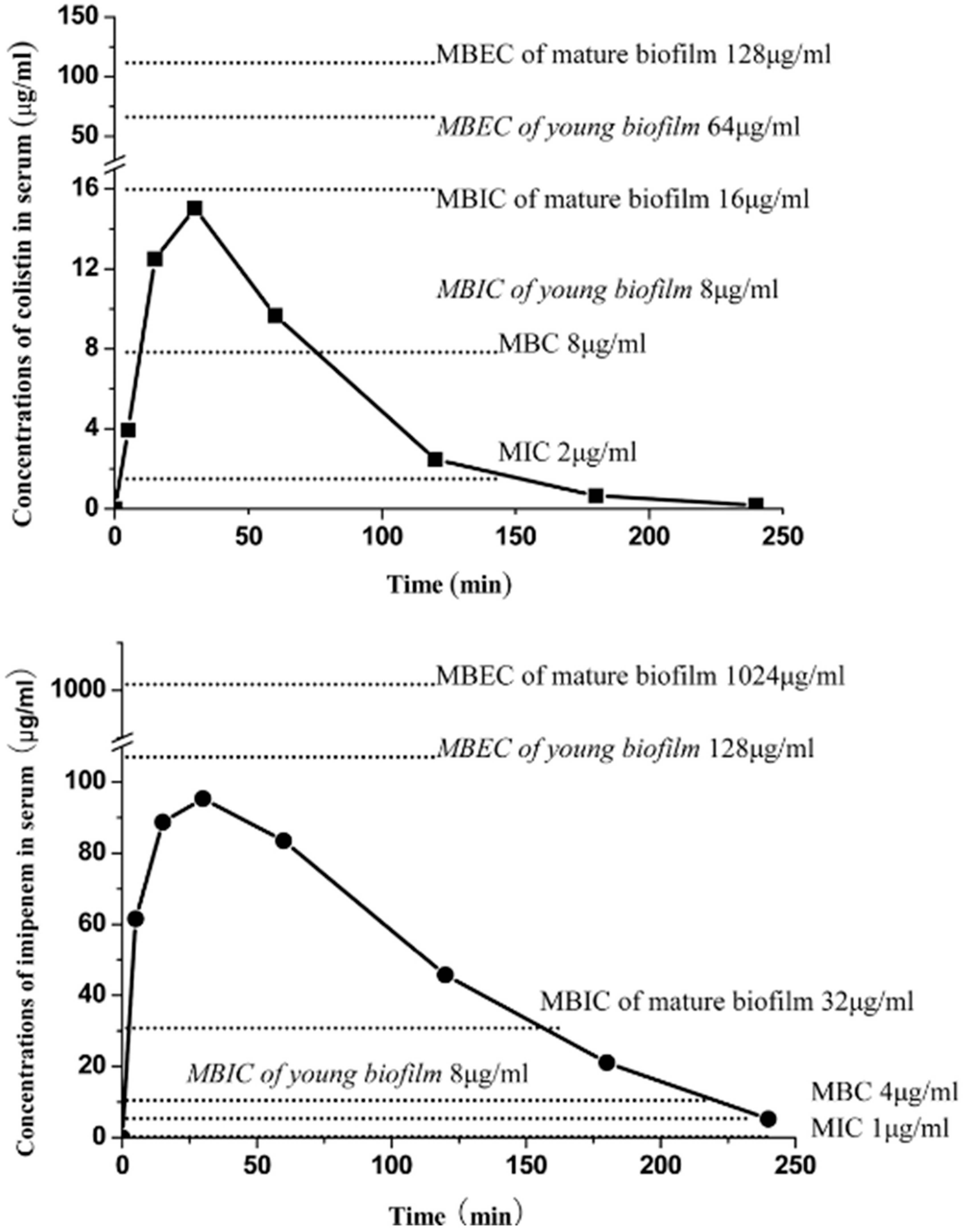
3.2. Antibiotics and Anaerobic Condition in Biofilms
4. The Way Forward—Circumvention of the Antibiotic Tolerance of P. aeruginosa Biofilms
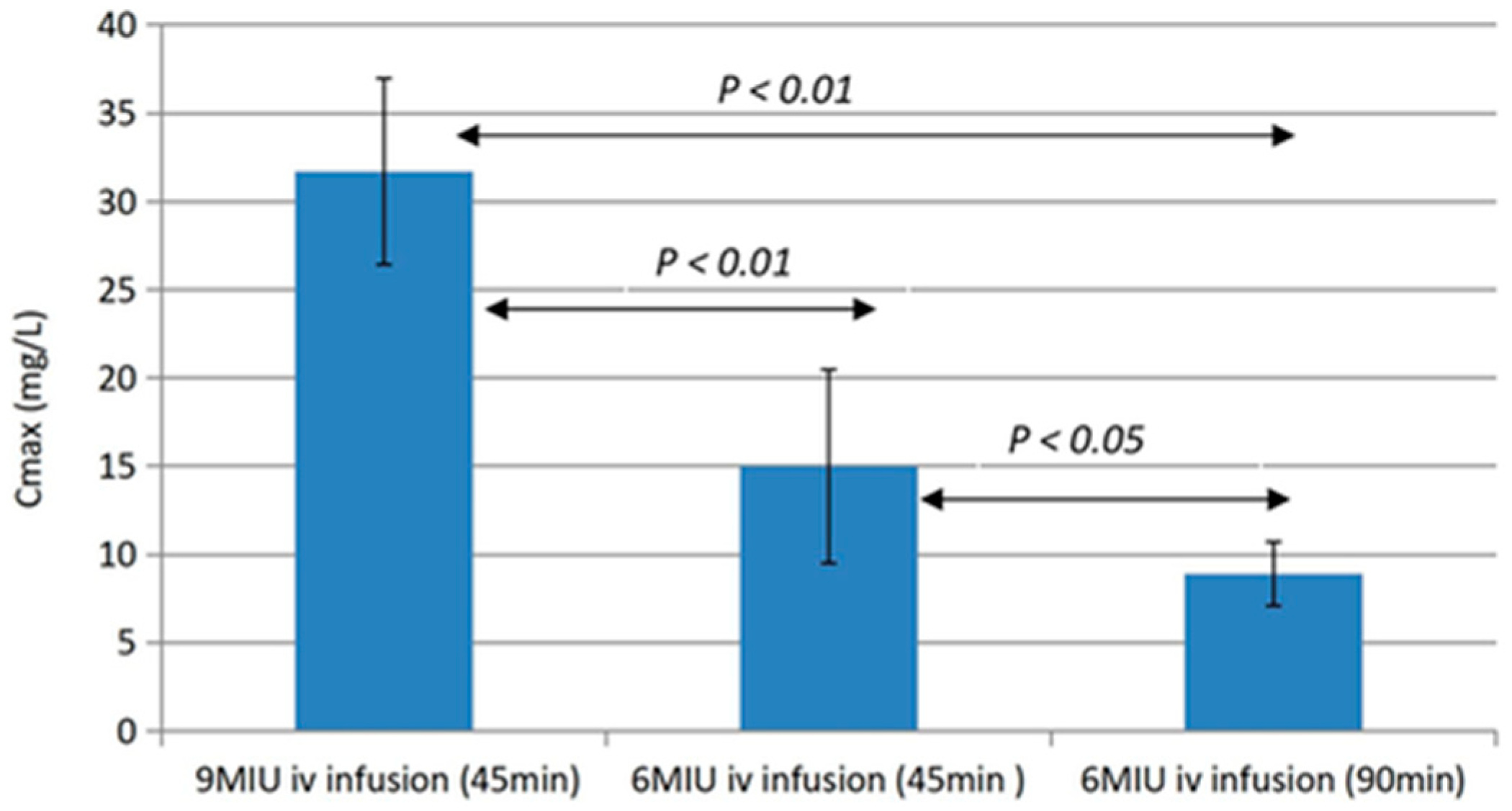
4.1. Topical Antibiotic Treatment of Biofilm Infections
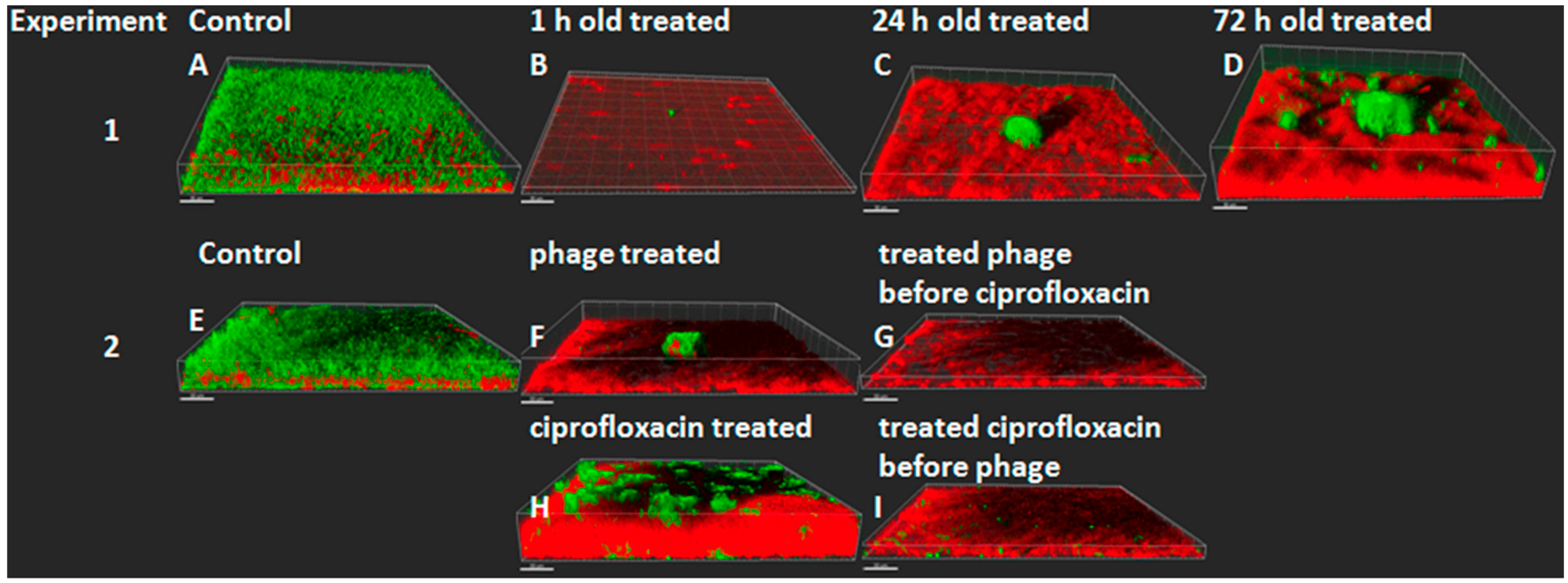
4.2. Bacteriophage Therapy
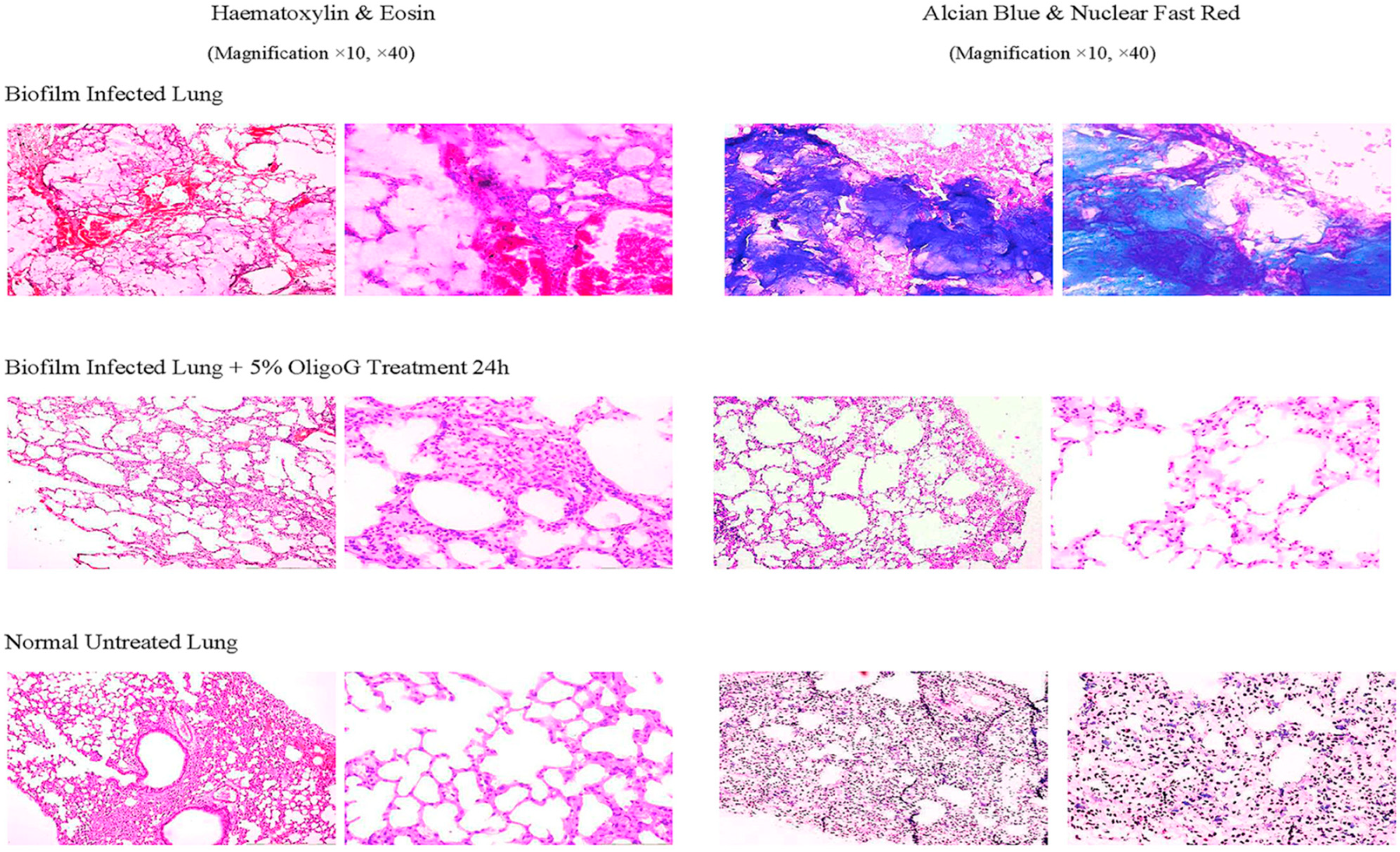
4.3. Destruction of the Biofilm Matrix
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE pathogens: Antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofu, O.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.-Ø.; Høiby, N. Tolerance and resistance of biofilm infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Bassi, G.L.; Coenye, T.; Donelli, G.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Holá, V.; Imbert, C.; Kirketerp-Møller, K.; et al. ESCMID* guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of biofilm infections 2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, S1–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Moser, C.; Oliver, A.; Williams, C.; Ramage, G.; Borghi, E.; Azeredo, J.; Macia, M.D. For the ESGB.: Time to update the ESCMID Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of biofilm infections? Biofilm 2023, 6, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrici, A. Studies of freshwater bacteria. 1. A direct microscopic technique. J. Bacteriol. 1933, 25, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobell, C.E.; Allen, E. The significance of marine bacteria in the biofouling of submerged surfaces. J. Bacteriol. 1935, 29, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N. A personal history of research on microbial biofilms and biofilm infections. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 70, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Ciofu, O. Section II Bacteriology. In Pseudomonas in Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 13th ed.; Caroll, K.C., Ed.; American Society of Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Crone, S.; Vives-Flórez, M.; Kvich, L.; Saunders, A.M.; Malone, M.; Nicolaisen, M.H.; Martínez-García, E.; Rojas-Acosta, C.; Catalina Gomez-Puerto, M.; Calum, H.; et al. The environmental occurrence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Apmis 2020, 128, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peix, A.; Ramírez-Bahena, M.H.; Velázquez, E. The current status on the taxonomy of Pseudomonas revisited: An update. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 57, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhede, M.; Kragh, K.N.; Qvortrup, K.; Allesen-Holm, M.; van Gennip, M.; Christensen, L.D.; Jensen, P.; Nielsen, A.K.; Parsek, M.; Wozniak, D.; et al. Phenotypes of non-attached Pseudomonas aeruginosa aggregates resemble surface attached biofilm. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Henneberg, K.-Å.; Wang, H.; Stavnsbjerg, C.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Ciofu OJohansen, U.R.; Sams, T. Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibition zone during tobramycin disk diffusion is due to a transition from planktonic to biofilm mode of growth. Internat. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Ciofu, O.; Song, Z.; Høiby, N. Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics of colistin and imipenem on mucoid and non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4469–4474. [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Alhede, M.; Alhede, M.; Eickhardt-Sorensen, S.R.; Moser, C.; Kuhl, M.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Høiby, N. The in vivo biofilm. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Lewandowski, Z.; Caldwell, D.E.; Korber, D.R.; Lappin-Scott, H.M. Microbial biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 711–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, C.; Christensen, B.B.; Johansen, T.; Nielsen, A.T.; Andersen, J.B.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S. Distribution of bacterial growth activity in flow-chamber biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4108–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, K.N.; Alhede, M.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Moser, C.; Scheike, T.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Poulsen, S.S.; Eickhardt, S.; Trøstrup, H.; Christophersen, L.; et al. Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes restrict the Growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Lungs of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 4477–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Barat, L.; Ciofu, O.; Kragh, K.N.; Pressler, T.; Johansen, U.; Motos, A.; Torres, A.; Høiby, N. Phenotypic shift of the P. aeruginosa populations form cystic fibrosis lungs after 2-week antipseudomonal treatment. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Ciofu, O.; Song, Z.; Høiby, N. In vivo pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of colistin and imipenem on biofilm Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimic Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2683–2690. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Christophersen, L.; Kolpen, M.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Sneppen, K.; Høiby, N.; Moser, C.; Sams, T. Diffusion retardation by binding of tobramycin in an alginate biofilm model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.C.; Nielsson, M.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Høiby, N.; Nielsen, T.E.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Extracellular DNA shields against aminoglycosides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2352–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagge, N.; Schuster, M.; Hentzer, M.; Ciofu, O.; Givskov, M.; Greenberg, P.; Høiby, N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms exposed to imipenem exhibit changes in global gene expression and beta-lactamase and alginate production. Antimicr. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christophersen, L.; Lerche, C.J.; Laulund, A.S.; Thomsen, K.; Sams, T.; Høiby, N.; Moser, C. In vivo demonstration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms as independent pharmacological microcompartments results in bacterial regrowth. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpen, M.; Hansen, C.R.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Christensen, L.D.; van Gennip, M.; Ciofu, O.; Mandsberg, L.; Kharazmi, A.; Döring, G.; et al. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes consume oxygen in sputum from chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in cystic fibrosis. Thorax 2010, 65, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worlitzsch, D.; Tarran, R.; Ulrich, M.; Schwab, U.; Cekici, A.; Meyer, K.C.; Birrer, P.; Bellon, G.; Berger, J.; Weiss, T.; et al. Effect of reduced mucus oxygen concentration in airway Pseudomonas infection of cystic fibrosis patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Line, L.; Alhede, M.; Kolpen, M.; Kühl, M.; Ciofu, O.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Toyofuku, M.; Nomura, N.; Høiby, N.; et al. Physiological levels of nitrate support anoxic growth by denitrification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at growth rates reported in cystic fibrosis lungs and sputum. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumanen, E.; Cozens, R.; Tosch, W.; Zak, O.; Tomasz, A. The rate of killing of Escherichia coli by beta-lactam antibiotics is strictly proportional to the rate of bacterial growth. J. General. Microbiol. 1986, 132, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, D.J.; Collins, J.J.; Walker, G.C. Unraveling the physiological complexities of antibiotic lethality. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, J.; Rodríguez-Beltrán, J.; Matic, I. Antibiotic-induced genetic variation: How it arises and how it can be prevented. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 72, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, K.M.; Wassermann, T.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Wang, H.; Molin, S.; Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O. Sub-lethal ciprofloxacin treatment leads to rapid development of high-level ciprofloxacin resistance during long-term experimental evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.N.; Porse, A.; Abdelsamad, A.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O. Lack of KatA catalase in P. aeruginosa accelerates evolution of antibiotic resistance in ciprofloxacin-treated biofilms. Antimicr. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochmann, R.P.; Toft, A.; Ciofu, O.; Briales, A.; Kolpen, M.; Hempel, C.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Høiby, N.; Jensen, P.Ø. The bactericidal effect of colistin on planktonic Pseudomonas aeruginosa is independent of hydroxolyl radical formation. Intern. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 43, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabnis, A.; Hagart, K.L.; Klöckner, A.; Becce, M.; Evans, L.E.; Furniss, R.C.D.; Mavridou, D.A.; Murphy, R.; Stevens, M.M.; Davies, J.C.; et al. Colistin kills bacteria by targeting lipopolysaccharide in the cytoplasmic membrane. eLife 2021, 10, e65836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nang, S.C.; Azad, M.A.K.; Velkov, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J. Rescuing the last-line polymyxins: Achievement and challenges. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 679–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.K.; Brannon, M.; Stevens, L.; Johansen, H.K.; Selgrade, S.; Miller, S.; Høiby, N.; Moskowitz, S. PhoQ mutations promote lipid A modification and polymyxin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa found in colistin-treated cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5761–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, S.; Brannon, M.K.; Dasgupta, N.; Pier, M.; Sgambati, N.; Miller, A.; Selgrade, S.E.; Miller, S.I.; Denton, M.; Conway, S.P.; et al. PmrB mutations promote polymyxin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from colistin-treated cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutu, A.D.; Sgambati, N.; Strasbourger, P.; Brannon, M.K.; Jacobs, M.A.; Haugen, E.; Kaul, R.K.; Johansen, H.K.; Høiby, N.; Moskowitz, S.M. Polymyxin resistance of Pseudomonas phoQ mutants is dependent on additional two-component regulatory systems. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 57, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.R.W. The role of the cell envelope in resistance. In Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Brown, M.R.W., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 71–107. [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland, H.E.; Farley, L.B. Adaptive resistance to polymyxin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa due to an outer membrane impermeability mechanism. Can. J. Microbiol. 1982, 28, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, J.B.; Lewenza, S.; Hancock, R.E.W. Cationic antimicrobial peptides activate a two-component regulatory system, PmrA-PmrB, that regulates resistance to polymyxin B and cationic antimicrobial peptides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamp, S.J.; Gjermansen, M.; Johansen, H.K.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Tolerance to the antimicrobial peptide colistin in P. aeruginosa biofilms is linked to metabolically active cells, and depends on the pmr and mexAB-oprM genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
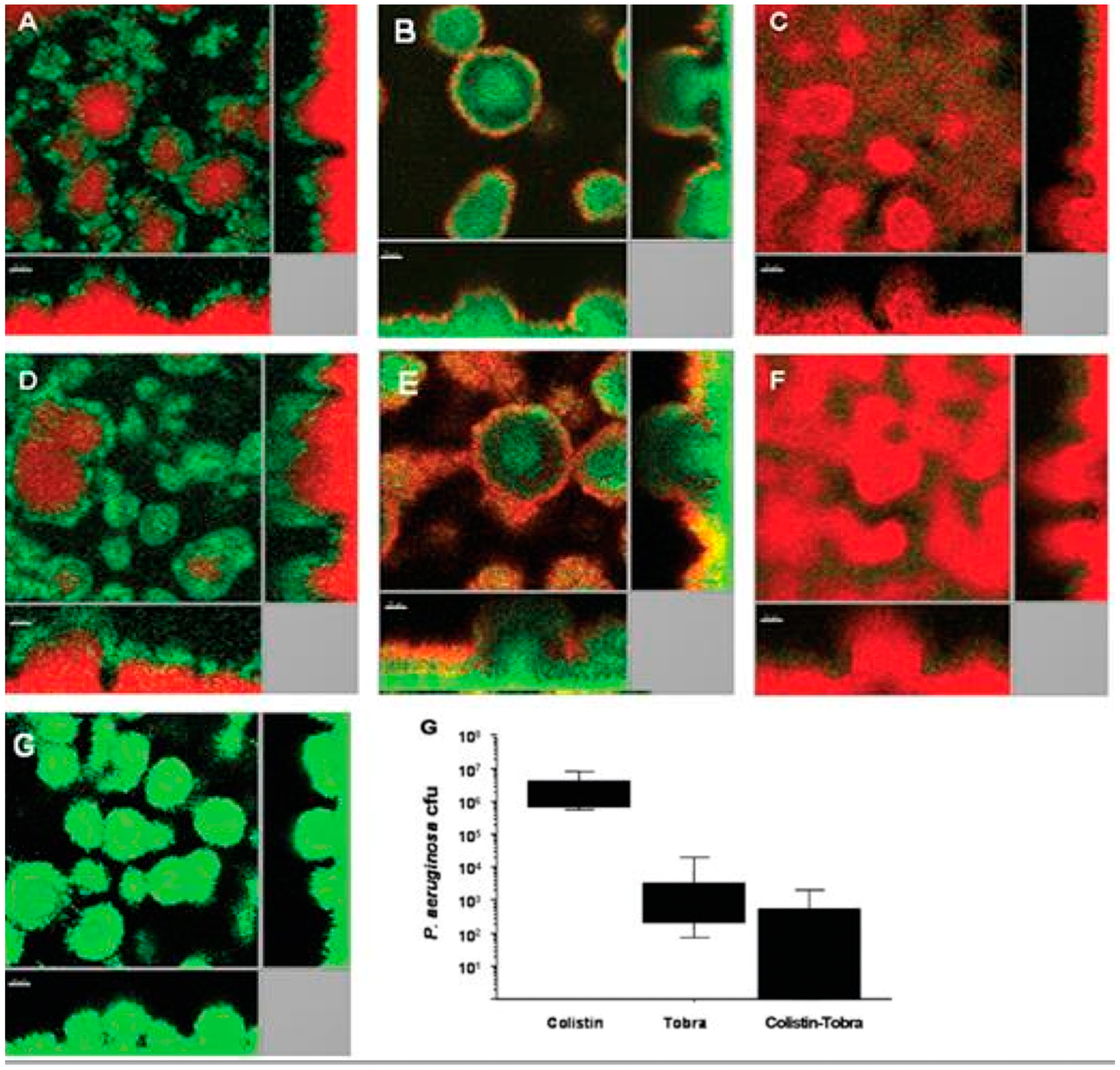
- Herrmann, G.; Yang, L.; Wu, H.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Høiby Ulrich, M.; Molin, S.; Riethmüller, J.; Döring, G. Colistin-tobramycin combinations are superior to monotherapy concerning killing of biofilm Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerius, N.H.; Koch, C.; Høiby, N. Prevention of chronic colonization with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with Cystic Fibrosis by early treatment with Ciprofloxacin and inhalation with Colistin. Lancet 1991, 338, 725–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armengol, E.; Kragh, N.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Sierra, J.M.; Higazy, D.; Vinas, M.; Høiby, N. Colistin enhances rifampicin’s antimicrobial action in colistin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e0164122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, S.M.; Foster, J.; Emerson, J.; Burns, J.L. Clinically feasible biofilm susceptibility assay for isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpen, M.; Mousav, N.; Sams, T.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Ciofu, O.; Mose, C.; Kühl, M.; Høiby, N.; Jense, P.Ø. Reinforcement of the bactericidal effect of ciprofloxacin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm by hyperbar oxygen treatment. Intern. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, S.A.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O.; Kragh, K.N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Kolpen, M. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment increases killing of aggregating Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.L.; van Dalfsen, J.M.; Shawar, R.M.; Otto, K.L.; Garber, R.L.; Quan, J.M.; Montgomery, A.B.; Albers, G.M.; Ramsey, B.W.; Smith, A.L. Effect of chronic intermittent administration of inhaled tobramycin on respiratory microbial flora in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 179, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Green, K.; Pressler, T.; Skov, M.; Katzenstein, T.L.; Wu, X.; Høiby, N. Optimization of colistin dosing regimen for cystic fibrosis patients with chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm lung infection. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 575–580. [Google Scholar]
- Geller, D.E.; Flume, P.A.; Staab, D.; Fischer, R.; Loutit, J.S.; Conrad, D.J. Levofloxacin inhalation solution (MP-376) in patients with cystic fibrosis with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. J. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann, C.; Sherwin, C.M.T.; Ampofo, K.; Spigarelli, M.G. Development of levofloxacin inhalation solution to treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2014, 8, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratjen, F.; Rietschel, E.; Kasel, D.; Schwiertz, R.; Starke, K.; Beier, H.; van Koningsbruggen, S.; Grasemann, H. Pharmacokinetics of inhaled colistin in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasnæs, K.; Nielsen, K.G.; Arndal, E.; von Buchwald, C.; Pressler, T.; Høiby, N. Autologous fibrin sealant co-delivered with antibiotics is a robust method for topical antibiotic treatment after sinus surgery. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2021, 141, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasnæs, K.; Alanin, K.; Nielsen, K.G.; Jørgensen, M.M.; von Buchwald, C.; Høiby, N.; Johannesen, H.H.; Mortensen, J. The accessibility of topical treatment in the paranasal sinuses on operated cystic fibrosis patients assessed by scintigraphy. Rhinology 2018, 56, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, K.; Rørbo, N.; Rybtke, M.L.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Høiby, N.; Midedelboe, M.; Ciofu, O. P. aeruginosa flow-cell biofilms are enhanced by repeated phage treatments but can be eradicated by phage-ciprofloxacin combinations. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77, ftz011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinet, M.G.; Lohde, M.; Higazy, D.; Brandt, C.; Pletz, M.W.; Middelboe, M.; Makarewicz, O.; Ciofu, O. Diversification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm populations under repeated phage exposures decreases the efficacy of the treatment. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeniyi, B.; Birch-Andersen, A.; Mansa, B.; Rosdahl, V.T.; Høiby, N. Morphology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa phages from sputum of cystic fibrosis patients and from the phage typing set. Apmis 1991, 99, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saussereau, E.; Vachier, I.; Chiron, R.; Godbert, B.; Sermet, I.; Dufour, N.; Pernay, J.-P.; De Vos, D.; Carrié, F.; Molinari, N.; et al. Effectiveness of bacteriophages in the sputum of cystic fibrosis patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hraiech, S.; Brégeon, F.; Rolain, J.-M. Bacteriophage-based therapy in cystic fibrosis-associated Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: Rationale and current status. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 3653–3663. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, K.-M.; Stick, S.M.; Kicic, A. Pulmonary bacteriophage and cystic fibrosis airway mucus: Friends or foes? Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1088494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, Z.; Ciofu, O.; Onsøyen, E.; Rye, P.D.; Høiby, N. OligoG CF-5/20 disruption of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm in a murine lung infection model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2620–2626. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, C.M.; Lerche, C.J.; Thomsen, K.; Jensen, T.H.; Schierbeck, J.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Ciofu, O.; Høiby, N. Antibiotic therapy as personalized medicine—General considerations and complicating factors. Apmis 2019, 127, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Høiby, N.; Moser, C.; Ciofu, O. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Frontline of the Greatest Challenge of Biofilm Infection—Its Tolerance to Antibiotics. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112115
Høiby N, Moser C, Ciofu O. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Frontline of the Greatest Challenge of Biofilm Infection—Its Tolerance to Antibiotics. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(11):2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112115
Chicago/Turabian StyleHøiby, Niels, Claus Moser, and Oana Ciofu. 2024. "Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Frontline of the Greatest Challenge of Biofilm Infection—Its Tolerance to Antibiotics" Microorganisms 12, no. 11: 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112115
APA StyleHøiby, N., Moser, C., & Ciofu, O. (2024). Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Frontline of the Greatest Challenge of Biofilm Infection—Its Tolerance to Antibiotics. Microorganisms, 12(11), 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112115






