Antagonistic Effects of Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum 090104 on Respiratory Pathogens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms
2.2. Autoaggregation Test
2.3. Coaggregation Test
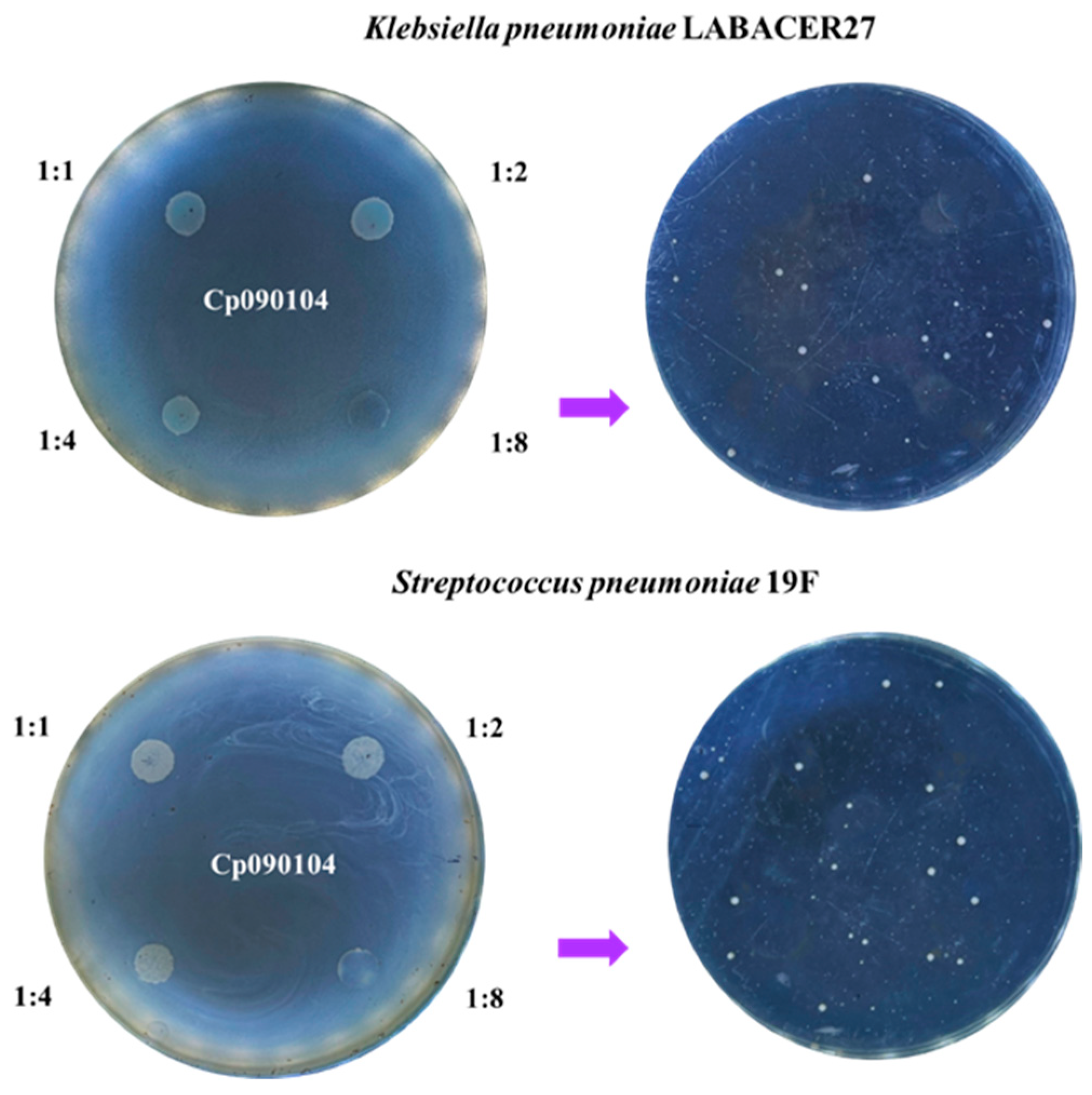
2.4. Inhibitory Activity Assay
2.5. Biofilm Formation Assay
2.6. Inhibition of Biofilm Formation Assay
2.7. Inhibition of Hemolytic Activity Assay
2.8. Morphology of Respiratory Pathogen Colonies
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study of the Autoaggregation and Coaggregation Capacity of C. pseudodiphtheriticum 090104
3.2. Evaluation of C. pseudodiphtheriticum 090104 Capacity to Inhibit the Growth of Pathogens
3.3. Study of C. pseudodiphtheriticum 090104 Capacity to Form and Inhibit Biofilms
3.4. Effect of C. pseudodiphtheriticum 090104 on the Phenotype of Respiratory Pathogens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Zyl, W.F.; Deane, S.M.; Dicks, L.M. Molecular insights into probiotic mechanisms of action employed against intestinal pathogenic bacteria. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1831339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalalifar, S.; Mirzaei, R.; Motallebirad, T.; Razavi, S.; Talebi, M. The emerging role of probiotics and their derivatives against biofilm-producing MRSA: A scoping review. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 4959487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazziotta, C.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Torreggiani, E.; Rotondo, J.C. Probiotics mechanism of action on immune cells and beneficial effects on human health. Cells 2023, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Probiotics: An overview of beneficial effects. In Lactic Acid Bacteria: Genetics, Metabolism and Applications: Proceedings of the Seventh Symposium on Lactic Acid Bacteria: Genetics, Metabolism and Applications, 1–5 September 2002, Egmond aan Zee, The Netherlands; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Collinson, S.; Deans, A.; Padua-Zamora, A.; Gregorio, G.V.; Li, C.; Dans, L.F.; Allen, S.J. Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD003048. [Google Scholar]
- Villena, J.; Li, C.; Vizoso-Pinto, M.G.; Sacur, J.; Ren, L.; Kitazawa, H. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum as a potential adjuvant and delivery system for the development of SARS-CoV-2 oral vaccines. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, E.; Stevens, B.; An, M.; Lam, V.; Ainsworth, M.; Dihle, P.; Stearns, J.; Dombrowski, A.; Rego, D.; Segars, K. Utilizing probiotics for the prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 689958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocchi, A.; Cabana, M.D.; Mennini, M. Current use of probiotics and prebiotics in allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 2219–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugger, S.D.; Eslami, S.M.; Pettigrew, M.M.; Escapa, I.F.; Henke, M.T.; Kong, Y.; Lemon, K.P. Dolosigranulum pigrum cooperation and competition in human nasal microbiota. mSphere 2020, 5, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladysheva, I.V.; Cherkasov, S.V. Antibiofilm activity of cell-free supernatants of vaginal isolates of Corynebacterium amycolatum against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menberu, M.A.; Cooksley, C.; Ramezanpour, M.; Bouras, G.; Wormald, P.J.; Psaltis, A.J.; Vreugde, S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of probiotic properties of Corynebacterium accolens isolated from the human nasal cavity. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 255, 126927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, J.S.; Pankey, J.W.; Duthie, A.H. Growth responses of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus agalactiae to Corynebacterium bovis metabolites. J. Dairy Sci. 1987, 70, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, M.M.; Freire, M.O.; Gabrilska, R.A.; Rumbaugh, K.P.; Lemon, K.P. Staphylococcus aureus shifts toward commensalism in response to Corynebacterium species. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 212804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, B.L.; Dickey, S.W.; Plaut, R.D.; Riggins, D.P.; Stibitz, S.; Otto, M.; Merrell, D.S. Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum exploits Staphylococcus aureus virulence components in a novel polymicrobial defense strategy. MBio 2019, 10, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, B.L.; Bansal, G.; Hewlett, K.H.; Arora, A.; Schaffer, S.D.; Kamau, E.; Merrell, D.S. Antimicrobial activity of clinically isolated bacterial species against Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, K.J.; Jaberi Vivar, A.C.; Arenas, V.; Andani, S.; Janoff, E.N.; Clark, S.E. Corynebacterium species inhibit Streptococcus pneumoniae colonization and infection of the mouse airway. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 804935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsuzzaman, M.; Dahal, R.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, J. Genome insight and probiotic potential of three novel species of the genus Corynebacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1225282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalili, D.; Amini, M.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Fazeli, M.R.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Samadi, N. Isolation and structural characterization of Coryxin, a novel cyclic lipopeptide from Corynebacterium xerosis NS5 having emulsifying and anti-biofilm activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz Moyano, R.; Raya Tonetti, F.; Tomokiyo, M.; Kanmani, P.; Vizoso-Pinto, M.G.; Kim, H.; Quilodrán-Vega, S.; Melnikov, V.; Alvarez, S.; Takahashi, H.; et al. The ability of respiratory commensal bacteria to beneficially modulate the lung innate immune response is a strain dependent characteristic. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Clua, P.; Vizoso-Pinto, M.G.; Rodriguez, C.; Alvarez, S.; Melnikov, V.; Takahashi, H.; Kitazawa, H.; Villena, J. Respiratory commensal bacteria Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum improves resistance of infant mice to respiratory syncytial virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae superinfection. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz Moyano, R.; Raya Tonetti, F.; Fukuyama, K.; Elean, M.; Tomokiyo, M.; Suda, Y.; Melnikov, V.; Kitazawa, H.; Villena, J. The respiratory commensal bacterium Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum as a mucosal adjuvant for nasal vaccines. Vaccines 2023, 11, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jure, M.A.; Albarracin, L.; Vargas, J.M.; Maidana, S.D.; Zamar, J.C.; Kitazawa, H.; Villena, J. Draft genome sequences of two hypermucoviscous carbapenem-resistant ST25 Klebsiella pneumoniae strains causing respiratory and systemic infections. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 26, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, D.K.; Khan, I.; Kang, S.C. Anti-bacterial susceptibility profiling of Weissella confusa DD_A7 against the multidrug-resistant ESBL-positive E. coli. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.I.; Mizan, M.F.R.; Roy, P.K.; Nahar, S.; Toushik, S.H.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Ha, S.D. Listeria monocytogenes biofilm inhibition on food contact surfaces by application of postbiotics from Lactobacillus curvatus B. 67 and Lactobacillus plantarum M. 2. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishna, A. In vitro evaluation of adhesion and aggregation abilities of four potential probiotic strains isolated from guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunk, T.; Khalil, H.S.; Leo, J.C. Bacterial autoaggregation. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.M.; Versalovic, J. Probiotics-host communication: Modulation of signaling pathways in the intestine. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Meriluoto, J.; Salminen, S. Adhesion and aggregation properties of probiotic and pathogen strains. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, P.K.; Trivedi, D.; Thakore, K.; Chaudhary, H.; Giri, S.S.; Seshadri, S. Isolation and characterization of probiotic properties of lactobacilli isolated from rat fecal microbiota. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denkova, R.; Goranov, B.; Teneva, D.; Denkova, Z.; Kostov, G. Antimicrobial activity of probiotic microorganisms: Mechanisms of interaction and methods of examination. Antimicrob. Res. Nov. Bioknowl. Educ. Programs 2017, 1, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Donlan, R.M. Biofilms: Microbial life on surfaces. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jałowiecki, Ł.; Żur, J.; Chojniak, J.; Ejhed, H.; Płaza, G. Properties of antibiotic-resistant bacteria isolated from onsite wastewater treatment plant in relation to biofilm formation. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidhya, S.K. Isolation and Phenotypic Characterisation of Bacterial Isolates from Catheter Related Blood Stream Infections in Patients on Hemodialysis in a Tertiary Care Hospital. 2019. Available online: https://oa.mg/work/2997926051 (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Stepanovic, S.; Vukovic, D.; Dakic, I.; Savic, B.; Svabic-Vlahovic, M. Modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez Ibarreche, M.P.; Castellano, P.; Vignolo, G. Evaluation of anti-Listeria meat borne Lactobacillus for biofilm formation on selected abiotic surfaces. Meat Sci. 2000, 96, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khusro, A.; Aarti, C.; Barbabosa-Pilego, A.; Rojas Hernandez, S. Anti-pathogenic, antibiofilm, and technological properties of fermented food associated Staphylococcus succinus strain AAS2. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faris, Y.; Atya, A. Probiotic characteristics of Enterococcus spp. Bacteria isolated from different sources. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2023, 90, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlumi, A.; Panahi, B.; Hejazi, M.A.; Nami, Y. Probiotic potential characterization and clustering using unsupervised algorithms of lactic acid bacteria from saltwater fish samples. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarelli, A.; Cabanel, N.; Rosinski-Chupin, I.; Zongo, P.D.; Naas, T.; Bonnin, R.A.; Glaser, P. Diversity of mucoid to non-mucoid switch among carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, L. Adhesion properties of toxigenic corynebacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, L.; Möller, J.; Burkovski, A. Interactions between the re-emerging pathogen Corynebacterium diphtheriae and host cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.C.D.; Santos, L.S.D.; Gomes, D.L.R.; Sabbadini, P.S.; Santos, C.S.D.; Camello, T.C.F.; Guaraldi, A.L.D.M. Aggregative adherent strains of Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum enter and survive within HEp-2 epithelial cells. Memórias Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2012, 107, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladysheva, I.V.; Chertkov, K.L.; Cherkasov, S.V.; Khlopko, Y.A.; Kataev, V.Y.; Valyshev, A.V. Probiotic potential, safety properties, and antifungal activities of Corynebacterium amycolatum ICIS 9 and Corynebacterium amycolatum ICIS 53 strains. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi, S.; Ardekani, A.M. Bacterial aggregation and biofilm formation in a vortical flow. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 044114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andryukov, B.G.; Romashko, R.V.; Efimov, T.A.; Lyapun, I.N.; Bynina, M.P.; Matosova, E.V. Mechanisms of adhesive–cohesive interaction of bacteria in the formation of biofilm. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 2020, 35, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Sawant, S.; Karodia, N.; Rahman, A. Staphylococcus aureus biofilm: Morphology, genetics, pathogenesis and treatment strategies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrivel, A.; Ramasamy, M.; Vetrivel, P.; Natchimuthu, S.; Arunachalam, S.; Kim, G.S.; Murugesan, R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and its control. Biologics 2021, 1, 312–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.E.S.; Destro, G.; Vieira, B.; Lima, A.S.; Ferraz, L.F.C.; Hakansson, A.P.; Converso, T.R. Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms and their role in disease pathogenesis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 877995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zomuansangi, R.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, B.P.; Singh, G.; Deka, P.; Song, J.J.; Yadav, M.K. Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilms and human infectious diseases: A review. In Understanding Microbial Biofilms; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 475–483. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Wu, C.; Yang, W.; Liang, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, L. Recent advance in surface modification for regulating cell adhesion and behaviors. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Mukherjee, D.; Ray, R.R. Introduction to bacterial biofilm and acute infections. In Biofilm-Mediated Diseases: Causes and Controls; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bendinger, B.; Rijnaarts, H.H.; Altendorf, K.; Zehnder, A.J. Physicochemical cell surface and adhesive properties of coryneform bacteria related to the presence and chain length of mycolic acids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 3973–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkovski, A. Cell envelope of corynebacteria: Structure and influence on pathogenicity. ISRN Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 935736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Mattson, D.; Wald, A. Corynebacterium jeikeium bacteremia in bone marrow transplant patients with Hickman catheters. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001, 27, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaszewska, A.K.; Brewczynska, A.; Szewczyk, E.M. Hydrophobicity and biofilm formation of lipophilic skin corynebacteria. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Iihara, H.; Uno, T.; Hara, Y.; Ohkusu, K.; Hata, H.; Ohashi, Y. Suture-related keratitis caused by Corynebacterium macginleyi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3833–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.C.; Dos Santos, L.S.; Sousa, L.P.; Faria, Y.V.; Ramos, J.N.; Sabbadini, P.S.; Da Santos, C.S.; Nagao, P.E.; Vieira, V.V.; Gomes, D.L.R.; et al. Biofilm formation and fibrinogen and fibronectin binding activities by Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum invasive strains. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, L.; Trejo, F.M.; De Antoni, G.; Golowczyc, M.A. Lactobacillus strains inhibit biofilm formation of Salmonella sp. isolates from poultry. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawistowska-Rojek, A.; Kośmider, A.; Stępień, K.; Tyski, S. Adhesion and aggregation properties of Lactobacillaceae strains as protection ways against enteropathogenic bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfa, P.; Brambilla, L.; Giardina, S.; Masciarelli, M.; Squarzanti, D.F.; Carlomagno, F.; Meloni, M. Evaluation of antimicrobial, antiadhesive and co-aggregation activity of a multi-strain probiotic composition against different urogenital pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borah, M.; Konwar, B.K.; Mandal, M. Isolation and characterization of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria with antimicrobial properties from fermented bamboo shoots of arunachal pradesh. J. Plant Biol. Crop Res. 2023, 6, 1079. [Google Scholar]
- Idoui, T. Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus strains isolated from gizzard of local poultry. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2014, 6, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Hojjati, M.; Behabahani, B.A.; Falah, F. Aggregation, adherence, anti-adhesion and antagonistic activity properties relating to surface charge of probiotic Lactobacillus brevis gp104 against Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batoni, G.; Catelli, E.; Kaya, E.; Pompilio, A.; Bianchi, M.; Ghelardi, E.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Esin, S.; Maisetta, G. Antibacterial and antibiofilm effects of Lactobacilli strains against clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa under conditions relevant to cystic fibrosis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterniti, I.; Scuderi, S.A.; Cambria, L.; Nostro, A.; Esposito, E.; Marino, A. Protective effect of probiotics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of human corneal epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dulaimi, M.; Algburi, A.; Abdelhameed, A.; Mazanko, M.S.; Rudoy, D.V.; Ermakov, A.M.; Chikindas, M.L. Antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity of polymyxin e alone and in combination with probiotic strains of Bacillus subtilis katmira1933 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens b-1895 against clinical isolates of selected Acinetobacter spp.: A preliminary study. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dentice Maidana, S.; Ortiz Moyano, R.; Vargas, J.M.; Fukuyama, K.; Kurata, S.; Melnikov, V.; Villena, J. Respiratory commensal bacteria increase protection against hypermucoviscous carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST25 infection. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarracin, L.; Ortiz Moyano, R.; Vargas, J.M.; Andrade, B.G.; Cortez Zamar, J.; Dentice Maidana, S.; Villena, J. Genomic and immunological characterization of hypermucoviscous carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST25 isolates from Northwest Argentina. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiryukhina, N.V.; Melnikov, V.G.; Suvorov, A.V.; Morozova, Y.A.; Ilyin, V.K. Use of Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum for elimination of Staphylococcus aureus from the nasal cavity in volunteers exposed to abnormal microclimate and altered gaseous environment. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2013, 5, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauf, G.A.; Powers, M.J.; Herrera, C.M.; Trent, M.S.; Davies, B.W. Acinetobactin-mediated inhibition of commensal bacteria by Acinetobacter baumannii. mSphere 2022, 7, e00016-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegari, A.; Kheyrolahzadeh, K.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S.M.; Sharifi, S.; Memar, M.Y.; Zununi Vahed, S. The battle of probiotics and their derivatives against biofilms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalfallah, G.; Gartzen, R.; Möller, M.; Heine, E.; Lütticken, R. A new approach to harness probiotics against common bacterial skin pathogens: Towards living antimicrobials. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1557–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeu, J.E.; Lee, H.G.; Park, G.Y.; Lee, J.; Kang, M.S. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of Weissella cibaria against pathogens of upper respiratory tract infections. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Strain | Isolation | Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| K. pneumoniae LABACER27 | Bronchial lavage (pneumonia)—Padilla Hospital [22] | β-lactams |
| K. pneumoniae LABACER01 | Osteoarticular tissue (sepsis)—Padilla Hospital [22] | β-lactams, quinolones, gentamicin |
| P. aeruginosa | Sputum (pneumonia)—Padilla Hospital [this work] | Imipenem |
| S. aureus | Sputum (pharyngitis)—East Hospital [this work] | β-lactams, quinolones, aminoglycosides |
| A. baumannii | Sputum (pneumonia)—East Hospital [this work] | β-lactams, quinolones, aminoglycosides |
| S. pneumoniae 19F | Sputum (pneumonia)—Malbrán Institute [this work] | MLS 1, tetracycline, vancomycin |
| Pathogen | Type of Hemolysis | Hemolysis in the Presence of | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cp090104 | Supernatant | ||
| K. pneumoniae LABACER27 | γ | γ | γ |
| K. pneumoniae LABACER01 | γ | γ | γ |
| P. aeruginosa | β | No activity | β |
| S. aureus | β | No activity | β |
| A. baumannii | γ | γ | γ |
| S. pneumoniae 19F | α | No activity | α |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz Moyano, R.; Dentice Maidana, S.; Imamura, Y.; Elean, M.; Namai, F.; Suda, Y.; Nishiyama, K.; Melnikov, V.; Kitazawa, H.; Villena, J. Antagonistic Effects of Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum 090104 on Respiratory Pathogens. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071295
Ortiz Moyano R, Dentice Maidana S, Imamura Y, Elean M, Namai F, Suda Y, Nishiyama K, Melnikov V, Kitazawa H, Villena J. Antagonistic Effects of Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum 090104 on Respiratory Pathogens. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(7):1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071295
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz Moyano, Ramiro, Stefania Dentice Maidana, Yoshiya Imamura, Mariano Elean, Fu Namai, Yoshihito Suda, Keita Nishiyama, Vyacheslav Melnikov, Haruki Kitazawa, and Julio Villena. 2024. "Antagonistic Effects of Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum 090104 on Respiratory Pathogens" Microorganisms 12, no. 7: 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071295
APA StyleOrtiz Moyano, R., Dentice Maidana, S., Imamura, Y., Elean, M., Namai, F., Suda, Y., Nishiyama, K., Melnikov, V., Kitazawa, H., & Villena, J. (2024). Antagonistic Effects of Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum 090104 on Respiratory Pathogens. Microorganisms, 12(7), 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071295








