Impact of Intercropping Five Medicinal Plants on Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Community Structure in Camellia oleifera Plantations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Collection of Soil Samples
2.3. Soil Chemical Property Analyses
2.4. Soil Enzyme Activity Analyses
2.5. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Effects of Intercropping Medicinal Plants with C. oleifera on Soil Properties and Enzyme Activities
3.1.1. Soil Properties
3.1.2. Soil Enzyme Activities
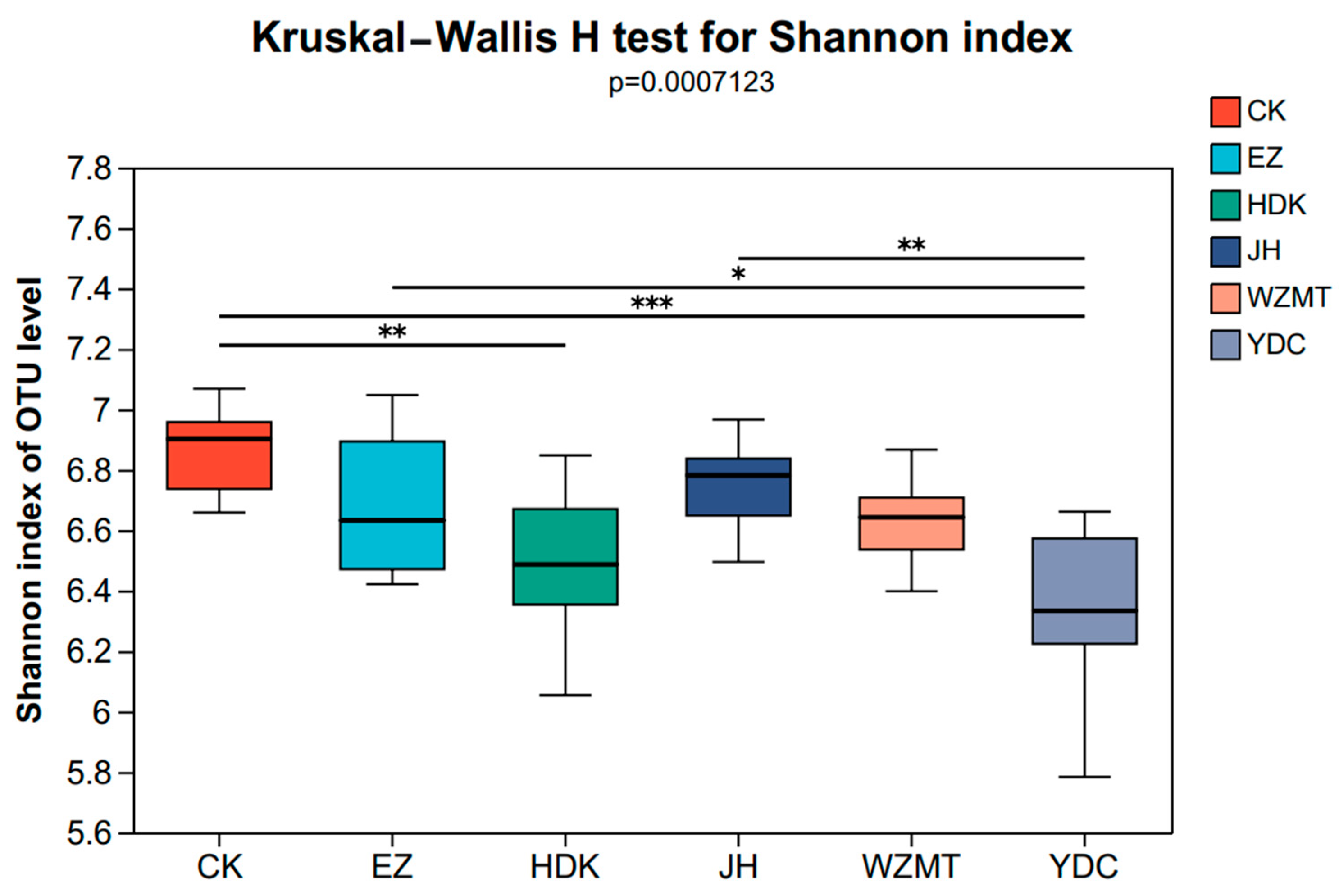
3.2. Effects of Intercropping Medicinal Plants with C. oleifera on Microbial Diversity
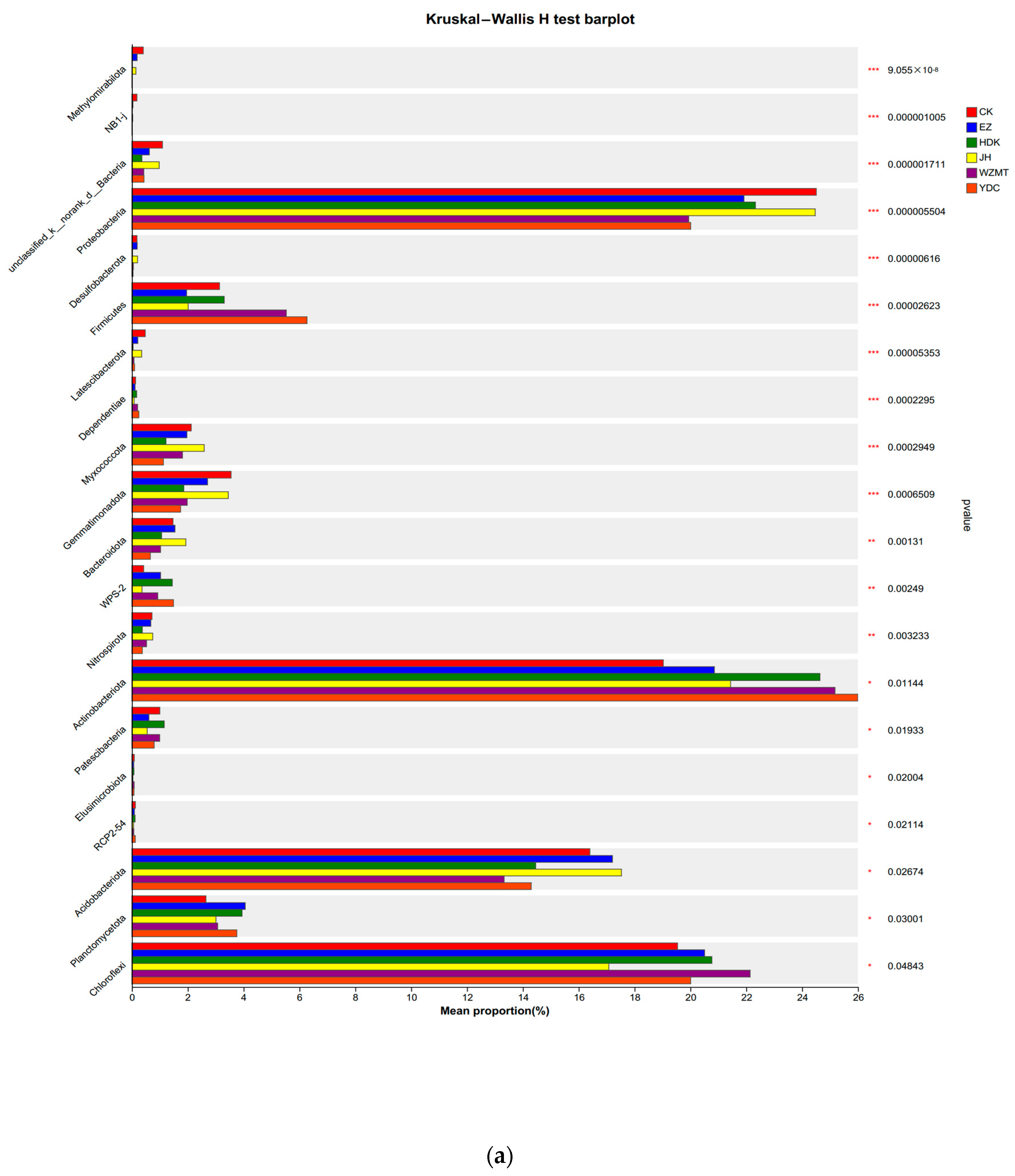
3.3. Effects of Intercropping Medicinal Plants with C. oleifera on Community Structure
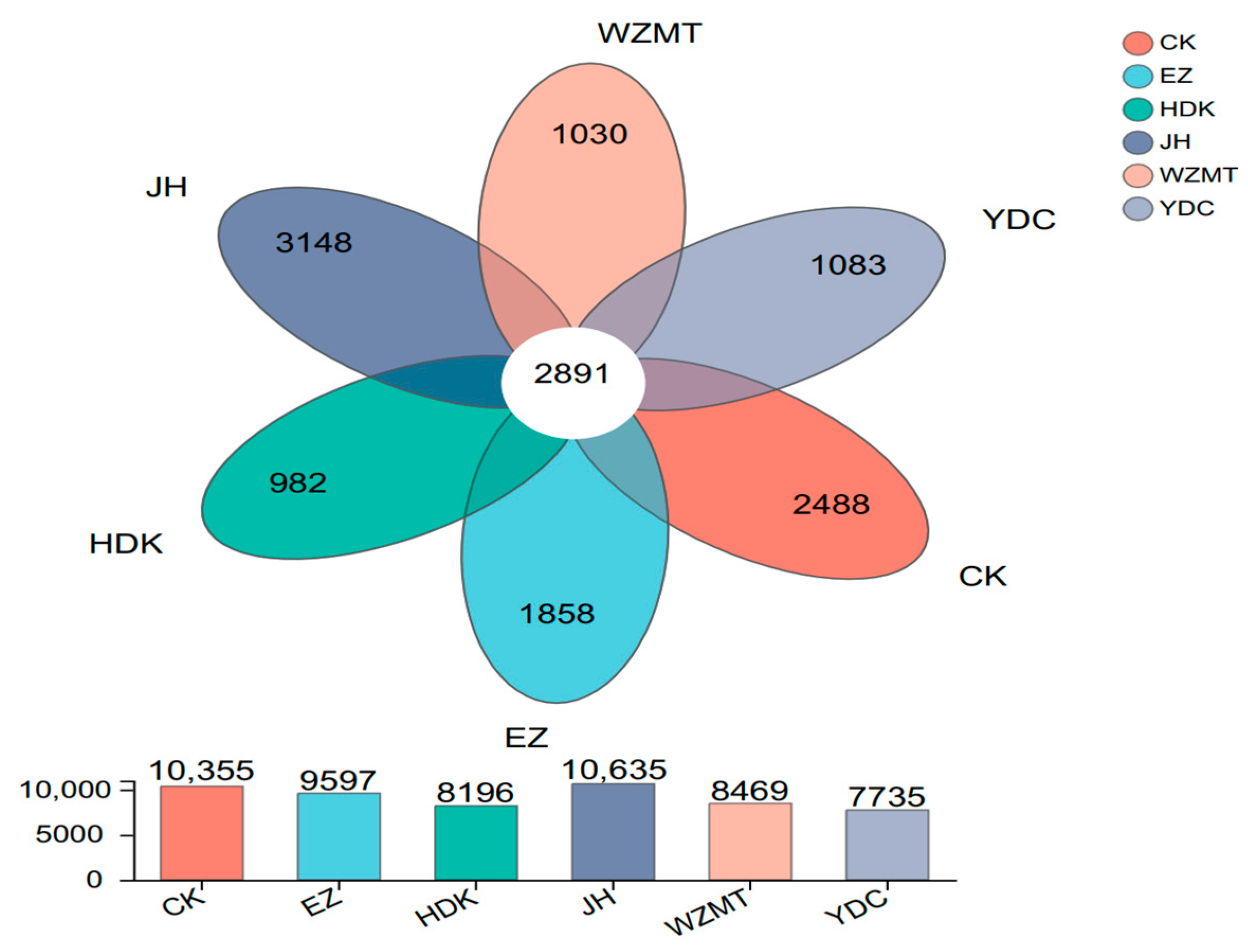
3.3.1. Community Structure on OTU Level
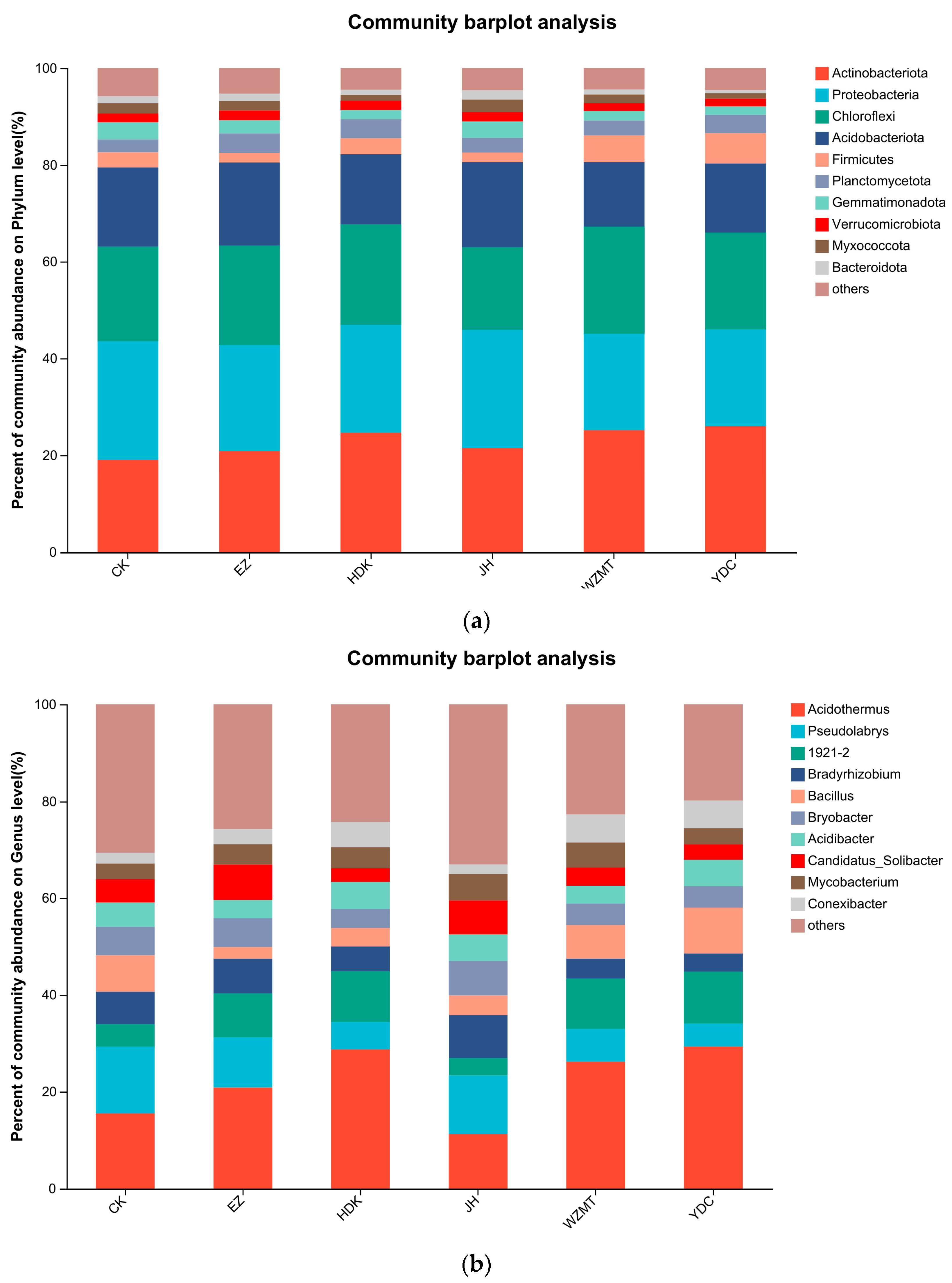
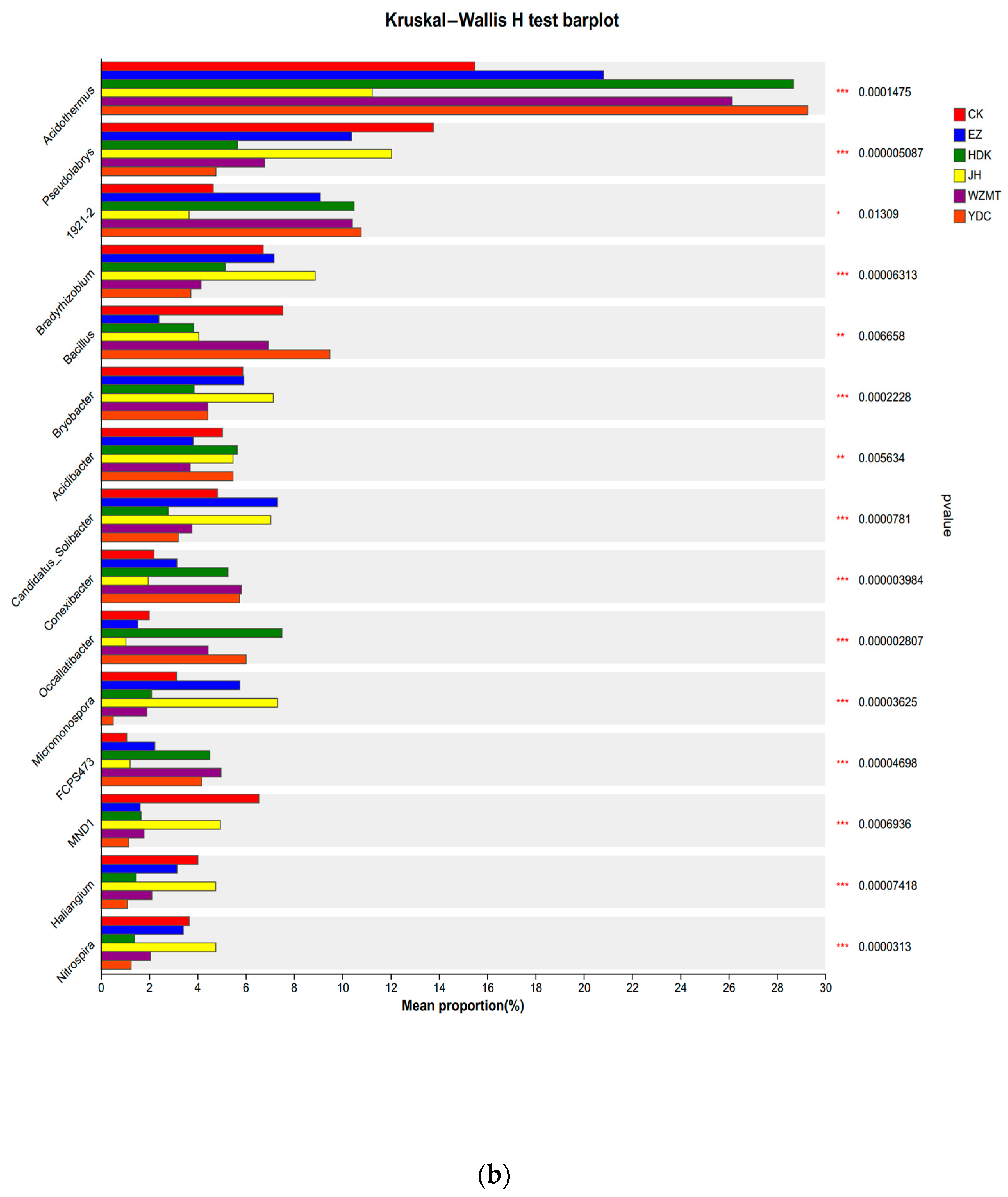
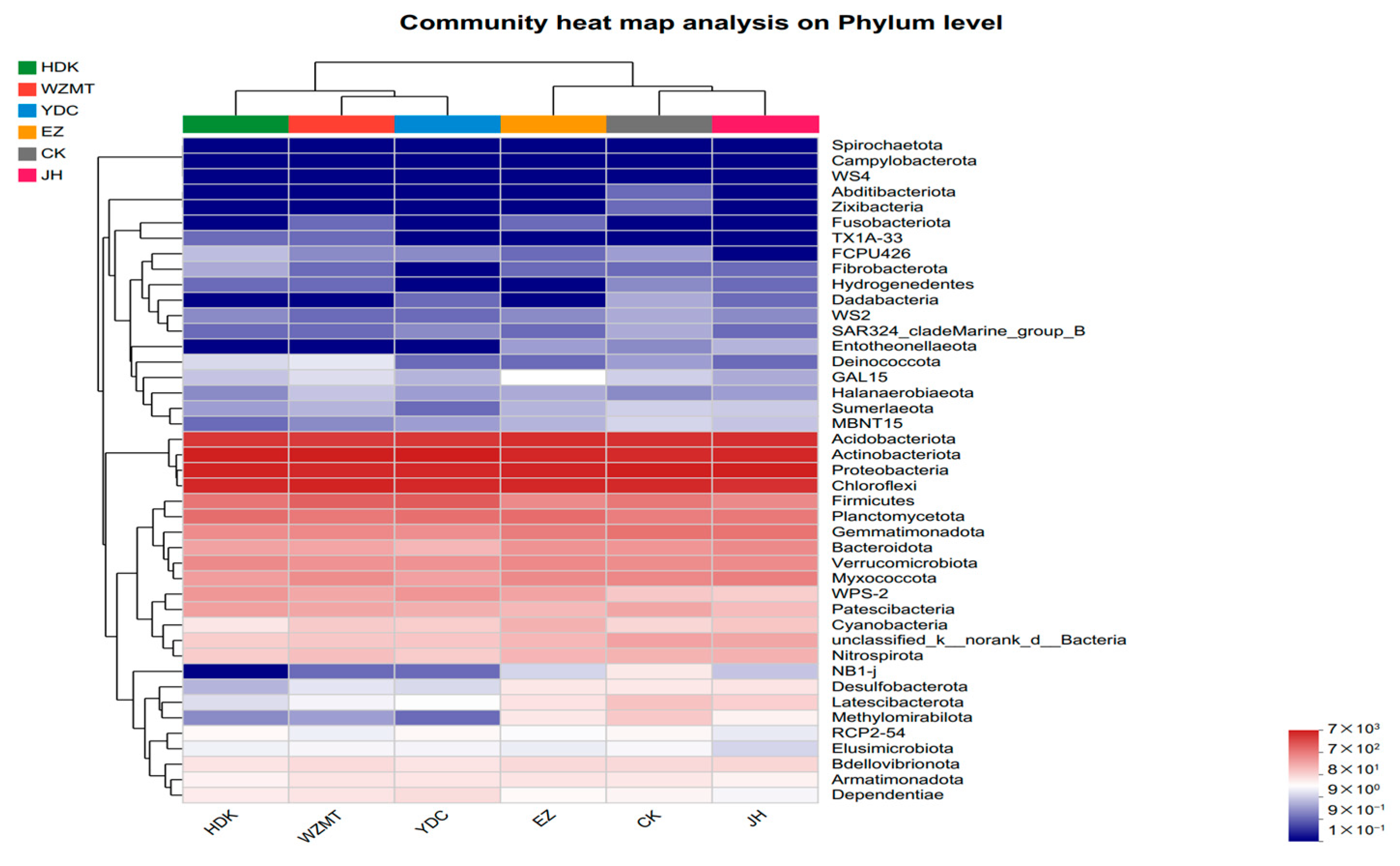
3.3.2. Community Structure on Genus and Phylum Level
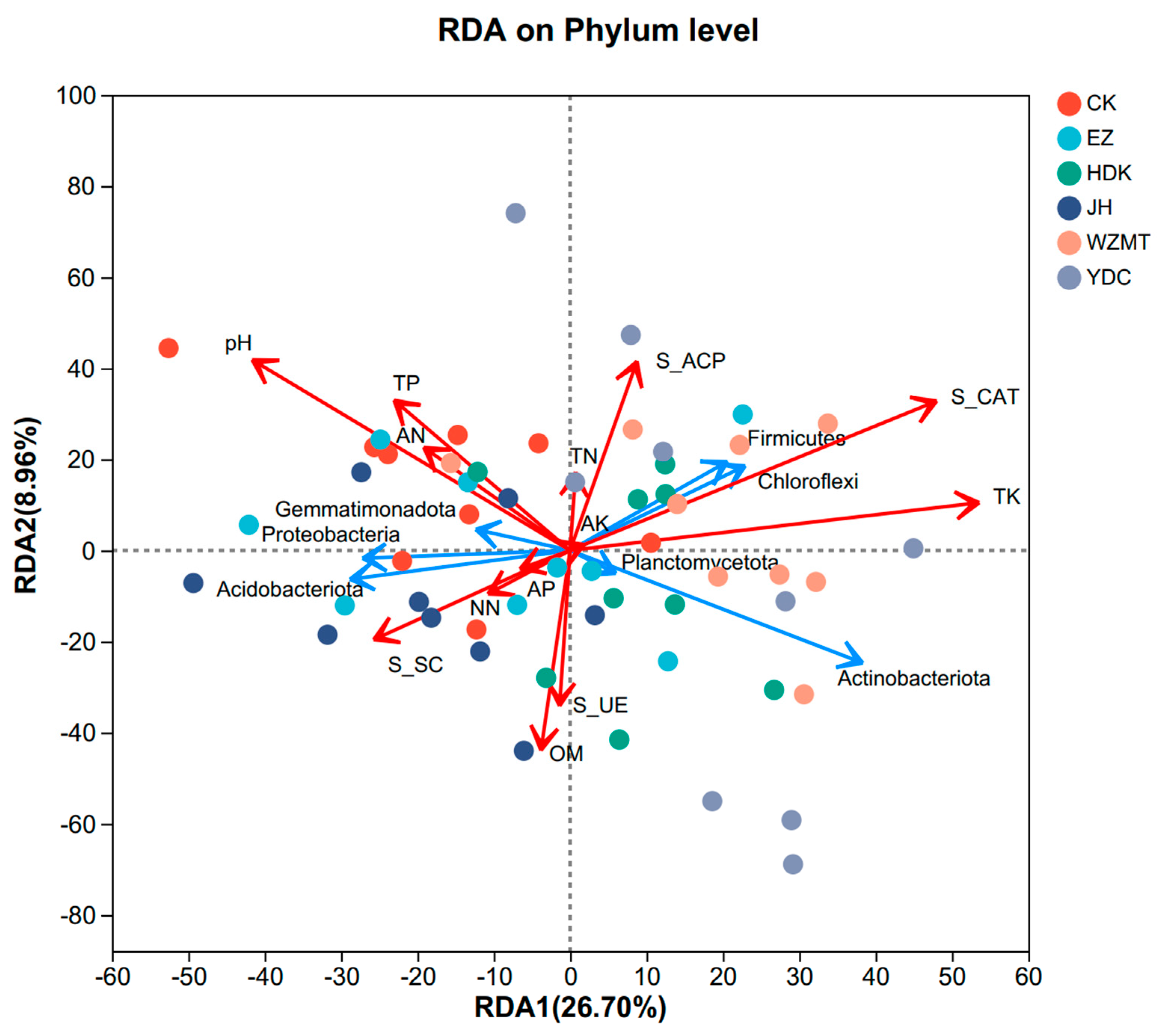
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Soil Properties, Enzyme Activities and Soil Microbiome
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects on Soil Chemical Properties and Enzyme Activities after Intercropping Medicinal Plants with C. oleifera
4.2. Effects on Soil Microbial Diversity and Structure after Intercropping Medicinal Plants with C. oleifera
4.2.1. Soil Microbial Diversity
4.2.2. Soil Microbial Community Structure
4.3. The Correlation between Soil Chemical Properties, Enzyme Activities, and Soil Microbial Community
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Wu, L.C.; Chen, D.; Yu, Z.G.; Wei, C.J. Development of a soil quality index for Camellia oleifera forestland yield under three different parent materials in Southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 176, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.T.; Shen, X.F.; Chen, Y. Effects of intercropping peanut on soil nutrient status and microbial activity within young Camellia oleifera plantation. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Chen, J.F.; Zhou, J.H.; Ai, W.S.; Chen, L.S. Plantation quality assessment of Camellia oleifera in mid-subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 186, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.L.; Yuan, J. Impact of Agro-Farming Activities on Microbial Diversity of Acidic Red Soils in a Camellia Oleifera Forest. Rev. Bras. Ciencia Solo 2019, 43, e0190044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.J.H.; Tahir, M.; Rizvi, V.; Kohli, R.; Ansari, A. Allelopathic interactions in agroforestry systems. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1999, 18, 773–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Gao, G.B.; Wu, Z.Z.; Wen, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhong, Z.Z.; Yang, C.B.; Bian, F.Y.; Gai, X. Responses of soil nutrients and microbial communities to intercropping medicinal plants in moso bamboo plantations in subtropical China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 2301–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Z.; Cai, Q.Z.; Liao, P.R.; Jiang, X.L.; Tang, X.M.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, L.Y. Effects of Fallopia multiflora–Andrographis paniculata intercropping model on yield, quality, soil nutrition and rhizosphere microorganisms of F. multiflora. Plant Soil 2021, 467, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, D.W.; Northfield, T.D.; Strand, M.R.; Snyder, W.E. Organic agriculture promotes evenness and natural pest control. Nature 2010, 466, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Z.; Wei, Y.W.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, W.X.; Bai, X.J.; Zhou, Y.B. Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Intercropping System in Northwest Liaoning. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lei, J.J.; Peng, Y.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, B.W.; Chen, Y.Z.; Xu, Y.C.; Farooq, T.H.; Wu, X.H.; Wang, J.; et al. Impact of Intercropping on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Nutrient Loss in Camellia oleifera Forests on Entisol Soil. Forests 2024, 15, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.H.Z.; Zhou, T.; He, Z.; Peng, Y.Y.; Lei, J.J.; Dong, J.Y.; Wu, X.H.; Wang, J.; Yan, W.D. Effects of Straw Mulching on Soil Properties and Enzyme Activities of Camellia oleifera–Cassia Intercropping Agroforestry Systems. Plants 2023, 12, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.D. Analysis Method of Soil and Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 25–108. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.Y. Soil Enzymology and Its Methodology; Agriculture Publishing Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 274–353. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.; Din, A.U.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Lei, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, G. Anti-atherosclerotic effects of Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC 14917 in ApoE−/− mice through modulation of proinflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6337–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utobo, E.B.; Tewari, L. Soil Enzymes as Bioindicators of Soil Ecosystem Status. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2015, 13, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.M.; Muneer, M.A.; Li, J.; Hou, W.; Ma, C.C.; Jiao, J.B.; Cai, Y.Y.; Chen, X.H.; Wu, L.Q.; Zheng, C.Y. Integrated Nutrient Management Significantly Improves Pomelo (Citrus grandis) Root Growth and Nutrients Uptake under Acidic Soil of Southern China. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, S.; Bhat, R.; Kannan, C.; Balasimha, D. Impact of intercropping of medicinal and aromatic plants with organic farming approach on resource use efficiency in arecanut (Areca catechu L.) plantation in India. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.N.; Zhang, F.S.; Marschner, P.; Fan, F.L.; Gao, H.M.; Bao, X.G.; Sun, J.H.; Li, L. Effect of intercropping on crop yield and chemical and microbiological properties in rhizosphere of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), maize (Zea mays L.), and faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antil, R.; Lovell, R.; Hatch, D.; Jarvis, S. Mineralization of nitrogen in permanent pastures amended with fertilizer or dung. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 33, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.A.; Barnard, R.L.; Marhan, S.; Niklaus, P.A. Effects of drought and N-fertilization on N cycling in two grassland soils. Oecologia 2013, 171, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Z.L.; Liu, R.N.; Wang, J. Location variation of curcuminoids content in Curcuma longa rhizome and CCA analysis with environmental factors. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 2011, 68, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabborova, D.; Choudhary, R.; Karunakaran, R.; Ercisli, S.; Ahlawat, J.; Sulaymanov, K.; Azimov, A.; Jabbarov, Z. The Chemical Element Composition of Turmeric Grown in Soil-Climate Conditions of Tashkent Region, Uzbekistan. Plants 2021, 10, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, G.H. Predicting soil N mineralization using organic matter fractions and soil properties: A re-analysis of literature data. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 45, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, N.; Van Antwerpen, R.; Ramburan, S. Soil organic matter under sugarcane: Levels, composition and dynamics. Int. Sugar J. 2017, 119, 140–144. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344218835 (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Bandick, A.K.; Dick, R.P. Field management effects on soil enzyme activities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Frey, B. Soil respiration and microbial properties in an acid forest soil: Effects of wood ash. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasvaran, K.; Alallam, B.; Lim, V. Optimisation of the extraction of crude polysaccharides from Clinacanthus nutans leaves for antioxidant applications: Content analysis, chemometrics and metabolomics analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 202, 117086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Ghafoor, K.; Sahena, F.; Hakim, M.A.; Rafii, M.Y.; Abir, H.M.; Bostanudin, M.F.; Perumal, V.; Khatib, A. In vitro antioxidant and, α-glucosidase inhibitory activities and comprehensive metabolite profiling of methanol extract and its fractions from Clinacanthus nutans. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K.; Shamsuzzaman, S.M.; Lo, L.Q.; Medom, M.; Hasan, M. Effects of salinity on growth, antioxidant contents and proximate compositions of sabah snake grass (Clinacanthus nutans (burm. F.) Landau). Bangladesh J. Bot. 2017, 46, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Chang, S.X. Meta-analysis shows that plant mixtures increase soil phosphorus availability and plant productivity in diverse ecosystems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 6, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, O.; Sardans, J.; Fernández-Martínez, M.; Molowny-Horas, R.; Janssens, I.A.; Ciais, P.; Goll, D.; Richter, A.; Obersteiner, M.; Asensio, D.; et al. Global patterns of phosphatase activity in natural soils. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Tian, L.; Ma, L.; Tian, C. Community Structure of Rhizomicrobiomes in Four Medicinal Herbs and Its Implication on Growth Management. Microbiology 2018, 87, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.F.; Mayes, M.A.; Wang, G.S. Kinetic parameters of phosphatase: A quantitative synthesis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.J.; Liao, Y.W.K.; Pan, C.; Li, X.G. Positive effects of intercropping on soil phosphatase activity depend on the application scenario: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Z.; He, J.; Tian, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, F.; Qin, K.; Wang, J. Intercropping Wolfberry with Gramineae plants improves productivity and soil quality. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 292, 110632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Li, B.X.; Xu, C.Y.; Raza, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.Z.; Fu, Y.N.; Hu, J.Y.; Imoulan, A.; Hussain, M.; et al. Intercropping Walnut and Tea: Effects on Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Communities. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 852342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Kumar, U.; Mo, J.; Shakoor, A.; Wang, J.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Tufail, M.A.; Chen, X.Y.; Yan, W.D. Intercropping of Peanut-Tea Enhances Soil Enzymatic Activity and Soil Nutrient Status at Different Soil Profiles in Subtropical Southern China. Plants 2021, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.M.; Cheng, Z.H.; Lv, J.; Xie, J.M.; Ma, N.; Yu, J.H. A green garlic (Allium sativum L.) based intercropping system reduces the strain of continuous monocropping in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) by adjusting the micro-ecological environment of soil. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros-Silva, M.; Franck, W.L.; Borba, M.P.; Pizzato, S.B.; Strodtman, K.N.; Emerich, D.W.; Stacey, G.; Poacco, J.C.; Carlini, C.R. Soybean Ureases, but Not That of Bradyrhizobium japonicum, Are Involved in the Process of Soybean Root Nodulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3517–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, L.; Castronuovo, D.; Perniola, M.; Cicco, N.; Candido, V. Evaluation of corm origin and climatic conditions on saffron (Crocus sativus L.) yield and quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5858–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yu, D.; Hu, A.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, C. Effects of green manure intercropping on soil nutrient content and bacterial community structure in litchi orchards in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1059800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Liu, G.; Cheng, Y. The mechanism effects of root exudate on microbial community of rhizosphere soil of tree, shrub, and grass in forest ecosystem under N deposition. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.G.; Sang, M.K.; An, J.H.; Kim, S.; Jin, Y.J.; Song, J. Changes in the Composition and Microbial Community of the Pepper Rhizosphere in Field with Bacterial Wilt Disease. Plant Pathol. J. 2022, 38, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Guleria, S.; Balgir, P.P.; Walia, A.; Mahajan, R.; Mehta, P.; Shirkot, C.K. Tricalcium phosphate solubilization and nitrogen fixation by newly isolated Aneurinibacillus aneurinilyticus CKMV1 from rhizosphere of Valeriana jatamansi and its growth promotional effect. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naureen, Z.; Rehman, N.U.; Hussain, H.; Gilani, S.A.; Khan, A.L.; Harrasi, A.A. Exploring the potentials of Lysinibacillus sphaericus ZA9 for plant growth promotion and biocontrol activities against phytopathogenic fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 252103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichorst, S.A.; Kuske, C.R.; Schmidt, T.M. Influence of plant polymers on the distribution and cultivation of bacteria in the phylum Acidobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, A.; Matsushita, N.; Hougetsu, T. Nodulation in black locust by the Gammaproteobacteria Pseudomonas sp. and the Betaproteobacteria Burkholderia sp. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 33, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, E.V.; Just, C.L.; Schilling, K.; Streeter, M.; Mattes, T.E. Reconnaissance of Oxygenic Denitrifiers in Agriculturally Impacted Soils. mSphere 2023, 8, e00571-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viso, N.P.; Ortiz, J.; Maury, M.; Frene, J.P.; Iocoli, G.A.; Lorenzon, C.; Rivarola, M.; García, F.O.; Gudelj, V.; Faggioli, V.S. Long-term maintenance rate fertilisation increases soil bacterial-archaeal community diversity in the subsoil and N-cycling potentials in a humid crop season. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 193, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yu, G.; Sun, Y.B.; Zhang, H.L.; Tian, X.; Xia, B. Characteristics of Soil Microbial Community Structure and Environmental Driving Factors in Farmland around Mercury Mining Areas. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4342–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lin, D.; Guan, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, G.; Zhu, D.; Peng, C. Effect of herbicide used with years (8 + 1) on soil enzymic activity and microbial population diversity. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2490–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pei, H.; Xie, H. Influence of allyl isothiocyanate on the soil microbial community structure and composition during pepper cultivation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Feng, J.; Zheng, L.; Huang, J.B.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.H. Intercropping with marigold promotes soil health and microbial structure to assist in mitigating tobacco bacterial wilt. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 102, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Li, J.S.; Xiao, N.W.; Qi, Y.; Fu, G.; Liu, G.H.; Qiao, M.P. Urban-development-induced Changes in the Diversity and Composition of the Soil Bacterial Community in Beijing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.D.; Hao, J.J.; Schachtman, D.P. Alkaline soil pH affects bulk soil, rhizosphere and root endosphere microbiomes of plants growing in a Sandhills ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiab028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Ni, Y.; Liang, W.; Wang, J.; Chu, H. Distinct soil bacterial communities along a small-scale elevational gradient in alpine tundra. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 147551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amtmann, A.; Troufflard, S.; Armengaud, P. The effect of potassium nutrition on pest and disease resistance in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, T.M.D.; Zeng, J.Y.; Man, X.L. Soil fungal and bacterial communities in southern boreal forests of the Greater Khingan Mountains and their relationship with soil properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Peng, H.; Ji, X.L.; Chen, X.L.; Zhou, H.M. Effect of stand age on soil microbial communities of a plantation Ormosia hosiei forest in southern China. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 62, 10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | pH | OM (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | NN (mg/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | TP (g/Kg) | AP (mg/kg) | TK (g/kg) | AK (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKZ | 5.35 ± 0.59 | 15.43 ± 1.69 | 1.84 ± 0.42 | 161.67 ± 8.08 | 427.67 ± 10.07 | 2.7 ± 0.54 * | 50.53 ± 1.69 | 3.58 ± 0.27 | 18.13 ± 8.74 ** |
| CKK | 5.37 ± 0.26 | 15 ± 1.14 | 1.87 ± 0.2 | 124 ± 11.53 | 426.67 ± 12.66 | 4.47 ± 0.41 | 49.73 ± 4.22 | 3.09 ± 0.21 | 7.97 ± 0.4 |
| CKY | 5.89 ± 0.07 | 13.77 ± 1.76 ** | 1.27 ± 0.04 ** | 109.67 ± 7.64 ** | 112.33 ± 4.04 ** | 4.02 ± 1.24 | 48.07 ± 3.95 | 2.91 ± 0.44 * | 9.23 ± 3.8 |
| EZZ | 4.43 ± 0.27 | 15.1 ± 0.36 | 4.17 ± 0.35 | 537 ± 21.63 * | 362.67 ± 4.73 | 3.17 ± 0.95 | 53.27 ± 6 | 3.71 ± 0.19 | 19.8 ± 7.63 |
| EZK | 4.26 ± 0.24 | 15.3 ± 0.26 | 1.28 ± 0.11 ** | 593.67 ± 20.21 * | 596.33 ± 6.66 ** | 3.29 ± 0.14 | 47.9 ± 9.56 | 3.45 ± 0.22 | 11.3 ± 1.78 |
| EZY | 5.46 ± 0.54 ** | 16.13 ± 0.35 * | 6.66 ± 1.08 ** | 832 ± 51.97 ** | 212 ± 9.54 | 4.21 ± 0.97 | 76.5 ± 16.85 ** | 3.45 ± 0.1 | 21.67 ± 1.29 ** |
| JHZ | 4.29 ± 0.15 | 15.93 ± 0.38 | 3.75 ± 0.48 | 258.33 ± 3.21 | 132 ± 6.08 | 3.33 ± 0.08 | 79.07 ± 14.17 | 2.82 ± 0.34 | 20.3 ± 2.91 |
| JHK | 3.91 ± 0.07 ** | 16.47 ± 0.06 ** | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 250.67 ± 18.23 | 99.67 ± 4.04 | 2.91 ± 0.33 | 57.07 ± 1.72 * | 2.8 ± 0.13 | 19.97 ± 4.45 |
| JHY | 4.71 ± 0.05 | 15.47 ± 0.47 | 7.13 ± 0.31 ** | 245 ± 12.77 | 107 ± 2.65 | 4.02 ± 0.94 * | 73.93 ± 4.58 | 2.85 ± 0.1 | 32.5 ± 5.15 ** |
| HDKZ | 4.02 ± 0.05 | 16.33 ± 0.21 ** | 2.11 ± 0.17 | 342.67 ± 22.23 | 96.33 ± 2.52 | 1.76 ± 0.25 | 45.87 ± 2.33 | 3.44 ± 0.08 | 18.13 ± 0.7 |
| HDKK | 3.99 ± 0.08 | 15.63 ± 0.57 | 3.55 ± 0.14 | 373.67 ± 10.21 | 132.67 ± 8.39 | 2.46 ± 0.18 | 49.63 ± 1.7 | 3.62 ± 0.21 | 17.67 ± 2.87 |
| HDKY | 4.82 ± 0.14 * | 15.3 ± 0.17 | 2.33 ± 0.19 | 291.33 ± 65.58 | 190.67 ± 1.53 * | 2.71 ± 0.12 | 44.37 ± 4.25 | 3.73 ± 0.11 | 30.1 ± 4.09 * |
| YDCZ | 4.14 ± 0.07 | 15.53 ± 0.61 | 1.85 ± 0.24 | 254 ± 28.35 | 93 ± 3.61 | 2.46 ± 0.21 | 70.9 ± 1.42 | 3.87 ± 0.03 | 20.9 ± 1.11 |
| YDCK | 4.1 ± 0.12 | 15.97 ± 0.8 | 2.37 ± 0.24 | 232 ± 1.73 | 99.33 ± 2.52 | 2.55 ± 0.45 | 58.47 ± 9.6 | 4.59 ± 0.33 * | 20.8 ± 5.31 |
| YDCY | 4.75 ± 0.25 * | 12.87 ± 0.75 ** | 9.09 ± 0.33 ** | 345 ± 50.48 * | 94.67 ± 6.03 | 4.39 ± 0.7 * | 89.1 ± 11.17 * | 4.16 ± 0.64 | 31.17 ± 12.98 ** |
| WZMTZ | 4.37 ± 0.08 | 16.4 ± 0.4 ** | 3.16 ± 0.21 | 224 ± 9.54 | 118.33 ± 4.51 | 2.21 ± 0.15 | 52.6 ± 0.95 | 4.15 ± 0.43 | 18.4 ± 1.3 |
| WZMTK | 4.53 ± 0.42 | 15.23 ± 0.38 | 3.25 ± 0.36 | 240.67 ± 5.69 | 73 ± 3.61 ** | 2.37 ± 0.25 | 45.83 ± 0.51 | 4.28 ± 0.1 | 14.53 ± 0.87 |
| WZMTY | 4.74 ± 0.18 | 15.77 ± 0.61 | 5.36 ± 0.25 * | 199 ± 24.25 | 203.33 ± 5.51 * | 3.6 ± 1.27 * | 61.17 ± 4.5 * | 3.99 ± 0.45 | 21.17 ± 1.16 * |
| Samples | S-CAT (mg/g) | S-ACP (mg/g) | S-SC (mg/g) | S-UE (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKZ | 5.05 ± 0.59 | 1.01 ± 0.03 | 2.3 ± 0.27 | 0.73 ± 0.08 |
| CKK | 5.79 ± 0.75 | 1.59 ± 0.05 | 1.86 ± 0.06 | 0.47 ± 0.08 |
| CKY | 5.42 ± 0.17 | 2.46 ± 0.37 * | 1.43 ± 0.04 | 0.56 ± 0.03 |
| EZZ | 4.46 ± 0.52 | 1.58 ± 0.09 | 7.24 ± 0.11 | 1.02 ± 0.05 * |
| EZK | 5.26 ± 0.32 * | 2.57 ± 0.11 | 6.48 ± 0.27 | 0.57 ± 0.06 |
| EZY | 4.12 ± 0.84 | 3.54 ± 0.15 * | 6.79 ± 0.28 | 0.66 ± 0.05 |
| JHZ | 4.07 ± 0.48 | 1.54 ± 0.12 | 3.87 ± 0.43 | 1.62 ± 0.06 ** |
| JHK | 2.49 ± 0.29 ** | 2.64 ± 0.16 | 4.88 ± 0.37 | 1.56 ± 0.1 ** |
| JHY | 4.22 ± 0.26 | 3.6 ± 0.04 * | 9.15 ± 0.75 ** | 1.23 ± 0.09 * |
| HDKZ | 4.45 ± 0.37 | 1.55 ± 0.1 | 2.96 ± 0.14 | 1.26 ± 0.07 |
| HDKK | 4.28 ± 0.09 | 2.4 ± 0.08 | 3.01 ± 0.11 | 0.77 ± 0.08 |
| HDKY | 5.59 ± 1.05 * | 3.78 ± 0.22 * | 6.29 ± 0.77 ** | 1.53 ± 0.05 |
| YDCZ | 5.87 ± 0.72 | 2.14 ± 0.05 | 3.08 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.07 |
| YDCK | 4.41 ± 0.4 | 3.39 ± 0.03 | 3.02 ± 0.37 | 1.02 ± 0.01 |
| YDCY | 7.69 ± 0.46 ** | 5.45 ± 0.19 ** | 2.72 ± 0.27 | 0.82 ± 0.09 |
| WZMTZ | 8.02 ± 0.63 | 1.56 ± 0.13 | 3.44 ± 0.2 | 0.85 ± 0.05 |
| WZMTK | 8.46 ± 0.64 | 2.42 ± 0.14 | 3.74 ± 0.68 | 0.89 ± 0.06 |
| WZMTY | 9.39 ± 0.88 * | 3.56 ± 0.12 * | 2.94 ± 0.76 | 0.68 ± 0.1 |
| Sample | OTU_Num | Sequences | Sobs | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKZ | 3617 | 25,851 | 644 | 4.95 | 0.015 | 751 | 750 | 0.995 |
| CKK | 3106 | 25,851 | 600 | 4.9 | 0.014 | 705 | 718 | 0.995 |
| CKY | 3256 | 25,851 | 625 | 4.99 | 0.013 | 712 | 714 | 0.996 |
| EZZ | 3447 | 25,851 | 634 | 5.01 | 0.013 | 746 | 758 | 0.995 |
| EZK | 2748 | 25,851 | 498 | 4.44 | 0.025 | 569 | 567 | 0.996 |
| EZY | 2989 | 25,851 | 588 | 4.87 | 0.017 | 663 | 668 | 0.996 |
| JHZ | 3368 | 25,851 | 632 | 5 | 0.014 | 723 | 723 | 0.995 |
| JHK | 3005 | 25,851 | 565 | 4.87 | 0.016 | 649 | 650 | 0.996 |
| JHY | 3239 | 25,851 | 587 | 4.9 | 0.016 | 661 | 674 | 0.996 |
| HDKZ | 2679 | 25,851 | 539 | 4.6 | 0.022 | 631 | 633 | 0.996 |
| HDKK | 2269 | 25,851 | 470 | 4.32 | 0.03 | 554 | 553 | 0.996 |
| HDKY | 3132 | 25,851 | 585 | 4.86 | 0.017 | 676 | 691 | 0.996 |
| YDCZ | 2193 | 25,851 | 454 | 4.26 | 0.035 | 537 | 543 | 0.996 |
| YDCK | 2600 | 25,851 | 520 | 4.52 | 0.024 | 617 | 617 | 0.996 |
| YDCY | 2542 | 25,851 | 525 | 4.63 | 0.022 | 609 | 604 | 0.996 |
| WZMTZ | 2970 | 25,851 | 614 | 4.9 | 0.016 | 713 | 729 | 0.995 |
| WZMTK | 2254 | 25,851 | 532 | 4.45 | 0.029 | 609 | 606 | 0.996 |
| WZMTY | 2678 | 25,851 | 541 | 4.73 | 0.019 | 624 | 640 | 0.996 |
| Method | Statistic | p Value | Permutation Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANOSIM | 0.503 | 0.001 | 999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bajiu, A.; Gao, K.; Zeng, G.; He, Y. Impact of Intercropping Five Medicinal Plants on Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Community Structure in Camellia oleifera Plantations. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081616
Bajiu A, Gao K, Zeng G, He Y. Impact of Intercropping Five Medicinal Plants on Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Community Structure in Camellia oleifera Plantations. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(8):1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081616
Chicago/Turabian StyleBajiu, Azuo, Kai Gao, Guangyu Zeng, and Yuanhao He. 2024. "Impact of Intercropping Five Medicinal Plants on Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Community Structure in Camellia oleifera Plantations" Microorganisms 12, no. 8: 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081616
APA StyleBajiu, A., Gao, K., Zeng, G., & He, Y. (2024). Impact of Intercropping Five Medicinal Plants on Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Community Structure in Camellia oleifera Plantations. Microorganisms, 12(8), 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081616




