AraC Functional Suppressors of Mutations in the C-Terminal Domain of the RpoA Subunit of the Escherichia coli RNA Polymerase
Abstract
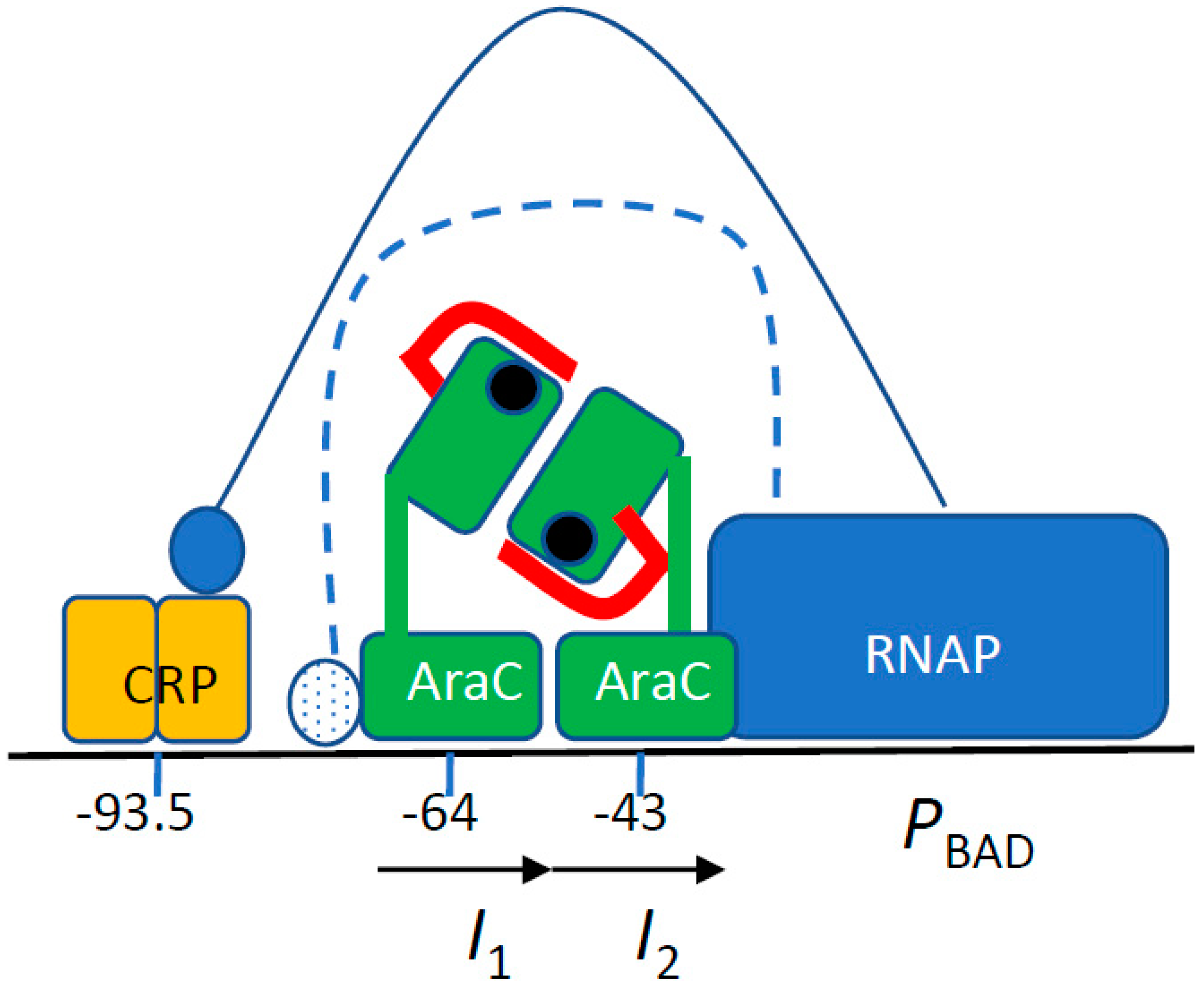
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results
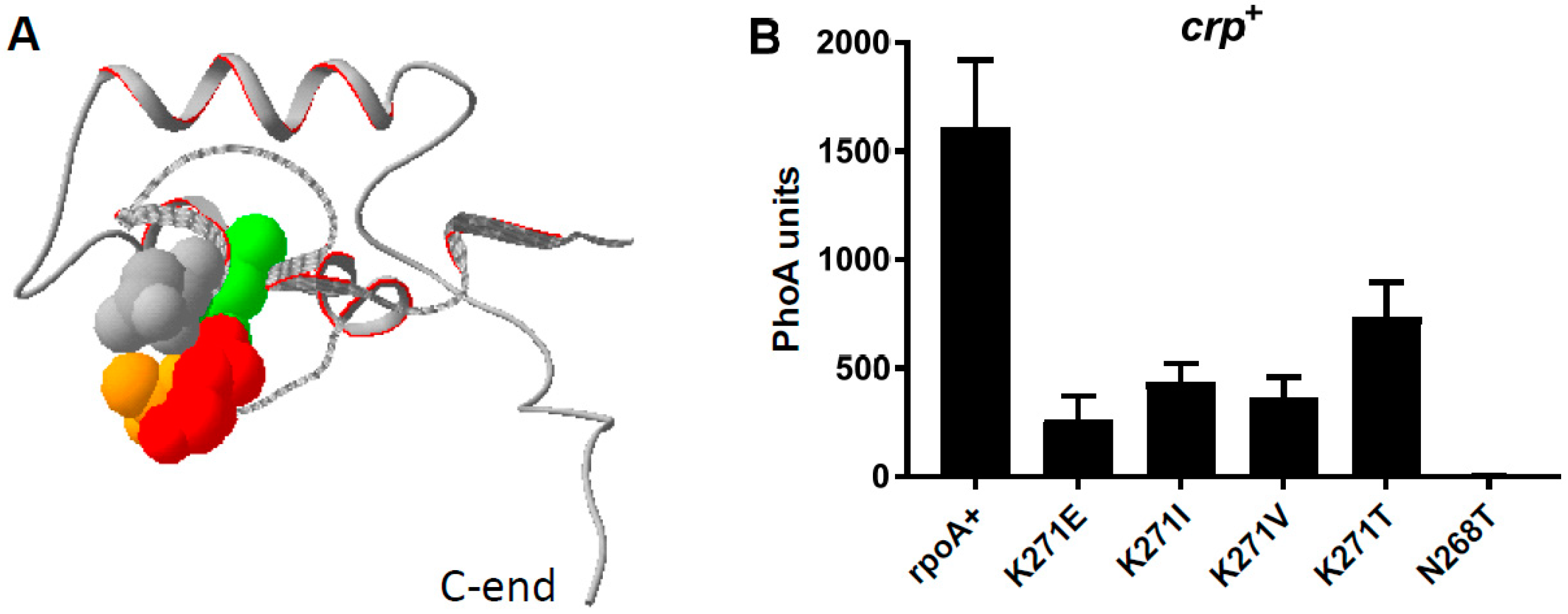
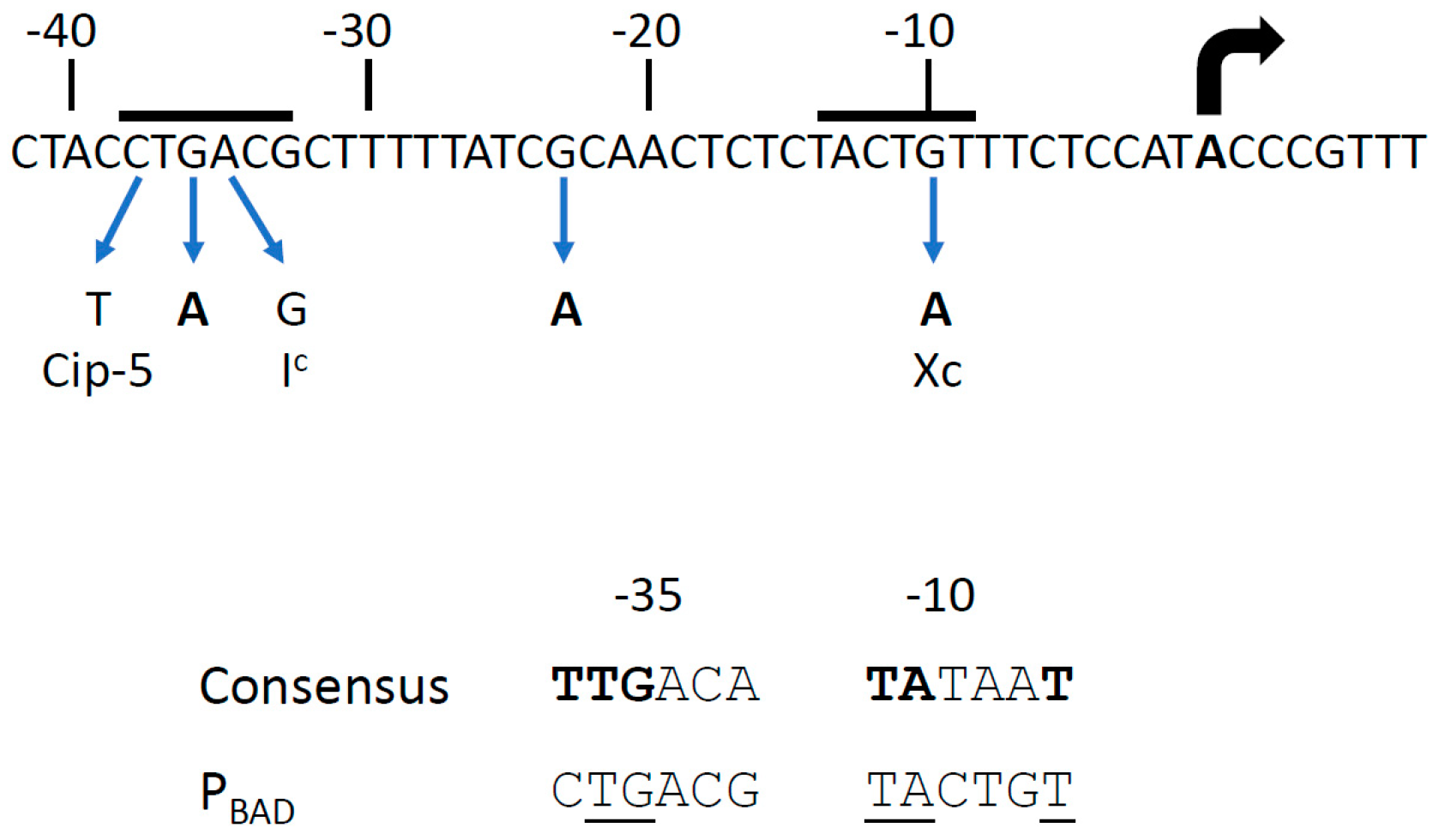
3.1. RpoA Mutations in the α-CTD Region That Interfere with PBAD Expression
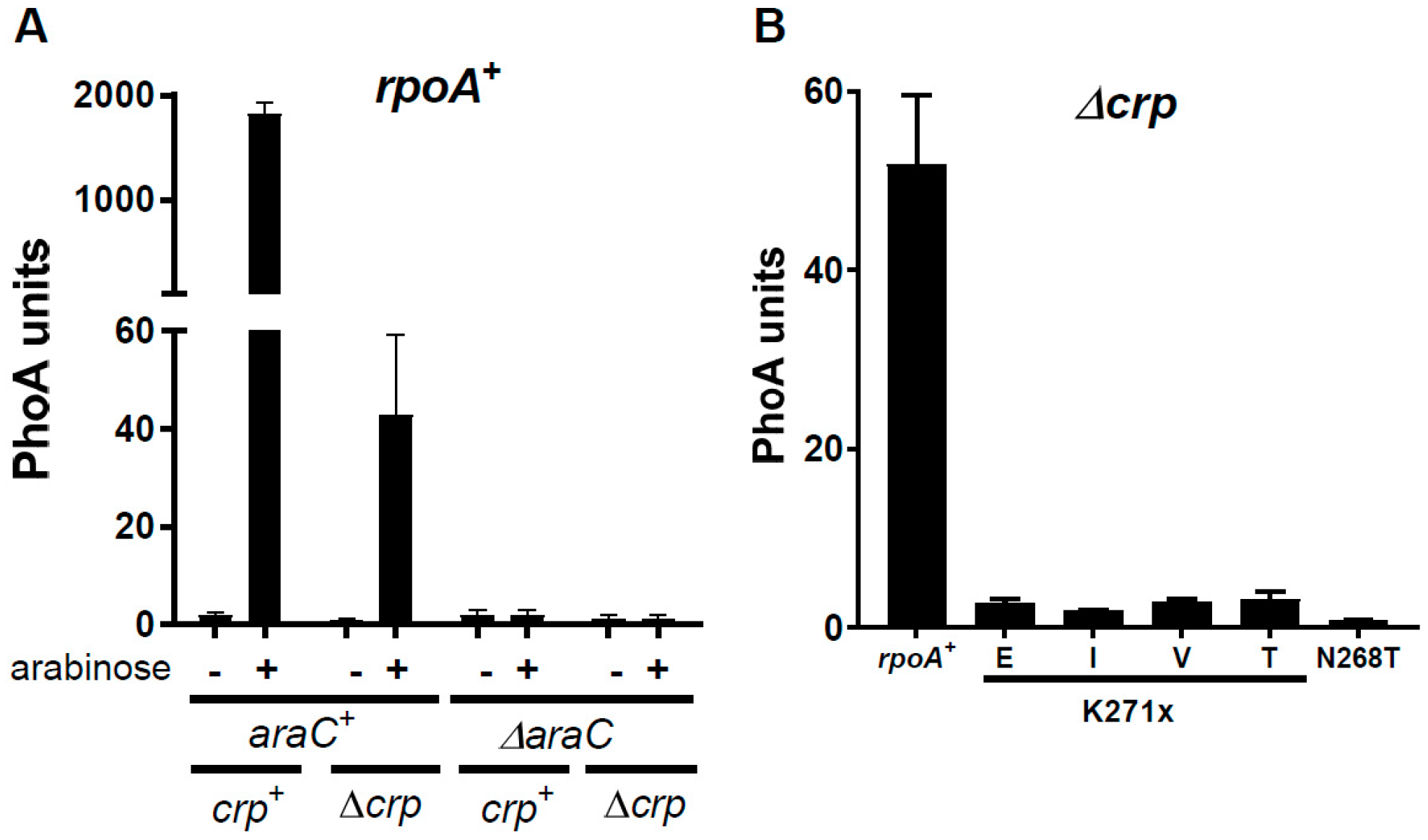
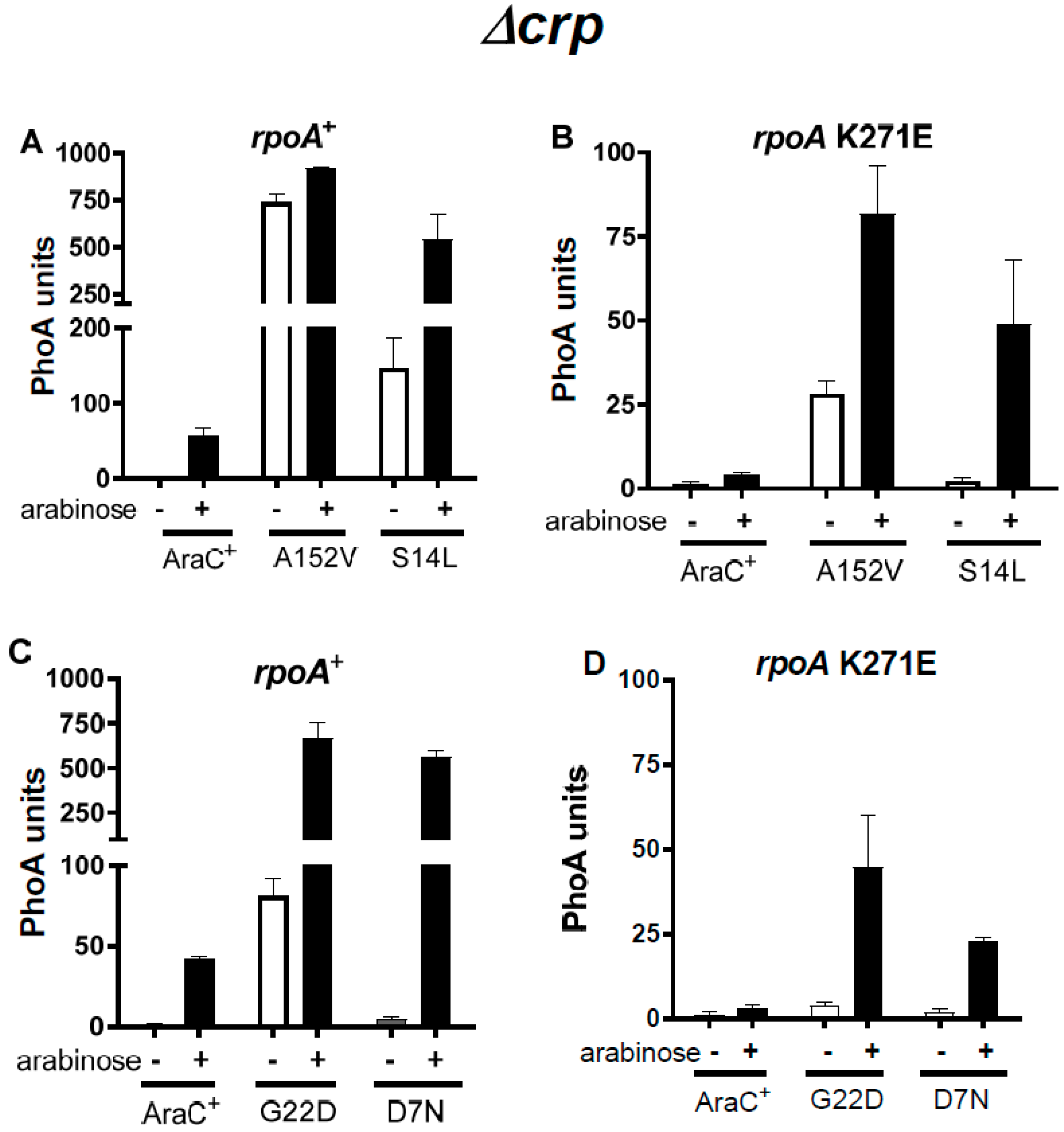
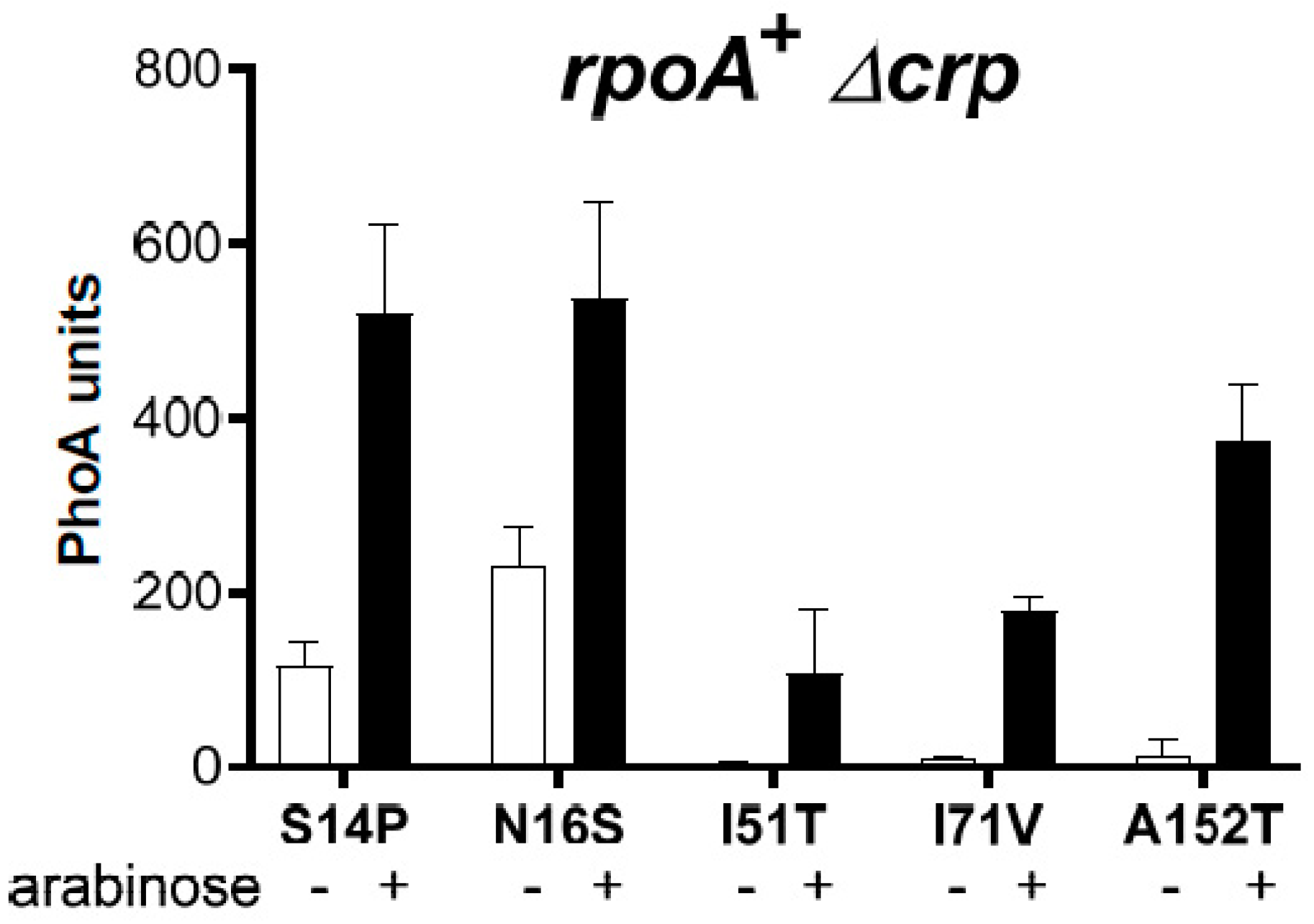
3.2. Suppressors of the rpoA Mutations
3.3. The Activity of the AraC Mutant Proteins Requires the α-CTD of RpoA
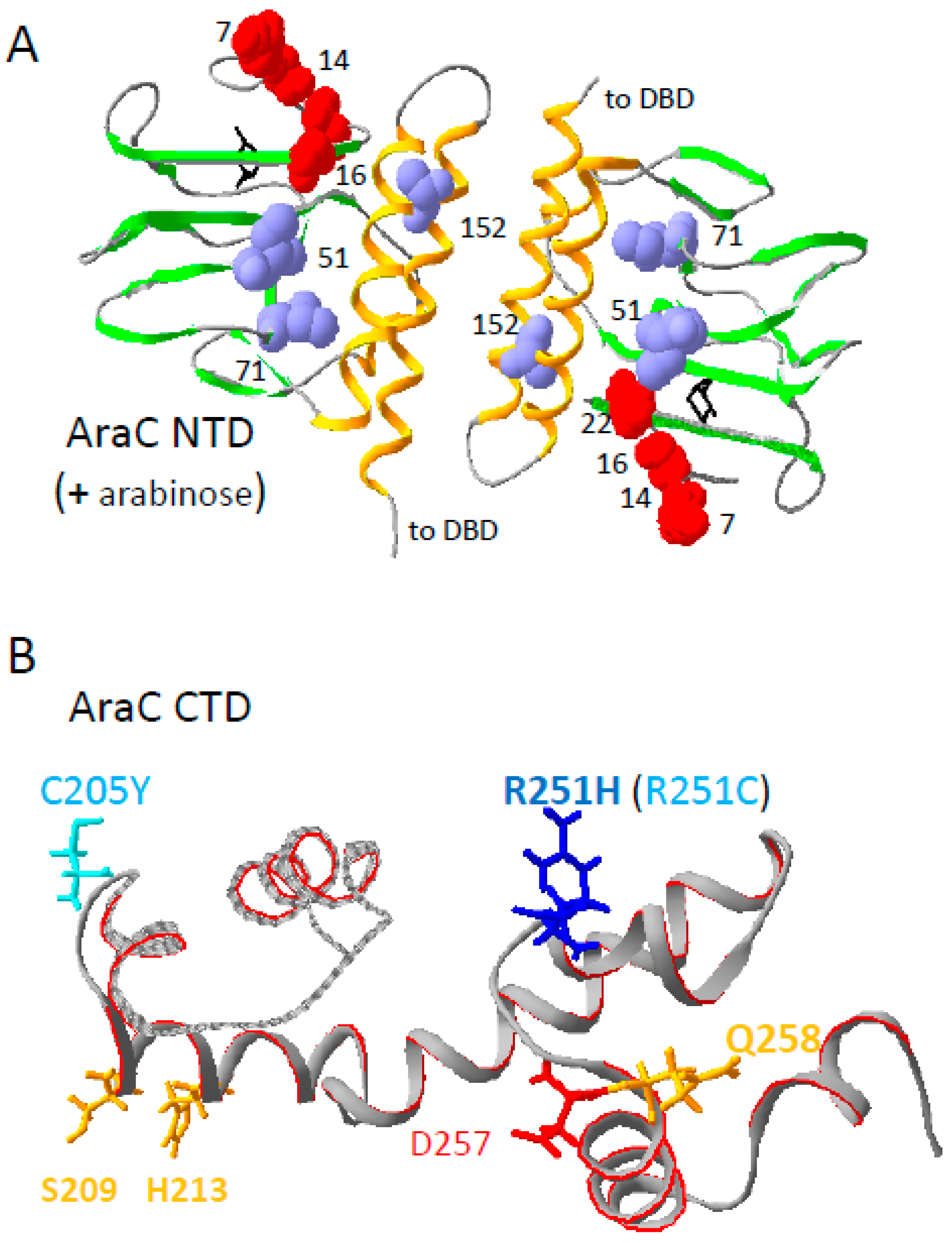
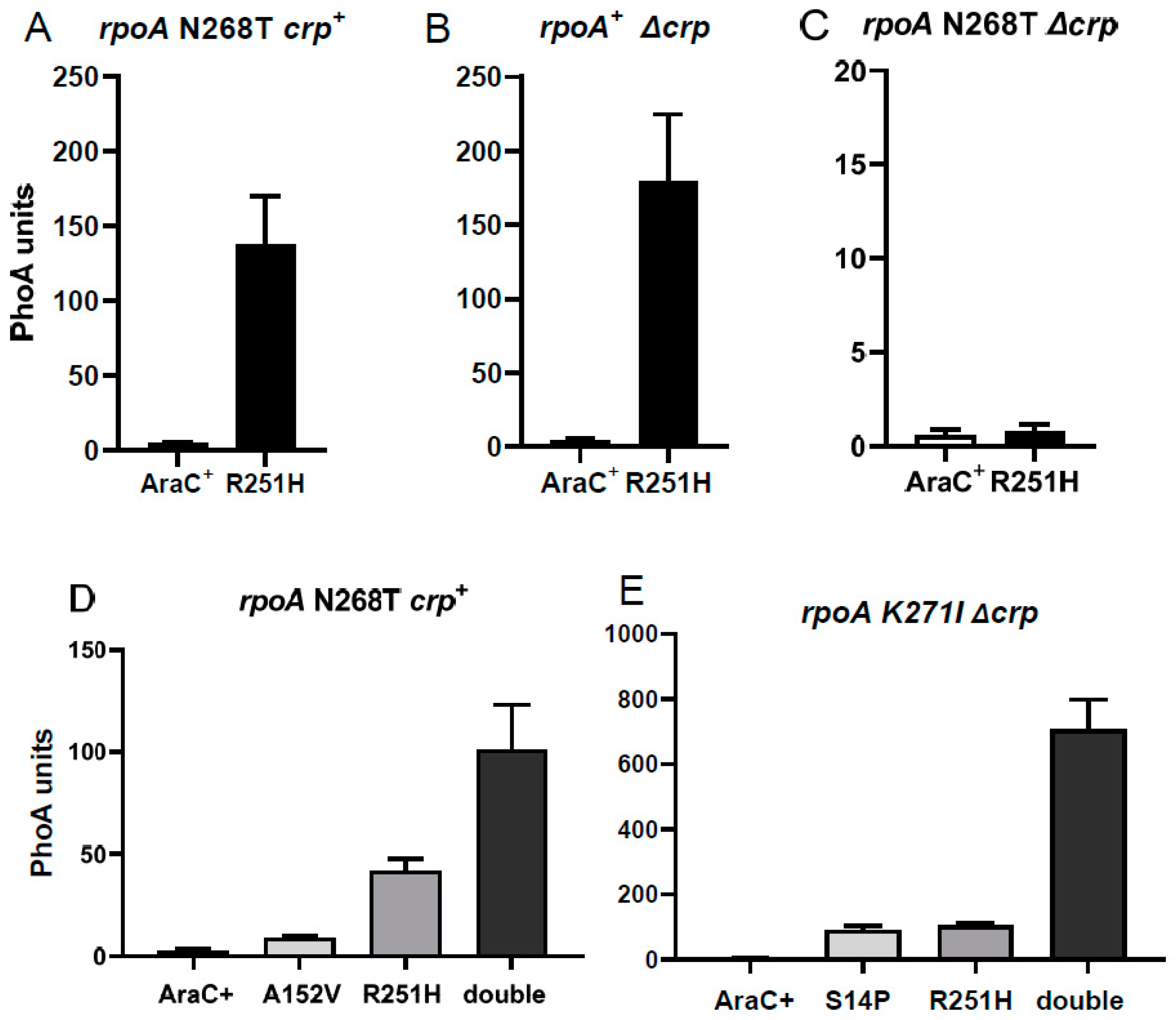
3.4. A Suppressor of RpoA N268T Synergizes with Mutations in the NTD of AraC
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-CTD | C-terminal domain of RpoA |
| α–NTD | N-terminal domain of RpoA |
| AraC-NTD | N-terminal domain of AraC |
References
- Englesberg, E.; Irr, J.; Power, J.; Lee, N. Positive control of enzyme synthesis by gene C in the L-arabinose system. J. Bacteriol. 1965, 90, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.D.; Schleif, R. A new and unexpected domain-domain interaction in the AraC protein. Proteins 2012, 80, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleif, R. Regulation of the L-arabinose operon of Escherichia coli. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleif, R. AraC protein: A love-hate relationship. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2003, 25, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Reeder, T.; Schleif, R. Transcription activation parameters at ara pBAD. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 258, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hahn, S.; Dunn, T.; Schleif, R. Upstream repression and CRP stimulation of the Escherichia coli L-arabinose operon. J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 180, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Schleif, R. Catabolite gene activator protein mutations affecting activity of the araBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busby, S.; Ebright, R.H. Transcription activation by catabolite activator protein (CAP). J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 293, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, L.M.; Belin, D.; Carson, M.J.; Beckwith, J. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 4121–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Fujita, N.; Ishihama, A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Deletion analysis of the amino-terminal assembly domain. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 242, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Thomas, M.S.; Keen, J.; Glass, R.E. A nested set of C-terminal deletions of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase define regions concerned with assembly, proteolysis, stabilization and transcriptional activation in vivo. Genes Cells 1997, 2, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.D.; Silhavy, T.J. Alpha: The Cinderella subunit of RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 14515–14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, G.S.; Niu, W.; Tebbutt, J.; Ebright, R.H.; Busby, S.J. Requirement for two copies of RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal domain for synergistic transcription activation at complex bacterial promoters. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2557–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoff, B.; Yang, H.; Lawson, C.L.; Parkinson, G.; Liu, J.; Blatter, E.; Ebright, Y.W.; Berman, H.M.; Ebright, R. Structural basis of transcription activation: The CAP-alpha CTD-DNA complex. Science 2002, 297, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, W.; Gosink, K.K.; Salomon, J.; Igarashi, K.; Zou, C.; Ishihama, A.; Severinov, K.; Gourse, R.L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science 1993, 262, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourse, R.L.; Ross, W.; Gaal, T. UPs and downs in bacterial transcription initiation: The role of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase in promoter recognition. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 37, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.H.; Negishi, T.; Shirakawa, M.; Yamazaki, T.; Fujita, N.; Ishihama, A.; Kyogoku, Y. Solution structure of the activator contact domain of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit. Science 1995, 270, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Gonzalez, S.; Birktoft, J.J.; Lawson, C.L. Structure of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal domain. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, S.M.; Aiyar, S.E.; Gourse, R.L.; Johnson, R.C. The C-terminal domains of the RNA polymerase alpha subunits: Contact site with Fis and localization during co-activation with CRP at the Escherichia coli proP P2 promoter. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 316, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Hong, C.; Huang, R.K.; Yu, Z.; Steitz, T.A. Structural basis of bacterial transcription activation. Science 2017, 358, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, A.; Schleif, R. Recognition of overlapping nucleotides by AraC and the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5076–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadaban, M.J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J. Mol. Biol. 1976, 104, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belin, D.; Plaia, G.; Boulfekhar, Y.; Silva, F. Escherichia coli SecG is required for residual export mediated by mutant signal sequences and for SecY-SecE complex stability. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Ara, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takai, Y.; Okumura, Y.; Baba, M.; Datsenko, K.A.; Tomita, M.; Wanner, B.L.; Mori, H. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: The Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 2006.0008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.H. A Short Course in Bacterial Genetics; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Giffard, P.M.; Booth, I.R. The rpoA341 allele of Escherichia coli specifically impairs the transcription of a group of positively-regulated operons. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1988, 214, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaia, G. Ruolo di SecG nel Trasporto Proteico in Escherichia coli e Studio di una Proteina Sconosciuta del Fago T4. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bost, S.; Belin, D. A new genetic selection identifies essential residues in SecG, a component of the Escherichia coli protein export machinery. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4412–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattenberger, Y.; Silva, F.; Belin, D. 55.2, a phage T4 ORFan gene, encodes an inhibitor of Escherichia coli topoisomerase I and increases phage fitness. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarafa, C.; Remold-O’Donnell, E. The ovalbumin serpins revisited: Perspective from the chicken genome of clade B serpin evolution in vertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11367–11372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belin, D.; Guzman, L.M.; Bost, S.; Konakova, M.; Silva, F.; Beckwith, J. Functional activity of eukaryotic signal sequences in Escherichia coli: The ovalbumin family of serine protease inhibitors. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 335, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belin, D. In vivo analysis of protein translocation to the Escherichia coli periplasm. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 619, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, K.; Belin, D. A novel class of secA alleles that exert a signal-sequence-dependent effect on protein export in Escherichia coli. Genetics 2002, 162, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.S.; Glass, R.E. Escherichia coli rpoA mutation which impairs transcription of positively regulated systems. Mol. Microbiol. 1991, 5, 2719–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochowska, A.; Iwanicka-Nowicka, R.; Zaim, J.; Witkowska-Zimny, M.; Bolewska, K.; Hryniewicz, M.M. Identification of activating region (AR) of Escherichia coli LysR-type transcription factor CysB and CysB contact site on RNA polymerase alpha subunit at the cysP promoter. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.; Huo, L.; Schleif, R.F. The DNA loop model for ara repression: AraC protein occupies the proposed loop sites in vivo and repression-negative mutations lie in these same sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 3654–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englesberg, E.; Sheppard, D.; Squires, C.; Meronk, F., Jr. An analysis of “revertants” of a deletion mutant in the C gene of the L-arabinose gene complex in Escherichia coli B-r: Isolation of initiator constitutive mutants (Ic). J. Mol. Biol. 1969, 43, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cass, L.G.; Horwitz, A.H.; Wilcox, G. The araIc mutation in Escherichia coli B/r. J. Bacteriol. 1981, 146, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colome, J.; Wilcox, G.; Englesberg, E. Constitutive mutations in the controlling site region of the araBAD operon of Escherichia coli B/r that decrease sensitivity to catabolite repression. J. Bacteriol. 1977, 129, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shultzaberger, R.K.; Chen, Z.; Lewis, K.A.; Schneider, T.D. Anatomy of Escherichia coli sigma70 promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.J.; Gryczynski, U.; Schleif, R. Mutational analysis of residue roles in AraC function. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 328, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirla, S.; Chien, J.Y.; Schleif, R. Constitutive mutations in the Escherichia coli AraC protein. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2668–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvoisin, R.M.; Belin, D.; Krisch, H.M. A plasmid expression vector that permits stabilization of both mRNAs and proteins encoded by the cloned genes. Gene 1986, 45, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slauch, J.M.; Russo, F.D.; Silhavy, T.J. Suppressor mutations in rpoA suggest that OmpR controls transcription by direct interaction with the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 7501–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Camakaris, H.; Yang, J.; Fujii, T.; Pittard, J. Activation by TyrR in Escherichia coli K-12 by Interaction between TyrR and the alpha-Subunit of RNA Polymerase. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e0025221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, S.; Ishikawa, S.; Chumsakul, O.; Ogasawara, N.; Oshima, T. The Role of alpha-CTD in the Genome-Wide Transcriptional Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, R.S.; Igarashi, K.; Ishihama, A. Functional specialization within the alpha-subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 221, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaal, T.; Ross, W.; Blatter, E.E.; Tang, H.; Jia, X.; Krishnan, V.V.; Assa-Munt, N.; Ebright, R.H.; Gourse, R.L. DNA-binding determinants of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase: Novel DNA-binding domain architecture. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiyar, S.E.; McLeod, S.M.; Ross, W.; Hirvonen, C.A.; Thomas, M.S.; Johnson, R.C.; Gourse, R.L. Architecture of Fis-activated transcription complexes at the Escherichia coli rrnB P1 and rrnE P1 promoters. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 316, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierska, B.; Lee, D.J.; Wegrzyn, G.; Busby, S.J.; Thomas, M.S. Role of the RNA polymerase alpha subunits in CII-dependent activation of the bacteriophage lambda pE promoter: Identification of important residues and positioning of the alpha C-terminal domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kedzierska, B.; Szambowska, A.; Herman-Antosiewicz, A.; Lee, D.J.; Busby, S.J.; Wegrzyn, G.; Thomas, M. The C-terminal domain of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit plays a role in the CI-dependent activation of the bacteriophage lambda pM promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 2311–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, T.R.; Igo, M.M. Mutations in the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase that affect the regulation of porin gene transcription in Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 5460–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- King, R.A.; Anders, D.L.; Christie, G.E. Site-directed mutagenesis of an amino acid residue in the bacteriophage P2 ogr protein implicated in interaction with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 3313–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soisson, S.M.; MacDougall-Shackleton, B.; Schleif, R.; Wolberger, C. Structural basis for ligand-regulated oligomerization of AraC. Science 1997, 276, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviola, B.; Seabold, R.; Schleif, R.F. Arm-domain interactions in AraC. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 278, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zou, C.; Fujita, N.; Igarashi, K.; Ishihama, A. Mapping the cAMP receptor protein contact site on the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 2599–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Fujita, N.; Ishihama, A. Transcription factor recognition surface on the RNA polymerase alpha subunit is involved in contact with the DNA enhancer element. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 4358–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holcroft, C.C.; Egan, S.M. Roles of cyclic AMP receptor protein and the carboxyl-terminal domain of the alpha subunit in transcription activation of the Escherichia coli rhaBAD operon. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3529–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rodgers, M.E.; Schleif, R. Solution structure of the DNA binding domain of AraC protein. Proteins 2009, 77, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]



| rpoA Substitutions | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxic Protein | N268T | L270F | K271E | K271I | K271V | K271T | A272E |
| T4 vs.1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| PAI2::PhoA | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||
| T4 55.2 | 1 | ||||||
| growth phenotypes | |||||||
| MC-melibiose | W | R | W | K | K | K | W |
| min-glucose | no | yes | no | no | no | no | no |
| +cys-Met | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belin, D.; Costafrolaz, J.; Silva, F. AraC Functional Suppressors of Mutations in the C-Terminal Domain of the RpoA Subunit of the Escherichia coli RNA Polymerase. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091928
Belin D, Costafrolaz J, Silva F. AraC Functional Suppressors of Mutations in the C-Terminal Domain of the RpoA Subunit of the Escherichia coli RNA Polymerase. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(9):1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091928
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelin, Dominique, Jordan Costafrolaz, and Filo Silva. 2024. "AraC Functional Suppressors of Mutations in the C-Terminal Domain of the RpoA Subunit of the Escherichia coli RNA Polymerase" Microorganisms 12, no. 9: 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091928
APA StyleBelin, D., Costafrolaz, J., & Silva, F. (2024). AraC Functional Suppressors of Mutations in the C-Terminal Domain of the RpoA Subunit of the Escherichia coli RNA Polymerase. Microorganisms, 12(9), 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091928






