First Report on the Emergence of Neopestalotiopsis rosae as a Severe Economic Threat to Strawberry Production in Germany
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Pathogen Isolation
2.2. Morphological Characterization
2.3. Pathogenicity Test
2.4. Re-Isolation of Fungal Strains from Greenhouse Plants
2.5. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.6. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Evolutionary Analysis by Maximum Likelihood Method
2.8. Maximum Parsimony Analysis of Taxa
2.9. Bayesian Inference Analysis
3. Results
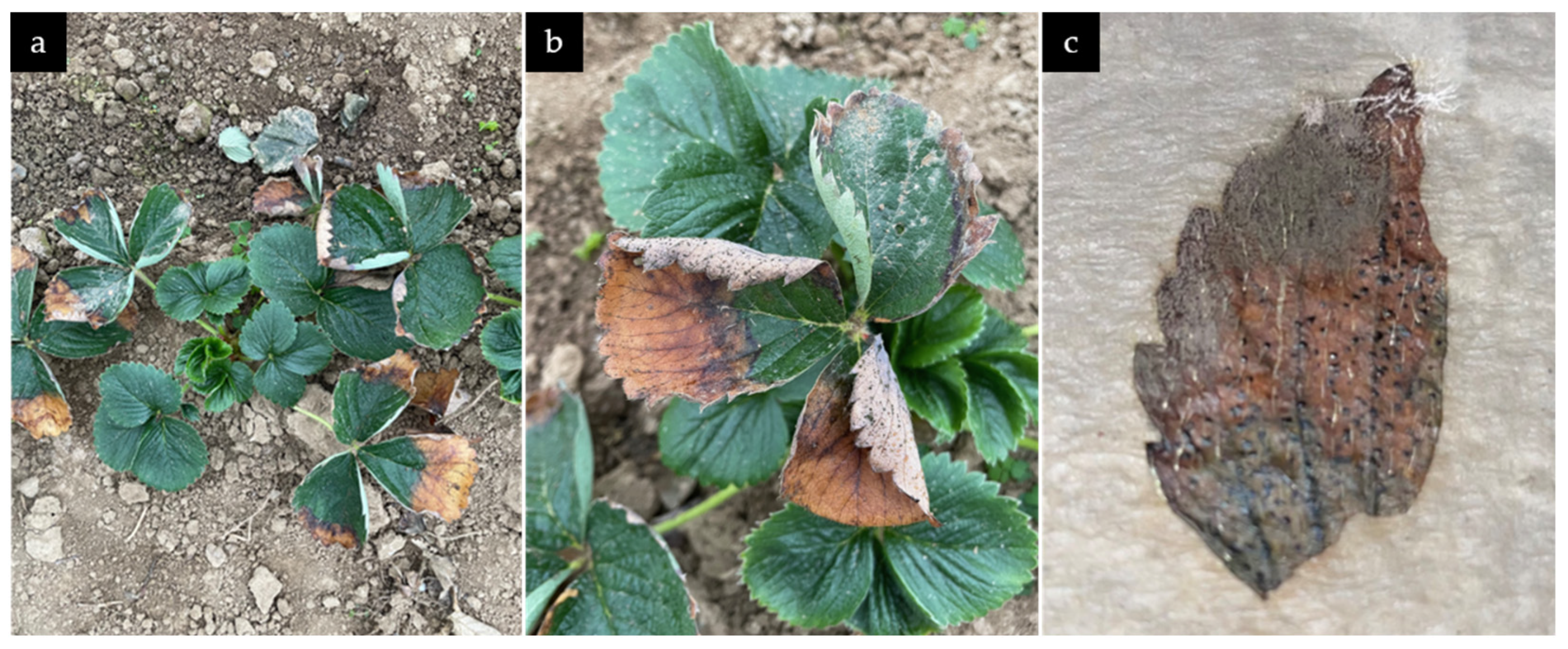
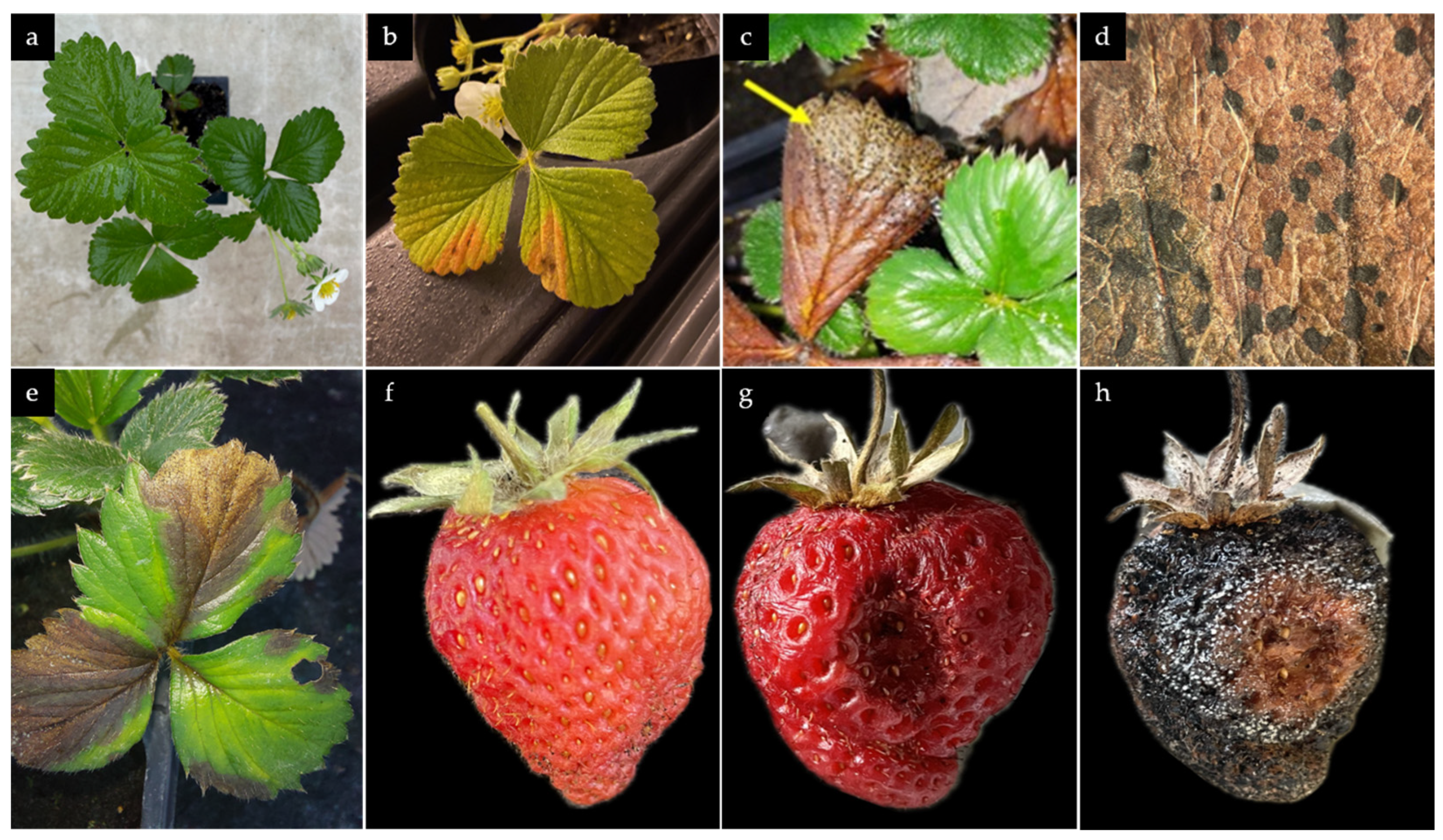
3.1. Symptoms of N. rosae on Naturally Infected Strawberry Plants
3.2. Morphological Characterization
3.3. Pathogenicty Test and Re-isolation of N. rosae from Inoculated Plant Material
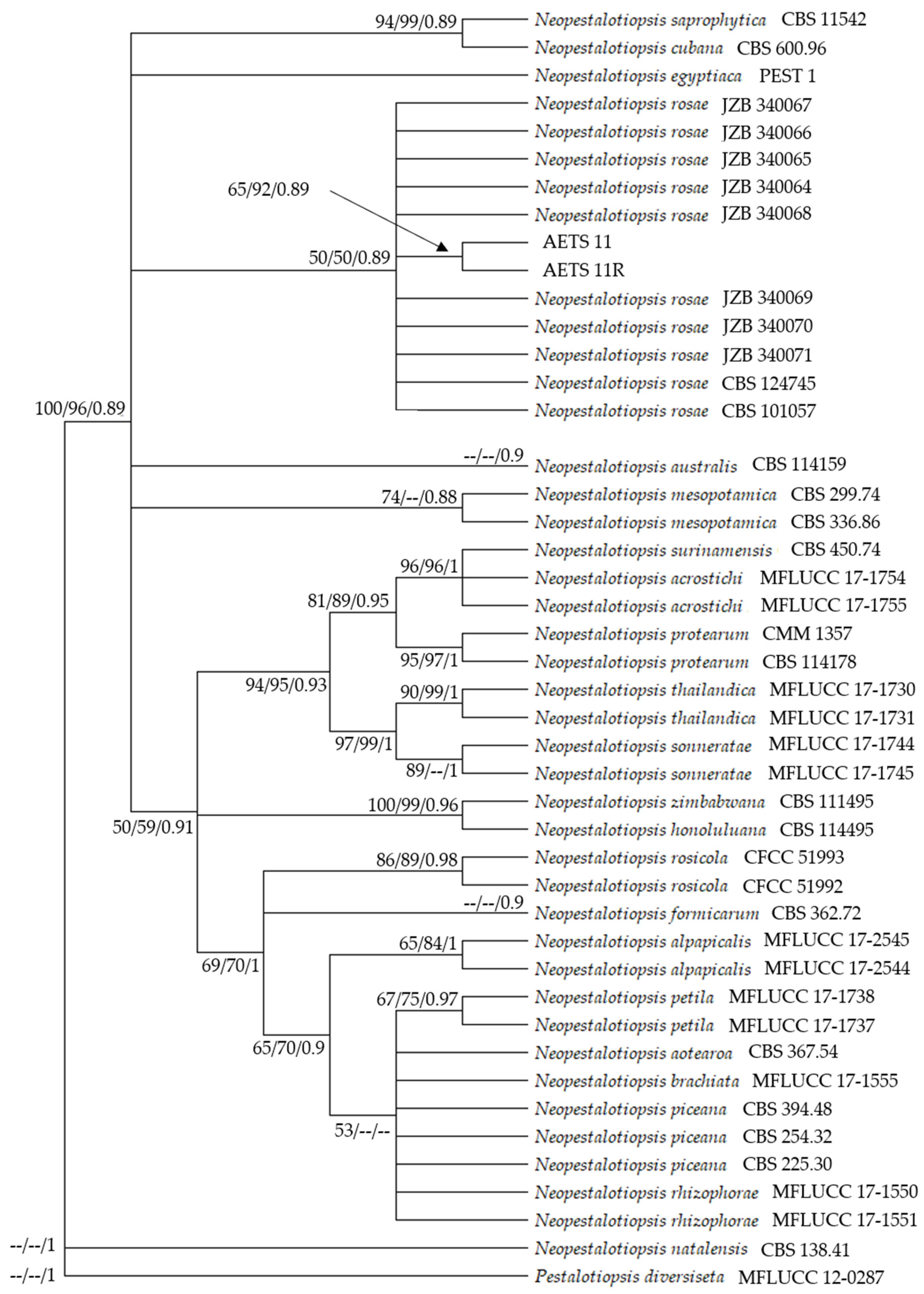
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Taxa | Strain | Host | Country | ITS | β-Tubulin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. alpapicalis | MFLUCC 17–2544a | Rhizophora mucronata | Thailand | MK357772 | MK463545 |
| MFLUCC 17–2545 | Symptomatic leaves of Rhizophora apiculata | Thailand | MK357773 | MK463546 | |
| N. aotearoa | CBS 367.54a | Canvas | New Zealand | KM199369 | KM199454 |
| N. acrostichi | MFLUCC 17–1754a | Acrostichum aureum | Thailand | MK764272 | MK764338 |
| MFLUCC 17–1755 | Acrostichum aureum | Thailand | MK764273 | MK764339 | |
| N. australis | CBS 114159a | Telopea sp. | Australia | KM199348 | KM199432 |
| N. brachiata | MFLUCC 17–1555a | Rhizophora apiculata | Thailand | MK764274 | MK764340 |
| N. cubana | CBS 600.96a | Leaf litter | Cuba | KM199347 | KM199438 |
| N. egyptiaca | PEST1 | Mangifera indica | Egypt | KP943747 | KP943746 |
| N. formicarum | CBS 362.72a | Dead ant | Ghana | KM199358 | KM199455 |
| N. honoluluana | CBS 114495a | Telopea sp. | USA | KM199364 | KM199457 |
| N. mesopotamica | CBS 336.86a | Pinus bruti | Iraq | KM199362 | KM199441 |
| CBS 299.74 | Eucalyptus sp. | Turkey | KM199361 | KM199435 | |
| N. natalensis | CBS 138.41a | Acacia mollissima | South Africa | NR_156288 | KM199466 |
| N. piceana | CBS 394.48a | Picea sp. | UK | KM199368 | KM199453 |
| CBS 254.32 | Cocos nucifera | Indonesia | KM199372 | KM199452 | |
| CBS 225.30 | Mangifera indica | - | KM199371 | KM199451 | |
| N. protearum | CBS 114178a | Leucospermum cuneiforme cv. “Sunbird” | Zimbabwe | JN712498 | KM199463 |
| CMM1357 | - | - | KY549597 | KY549632 | |
| N. rhizophorae | MFLUCC 17–1550a | Rhizophora mucronata | Thailand | MK764277 | MK764343 |
| MFLUCC 17–1551 | Rhizophora mucronata | Thailand | MK764278 | MK764344 | |
| N. rosae | CBS 101057a | Rosa sp. | New Zealand | KM199359 | KM199429 |
| JZB340064 | Fragaria × ananassa | China | MN495972 | MN968336 | |
| JZB340065 | Fragaria × ananassa | China | MN495973 | MN968337 | |
| JZB340066 | Fragaria × ananassa | China | MN495974 | MN968338 | |
| JZB340067 | Fragaria × ananassa | China | MN495976 | MN968339 | |
| JZB340068 | Fragaria × ananassa | China | MN495975 | MN968340 | |
| JZB340069 | Fragaria × ananassa | China | MN495977 | MN968341 | |
| JZB340070 | Fragaria × ananassa | China | MN495967 | MN968342 | |
| JZB340071 | Fragaria × ananassa | China | MN495978 | MN968343 | |
| AETS11 | Fragaria × ananassa | Germany | PQ511123 | PQ584291 | |
| AETS11R | Fragaria × ananassa | Germany | PQ511124 | PQ621801 | |
| CBS 124745 | Paeonia suffruticosa | USA | KM199360 | KM199430 | |
| N. rosicola | CFCC 51992a | Rosa chinensis | China | KY885239 | KY885245 |
| CFCC 51993 | Rosa chinensis | China | KY885240 | KY885246 | |
| N. saprophytica | CBS 115452 | Magnolia sp. | China | KM199345 | KM199433 |
| N. sonneratae | MFLUCC 17–1745a | Sonneronata alba | Thailand | MK764279 | MK764345 |
| MFLUCC 17–1744 | Sonneronata alba | Thailand | MK764280 | MK764346 | |
| N. surinamensis | CBS 450.74a | Soil under Elaeis guineensis | Suriname | KM199351 | KM199465 |
| N. thailandica | MFLUCC 17–1730a | Rhizophora mucronata | Thailand | MK764281 | MK764347 |
| MFLUCC 17–1731 | Rhizophora mucronata | Thailand | MK764282 | MK764348 | |
| N. zimbabwana | CBS 111495a | Leucospermum cunciforme cv. “Sunbird” | Zimbabwe | JX556231 | KM199456 |
| Pestalotiopsis diversiseta | MFLUCC 12–0287a | Rhododendron sp. | China | JX399009 | JX399040 |
References
- Garrido, C.; Carbú, M.; Fernández-Acero, F.J.; González-Rodríguez, V.E.; Cantoral, J. New Insights in the Study of Strawberry Fungal Pathogens. In Genes, Genomes and Genomics; Husaini, A.M., Mercado, J.A., Eds.; Global Science Books: East Sussex, UK, 2011; Volume 5, pp. 24–39. ISBN 978-4-903313-81-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, R.; Geppert, J.; Funken, E.; Stamminger, R. Consumers Perceptions and Preference for Strawberries—A Case Study from Germany. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2015, 15, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, P.R.; McNicol, R.J.; Williamson, B. Infection of Strawberry Flowers by Botrytis cinerea and Its Relevance to Grey Mould Development. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1986, 109, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnell, P.S.; Gubler, W.D. Taxonomy and Morphology of Colletotrichum Species Pathogenic to Strawberry. Mycologia 1992, 84, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, C.; González-Rodríguez, V.E.; Carbú, M.; Husaini, A.M.; Cantoral, J. Fungal Diseases of Strawberry and Their Diagnosis. In Strawberry: Growth, Development and Diseases; Husaini, A.M., Neri, D., Eds.; Cabi Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2016; pp. 157–195. ISBN 978-1-78064-663-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embaby, E.M. Pestalotia Fruit Rot on Strawberry Plants in Egypt. Egypt. J. Phytopathol. 2007, 35, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, F.A.; Silva, I.T.; Antunes Cruz, M.F.; Carré-Missio, V. The Infection Process of Pestalotiopsis longisetula Leaf Spot on Strawberry Leaves. J. Phytopathol. 2014, 162, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, C.M. A Strawberry Fruit Rot Caused by Pestalotia longisetula. Phytopathology 1973, 63, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenneth, R.G.; Barkai-golan, R.; Netzer, D. A Pestalotia Fruit Rot of Strawberries in Israel. Plant Dis. Report. 1968, 52, 472–474. [Google Scholar]
- Rajnish, K.; Gautam, H.R. Prevalence and Management of Pestalotia Leaf Spot (Pestalotia sp.) of Strawberry. Int. J. Econ. Plants 2022, 9, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Crous, P.W. Pestalotiopsis Revisited. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 79, 121–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoubi, N.; Soleimani, M.J. Strawberry Fruit Rot Caused by Neopestalotiopsis iranensis sp. nov., and N. mesopotamica. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Chutia, M.; Das, K.; Jha, D.K. Factors Affecting Sporulation of Pestalotiopsis disseminata Causing Grey Blight Disease of Persea bombycina Kost., the Primary Food Plant of Muga Silkworm. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, F.; Kobayashi, T.; Watanabe, H.; Izawa, H. Addition of Pestalotiopsis spp. to Leaf Spot Pathogens of Japanese Persimmon. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2003, 69, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollar-Alviter, A.; Silva-Rojas, H.V.; Fuentes-Aragón, D.; Acosta-González, U.; Martínez-Ruiz, M.; Parra-Robles, B.E. An Emerging Strawberry Fungal Disease Associated with Root Rot, Crown Rot and Leaf Spot Caused by Neopestalotiopsis rosae in Mexico. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-Y.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-M.; Ariyawansa, H.-A.; Chung, C.-L.; Chung, P.-C. First Report of Neopestalotiopsis rosae Causing Leaf Blight and Crown Rot on Strawberry in Taiwan. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, V.G.; Meneguzzi, N.G.; Ibañez, J.M.; Lattar, T.E.; Kirschbaum, D.S. First Report of Neopestalotiopsis clavispora Causing Root and Crown Rot on Strawberry Plants in Argentina. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machín, A.; González, P.; Vicente, E.; Sánchez, M.; Estelda, C.; Ghelfi, J.; Silvera-Pérez, E. First Report of Root and Crown Rot Caused by Neopestalotiopsis clavispora on Strawberry in Uruguay. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna, H.O.I.; Figueroa, F.J.R.; Casignia, Á.M.R.; Romero, P.I.Á.; Ferreira, A.F.T.A. Outbreaks of Crown Rot in Fragaria x ananassa Caused by Neopestalotiopsis mesopotamica in Ecuador. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2021, 33, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, J.S.; Forcelini, B.B.; Wang, N.-Y.; Ruschel, R.G.; Mertely, J.C.; Peres, N.A. Outbreak of Leaf Spot and Fruit Rot in Florida Strawberry Caused by Neopestalotiopsis spp. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Gelain, J.; Marin, M.V.; Peres, N.A.; Schnabel, G. Development of a Molecular Tool for Identification of a New Neopestalotiopsis sp. Associated with Disease Outbreaks on Strawberry. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, S.; Maniruzzam, S.; Sabbir, A.; Alam, N. Neopestalotiopsis chrysea Causing Leaf Spot Disease of Strawberry Plants in Bangladesh. J. Plant Sci. 2022, 17, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Harishchandra, D.; Jia, J.; Zuo, Q.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Yan, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Role of Neopestalotiopsis Rosae in Causing Root Rot of Strawberry in Beijing, China. Crop Prot. 2021, 147, 105710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, R.; Poonacha, T.T.; Chethan, D.; Karan, R.; Kruthika, R.; Khan, F.; Ashwini, K.S.; Bevanur, A.; Vani, Y.; Ramesh, G.V.; et al. Neopestalotiopsis rosae, a Novel Pathogen Causing Leaf Blight and Crown Rot of Strawberries in India. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 133, 102377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, M.; Aguado, A.; De los Santos, B. First Report of Root and Crown Rot Caused by Pestalotiopsis clavispora (Neopestalotiopsis clavispora) on Strawberry in Spain. Plant Dis. 2015, 100, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardi, G.; Bergeretti, F.; Gullino, M.L.; Garibaldi, A. First Report of Neopestalotiopsis clavispora Causing Root and Crown Rot on Strawberry in Italy. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, T.A.; Kamel, S.M.; Ismail, A.M.; El-Ganainy, S. Characterization and Chemical Control of Neopestalotiopsis rosae the Causal Agent of Strawberry Root and Crown Rot in Egypt. Egypt. J. Phytopathol. 2018, 46, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.-C.; Wu, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-W.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Hu, H.-P.; Hung, T.-H.; Tzean, S.-S.; Chung, C.-L. Diversity and Pathogenicity of Colletotrichum species Causing Strawberry Anthracnose in Taiwan and Description of a New Species, Colletotrichum miaoliense sp. nov. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P.K. Verticillium Disease of Strawberries. Can. J. Bot. 1961, 39, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, S.T.; Gordon, T.R. Management of Fusarium Wilt of Strawberry. Crop Prot. 2015, 73, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, N.L.; Howells, D.V. The Phytophthora Disease of Strawberry. Sci. Hortic. 1936, 4, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hemelrijck, W.; Ceustermans, A.; Van Campenhout, J.; Lieten, P.; Bylemans, D. Crown Rot in Strawberry Caused by Pestalotiopsis. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1156, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlovsky, P. Inhibition of Imidazolegly Cerolphosphate Dehydratase of Phytophthora parasitica by Aminotriazole in situ and after Cloning and Expression of the Respective Gene (HIS3) in Escherichia coli. J. Phytopathol. 1994, 141, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Coloe, S.; Baird, R.; Pedersen, J. Rapid Mini-Preparation of Fungal DNA for PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innis, M.A.; Gelfand, D.H.; Sninsky, J.J.; White, T.J. PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-08-088671-8. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of Primer Sets Designed for Use with the PCR to Amplify Conserved Genes from Filamentous Ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two Divergent Intragenomic rDNA ITS2 Types within a Monophyletic Lineage of the Fungus Fusarium Are Nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI National Center for Biotechnology; Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Norphanphoun, C. Morphological and Phylogenetic Characterization of Novel Pestalotioid Species Associated with Mangroves in Thailand. Mycosphere 2019, 10, 531–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; Yano, T. Dating of the Human-Ape Splitting by a Molecular Clock of Mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-19-513585-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Jeewon, R.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, T.; Hyde, K. Phylogenetic Diversity of Endophytic Pestalotiopsis species in Pinus armandii and Ribes spp.: Evidence from rDNA and Beta-Tubulin Gene Phylogenies. Fungal Divers. 2007, 24, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, J.L. (Ed.) Compendium of Strawberry Diseases; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1984; p. 68. ISBN 0-89054-054-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pugliese, M.; Gilardi, G.; Guarnaccia, V.; Garibaldi, A.; Gullino, M.L. First Report of Gnomoniopsis fragariae Causing Leaf Spots on Strawberry in Italy. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, A.M.J.; Munoz, G.; Collins, C.; Brannen, P. First Report of the New Neopestalotiopsis species Causing Strawberry Leaf Spot and Fruit Rot in Georgia. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljawasim, B.D.; Samtani, J.B.; Rahman, M. New Insights in the Detection and Management of Anthracnose Diseases in Strawberries. Plants 2023, 12, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthman, J. Wilted: Pathogens, Chemicals, and the Fragile Future of the Strawberry Industry; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019; p. 322. ISBN 978-0-520-30527-4. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schierling, T.E.; Voegele, R.T.; El-Hasan, A. First Report on the Emergence of Neopestalotiopsis rosae as a Severe Economic Threat to Strawberry Production in Germany. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010006
Schierling TE, Voegele RT, El-Hasan A. First Report on the Emergence of Neopestalotiopsis rosae as a Severe Economic Threat to Strawberry Production in Germany. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchierling, Tom E., Ralf T. Voegele, and Abbas El-Hasan. 2025. "First Report on the Emergence of Neopestalotiopsis rosae as a Severe Economic Threat to Strawberry Production in Germany" Microorganisms 13, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010006
APA StyleSchierling, T. E., Voegele, R. T., & El-Hasan, A. (2025). First Report on the Emergence of Neopestalotiopsis rosae as a Severe Economic Threat to Strawberry Production in Germany. Microorganisms, 13(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010006







