AcfA Regulates the Virulence and Cell Envelope Stress Response of Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Culture Conditions
2.2. Construction of the Mutant ΔacfA Strain and the Complemented Strain acfA+
2.3. Measurement of Bacterial Growth
2.4. RNA-Seq Analysis
2.5. Quantitative Realtime PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Biofilm Assay
2.7. Kanagawa Phenomenon (KP) Test
2.8. In Vitro Mucus Adhesion Assay
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Observation
2.10. Stress Response Assay
2.11. Fish Infection Assay
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Alteration Caused by Deletion of acfA in Vibrio parahaemolyticus
3.2. AcfA Is Essential for Environmental Stress Adaptation in V. parahaemolyticus
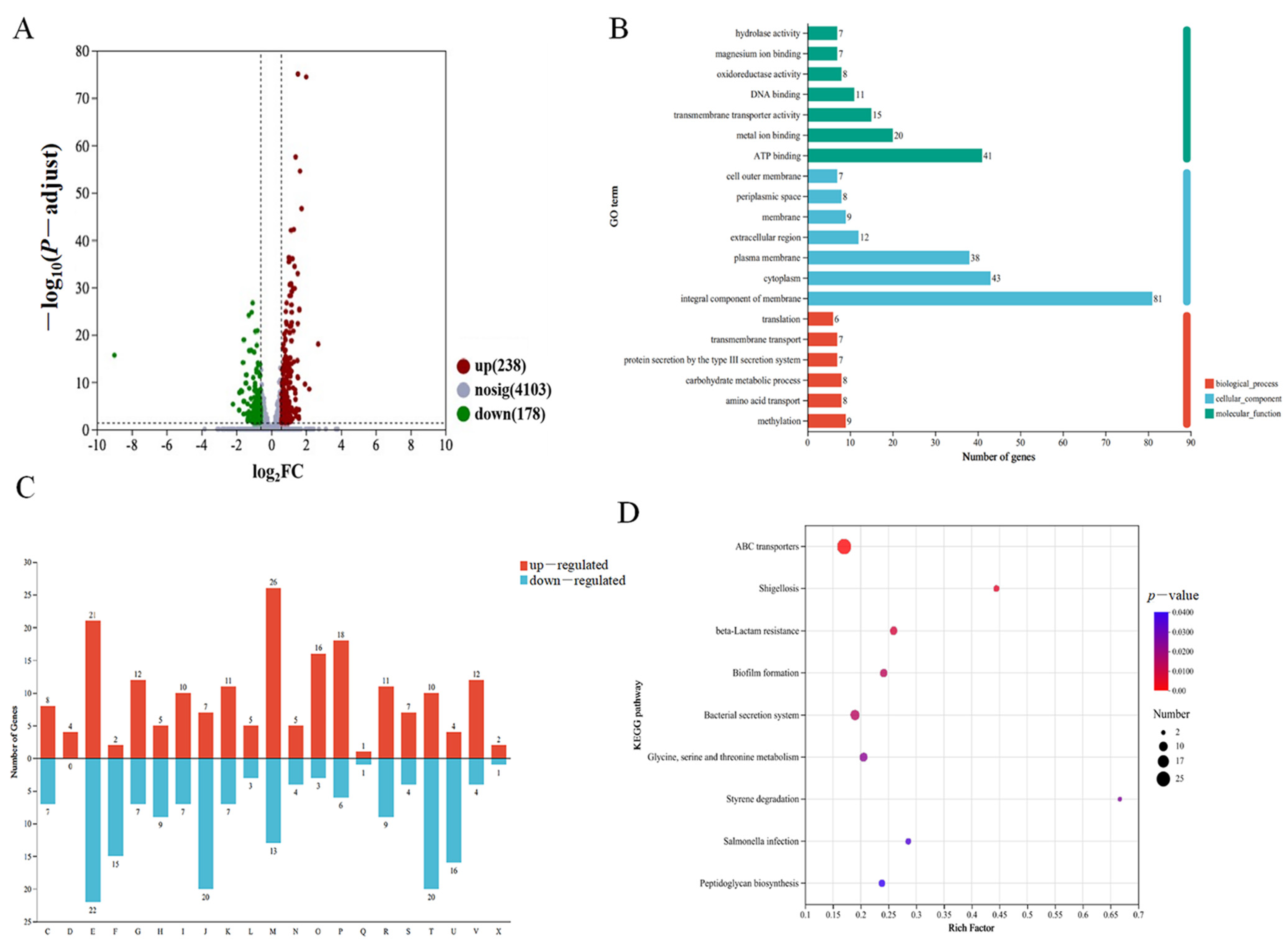
3.3. General Features of the Transcriptome Profile
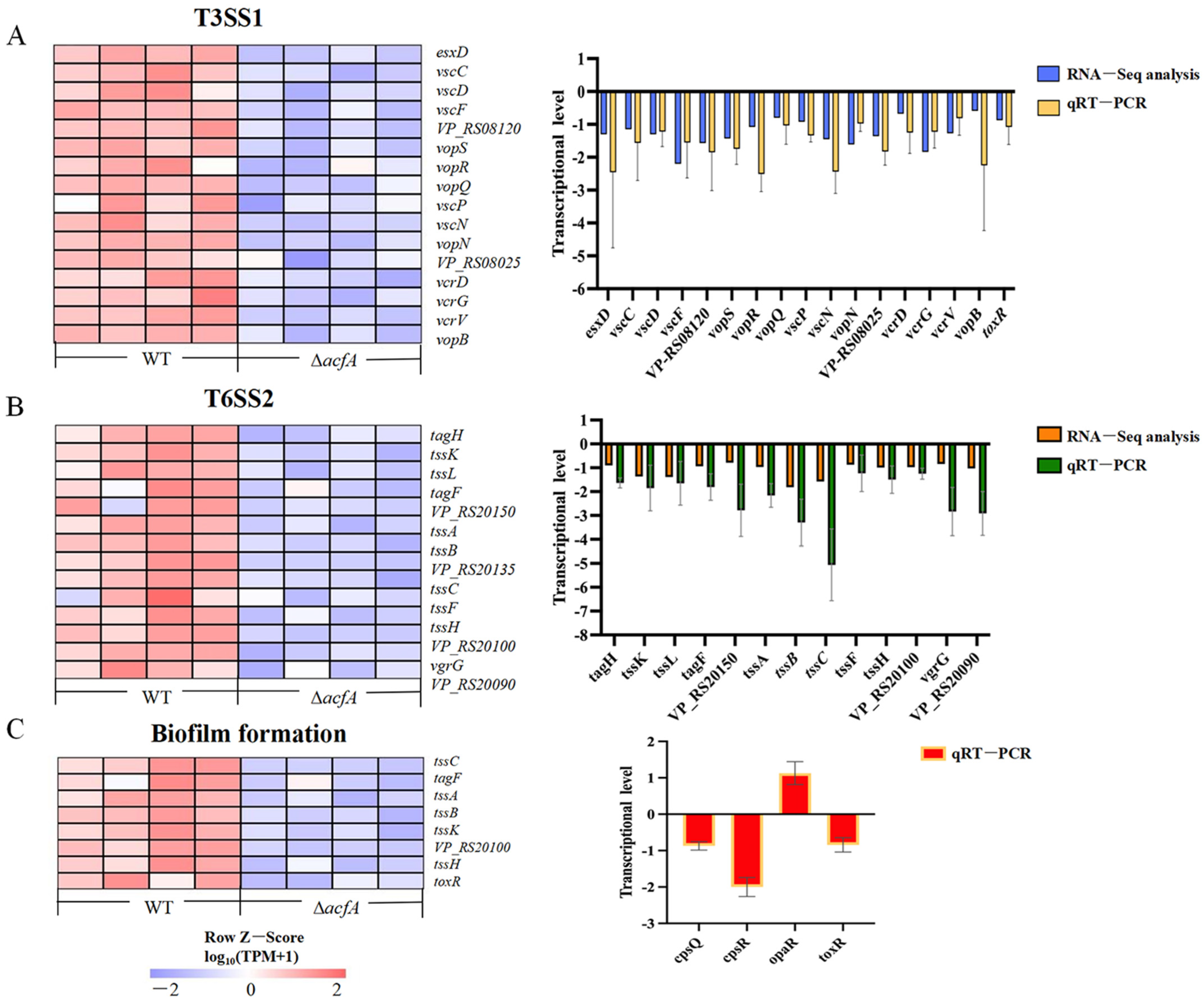
3.4. Validation of the Transcriptome Data by qRT-PCR
3.5. AcfA Supports the Type III Secretion System, the Type VI Secretion System, and Biofilm Formation in V. parahaemolyticus
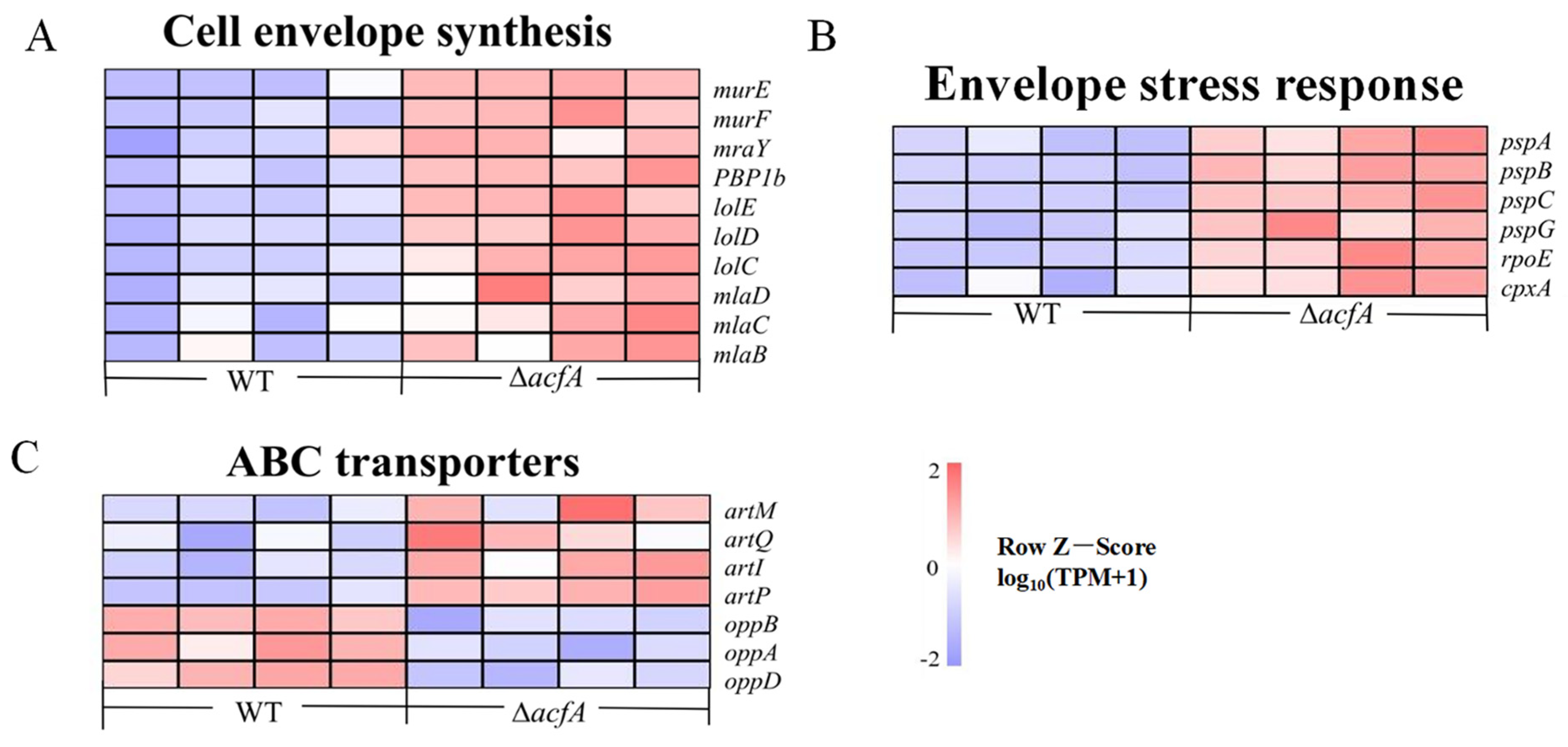
3.6. Deletion of acfA Caused Disorder of the Cell Envelope
3.7. Deletion of acfA Caused Enhancement of the Envelope Stress Response System in V. parahaemolyticus
3.8. AcfA Had an Impact on the Arginine Transport System in V. parahaemolyticus
3.9. Deletion of acfA Led to Impairment of the Oligopeptide Permease System in V. parahaemolyticus
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.; Xu, J.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Deng, N.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, D. Vibrio parahaemolyticus flagellin F (FlaF) induces the inflammatory response of the Tetraodon nigroviridis through the TLR5M. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shangguan, W.; Wang, J.; Liao, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhong, Q. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the antibiofilm mechanism of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus MS1 against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. LWT 2023, 176, 114529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Liu, C. Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A concern of seafood safety. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, C.A.; Calder, T.J.; Orth, K. Vibrio parahaemolyticus cell biology and pathogenicity determinants. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, K.M.; Mekalanos, J.J. Characterization of the Vibrio cholerae ToxR regulon: Identification of novel genes involved in intestinal colonization. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, H.; Pi, D.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X. Virulence properties of Vibrio vulnificus isolated from diseased zoea of freshness shrimp Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adade, N.E.; Aniweh, Y.; Mosi, L.; Valvano, M.A.; Duodu, S.; Ahator, S.D. Comparative analysis of Vibrio cholerae isolates from Ghana reveals variations in genome architecture and adaptation of outbreak and environmental strains. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 998182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Cheng, H.; Pang, H.; Jian, J.; Wu, Z. AcfA is an essential regulator for pathogenesis of fish pathogen Vibrio alginolyticus. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 213, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, S.; Jian, J. Protection against Vibrio alginolyticus in pearl gentian grouper (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂Epinephelus lanceolatu) immunized with an acfA-deletion live attenuated vaccine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, B.; Tang, J.; Jian, J. Expression and immunogenicity analysis of accessory colonization factor A from Vibrio alginolyticus strain HY9901. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, D.L.; O'Toole, R.; Horstedt, P.; Wolf-Watz, H. Flagellin A is essential for the virulence of Vibrio anguillarum. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, V.; Bäckman, A.; Bagdasarian, M. A series of wide-host-range low-copy-number vectors that allow direct screening for recombinants. Gene 1991, 97, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Huang, L.; Yan, Q.; Qin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lin, M.; Xu, X.; Zheng, J. The TCA pathway is an important player in the regulatory network governing Vibrio alginolyticus adhesion under adversity. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, N.; Ren, J.; Liu, W.; Zhou, C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Han, J.; et al. Comprehensive insights into the metabolism characteristics of small RNA Qrr4 in Vibrio alginolyticus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1887–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Wang, K.; Lu, T.; Li, L.; Jiao, X. Vibrio parahaemolyticus CadC regulates acid tolerance response to enhance bacterial motility and cytotoxicity. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, T.; Hiyoshi, H.; Okada, R.; Matsuda, S.; Gotoh, K.; Iida, T. Regulation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus T3SS2 gene expression and function of T3SS2 effectors that modulate actin cytoskeleton. Cell. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, L.; Xue, J.; Li, W.; Ren, J.; Tang, F.; Liu, Y.; Xue, F.; Dai, J. VscF in T3SS1 helps to translocate VPA0226 in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 652432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; de Souza Santos, M.; Lee, J.; Law, H.T.; Chimalapati, S.; Verdu, E.F.; Orth, K.; Vallance, B.A.; Vance, R. A novel mouse model of enteric Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection reveals that the Type III secretion system 2 effector VopC plays a key role in tissue invasion and gastroenteritis. mBio 2019, 10, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Gewurz, B.E.; Ritchie, J.M.; Takasaki, K.; Greenfeld, H.; Kieff, E.; Davis, B.M.; Waldor, M.K. A Vibrio parahaemolyticus T3SS effector mediates pathogenesis by independently enabling intestinal colonization and inhibiting TAK1 Activation. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Meng, H.; Gu, D.; Li, Y.; Jia, M. Molecular mechanisms of Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenesis. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 222, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Kinch, L.N.; Ray, A.; Dalia, A.B.; Cong, Q.; Nunan, L.M.; Camilli, A.; Grishin, N.V.; Salomon, D.; Orth, K. Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease(AHPND)-causing Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains maintain an antibacterial Type VI Secretion System with versatile effector repertoires. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00737-00717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Wu, B.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, W. Putative type VI secretion systems of Vibrio parahaemolyticus contribute to adhesion to cultured cell monolayers. Arch. Microbiol. 2012, 194, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Gao, H.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Xue, X.; Yang, W.; Ni, B.; Hu, L. OpaR controls the metabolism of c-di-GMP in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 676436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimbrough, J.H.; Cribbs, J.T.; McCarter, L.L. Homologous c-di-GMP-binding Scr transcription factors orchestrate biofilm development in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 202, e00723-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.B.; Chodur, D.M.; Antunes, L.C.M.; Trimble, M.J.; McCarter, L.L. Output targets and transcriptional regulation by a cyclic dimeric GMP-responsive circuit in the Vibrio parahaemolyticus Scr network. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathelié Guinlet, M.; Asmar, A.T.; Collet, J.F.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Bacterial cell mechanics beyond peptidoglycan. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugg, T.D.; Braddick, D.; Dowson, C.G.; Roper, D.I. Bacterial cell wall assembly: Still an attractive antibacterial target. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlier, D.; Bervoets, I. Regulation of arginine biosynthesis, catabolism and transport in Escherichia coli. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 1103–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Huang, L.; Su, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yan, Q. Contributions of the oligopeptide permeases in multistep of Vibrio alginolyticus pathogenesis. MicrobiologyOpen 2017, 6, e00511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Shao, Z.; Hao, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.; Hou, H.; Hu, D.; Wang, C.; Pan, X. Identification of oligopeptide-binding protein (OppA) and its role in the virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silhavy, T.J.; Kahne, D.; Walker, S. The bacterial cell envelope. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A. Structure, function and dynamics in the mur family of bacterial cell wall ligases. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 362, 640–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, K.T.; Sala, F.A.; Miyachiro, M.M.; Job, V.; Trindade, D.M.; Dessen, A. Architecture and genomic arrangement of the MurE–MurF bacterial cell wall biosynthesis complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2219540120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeske, A.J.; Riley, E.P.; Robins, W.P.; Uehara, T.; Mekalanos, J.J.; Kahne, D.; Walker, S.; Kruse, A.C.; Bernhardt, T.G.; Rudner, D.Z. SEDS proteins are a widespread family of bacterial cell wall polymerases. Nature 2016, 537, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjodt, M.; Rohs, P.D.A.; Gilman, M.S.A.; Erlandson, S.C.; Zheng, S.; Green, A.G.; Brock, K.P.; Taguchi, A.; Kahne, D.; Walker, S.; et al. Structural coordination of polymerization and crosslinking by a SEDS–bPBP peptidoglycan synthase complex. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstedt, E.; Kahne, D.; Ruiz, N. Assembly and maintenance of lipids at the bacterial outer membrane. Chem. Rev. 2020, 121, 5098–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRae, M.R.; Puvanendran, D.; Haase, M.A.B.; Coudray, N.; Kolich, L.; Lam, C.; Baek, M.; Bhabha, G.; Ekiert, D.C. Protein–protein interactions in the Mla lipid transport system probed by computational structure prediction and deep mutational scanning. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, F.; Place, N.M.; Mekalanos, J.J. Analysis of lipoprotein transport depletion in Vibrio cholerae using CRISPRi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17013–17022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macritchie, D.M.; Raivio, T.L.; Slauch, J.M. Envelope stress responses. EcoSal Plus 2009, 3, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines Menges, B.; Whitaker, W.B.; Boyd, E.F. Alternative sigma factor RpoE is important for Vibrio parahaemolyticus cell envelope stress response and intestinal colonization. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3667–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennetzdorfer, N.; Höfler, T.; Wölflingseder, M.; Tutz, S.; Schild, S.; Reidl, J. σE controlled regulation of porin OmpU in Vibrio cholerae. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 115, 1244–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacikova, G.; Skorupski, K. The alternative sigma factor σE plays an important role in intestinal survival and virulence in Vibrio cholerae. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5355–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhaye, A.; Collet, J.-F.; Laloux, G.; Bassler, B. Fine-Tuning of the Cpx envelope stress response is required for cell wall homeostasis in Escherichia coli. mBio 2016, 7, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhaye, A.; Laloux, G.; Collet, J.F. The lipoprotein NlpE is a Cpx sensor that serves as a sentinel for protein sorting and folding defects in the Escherichia coli envelope. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, K.; Silhavy, T.J. Surface sensing and adhesion of Escherichia coli controlled by the Cpx-signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2287–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, R.L.; Court, E.A.; Waldon, J.L.; Schock, K.A.; Raivio, T.L. Impaired efflux of the siderophore enterobactin induces envelope stress in Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, N.; Pukatzki, S.; Raivio, T.L. The Vibrio cholerae Cpx envelope stress response senses and mediates adaptation to low iron. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.L.; Bina, X.R.; Slamti, L.; Waldor, M.K.; Bina, J.E. Reciprocal regulation of resistance-nodulation-division efflux systems and the Cpx two-component system in Vibrio cholerae. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2980–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, C.M.; Nag, D.; Withey, J.H.; Matson, J.S. Characterization of the Vibrio cholerae phage shock protein response. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00761-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Strain or Plasmid | Relevant Characteristics | Reference or Source |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | ||
| DH5α λpir | Host for π-requiring plasmids | Lab collection |
| SM10 λpir | Host for π-requiring plasmids, conjugal donor | Lab collection |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | ||
| RIMD2210633 | Clinical isolate, Ampr | Lab collection |
| ∆acfA | RIMD2210633, in-frame deletion in acfA,Ampr | This study |
| acfA+ | ∆acfA carrying the complementary plasmid, pMMB207-acfA, Ampr, Cmr | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pDM4 | Suicide vector, pir dependent, R6K, SacBR, Cmr | [11] |
| pMMB207 | IncQ lacIq Δbla Ptac-laclacZa, Cmr | [12] |
| pDM4-∆acfA | pDM4 with the acfA fragment deleted 4th to 645th nucleotides, Cmr | This study |
| pMMB207-acfA | pMMB207 with the intact acfA gene | This study |
| Primers | Sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| acfA-up-F | GAGCGGATAACAATTTGTGGAATCCCGGGATAACTCGGACGGAGACCA |
| acfA-up-R | CCTTAAATTACATTCTAATTTTGCCTCTTCAAATC |
| acfA-down-F | AATTAGAATGTAATTTAAGGAAACGATAATGAAAA |
| acfA-down-R | GCGGAGTGTATATCAAGCTTATCGATACCAACCGTATCATTCCCGTA |
| acfA-out-F | TTTCGGGTGGTGGCGTGGAC |
| acfA-out-R | TCCGAATCCTCTACCACTTA |
| acfA-in-F | CCTGCTCAGTTTCGGTAT |
| acfA-in-R | CCTTGGCGTCGTATTGTG |
| acfA-com-F | TCGGTACCCGGGGATCCTCTAGTAAGGAGGTAGGATAATAATGAACAAAACACTTCTTGCGTTAC |
| acfA-com-R | TCCGCCAAAACAGCCAAGCTTTAGTGATGATGATGATGATGAAAGTAGTAAGTTGTGCCTACG |
| Bacterial Strain | Number of Bacteria (Cells) |
|---|---|
| WT | 1101 |
| ΔacfA | 174 |
| acfA+ | 1443 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Lei, H.; Cao, J.; Xie, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, Y. AcfA Regulates the Virulence and Cell Envelope Stress Response of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010007
Liu H, Lei H, Cao J, Xie Z, Shi Y, Zhao Y. AcfA Regulates the Virulence and Cell Envelope Stress Response of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huan, Huayu Lei, Juanjuan Cao, Zhaobang Xie, Yile Shi, and Yanni Zhao. 2025. "AcfA Regulates the Virulence and Cell Envelope Stress Response of Vibrio parahaemolyticus" Microorganisms 13, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010007
APA StyleLiu, H., Lei, H., Cao, J., Xie, Z., Shi, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2025). AcfA Regulates the Virulence and Cell Envelope Stress Response of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microorganisms, 13(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010007





