Inquilinus Species Infections in Humans—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
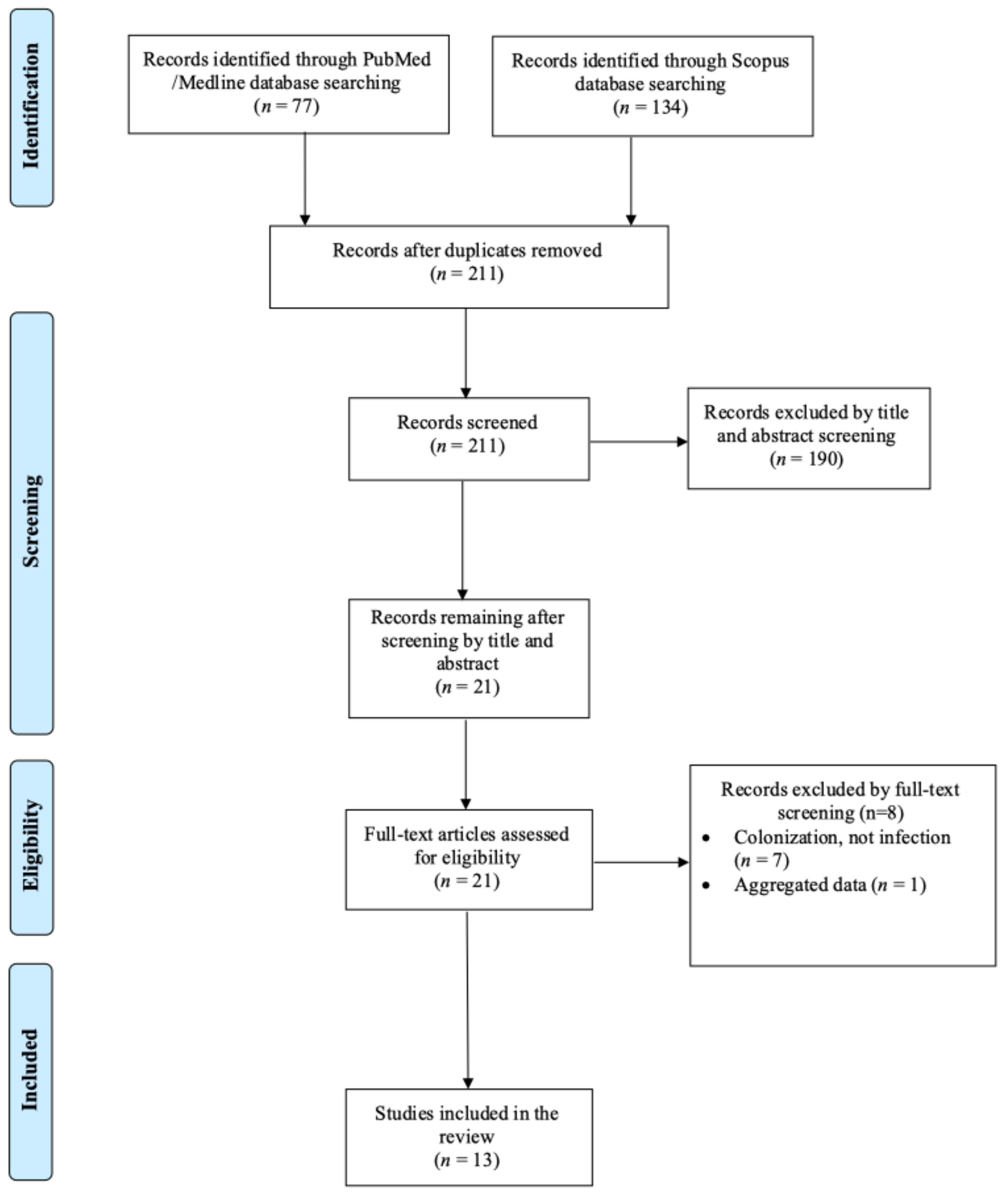
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction and Definitions
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Included Studies’ Characteristics
3.2. Epidemiology of Inquilinus spp. Infections
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance and Microbiology of Inquilinus spp. Infections
3.4. Clinical Presentation of Inquilinus spp. Infections
3.5. Treatment and Outcome of Inquilinus Infections
3.6. Lower Respiratory Tract Infection Due to Inquilinus Infection
3.7. Bacteremia Due to Inquilinus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grasemann, H.; Ratjen, F. Cystic Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1693–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, T.; Ramsey, B.W. Cystic Fibrosis: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, A.C.; Waters, V.J. Microbiology of Cystic Fibrosis Airway Disease. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 40, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, C.; Cantin, A.M. Cystic Fibrosis: Pathophysiology of Lung Disease. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 40, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elborn, J.S. Identification and Management of Unusual Pathogens in Cystic Fibrosis. J. R. Soc. Med. 2008, 101 (Suppl. S1), S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitulle, C.; Citron, D.M.; Bochner, B.; Barbers, R.; Appleman, M.D. Novel Bacterium Isolated from a Lung Transplant Patient with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3851–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenye, T.; Goris, J.; Spilker, T.; Vandamme, P.; LiPuma, J.J. Characterization of Unusual Bacteria Isolated from Respiratory Secretions of Cystic Fibrosis Patients and Description of Inquilinus Limosus Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinnurun, O.M.; Riedel, T.; Müller, S.; Bunk, B.; Schröttner, P. Current Knowledge on Inquilinus Limosus, a Scarcely Researched Human Pathogen. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiratisin, P.; Koomanachai, P.; Kowwigkai, P.; Pattanachaiwit, S.; Aswapokee, N.; Leelaporn, A. Early-Onset Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis Caused by Inquilinus sp. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 56, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.; Murphy, B.S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Anstead, M.I.; Feola, D.J. Mucoid Inquilinus Limosus in a Young Adult with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009, 44, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeman, E.; Shivam, A.; Downton, T.D.; Glanville, A.R. Bacteremic Inquilinus Limosus Empyema in an Australian Lung Transplant Patient with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2015, 34, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, K.E.; Rhoads, D.D.; Wilson, D.A.; Highland, K.B.; Richter, S.S.; Procop, G.W. Inquilinus Limosus in Pulmonary Disease: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 86, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poore, T.S.; Virella-Lowell, I.; Guimbellot, J.S. Potential Pathogenicity of Inquilinus Limosus in a Pediatric Patient with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, E21–E23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, L.; Andersson, M.; Ives, A.; Hull, J.; Chapman, S.; Flight, W. Familial Cluster of Inquilinus Limosus Infection among Three Brothers with Cystic Fibrosis. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 34, 101487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-López, A.L.; Bustamante, A.E.; González, G.M.; Llaca-Diaz, J.M.; Sánchez-González, A. Inquilinus Limosus Isolated from a Patient with Chronic Cystic Fibrosis. First Report in Mexico and Evidence That Co-Infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Promotes the Accelerated and Increased Formation of Extracellular Neutrophil Traps. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 40, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobell, J.T.; Ferdinand, C.; Young, D.C. Continuous Infusion Meropenem and Ticarcillin-Clavulanate in Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2014, 49, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmoldt, S.; Latzin, P.; Heesemann, J.; Griese, M.; Imhof, A.; Hogardt, M. Clonal Analysis of Inquilinus Limosus Isolates from Six Cystic Fibrosis Patients and Specific Serum Antibody Response. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittar, F.; Leydier, A.; Bosdure, E.; Toro, A.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Boniface, S.; Stremler, N.; Dubus, J.-C.; Sarles, J.; Raoult, D.; et al. Inquilinus Limosus and Cystic Fibrosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron, R.; Marchandin, H.; Counil, F.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Freydière, A.-M.; Bellon, G.; Husson, M.-O.; Turck, D.; Brémont, F.; Chabanon, G.; et al. Clinical and Microbiological Features of Inquilinus Sp. Isolates from Five Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3938–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfour, E.; Zrounba, M.; Roux, A.; Revillet, H.; Vallée, A.; Vasse, M. Inquilinus limosus Bacteremia in Lung Transplant Recipient after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shteinberg, M.; Haq, I.J.; Polineni, D.; Davies, J.C. Cystic Fibrosis. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2021, 397, 2195–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, B.; Cai, L.-H.; Ehre, C.; Kesimer, M.; Hill, D.B.; Sheehan, J.K.; Boucher, R.C.; Rubinstein, M. A Periciliary Brush Promotes the Lung Health by Separating the Mucus Layer from Airway Epithelia. Science 2012, 337, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbdulWahab, A.; Taj-Aldeen, S.J.; Ibrahim, E.B.; Talaq, E.; Abu-Madi, M.; Fotedar, R. Discrepancy in MALDI-TOF MS Identification of Uncommon Gram-Negative Bacteria from Lower Respiratory Secretions in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2015, 8, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipuma, J.J. The Changing Microbial Epidemiology in Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiman, L.; Waters, V.; LiPuma, J.J.; Hoffman, L.R.; Alby, K.; Zhang, S.X.; Yau, Y.C.; Downey, D.G.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Bouchara, J.-P.; et al. Practical Guidance for Clinical Microbiology Laboratories: Updated Guidance for Processing Respiratory Tract Samples from People with Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e00215-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigos, T.; Dollat, M.; Magallon, A.; Folletet, A.; Bador, J.; Abid, M.; Amara, M.; Beauruelle, C.; Belmonte, O.; Boyer, P.; et al. Distribution of Achromobacter Species in 12 French Cystic Fibrosis Centers in 2020 by a Retrospective MALDI-TOF MS Spectrum Analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e02422-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziagorou, E.; Orenti, A.; Drevinek, P.; Kashirskaya, N.; Mei-Zahav, M.; De Boeck, K.; on behalf of the ECFSPR. Changing Epidemiology of the Respiratory Bacteriology of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis-Data from the European Cystic Fibrosis Society Patient Registry. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degand, N.; Carbonnelle, E.; Dauphin, B.; Beretti, J.-L.; Le Bourgeois, M.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Segonds, C.; Berche, P.; Nassif, X.; Ferroni, A. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry for Identification of Nonfermenting Gram-Negative Bacilli Isolated from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3361–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellinghausen, N.; Essig, A.; Sommerburg, O. Inquilinus Limosus in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador-García, C.; Yagüe-Guirao, G.; Pastor-Vivero, M.D.; Sáez-Nieto, J.A. Chronic Colonization of Inquilinus limosus in a Patient with Cystic Fibrosis: First Report in Spain. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2013, 31, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.T.; Chan, H.Y. Oral Flora of Domestic Cats in Hong Kong: Identification of Antibiotic-Resistant Strains. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröttner, P.; Gunzer, F.; Schüppel, J.; Rudolph, W.W. Identification of Rare Bacterial Pathogens by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and MALDI-TOF MS. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2016, 113, 53176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, P.; Abat, C.; Rolain, J.M.; Colson, P.; Lagier, J.-C.; Gouriet, F.; Fournier, P.E.; Drancourt, M.; La Scola, B.; Raoult, D. Identification of Rare Pathogenic Bacteria in a Clinical Microbiology Laboratory: Impact of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2182–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Rolain, J.-M. Use of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry for Identification of Bacteria That Are Difficult to Culture. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 92, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicatiello, A.G.; Iula, D.V.; Pagliuca, C.; Pastore, G.; Pagliarulo, C.; Catania, M.R.; Catania, M.R.; Colicchio, R.; Picardi, M.; Raia, V.; et al. Identification of Inquilinus limosus in Cystic Fibrosis: A First Report in Italy. New Microbiol. 2014, 37, 567–571. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães, A.P.; Lopes, S.P.; Pereira, M.O. Insights into Cystic Fibrosis Polymicrobial Consortia: The Role of Species Interactions in Biofilm Development, Phenotype, and Response to In-Use Antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govan, J.R.; Fyfe, J.A.; Jarman, T.R. Isolation of Alginate-Producing Mutants of Pseudomonas Fluorescens, Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas mendocina. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1981, 125, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herasimenka, Y.; Cescutti, P.; Impallomeni, G.; Rizzo, R. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Inquilinus limosus, a New Pathogen of Cystic Fibrosis Patients: Novel Structures with Usual Components. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, Y.A.; Debandi, M.; Carrica, M.D.C.; Hayes, J.A.; Rodriguez, M.E. Intracellular Replication of Inquilinus limosus in Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 171, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, S.P.; Azevedo, N.F.; Pereira, M.O. Emergent Bacteria in Cystic Fibrosis: In Vitro Biofilm Formation and Resilience under Variable Oxygen Conditions. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 678301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hector, A.; Kirn, T.; Ralhan, A.; Graepler-Mainka, U.; Berenbrinker, S.; Riethmueller, J.; Hogardt, M.; Wagner, M.; Pfleger, A.; Autenrieth, I.; et al. Microbial Colonization and Lung Function in Adolescents with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2016, 15, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Is Immunity the Second Function of Chromatin? J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Alemán, S.R.; Campos-García, L.; Palma-Nicolas, J.P.; Hernández-Bello, R.; González, G.M.; Sánchez-González, A. Understanding the Entanglement: Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, M.; Conza, J.D.; Gutkind, G. Draft Genome Sequence of Inquilinus limosus Strain MP06, a Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Isolate. Braz. J. Microbiol. Publ. Braz. Soc. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 943–944. [Google Scholar]
- Gradel, K.O.; Jensen, U.S.; Schønheyder, H.C.; Østergaard, C.; Knudsen, J.D.; Wehberg, S.; Søgaard, M.; Danish Collaborative Bacteraemia Network (DACOBAN). Impact of Appropriate Empirical Antibiotic Treatment on Recurrence and Mortality in Patients with Bacteraemia: A Population-Based Cohort Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.; Jahnke, N. Single versus Combination Intravenous Anti-Pseudomonal Antibiotic Therapy for People with Cystic Fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 6, CD002007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doern, C.D. When Does 2 plus 2 Equal 5? A Review of Antimicrobial Synergy Testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4124–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, C.H.; Heltshe, S.L.; West, N.E.; Skalland, M.; Sanders, D.B.; Jain, R.; Barto, T.L.; Fogarty, B.; Marshall, B.C.; VanDevanter, D.R.; et al. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Antimicrobial Duration for Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Exacerbation Treatment. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Hamard, C.; Kanaan, R.; Boussaud, V.; Grenet, D.; Abély, M.; Hubert, D.; Munck, A.; Lemonnier, L.; Burgel, P.-R. Causes of Death in French Cystic Fibrosis Patients: The Need for Improvement in Transplantation Referral Strategies! J. Cyst. Fibros. 2016, 15, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, D.; Roy, C.; Cornet, M.; Bucher, J.; Boussaud, V.; Pimpec-Barthes, F.L.; Pontailler, M.; Raisky, O.; Lopez, V.; Barbanti, C.; et al. Acute Respiratory Failure Due to Pulmonary Exacerbation in Children with Cystic Fibrosis Admitted in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: Outcomes and Factors Associated with Mortality. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuba, M.; Attaway, A.; Zein, J.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Strausbaugh, S.; Jacono, F.; Dasenbrook, E.C. Mortality in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis Requiring Mechanical Ventilation. Cross-Sectional Analysis of Nationwide Events. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, V.; Atenafu, E.G.; Lu, A.; Yau, Y.; Tullis, E.; Ratjen, F. Chronic Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infection and Mortality or Lung Transplantation in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author, Year | Number of Patients * | Gender | Age (Years) | Site of Infection (%) | Treatment (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kiratisin et al., 2006 [9] | 1 | Female | 38 | Infective endocarditis, bacteremia | Carbapenem |
| Hayes et al., 2009 [10] | 1 | Male | 20 | LRTI | Quinolone, aminoglycoside |
| Goeman et al., 2015 [11] | 1 | Male | 31 | LRTI, bacteremia | Carbapenem, aminoglycoside |
| McHugh et al., 2016 [12] | 1 | Female | 60 | LRTI | Quinolone |
| Poore et al., 2016 [13] | 1 | Male | 6 | LRTI | Carbapenem, quinolone, aminoglycoside |
| Watson et al., 2021 [14] | 3 | 3 Males | 10, 13, and 22 | LRTI | NR 3 (100) |
| Ríos-López et al., 2022 [15] | 1 | Male | 12 | LRTI | Quinolone |
| Farfour et al., 2023 [20] | 3 | 1 Male 2 Females | 22, 31, and 45 | LRTI 3 (100), bacteremia 1 (33.3) | Cephalosporin 1 (33.3) NA 1 (33.3) Carbapenem 2 (66.7) Quinolone 2 (66.7) Aminoglycoside 2 (66.7) |
| Zobell et al., 2014 [16] | 1 | Female | 13 | LRTI | Carbapenem, aminoglycoside |
| Pitulle et al., 1999 [6] | 1 | Female | 22 | LRTI | NR |
| Chiron et al., 2005 [19] | 3 | 1 Female 2 Males | 10, 13, and 18 | LRTI 3 (100) | Carbapenem 3 (100) Aminoglycoside 2 (66.7) Quinolone 2 (66.7) |
| Schmoldt et al., 2006 [17] | 5 | 2 Males 3 Females | 16, 17, 19, 20, and 35 | LRTI 5 (100) | Carbapenem 4 (80) Quinolone 3 (60) Aminoglycoside 3 (60) |
| Bittar et al., 2008 [18] | 3 | 3 Males | 2, 15, and 21 | LRTI 3 (100) | NR 3 (100) |
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 25) * | LRTI (n = 24) * | Bacteremia (n = 3) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 19 (13–26.5) | 18.5 (13–22) | 38 (31–45) |
| Male gender, n (%) | 15 (60) | 15 (62.5) | 1 (33.3) |
| Predisposing factors | |||
| Cystic fibrosis, n (%) | 23 (92) | 23 (95.8) | 2 (66.7) |
| Lung transplantation, n (%) | 5 (20) | 5 (20.8) | 2 (66.7) |
| Bronchiectasis and recurrent bronchitis, n (%) | 1 (4) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0) |
| Chronic heart disease, n (%) | 1/19 (5.3) | 0/18 (0) | 1/2 (50) |
| Previous antimicrobial use within three months, n (%) | 9/10 (90) | 9/10 (90) | 2/2 (100) |
| Lower respiratory tract infection, n (%) | 24 (96) | 24 (100) | 2 (66.7) |
| Bacteremia, n (%) | 3/23 (13) | 2/22 (9.1) | 3 (100) |
| Infective endocarditis, n (%) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (33.3) |
| Polymicrobial infection, n (%) | 17/22 (77.3) | 17/21 (81) | 17/22 (77.3) |
| Clinical characteristics | |||
| Fever, n (%) | 5/22 (22.7) | 4/21 (19) | 3 (100) |
| Sepsis, n (%) | 0/23 (0) | 0/22 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Treatment | |||
| Carbapenem, n (%) | 13/19 (68.4) | 12/18 (66.7) | 3 (100) |
| Quinolone, n (%) | 11/19 (57.9) | 11/18 (61.1) | 1 (33.3) |
| Aminoglycoside, n (%) | 10/19 (52.6) | 10/18 (55.6) | 2 (66.7) |
| Cephalosporin, n (%) | 1/19 (5.3) | 1/18 (5.6) | 1 (33.3) |
| Surgical management, n (%) | 2/20 (10) | 2/19 (10.5) | 1 (33.3) |
| Treatment duration, days, median (IQR) | 28 (14–42) | 22 (13–42) | 42 (16–84) |
| Outcomes | |||
| Deaths due to infection, n (%) | 1 (4) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0) |
| Deaths overall, n (%) | 1 (4) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0) |
| Antimicrobial Agent | Number of Patients * | Resistance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 16/16 | 100 |
| Aztreonam | 14/14 | 100 |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | 6/7 | 85.7 |
| Aminoglycosides | 5/11 | 45.5 |
| Quinolones | 1/10 | 10 |
| Carbapenems | 1/16 | 6.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasilopoulou, A.; Panayiotou, T.; Baliou, S.; Tsantes, A.G.; Ioannou, P. Inquilinus Species Infections in Humans—A Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030592
Vasilopoulou A, Panayiotou T, Baliou S, Tsantes AG, Ioannou P. Inquilinus Species Infections in Humans—A Narrative Review. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(3):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030592
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasilopoulou, Anastasia, Takis Panayiotou, Stella Baliou, Andreas G. Tsantes, and Petros Ioannou. 2025. "Inquilinus Species Infections in Humans—A Narrative Review" Microorganisms 13, no. 3: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030592
APA StyleVasilopoulou, A., Panayiotou, T., Baliou, S., Tsantes, A. G., & Ioannou, P. (2025). Inquilinus Species Infections in Humans—A Narrative Review. Microorganisms, 13(3), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030592







