Abstract
(1) Background: Bartonella spp. are zoonotic bacteria with small mammals as main reservoirs. Bartonella spp. prevalence in small mammals from Myanmar and Sri Lanka are yet unknown. (2) Methods: Small mammals were snap trapped in Sri Lanka and Myanmar in urban surroundings. Spleens-derived DNA was screened for Bartonella spp. using conventional PCR based on three target genes. Positive samples were sequenced. (3) Results: 994 small mammals were collected comprising 6 species: Bandicota bengalensis, Bandicota indica, Rattus exulans, Rattus rattus, Mus booduga, and Suncus murinus. In Myanmar, the Bartonella prevalence in Bandicoot rats (68.47%) was higher than in Rattus rattus (41.67%), Rattus exulans (21.33%), and Suncus murinus (3.64%). Furthermore the prevalence in Myanmar (34%, n = 495) was twice as high as in Sri Lanka (16%, n = 499). In Sri Lanka, Bartonella spp. occurred almost exclusively in R. rattus. In Myanmar, Bartonella kosoyi was mainly detected (56%), followed by Bartonella sp. KM2529 (15%), Bartonella sp. SE-Bart D (12%) and Bartonella henselae (1%). In Sri Lanka, B. phoceensis (60%) and Bartonella sp. KM2581 (33%) were predominant. (4) Conclusions: Bartonella spp. were detected in all investigated small mammal species from Myanmar and Sri Lanka for the first time. Bartonella kosoyi and B. henselae are zoonotic. As these small mammals originated from urban settlements, human bartonellosis seems likely to occur.
1. Introduction
The genus Bartonella includes over 40 species and subspecies [1] of gram-negative, hemotropic, facultative intracellular bacteria that infect endothelial cells and erythrocytes of mammalian hosts. Bartonella spp. are vector-borne and commonly transmitted via blood-sucking arthropods. Rodents are known to be the main reservoir of different Bartonella spp. with fleas the main vector within and between rodent populations [2,3]. Among the variety of zoonotic Bartonellae, Bartonella elizabethae, Bartonella grahamii, B. henselae, Bartonella tribocorum, and Bartonella vinsonii subsp. arupensis are described in association with rodent reservoirs [2,4,5].
Bartonella spp. infections are associated with various human diseases such as cat-scratch disease (Bartonella henselae), trench fever (Bartonella quintana), and Oroya fever (Bartonella bacilliformis). Cases of bartonellosis associated with rodents are described from all over the world with clinical symptoms such as fever, muscle and joint pain, neuroretinitis, and endocarditis [6,7]. Regarding Asia, unspecific clinical symptoms are caused by B. henselae in human patients from Laos and Taiwan [8,9]. Further, Bartonella tamiae and other Bartonella spp. were found in febrile patients from Thailand [10]. Until now no cases of bartonellosis in humans have been reported from Sri Lanka and Myanmar. Due to the unspecific symptoms, and missing diagnostic tools, infections could have been overlooked.
Nonetheless, rodent-associated zoonotic Bartonellae can pose a risk in countries such as Myanmar and Sri Lanka where close contact between humans and rodents is common [5,11]. Myanmar covers an area of 676,552 km2 and population size is 54 million people [12] of which 70% live in rural areas and work in the agricultural sector achieving 30% of the gross domestic product [13,14]. About 21 million people live in Sri Lanka in an area of about 65,705 km2 [15]. As of 2018, 25.7% of the employed population works in the agricultural sector [16].
The genera Bandicota, Rattus and Mus include synanthropic pest rodent species that live in close contact with humans in those countries [17]. In other Asian countries many newly discovered Bartonella species and high Bartonella prevalence was detected in these rodents [2]. There are a few studies of Bartonella infections indicating prevalence ranging from 9 to 68% in urban rodents in Southeast Asia [18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. In comparison, little is known about the percentage of Bartonella-positive rodents in rural areas. Published reports are restricted to a study that considered Bartonella prevalence in small mammals across a gradient of human density that included five agricultural sites in Laos (11.9%) and Thailand (11.0%) [25].
In Myanmar, a previous study [26] detected Bartonella spp. prevalence in fleas associated with cats and rodents in an area along the Thai-Myanmar border. Six out of 90 fleas were tested positive for Bartonella DNA and a newly described Bartonella species was detected from one flea collected from a Rattus surifer [26]. In Sri Lanka, a study analyzed Bartonella spp. infections in dogs with positive individuals showing even multiple infections [27].
To date, no study of Bartonella prevalence in small mammals as possible reservoir hosts has been conducted in Myanmar and Sri Lanka. Because of the close contact between rodents and humans in various parts of these countries, it is important to study rodent-associated Bartonella spp. to assess the risk for human health and companion animals.
Thus, the main aim of this study was to detect small mammal species living close to human settlements in Myanmar and Sri Lanka and to evaluate the Bartonella prevalence in those small mammal species for the first time. Another purpose was to identify the Bartonella species in these samples by molecular techniques to evaluate their zoonotic potential.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
Small mammals were trapped at five sites in Myanmar and Sri Lanka in the years 2018 and 2019. Traps were set in villages at structures used for rice storage and rice processing in Myanmar and Sri Lanka (Figure 1).
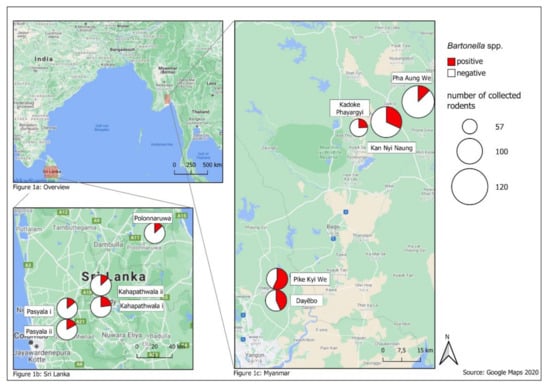
In Myanmar, study sites were located in granaries or mills in the rural delta and coastal zone, where the main agricultural production is located. Dayēbo (17°6′19.548″ N; 96°14′44.124″ E) and Pike Kye We (17°4′58.926″ N; 96°0′0″ E) are rural areas mainly characterized by rice production [28]. At the sites Kan Nyi Naung (17°6′50.036″ N; 96°43′40.404″ E), Kadoke Phayargyi (17°41′20.188″ N; 96°35′30.933″ E) and Pha Aung We (17°46′18.581″ N; 96°41′10.046″ E) subsistence agriculture prevails [29]. The climatological conditions in Myanmar are divided in a dry season (November–May) and a wet season (June–October) [30].
Small mammal trapping in Sri Lanka was conducted in Pasyala (Gampaha District) i (7°9′0.742″ N; 80°8′14.006″ E), Pasyala (Gampaha District) ii (7°9′12.085″ N; 80°8′4.459″ E), Kahapathwala (Kurunegala District) i (7°23′34.674″ N; 80°27′52.981″ E) and Kahapathwala (Kurunegala District) ii (7°23′43.318″ N; 80°28′27.04″ E) that are characterized by an increase in housing units indicating population growth in these areas. Sinhapura (Polonnaruwa District) i (8°1′17.976″ N; 81°1′19.091″ E) is characterized by rural agriculture with 39.1% employment in this sector [31,32,33]. There is a dry (minor) season (April–August) and a wet (major) season (October–February) [34].
2.2. Sampling of Small Mammals, Preparation of Samples and DNA Extraction
Small mammals were obtained and killed by snap trapping as part of regular pest rodent control operations. In the countries where the work was conducted, snap trapping is not regarded as animal experimentation. Hence, no animal ethics permits were required. In Myanmar, small mammals were trapped from June to December in 2018 and from May to December in 2019. In each site, 10 snap traps (Kness, big-snap-E rat trap) and 5 local-made bamboo traps were baited with unhulled rice and set opportunistically in and around 10 small-holder rice storage facilities for 450 trap nights per site and year (total trap nights; 4500). In Sri Lanka, small mammals were captured in two trapping sessions in June–December 2018 and two trapping sessions in March–August 2019 (for details see [35]). In each of the five sites, 10 snap traps (Kness, big-snap-E rat trap) were baited with unhulled rice and roasted coconut and set for three consecutive nights per session opportunistically in and around ten small-holder rice storage or rice processing facilities resulting in 600 trap nights per site and year (total trap nights: 6000).
Trapped small mammals were identified to species level based on morphology [17] supplemented by phylogenetic analysis of a partial fragment of the cytochrome b gene [35]. Standard body measurements were recorded, and several organ samples were collected including the spleen. Spleen samples were stored in 70% ethanol until processing and analyses for Bartonella spp.
Before processing the spleen samples for DNA extraction, the ethanol was washed out with phosphate-buffered-saline (PBS, pH 7.2) by transferring in PBS and incubating for four hours and drying afterwards. Then, all samples were homogenized with 0.6 g sterile ceramic beads (sized 1.4 mm, Peqlab Biotechnologie, Erlangen, Germany) four times the sample’s weight with PBS (pH 7.2). The Precellys® 24 tissue homogenizer (Bertin Technologies, Montigny Le Bretonneux, France) was used for mechanical disruption with 5500 rpm for 2 × 15 s with a 10 s break between both runs.
Afterwards the DNA was extracted using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The DNA samples were measured qualitatively and quantitatively with the NanoDrop ND-1000 (PeqLab Biotechnologie GmbH). Samples with a DNA concentration >40 ng/μL were diluted with the kit’s elution buffer to receive a DNA concentration of 20–40 ng/μL for each sample.
2.3. Detection of Bartonella spp. and Sequence Analysis
The presence of Bartonella spp. was detected in DNA samples by conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) targeting the NADH dehydrogenase subunit (nuoG) with an amplicon size of 346 base pairs (bp). Additionally, all samples were further analyzed in two PCRs targeting the gltA gene (378 bp) and a fragment of the 16S-23S rRNA ITS region (453–780 bp) [36,37,38,39].
The amplicon of the nuoG was detected with previously published PCR protocols and the genus specific primers nuoGF (5′-GGCGTGATTGTTCTCGTTA-3′) and nuoGR (5′-CACGACCACGGCTATCAAT-3′) [39]. For the detection of Bartonella spp. DNA based on the gltA gene the genus specific primers BhCS.781p (5′-GGGGACCAGCTCATGGTGG-3′) and BhCS.1137n (5′-AATGCAAAAAGAACAGTAAACA-3′) were used. The amplification consisted of 45 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 53 °C for 30 s and elongation at 72 °C for 1 min [36,38]. The amplification of the 16S-23S rRNA ITS region was performed with forward (Ba325s: 5′-CTTCAGATGATGATCCCAAGCCTTCTGGCG-3′) and reverse primers (Ba1100as: 5′-GAACCGACGACCCCCTGCTTGCAAAGC-3′) as previously published, after minimal modifications in the set-up of the amplification run: 40 cycles for 30 s at 94 °C, for 30 s at 66 °C, for 50 s at 72 °C [37].
PCR products were prepared with DNA Gel Loading Dye (6×) (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics UAB, Vilnius, Lithuania) for gel electrophoresis in 2% agarose. The results were visualized by UV light using the UVP GelSolo streamlined gel documentation (Analytik Jena AG, Jena, Germany). Afterwards 125 positive samples were selected for sequencing to cover all small mammal species detected at each location in Myanmar and Sri Lanka in both seasons of each collection year. The samples were purified for sequencing using the NucleoSpin Gel and PCR clean-up kit (Macherey-Nagel GmbH & Co. KG, Düren, Germany) as recommended by the manufacturer. Further, samples were sequenced commercially with forward and reverse primers of the 16S-23S rRNA ITS region (Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Klinische Forschung, Leipzig, Germany). The sequences were trimmed using Bionumerics v.7.6.1. (Applied Maths Inc., Austin, TX, USA) and compared to available data in GenBank with BLASTn (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 25 February 2021)) [40]. Obtained sequences were uploaded in GenBank under the following accession numbers (MW194932-MW194978, MW222168-MW222177, MW233783-MW233857).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Confidence intervals (95% CI) for the prevalence of Bartonella spp. in small mammals were determined by the Clopper and Pearson method [41] with setting the level of alpha to 0.05 using GraphPad Prism Software v. 4.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
The independence of compared prevalence rates concerning small mammal species, age, sex, trapping year, season, and in Myanmar additionally regarding the habitat, was tested using Pearson’s Chi-squared test. Tests with two variables were considered to be significant if P (probability) < 0.05. Only samples tested positive for all three target genes were considered positive for Bartonella spp.
3. Results
3.1. Captured Small Mammal Species
In Myanmar, 495 small mammals were trapped belonging to five species: Bandicota bengalensis (n2018 = 94; n2019 = 61); B. indica (n2018 = 6; n2019 = 2); Rattus exulans (n2018 = 59; n2019 = 91); R. rattus (n2018 = 51; n2019 = 21); Suncus murinus (n2018 = 36; n2019 = 74) (Table 1). Of these small mammals, 329 were caught at mills (B. bengalensis: 149, B. indica: 8, R. exulans: 67, R. rattus: 22, S. murinus: 83) and 166 at granaries (B. bengalensis: 6, R. exulans: 83, R. rattus: 50, S. murinus: 27). In Sri Lanka, 499 small mammals were captured representing six species: B. bengalensis (n2019 = 1); B. indica (n2018 = 5; n2019 = 8); Mus booduga (n2018 = 4); R. exulans (n2018 = 2; n2019 = 3); R. rattus (n2018 = 206; n2019 = 227); S. murinus (n2018 = 33; n2019 = 10) (Table 2). All small mammals from Sri Lanka were caught at village stores.

Table 1.
Number of small mammal species collected at different study sites from Myanmar.

Table 2.
Number of small mammal species collected at different study sites from Sri Lanka.
3.2. Bartonella spp. Prevalence in Small Mammals
Overall 248 out of 994 samples (25%; 95% CI: 22.3–27.8%) tested positive for Bartonella spp. DNA by conventional PCR targeting all three target genes altogether (Table 3). Altogether 168 out of 495 (34%; 95% CI: 29.8–38.3%) small mammals in Myanmar and 80 out of 499 (16%; 95% CI: 12.9–19.6%) small mammals in Sri Lanka were positive. The prevalence in Myanmar was significantly higher compared to Sri Lanka (χ2 = 42.556, df = 1, P < 0.0001).

Table 3.
Prevalence of Bartonella spp. DNA in small mammals from Sri Lanka and Myanmar targeting the nuoG, gltA gene and the 16s rRNA 23s rRNA ITS.
In Myanmar, the prevalence ranged in 2018 from 7% in Pha Aung We to 46% in Pike Kye We and in 2019 from 15% in Pha Aung We to 70% in Pike Kye We (Figure 1). The prevalence of the adjacent sites Pike Kye We and Dayēbo were higher than at Kadoke Phayargyi, Pha Aung We and Kan Nyi Naung (χ2 = 41.273, df = 1, P < 0.0001). In contrast, Bartonella prevalence in Sri Lanka was similar between years (10–28%) and sites (10–28%) (Figure 1).
In Myanmar, prevalence was higher in Bandicota than in Rattus spp. and S. murinus (χ2 = 88.894, df = 1, P < 0.0001). The prevalence of Bartonella in the genus Rattus was significantly higher compared to S. murinus (χ2 = 27.250, df = 1, P < 0.0001) in Myanmar. Likewise, in Sri Lanka the prevalence in R. rattus was higher than in all other small mammal species which were caught by lower numbers (χ2 = 10.697, df = 1, P = 0.0011).
No significant difference in the prevalence of Bartonella spp. in Myanmar was detected between males and females (χ2 = 0.253, df = 1, P = 0.6153), between the years 2018 and 2019 (χ2 = 1.527, df = 1, P = 0.2165) and the rainy and dry season (χ2 = 0.005, df = 1, P = 0.9429). In Myanmar, the prevalence of Bartonella in small mammals caught in granaries was significantly higher than in small mammals caught in mills (χ2 = 5.198, df = 1, P = 0.0226). However, due to the unequal distribution of small mammal species in granaries and mills, these results may be regarded as slightly distorting. The prevalence of adult small mammals was significantly higher compared to the lower prevalence of sub-adult small mammals (χ2 = 54.035, df = 1, P < 0.0001). There was no significant difference in Sri Lanka for the Bartonella prevalence between adults and sub-adults (χ2 = 0.028, df = 1, P = 0.8677), males and females (χ2 = 0.076, df = 1, P = 0.7826), the years 2018 and 2019 (χ2 = 0.000, df = 1, P = 0.9844), and the seasons (χ2 = 0.005, df = 1, P = 0.9443) [34] (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2).
Several Bartonella co-infections were detected in small mammals from Myanmar and Sri Lanka. In Myanmar 30 out of 168 positively tested small mammals (18%, 95% CI: 12.4–24.5%) with double infections were detected by PCR targeting the ITS region. Double infections in Myanmar were most common in B. bengalensis (21/96; 22%, 95% CI: 14.1–31.5%) and R. rattus (7/30; 23%, 95% CI: 9.9–42.3%) and at the sites Dayēbo (12/45; 27%, 95% CI: 14.6–41.9%) and Kadoke Phayargyi (4/14; 29%, 95% CI: 8.4–58.1%). In Sri Lanka, 11 out of 80 positively tested samples (14%, 95% CI: 7.1–23.3) showed double infections. Here, co-infections were detected only in one rodent species, R. rattus, caught at the sites Pasyala and Kahapathwala.
3.3. Sequence Analysis of Bartonella-Positive Samples
Sequence analyses were performed for 125 Bartonella-positive samples based on the ITS region (53%) and 11 different Bartonella strains were detected (Table 4). In Myanmar, the predominantly detected species was B. kosoyi (41/73; 56%, 95% CI: 44.1–67.8%). Bartonella sp. KM2529 (11/73; 15%, 95% CI: 7.8–25.4%) and Bartonella sp. SE-Bart-D (9/73; 1%, 95% CI: 5.8–22.1%) were detected in small mammals from Myanmar as well. The most frequently identified Bartonella species in Sri Lanka was B. phoceensis (25/42; 60%, 95% 95% CI: 43.3–74.4%) followed by Bartonella spp. KM2581 (14/42; 33%, 95% CI: 19.6–49.6%). The detected Bartonella spp. were evenly distributed and no effect of small mammal species, age, season and habitat was apparent. However, B. kosoyi. was exclusively detected in B. indica from Myanmar.

Table 4.
Sequencing results of 125 previously selected Bartonella-positive samples from Myanmar and Sri Lanka.
Two different Bartonella spp., (Accession Number: EF407566) and (Acc. No.: EF213776) were detected in one R. exulans caught in Kan Nyi Naung, Myanmar. Two R. norvegicus from China were earlier positive for Bartonella sp. RN25BJ, respectively, Bartonella sp. RN28BJ. Furthermore, 10 samples showed <97% identity with sequences in GenBank, but 98–100% within group-similarity and can be assembled in groups with >98% agreement (Table 4). Group 1 consists of three samples from Myanmar and showed high similarities to Bartonella sp. KM 2529. Group 2 consists of four samples from R. rattus caught at two different sites (Pasyala and Kahapathwala) in Sri Lanka which are most similar to Bartonella sp. SE-Bart-D. Three samples from S. murinus caught in 2019 at two different sites in Myanmar form Group 3 and show high similarity to an uncultured Bartonella clone 5199 (Table 4). Seven samples were not considered Bartonella-positive as they yielded only a similarity <92% with other sequences from the current study and sequences in GenBank.
4. Discussion
This study presents the first detection of Bartonella spp. in small mammals from Myanmar and Sri Lanka suggesting their potential as reservoirs. In this study, up to five different small mammal species occurred sympatrically in Myanmar and Sri Lanka. The two genera Bandicota and Rattus caught in this study belong to the major agricultural pest species in these countries [17]. Moreover, the invasive species S. murinus which has its origin in India was found in this study [42]. Mus booduga which was also detected is known as field mouse and not as true commensal in India, Sri Lanka, and Nepal [17]. Rodents, especially of the species R. rattus and R. exulans occur mainly in villages and less in cropping areas, however, R. rattus is also known for causing significant damage in agriculture in South Asia [17]. Further, Bandicoot rats are reported from all sorts of human dwellings, but especially B. bengalensis is known as a major pest. The population density of B. indica is lower compared to other rodent species and is identified as minor pest species [17]. In Myanmar and Sri Lanka, the mentioned small mammal species are moreover known as reservoirs of zoonotic pathogens such as the Hantaan virus and Leptospira spp. [43,44,45] which adds relevance to the livelihoods of people beyond their importance as considerable pest rodents [17]. The inevitable proximity of humans and rodents [46] is likely to increase the risk of transmission of zoonotic pathogens from rodents to humans. This is confirmed by high antibody titers of the Hantaan virus in rodents and in humans living in close contact with rodents in Thailand and Taiwan [47,48]. The commensal shrew S. murinus is a reservoir for Yersinia pestis and responsible for recent human plague outbreaks in Vietnam [49]. In Sri Lanka, Y. pestis was isolated from Bandicoot rats, but reports about plague hosts in Myanmar are missing [50].
Especially in Southeast Asia rodent-associated infectious diseases are emerging [51]. The Bartonella spp. clade associated with rodents shows a wide disparity regarding Bartonella species and potential hosts [52]. Several studies showed prevalence rates ranging from 9 to 67% in urban rodents from Thailand (55.6–67.6% [18]), Laos (10.1–30.4% [22]), China (9.3–42.9%) [20,21], and Malaysia (13.5–13.8% [24]). The Bartonella spp. prevalence in this study (34% Myanmar, 16% Sri Lanka) are in agreement with the previously mentioned studies [5].
The prevalence of Bartonella in small mammals from Sri Lanka was significantly lower than in Myanmar. In Sri Lanka, the cosmopolitan species R. rattus was introduced via ship trading to this island [53]. A possible explanation for the significantly lower prevalence in Sri Lanka could be first of all the absence of some parasites, which function as vectors (e.g., Xenopsylla cheopis) [5]. Moreover, ecological conditions on an island may limit the reproduction of the arthropod vector as it is the case in the Canary Islands. The study showed major variants of the Bartonella spp. prevalence in rodents at different islands. An explanation for this distribution was the varying ecological condition affecting the flea populations as essential vectors for the infection of rodents [54]. Various potential vectors are known for Bartonella spp.; however, the interaction between host and vector has not been clarified, yet [55]. The missing connection to continental rat populations may suppress reintroduction of suitable arthropod hosts and it can affect the presence and population size of competent rodent hosts in Sri Lanka but not in Myanmar [5].
Statistical analyses revealed significant differences in Bartonella spp. prevalence among small mammal species in Myanmar. Bandicoot rats had the highest (63%) and S. murinus the lowest prevalence (4%). In a recent study in Nepal, a low prevalence of Bartonella spp. was detected in B. bengalensis (26.3%) and high prevalence in S. murinus (64.1%) while R. rattus (43.3%) was intermediate. In Bangladesh both B. bengalensis (63.2%) and S. murinus (42.9%) showed higher prevalence than R. rattus [19,23]. The low prevalence of S. murinus might be due to a lack of host-specific vectors in Sri Lanka in our study. However, information about the ectoparasite fauna of S. murinus is lacking. Additionally, low Bartonella prevalence was detected in other insectivores (Sorex araneus) in England [56]. Investigations of S. araneus showed that some blood-sucking arthropods harboring rare Bartonella spp. may feed and transmit these Bartonella spp. exclusively to shrews. Furthermore, S. araneus was found to be less affected by ectoparasites compared to endemic rodents [56]. Therefore, the high prevalence of S. murinus may be related to an adapted ectoparasite fauna in Bangladesh but not in Myanmar or Sri Lanka. In Sri Lanka, the predominant rodent species R. rattus showed the highest prevalence (18%)—apart from the single B. bengalensis, which also tested positive. The prevalence for R. rattus and the high prevalence of B. bengalensis in Myanmar are in line with R. rattus in Asia (Malaysia: 13.5% [24], Laos: 10.1% [22], Taiwan: 10% [57]).
In Myanmar, the prevalence was higher in urban sites (Pike Kye We and Dayēbo) compared to the three rural sites. In line with our study, other authors reported higher prevalence of Bartonella spp. in small mammals from urban regions [58,59,60]. A possible explanation could be better conditions in cities for commensal rodents and thus for blood-sucking arthropods that serve as vectors for Bartonella spp., which can infect several mammals [5]. However, no significant difference in the prevalence of Bartonella spp. in Sri Lanka was detected concerning the different sites. All small mammals were caught in small-holder rice storage facilities in Sri Lanka and thus conditions were not as contrasting as at the sites in Myanmar.
In Myanmar, the prevalence in adult small mammals showed significantly higher prevalence than in subadults, possibly due to the life cycle of Bartonella spp. These bacteria can persist in the reservoir host without harming them drastically [61]. In contrast, Kosoy et al. [62] reported an increase in prevalence during the development of rodents especially from juveniles to subadults and detected lower prevalence in adult cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus). The decrease of prevalence may be due to the development of immunity with age [62]. No differences in Bartonella prevalence according to age were detected in Sri Lanka. This might have been caused by the different small mammal species compositions. In Myanmar, high prevalence of Bartonella spp. was detected in B. bengalensis and B. indica and in Sri Lanka especially in R. rattus. Paziewska et al. [63] showed that the course of Bartonella infections depends on specific host-pathogen interactions. Myodes glareolus overcomes Bartonella infections within 1–2 months, however the length of time it takes to overcome the infection in Apodemus flavicollis is not definitely known. Furthermore, reinfections in M. glareolus were detected less frequently than in A. flavicollis [63]. Thus, Bartonella infections may persist in Bandicota spp. (more often collected in Myanmar) longer than in Rattus spp. (more often collected in Sri Lanka), which would explain the contrasting results in both countries.
In the present study, there was no effect of the seasons. Morway et al. showed that Bartonella prevalence rates were influenced by climatic conditions [64]. Moreover, a study detected higher Bartonella prevalence in rodents in Cambodia, Lao PDR, and Thailand during the wet season, because at that time there may be better living conditions for the vectors [65]. The lack of an effect of season may have been caused by the different composition of the small mammal community in our study during the year. Our results are in line with Kosoy et al. and others who showed no significant differences in Bartonella prevalence according to the small mammals’ sex [62]. No significant effect of sex was detected in other parts of Southeast Asia as well [65].
Kosoy et al. [66] showed that rodents are infected with different Bartonella spp. strains for a long time and that single strains replace each other. This infection strategy may have an impact on the probability of double infections in small mammals [66]. However, it is also known that reservoir hosts like rodents tolerate Bartonella spp. infections with more than one species and related Bartonella strains [67]. This diversity was explained by a lacking immune response of the reservoir hosts. Studies of Bartonella co-infections in small mammals are rare. In the current study, double infections were observed in 30 small mammals (18%) in Myanmar and 11 small mammals (14%) in Sri Lanka. We identified double infections in B. bengalensis, R. rattus, and R. exulans in Myanmar and exclusively in R. rattus in Sri Lanka at all sites. High co-infection rates (56%) with two or more genotypes, including recombinant variants, were detected in gerbils and fleas from Israel [68]. In Taiwan, a high prevalence was found in fleas and lice (64.7–64.9%), while a lower prevalence was found in small mammals (31.4%). Therefore, the sequencing results support the thesis of vectors bearing more different Bartonella spp. than their hosts [69]. In Southeast Asia, multiple infections are only reported in cats showing lower prevalence compared to our results (Thailand: 5.3–7.69%, China: 4.34%) [70,71,72].
Our sequence analysis of Bartonella-positive samples identified 11 different Bartonella strains. Moreover, B. kosoyi, first described in 2019, was the predominant species for the samples from Myanmar. Analysis confirmed a phylogenetic association of B. kosoyi with the zoonotic B. grahamii, B. tribocorum, and B. elizabethae [1]. Bartonella elizabethae and B. elizabethae-like species show host-specificity for rodents of the genus Rattus but can infect other small mammals like Bandicoot rats and S. murinus as well [5]. We detected B. kosoyi mainly in Bandicoot rats (B. bengalensis: 21/29, B. indica: 6/6). Before the Tel Aviv strain was named B. kosoyi sp. nov., this strain had been detected in Bandicoot rats and R. rattus from Bangladesh [19], Portugal [73] and Nepal [23]. Further, the Tel Aviv Strain was associated with a case of human lymphadenopathy and fever in Georgia [74]. Therefore, the zoonotic potential seems likely for B. kosoyi.
Some of the sequencing results from Myanmar were highly similar (99.81–100%) to Bartonella sp. SE-Bart-D isolated from the Oriental rat flea (X. cheopis) in Egypt. Bartonella sp. SE-Bart-D shared 85–90% similarity with B. tribocorum, B. grahamii, and B. elizabethae, which are all known as zoonotic agents [75].
In Sri Lanka, Bartonella phoceensis was the predominant result for all sequenced samples. Bartonella phoceensis was first detected along with Bartonella rattimassiliensis in France in 2004 [76]. Since then, B. phoceensis was detected in small mammals from Asia. In Japan and Thailand B. phoceensis was detected in R. rattus [67,77] and in Indonesia in S. murinus and Rattus tanezumi [78]. Moreover, B. phoceensis was associated, with a similarity of 94%, with uncultured Bartonella species found in Rattus norvegicus from Taiwan [57]. Until now, B. phoceensis is not recognized as a zoonotic agent and no case of human illness has been described.
Bartonella henselae was detected in one S. murinus from Myanmar in the current study. The organism with the highest similarity B. henselae Q5BJ-CW was first isolated from a dog in China. Bartonella henselae is known to be mostly transmitted by wild and domestic cats to humans [79]. Cat scratch disease caused by B. henselae, is associated with fever and regional lymphadenopathy [7]. Though not being considered as the main reservoir, rodents were reported as carriers of B. henselae in Italy and New Zealand. Therefore, rodents can be a source of infection due to close contact to humans [4,80]. Due to unspecific symptoms and neglected awareness, Bartonella spp. can be an underestimated threat to public health. Although the number of zoonotic Bartonella spp. has emerged, bartonellosis in humans is reported very rarely [3].
5. Conclusions
Bartonella spp. were detected for the first time in small mammals from Myanmar (34%) and Sri Lanka (16%) in this study. The high prevalence is in line with previously reported results from other countries in Southeast Asia. The reasons for the lower prevalence in Sri Lanka may be missing vectors or different ecological conditions. All examined small mammal species were Bartonella-positive in Myanmar and Sri Lanka. Eleven different Bartonella strains were detected of which three are considered potentially zoonotic. Thus, small mammals may serve as reservoir hosts for zoonotic Bartonella spp. in these countries. In Myanmar and Sri Lanka, contact between humans and rodents is frequent in rice storage and processing facilities. With an increasing degree of urbanization and thus more frequent contact between humans and rodents, these rodent-associated pathogens may pose a higher risk for human health.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/9/3/658/s1, Table S1: Bartonella prevalence in rodents from Myanmar according to sex, age, year and season, Table S2: Bartonella prevalence in small mammals from Sri Lanka according to sex, age, year and season.
Author Contributions
M.P., A.O., and J.J. planned the study; N.M.H., P.P.M., S.R.S., and V.S. conducted fieldwork and organ sampling; A.P.P. ran the cytochrome-b species identification; I.B. and A.O. prepared the samples in the laboratory, tested the samples for Bartonella spp. and performed the sequence analysis; I.B. and A.O. performed the statistical analysis; I.B. wrote a draft of the manuscript; A.O., M.P., N.M.H., S.R.S., V.S., and J.J. reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was partially funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (FKZ 01DP17063) awarded to J.J. We acknowledge support from the German Research Foundation (DFG) and Leipzig University within the program of Open Access Publishing.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, because snap trapping small mammals is not regarded animal experimentation by national regulation.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank farmers for assistance in fieldwork, the Rice Research Development Institute in Sri Lanka and the Department of Agriculture, Myanmar and Julius Kühn-Institute, Germany for institutional support. Furthermore, we thank Dana Rüster, Nina Król, Evelin Brumme and Judith Reusch for the excellent technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gutiérrez, R.; Shalit, T.; Markus, B.; Yuan, C.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Elad, D.; Harrus, S. Bartonella kosoyi sp. nov. and Bartonella krasnovii sp. nov., two novel species closely related to the zoonotic Bartonella elizabethae, isolated from black rats and wild desert rodent-fleas. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulouis, H.-J.; Chao-Chin, C.; Henn, J.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Chomel, B.B. Factors associated with the rapid emergence of zoonotic Bartonella infections. Vet. Res. 2005, 36, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, R.; Krasnov, B.R.; Morick, D.; Gottlieb, Y.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Harrus, S. Bartonella infection in rodents and their flea ectoparasites: An overview. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divari, S.; Pregel, P.; Zanet, S.; Ferroglio, E.; Giannini, F.; Scaglione, F.; Grinberg, A.; Biolatti, B.; Bollo, E. PCR detection of Bartonella spp. in rats (Rattus rattus) and mice (Apodemus spp.) of Pianosa Island, Italy. J. Comp. Pathol. 2019, 166, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, M.; Bai, Y. Bartonella bacteria in urban rats: A Movement from the jungles of southeast Asia to metropoles around the globe. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.E.; Neuman, M.A. Bartonella spp. as emerging human pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B.; Boulouis, H.-J.; Maruyama, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella spp. in Pets and effect on human health. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanavong, S.; Fournier, P.-E.; Chu, V.; Frichitthavong, K.; Kesone, P.; Mayxay, M.; Mirabel, M.; Newton, P.N. Bartonella henselae Endocarditis in Laos—The Unsought Will Go Undetected. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.; Fung, C.P.; Lee, N.; Shieh, W.B. Cat-scratch disease caused by Bartonella henselae: The first case report in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1998, 97, 569–572. [Google Scholar]
- Kosoy, M.; Peruski, L.F.; Maloney, S.A.; Boonmar, S.; Sitdhirasdr, A.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Baggett, H.; Morway, C.; Bai, Y.; Sheff, K.; et al. Identification of Bartonella infections in febrile human patients from thailand and their potential animal reservoirs. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.C.; Ghersi, B.M.; Alda, F.; Firth, C.; Frye, M.J.; Bai, Y.; Osikowicz, L.M. Riegel, rodent-borne Bartonella infection varies according to host species within and among cities. EcoHealth 2017, 14, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzinger. Myanmar (Birma)—Grunddaten, Geographie, Bevölkerung. 2021. Available online: http://www.munzinger.de/document/03000BUR010 (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Irrigation. Second Short Term Five Year Agriculture Policies and Strategic Thrusts. Ministy of Agriculture: Naypyidaw, Myanmar, 2017. Available online: https://www.moali.gov.mm/en/content/about-ministry (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Kudo, T. Industrial Development in Myanmar: Prospects and Challenges; Institute of Developing Economies Japan External Trade Organization: Chiba, Japan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Munzinger. Sri Lanka—Grunddaten, Geographie, Bevölkerung. Available online: http://www.munzinger.de/document/03000LKA010 (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Plecher, H. Employment by economic sector in Sri Lanka 2019. In The Statistic Shows the Distribution of Employment in Sri Lanka by Economic Sector from 2009 to 2019. In 2019, 24.52 Percent of the Employees in Sri Lanka Were Active in the Agricultural Sector, 29.66 Percent in Industry and 45.83 Percent in the Service Sector. Sri Lanka: Distribution of Employment by Economic Sector from 2009 to 2019; Statista: Hamburg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aplin, K.P.; Brown, P.R.; Jacob, J.; Krebs, C.J.; Singleton, G.R. Field Methods for Rodent Studies in Asia and the Indo-Pacific; Australian Center for International Agriculture Research: Canberra, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Inoue, K.; Kabeya, H.; Sato, S.; Takada, T.; Pangjai, D.; Chiu, S.-H.; Fujita, H.; Kawabata, H.; Takada, N. Prevalence and diversity of Bartonella species in wild small mammals in Asia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Kabeya, H.; Breiman, R.F.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Sheff, K.W.; Montgomery, S.P.; Kosoy, M.Y. Bartonella strains in small mammals from Dhaka, Bangladesh, related to Bartonella in America and Europe. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, B.; Kosoy, M.Y.; Maupin, G.O.; Tsuchiya, K.R.; Gage, K.L. Genetic and ecologic characteristics of Bartonella communities in rodents in southern China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 66, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, G.-W.; Yao, M.-L.; Luo, W.; Su, L.-Q. Study on the prevalence and genotypes of Bartonella species in rodent hosts from Fujian coastal regions. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2009, 30, 989–992. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, E.; Khamphoukeo, K.; Grice, D.; Newton, P.N.; Roux, V.; Aplin, K.; Raoult, D.; Rolain, J.M. Molecular detection of Bartonella species in rodents from the Lao PDR. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gundi, V.A.K.B.; Kosoy, M.Y.; Myint, K.S.A.; Shrestha, S.K.; Shrestha, M.P.; Pavlin, J.A.; Gibbons, R.V. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Bartonella species detected in different tissues of small mammals in Nepal. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 8247–8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tay, S.T.; Mokhtar, A.S.; Low, K.C.; Zain, S.N.M. Isolation and molecular identification of Bartonellae from wild rats (Rattus Species) in Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiyipong, T.; Jittapalapong, S.; Morand, S.; Raoult, D.; Rolain, J.-M. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Bartonella spp. in small mammals from Southeastern Asia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8463–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Sanogo, O.Y.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Zeaiter, Z.; Chauvancy, G.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Miller, R.S.; Telford, S.R.; Wongsrichanalai, C.; Raoult, D. Identification of Rickettsia spp. And Bartonella spp. in Fleas from the Thai-Myanmar Border. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 990, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, E.C.; Chomel, B.B.; Singhasivanon, O.-U.; Namekata, D.Y.; Kasten, R.W.; Kass, P.H.; Cortés-Vecino, J.A.; Gennari, S.M.; Rajapakse, R.P.; Huong, L.T.; et al. Bartonella infection in urban and rural dogs from the tropics: Brazil, Colombia, Sri Lanka and Vietnam. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 141, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisbrod, A.; Dunn, L. Township Report; International Grow Centre: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ACAPS. Myanmar: Floods in Bago Region; ACAPS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://www.acaps.org/sites/acaps/files/products/files/20180910_acaps_start_briefing_note_floods_in_myanmar.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- San, A.M.; Hamada, Y. Reproductive Seasonality of Myanmar Long-tailed Macaque (Macaca fascicularis aurea). Trop. Nat. Hist. 2009, 9, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Urban Development Authority Ministry of Megapolis and Western Development. Polonnaruwa Urban Development Plan 2019–2030; Urban Development Authority Ministry of Megapolis and Western Development: Battaramulla, Sri Lanka, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Census and Statistics. Sri Lanka Labour Force Survey Annual Report—2018; Department of Census & Statistic: Battaramulla, Sri Lanka, 2019; ISBN 978-955-702-141-6. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Census and Statistics. Sri Lanka Labour Force Survey Annual Report—2019; Department of Census & Statistic: Battaramulla, Sri Lanka, 2019; ISBN 978-955-702-187-4. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, C.; Weatherhead, E.; Knox, J.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J. Predicting the impacts of climate change—A case study of paddy irrigation water requirements in Sri Lanka. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 93, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyo, M.H.; Siriwardana, R.S.; Vincent, S.; Lionel, M.; Grant, R.; Singleton, J.J. Rodent communities and rodent damage in rice fields and storage facilities in Sri Lanka. Crop. Prot. in review.
- Norman, A.F.; Regnery, R.; Jameson, P.; Greene, C.; Krause, D.C. Differentiation of Bartonella-like isolates at the species level by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism in the citrate synthase gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, R.G.; Chomel, B.; Hegarty, B.C.; Henn, J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. A Bartonella vinsonii berkhoffii typing scheme based upon 16S–23S ITS and Pap31 sequences from dog, coyote, gray fox, and human isolates. Mol. Cell. Probes 2006, 20, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosoy, M.Y.; Jones, D.C.; Green, D.; Marston, E.L.; Childs, J.E.; Regnery, R.L.; Tzianabos, T.; Olson, J.G.; Maupin, G.O. Distribution, diversity, and host specificity of bartonella in rodents from the Southeastern United States. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colborn, J.M.; Kosoy, M.Y.; Motin, V.L.; Telepnev, M.V.; Valbuena, G.; Myint, K.S.; Fofanov, Y.; Putonti, C.; Feng, C.; Peruski, L. Improved Detection of Bartonella DNA in mammalian hosts and arthropod vectors by real-time PCR using the NADH dehydrogenase gamma subunit (nuoG). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4630–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clopper, C.J.; Pearson, E.S. The Use of confidence or fiducial limits illustrated in the case of the binomial. Biometrika 1934, 26, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnham, K.J.; Roy, S.S.; Seymour, A.; Mauremootoo, J.; Jones, C.G.; Harris, S. Eradicating Indian Musk Shrews (Suncus Murinus, Soricidae) from Mauritian Offshore Islands. In Turning the Tide the Eradication of Invasive Species; Veitch, C.R., Clout, M.N., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland; Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 342–349. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, S.; Kikuchi, F.; Bawm, S.; Sơn, N.T.; Lin, K.S.; Tú, V.T.; Aoki, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Tanaka-Taya, K.; Morikawa, S.; et al. Molecular Phylogeny of Mobat viruses (Hantaviridae) in Myanmar and Vietnam. Viruses 2019, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoriano, A.F.B.; Smythe, L.D.; Gloriani-Barzaga, N.; Cavinta, L.L.; Kasai, T.; Limpakarnjanarat, K.; Ong, B.L.; Gongal, G.; Hall, J.; Coulombe, C.A.; et al. Leptospirosis in the Asia Pacific region. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W. Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome. In The Bunyaviridae; Ellion, R.M., Plyusnin, A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mdangi, M.; Mulungu, L.; Massawe, A.; Eiseb, S.; Tutjavi, V.; Kirsten, F.; Mahlaba, T.; Malebane, P.; Von Maltitz, E.; Monadjem, A.; et al. Assessment of rodent damage to stored maize (Zea mays L.) on smallholder farms in Tanzania. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2013, 59, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.L.; Chen, C.J.; Yen, T.S.; Lien, J.C.; Yang, C.S. Seroepidemiology of Hantaan virus infection in Taiwan. J. Med. Virol. 1996, 50, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwell, M.R.; Ward, G.S.; Tingpalapong, M.A.; LeDuc, J.W. Serologic evidence of Hantaan-like virus in rodents and man in Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1985, 16, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.D.; Quy, D.V.; Gibson, F.L.; Dung, T.C.; Cavanaugh, D.C.; Quv, D.V. Ecology of Plague in Vietnam, I. Role of Suncus murinus. Exp. Biol. Med. 1967, 124, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubyanskiy, V.M.; Yeszhanov, A.B. Ecology of Yersinia pestis and the epidemiology of plague. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 918, 101–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasdell, K.R.; Bordes, F.; Chaisiri, K.; Chaval, Y.; Claude, J.; Cosson, J.-F.; Latinne, A.; Michaux, J.; Morand, S.; Pagès, M.; et al. Progress on research on rodents and rodent-borne zoonoses in South-east Asia. Wildl. Res. 2015, 42, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Dehio, C. Role of distinct type-IV-secretion systems and secreted effector sets in host adaptation by pathogenic Bartonella species. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, M.; Khan, S.; Eager, H.; Atkulwar, A.; Searle, J.B. Phylogeography of the black rat Rattus rattus in India and the implications for its dispersal history in Eurasia. Biol. Invasions 2018, 21, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Yanes, E.; Martin-Alonso, A.; Martin-Carrillo, N.; Livia, K.G.; Marrero-Gagliardi, A.; Valladares, B.; Feliu, C.; Foronda, P. Bartonella in Rodents and Ectoparasites in the Canary Islands, Spain: New Insights into Host-Vector-Pathogen Relationships. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 75, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-L.; Chang, C.-C.; Chuang, S.-T.; Chomel, B.B. Bartonella species and their ectoparasites: Selective host adaptation or strain selection between the vector and the mammalian host? Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 34, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, D.P.; Bown, K.J.; Stockley, P.; Hurst, J.L.; Bennett, M.; Birtles, R.J. Haemoparasites of common shrews (Sorex araneus) in Northwest England. Parasitology 2007, 134, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.-W.; Tung, K.-C.; Chen, W.-C.; Lin, J.-W.; Chien, L.-J.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Wang, H.-C.; Chomel, B.B.; Chang, C.-C. Epidemiology of Bartonella infection in rodents and shrews in Taiwan. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamani, J.; Morick, D.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Harrus, S. Prevalence and diversity of Bartonella Species in commensal rodents and ectoparasites from Nigeria, West Africa. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliday, J.E.B.; Knobel, D.L.; Agwanda, B.; Bai, Y.; Breiman, R.F.; Cleaveland, S.; Njenga, M.K.; Kosoy, M. Prevalence and Diversity of Small Mammal-Associated Bartonella Species in Rural and Urban Kenya. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasdell, K.R.; Perera, D.; Firth, C. High prevalence of rodent-borne Bartonella spp. in urbanizing environments in Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schülein, R.; Seubert, A.; Gille, C.; Lanz, C.; Hansmann, Y.; Piémont, Y.; Dehio, C. Invasion and persistent intracellular colonization of erythrocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, M.; Mandel, E.; Green, D.; Marston, E.; Childs, J. Prospective studies of Bartonella of rodents. Part, I. Demographic and temporal patterns in population dynamics. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2004, 4, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewska, A.; Harris, P.D.; Zwolińska, L.; Bajer, A.; Siński, E. Differences in the ecology of Bartonella infections of Apodemus flavicollis and Myodes glareolusin a boreal forest. Parasitology 2012, 139, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morway, C.; Kosoy, M.; Eisen, R.; Montenieri, J.; Sheff, K.; Reynolds, P.J.; Powers, N. A longitudinal study of Bartonella infection in populations of woodrats and their fleas. J. Vector Ecol. 2008, 33, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiyipong, T.; Morand, S.; Jittapalapong, S.; Rolain, J.-M. Bartonella spp. infections in Rodents of Cambodia, Lao PDR, and Thailand: Identifying Risky Habitats. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, M.; Mandel, E.; Green, D.; Marston, E.; Jones, D.; Childs, J. Prospective studies of Bartonella of rodents. Part II. Diverse infections in a single rodent community. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2004, 4, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Maruyama, S.; Kabeya, H.; Yamada, N.; Ohashi, N.; Sato, Y.; Yukawa, M.; Masuzawa, T.; Kawamori, F.; Kadosaka, T.; et al. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Bartonella species isolated from wild rodents in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5086–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gutiérrez, R.; Cohen, C.; Flatau, R.; Marcos-Hadad, E.; Garrido, M.; Halle, S.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Covo, S.; Hawlena, H.; Harrus, S. Untangling the knots: Co-infection and diversity of Bartonella from wild gerbils and their associated fleas. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 4787–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.-L.; Kass, P.H.; Chang, C.-C.; Chomel, B.B.; Chuang, S.-T. Bartonella species in small mammals and their ectoparasites in Taiwan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Zhu, C.; Wu, Y.; Pan, X.; Hua, X. Bacteriological and molecular identification of Bartonella species in cats from different regions of China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assarasakorn, S.; Veir, J.; Hawley, J.; Brewer, M.; Morris, A.; Hill, A.; Lappin, M. Prevalence of Bartonella species, hemoplasmas, and Rickettsia felis DNA in blood and fleas of cats in Bangkok, Thailand. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.; Poapolathep, A.; Morita, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Chang, C.C.; Sakai, T.; Kasten, R.W.; Boonmar, S.; Chalarmchaikit, T.; Katsube, Y.; et al. Prevalence of Bartonella species and 16s rRNA gene types of Bartonella henselae from domestic cats in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 65, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, B.A.; Regnery, R.L.; Beati, L.; Bacellar, F.; Rood, M.; Glass, G.G.; Marston, E.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Jones, D.; Childs, J.E. Rats of the genus Rattus are reservoir hosts for pathogenic Bartonella species: An old world origin for a new world disease? J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandelaki, G.; Malania, L.; Bai, Y.; Chakvetadze, N.; Katsitadze, G.; Imnadze, P.; Nelson, C.; Harrus, S.; Kosoy, M. Human lymphadenopathy caused by ratborne Bartonella, Tbilisi, Georgia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftis, A.D.; Reeves, W.K.; Szumlas, D.E.; Abbassy, M.M.; Helmy, I.M.; Moriarity, J.R.; Dasch, G.A. Surveillance of Egyptian fleas for agents of public health significance: Anaplasma, Bartonella, Coxiella, Ehrlichia, Rickettsia, and Yersinia pestis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 41–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundi, V.A.K.B.; Davoust, B.; Khamis, A.; Boni, M.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Isolation of Bartonella rattimassiliensis sp. nov. and Bartonella phoceensis sp. nov. from European Rattus norvegicus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3816–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Kosoy, M.Y.; Peruski, L.F.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Richardson, J.H. Prevalence and genetic heterogeneity of Bartonella strains cultured from rodents from 17 provinces in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 81, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winoto, I.L.; Goethert, H.; Ibrahim, I.N.; Yuniherlina, I.; Stoops, C.; Susanti, I.; Kania, W.; Maguire, J.D.; Bangs, M.J.; Telford, S.R., III. Bartonella species in rodents and shrews in the greater Jakarta area. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2005, 36, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Chomel, B.B.; Boulouis, H.J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Cat scratch disease and other zoonotic Bartonella infections. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helan, J.V.G.; Grinberg, A.; Gedye, K.; Potter, M.A.; Harrus, S. Molecular detection of Bartonella coopersplainsensis and B. henselae in rats from New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2018, 66, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).