A Yarrowia lipolytica Strain Engineered for Pyomelanin Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain and Plasmid Construction
2.2. Strain Sequencing and Integration Site Identification
2.3. Media and Culture Conditions
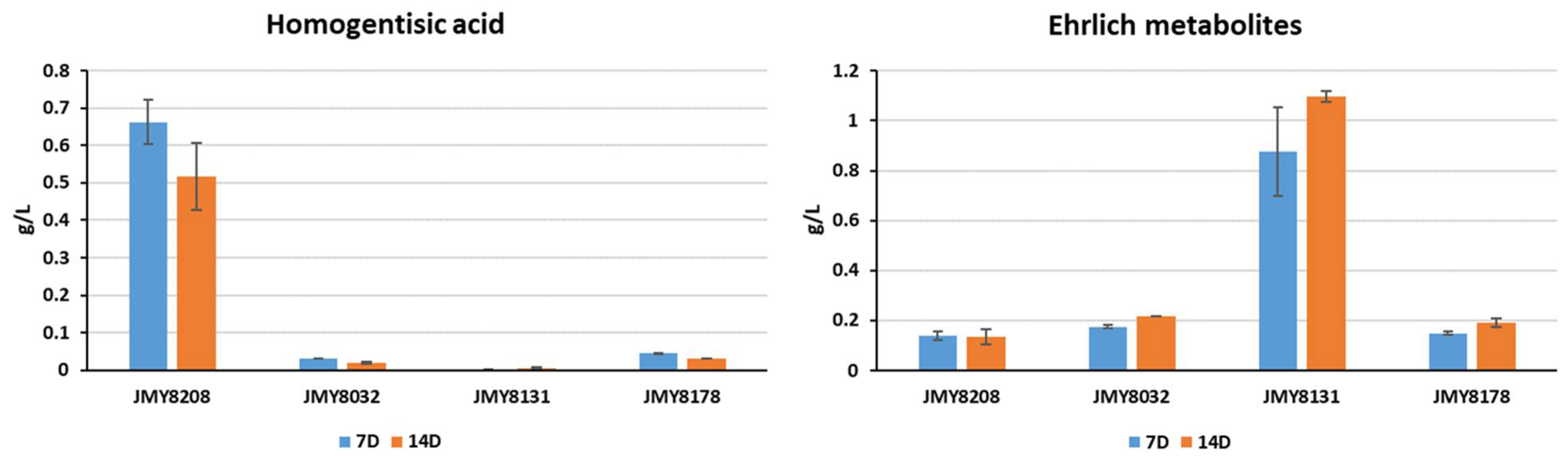
2.4. HPLC Analysis
2.5. Pyomelanin Purification
3. Results
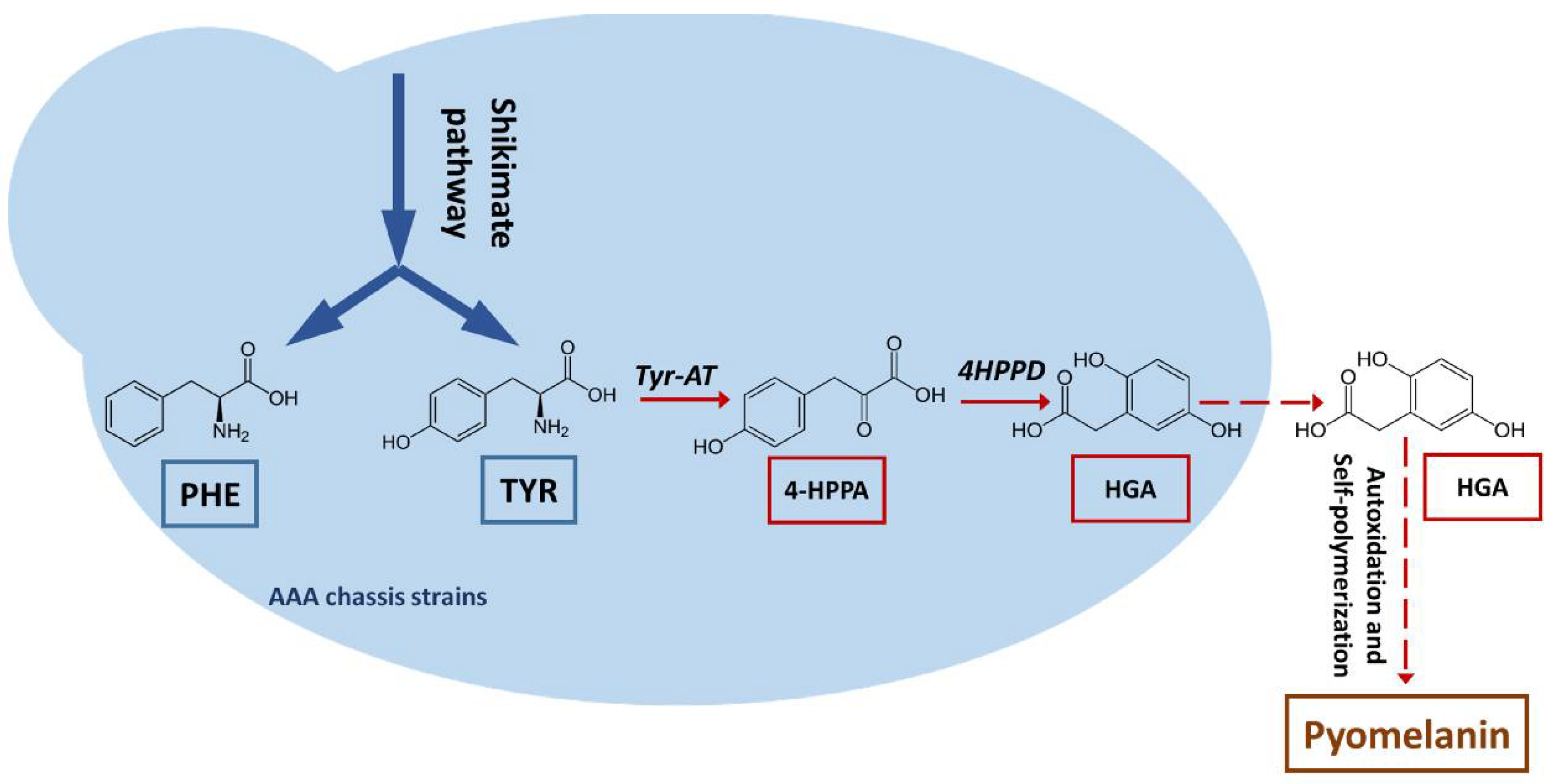
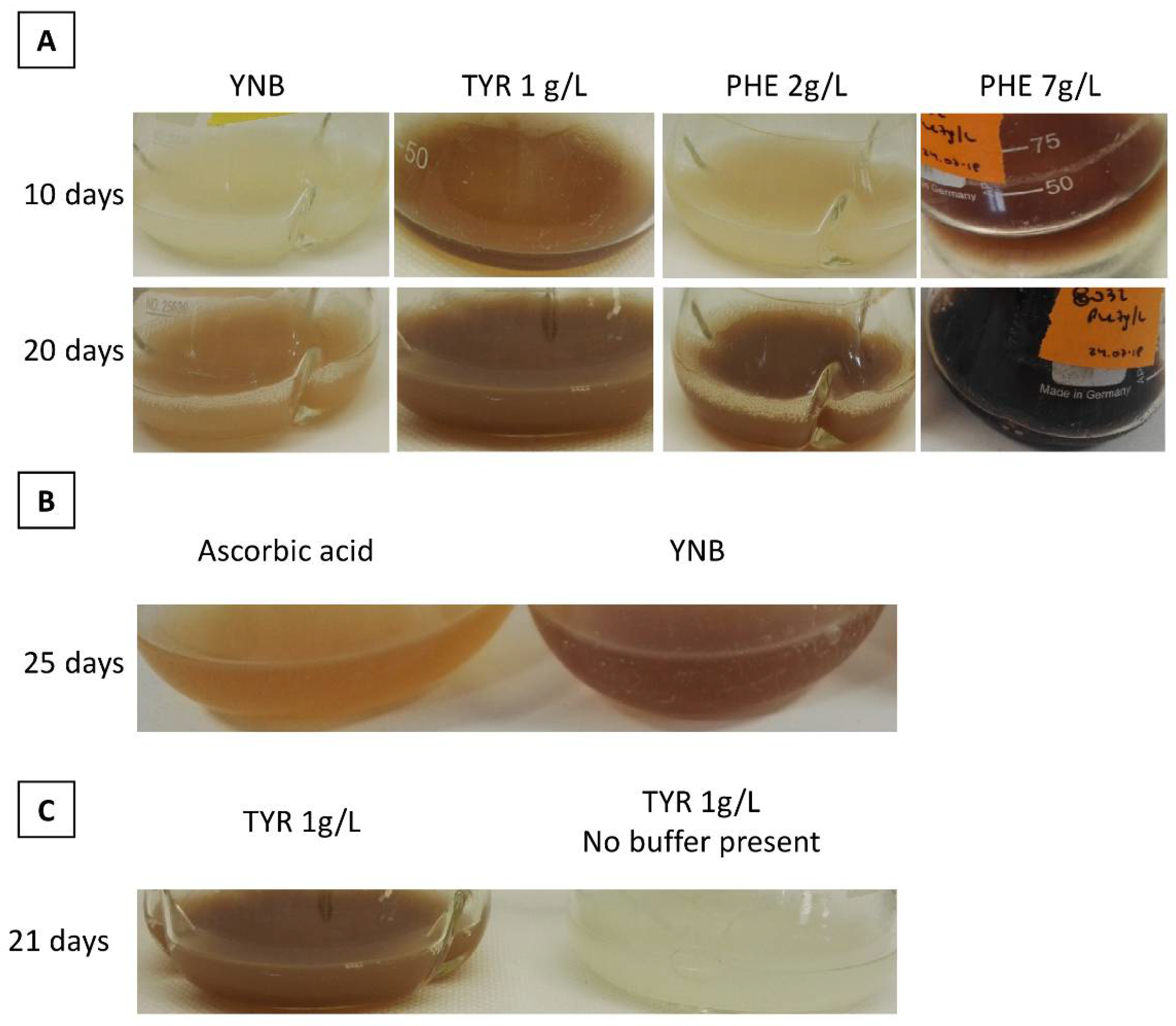
3.1. Production of a Brown Pigment by Yarrowia Lipolytica
3.2. Characterization of the Brown Pigment
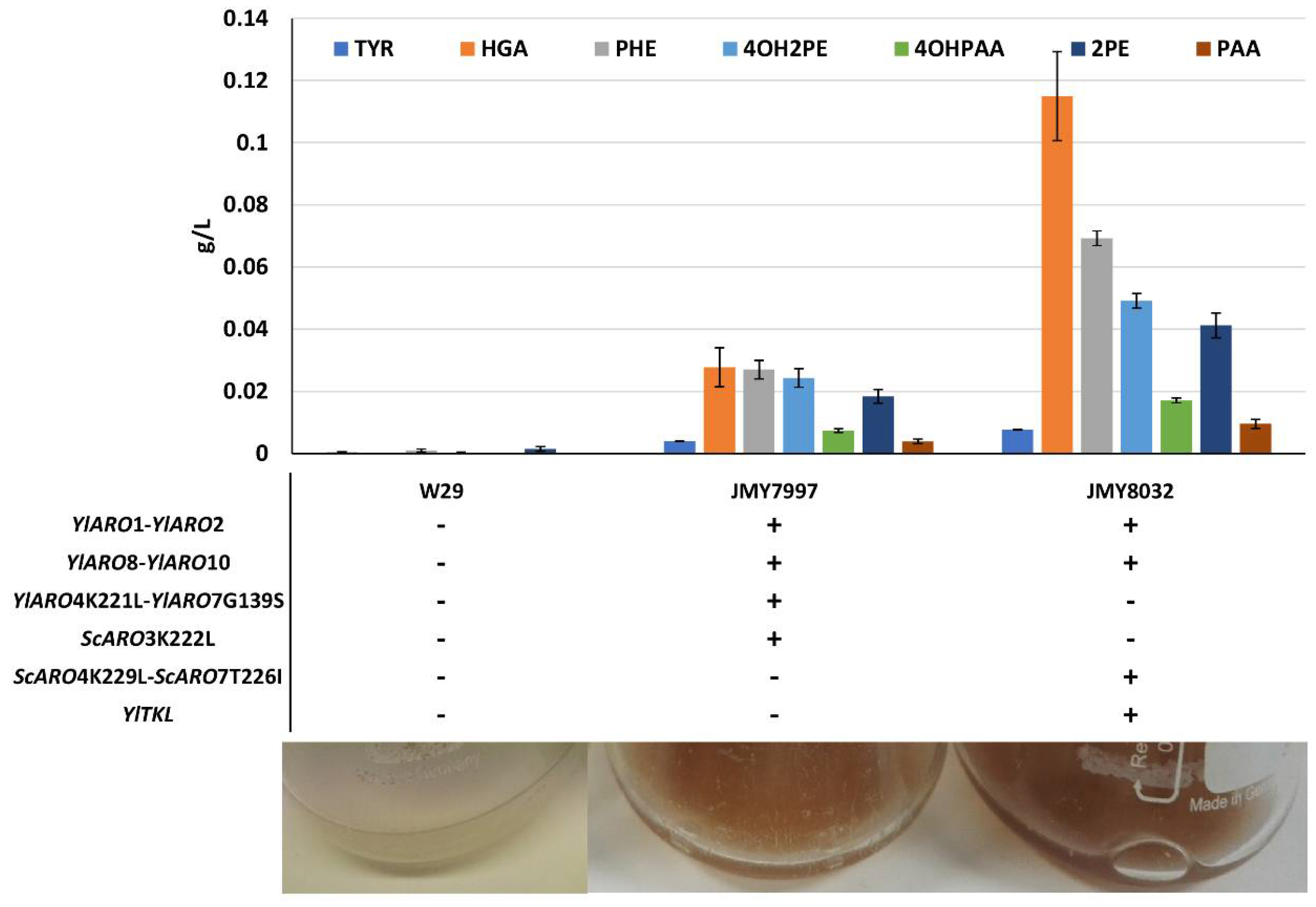
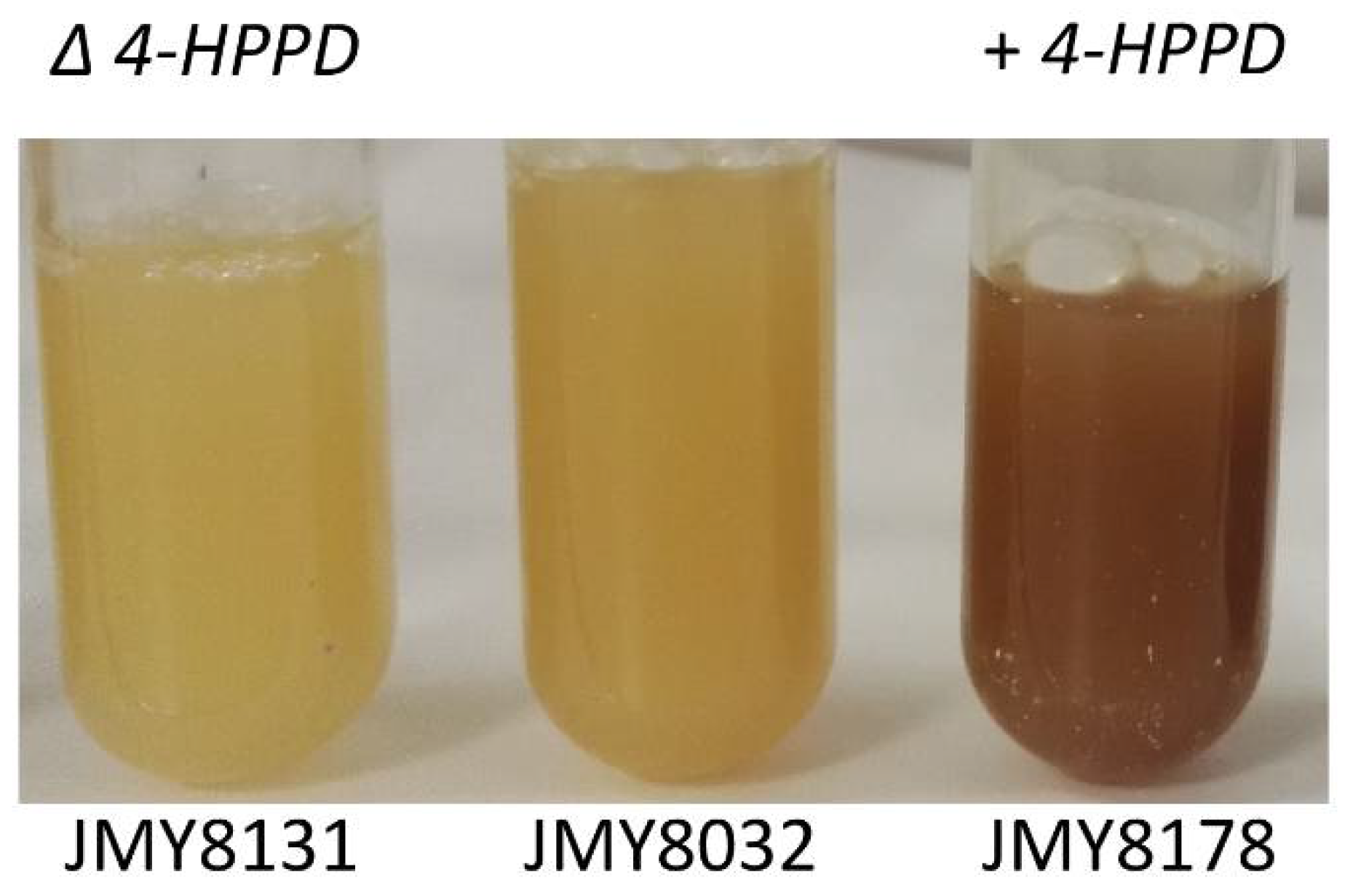
3.3. Characterization and Improvement of the Pyomelanin Production Pathway
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plonka, P.M.; Grabacka, M. Melanin synthesis in microorganisms--biotechnological and medical aspects. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2006, 53, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-M.; Liu, J.-H.; Hsu, H.-W.; Lin, H.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y. Mechanical and photo-fragmentation processes for nanonization of melanin to improve its efficacy in protecting cells from reactive oxygen species stress. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 064701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elobeid, A.S.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Abdelhalim, M.A.K.; Haseeb, A.M. Pharmacological Properties of Melanin and its Function in Health. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 120, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solano, F. Melanin and Melanin-Related Polymers as Materials with Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications—Cuttlefish Ink and Mussel Foot Proteins as Inspired Biomolecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.-Y.; Choi, M.; Jeong, D.-W.; Park, S.; Park, H.; Jang, K.-S.; Choi, K.-Y. Synthesis and chemical composition analysis of protocatechualdehyde-based novel melanin dye by 15T FT-ICR: High dyeing performance on soft contact lens. Dyes Pigments 2019, 160, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Wu, W.; Chun, S.-E.; Whitacre, J.F.; Bettinger, C.J. Biologically derived melanin electrodes in aqueous sodium-ion energy storage devices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20912–20917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bothma, J.P.; De Boor, J.; Divakar, U.; Schwenn, P.E.; Meredith, P. Device-Quality Electrically Conducting Melanin Thin Films. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3539–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, Y.A.G. Uptake of Radionuclides by Some Fungi. Mycobiology 2004, 32, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, M.; Girme, G.; Bankar, A.; Ravikumar, A.; Zinjarde, S. 3, 4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine-derived melanin from Yarrowia lipolytica mediates the synthesis of silver and gold nanostructures. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiran, G.S.; Dhasayan, A.; Lipton, A.N.; Selvin, J.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A. Melanin-templated rapid synthesis of silver nanostructures. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, L.M.; Martinez, A.; Gosset, G. Production of Melanins with Recombinant Microorganisms. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Rao, Z.; Yang, T.; Man, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.-T. Cloning and identification of a novel tyrosinase and its overexpression in Streptomyces kathirae SC-1 for enhancing melanin production. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carreira, A.; Ferreira, L.; Loureiro, V. Production of brown tyrosine pigments by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, A.; Paloma, L.; Loureiro, V. Pigment producing yeasts involved in the brown surface discoloration of ewes’ cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 41, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, A.; Ferreira, L.M.; Loureiro, V. Brown Pigments Produced by Yarrowia lipolytica Result from Extracellular Accumulation of Homogentisic Acid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3463–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben Tahar, I.; Fickers, P.; Dziedzic, A.; Płoch, D.; Skóra, B.; Kus-Liśkiewicz, M. Green pyomelanin-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Modelling and design, physico-chemical and biological characteristics. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Inouhe, M.; Tohoyama, H.; Joho, M. Characteristics of copper tolerance in Yarrowia lipolytica. BioMetals 2006, 20, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, M.; Sambre, D.; Gaikawad, S.; Joshi, S.; Bankar, A.; Kumar, A.R.; Zinjarde, S. Psychrotrophic yeast Yarrowia lipolytica NCYC 789 mediates the synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles via cell-associated melanin. AMB Express 2013, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larroude, M.; Nicaud, J.; Rossignol, T. Yarrowia lipolytica chassis strains engineered to produce aromatic amino acids via the shikimate pathway. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larroude, M.; Park, Y.; Soudier, P.; Kubiak, M.; Nicaud, J.; Rossignol, T. A modular Golden Gate toolkit for Yarrowia lipolytica synthetic biology. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carly, F.; Vandermies, M.; Telek, S.; Steels, S.; Thomas, S.; Nicaud, J.-M.; Fickers, P. Enhancing erythritol productivity in Yarrowia lipolytica using metabolic engineering. Metab. Eng. 2017, 42, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fickers, P.; Le Dall, M.; Gaillardin, C.; Thonart, P.; Nicaud, J. New disruption cassettes for rapid gene disruption and marker rescue in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 55, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larroude, M.; Trabelsi, H.; Nicaud, J.-M.; Rossignol, T. A set of Yarrowia lipolytica CRISPR/Cas9 vectors for exploiting wild-type strain diversity. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Dall, M.T.; Nicaud, J.M.; Gaillardin, C. Multiple-copy integration in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Curr. Genet. 1994, 26, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, G.; Gaillardin, C. Yarrowia lipolytica. In Non-Conventional Yeasts in Biotechnology; Wolf, K., Breuning, K.D., Barth, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996; pp. 313–388. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. Subgroup GPDP. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Tahar, I.; Kus-Liśkiewicz, M.; Lara, Y.; Javaux, E.; Fickers, P. Characterization of a nontoxic pyomelanin pigment produced by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol. Prog. 2020, 36, e2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turick, C.E.; Knox, A.S.; Becnel, J.M.; Ekechukwu, A.A.; Milliken, C.E. Properties and Function of Pyomelanin. In Biopolymers; Elnashar, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben-David, Y.; Zlotnik, E.; Zander, I.; Yerushalmi, G.; Shoshani, S.; Banin, E. SawR a new regulator controlling pyomelanin synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 206, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Ruan, L.; Tao, J.; Peng, D.; Zheng, J.; Sun, M. Single Amino Acid Substitution in Homogentisate Dioxygenase Affects Melanin Production in Bacillus thuringiensis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, C.; Holz, M.; Barth, G. Production of Organic Acids by Yarrowia lipolytica. In Yarrowia lipolytica: Biotechnological Applications; Barth, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 25, pp. 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Wang, Y.; Qian, M.; Chen, X.; Hu, X. Preparation and Properties of the Melanin from Lachnum singerianum. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 11, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Schmaler-Ripcke, J.; Sugareva, V.; Gebhardt, P.; Winkler, R.; Kniemeyer, O.; Heinekamp, T.; Brakhage, A.A. Production of Pyomelanin, a Second Type of Melanin, via the Tyrosine Degradation Pathway in Aspergillus fumigatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 75, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flydal, M.I.; Martinez, A. Phenylalanine hydroxylase: Function, structure, and regulation. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Yarrowia lipolytica Strains Used in This Study | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Genotype | Auxotrophy | Reference |
| JMY195, Po1d | MATA ura3-302 leu2-270 xpr2-322 | Ura−, Leu− | [25] |
| JMY7997 | Po1d + LEU2ex-YlARO1-YlARO2 + URA3ex-YlARO4K221L-YlARO7G139S + HPHex-ScARO3K222L + NATex-YlARO8-YlARO10 | Prototroph | This study |
| JMY8032 | Po1d + URA3ex-YlARO1-YlARO2 + LEU2ex(recovered)ScARO4K229L-ScARO7T226I + LEU2ex-YlTKL+ NATex-YlARO8-YlARO10 | Prototroph | [19] |
| JMY8107 | JMY8032 with LEU2ex and NATex marker recovered | Leu− | This study |
| JMY8131 | JMY8107 Δ-4hppd | Prototroph | This study |
| JMY8178 | JMY8032 + HPHex-Yl4HPPD | Prototroph | This study |
| JMY8208 | JMY8032 + (HPHex-Yl4HPPD) multicopies | Prototroph | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larroude, M.; Onésime, D.; Rué, O.; Nicaud, J.-M.; Rossignol, T. A Yarrowia lipolytica Strain Engineered for Pyomelanin Production. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040838
Larroude M, Onésime D, Rué O, Nicaud J-M, Rossignol T. A Yarrowia lipolytica Strain Engineered for Pyomelanin Production. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(4):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040838
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarroude, Macarena, Djamila Onésime, Olivier Rué, Jean-Marc Nicaud, and Tristan Rossignol. 2021. "A Yarrowia lipolytica Strain Engineered for Pyomelanin Production" Microorganisms 9, no. 4: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040838
APA StyleLarroude, M., Onésime, D., Rué, O., Nicaud, J.-M., & Rossignol, T. (2021). A Yarrowia lipolytica Strain Engineered for Pyomelanin Production. Microorganisms, 9(4), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040838






