Characterization of Two New Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O103-Infecting Phages Isolated from an Organic Farm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Bacteriophage Isolation and Purification
2.3. Biological Characteristics
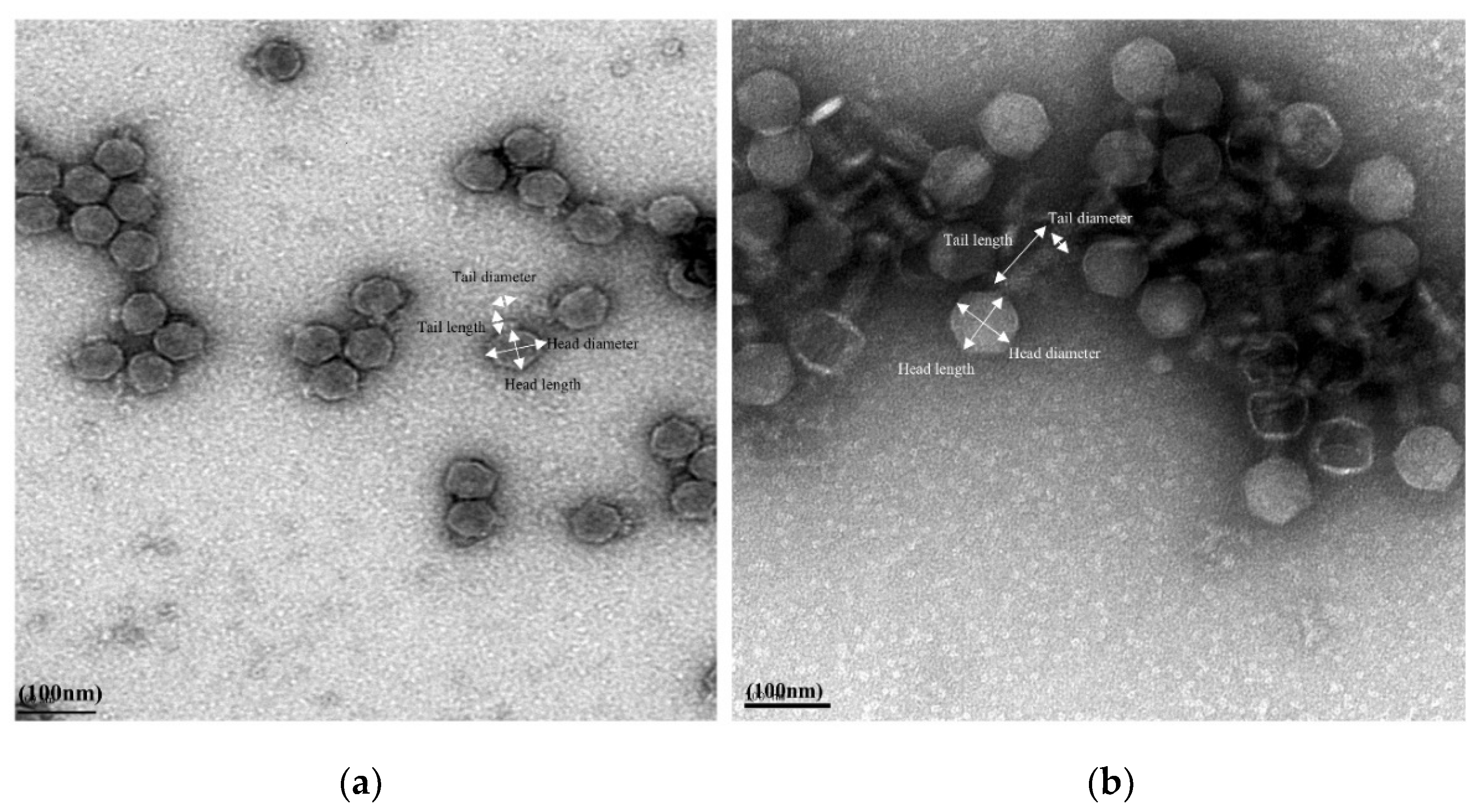
2.3.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.3.2. One-Step Growth Curves
2.4. Antimicrobial Activities
2.4.1. Host Range
2.4.2. Bacterial Challenge Assay
2.5. Genomic Characteristics
2.5.1. Phage DNA Extraction and Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.5.2. Comparative Analysis
2.5.3. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Biological Characterization of Phages
3.2. Host Range of the Phages
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity against STEC O103 Pathogens
3.4. General Genomic Characterization
3.5. Comparative Analysis of Phage Ro103C3lw
3.6. Comparative Analysis of Phage Pr103Blw
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mushegian, A.R. Are there 1031 virus particles on earth, or more, or fewer? J. Bacteriol. 2020, 202, e00052-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrojo, A.; Alcamí, A. Aquatic viral metagenomics: Lights and shadows. Virus Res. 2017, 239, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clokie, M.R.J.; Millard, A.D.; Letarov, A.V.; Heaphy, S. Phages in nature. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T. (Ed.) Bacteriophage Ecology: Population Growth, Evolution, and Impact of Bacterial Viruses; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Erez, Z.; Steinberger-Levy, I.; Shamir, M.; Doron, S.; Stokar-Avihail, A.; Peleg, Y.; Melamed, S.; Leavitt, A.; Savidor, A.; Albeck, S.; et al. Communication between viruses guides lysis-lysogeny decisions. Nature 2017, 541, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paepe, M.; Leclerc, M.; Tinsley, C.R.; Petit, M.A. Bacteriophages: An underestimated role in human and animal health? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.W.; Suttle, C.A. Viruses and Nutrient Cycles in the Sea: Viruses play critical roles in the structure and function of aquatic food webs. Bioscience 1999, 49, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedrick, R.M.; Guerrero-Bustamante, C.A.; Garlena, R.A.; Russell, D.A.; Ford, K.; Harris, K.; Gilmour, K.C.; Soothill, J.; Jacobs-Sera, D.; Schooley, R.T.; et al. Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolesnikova, S.G.; Tulyakova, E.N.; Moiseeva, I.Y. Phage therapy: Present and future. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 784, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodridge, L.D.; Bisha, B. Phage-based biocontrol strategies to reduce foodborne pathogens in foods. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T. Bacteriophages of Ralstonia solanacearum: Their Diversity and Utilization as Biocontrol Agents in Agriculture. In Bacteriophages; Kurtboke, I., Ed.; In Tech-Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 113–138. [Google Scholar]
- Karunasagar, I.; Shivu, M.M.; Girisha, S.K.; Krohne, G.; Karunasagar, I. Biocontrol of pathogens in shrimp hatcheries using bacteriophages. Aquaculture 2007, 268, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W. Pathogenesis and diagnosis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 450–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC National Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) Surveillance. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nationalsurveillance/ecoli-surveillance.html (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- CDC Multistate Outbreak of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infections Linked to Leafy Greens (Final Update). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ecoli/2017/o157h7-12-17/index.html (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- CDC, Outbreak of E. coli Infections Linked to Ground Beef. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ecoli/2019/o103-04-19/index.html (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- CDC, Outbreak of E. coli Infections Linked to Clover Sprouts. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ecoli/2020/o103h2-02-20/index.html (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Mylius, M.; Dreesman, J.; Pulz, M.; Pallasch, G.; Beyrer, K.; Claußen, K.; Allerberger, F.; Fruth, A.; Lang, C.; Prager, R.; et al. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O103:H2 outbreak in Germany after school trip to Austria due to raw cow milk, 2017—The important role of international collaboration for outbreak investigations. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruth, A.; Prager, R.; Tietze, E.; Rabsch, W.; Flieger, A. Molecular epidemiological view on Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli causing human disease in Germany: Diversity, prevalence, and outbreaks. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, D.; Gu, A.Z.; Zeng, S.; He, M. Bacterial regrowth in water reclamation and distribution systems revealed by viable bacterial detection assays. Chemosphere. 2016, 144, 2165–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, M.T.; Marine, S.C.; Everts, K.L.; Micallef, S.A. Drip line flushing with chlorine may not be effective in reducing bacterial loads in irrigation water distribution systems. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichel, N.; Vivar, M.; Fuentes, M. The problem of drinking water access: A review of disinfection technologies with an emphasis on solar treatment methods. Chemosphere. 2019, 218, 1014–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazi, M.; Annapure, U.S. Bacteriophage biocontrol of foodborne pathogens. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.N.; Abuladze, T.; Li, M.; Woolston, J.; Sulakvelidze, A. Bacteriophage cocktail significantly reduces or eliminates Listeria monocytogenes contamination on lettuce, apples, cheese, smoked salmon and frozen foods. Food Microbiol. 2015, 52, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhard, R.G.; Kalinowski, R.M.; Bodnaruk, P.W.; Eifert, J.D.; Boyer, R.R.; Duncan, S.E.; Bailey, R.H. Fate of Listeria on various food contact and noncontact surfaces when treated with bacteriophage. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitiemwong, N.; Hazeleger, W.C.; Beumer, R.R. Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes by disinfectants and bacteriophages in suspension and stainless steel carrier tests. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Patel, J.R.; Conway, W.S.; Ferguson, S.; Sulakvelidze, A. Effectiveness of bacteriophages in reducing Escherichia coli O157:H7 on fresh-cut cantaloupes and lettuce. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.; LaBossiere, B.; Switt, A.I.M.; Delaquis, P.; Goodridge, L.; Levesque, R.C.; Danyluk, M.D.; Wang, S. Characterization of four novel bacteriophages isolated from British Columbia for control of non-typhoidal Salmonella in vitro and on sprouting alfalfa seeds. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, H.T.P. Phage-induced diversification improves host evolvability. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.H.; Park, M.K. Recent trends in Salmonella outbreaks and emerging technology for biocontrol of Salmonella using phages in foods: A review. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 2075–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Flynn, G.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Coffey, A. Evaluation of a cocktail of three bacteriophages for biocontrol of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3417–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudva, I.T.; Jelacic, S.; Tarr, P.I.; Youderian, P.; Hovde, C.J. Biocontrol of Escherichia coli O157 with O157-specific bacteriophages. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3767–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarillas, L.; Chaidez, C.; González-Robles, A.; Lugo-Melchor, Y.; León-Félix, J. Characterization of novel bacteriophage phiC119 capable of lysing multidrugresistant Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Niu, Y.D.; Stanford, K.; Kropinski, A.M.; Ackermann, H.W.; Johnson, R.P.; She, Y.M.; Ahmed, R.; Villegas, A.; McAllister, T.A. Genomic, proteomic and physiological characterization of a T5-like bacteriophage for control of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.-T.; Salvador, A.; Harden, L.A.; Liu, F.; Lavenburg, V.M.; Li, R.W.; Wu, V.C.H. Characterization of a lytic bacteriophage as an antimicrobial agent for biocontrol of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O145 strains. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.-T.; Lavenburg, V.M.; Lennon, M.; Salvador, A.; Hsu, A.L.; Wu, V.C.H. The effects of environmental factors on the prevalence and diversity of bacteriophages lytic against the top six non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli on an organic farm. J. Food Saf. 2020, e12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-T.; Sun, X.; Quintela, I.A.; Bridges, D.F.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Salvador, A.; Wu, V.C.H. Discovery of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC)-Specific Bacteriophages from Non-fecal Composts Using Genomic Characterization. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, Y.T.; Salvador, A.; Sun, X.; Wu, V.C. Complete genome sequence of a Shiga toxin-converting bacteriophage, Escherichia phage Lys12581Vzw, induced from an outbreak Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strain. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00793-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.; Krueger, F.; Seconds-Pichon, A.; Biggins, F.; Wingett, S. FastQC. A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; Babraham Bioinformatics, Babraham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garneau, J.R.; Depardieu, F.; Fortier, L.C.; Bikard, D.; Monot, M. PhageTerm: A tool for fast and accurate determination of phage termini and packaging mechanism using next-generation sequencing data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinheinz, K.A.; Joensen, K.G.; Larsen, M.V. Applying the ResFinder and VirulenceFinder web-services for easy identification of acquired antibiotic resistance and E. coli virulence genes in bacteriophage and prophage nucleotide sequences. Bacteriophage 2014, 4, e27943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lund, O.; Hasman, H.; Kaas, R.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Real-time whole-genome sequencing for routine typing, surveillance, and outbreak detection of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, E.M.; Rodney Brister, J. How to name and classify your phage: An informal guide. Viruses 2017, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, J.E.; Magadán, A.H.; Sabri, M.; Moineau, S. Revenge of the phages: Defeating bacterial defences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedon, S.T.; Hyman, P.; Thomas, C. Experimental Examination of Bacteriophage Latent-Period Evolution as a Response to Bacterial Availability. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 7499–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T.; Herschler, T.D.; Stopar, D. Bacteriophage Latent-Period Evolution as a Response to Resource Availability. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4233–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R. Phage lysis: Three steps, three choices, one outcome. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, S.; Rousseau, G.M.; Labrie, S.J.; Tremblay, D.M.; Kourda, R.S.; Slama, K.B.; Moineau, S. Characterization of two polyvalent phages infecting Enterobacteriaceae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, E.J.; Berry, J.; Tran, T.A.T.; Niu, L.; Struck, D.K.; Young, R. Rz/Rz1 Lysis Gene Equivalents in Phages of Gram-negative Hosts. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 73, 1098–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajsík, M.; Oslanecová, L.; Szemes, T.; Hýblová, M.; Bilková, A.; Drahovská, H.; Turňa, J. Characterization and genome sequence of Dev2, a new T7-like bacteriophage infecting Cronobacter turicensis. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 3013–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, P.L.; Roecklein, J.A.; SenGupta, D.; Fields, S. A protein linkage map of Escherichia coli bacteriophage T7. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Kang, C. Lysis Delay and Burst Shrinkage of Coliphage T7 by Deletion of Terminator T Reversed by Deletion of Early Genes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drulis-Kawa, Z.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Maciejewska, B. Bacteriophages and Phage-Derived Proteins—Application Approaches. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 1757–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.P.; Oliveira, H.; Melo, L.D.R.; Sillankorva, S.; Azeredo, J. Bacteriophage-encoded depolymerases: Their diversity and biotechnological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, A.; Ceyssens, P.J.; T’Syen, J.; van Praet, H.; Noben, J.P.; Shaburova, O.V.; Krylov, V.N.; Volckaert, G.; Lavigne, R. The t7-related pseudomonas putida phage φ15 displays virion-associated biofilm degradation properties. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, D.R.; Parracho, H.M.R.T.; Walker, J.; Sharp, R.; Hughes, G.; Werthén, M.; Lehman, S.; Morales, S. Bacteriophages and biofilms. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, L.E.; Veljkovic, M.; Fieseler, L. Diversity and Function of Phage Encoded Depolymerases. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Olia, A.S.; Cingolani, G. Architecture of viral genome-delivery molecular machines. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stummeyer, K.; Schwarzer, D.; Claus, H.; Vogel, U.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; Mühlenhoff, M. Evolution of bacteriophages infecting encapsulated bacteria: Lessons from Escherichia coli K1-specific phages. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, Y.; Fieseler, L.; Klumpp, J.; Eugster, M.R.; Zurfluh, K.; Duffy, B.; Loessner, M.J. The tail-associated depolymerase of Erwinia amylovora phage L1 mediates host cell adsorption and enzymatic capsule removal, which can enhance infection by other phage. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2168–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Paff, M.L.; Molineux, I.J.; Bull, J.J. Therapeutic application of phage capsule depolymerases against K1, K5, and K30 capsulated E. coli in mice. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, J.; Yan, G.; Lei, L.; Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Zhou, L.; Gao, A.; Feng, X.; Han, W.; et al. Identification and characterization of Dpo42, a novel depolymerase derived from the Escherichia coli phage vB_EcoM_ECOO78. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korf, I.H.E.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Kropinski, A.M.; Nimtz, M.; Rohde, M.; van Raaij, M.J.; Wittmann, J. Still something to discover: Novel insights into Escherichia coli phage diversity and taxonomy. Viruses 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumunang, E.W.; McAllister, T.A.; Stanford, K.; Anany, H.; Niu, Y.D.; Ateba, C.N. Characterization of non-O157 STEC infecting bacteriophages isolated from cattle faeces in North-West South Africa. Microorganisms. 2019, 7, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkowitz, E.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Orton, R.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Smith, D.B. Virus taxonomy: The database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D708–D717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobrega, F.L.; Vlot, M.; de Jonge, P.A.; Dreesens, L.L.; Beaumont, H.J.E.; Lavigne, R.; Dutilh, B.E.; Brouns, S.J.J. Targeting mechanisms of tailed bacteriophages. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedon, S.T. Phage therapy dosing: The problem(s) with multiplicity of infection (MOI). Bacteriophage 2016, 6, e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Q.; Mai, G.; Yang, J.; Deng, D.; Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y. In Vitro design and evaluation of phage cocktails against Aeromonas salmonicida. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrie, S.J.; Samson, J.E.; Moineau, S. Bacteriophage resistance mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strotskaya, A.; Savitskaya, E.; Metlitskaya, A.; Morozova, N.; Datsenko, K.A.; Semenova, E.; Severinov, K. The action of Escherichia coli CRISPR-Cas system on lytic bacteriophages with different lifestyles and development strategies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, R.H.; Madsen, L.; Dalsgaard, I.; Castillo, D.; Kalatzis, P.G.; Middelboe, M. Effect of Bacteriophages on the Growth of Flavobacterium psychrophilum and Development of Phage-Resistant Strains. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middelboe, M. Bacterial growth rate and marine virus-host dynamics. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 40, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, S.; Vicente, A.C. Global in-silico scenario of tRNA genes and their organization in virus genomes. Viruses 2019, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly-Bechet, M.; Vergassola, M.; Rocha, E. Causes for the intriguing presence of tRNAs in phages. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Alvi, I.A.; Tabassum, R.; Rehman, S.U. TAC1, an unclassified bacteriophage of the family Myoviridae infecting Acinetobacter baumannii with a large burst size and a short latent period. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whichard, J.M.; Weigt, L.A.; Borris, D.J.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; Kapur, V.; William Pierson, F.; Lingohr, E.J.; She, Y.M.; Kropinski, A.M.; et al. Complete genomic sequence of Bacteriophage Felix O1. Viruses 2010, 2, 710–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Host Panel | Serogroups | Bacterial Isolates | Phage | Bacterial Sources # | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ro103C3lw | Pr103Blw | ||||
| Generic E. coli | O157 | ATCC 43888 | − * | − | human feces |
| ATCC 13706 | − | − | n/a | ||
| DH5α | ++ | + | n/a | ||
| STEC | O26 | STEC O26:H- (RM18132) | − | +++ | water |
| O26 | STEC O26:H- (RM17133) | − | + | water | |
| O45 | STEC O45:H- (RM10729) | − | − | cattle | |
| O45 | STEC O45:H16 (RM13752) | − | − | cattle | |
| O103 | STEC O103:H2 (RM13322) | +++ | +++ | cattle feces | |
| O103 | STEC O103:H2 (RM10744) | +++ | +++ | cattle feces | |
| O111 | STEC O111:H- (RM11765) | − | ++ | water | |
| O111 | STEC O111:H- (RM14488) | − | − | water | |
| O121 | STEC O121:H19 (96-1585) | − | − | human feces ø | |
| O121 | STEC O121:H- (RM8082) | − | − | cattle feces | |
| O145 | STEC O145:H- (RM10808) | − | − | cattle feces | |
| O145 | STEC O145:H+ (RM9872) | − | − | cattle feces | |
| O157 | STEC O157:H7 (RM18959) | − | + | water | |
| O157 | STEC O157:H7 (ATCC 35150) | − | + | human feces ø | |
| Salmonella | Salmonella Agona | − | − | environment | |
| Salmonella Anatum | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Berta | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Gallinarum | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Infantis | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Javiana | − | +++ | environment | ||
| Salmonella Mbandaka | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Oranienburg | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Derby 45340 | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Dublin 15480 | − | − | n/a | ||
| Salmonella Montevideo 51 | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Muenster | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Newport | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Saintpaul | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Thompson | − | − | environment | ||
| Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 14028 | − | − | chicken | ||
| Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 6962 | − | − | human feces ø | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liao, Y.-T.; Salvador, A.; Lavenburg, V.M.; Wu, V.C.H. Characterization of Two New Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O103-Infecting Phages Isolated from an Organic Farm. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071527
Zhang Y, Liao Y-T, Salvador A, Lavenburg VM, Wu VCH. Characterization of Two New Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O103-Infecting Phages Isolated from an Organic Farm. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(7):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071527
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yujie, Yen-Te Liao, Alexandra Salvador, Valerie M. Lavenburg, and Vivian C. H. Wu. 2021. "Characterization of Two New Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O103-Infecting Phages Isolated from an Organic Farm" Microorganisms 9, no. 7: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071527
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liao, Y.-T., Salvador, A., Lavenburg, V. M., & Wu, V. C. H. (2021). Characterization of Two New Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O103-Infecting Phages Isolated from an Organic Farm. Microorganisms, 9(7), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071527






