Uncovering the Worldwide Diversity and Evolution of the Virome of the Mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
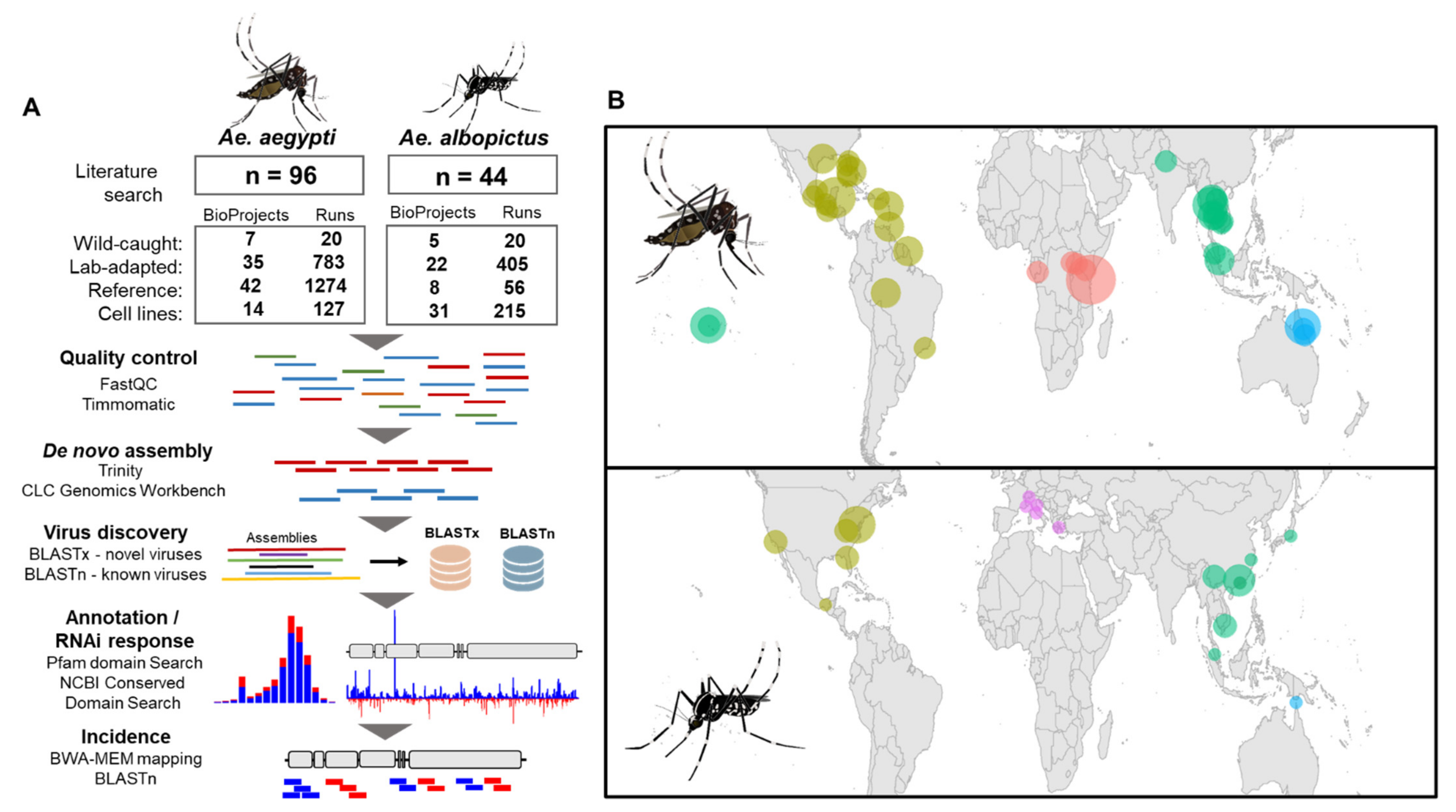
2.1. Collation of Metadata from Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus Virus Publications
2.2. Virus Discovery Pipeline
2.3. Virus Genome Annotation
2.4. Virus Coverage Statistics and Virus Incidence Heat Maps
2.5. Analysis of Virus-Derived Small RNAs in Aedes
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis of Aedes Viruses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Many Novel Viruses Are Associated with Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus Colonies and Cell Lines
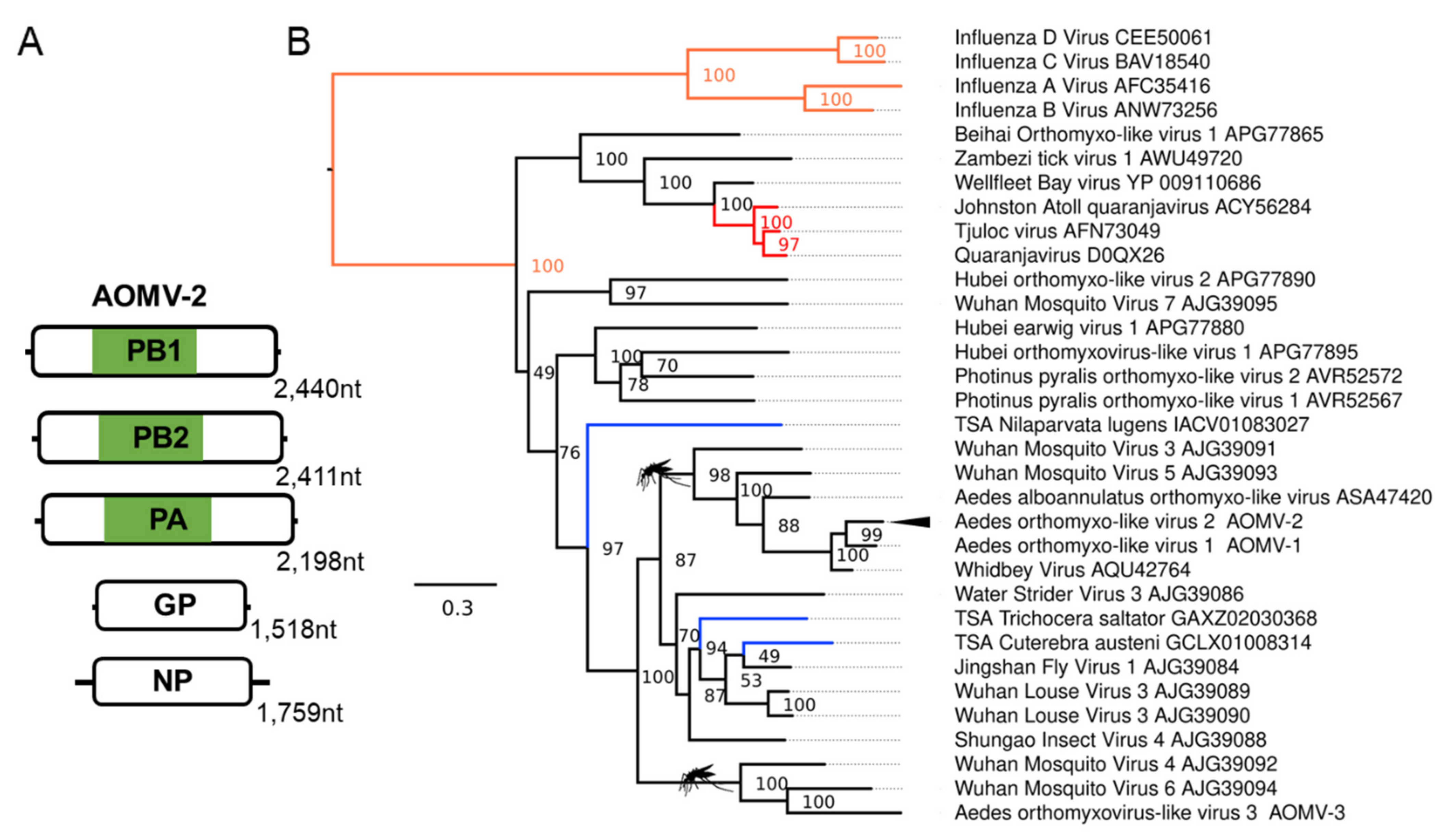
3.2. Novel Negative-Sense RNA Viruses Infecting Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus
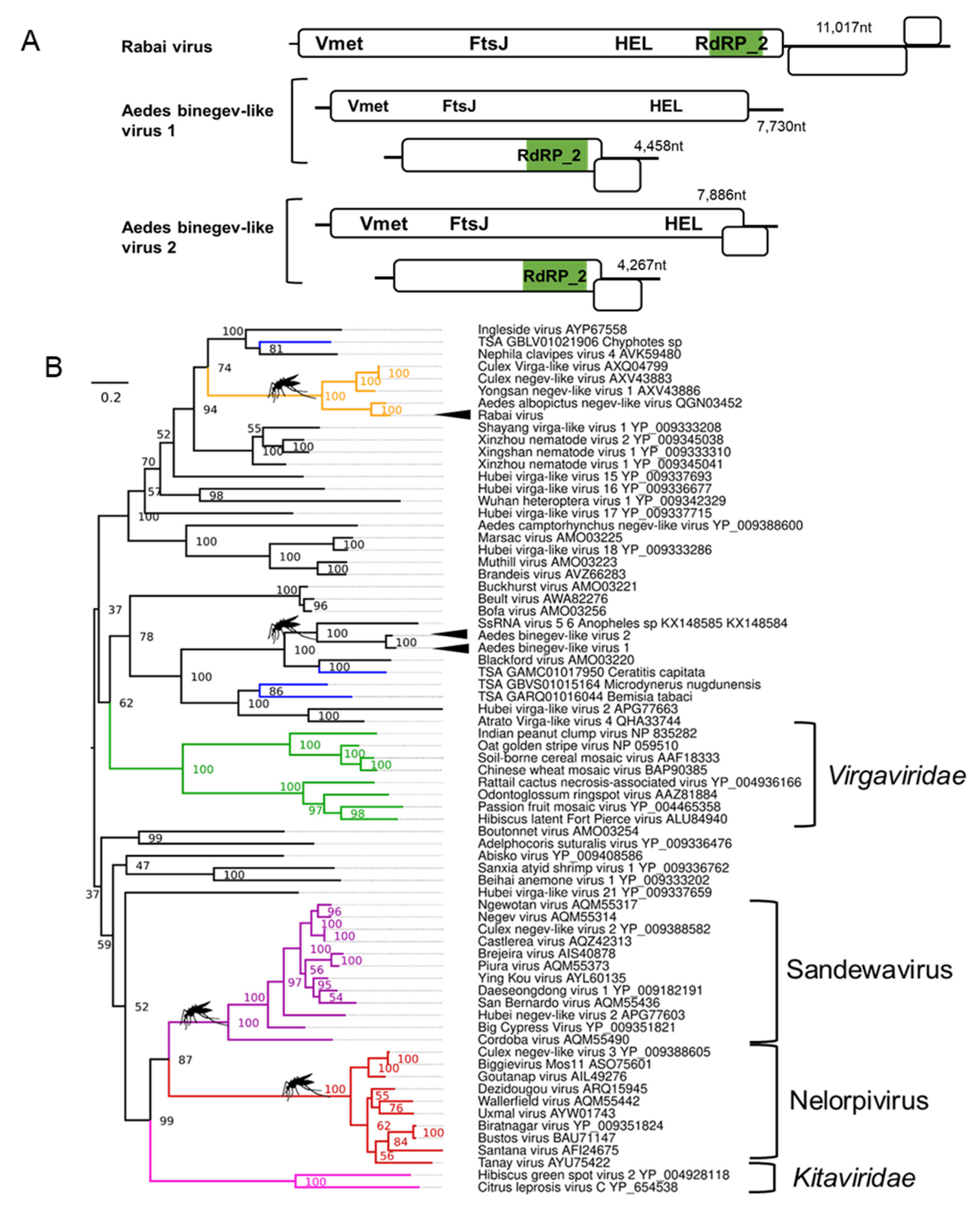
3.3. Novel Positive-Sense RNA Negev-like Viruses Infecting Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus
3.4. Binegeviruses: A Novel Negev-Related Taxon with Bi-Segmented Genomes in Aedes Mosquitoes
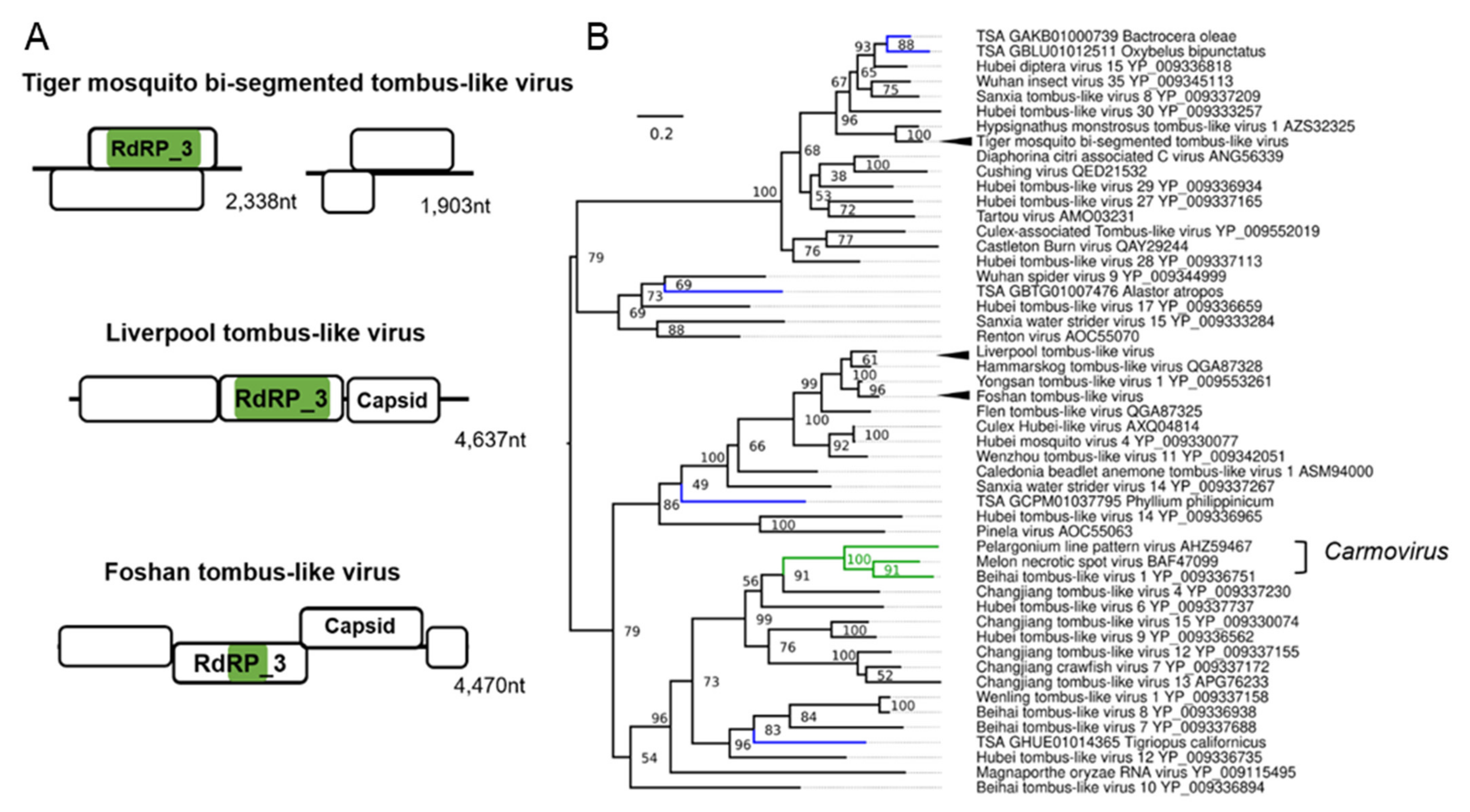
3.5. Tombus-Noda Viruses in Aedes
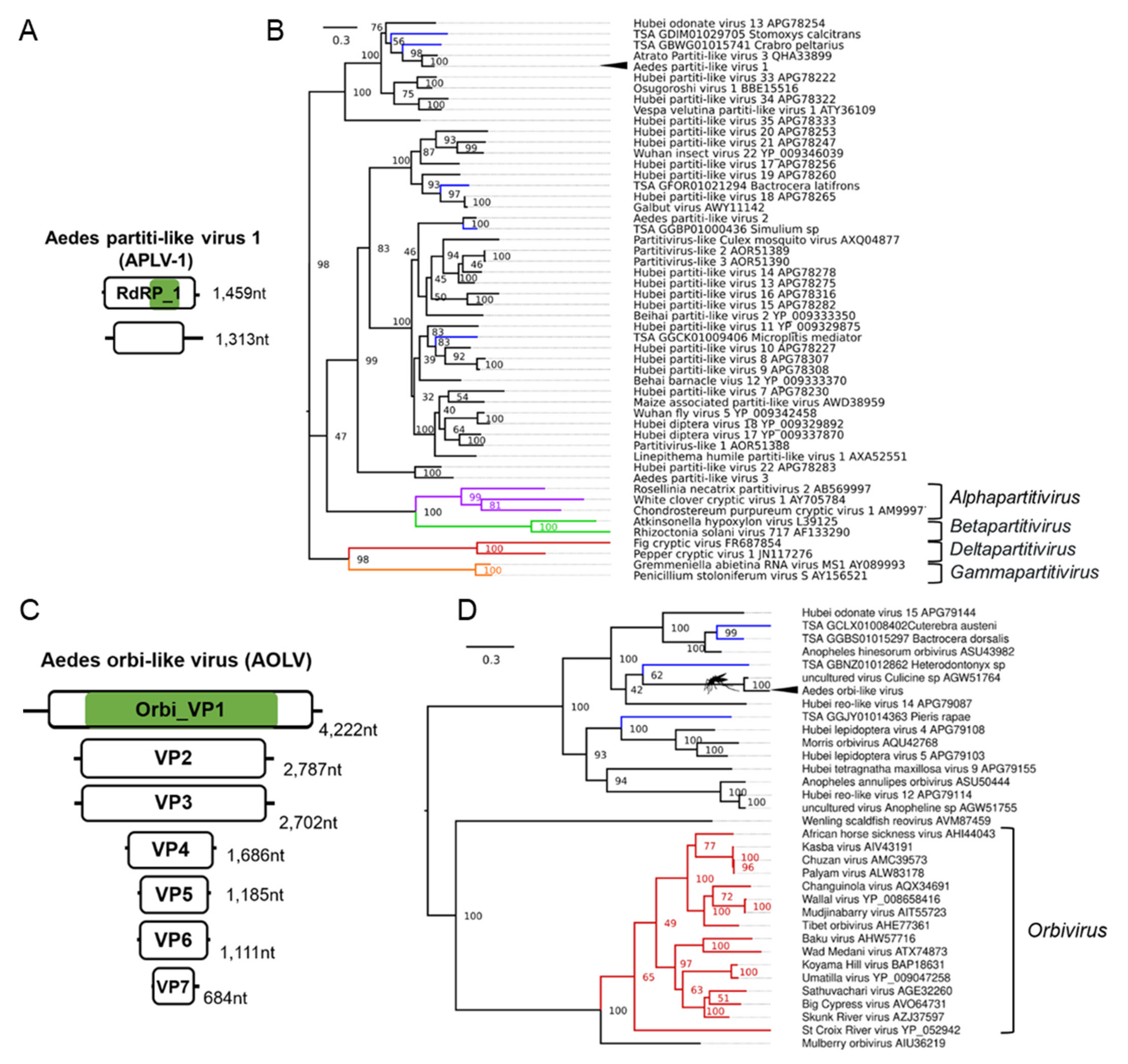
3.6. Double-Stranded RNA Viruses Infecting Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus
3.7. DNA Viruses of Aedes Mosquitoes
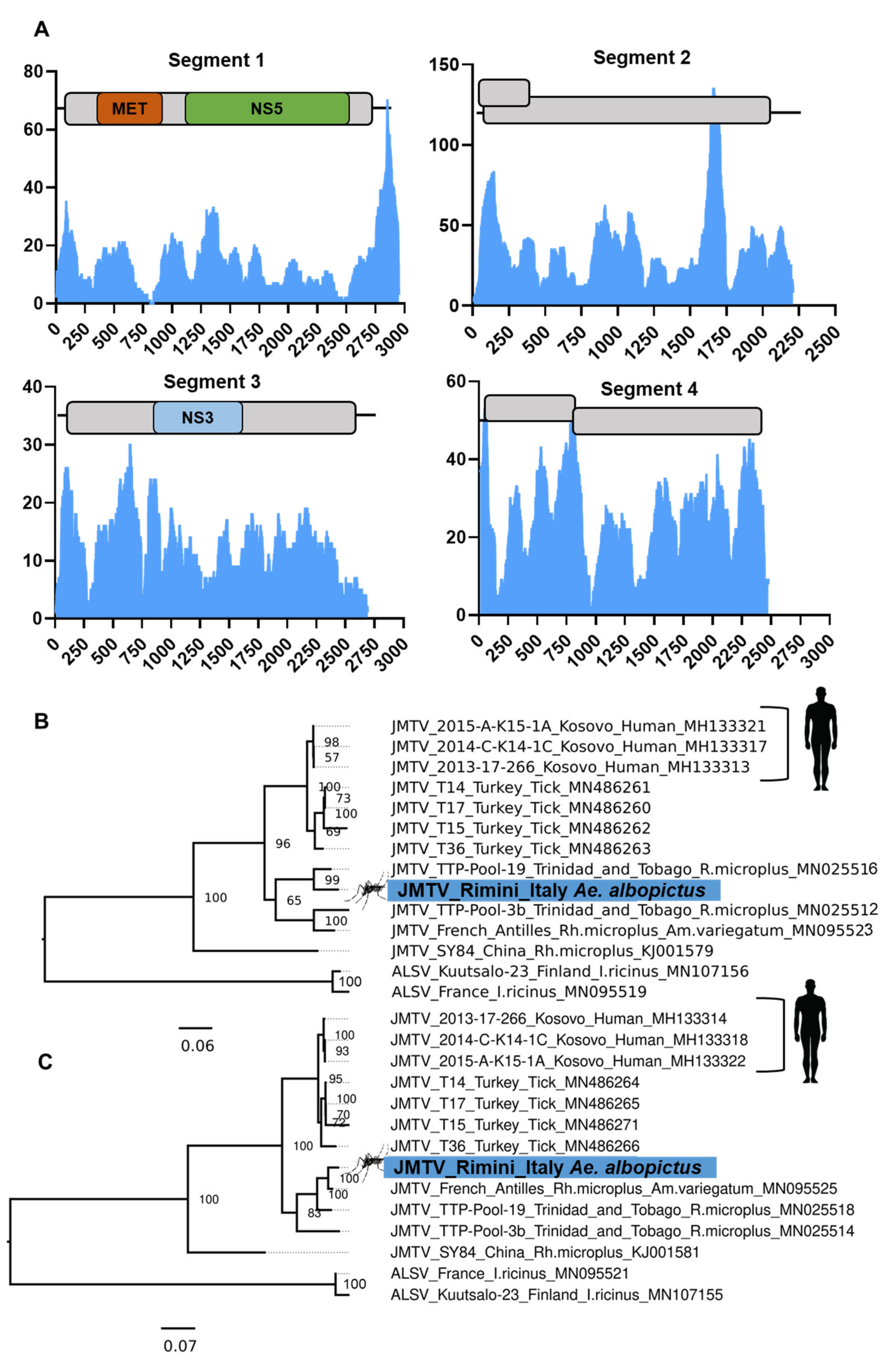
3.8. Evidence of the Jingmen Tick Virus (Flaviviridae) in an Ae. albopictus Mosquito Colony
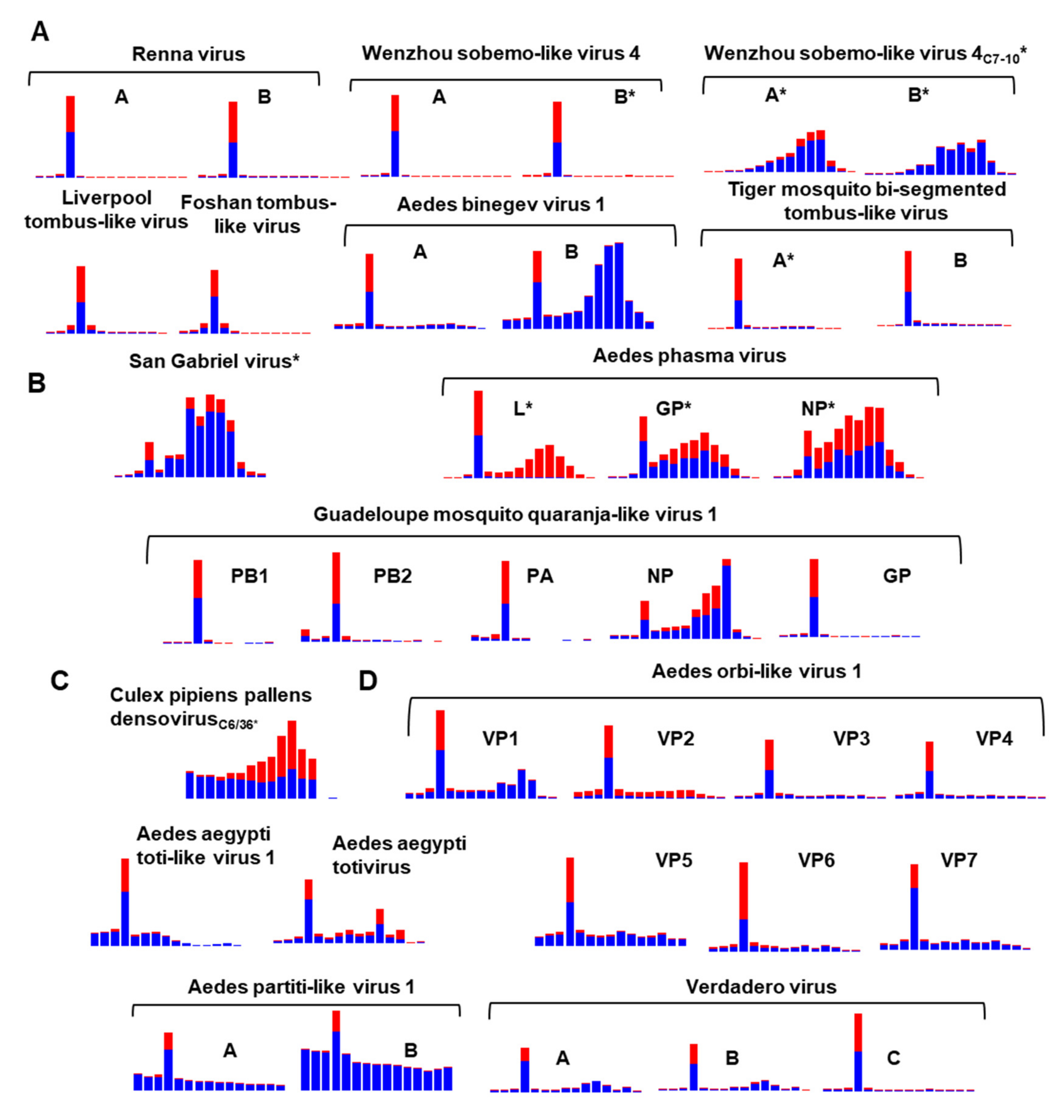
3.9. Diversity of the RNAi Response against ISVs of Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus
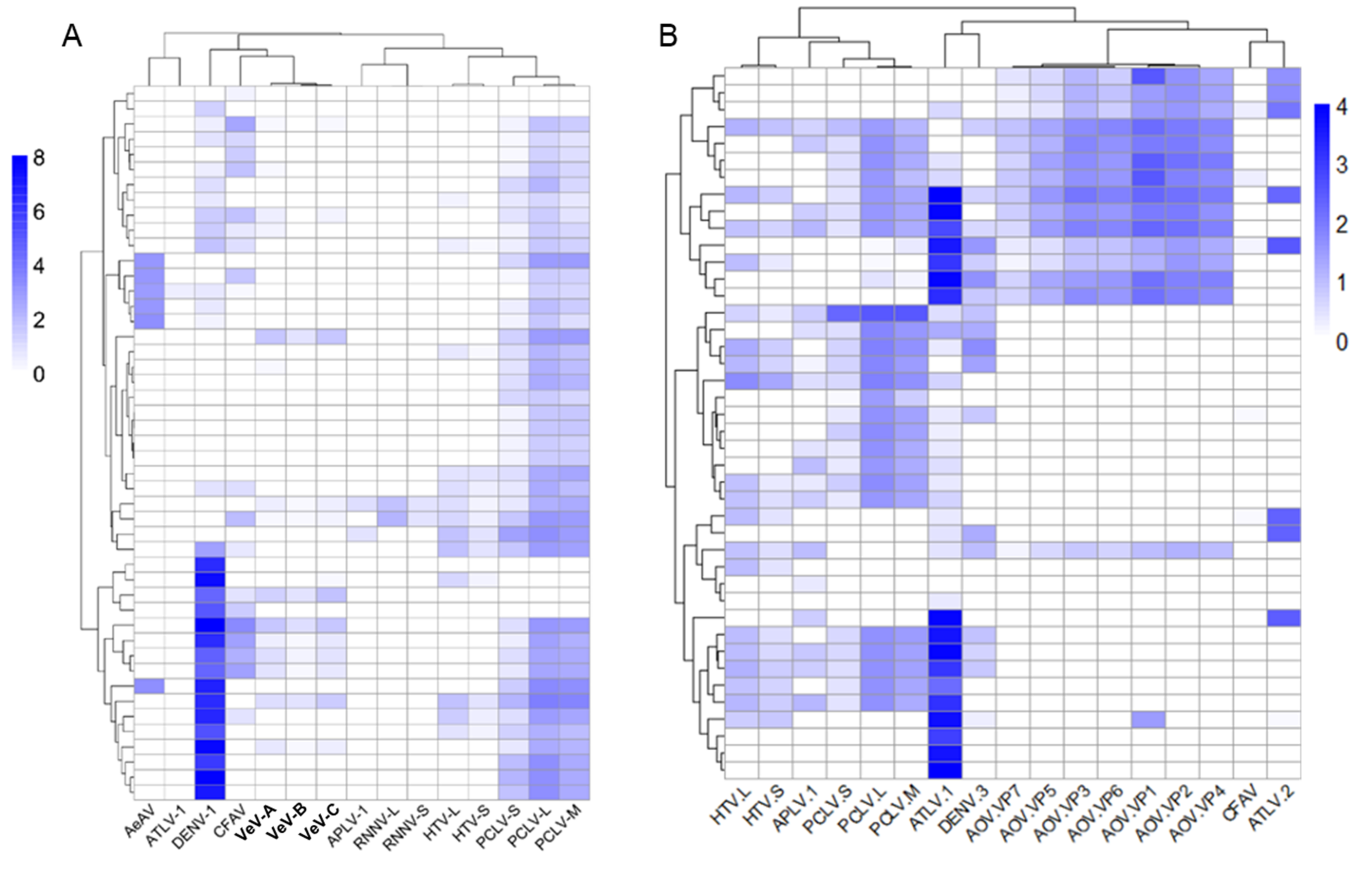
3.10. Differentially Abundant ISVs in Aedes Laboratory Colonies
3.11. Individual Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus Mosquitoes from the Same Colony Harbour Heterogeneous Virus Populations
3.12. Composition of Viruses in Commonly Used Aedes Cell Lines Reveals Super-Infection of ISVs in Wolbachia Transfected Cell Lines
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kraemer, M.U.; Sinka, M.E.; Duda, K.A.; Mylne, A.Q.; Shearer, F.M.; Barker, C.M.; Moore, C.G.; Carvalho, R.G.; Coelho, G.E.; Van Bortel, W.; et al. The global distribution of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus. eLife 2015, 4, e08347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, W.A. The biology of Aedes albopictus. J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. Suppl. 1988, 1, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kamara, F.; Zhou, G.; Puthiyakunnon, S.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, X.G. Urbanization increases Aedes albopictus larval habitats and accelerates mosquito development and survivorship. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Neto, J.A.; Powell, J.R.; Bonizzoni, M. Aedes aegypti vector competence studies: A review. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 67, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, N.G. Critical review of the vector status of Aedes albopictus. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2004, 18, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Rua, A.; Zouache, K.; Girod, R.; Failloux, A.B.; Lourenco-de-Oliveira, R. High level of vector competence of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus from ten American countries as a crucial factor in the spread of Chikungunya virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6294–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzid, M.; Colon-Gonzalez, F.J.; Lung, T.; Lake, I.R.; Hunter, P.R. Climate change and the emergence of vector-borne diseases in Europe: Case study of dengue fever. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, L.; Scott, T.W.; Gubler, D.J. Consequences of the expanding global distribution of Aedes albopictus for dengue virus transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, C.L.; Ryman, K.D. Yellow fever: A reemerging threat. Clin. Lab. Med. 2010, 30, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, D.; Gubler, D.J. Zika Virus. Clin. Microbiol Rev. 2016, 29, 487–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsky, H.C.; Matranga, C.B.; Wohl, S.; Schaffner, S.F.; Freije, C.A.; Winnicki, S.M.; West, K.; Qu, J.; Baniecki, M.L.; Gladden-Young, A.; et al. Zika virus evolution and spread in the Americas. Nature 2017, 546, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemin, J.B.; Mee, P.T.; Lynch, S.E.; Vedururu, R.; Trinidad, L.; Paradkar, P. Zika vector transmission risk in temperate Australia: A vector competence study. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monath, T.P. Yellow fever: An update. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2001, 1, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, L.D.; Ciota, A.T. Dissecting vectorial capacity for mosquito-borne viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigle, L.T.; McGraw, E.A. Expanding the canon: Non-classical mosquito genes at the interface of arboviral infection. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 109, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Rasgon, J.L.; Hughes, G.L. The microbiome modulates arbovirus transmission in mosquitoes. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, R.; Asgari, S. Aedes Anphevirus: An Insect-Specific Virus Distributed Worldwide in Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes That Has Complex Interplays with Wolbachia and Dengue Virus Infection in Cells. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00224-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Asad, S.; Khromykh, A.A.; Asgari, S. Cell fusing agent virus and dengue virus mutually interact in Aedes aegypti cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson-Peters, J.; Yam, A.W.; Lu, J.W.; Setoh, Y.X.; May, F.J.; Kurucz, N.; Walsh, S.; Prow, N.A.; Davis, S.S.; Weir, R.; et al. A new insect-specific flavivirus from northern Australia suppresses replication of West Nile virus and Murray Valley encephalitis virus in co-infected mosquito cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Mendelin, S.; McLean, B.J.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Hall, R.A.; van den Hurk, A.F. The insect-specific Palm Creek virus modulates West Nile virus infection in and transmission by Australian mosquitoes. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasar, F.; Erasmus, J.H.; Haddow, A.D.; Tesh, R.B.; Weaver, S.C. Eilat virus induces both homologous and heterologous interference. Virology 2015, 484, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidaliuk, A.; Miot, E.F.; Lequime, S.; Moltini-Conclois, I.; Delaigue, F.; Dabo, S.; Dickson, L.B.; Aubry, F.; Merkling, S.H.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; et al. Cell-Fusing Agent Virus Reduces Arbovirus Dissemination in Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes In Vivo. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00705-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, R.; Kato, F.; Kobayashi, D.; Murota, K.; Takasaki, T.; Tajima, S.; Lim, C.K.; Saijo, M.; Isawa, H.; Sawabe, K. Persistent viruses in mosquito cultured cell line suppress multiplication of flaviviruses. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosimann, A.L.; Bordignon, J.; Mazzarotto, G.C.; Motta, M.C.; Hoffmann, F.; Santos, C.N. Genetic and biological characterization of a densovirus isolate that affects dengue virus infection. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2011, 106, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.J.; Frydman, H.M.; Connor, J.H. Dual Insect specific virus infection limits Arbovirus replication in Aedes mosquito cells. Virology 2018, 518, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Neville, P.; Nicholson, J.; Eden, J.S.; Imrie, A.; Holmes, E.C. High-Resolution Metatranscriptomics Reveals the Ecological Dynamics of Mosquito-Associated RNA Viruses in Western Australia. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00680-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.L.; Waldron, F.M.; Robertson, S.; Crowson, D.; Ferrari, G.; Quintana, J.F.; Brouqui, J.M.; Bayne, E.H.; Longdon, B.; Buck, A.H.; et al. The Discovery, Distribution, and Evolution of Viruses Associated with Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauver, J.R.; Akter, S.; Morales, A.I.O.; Black, W.C.T.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Stenglein, M.D.; Ebel, G.D.; Weger-Lucarelli, J. A reverse-transcription/RNase H based protocol for depletion of mosquito ribosomal RNA facilitates viral intrahost evolution analysis, transcriptomics and pathogen discovery. Virology 2018, 528, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, J.A.; Liu, R.M.; Bennett, S.N. RNA shotgun metagenomic sequencing of northern California (USA) mosquitoes uncovers viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabin, L.R.; Zheng, Q.; Thekkat, P.; Yang, J.; Hannon, G.J.; Gregory, B.D.; Tudor, M.; Cherry, S. Dicer-2 processes diverse viral RNA species. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachandran, B.; Hussain, M.; Asgari, S. RNA interference as a cellular defense mechanism against the DNA virus baculovirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13729–13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, A.C.; Nijhof, A.M.; Fick, W.; Stutzer, C.; Maritz-Olivier, C. RNAi in Arthropods: Insight into the Machinery and Applications for Understanding the Pathogen-Vector Interface. Genes 2012, 3, 702–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Lu, R.; Lau, N.; Lai, E.C.; Li, W.X.; Ding, S.W. Virus discovery by deep sequencing and assembly of virus-derived small silencing RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, E.R.; Olmo, R.P.; Paro, S.; Ferreira, F.V.; de Faria, I.J.; Todjro, Y.M.; Lobo, F.P.; Kroon, E.G.; Meignin, C.; Gatherer, D.; et al. Sequence-independent characterization of viruses based on the pattern of viral small RNAs produced by the host. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 6191–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzourakis, A.; Gifford, R.J. Endogenous viral elements in animal genomes. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Horst, A.M.; Nigg, J.C.; Dekker, F.M.; Falk, B.W. Endogenous Viral Elements Are Widespread in Arthropod Genomes and Commonly Give Rise to PIWI-Interacting RNAs. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02124-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Koonin, E.V. Iterated profile searches with PSI-BLAST–A tool for discovery in protein databases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, S.; Hasebe, M.; Tomita, M.; Yanagawa, H. Systematic identification of cell cycle-dependent yeast nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins by prediction of composite motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10171–10176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, R.; Naccache, F.; Ndiaye, E.H.; Fall, G.; Castelli, I.; Luhken, R.; Medlock, J.; Cull, B.; Hesson, J.C.; Montarsi, F.; et al. Identification and RNAi Profile of a Novel Iflavirus Infecting Senegalese Aedes vexans arabiensis Mosquitoes. Viruses 2020, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Silla-Martinez, J.M.; Gabaldon, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, C.S.; Baier, F.; Omondi, A.B.; Spitzer, S.A.; Lutomiah, J.; Sang, R.; Ignell, R.; Vosshall, L.B. Evolution of mosquito preference for humans linked to an odorant receptor. Nature 2014, 515, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Altan, E.; Deng, X.; Barker, C.M.; Fang, Y.; Coffey, L.L.; Delwart, E. Virome of >12 thousand Culex mosquitoes from throughout California. Virology 2018, 523, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.J.; Cox, R.; Tsao, J.; Rowse, M.; Qiu, S.; Luo, M. Common mechanism for RNA encapsidation by negative-strand RNA viruses. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3766–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gamez, S.; Antoshechkin, I.; Mendez-Sanchez, S.C.; Akbari, O.S. The Developmental Transcriptome of Ae. albopictus, a Major Worldwide Human Disease Vector. G3 2020, 10, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Srivastav, S.P.; Gamez, S.; Dayama, G.; Feitosa-Suntheimer, F.; Patterson, E.I.; Johnson, R.M.; Matson, E.M.; Gold, A.S.; Brackney, D.E.; et al. A mosquito small RNA genomics resource reveals dynamic evolution and host responses to viruses and transposons. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangeul, L.; Blanc, H.; Saleh, M.C.; Suzuki, Y. Differential Small RNA Responses against Co-Infecting Insect-Specific Viruses in Aedes albopictus Mosquitoes. Viruses 2020, 12, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Wen, S.; Tian, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis of Flaviviridae in Mosquito Viromes Isolated From Yunnan Province in China Reveals Genes From Dengue and Zika Viruses. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubacki, J.; Flacio, E.; Qi, W.; Guidi, V.; Tonolla, M.; Fraefel, C. Viral Metagenomic Analysis of Aedes albopictus Mosquitos from Southern Switzerland. Viruses 2020, 12, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, A.C.; Gill, A.C.; Armstrong, S.D.; Hartley, C.S.; Xia, D.; Wastling, J.M.; Makepeace, B.L. Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of the global response of Wolbachia to doxycycline-induced stress. ISME J. 2014, 8, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.; Asgari, S. Altered gene expression profile of Wolbachia pipientis wAlbB strain following transinfection from its native host Aedes albopictus to Aedes aegypti cells. Mol. Microbiol. 2020, 115, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfit, M.; Algama, M.; Keith, J.M.; McGraw, E.A.; Popovici, J. Discovery of putative small non-coding RNAs from the obligate intracellular bacterium Wolbachia pipientis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118595. [Google Scholar]
- Teramoto, T.; Huang, X.; Armbruster, P.A.; Padmanabhan, R. Infection of Aedes albopictus Mosquito C6/36 Cells with the wMelpop Strain of Wolbachia Modulates Dengue Virus-Induced Host Cellular Transcripts and Induces Critical Sequence Alterations in the Dengue Viral Genome. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00581-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayoral, J.G.; Etebari, K.; Hussain, M.; Khromykh, A.A.; Asgari, S. Wolbachia infection modifies the profile, shuttling and structure of microRNAs in a mosquito cell line. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96107. [Google Scholar]
- Mayoral, J.G.; Hussain, M.; Joubert, D.A.; Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; O’Neill, S.L.; Asgari, S. Wolbachia small noncoding RNAs and their role in cross-kingdom communications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18721–18726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.B.; Su, X.H.; Bonizzoni, M.; Zhong, D.B.; Li, Y.J.; Zhou, G.F.; Nguyen, H.; Tong, S.; Yan, G.Y.; Chen, X.G. Comparative transcriptome analysis and RNA interference reveal CYP6A8 and SNPs related to pyrethroid resistance in Aedes albopictus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Jiang, X.T.; Gu, J.B.; Xu, M.; Wu, Y.; Deng, Y.H.; Zhang, C.; Bonizzoni, M.; Dermauw, W.; Vontas, J.; et al. Genome sequence of the Asian Tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus, reveals insights into its biology, genetics, and evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, e5907–e5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.B.; Basu, S.; Jiang, X.; Qi, Y.; Timoshevskiy, V.A.; Biedler, J.K.; Sharakhova, M.V.; Elahi, R.; Anderson, M.A.; Chen, X.G.; et al. Sex Determination. A male-determining factor in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Science 2015, 348, 1268–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, F.; Salvemini, M.; Fiorillo, C.; Nolan, T.; Zwiebel, L.J.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Arca, B. Deciphering the olfactory repertoire of the tiger mosquito Aedes albopictus. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedururu, R.K.; Neave, M.J.; Tachedjian, M.; Klein, M.J.; Gorry, P.R.; Duchemin, J.B.; Paradkar, P.N. RNASeq Analysis of Aedes albopictus Mosquito Midguts after Chikungunya Virus Infection. Viruses 2019, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; Qin, X.C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.P.; Eden, J.S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.H.; Quarles, K.A.; Yang, Y.; Tanguy, M.; Frézal, L.; Smith, S.A.; Sharma, P.P.; Cordaux, R.; Gilbert, C.; Giraud, I. Pan-arthropod analysis reveals somatic piRNAs as an ancestral defence against transposable elements. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bona, A.C.; Chitolina, R.F.; Fermino, M.L.; de Castro Poncio, L.; Weiss, A.; Lima, J.B.; Paldi, N.; Bernardes, E.S.; Henen, J.; Maori, E. Larval application of sodium channel homologous dsRNA restores pyrethroid insecticide susceptibility in a resistant adult mosquito population. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, C.; Ahmed-Braimah, Y.H.; Amaro, I.A.; Harrington, L.C.; Wolfner, M.F.; Avila, F.W. Mating and blood-feeding induce transcriptome changes in the spermathecae of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Alto, B.W.; Shin, D.; Yu, F. The Effect of Permethrin Resistance on Aedes aegypti Transcriptome Following Ingestion of Zika Virus Infected Blood. Viruses 2018, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Nie, K.; Du, S.; Qiu, J.; Pang, X.; Wang, P.; Cheng, G. Flavivirus NS1 protein in infected host sera enhances viral acquisition by mosquitoes. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.M.; Martin-Martin, I.; Arca, B.; Calvo, E. A Deep Insight into the Sialome of Male and Female Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.S.; Barron, M.S.; Lovin, D.D.; Cunningham, J.M.; Eng, M.W.; Chadee, D.D.; Li, J.; Severson, D.W. A transcriptomic survey of the impact of environmental stress on response to dengue virus in the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewski, M.; Rasic, G.; Darbro, J.; Krause, L.; Poo, Y.S.; Filipovic, I.; Parry, R.; Asgari, S.; Devine, G.; Suhrbier, A. Mapping the virome in wild-caught Aedes aegypti from Cairns and Bangkok. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyles, S.M.; Mavian, C.N.; Finol, E.; Ukhanova, M.; Stephenson, C.J.; Hamerlinck, G.; Kang, S.; Baumgartner, C.; Geesey, M.; Stinton, I.; et al. Under-the-Radar Dengue Virus Infections in Natural Populations of Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes. mSphere 2020, 5, e00316-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Poelchau, M.F.; Armbruster, P.A. Global Transcriptional Dynamics of Diapause Induction in Non-Blood-Fed and Blood-Fed Aedes albopictus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimoto, H.; Hanley, K.A.; Sundararajan, A.; Devitt, N.P.; Schilkey, F.D.; Hansen, I.A. Dengue virus serotype 2 infection alters midgut and carcass gene expression in the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0171345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, C.J.; Cassone, B.J.; Piermarini, P.M. Transcriptomic evidence for a dramatic functional transition of the malpighian tubules after a blood meal in the Asian tiger mosquito Aedes albopictus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, E.Z.; Goic, B.; Tome-Poderti, L.; Frangeul, L.; Boussier, J.; Gausson, V.; Blanc, H.; Vallet, T.; Loyd, H.; Levi, L.I.; et al. Dicer-2-Dependent Generation of Viral DNA from Defective Genomes of RNA Viruses Modulates Antiviral Immunity in Insects. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 353–365.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batz, Z.A.; Goff, A.C.; Armbruster, P.A. MicroRNAs are differentially abundant during Aedes albopictus diapause maintenance but not diapause induction. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2017, 26, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelchau, M.F.; Reynolds, J.A.; Denlinger, D.L.; Elsik, C.G.; Armbruster, P.A. A de novo transcriptome of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus, to identify candidate transcripts for diapause preparation. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelchau, M.F.; Reynolds, J.A.; Denlinger, D.L.; Elsik, C.G.; Armbruster, P.A. Transcriptome sequencing as a platform to elucidate molecular components of the diapause response in the Asian tiger mosquito Aedes albopictus. Physiol. Entomol. 2013, 38, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelchau, M.F.; Reynolds, J.A.; Elsik, C.G.; Denlinger, D.L.; Armbruster, P.A. Deep sequencing reveals complex mechanisms of diapause preparation in the invasive mosquito, Aedes albopictus. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20130143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellone, R.; Lequime, S.; Jupille, H.; Goertz, G.P.; Aubry, F.; Mousson, L.; Piorkowski, G.; Yen, P.S.; Gabiane, G.; Vazeille, M.; et al. Experimental adaptation of dengue virus 1 to Aedes albopictus mosquitoes by in vivo selection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelman, Z.N.; Anderson, M.A.; Wiley, M.R.; Murreddu, M.G.; Samuel, G.H.; Morazzani, E.M.; Myles, K.M. Cooler temperatures destabilize RNA interference and increase susceptibility of disease vector mosquitoes to viral infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatini, U.; Masri, R.A.; Cosme, L.V.; Koren, S.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Biedler, J.K.; Krsticevic, F.; Johnston, J.S.; Halbach, R.; Crawford, J.E.; et al. Improved reference genome of the arboviral vector Aedes albopictus. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconcini, M.; Pischedda, E.; Houé, V.; Palatini, U.; Lozada-Chávez, N.; Sogliani, D.; Failloux, A.B.; Bonizzoni, M. Profile of Small RNAs, vDNA Forms and Viral Integrations in Late Chikungunya Virus Infection of Aedes albopictus Mosquitoes. Viruses 2021, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lai, Z.; Jin, B.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.G.; Gu, J. Differentiation of Long Non-Coding RNA and mRNA Expression Profiles in Male and Female Aedes albopictus. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelman, Z.N.; Anderson, M.A.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Myles, K.M. Sindbis virus induces the production of a novel class of endogenous siRNAs in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2012, 21, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Criscione, F.; Liang, S.; Tu, Z. MicroRNAs of two medically important mosquito species: Aedes aegypti and Anopheles stephensi. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2015, 24, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedler, J.K.; Hu, W.; Tae, H.; Tu, Z. Identification of early zygotic genes in the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti and discovery of a motif involved in early zygotic genome activation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Biedler, J.K.; Qi, Y.; Hall, A.B.; Tu, Z. Complete Dosage Compensation in Anopheles stephensi and the Evolution of Sex-Biased Genes in Mosquitoes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 1914–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Fu, X.; Zhu, J. Juvenile hormone-regulated alternative splicing of the taiman gene primes the ecdysteroid response in adult mosquitoes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, e7738–e7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Aliota, M.T.; Mayhew, G.F.; Erickson, S.M.; Christensen, B.M. Dual RNA-seq of parasite and host reveals gene expression dynamics during filarial worm-mosquito interactions. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, S.T.; Maertens, B.L.; Dunham, T.J.; Rodgers, C.P.; Brehm, A.L.; Miller, M.R.; Williams, A.M.; Foy, B.D.; Stenglein, M.D. Partitiviruses Infecting Drosophila melanogaster and Aedes aegypti Exhibit Efficient Biparental Vertical Transmission. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01070-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonizzoni, M.; Dunn, W.A.; Campbell, C.L.; Olson, K.E.; Marinotti, O.; James, A.A. Complex modulation of the Aedes aegypti transcriptome in response to dengue virus infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, A.; Gamez, S.; Li, M.; Antoshechkin, I.; Li, H.H.; Wang, H.W.; Chen, C.H.; Klein, M.J.; Duchemin, J.B.; Paradkar, P.N.; et al. Engineered resistance to Zika virus in transgenic Aedes aegypti expressing a polycistronic cluster of synthetic small RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3656–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etebari, K.; Osei-Amo, S.; Blomberg, S.P.; Asgari, S. Dengue virus infection alters post-transcriptional modification of microRNAs in the mosquito vector Aedes aegypti. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slonchak, A.; Hugo, L.E.; Freney, M.E.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Amarilla, A.A.; Torres, F.J.; Setoh, Y.X.; Peng, N.Y.G.; Sng, J.D.J.; Hall, R.A.; et al. Zika virus noncoding RNA suppresses apoptosis and is required for virus transmission by mosquitoes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimalasiri-Yapa, B.; Barrero, R.A.; Stassen, L.; Hafner, L.M.; McGraw, E.A.; Pyke, A.T.; Jansen, C.C.; Suhrbier, A.; Yakob, L.; Hu, W.; et al. Temperature modulates immune gene expression in mosquitoes during arbovirus infection. Open Biol. 2021, 11, 200246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.; Allen, S.L.; Herbert, R.I.; McGraw, E.A.; Chenoweth, S.F. The Transcriptional Response of Aedes aegypti with Variable Extrinsic Incubation Periods for Dengue Virus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 3141–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etebari, K.; Hegde, S.; Saldana, M.A.; Widen, S.G.; Wood, T.G.; Asgari, S.; Hughes, G.L. Global Transcriptome Analysis of Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes in Response to Zika Virus Infection. mSphere 2017, 2, e00456-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana, M.A.; Etebari, K.; Hart, C.E.; Widen, S.G.; Wood, T.G.; Thangamani, S.; Asgari, S.; Hughes, G.L. Zika virus alters the microRNA expression profile and elicits an RNAi response in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.G.; Tesla, B.; Horacio, E.C.A.; Nahum, L.A.; Brindley, M.A.; de Oliveira Mendes, T.A.; Murdock, C.C. Temperature Dramatically Shapes Mosquito Gene Expression With Consequences for Mosquito-Zika Virus Interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Etebari, K.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; van den Hurk, A.F.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Vatipally, S.; Schnettler, E.; Hall, R.; Asgari, S. Understanding the role of microRNAs in the interaction of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes with an insect-specific flavivirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1892–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattel, J.; Haberkorn, C.; Laporte, F.; Gaude, T.; Cumer, T.; Renaud, J.; Sutherland, I.W.; Hertz, J.C.; Bonneville, J.; Arnaud, V.; et al. A genomic amplification affecting a carboxylesterase gene cluster confers organophosphate resistance in the mosquito Aedes aegypti: From genomic characterization to high-throughput field detection. Evol. Appl. 2021, 14, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrinet, J.; Srivastava, P.; Sunil, S. Transcriptome analysis of Aedes aegypti in response to mono-infections and co-infections of dengue virus-2 and chikungunya virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Modahl, C.M.; Tan, S.T.; Wong Wei Xiang, B.; Misse, D.; Vial, T.; Kini, R.M.; Pompon, J.F. JNK pathway restricts DENV2, ZIKV and CHIKV infection by activating complement and apoptosis in mosquito salivary glands. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, M.M.; Sessions, O.M.; Gubler, D.J.; Ooi, E.E. Production of Infectious Dengue Virus in Aedes aegypti Is Dependent on the Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbach, R.; Miesen, P.; Joosten, J.; Taskopru, E.; Rondeel, I.; Pennings, B.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Merkling, S.H.; Koenraadt, C.J.; Lambrechts, L.; et al. A satellite repeat-derived piRNA controls embryonic development of Aedes. Nature 2020, 580, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degner, E.C.; Ahmed-Braimah, Y.H.; Borziak, K.; Wolfner, M.F.; Harrington, L.C.; Dorus, S. Proteins, Transcripts, and Genetic Architecture of Seminal Fluid and Sperm in the Mosquito Aedes aegypti. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2019, 18, S6–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raquin, V.; Merkling, S.H.; Gausson, V.; Moltini-Conclois, I.; Frangeul, L.; Varet, H.; Dillies, M.A.; Saleh, M.C.; Lambrechts, L. Individual co-variation between viral RNA load and gene expression reveals novel host factors during early dengue virus infection of the Aedes aegypti midgut. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, M.W.; Clemons, A.; Hill, C.; Engel, R.; Severson, D.W.; Behura, S.K. Multifaceted functional implications of an endogenously expressed tRNA fragment in the vector mosquito Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Beller, L.; Deboutte, W.; Yinda, K.C.; Delang, L.; Vega-Rua, A.; Failloux, A.B.; Matthijnssens, J. Stable distinct core eukaryotic viromes in different mosquito species from Guadeloupe, using single mosquito viral metagenomics. Microbiome 2019, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, G.K.; Ayllon, M.A.; Bao, Y.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Blasdell, K.R.; Briese, T.; Brown, P.A.; Bukreyev, A.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; et al. Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: Update 2019. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1967–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedururu, R.K.; Neave, M.J.; Sundaramoorthy, V.; Green, D.; Harper, J.A.; Gorry, P.R.; Duchemin, J.B.; Paradkar, P.N. Whole Transcriptome Analysis of Aedes albopictus Mosquito Head and Thorax Post-Chikungunya Virus Infection. Pathogens 2019, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilakis, N.; Forrester, N.L.; Palacios, G.; Nasar, F.; Savji, N.; Rossi, S.L.; Guzman, H.; Wood, T.G.; Popov, V.; Gorchakov, R.; et al. Negevirus: A proposed new taxon of insect-specific viruses with wide geographic distribution. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2475–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallies, R.; Kopp, A.; Zirkel, F.; Estrada, A.; Gillespie, T.R.; Drosten, C.; Junglen, S. Genetic characterization of goutanap virus, a novel virus related to negeviruses, cileviruses and higreviruses. Viruses 2014, 6, 4346–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauver, J.R.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Krajacich, B.J.; Weger-Lucarelli, J.; Lakin, S.M.; Fakoli, L.S., 3rd; Bolay, F.K.; Diclaro, J.W., 2nd; Dabire, K.R.; Foy, B.D.; et al. West African Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes harbor a taxonomically diverse virome including new insect-specific flaviviruses, mononegaviruses, and totiviruses. Virology 2016, 498, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, C.L.; Longdon, B.; Lewis, S.H.; Obbard, D.J. Twenty-Five New Viruses Associated with the Drosophilidae (Diptera). Evol Bioinform Online 2016, 12, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.J.; Adkins, S.; Bragard, C.; Gilmer, D.; Li, D.; MacFarlane, S.A.; Wong, S.M.; Melcher, U.; Ratti, C.; Ryu, K.H.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Virgaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1999–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morazzani, E.M.; Wiley, M.R.; Murreddu, M.G.; Adelman, Z.N.; Myles, K.M. Production of virus-derived ping-pong-dependent piRNA-like small RNAs in the mosquito soma. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, S.; Salem, N.; Falk, B.W. Complete Genome Sequence of Diaphorina citri-associated C virus, a Novel Putative RNA Virus of the Asian Citrus Psyllid, Diaphorina citri. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00639-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchibhatla, D.B.; Sherman, W.A.; Chung, B.Y.; Cook, S.; Schneider, G.; Eisenhaber, B.; Karlin, D.G. Powerful sequence similarity search methods and in-depth manual analyses can identify remote homologs in many apparently “orphan” viral proteins. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.; Chung, B.Y.; Bass, D.; Moureau, G.; Tang, S.; McAlister, E.; Culverwell, C.L.; Glucksman, E.; Wang, H.; Brown, T.D.; et al. Novel virus discovery and genome reconstruction from field RNA samples reveals highly divergent viruses in dipteran hosts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.M.; Rasgon, J.L. Densonucleosis viruses (‘densoviruses’) for mosquito and pathogen control. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2018, 28, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotmore, S.F.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Canuti, M.; Chiorini, J.A.; Eis-Hubinger, A.M.; Hughes, J.; Mietzsch, M.; Modha, S.; Ogliastro, M.; Penzes, J.J.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Parvoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Hoiczyk, E.; Rasgon, J.L. Viral paratransgenesis in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Bonilla, R.G.; Yocupicio-Monroy, M.; Marchat, L.A.; De Nova-Ocampo, M.A.; del Angel, R.M.; Salas-Benito, J.S. Analysis of the miRNA profile in C6/36 cells persistently infected with dengue virus type 2. Virus Res. 2017, 232, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lai, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, P.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Gu, J. A Novel Densovirus Isolated From the Asian Tiger Mosquito Displays Varied Pathogenicity Depending on Its Host Species. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.C.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Gao, D.Y.; He, J.R.; Wang, J.B.; Li, C.X.; Kang, Y.J.; Yu, B.; et al. A tick-borne segmented RNA virus contains genome segments derived from unsegmented viral ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6744–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Liu, H.B.; Ni, X.B.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Zheng, Y.C.; Song, J.L.; Li, J.; Jiang, B.G.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Emergence of human infection with Jingmen tick virus in China: A retrospective study. EBioMedicine 2019, 43, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerich, P.; Jakupi, X.; von Possel, R.; Berisha, L.; Halili, B.; Gunther, S.; Cadar, D.; Ahmeti, S.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J. Viral metagenomics, genetic and evolutionary characteristics of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever orthonairovirus in humans, Kosovo. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmer, J.; Alafndi, A.; Gabrieli, P. Fat body-specific vitellogenin expression regulates host-seeking behaviour in the mosquito Aedes albopictus. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmam, S.; Bigot, T.; Chretien, D.; Gondard, M.; Perot, P.; Pommelet, V.; Dufour, E.; Petres, S.; Devillers, E.; Hoem, T.; et al. Insights into the Host Range, Genetic Diversity, and Geographical Distribution of Jingmenviruses. mSphere 2019, 4, e00645-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameroff, S.; Tokarz, R.; Charles, R.A.; Jain, K.; Oleynik, A.; Che, X.; Georges, K.; Carrington, C.V.; Lipkin, W.I.; Oura, C. Viral Diversity of Tick Species Parasitizing Cattle and Dogs in Trinidad and Tobago. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckert, C.; Prasad, A.N.; Garcia-Luna, S.M.; Robison, A.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Weger-Lucarelli, J.; Ebel, G.D. Small RNA responses of Culex mosquitoes and cell lines during acute and persistent virus infection. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 109, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batson, J.; Dudas, G.; Haas-Stapleton, E.; Kistler, A.L.; Li, L.M.; Logan, P.; Ratnasiri, K.; Retallack, H. Single mosquito metatranscriptomics identifies vectors, emerging pathogens and reservoirs in one assay. eLife 2021, 10, e68353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Zhao, L.; Atoni, E.; Zeng, W.; Hu, X.; Matthijnssens, J.; Yuan, Z.; Xia, H. Stability of the Virome in Lab- and Field-Collected Aedes albopictus Mosquitoes across Different Developmental Stages and Possible Core Viruses in the Publicly Available Virome Data of Aedes Mosquitoes. mSystems 2020, 5, e00640-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackney, D.E.; Scott, J.C.; Sagawa, F.; Woodward, J.E.; Miller, N.A.; Schilkey, F.D.; Mudge, J.; Wilusz, J.; Olson, K.E.; Blair, C.D.; et al. C6/36 Aedes albopictus cells have a dysfunctional antiviral RNA interference response. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obbard, D.J. Expansion of the metazoan virosphere: Progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 31, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, G. Early history of laboratory breeding of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) focusing on the origins and use of selected strains. J. Med. Entomol. 2010, 47, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.R.; Mitchell, C.J. Genetic selection of a flavivirus-refractory strain of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1991, 45, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weger-Lucarelli, J.; Ruckert, C.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Misencik, M.J.; Armstrong, P.M.; Stenglein, M.D.; Ebel, G.D.; Brackney, D.E. Adventitious viruses persistently infect three commonly used mosquito cell lines. Virology 2018, 521, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stollar, V.; Thomas, V.L. An agent in the Aedes aegypti cell line (Peleg) which causes fusion of Aedes albopictus cells. Virology 1975, 64, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, A.; Harrap, K.A.; Casals, J.; Stollar, V. Morphological, Biochemical, and Serological Studies on a Viral Agent (Cfa) Which Replicates in and Causes Fusion of Aedes-Albopictus (Singh) Cells. Virology 1976, 74, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammisa-Parks, H.; Cisar, L.A.; Kane, A.; Stollar, V. The complete nucleotide sequence of cell fusing agent (CFA): Homology between the nonstructural proteins encoded by CFA and the nonstructural proteins encoded by arthropod-borne flaviviruses. Virology 1992, 189, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maringer, K.; Yousuf, A.; Heesom, K.J.; Fan, J.; Lee, D.; Fernandez-Sesma, A.; Bessant, C.; Matthews, D.A.; Davidson, A.D. Proteomics informed by transcriptomics for characterising active transposable elements and genome annotation in Aedes aegypti. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giallonardo, F.; Audsley, M.D.; Shi, M.; Young, P.R.; McGraw, E.A.; Holmes, E.C. Complete genome of Aedes aegypti anphevirus in the Aag2 mosquito cell line. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, B.J.; Dainty, K.R.; Flores, H.A.; O’Neill, S.L. Differential suppression of persistent insect specific viruses in trans-infected wMel and wMelPop-CLA Aedes-derived mosquito lines. Virology 2019, 527, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzke, K.; Leggewie, M.; Sreenu, V.B.; Jansen, S.; Heitmann, A.; Welch, S.R.; Brennan, B.; Elliott, R.M.; Tannich, E.; Becker, S.C.; et al. Detection, infection dynamics and small RNA response against Culex Y virus in mosquito-derived cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.; Kittayapong, P.; Braig, H.; Andreadis, T.; Gonzalez, J.; Tesh, R. Insect densoviruses may be widespread in mosquito cell lines. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousset, F.X.; Barreau, C.; Boublik, Y.; Cornet, M. A parvo-like virus persistently infecting a C6/36 clone of Aedes albopictus mosquito cell line and pathogenic for Aedes aegypti larvae. Virus Res. 1993, 29, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boublik, Y.; Jousset, F.X.; Bergoin, M. Complete nucleotide sequence and genomic organization of the Aedes albopictus parvovirus (AaPV) pathogenic for Aedes aegypti larvae. Virology 1994, 200, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, A. Isolation of a singhs Aedes albopictus cell Clone sensitive to Dengue and chikungunya viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1978, 40, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, R.; Bishop, C.; De Hayr, L.; Asgari, S. Density-dependent enhanced replication of a densovirus in Wolbachia-infected Aedes cells is associated with production of piRNAs and higher virus-derived siRNAs. Virology 2019, 528, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalsky, R.L.; Vanlandingham, D.L.; Scholle, F.; Higgs, S.; Cullen, B.R. Identification of microRNAs expressed in two mosquito vectors, Aedes albopictus and Culex quinquefasciatus. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.J.; Isern, S.; Michael, S.F.; Corley, R.B.; Connor, J.H.; Frydman, H.M. Variable Inhibition of Zika Virus Replication by Different Wolbachia Strains in Mosquito Cell Cultures. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00339-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnettler, E.; Sreenu, V.B.; Mottram, T.; McFarlane, M. Wolbachia restricts insect-specific flavivirus infection in Aedes aegypti cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 3024–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Provisional Virus Name; Host | Closest Relative; Genbank ID; Host | Classification: Order (O); Family (F); Genus (G) | Geographical Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formosus virus; Aedes aegypti | Isfahan virus; YP_007641386.1; Phlebotomus papatasi | O: Mononegavirales; F: Rhabdoviridae | Laboratory colonies: Bundibugyo, Uganda (U30) [54] |
| San Gabriel virus; Aedes albopictus | Wuhan ant virus; YP_009304559.1; Camponotus japonicus | O: Mononegavirales; F: Rhabdoviridae | Laboratory colonies: San Gabriel Valley, Los Angeles County USA [57,58]; Kawasaki, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan [59]; Wild-caught mosquitoes: Yunnan, China [60]; Ticino, Muzzano, Switzerland [61] Cell lines: Aedes albopictus cells: RML-12.wMelPop [62], Aa23 cells and derivatives [63], C6/36.wMelPop [64,65] Aedes aegypti cells: Aag2.wMelPop [66,67] |
| Longgang virus (LMCV); Aedes albopictus | Shayang fly virus 1; YP_009300663.1; Atherigona orientalis | O: Mononegavirales; likely Chuvirus | Laboratory colonies: Longgang district, Shenzhen, China [68]. |
| Aedes orthomyxo-like virus 2 (AOMV-2); Aedes albopictus | Whidbey virus; AQU42764.1; Aedes dorsalis | F: Orthomyxoviridae | Laboratory colonies: Foshan, China [69,70]; Italy, Rome [71]; Torres strait island, Australia [72]. Wild-caught mosquitoes: Zhejiang, China [73] |
| Rabai virus; Aedes aegypti | Yongsan negev-like virus 1; AXV43886.1; Culex inatomii | Unclassified Negevirus taxon related to F: Virgaviridae | Laboratory colonies: Rabai, Kenya (K2, K4) [54] |
| Aedes binegev-like virus 1 (AeBNV-1); Aedes aegypti | ssRNA virus-like 6 genomic sequence KX148585.1; Anopheles gambiae | Unclassified Negevirus taxon related to F: Virgaviridae | Laboratory colonies: Miami, Florida, USA [74]; Nova Iguaçu Rio de Janeiro, Brazil [75]; Bangkok, Thailand [76]; Key West & Orlando, USA [77]; Liverpool Colony [78,79]; Curepe, Trinidad [80] Wild-caught: Bangkok, Thailand [81]; Manatee County, USA [82]; Miami, USA [12]. |
| Aedes binegev-like virus 2; (AeBNV-2) Aedes albopictus | ssRNA virus-like 6 genomic sequence KX148585.1; Anopheles gambiae | Unclassified Negevirus taxon related to F: Virgaviridae | Laboratory colonies: Longgang District, Shenzhen, China [68]; Manassas, USA [83]. |
| Tiger mosquito bi-segmented tombus-like virus (TMTLV); Aedes albopictus | Culex mosquito virus 1; AXQ04816.1; Culex sp. | Related to the arthropod infecting F: Nodaviridae and F: Tombusviridae | Laboratory colonies: Gainesville (MRA-804), USA [84,85]; Phu Hoa, Binh Duong Province, Vietnam [59,86]; Manassas, USA [83,87,88,89,90]; Nice, France [91]; Wise County, Virginia, USA [92]; Foshan, China [93,94,95]; Kawasaki, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan [59]. |
| Liverpool tombus-like virus (LTLV) Aedes albopictus, Aedes aegypti | Hammarskog tombus-like virus; QGA87328.1 Coquillettidia richiardii | Related to the arthropod infecting F: Nodaviridae and F: Tombusviridae | Laboratory colonies: Liverpool strains [70,96,97,98,99,100,101], Poza Rica, Mexico [102]; Chetumal (CTM), Mexico [103]; Higgs White Eye (HWE) strain (Variant of Rex-D), Puerto Rico [104]. |
| Aedes orbi-like virus (AOLV); Aedes aegypti | uncultured virus; AGW51764.1; Culicine sp. | F: Reoviridae G: Orbivirus | Laboratory colonies: Cairns, Innisfail, and North QLD Australia [105,106,107,108] Wild-caught: Cairns, Australia [81] |
| Aedes partiti-like virus 1 (APLV-1); Aedes aegypti | Hubei partiti-like virus 34; APG78322.1; Chinese land snail | F: Partitiviridae | Laboratory colonies: Rabai, Kenya (K2, K4, K14) [54]; Galveston, USA [109,110]; Tapachula, Mexico [111]; Cairns, Innisfail, Townsville, Australia [105,106,107,108,112]; Laos [113]; New Delhi, India [114]; Singapore [115,116]; Kamphaeng Phet, Thep Na Korn and Bangkok, Thailand [117,118,119]; Curepe, Trinidad [80,120] Wild-caught: Bangkok, Thailand [81], Cairns, Australia [81]; Manatee County, USA [82]; Miami, USA [12]; Les Abymes & Petit-Bourg, Guadeloupe [121] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parry, R.; James, M.E.; Asgari, S. Uncovering the Worldwide Diversity and Evolution of the Virome of the Mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081653
Parry R, James ME, Asgari S. Uncovering the Worldwide Diversity and Evolution of the Virome of the Mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(8):1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081653
Chicago/Turabian StyleParry, Rhys, Maddie E James, and Sassan Asgari. 2021. "Uncovering the Worldwide Diversity and Evolution of the Virome of the Mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus" Microorganisms 9, no. 8: 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081653
APA StyleParry, R., James, M. E., & Asgari, S. (2021). Uncovering the Worldwide Diversity and Evolution of the Virome of the Mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Microorganisms, 9(8), 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081653







