Effect of Stocking Density during CO2 Stunning of Pigs on Induction Time and Activity Level Measured Using AI
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Lairage, Driving and Stunning Procedure
2.2. Recording of Video during Stunning
2.3. Analysis of Video Recordings of Animal Behaviour
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
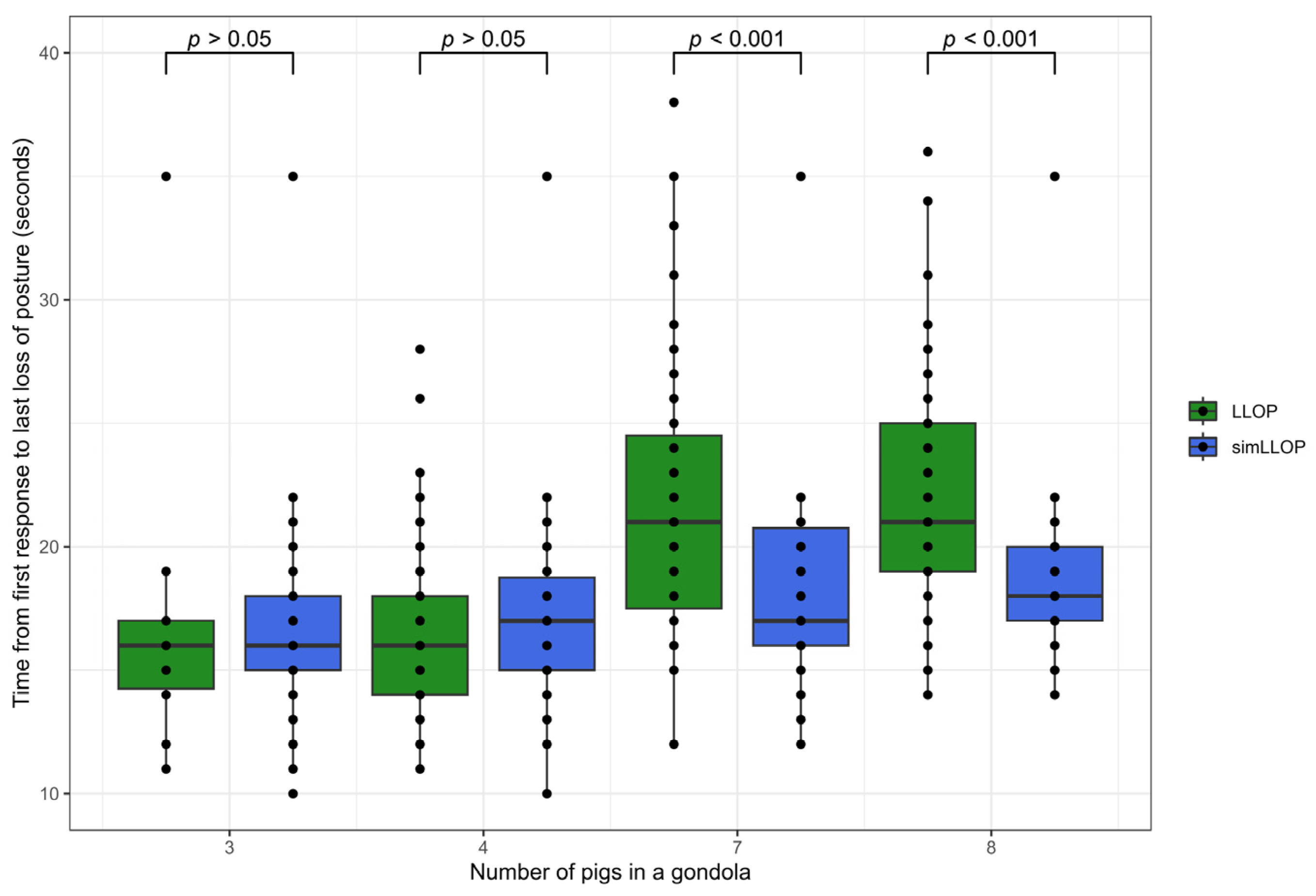
3.1. Time from First Response to Loss of Posture
3.2. Mean Activity Level during Stunning
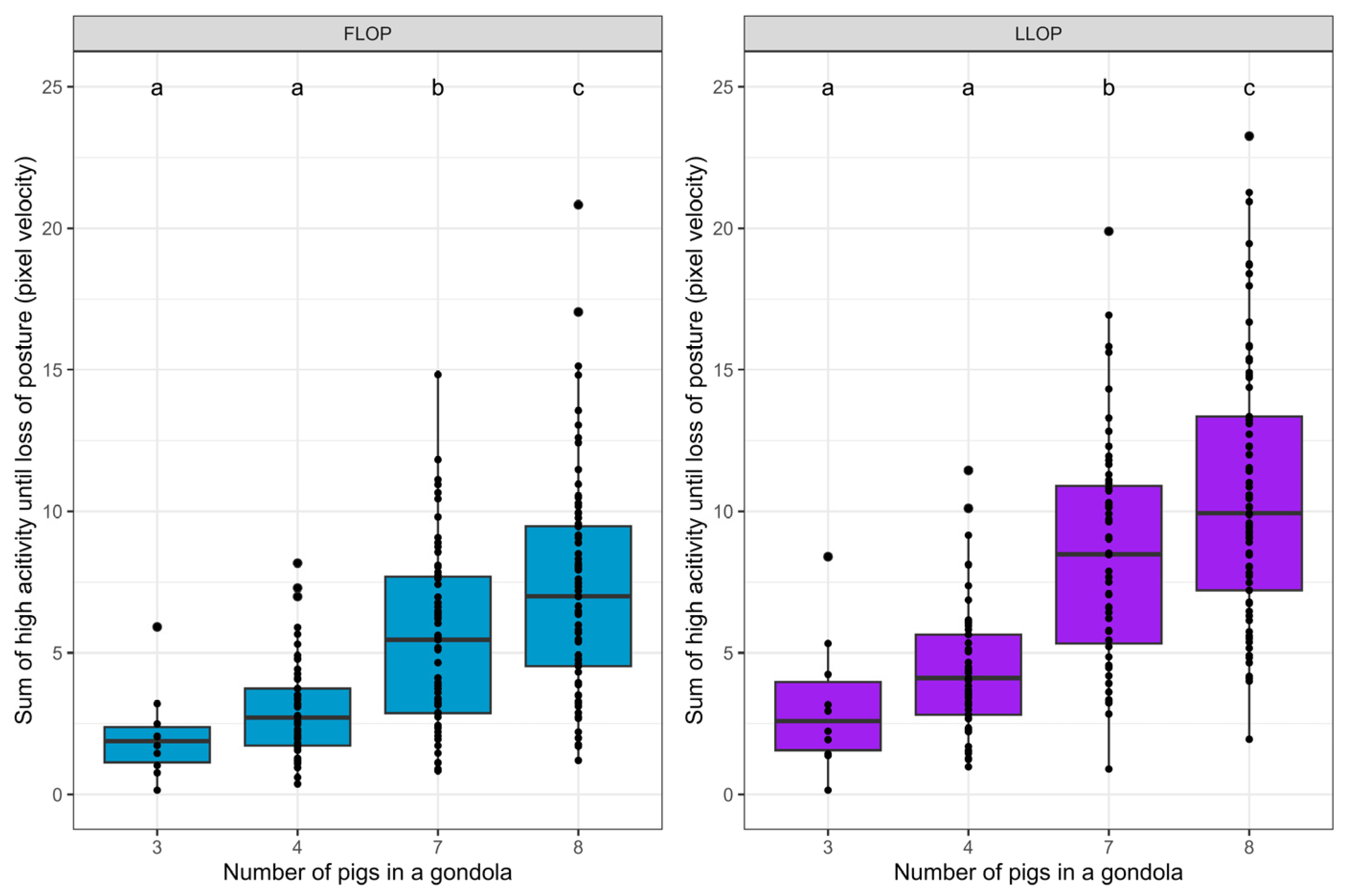
3.3. Levels of High Activity during Stunning
4. Discussion
4.1. Criteria for Method Selection
4.2. Method of Behavioural Assessment
4.3. Study Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nielsen, S.S.; Alvarez, J.; Bicout, D.J.; Calistri, P.; Depner, K.; Drewe, J.A.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Gonzales Rojas, J.L.; Schmidt, C.G.; Michel, V. Welfare of pigs at slaughter. EFSA 2020, 18, e06148. [Google Scholar]
- Hognestad, B.W.; Digranes, N.A.; Opsund, V.G.; Espenes, A.; Haga, H.A. CO2 stunning in pigs: Physiological deviations at onset of excitatory behaviour. Animal 2023, 13, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, A.R.; Flammer, S.A.; Beausoleil, N.J.; Berg, C.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Pinillos, R.G.; Golledge, H.D.R.; Marahrens, M.; Meyer, R.; Schnitzer, T.; et al. Humanely Ending the Life of Animals: Research Priorities to Identify Alternatives to Carbon Dioxide. Animals 2019, 9, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.B.M.; Gregory, N.G. Welfare Implications of the Gas Stunning of Pigs 1. Determination of Aversion to the Initial Inhala-tion of Carbon Dioxide or Argon. Anim. Welf. 1995, 4, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, A.E.; Allen, J.E.; Dahdaleh, N.S.; Drebot, I.I.; Coryell, M.W.; Wunsch, A.M.; Lynch, C.M.; Faraci, F.M.; Howard, M.A., 3rd; Welsh, M.J.; et al. The amygdala is a chemosensor that detects carbon dioxide and acidosis to elicit fear behavior. Cell 2009, 139, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.B.M.; Gregory, N.G. Welfare Implications of the Gas Stunning of Pigs 2. Stress of Induction of Anaesthesia. Anim. Welf. 1996, 5, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, A.; Cruz, J.; Gispert, M.; Carrion, D.; Torre, R.; Diestre, A.; Manteca, X. Aversion to carbon dioxide stunning in pigs: Effect of carbon dioxide concentration and halothane genotype. Anim. Welf. 2007, 16, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.M.; Berman, P.R. Mechanism of excitation of aplysia neurons by carbon dioxide. J. Gen. Physiol. 1970, 56, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antkowiak, B. How do general anaesthetics work? Sci. Nat. 2001, 88, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Call for Proposal on ‘Pig Stunning’ Grant for the Development of Non-Aversive Stunning Methods for Pigs; European Health and Digital Executive Agency (Hadea): Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- EURCAW-Pigs. Available online: https://eurcaw-pigs.eu/ (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Lechner, I.; Léger, A.; Zimmermann, A.; Atkinson, S.; Schuppers, M. Discomfort period of fattening pigs and sows stunned with CO2: Duration and potential influencing factors in a commercial setting. Meat Sci. 2021, 179, 108535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongman, E.C.; Woodhouse, R.; Rise, M.; Rault, J.L. Pre-slaughter factors linked to variation in responses to carbon dioxide gas stunning in pig abattoirs. Animal 2021, 15, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlouw, E.M.C.; Deiss, V.; Astruc, T. Stunning of pigs with different gas mixtures: Behavioural and physiological reactions. Meat Sci. 2021, 175, 108452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhe, W.Y.; Melkie, B.T.; Lema, F.G.; Getnet, M.; Chekol, W.B. The Overlooked Problem among Surgical Patients: Preoperative Anxiety at Ethiopian University Hospital. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 912743. [Google Scholar]
- Inal, Y.F.; Camgoz, Y.Y.; Daskaya, H.; Kocoglu, H. The Effect of Preoperative Anxiety and Pain Sensitivity on Preoperative Hemodynamics, Propofol Consumption, and Postoperative Recovery and Pain in Endoscopic Ultrasonography. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmetovic-Djug, J.; Hasukic, S.; Djug, H.; Hasukic, B.; Jahic, A. Impact of Preoperative Anxiety in Patients on Hemodynamic Changes and a Dose of Anesthetic During Induction of Anesthesia. Med. Arch. 2017, 71, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, D.N.; Matthews, N. Conversion of muscle to meat|Slaughter-line operation and pork quality. In Encyclopedia of Meat Sciences, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sindhøj, E.; Lindahl, C.; Bark, L. Review: Potential alternatives to high-concentration carbon dioxide stunning of pigs at slaughter. Animal 2021, 15, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, S.; Algers, B.; Pallisera, J.; Velarde, A.; Llonch, P. Animal Welfare and Meat Quality Assessment in Gas Stunning during Commercial Slaughter of Pigs Using Hypercapnic-Hypoxia (20% CO2 2% O2) Compared to Acute Hypercapnia (90% CO2 in Air). Animals 2020, 10, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Holleben, K.; Von Wenzlawowicz, M. CO2-Stunning of Pigs. An Example of Behaviour during Induction and Overview of Gas Concentration and Other Key Parameters during Routine Slaughter of Pigs in Modern Low Stress Group Stunning Devices. FSVO/UFAW/HAS. Online Symposium–Humanely Ending the Life of Animals. Session 2. 2020. Available online: https://www.hsa.org.uk/news-events/fsvo-ufaw-hsa-online-symposium-a-humanely-ending-the-life-of-animals (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Zhang, L.; Guo, W.; Lv, C.; Guo, M.; Yang, M.; Fu, Q.; Liu, X. Advancements in artificial intelligence technology for improving animal welfare: Current applications and research progress. Anim. Res. One Health 2024, 2, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teed, Z.; Deng, J. RAFT: Recurrent All-Pairs Field Transforms for Optical Flow; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, M.; Gerritzen, M.; Velarde, A.; Hellebrekers, L.; Kemp, B. Time to Loss of Consciousness and Its Relation to Behavior in Slaughter Pigs during Stunning with 80 or 95% Carbon Dioxide. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kells, N.; Ngaio, B.; Craig, J.; Mhairi, S. Evaluation of Different Gases and Gas Combinations for On-Farm Euthanasia of Pre-Weaned Pigs. Animals 2018, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çavuşoğlu, E.; Rault, J.L.; Gates, R.; Lay, D.C., Jr. Behavioral Response of Weaned Pigs during Gas Euthanasia with CO2, CO2 with Butorphanol, or Nitrous Oxide. Animals 2020, 10, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Düpjan, S.; Schön, P.C.; Puppe, B.; Tuchscherer, A.; Manteuffel, G. Differential vocal responses to physical and mental stressors in domestic pigs (Sus scrofa). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 114, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; Nordquist, R.E.; Van der Staay, F.J. A review of behavioural methods to study emotion and mood in pigs, Sus scrofai. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2014, 159, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Criteria | Definition |
|---|---|
| First response | A response is recorded after the gondola has commenced the descent. At least one pig responds with alertness by either a sudden, typically small, movement (most pigs are not moving just before the descent) or raising the head with increased sniffing. |
| Loss of posture (LOP) | The pig either lies down and is no longer able to regain a standing or sitting posture, or the pig remains in a sitting posture against the wall or other pigs while displaying opisthotonos, indicating that the pig is not able to remain in a sitting posture, but is mechanically prevented from lying down. |
| Group Size in Gondola | Group Size in Gondola | FLOP (p-Values) | LLOP (p-Values) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 0.4115 | 0.2866 |
| 7 | 0.0015 | 0.0052 | |
| 8 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | |
| 4 | 7 | <0.0001 | 0.0049 |
| 8 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| 7 | 8 | 0.0210 | 0.1090 |
| Group Size in Gondola | Group Size in Gondola | FLOP (p-Values) | LLOP (p-Values) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 0.5782 | 0.3513 |
| 7 | 0.0036 | 0.0004 | |
| 8 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| 4 | 7 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 8 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| 7 | 8 | 0.0274 | 0.0364 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonnichsen, R.; Hansen, C.; Søndergaard, J.R.; Schrøder-Petersen, D.L. Effect of Stocking Density during CO2 Stunning of Pigs on Induction Time and Activity Level Measured Using AI. Animals 2024, 14, 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131953
Bonnichsen R, Hansen C, Søndergaard JR, Schrøder-Petersen DL. Effect of Stocking Density during CO2 Stunning of Pigs on Induction Time and Activity Level Measured Using AI. Animals. 2024; 14(13):1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131953
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonnichsen, Rikke, Claus Hansen, Jon Raunkjær Søndergaard, and Dorte Lene Schrøder-Petersen. 2024. "Effect of Stocking Density during CO2 Stunning of Pigs on Induction Time and Activity Level Measured Using AI" Animals 14, no. 13: 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131953
APA StyleBonnichsen, R., Hansen, C., Søndergaard, J. R., & Schrøder-Petersen, D. L. (2024). Effect of Stocking Density during CO2 Stunning of Pigs on Induction Time and Activity Level Measured Using AI. Animals, 14(13), 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131953





