Tick Infestation and Molecular Detection of Tick-Borne Pathogens from Indian Long-Eared Hedgehogs (Hemiechinus collaris) in Pakistan
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
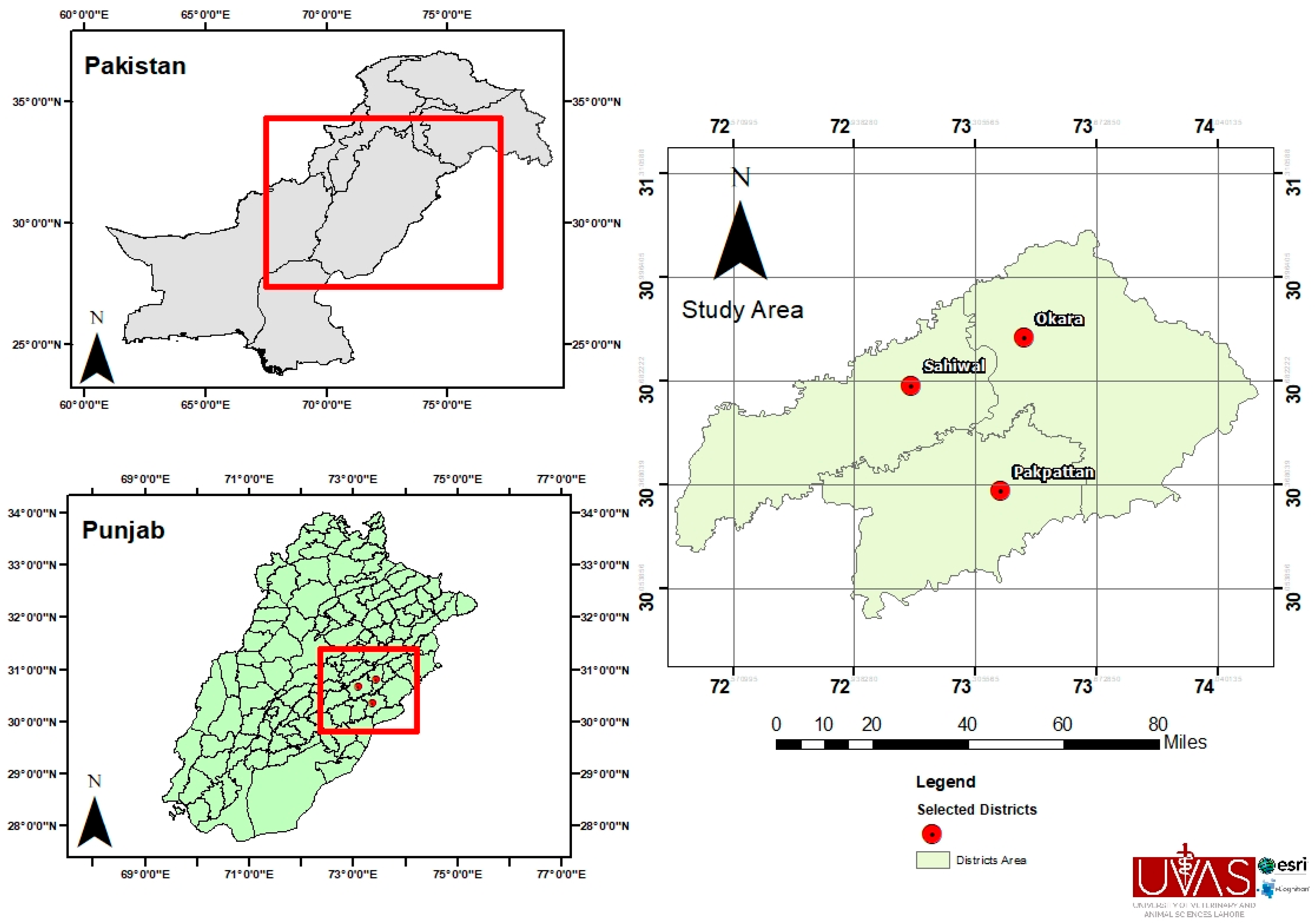
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling and Data Collection
2.3. Tick Identification
2.4. DNA Extraction from Ticks and Blood
2.5. PCR Confirmation of Tick Species
2.6. PCR Screening for Microbes
2.7. Sequencing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Tick Infestation
3.2. Prevalence of TBPs in Hedgehog Blood and Ticks
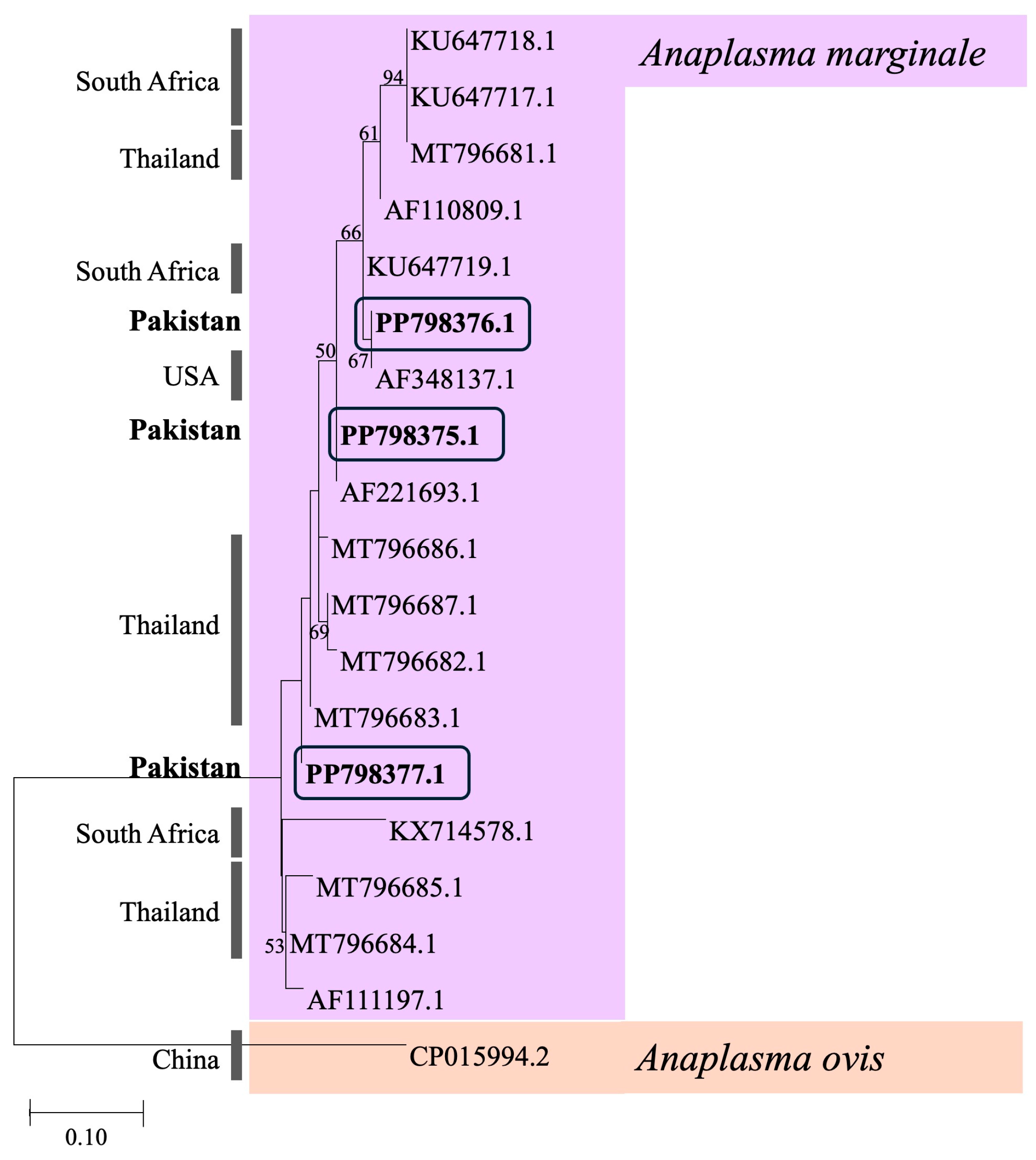
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aslam, B.; Hussain, I.; Zahoor, M.A. Prevalence of Borrelia anserinain Argas ticks. Pak. J. Zool. 2015, 47, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Ijaz, M.; Durrani, A.Z. Epidemiological aspects of bovine tick infestation in the river Ravi region, Lahore. Pak. J. Zool. 2016, 48, 563–567. [Google Scholar]
- Kasi, K.K.; von Arnim, F.; Schulz, A.; Rehman, A.; Chudhary, A.; Oneeb, M.; Sas, M.A.; Jamil, T.; Maksimov, P.; Sauter-Louis, C.; et al. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in ticks collected from livestock in Balochistan, Pakistan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, S.J.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Potkonjak, A.; Mihalca, A.D.; Zeller, H. Tick-borne diseases and co-infection Current considerations. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Khan, M.A.; Zahid, H.; Yaseen, P.M.; Qayash, K.M.; Nawab, J.; Ur Rehman, Z.; Ateeq, M.; Khan, S.; Ibrahim, M. Seasonal Dynamics, Record of Ticks Infesting Humans, Wild and Domestic Animals and Molecular Phylogeny of Rhipicephalus microplus in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 10793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, A.Z.; Kamal, N. Identification of ticks and detection of blood protozoa in Friesian cattle by polymerase chain reaction test and estimation of blood parameters in district Kasur, Pakistan. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2008, 40, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, A.; Abbas, T.; Sandhu, Z.U.D. Tick-borne diseases of bovines in Pakistan major scope for future research and improved control. Parasites Vec. 2015, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rjeibi, M.R.; Darghouth, M.A.; Rekik, M.; Amor, B.; Sassi, L.; Gharbi, M. First Molecular Identification and Genetic Characterization of Theileria lestoquardi in Sheep of the Maghreb Region. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.M.; Esmaeilnejad, B.; Jalilzadeh-Amin, G. Molecular detection, infection rate and vectors of Theileria lestoquardi in goats from West Azerbaijan province, Iran. Vet. Res. Forum 2017, 8, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Benkacimi, L.; Diarra, A.Z.; Bompar, J.M.; Jean-Michel, B.; Philippe, P. Microorganisms associated with hedgehog arthropods. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goz, Y.; Yilmaz, A.B.; Aydia, A.; Dic, L.Y. Ticks and Fleas infestation on east hedgehogs (Erinacens concolor) in Van province eastern region of Turkey. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2016, 10, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khodadadi, N.; Nabavi, R.; Sarani, A.; Saadati, D.; Ganjali, M.; Mihalca, A.D.; Otranto, D.; Sazmand, A. Identification of Anaplasma marginale in long-eared hedgehogs (Hemiechinus auritus) and their Rhipicephalus turanicus ticks in Iran. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuballa, J.; Oehme, R.; Hartelt, K.; Petney, T.; Bucher, T.; Kimmig, P.; Taraschewski, H. European hedgehogs as hosts for Borrelia spp., Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silaghi, C.; Skuballa, J.; Thiel, C.; Pfister, K.; Petney, T.; Pfaffle, M.; Taraschewski, H.; Passos, L. The European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus)—A suitable reservoir for variants of Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Ticks. Tick Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Javid, A.; von Fricken, M.E.; Rashid, M.I. Molecular epidemiology of Bartonella species from sympatric mammals collected in urban and rural areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Acta Trop. 2023, 243, 106940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafar, A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Galon, C.; Obregon, D.; Gasser, R.B.; Moutailler, S.; Jabbar, A. Bovine ticks harbour a diverse array of microorganisms in Pakistan. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.; Nijhofi, A.M.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Schauer, B.; Staubach, C.; Conraths, F.J. Distribution of ticks infesting ruminants and risk factors associated with high tick prevalence in livestock farms in the semi-arid and arid agro-ecological zones of Pakistan. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, M.; Nasir, S.; Rafique, A.; Yousaf, I.; Yousaf, M. Prevalence of tick infestation in farm animals from Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. Vet. J. 2019, 39, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.C.M.; Norcott, M.R.; Frost, L.M.; Cusdin, P. Normal hematological values of European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) from an English rehabilitation center. Vet. Rec. 2002, 9, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.B.; Keirans, J.E.; Horak, I.G. Genus Rhipicephalus (Acari, Ixodidae). A Guide to the Brown Ticks of the World; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Torioni de Echaide, S.; Knowles, D.P.; McGuire, T.C.; Palmer, G.H.; Suarez, C.E.; McElwain, T.F. Detection of cattle naturally infected with Anaplasma marginale in a region of endemicity by nested PCR and a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant major surface protein 5. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, U.; Ali, Q.; Zheng, L.; Rashid, I.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Numan, M.; Ashraf, K.; Evans, M.; Rafiq, S.; Oneeb, M.; et al. Contrasting population genetics of co-endemic cattle-and buffalo-derived Theileria annulata. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsu, C.H.; Marsh, T.L. Analysis of microbial communities with denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. Methods Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 41, 909–923. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiki, B.; Addis, M. Distribution of ixodid ticks on cattle in and around Holeta town, Ethiopia. Global Vet. 2011, 7, 527–531. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, P.Y.; Chomel, B.B. Hedgehog zoonoses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ogawa, M.; Brouqui, P. Transmission of Rickettsia massiliae in the tick, Rhipicephalus turanicus. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2005, 19, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrus, S.; Perlman, A.; Muncuoglu, K.Y. Molecular detection of Rickettsia massiliae, Rickettsia sibiricamongolitimonae and Rickettsia conoriiiseaelensis in ticks from Israel. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 17, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, J.L.; Davoust, B.; Socolovschi, C. Molecular detection of rickettsial agents in ticks and fleas collected from a European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) in Marseilles, France. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 35, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgani-Firouzjaee, T.; Pour-Reza, B.; Naem, S.; Tavassoli, M. Ectoparasitic infestations of the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) in Urmia city, Iran: First report. Vet. Res. Forum 2013, 4, 191. [Google Scholar]
- Nematollahi, A.; Helan, J.A.; Golezardy, H.; Zaboli, N.; Nourizi, M.; Azari, M. Parasitic Fauna of East European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus concolor) and their pathological aspects in Iran. Adv. Zool. Bot. 2014, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursali, A.; Keskin, A.; Tekin, S. Tick (Acari: Ixodida) infesting humans in the province of Kelkit Valley, a Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever endemic region in Turkey. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 59, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Shehla, S.; Zahid, H.; Ullah, F.; Zeb, I.; Ahmed, H.; da Silva Vaz, I., Jr.; Tanaka, T. Molecular survey and spatial distribution of Rickettsia spp. in ticks infesting free-ranging wild animals in Pakistan (2017–2021). Pathogens 2022, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkishe, A.A.; Peterson, A.T.; Samy, A.M. Climate change influences on the potential geographic distribution of the disease vector tick Ixodes ricinus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D. The hedgehog tick, Ixodes hexagonus (Leach, 1815) (Acari: Ixodidae); The natural history and ecology of a nest ectoparasite. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 23, 680–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, I.S. Ectoparasites of the long-eared hedgehog (Hemiechinus auratus) (Gmelin) in Ninevah district, Iraq. J. Biol. Sci. Res. 1987, 18, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Shubber, H.W.K.; Al-Hassani, N.A.W.; Mohammad, M.K. Ixoid ticks’ diversity in the middle and south of Iraq. Int. J. Recent Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar]
- Sajid, M.S.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, M.N. Point prevalence of hard ticks (Ixodids) infesting domestic ruminants of lower Punjab, Pakistan. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2008, 10, 349–351. [Google Scholar]
- Sajid, M.S.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, M.N. In vitro and in vivo efficacies of Ivermectin and Cypermethrin against the cattle tick Hyalomma anatolicum (Acari Ixodidae). Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, I.; Shabbir, R.M.K.; Subhani, M. Seasonal activity of tick infestation in goats and buffalo of Punjab Province (District Sargodha), Pakistan. Kafkas Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2014, 20, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Eabaid, F.A. A prevalence study of ectoparasites on the long-eared hedgehog (Hemiechinus auritus) in Al-Muthanna Province, Iraq. AL Qadisiyah J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 16, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyed, L.; Nagy, D.; Lang, Z. Features of Engorgement of Ixodes ricinus Ticks Infesting the Northern, White-Breasted Hedgehog in an Urban Park. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaglio, G.; Allen, S.; Bowden, L. Parasites of European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Britain Epidemiological study and coprological test evaluation. Eur. J. Wild. Res. 2010, 56, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffle, M.; Petney, T.; Skuballa, J. Comparative population dynamics of a generalist (Ixodes ricinus) and specialist tick (I. hexagonus) species from European hedgehogs. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2011, 54, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago, H.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Drechsler, R.M.; Alambiaga, I.; Monrós, J.S. Patterns of adult tick parasitization of coexisting European (Erinaceus europaeus) and Algerian (Atelerix algirus) hedgehog populations in eastern Iberia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahfari, S.; Ruyts, S.C.; Frazer-Mendelewska, E.; Jaarsma, R.; Verheyen, K.; Sprong, H. Melting pot of tick-borne zoonoses: The European hedgehog contributes to the maintenance of various tick-borne diseases in natural cycles urban and suburban areas. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, K.; Springer, A.; Brandes, F.; Reuschel, M.; Fehr, M.; Strube, C. Ectoparasites of European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Germany and their health impact. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuballa, J.; Petney, T.; Pfäffle, M.; Oehme, R.; Hartelt, K.; Fingerle, V.; Kimmig, P.; Taraschewski, H. Occurrence of different Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato genospecies including B. afzelii, B. bavariensis, and B. spielmanii in hedgehogs (Erinaceus spp.) in Europe. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondinini, C.; Doncaster, C.P. Roads as barriers to movement for hedgehogs. Funct. Ecol. 2002, 16, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.A.; Böhning-Gaese, K.; Fagan, W.F.; Fryxell, J.M.; Van Moorter, B.; Alberts, S.C.; Ali, A.H.; Allen, A.M.; Attias, N.; Avgar, T.; et al. Moving in the Anthropocene Global reductions in terrestrial mammalian movements. Science 2018, 359, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.D.; Taylor, J.L.; Randolph, S.E. Tick (Ixodes ricinus) abundance and seasonality at recreational sites in the UK hazards in relation to fine-scale habitat types revealed by complementary sampling methods. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2011, 2, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linske, M.A.; Williams, S.C.; Stafford, K.C., III; Ortega, I.M. Ixodes scapularis (Acari Ixodidae) reservoir host diversity and abundance impact on dilution of Borrelia burgdorferi (Spirochaetales Spirochaetaceae) in residential and woodland habitats in Connecticut, United States. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.; Conraths, F.J.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Krücken, J.; Nijhof, A.M. Epidemiology of tick-borne pathogens in the semi-arid and the arid agro-ecological zones of Punjab province, Pakistan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atif, F.A.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, H.J.; Ali, Z.; Ullah, S. Prevalence of cattle tick infestation in three districts of the Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. J. Sci. 2012, 64, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Ruszkowski, J.J.; Hetman, M.; Turlewicz-Podbielska, H.; Pomorska-Mól, M. Hedgehogs as a Potential Source of Zoonotic Pathogens—A Review and an Update of Knowledge. Animals 2021, 11, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, J.; Song, B.; Aziz, M.U.; Hussain, S.; Zarin, R.; Sparagano, O. Diversity and distribution of Theileria species and their vectors in ruminants from India, Pakistan and Bangladesh. Diversity 2022, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pathogen | Sequence | Target Region | Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anaplasma spp. | 5′-CAGAGCATTGACGCACTACC-3′ | msp1b | 245 | [22] |
| 5′-TCCAGACCTTCCCTAACTA-3′ | ||||
| Babesia spp. | 5′-AGAGGGACTCCTGTGCTTCA-‘3 | 18s rRNA | 321 | [23] |
| 5′-GACGAATCGGAAAAGCCACG-‘3 | ||||
| Theileria spp. | 5′-AAGTATAGCAACTGCTTTTGTT-3′ | Cyt-b | 517 | [23] |
| 5′-TCCTGCCATTGCCAAAAGTC-3′ |
| Variables | Category | Total Captured | Infested | Prevalence (%) | Chi-Square | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 27 | 8 | 29.6 | 0.465 | 0.563 |
| Male | 37 | 8 | 21.6 | |||
| Age | Adult | 48 | 11 | 22.9 | 0.505 | 0.519 |
| Young | 16 | 5 | 31.2 | |||
| Urbanicity | Rural | 38 | 10 | 26.3 | 0.769 | 0.506 |
| Urban | 26 | 6 | 23.1 | |||
| Habitat | Agriculture land | 35 | 9 | 25.7 | 0.885 | 0.559 |
| Animal farm | 29 | 7 | 24.1 | |||
| District | Okara | 23 | 6 | 26.1 | 0.030 | 0.985 |
| Pakpattan | 20 | 5 | 25.0 | |||
| Sahiwal | 21 | 5 | 23.8 |
| Variables | Category | Total | Prevalence (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 74 | 67.9 |
| Female | 35 | 32.1 | |
| Life stage | Adult | 100 | 91.7 |
| Nymph | 9 | 8.3 |
| Variables | Anaplasma marginale |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male (n = 8) | 1 (12.5%) |
| Female (n = 8) | 0 |
| Age | |
| Adult (n = 11) | 1 (9.1%) |
| Young (n = 5) | 0 |
| Urbanicity | |
| Rural (n = 10) | 1 (10.0%) |
| Urban (n = 6) | 0 |
| Location | |
| Okara (n = 6) | 0 |
| Pakpattan (n = 5) | 0 |
| Sahiwal (n = 5) | 1 (20.0%) |
| Variables | Category | Anaplasma marginale | Babesia bigemina | Theileria lestoquardi | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 2 (2.7%) | 1 (1.4%) | 2 (2.7%) | 74 |
| Female | 1 (2.9%) | 2 (5.7%) | 2 (5.7%) | 35 | |
| Life stage | Adult | 3 (3.0%) | 3 (3.0%) | 4 (4.0%) | 100 |
| Nymph | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.; von Fricken, M.E.; Azam, A.; Hassan, A.; Cleary, N.G.; Iftikhar, K.; Rashid, M.I.; Razzaq, A. Tick Infestation and Molecular Detection of Tick-Borne Pathogens from Indian Long-Eared Hedgehogs (Hemiechinus collaris) in Pakistan. Animals 2024, 14, 3185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14223185
Ali S, von Fricken ME, Azam A, Hassan A, Cleary NG, Iftikhar K, Rashid MI, Razzaq A. Tick Infestation and Molecular Detection of Tick-Borne Pathogens from Indian Long-Eared Hedgehogs (Hemiechinus collaris) in Pakistan. Animals. 2024; 14(22):3185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14223185
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Shahzad, Michael E. von Fricken, Asima Azam, Ahmad Hassan, Nora G. Cleary, Kiran Iftikhar, Muhammad Imran Rashid, and Abdul Razzaq. 2024. "Tick Infestation and Molecular Detection of Tick-Borne Pathogens from Indian Long-Eared Hedgehogs (Hemiechinus collaris) in Pakistan" Animals 14, no. 22: 3185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14223185
APA StyleAli, S., von Fricken, M. E., Azam, A., Hassan, A., Cleary, N. G., Iftikhar, K., Rashid, M. I., & Razzaq, A. (2024). Tick Infestation and Molecular Detection of Tick-Borne Pathogens from Indian Long-Eared Hedgehogs (Hemiechinus collaris) in Pakistan. Animals, 14(22), 3185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14223185







