Effect of Operational Conditions on Ammonia Recovery from Simulated Livestock Wastewater Using Gas-Permeable Membrane Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Method and Statistical Analysis
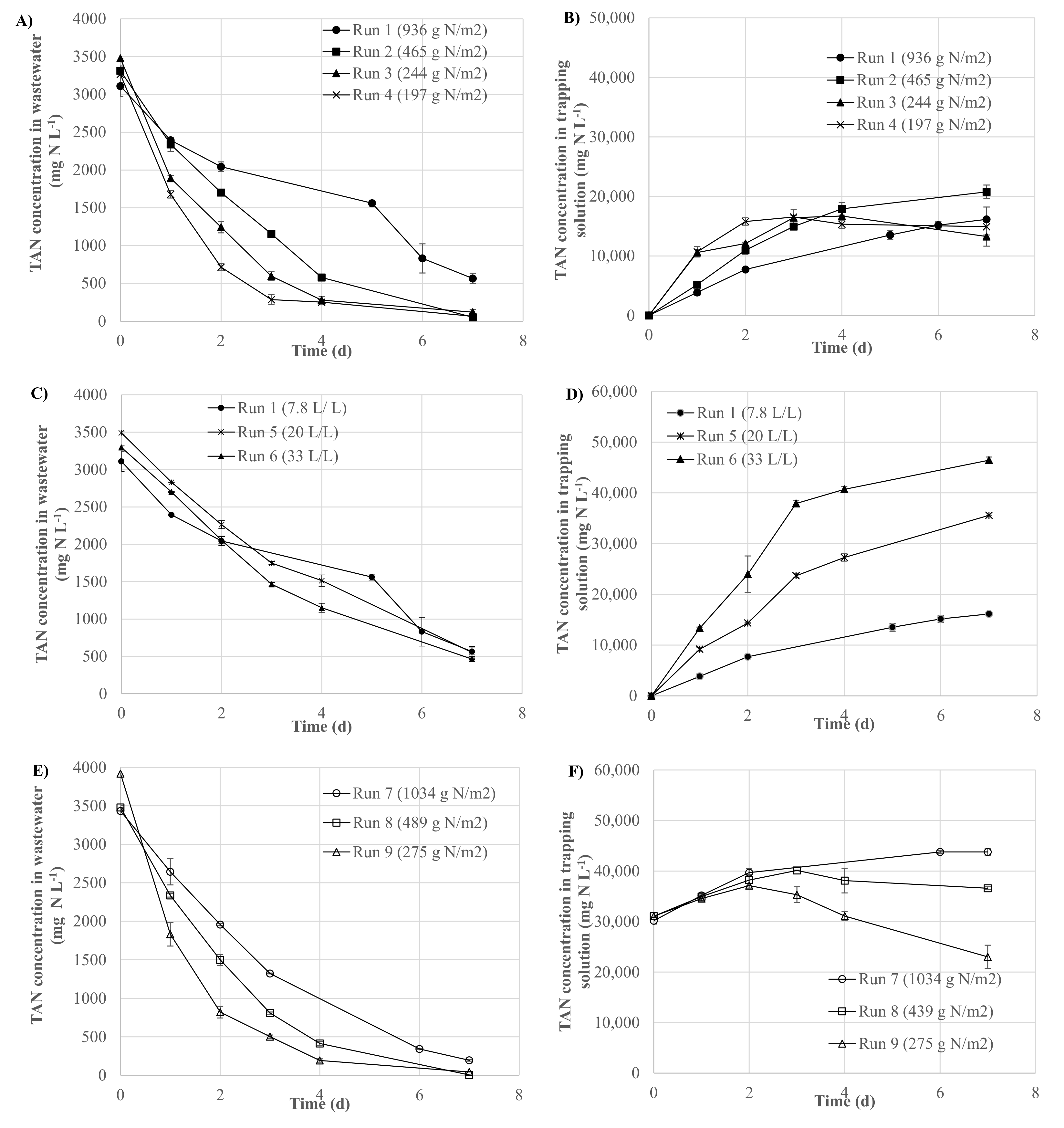
3. Results
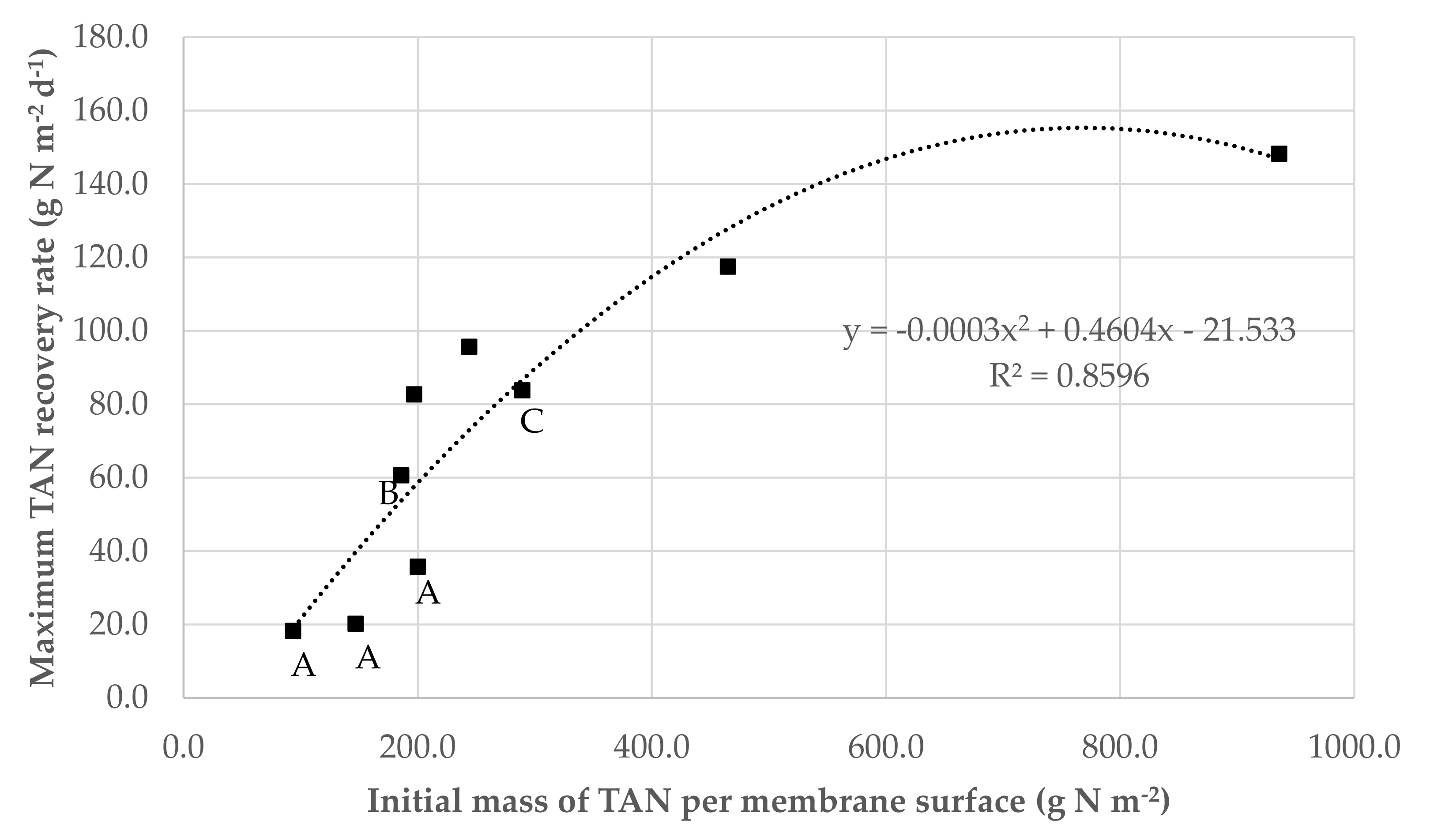
3.1. Effect of the Ratio of the Initial Mass of TAN in Wastewater Per Membrane Surface on GPM Performance
3.2. Effect of the Volume of Wastewater Per Volume of Acidic Trapping Solution Ratio on GPM Performance
3.3. Effect of the Initial TAN Concentration of the Acidic Trapping Solution on GPM Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Agriculture, Ammonia Emissions Statistics—Data Extracted in June 2015. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Agriculture_-_ammonia_emission_statistics (accessed on 30 June 2017).
- Webb, J.; Menzi, H.; Pain, B.F.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Dämmgen, U.; Hendriks, H.; Döhler, H. Managing ammonia emissions from livestock production in Europe. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 135, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, S.; Wolf, S. Intensive livestock operations, health, and quality of life among eastern North Carolina residents. Environ. Health. Perspect. 2000, 108, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.P.; Cooke, P.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Recovery of nitrogen-fertilizer from centrate of anaerobically digested sewage sludge via gas-permeable membrane. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmatí, A.; Flotats, X. Air stripping of ammonia from pig slurry: Characterization and feasibility as a pre-or post-treatment to mesophilic anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, L.; Massé, D.I.; Pellerin, Y.; Dubreuil, J. Osmotic pressure and substrate resistance during the concentration of manure nutrients by reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, Z.; Sánchez, E.; Weiland, P.; de Las Pozas, C.; Borja, R.; Mayari, R.; Rovirosa, N. Ammonia removal from anaerobically treated piggery manure by ion exchange in columns packed with homoionic zeolites. Chem. Eng. J. 1997, 66, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag-Demirer, S.; Demirer, G.N.; Chen, S. Ammonia removal from anaerobically digested dairy manure by struvite precipitation. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 3667–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanotti, M.B.; Szogi, A.A. Systems and Methods for Reducing Ammonia Emissions from Liquid Effluents and for Recovering the Ammonia. U.S. Patent 9,005,333 B1, 14 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.P.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Nitrogen-fertilizer recovery from the centrate of anaerobically digested sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.T.; Hwang, Y.H.; Shin, H.S. Application of PTFE membrane for ammonia removal in a membrane contactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 2944–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani Majd, A.M.; Mukhtar, S. Ammonia diffusion and capture into a tubular gas-permeable membrane using diluted acids. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Dube, P.J.; Vanotti, M.B.; Szogi, A.A.; Garcia-González, M.C. Enhancing recovery of ammonia from swine manure anaerobic digester effluent using gas-permeable membrane technology. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-González, M.C.; Vanotti, M.B.; Szogi, A.A. Recovery of ammonia from swine manure using gas-permeable membranes: Effect of aeration. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 152, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-González, M.C.; Vanotti, M.B. Recovery of ammonia from swine manure using gas-permeable membranes: Effect of waste strength and pH. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Filho, J.D.S.; Daguerre-Martini, S.; Vanotti, M.B.; Saez-Tovar, J.; Rosal, A.; Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Bustamante, M.A.; Moral, R. Recovery of ammonia in raw and co-digested swine manure using gas-permeable membrane technology. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riaño, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; Vanotti, M.; García-González, M.C. Application of gas-permeable membranes for-semi- continuous ammonia recovery from swine manure. Environments 2019, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-González, M.C.; Riaño-Irazábal, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; Hernández-González, D. Influencia del caudal de recirculación de la solución ácida en la captura de NH3 mediante la tecnología de membranas permeables a los gases. In Proceedings of the VI Jornadas de la Red Española de Compostaje, Valencia, Spain, 14–16 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Daguerre-Martini, S.; Vanotti, M.B.; Rodriguez-Pastor, M.; Rosal, A.; Moral, R. Nitrogen recovery from wastewater using gas-permeable membranes: Impact of inorganic carbon content and natural organic matter. Water Res. 2018, 137, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molinuevo-Salces, B.; Riaño, B.; Vanotti, M.B.; Hernández-González, D.; García–González, M.C. Pilot-scale demonstration of membrane-based nitrogen recovery from swine manure. Membranes 2020, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; Vanotti, M.B.; García-González, M.C. Ammonia recovery from digestate using gas-permeable membranes: A pilot-scale study. Environments 2021, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecino, X.; Reig, M.; Gibert, O.; Valderrama, C.; Cortina, J.L. Integration of liquid-liquid membrane contactors and electrodialysis for ammonium recovery and concentration as liquid fertilizer. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Waste Water APHA, 21st ed.; American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation: Denver, CO, USA; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- García-González, M.C.; Vanotti, M.B.; Szogi, A.A. Recovery of ammonia from anaerobically digested manure using gas-permeable membranes. Sci. Agric. 2016, 73, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-García, I.; Riaño, B.; Cuéllar-Franca, R.M.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; García-González, M.C. Environmental sustainability performance of a membrane-based technology for livestock wastewater treatment with nutrient recovery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Runs * | Volume of Wastewater (L) | Volume of Acidic Trapping Solution (L) | Initial Mass of TAN in Wastewater Per Membrane Surface (g N m−2) | Volume of wastewater Per Volume of Acidic Trapping Solution (L L−1) | Initial TAN Concentration in the Trapping Solution (g N L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.0 | 0.384 | 936 ± 82 | 7.8 | <0.1 |
| 2 | 1.4 | 0.180 | 465 ± 7 | 7.8 | <0.1 |
| 3 | 0.7 | 0.090 | 244 ± 0 | 7.8 | <0.1 |
| 4 | 0.6 | 0.077 | 197 ± 13 | 7.8 | <0.1 |
| 5 | 3.0 | 0.150 | 1051 ± 9 | 20.0 | <0.1 |
| 6 | 3.0 | 0.090 | 992 ± 13 | 33.3 | <0.1 |
| 7 | 3.0 | 0.384 | 1034 ± 28 | 7.8 | 30.2 ± 0.6 |
| 8 | 1.4 | 0.180 | 489 ± 6 | 7.8 | 31.0 ± 0.0 |
| 9 | 0.7 | 0.090 | 275 ± 0 | 7.8 | 31.0 ± 0.0 |
| Run * | Initial Mass of TAN in Wastewater per Membrane Surface (g N m−2) | TAN Concentration in the Trapping Solution (g N L−1) | Initial TAN (mg) | TAN Removed (mg) | TAN Recovered in the Trapping Solution (mg) ** | TAN Lost by Volatilization (mg) | TAN Removal Efficiency (%) | TAN Recovery Efficiency (%) | Maximum TAN Recovery Rate (g N m−2 d−1) | Average TAN Recovery Rate (g N m−2 d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 936 ± 82 | <0.1 | 9329 ± 821 | 7634 ± 205 | 6315 ± 45 | 1319 ± 456 | 81.8 ± 2.8 | 82.7 ± 5.1 | 148.5 ± 18.8 | 90.5 ± 0.7 |
| 2 | 465 ± 7 | <0.1 | 4637 ± 68 | 4562 ± 24 | 4356 ± 297 | 206 ± 209 | 98.4 ± 0.5 | 95.5 ± 4.7 | 117.5 ± 12.6 | 62.4 ± 4.3 |
| 3 | 244 ± 0 | <0.1 | 2435 ± 0 | 2350 ± 52 | 1851 ± 51 | 499 ± 103 | 96.5 ± 2.1 | 78.8 ± 3.9 | 95.6 ± 4.5 | 26.5 ± 0.7 |
| 4 | 197 ± 13 | <0.1 | 1960 ± 131 | 1921 ± 45 | 1534 ± 32 | 387 ± 122 | 98.0 ± 1.9 | 79.9 ± 5.4 | 82.6 ± 6.7 | 22.0 ± 0.5 |
| 7 | 1034 ± 28 | 30.2 ± 0.6 | 10,101 ± 280 | 9719 ± 111 | 6314 ± 207 | 3404 ± 130 | 94.3 ± 0.7 | 65.0 ± 0.1 | 210.0 ± 35.1 | 90.5 ± 3.0 |
| 8 | 489 ± 6 | 31.0 ± 0.0 | 4869 ± 59 | 4864 ± 30 | 3339 ± 4 | 1524 ± 63 | 99.9 ± 0.0 | 68.7 ± 0.9 | 121.2 ± 41.9 | 47.9 ± 0.1 |
| 9 | 275 ± 0 | 31.0 ± 0.0 | 2742 ± 0 | 2711 ± 0 | 691± 569 | 2020 ± 569 | 98.9 ± 0.0 | 25.5 ± 21.0 | 41.9 ± 19.2 | 9.9 ± 8.2 |
| Run * | Volume of Wastewater per Volume of Acidic Trapping Solution (L L−1) | Initial TAN (mg) | TAN Removed (mg) | TAN Recovered in the Trapping Solution (mg) | TAN Lost by Volatilization (mg) | TAN Removal Efficiency (%) | TAN Recovery Efficiency (%) | Maximum TAN Recovery Rate (g N m−2 d−1) | Average TAN Recovery Rate (g N m−2 d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.8 | 9329 ± 821 | 7634 ± 205 | 6315 ± 45 | 1319 ± 456 | 81.8 ± 2.8 | 82.7 ± 5.1 | 148.5 ± 18.8 | 90.5 ± 0.7 |
| 5 | 20.0 | 10,469 ± 8 | 8811 ± 31 | 6724 ± 153 | 2087 ± 373 | 84.2 ± 4.3 | 76.3 ± 2.8 | 163.6 ± 10.8 | 96.4 ± 1.1 |
| 6 | 33.3 | 9887 ± 129 | 8497 ± 22 | 7193 ± 58 | 1305 ± 43 | 85.9 ± 0.1 | 84.6 ± 0.3 | 185.4 ± 89.3 | 103.1 ± 0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riaño, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; Vanotti, M.B.; García-González, M.C. Effect of Operational Conditions on Ammonia Recovery from Simulated Livestock Wastewater Using Gas-Permeable Membrane Technology. Environments 2022, 9, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9060070
Riaño B, Molinuevo-Salces B, Vanotti MB, García-González MC. Effect of Operational Conditions on Ammonia Recovery from Simulated Livestock Wastewater Using Gas-Permeable Membrane Technology. Environments. 2022; 9(6):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9060070
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiaño, Berta, Beatriz Molinuevo-Salces, Matías B. Vanotti, and María Cruz García-González. 2022. "Effect of Operational Conditions on Ammonia Recovery from Simulated Livestock Wastewater Using Gas-Permeable Membrane Technology" Environments 9, no. 6: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9060070
APA StyleRiaño, B., Molinuevo-Salces, B., Vanotti, M. B., & García-González, M. C. (2022). Effect of Operational Conditions on Ammonia Recovery from Simulated Livestock Wastewater Using Gas-Permeable Membrane Technology. Environments, 9(6), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9060070







