Genome-Centered Metagenomics Analysis Reveals the Microbial Interactions of a Syntrophic Consortium during Methane Generation in a Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
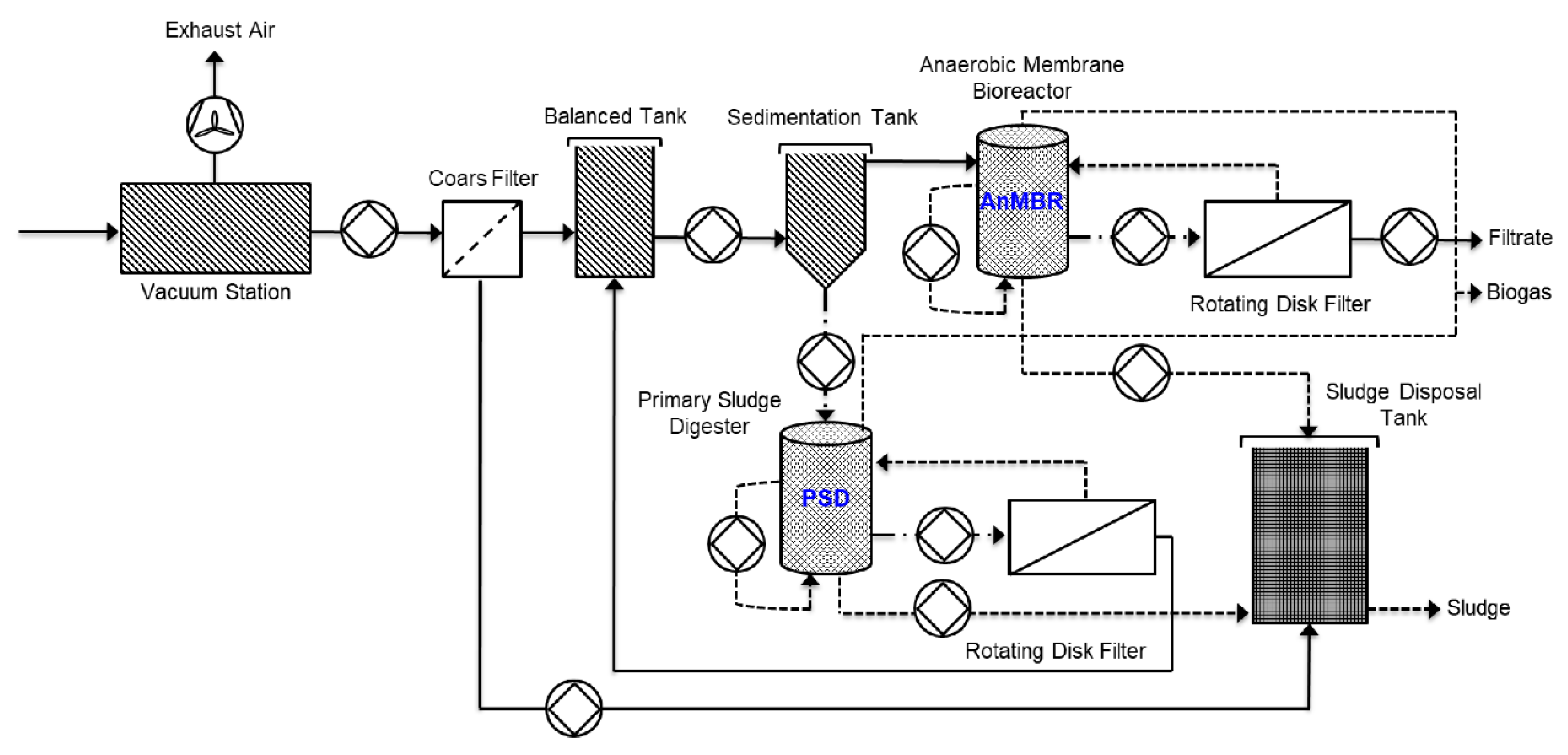
2.1. Description of a Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System
2.2. Sampling and Physicochemical Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Analysis
2.4. Metagenomic Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
2.5. Methanogenic Pathway of Predominant Species Determined by Genomic Binning
2.6. Statistics
2.7. Sequence Accession
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Operational Performance of the DWTS
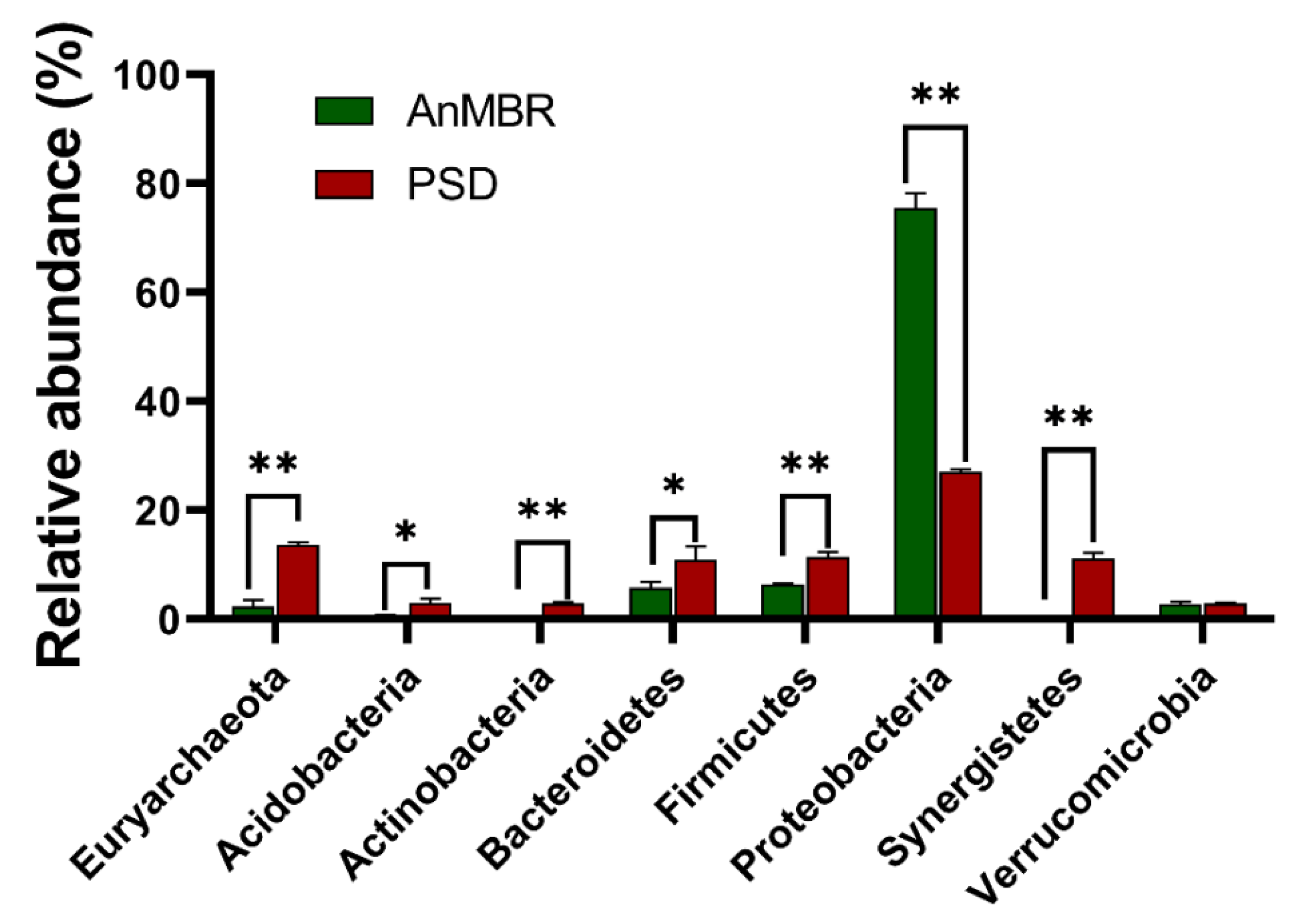
3.2. Characteristic Microorganisms in the PSD and AnMBR
3.3. Variation of Gene Functional Profiles of the PSD and AnMBR
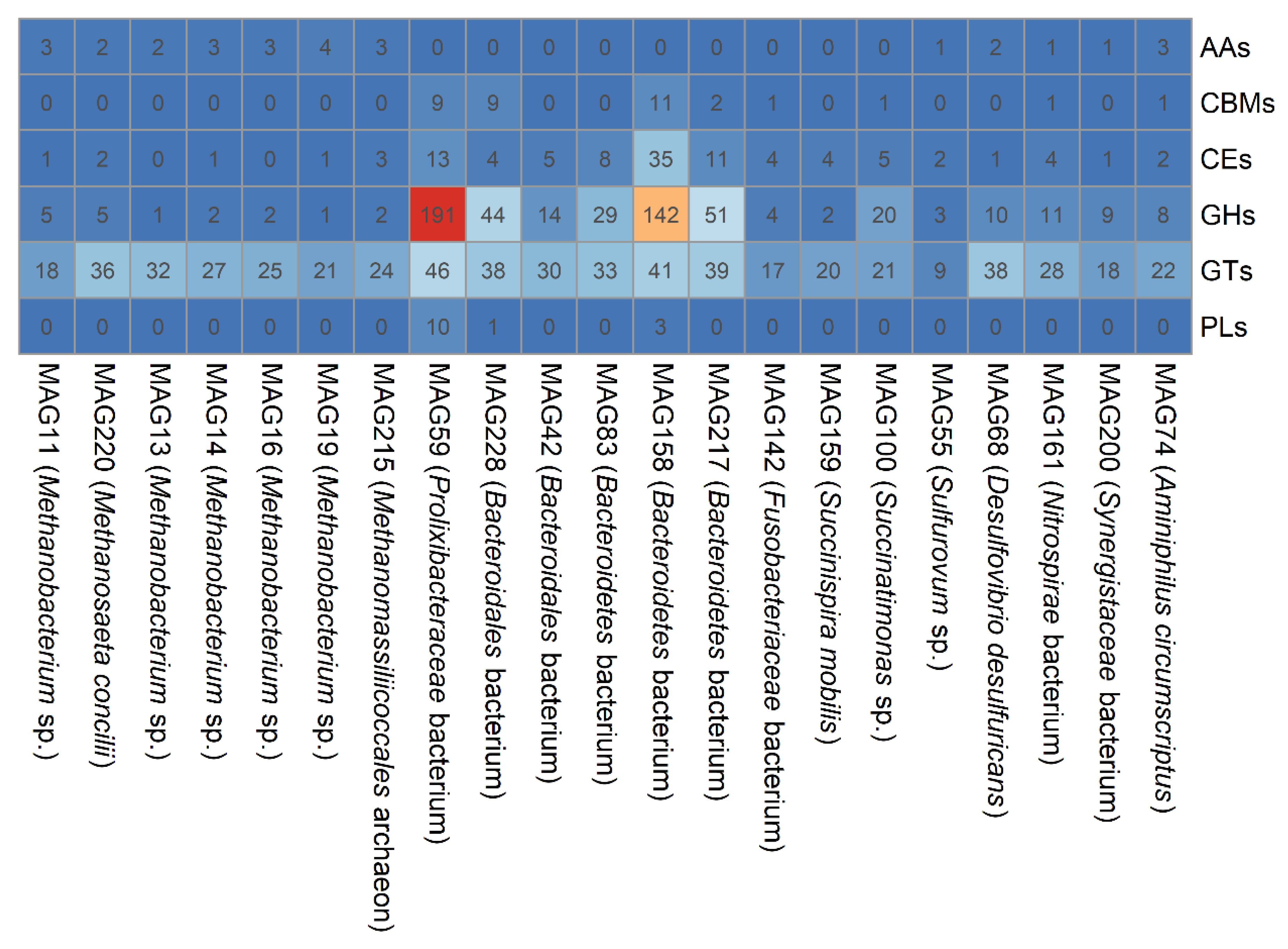
3.4. Phylogenetics of MAGs and Their Abundance in the PSD and AnMBR
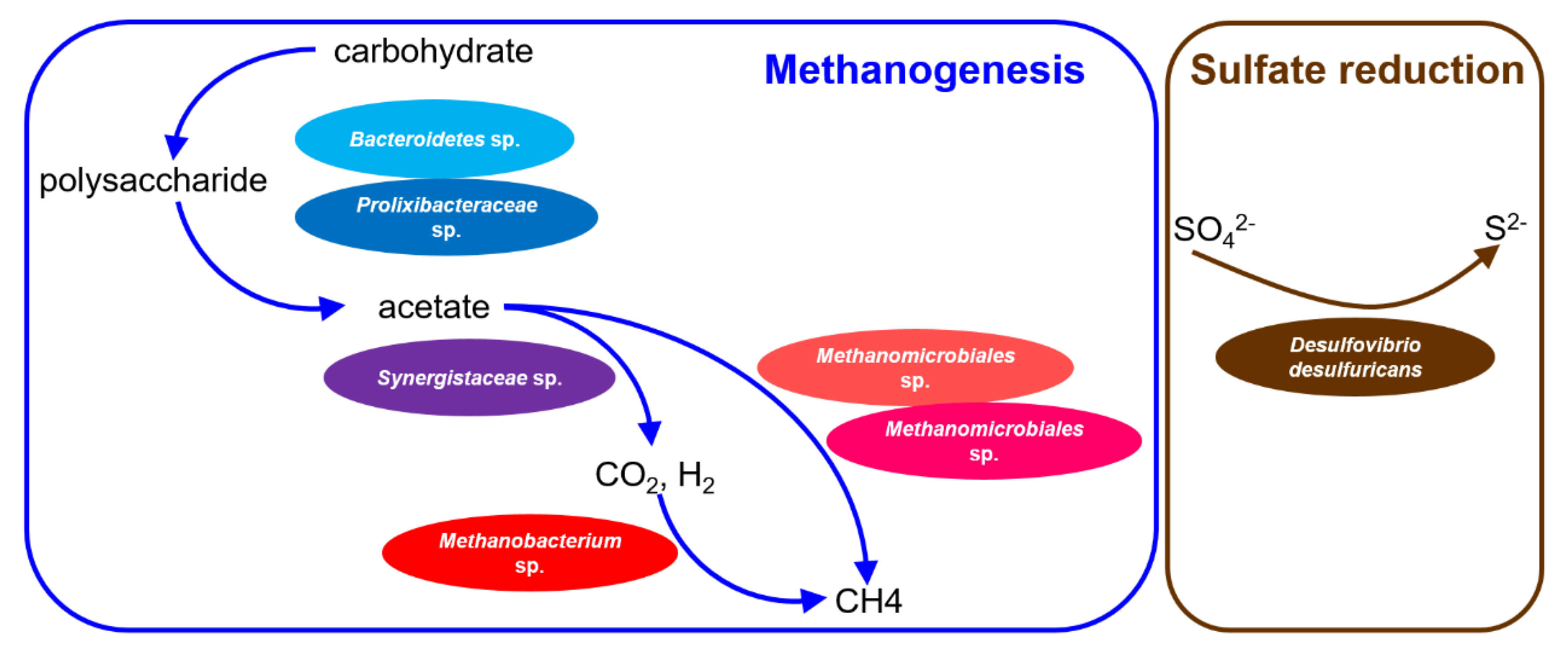
3.5. Microbial Interaction and Methane-Producing Pathways of the Dominant Species in the PSD and AnMBR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog. Energy. Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, Y.; Zeeman, G.; van Lier, J.B.; Lettinga, G. The role of sludge retention time in the hydrolysis and acidification of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins during digestion of primary sludge in CSTR systems. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.R.; Lang, N.L.; Cheung, K.H.M.; Spanoudaki, K. Factors controlling pathogen destruction during anaerobic digestion of biowastes. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvořák, L.; Gómez, M.; Dolina, J.; Černín, A. Anaerobic membrane bioreactors—A mini review with emphasis on industrial wastewater treatment: Applications, limitations and perspectives. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 19062–19076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, R.K.; Ersahin, M.E.; Ozgun, H.; Ozturk, I.; Jeison, D.; van der Zee, F.; van Lier, J.B. Potentials of anaerobic membrane bioreactors to overcome treatment limitations induced by industrial wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.J.; Chen, J.R.; Hong, H.C.; Zhang, Y. A review on anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Applications, membrane fouling and future perspectives. Desalination 2013, 314, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lee, J.; Han, G.; Hwang, S. Comprehensive analysis of microbial communities in full-scale mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digesters treating food waste-recycling wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabeo-Pérez, A.; Guerra-Rivera, G.; Ramos-Leal, M.; Klocke, M.; Jiménez-Hernández, J. Metagenomic approaches: Effective tools for monitoring the structure and functionality of microbiomes in anaerobic digestion systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwonterghem, I.; Jensen, P.D.; Ho, D.P.; Batstone, D.J.; Tyson, G.W. Linking microbial community structure, interactions and function in anaerobic digesters using new molecular techniques. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwonterghem, I.; Jensen, P.D.; Rabaey, K.; Tyson, G.W. Genome-centric resolution of microbial diversity, metabolism and interactions in anaerobic digestion. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 3144–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Gong, H.; Liu, X.; Giwa, A.S.; Wang, K. Evaluation of bacterial association in methane generation pathways of an anaerobic digesting sludge via metagenomic sequencing. Arch. Microbiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Xia, Y.; Lau, F.T.K.; Tang, D.T.W.; Fung, W.C.; Fang, H.H.P.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic analysis of sludge from full-scale anaerobic digesters operated in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5709–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundberg, C.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Larsson, M.; Alm, E.; Yekta, S.S.; Svensson, B.H.; Sørensen, S.J.; Karlsson, A. 454 pyrosequencing analyses of bacterial and archaeal richness in 21 full-scale biogas digesters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, J.P.; Li, J.B.; Zhang, S.H.; Yan, X.F.; Wang, Y.P.; Li, X.Z. The core populations and co-occurrence patterns of prokaryotic communities in household biogas digesters. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialek, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Collins, G.; Mahony, T.; O’Flaherty, V. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of methanogenic community development in high-rate anaerobic bioreactors. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanaro, S.; Treu, L.; Kougias, P.G.; De Francisci, D.; Valle, G.; Angelidaki, I. Metagenomic analysis and functional characterization of the biogas microbiome using high throughput shotgun sequencing and a novel binning strategy. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, A.; Bekel, T.; Diaz, N.N.; Dondrup, M.; Eichenlaub, R.; Gartemann, K.-H.; Krahn, I.; Krause, L.; Krömeke, H.; Kruse, O.; et al. The metagenome of a biogas-producing microbial community of a production-scale biogas plant fermenter analysed by the 454-pyrosequencing technology. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 136, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R.; Kovács, E.; Maróti, G.; Bagi, Z.; Rákhely, G.; Kovács, K.L. Characterization of a biogas-producing microbial community by short-read next generation DNA sequencing. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2012, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.X.; Huang, K.L.; Miao, Y.; Shi, P.; Liu, B.; Long, C.; Li, A.M. Metagenomic profiling of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in a tannery wastewater treatment plant. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.T.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Hui, R.K.H.; Tun, H.M.; Brar, M.S.; Park, T.J.; Chen, Y.; Leung, F.C. Towards a metagenomic understanding on enhanced biomethane production from waste activated sludge after pH 10 pretreatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Chu, Y.N.; Wang, X.M.; Ren, L.F.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.L.; Yan, J.B.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.X.; Li, S.Z. A pyrosequencing-based metagenomic study of methane-producing microbial community in solid-state biogas reactor. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, J.D.; Othman, M.Z.; Beale, D.J.; Joshi, D. The use of laboratory scale reactors to predict sensitivity to changes in operating conditions for full-scale anaerobic digestion treating municipal sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federation, W.E.; Association, A.P.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, S.T.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Caporaso, J.G.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME J. 2011, 5, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods. 2010, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Coutinho, P.M.; Rancurel, C.; Bernard, T.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): An expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 37, D233–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Leung, H.C.; Yiu, S.M.; Chin, F.Y. IDBA-UD: A de novo assembler for single-cell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods. 2012, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alneberg, J.; Bjarnason, B.S.; de Bruijn, I.; Schirmer, M.; Quick, J.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Loman, N.J.; Andersson, A.F.; Quince, C. CONCOCT: Clustering contigs on coverage and composition. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.4038. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Börnigen, D.; Morgan, X.C.; Huttenhower, C. PhyloPhlAn is a new method for improved phylogenetic and taxonomic placement of microbes. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Auch, A.F.; Qi, J.; Schuster, S.C. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, M.; Tang, H.X.; Ye, Y.Z. FragGeneScan: Predicting genes in short and error-prone reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, G.T.W.; Liu, A.C.; Weng, C.Y.; Chou, C.Y.; Wang, D. Inferring microbial interactions in thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic digestion of hog waste. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vrieze, J.; Saunders, A.M.; He, Y.; Fang, J.; Nielsen, P.H.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Ammonia and temperature determine potential clustering in the anaerobic digestion microbiome. Water Res. 2015, 75, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsyurbenko, O.R.; Friedrich, M.W.; Simankova, M.V.; Nozhevnikova, A.N.; Golyshin, P.N.; Timmis, K.N.; Conrad, R. Shift from acetoclastic to H2-dependent methanogenesis in a west siberian peat bog at low pH values and isolation of an acidophilic Methanobacterium strain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerholm, M.; Roos, S.; Schnürer, A. Syntrophaceticus schinkii gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic, syntrophic acetate-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a mesophilic anaerobic filter. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 309, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, N.D.; Sherry, A.; Grant, R.J.; Rowan, A.K.; Hubert, C.R.J.; Callbeck, C.M.; Aitken, C.M.; Jones, D.M.; Adams, J.J.; Larter, S.R.; et al. The quantitative significance of Syntrophaceae and syntrophic partnerships in methanogenic degradation of crude oil alkanes. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2957–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Ding, C.; Li, Q.; He, Q.; Dai, L.R.; Zhang, H. DNA-SIP reveals that Syntrophaceae play an important role in methanogenic hexadecane degradation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.Q.; Sun, D.Z.; Dang, Y.; Feng, X.L.; Huo, D.; Liu, C.Q.; Zheng, K.; Holmes, D.E. Metagenomic analysis reveals that activated carbon aids anaerobic digestion of raw incineration leachate by promoting direct interspecies electron transfer. Water Res. 2019, 161, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziels, R.M.; Sousa, D.Z.; Stensel, H.D.; Beck, D.A.C. DNA-SIP based genome-centric metagenomics identifies key long-chain fatty acid-degrading populations in anaerobic digesters with different feeding frequencies. ISME J. 2018, 12, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforno, T.P.; Lacerda, G.V.; Sierra-Garcia, I.N.; Okada, D.Y.; Macedo, T.Z.; Varesche, M.B.A.; Oliveira, V.M. Metagenomic analysis of the microbiome in three different bioreactor configurations applied to commercial laundry wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforno, T.P.; Macedo, T.Z.; Midoux, C.; Lacerda, G.V.; Rué, O.; Mariadassou, M.; Loux, V.; Varesche, M.B.A.; Bouchez, T.; Bize, A.; et al. Comparative metatranscriptomic analysis of anaerobic digesters treating anionic surfactant contaminated wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassa, J.; Maus, I.; Off, S.; Pühler, A.; Scherer, P.; Klocke, M.; Schlüter, A. Metagenome, metatranscriptome, and metaproteome approaches unraveled compositions and functional relationships of microbial communities residing in biogas plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 504–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrissat, B.; Bairoch, A. New families in the classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J. 1993, 293, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söllinger, A.; Schwab, C.; Weinmaier, T.; Loy, A.; Tveit, A.T.; Schleper, C.; Urich, T. Phylogenetic and genomic analysis of Methanomassiliicoccales in wetlands and animal intestinal tracts reveals clade-specific habitat preferences. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 92, fiv149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, P.; Stams, A.J.M.; Cheng, X.; Plugge, C.M. Growth- and substrate-dependent transcription of formate dehydrogenase and hydrogenase coding genes in Syntrophobacter fumaroxidans and Methanospirillum hungatei. Microbiology 2011, 157, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Liu, X.L.; Dong, X.Z. Methanosaeta harundinacea sp. nov., a novel acetate-scavenging methanogen isolated from a UASB reactor. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, H.; Berchtold, M.; Branke, J.; König, H.; Cypionka, H.; Babenzien, H.-D. Psychrotolerant sulfate-reducing bacteria from an oxic freshwater sediment description of Desulfovibrio cuneatus sp. nov. and Desulfovibrio litoralis sp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 21, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Nakagawa, S.; Shimamura, S.; Takai, K.; Horikoshi, K. Molecular characterization of inorganic sulfur-compound metabolism in the deep-sea epsilonproteobacterium Sulfurovum sp. NBC37-1. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotomi, M.; Nagai, F.; Watanabe, Y. CO2-dependent growth of Succinatimonas hippei YIT 12066T isolated from human feces. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 56, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, C.; Baena, S.; Fardeau, M.L.; Patel, B.K.C. Aminiphilus circumscriptus gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic amino-acid-degrading bacterium from an upflow anaerobic sludge reactor. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1914–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.H.; Farrell, K.A. Succinispira mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., a succinate-decarboxylating anaerobic bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1999, 49, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, H.S.; Yano, T.; Nishio, N.; Nagai, S. Biomethanation of H2 and CO2 by Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum in membrane and ceramic bioreactors. J. Ferment. Technol. 1987, 65, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militon, C.; Hamdi, O.; Michotey, V.; Fardeau, M.-L.; Ollivier, B.; Bouallagui, H.; Hamdi, M.; Bonin, P. Ecological significance of Synergistetes in the biological treatment of tuna cooking wastewater by an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18230–18238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, H.Z.; Chen, Y.; Gou, M.; Xia, Z.Y.; Hu, B.; Nie, Y.; Tang, Y.Q. Identification of novel butyrate- and acetate-oxidizing bacteria in butyrate-fed mesophilic anaerobic chemostats by DNA-based stable isotope probing. Microb. Ecol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thauer, R.K.; Kaster, A.-K.; Seedorf, H.; Buckel, W.; Hedderich, R. Methanogenic archaea: Ecologically relevant differences in energy conservation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwonterghem, I.; Evans, P.N.; Parks, D.H.; Jensen, P.D.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. Methylotrophic methanogenesis discovered in the archaeal phylum Verstraetearchaeota. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, I.; Wibberg, D.; Stantscheff, R.; Cibis, K.; Eikmeyer, F.-G.; König, H.; Pühler, A.; Schlüter, A. Complete genome sequence of the hydrogenotrophic Archaeon Methanobacterium sp. Mb1 isolated from a production-scale biogas plant. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 168, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Fujita, T.; Akada, S.; Tonouchi, A. Methanobacterium kanagiense sp. nov., a hydrogenotrophic methanogen, isolated from rice-field soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Leahy, S.C.; Jeyanathan, J.; Henderson, G.; Cox, F.; Altermann, E.; Kelly, W.J.; Lambie, S.C.; Janssen, P.H.; Rakonjac, J.; et al. The complete genome sequence of the methanogenic archaeon ISO4-H5 provides insights into the methylotrophic lifestyle of a ruminal representative of the Methanomassiliicoccales. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2016, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Loh, K.-C.; Lim, J.W.; Zhang, J. Bioinformatics analysis of metagenomics data of biogas-producing microbial communities in anaerobic digesters: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 2019, 100, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Tishel, R.; Eisenbach, M.; Wolfe, A.J. Cloning, characterization, and functional expression of acs, the gene which encodes acetyl coenzyme A synthetase in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 2878–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermler, U.; Grabarse, W.; Shima, S.; Goubeaud, M.; Thauer, R.K. Crystal structure of methyl-coenzyme M reductase: The key enzyme of biological methane formation. Science 1997, 278, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | AnMBR | PSD |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic retention time | 24 h | 40 days |
| solid retention time | ~200 days | ~200 days |
| Organic loading rate | 0.71 (g COD/L/d) | 0.16 (g VSS/L/d) |
| Biogas production a | 122 (L/kg COD) | 374 (l/kg VSS) |
| CH4% | 80~85 | 60~65 |
| pH | 7.11 | 7.25 |
| Temperature (°C) | 20 | 37 |
| TSS (%) b | 4.11 | 4.24 |
| VSS (%) c | 2.87 | 2.87 |
| ID | Classification b | N50 c | No Contigs | Total Length of Contigs (bp) | Average Contig Length (bp) | Max Contig Length (bp) | GC (%) | No of ORFs | Comple (%) d | Contam (%) d | Sequencing Depth e | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSD | AnMBR | |||||||||||
| MAGs100 | Succinatimonas sp. | 16,425 | 223 | 2,345,215 | 10,517 | 63,091 | 36.82 | 2223 | 97.76 | 2.87 | 0.34 | 8.39 |
| MAGs11 | Methanomicrobiales archaeon | 7037 | 436 | 2,646,689 | 6070 | 25,219 | 42.08 | 2833 | 79.45 | 5.23 | 3.74 | 2.48 |
| MAGs13 | Methanobacterium sp. | 12,305 | 204 | 1,869,900 | 9166 | 45,173 | 42.15 | 2081 | 83.94 | 0.84 | 38.34 | 6.63 |
| MAGs14 | Methanobacterium sp. | 23,088 | 142 | 2,296,620 | 16,173 | 116,341 | 38.15 | 2361 | 93.17 | 2.67 | 6.53 | 0.20 |
| MAGs142 | Fusobacteriaceae bacterium | 10,000 | 211 | 1,551,831 | 7355 | 39,904 | 30.14 | 1658 | 91.79 | 2.73 | 5.24 | 3.95 |
| MAGs158 | Bacteroidetes bacterium | 15,651 | 403 | 4,085,030 | 10,137 | 76,799 | 45.64 | 3587 | 96.19 | 5.24 | 5.64 | 1.13 |
| MAGs159 | Succinispira mobilis | 14,617 | 210 | 2,202,808 | 10,490 | 63,607 | 36.04 | 2197 | 96.86 | 2.89 | 3.39 | 1.81 |
| MAGs16 | Methanobacterium sp. | 17,780 | 478 | 2,301,104 | 4814 | 58,716 | 40.3 | 2679 | 84.46 | 2.4 | 54.29 | 17.46 |
| MAGs161 | Nitrospirae bacterium | 13,359 | 313 | 2,843,440 | 9084 | 46,148 | 55.18 | 2981 | 98.18 | 1.82 | 3.69 | 1.59 |
| MAGs19 | Methanobacterium sp. | 6795 | 310 | 1,680,516 | 5421 | 22,507 | 36.71 | 1935 | 80.65 | 1.6 | 2.81 | 2.43 |
| MAGs200 | Synergistaceae bacterium | 8450 | 288 | 1,824,470 | 6335 | 23,350 | 52.55 | 1,880 | 93.17 | 4.39 | 76.01 | 56.51 |
| MAGs215 | Methanomassiliicoccales archaeon | 9228 | 411 | 2,486,731 | 6050 | 61,395 | 58.07 | 2680 | 95.97 | 1.74 | 5.48 | 0.58 |
| MAGs217 | Bacteroidetes bacterium | 15,116 | 335 | 3,683,488 | 10,995 | 66,810 | 39.58 | 3130 | 92.58 | 2.96 | 0.21 | 28.36 |
| MAGs220 | Methanosaeta concilii | 7179 | 629 | 3,019,496 | 4800 | 30,000 | 51.53 | 3526 | 97.52 | 5.56 | 14.54 | 6.04 |
| MAGs228 | Bacteroidales bacterium | 12,901 | 289 | 2,635,062 | 9118 | 36,976 | 33.82 | 2753 | 93.66 | 6.74 | 2.52 | 4.45 |
| MAGs42 | Bacteroidales bacterium | 14,503 | 181 | 1,936,905 | 10,701 | 66,427 | 37.47 | 1825 | 94.76 | 2.43 | 3.99 | 30.15 |
| MAGs55 | Sulfurovum sp. | 13,025 | 191 | 1,771,721 | 9276 | 79,310 | 32.35 | 1982 | 96.11 | 0.55 | 4.98 | 9.31 |
| MAGs59 | Prolixibacteraceae bacterium | 11,407 | 605 | 5,015,715 | 8290 | 56,146 | 43.94 | 4635 | 98.3 | 4.03 | 0.27 | 9.23 |
| MAGs68 | Desulfovibrio desulfuricans | 16,359 | 309 | 3,388,200 | 10,965 | 100,792 | 57.99 | 2939 | 97.23 | 0.13 | 9.29 | 4.41 |
| MAGs74 | Aminiphilus circumscriptus | 17,094 | 277 | 3,001,628 | 10,836 | 60,241 | 60.61 | 2789 | 93.22 | 0 | 19.43 | 9.12 |
| MAGs83 | Bacteroidetes bacterium | 8876 | 512 | 3,069,843 | 5996 | 30,790 | 42.06 | 2924 | 94.35 | 4.91 | 0.77 | 54.82 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Ouyang, X.; Li, J.-P.; Liao, J.-J.; You, A.; Yue, X.; Xie, G.-J.; Liang, J.-L.; Li, J.-T. Genome-Centered Metagenomics Analysis Reveals the Microbial Interactions of a Syntrophic Consortium during Methane Generation in a Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010135
Zhang K, Zhang Y-L, Ouyang X, Li J-P, Liao J-J, You A, Yue X, Xie G-J, Liang J-L, Li J-T. Genome-Centered Metagenomics Analysis Reveals the Microbial Interactions of a Syntrophic Consortium during Methane Generation in a Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010135
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kun, Yan-Ling Zhang, Xin Ouyang, Jun-Peng Li, Jun-Jie Liao, Ao You, Xiu Yue, Guang-Jian Xie, Jie-Liang Liang, and Jin-Tian Li. 2020. "Genome-Centered Metagenomics Analysis Reveals the Microbial Interactions of a Syntrophic Consortium during Methane Generation in a Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System" Applied Sciences 10, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010135
APA StyleZhang, K., Zhang, Y.-L., Ouyang, X., Li, J.-P., Liao, J.-J., You, A., Yue, X., Xie, G.-J., Liang, J.-L., & Li, J.-T. (2020). Genome-Centered Metagenomics Analysis Reveals the Microbial Interactions of a Syntrophic Consortium during Methane Generation in a Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System. Applied Sciences, 10(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010135




