Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
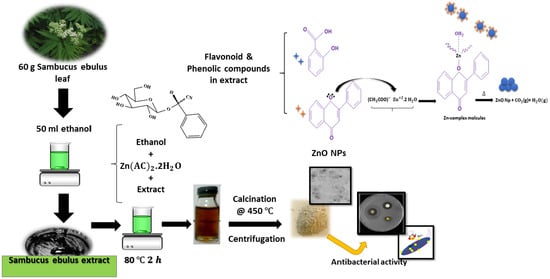
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Antibacterial Activity Test
2.3. Antioxidant Activity
2.4. Photocatalytic Activity
2.5. Analytical Methods
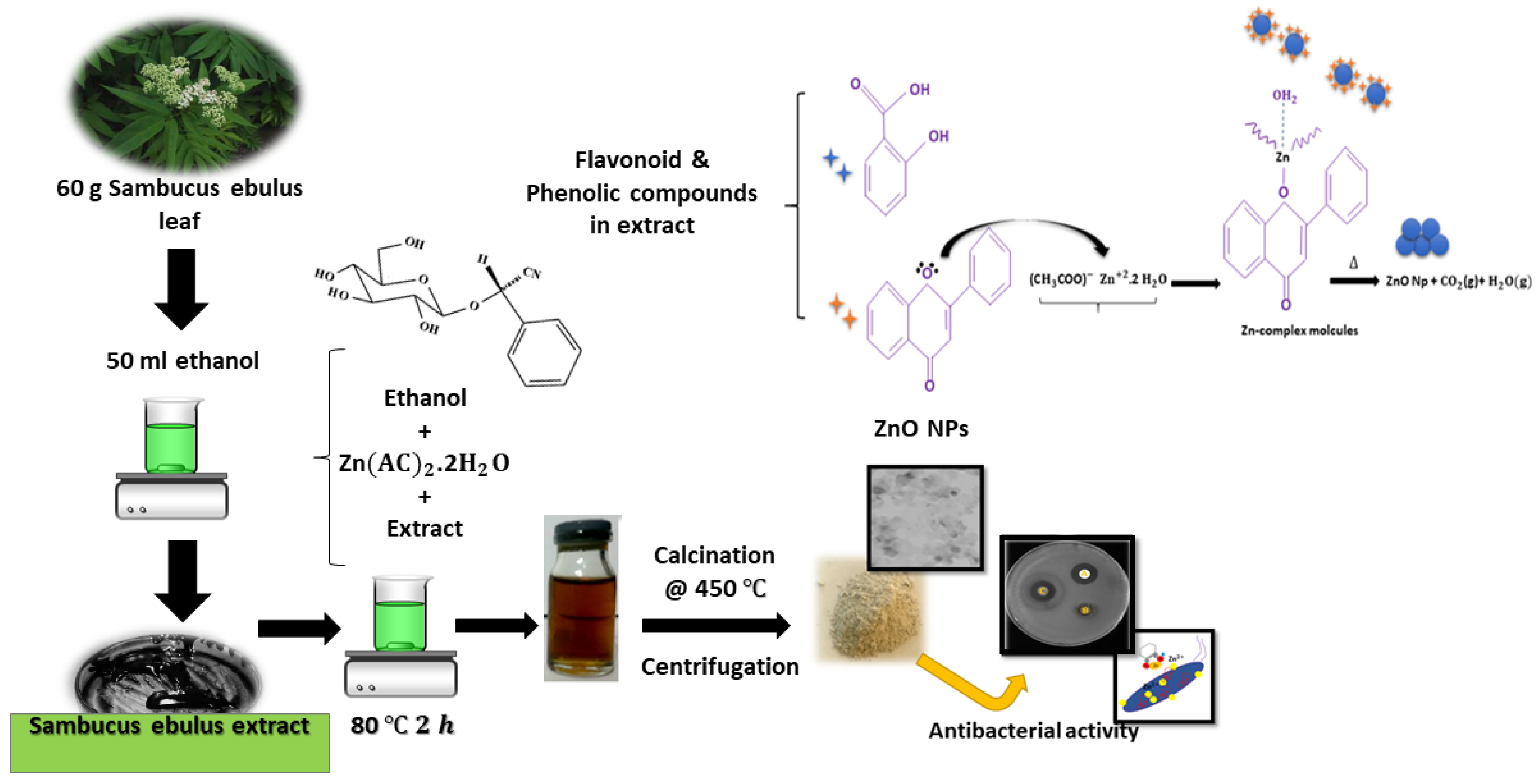
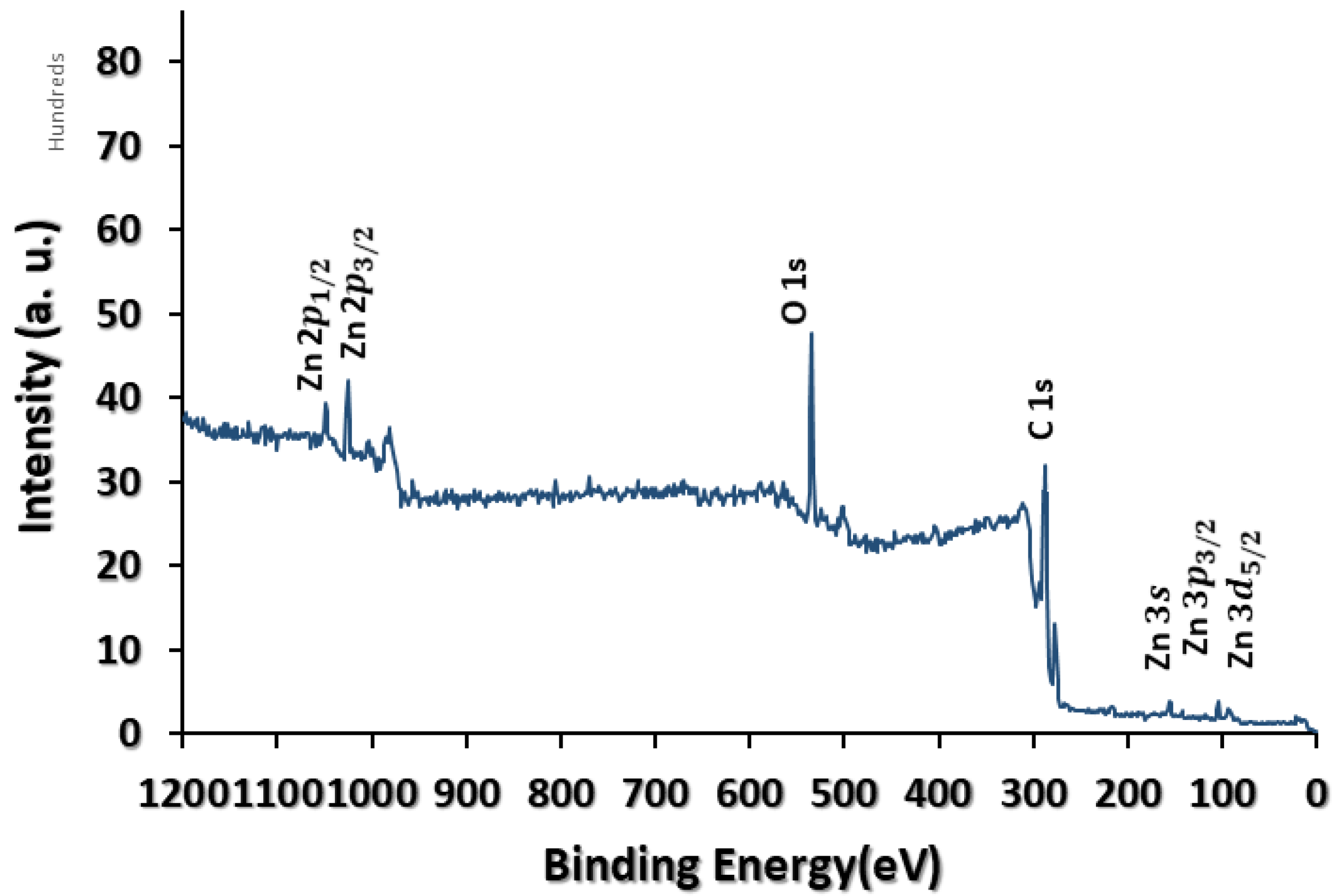
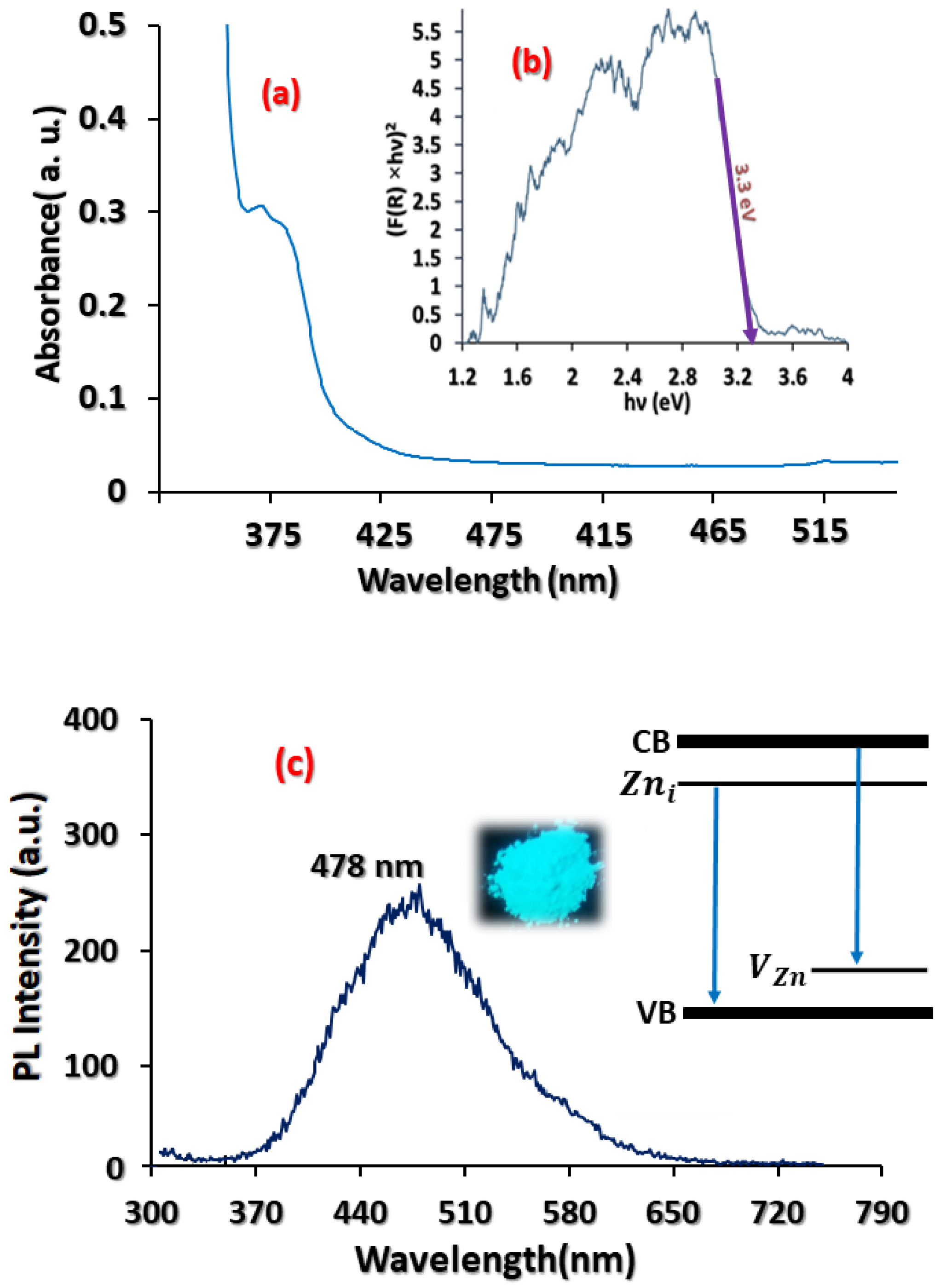
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterisation
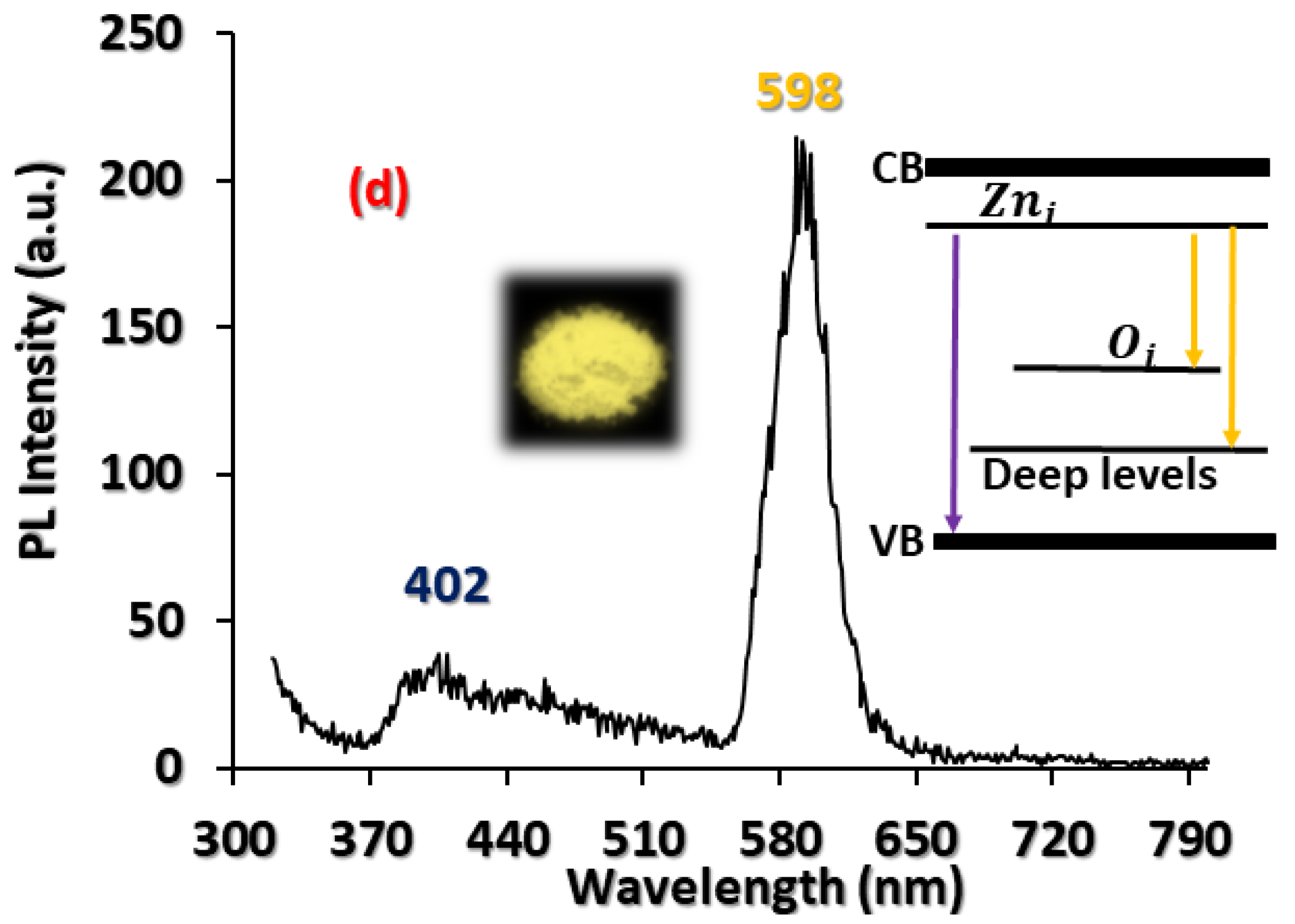
3.2. Optical Characterisation
3.3. Microstructural Characteristisation
3.4. Photocatalytic Tests
3.5. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yusof, H.M.; Mohamad, R.; Zaidan, U.H.; Rahman, N.A.A. Abdul Rahman, Sustainable microbial cell nanofactory for zinc oxide nanoparticles production by zinc-tolerant probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum strain TA4. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Podasca, V.-E.; Damaceanu, M.-D. Photopolymerized Films with ZnO and Doped ZnO Particles Used as Efficient Photocatalysts in Malachite Green Dye Decomposition. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.; Kim, J. Correlation between the Morphology of ZnO Layers and the Electroluminescence of Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.G.; Na, K.H.; Kim, W.T.; Park, D.C.; Yang, W.H.; Choi, W.Y. TiO2/ZnO Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning and Their Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Compared with TiO2 Nanofibers. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, H.; Sakharkar, M.; Nayak, A.; Kishore, U.; Khan, A. Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: An Overview; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 357–377. [Google Scholar]
- Vinardell, M.P.; Llanas, H.; Marics, L.; Mitjans, M. In Vitro Comparative Skin Irritation Induced by Nano and Non-Nano Zinc Oxide. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández, R.; Hernández-Reséndiz, J.R.; Martínez-Chávez, A.; Velázquez-Castillo, R.; Escobar-Alarcón, L.; Esquivel, K. X-ray diffraction Rietveld structural analysis of Au–TiO2 powders synthesized by sol–gel route coupled to microwave and sonochemistry. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 93, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhdi, M.; Tafreshi, M. The effects of gadolinium doping on the structural, morphological, optical, and photoluminescence properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation method. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc oxide-from synthesis to application: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolhoseinzadeh, A.; Sheibani, S. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of Cu2O nano-photocatalyst powder modified by ball milling and ZnO. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, H.M.; Mohamad, R.; Zaidan, U.H. Microbial synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their potential application as an antimicrobial agent and a feed supplement in animal industry: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awwad, A.M.; Amer, M.W.; Salem, N.M.; Abdeen, A.O. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) using Ailanthus altissima fruit extracts and antibacterial activity. Chem. Int. 2020, 6, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Ma, Q.; Ye, L.; Piao, G. The traditional medicine and modern medicine from natural products. Molecules 2016, 12, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sruthi, S.; Ashtami, J.; Mohanan, P. Biomedical application and hidden toxicity of Zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 10, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabadi, H.; Tajani, B.; Moradi, M.; Kamali, K.D.; Meena, R.; Honary, S.; Mahjoub, M.A.; Saravanan, M. Penicillium Family as Emerging Nanofactory for Biosynthesis of Green Nanomaterials: A Journey into the World of Microorganisms. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 30, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Ikram, S. A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and microbes: A prospect towards green chemistry. J. Photoch. Photobiol B. 2017, 166, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrosa, M.; Jiménez, P.; Tejero, J.; Cabrero, P.; Cordoba-Diaz, D.; Quinto, E.J.; Gayoso, M.J.; Girbés, T. Toxicity of the anti-ribosomal lectin ebulin f in lungs and intestines in elderly mice. Toxins 2015, 7, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sujitha, M.V.; Kannan, S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using citrus fruits (Citrus limon, Citrus reticulata and Citrus sinensis) aqueous extract and its characterization. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 102, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviya, S.; Santhanalakshmi, J.; Viswanathan, B.; Muthumary, J.; Srinivasan, K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Citrus sinensis peel extract and its antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanulla, A.M.; Sundaram, R. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using orange peel extract for antibacterial, cytotoxicity and humidity sensor applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 8, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, B.N.; Taranath, T.C. Limonia acidissima L. leaf mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: A potent tool against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2016, 5, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, H.K.N.; Mohana, N.C.; Nuthan, B.R.; Ramesha, K.P.; Rakshith, D.R.; Geetha, N.; Satich, S. Phyto-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous plant extract of Ocimum americanum and evaluation of its bioactivity. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raja, A.; AshokKumar, S.; Marthandam, R.P.; Jayachandiran, J.; Khatiwada, C.P.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Raman, R.G.; Swaminathan, M.; Kathiwada, C.P. Eco-friendly preparation of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Tabernaemontana divaricata and its photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 181, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavithra, N.; Lingaraju, K.; Raghu, G.; Nagaraju, G. Citrus maxima (pomelo) juice mediated eco-friendly synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Applications to photocatalytic, electrochemical sensor and antibacterial activities. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 185, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffy, K.; Shanthi, G.; Maroky, A.; Selvakumar, S. Enhanced antibacterial effects of green synthesized ZnO NPs using Aristolochia indica against multidrug resistant bacterial pathogens from diabetic foot ulcer. J. Infect. Public Health. 2018, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, A.; Yapaöz, M.A. Biomimetic synthesis, characterization and antibacterial efficacy of ZnO and Au nanoparticles using echinacea flower extract precursor. Mater. Res. Express. 2018, 5, 055403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Aloucheh, R.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Bayrami, A.; Latifi-Navid, S.; Asadi, A. Green synthesis of ZnO and ZnO/CuO nanocomposites in Mentha longifolia leaf extract: Characterization and their application as antibacterial agents. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 13596–13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaköse, E.; Çolak, H. Structural, electrical, and antimicrobial characterization of green synthesized ZnO nanorods from aqueous Mentha extract. MRS Commun. 2018, 8, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalia, H.; Baluja, S.; Chanda, S. Effect of pH on size and antibacterial activity of Salvadora oleoides leaf extract-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles. BioNanoScience 2017, 7, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supraja, N.; Prasad, T.N.K.V.; Krishna, T.G.; David, E. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy of Boswellia ovalifoliolata stem bark-extract-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zare, E.; Pourseyedi, S.; Khatami, M.; Darezereshki, E. Simple biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using nature’s source, and it’s in vitro bioactivity. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1146, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, N.; Saha, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Maiti, M.; Das, S.; Basu, R.; Nandy, P. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract: Effect of temperature on synthesis, anti-bacterial activity and antidiabetic activity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 4993–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.; Vadivel, S.; Dhar, S.S.; Debbarma, S.; Kumaravel, M. One-pot green synthesis of zinc oxide nano rice and its application as sonocatalyst for degradation of organic dye and synthesis of 2-benzimidazolederivatives. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 104, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrzadeh, M.; Saravi, S.S.S. The chemistry, pharmacology and clinical properties of Sambucus ebulus: A review. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Alamdari, S.; Ghamsari, M.S.; Tafreshi, M.J. Optimization of Gallium concentration to improve the performance of ZnO nanopowders for nanophotonic applications. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 4484–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Karkhaneh, A.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Ghamsari, M.S. Ultra-thin Hafnium doped ZnO films with enhaVnced optical transparency and electrical conductivity. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 055020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamsari, M.S.; Alamdari, S.; Razzaghi, D.; Pirlar, M.A. ZnO nanocrystals with narrow-band blue emission. J. Lumin. 2019, 205, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Tafreshi, M.; Ghamsari, M.S. Strong yellow-orange emission from aluminum and Indium co-doped ZnO nanostructures with potential for increasing the color gamut of displays. Appl. Phys. A. 2019, 125, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Ghamsari, M.S. The effects of indium precursors on the structural, optical and electrical properties of nanostructured thin ZnO films. Mater. Lett. 2017, 197, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamsari, M.S.; Alamdari, S.; Han, W.; Park, H.-H. Park, Impact of nanostructured thin ZnO film in ultraviolet protection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alamdari, S.; Ghamsari, M.S.; Ara, M.M.; Efafi, B. Highly concentrated IZO colloidal nanocrystals with blue/orange/ red three-color emission. Mater. Lett. 2015, 158, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Sasani Ghamsari, M.; Jafar Tafreshi, M. Synthesis, characterization and gas sensing properties of In-doped ZnO nanopowders. Nanochem. Res. 2017, 2, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Vafaee, M.; Ghamsari, M.S.; Radiman, S. Highly concentrated zinc oxide nanocrystals sol with strong blue emission. J. Lumin. 2011, 131, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pick, E.; Mizel, D. Rapid microassays for the measurement of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production by macrophages in culture using an automatic enzyme immunoassay reader. J. Immunol. Methods 1981, 46, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, J.O.; Campbell, I.D. Electron spin resonance observations of oxygen chemisorption on zinc oxide. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1973, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaftelen, H.; Ocakoglu, K.; Thomann, R.; Tu, S.; Weber, S.; Erdem, E. EPR and photoluminescence spectroscopy studies on the defect structure of ZnO nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 014113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efafi, B.; Ghamsari, M.S.; Aberoumand, M.A.; Ara, M.M.; Ghamsari, A.H.S.; Rad, H.H. Aluminum doped ZnO sol–gel derived nanocrystals: Raman spectroscopy and solid solubility characterization. Phys. Status Solidi A 2014, 211, 2426–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundrarajan, M.; Ambika, S.; Bharathi, K. Plant-extract mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pongamia pinnata and their activity against pathogenic bacteria. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, N.; Nandhakumar, E.; Priya, P.; Soni, D.; Vimalan, M.; Potheher, I.V. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using leaf extract of Tectona grandis (L.) and their anti-bacterial, anti-arthritic, anti-oxidant and in vitro cytotoxicity activities. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10347–10356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, M.; Popa, A.; Toloman, D.; Silipas, T.-D.; Vodnar, D.C. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized using extracts of Allium sativum, Rosmarinus officinalis and Ocimum basilicum. Acta Met. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2016, 29, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, R.; López-Ibáñez, R.; Dalchiele, E.A.; Ramos-Barrado, J.R.; Martín, F.; Leinen, D. Compositional and physico-optical characterization of 0–5%Al-doped zinc oxide films prepared by chemical spray pyrolysis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 095303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Gaashani, R.; Radiman, S.; Daud, A.; Tabet, N.; Al-Douri, Y. XPS and optical studies of different morphologies of ZnO nanostructures prepared by microwave methods. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayioglu, H.; Kut, D.; Merdan, N.; Eyupoglu, S. The effect of dyeing properties of fixing agent and plasma treatment on silk fabric dyed with natural dye extract obtained from Sambucus ebulus L. plant. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vafaee, M.; Ghamsari, M.S. Preparation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles by a novel sol–gel route. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3265–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetchakun, N.; Chaiwichain, S.; Inceesungvorn, B.; Pingmuang, K.; Phanichphant, S.; Minett, A.I.; Chen, J. BiVO4/CeO2 nanocomposites with high visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3718–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Tai, X.; Du, Z.; Yin, Y. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO sensitized by carbon quantum dots and application in phenol wastewater. Opt. Mater. 2020, 100, 109674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoepe, N.; Mbita, Z.; Mathipa, M.; Mketo, N.; Ntsendwana, B.; Hintsho-Mbita, N. Biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Monsonia burkeana for use in photocatalytic, antibacterial and anticancer applications. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16999–17000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, S.; Vaya, D.; Das, B.K. Photocatalytic degradation of Malachite Green dye by modified ZnO nanomaterial. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nava, O.; Morales, P.L.; Gutiérrez, C.M.G.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.; Castro-Beltrán, A.; Mota-González, M.; Olivas, A. Influence of Camellia sinensis extract on zinc oxide nanoparticle green synthesis. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1134, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambika, S.; Sundrarajan, M. Antibacterial behaviour of Vitex negundo extract assisted ZnO nanoparticles against pathogenic bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 146, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Karan, R.; Sinha, A.; Khare, S.K. Interaction and nanotoxic effect of ZnO and Ag nanoparticles on mesophilic and halophilic bacterial cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.; Ray, B.; Ranjit, K.T.; Manna, A.C. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle suspensions on a broad spectrum of microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 297, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jayaseelan, C.; Rahuman, A.A.; Kirthi, A.V.; Marimuthu, S.; Santhoshkumar, T.; Bagavan, A.; Gaurav, K.; Karthik, L.; Rao, K.V.B. Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Spectrochim. Acta A 2012, 90, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Mishra, A.K. White light emission from vegetable extracts. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavath, N.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles—an antimicrobial study. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Hancock, R.E.W. Adaptive and mutational resistance: Role of porins and efflux pumps in drug resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, O.; Komatsu, M.; Sawai, J.; Nakagawa, Z. Antibacterial activity of ZnO particle with crystallographic orientation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F.; Yang, D.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. One-step green synthesis of bimetallic Fe/Pd nanoparticles used to degrade Orange II. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 3030, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Guo, M.; Luo, F.; Chen, Z. One-step green synthesis of bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles by eucalyptus leaf extract: Biomolecules identification, characterization and catalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Kao, W.T. Heterojunction nanowires of AgxZn1-xO–ZnO photocatalytic and antibacterial activities under visible-light and dark conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2015, 119, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, H.; Kavaz, D.; Rizaner, N. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Albizia lebbeck stem bark, and evaluation of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities on human breast cancer cell lines. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.H.; Murali, M.; Satish, A.; Singh, S.B.; Gowtham, H.G.; Mahesh, H.M.; Lakshmeesha, T.R.; Amruthesh, K.N.; Jagannath, S. Bioactive and Biocompatible Nature of Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Simarouba glauca DC.: An Endemic Plant to Western Ghats, India. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanag, F.M.; Bayrami, A.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Pouran, S.R.; Mohammadi, F. Pouran, A comprehensive study on antidiabetic and antibacterial activities of ZnO nanoparticles biosynthesized using Silybum marianum L. seed extract. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashant, G.K.; Prashant, P.A.; Utpal, B.; Manoj, G.; Nagabhushana, B.M.; Ananda, S.; Krishnaiah, G.M.; Sathyananda, H.M. In vitro antibacterial and cytotoxicity studies of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by combustion assisted facile green synthesis. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2015, 1, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, N.J.; Apte, S.C.; Batley, G.E.; Gadd, G.E.; Casey, P.S. Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl 2 to a freshwater microalga subcapitata: The importance of particle solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8484–8490. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, H.; Menon, S.; Kumar, S.V.; Rajeshkumar, S. Mechanistic study on antibacterial action of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using green route. Chemico-Biol. Interact. 2018, 286, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakha, M.; Saleem, M.; Mallick, B.C.; Jha, S. The effects of interfacial potential on antimicrobial propensity of ZnO nanoparticle. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y.H.; Chan, C.M.N.; Ng, A.M.C.; Chan, H.T.; Chiang, M.W.L. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles with a modified surface under ambient illumination. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 475703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Palma, S.; Fisher, N.S.; Wong, S.S. Effect of morphology of ZnO nanostructures on their toxicity to marine algae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 102, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangeetha, G.; Rajeswari, S.; Venkatesh, R. Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 22, 693–700. [Google Scholar]
- Susheela, S.; Sunil, K.; Bulchandini, B.D.; Shalini, T.; Shelza, B. Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Int. J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. Res. 2013, 4, 341–346. [Google Scholar]







| Compound | Retention Time (min) | % | Compound | Retention Time (min) | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid | 5.50 | 1.20 | 14-methyl-Pentadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 41.12 | 0.67 |
| 1,3-dimethoxy- Propane | 5.60 | 0.17 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 41.81 | 9.3 |
| 1-Butanol | 6.41 | 2.38 | Hexadecanoic acid, ethyl ester | 42.43 | 0.33 |
| 1,1-diethoxy-2-Propanone | 11.68 | 0.66 | 9Z,12Z-Octadecadienoic acid, methyl ester | 44.39 | 0.36 |
| Isovaleric acid | 12.01 | 3.52 | 9Z,12Z,15Z-Octadecatrienoic acid, methyl ester | 44.52 | 1.2 |
| 4-vinylphenol | 24.27 | 1.6 | Phytol | 44.74 | 3.08 |
| D(-)-Quinic acid | 34.76 | 0.32 | α-Linilenic acid | 45.21 | 8.2 |
| Pentanoic acid | 36.22 | 0.28 | Octadecanoic acid | 45.52 | 2.62 |
| (-)-Loliolide | 41.03 | 0.42 | 9Z,12Z,15Z-Octadecatrienoic acid, ethyl ester, | 44.52 | 0.9 |
| Neophytadiene | 39.421 | 1.02 | Mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 52.02 | 51.41 |
| 9-Methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrido(1,2-a)pyrimidin-2-one | 39.76 | 2.50 | Octadecanoic acid (stearic acid) | 45.52 | 2.57 |
| 14-methyl-Pentadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 41.12 | 0.80 | D-alpha-Tocopherol(Vitamin E) | 64.15 | 0.69 |
| Lignocaine | 41.03 | 0.42 | 22,23 -dihydro Stigmasterol | 71.65 | 3.38 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alamdari, S.; Sasani Ghamsari, M.; Lee, C.; Han, W.; Park, H.-H.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Afarideh, H.; Ara, M.H.M. Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103620
Alamdari S, Sasani Ghamsari M, Lee C, Han W, Park H-H, Tafreshi MJ, Afarideh H, Ara MHM. Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103620
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlamdari, Sanaz, Morteza Sasani Ghamsari, Chan Lee, Wooje Han, Hyung-Ho Park, Majid Jafar Tafreshi, Hosein Afarideh, and Mohammad Hosein Majles Ara. 2020. "Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103620
APA StyleAlamdari, S., Sasani Ghamsari, M., Lee, C., Han, W., Park, H. -H., Tafreshi, M. J., Afarideh, H., & Ara, M. H. M. (2020). Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103620