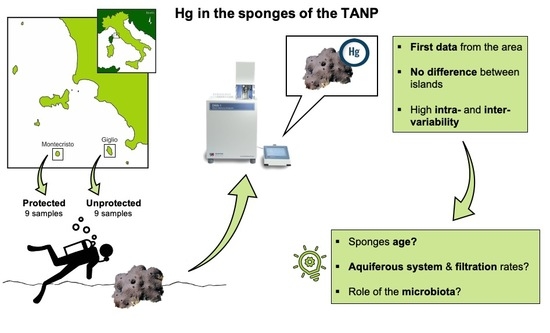
Hg Levels in Marine Porifera of Montecristo and Giglio Islands (Tuscan Archipelago, Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Samples Collection and Identification
2.3. Samples Treatment and Mercury Analysis
2.4. Accuracy
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramalhosa, E.C.D.; Pereira, E.; Duarte, A. Mercury behaviour in the water column of an impacted coastal lagoon: Ria de Aveiro (Portugal) as a case study. In Focus on Water Resource Research; Heikkinen, E., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 41–86. ISBN 978-1-60456-093-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, R.M. Mercury Effects in Natural Populations of Sea Anemone Actinia equina. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Biology, University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, F.M.; Kraepiel, A.M.; Amyot, M. The chemical cycle and bioaccumulation of mercury. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1998, 29, 543–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, S.M.; Tanton, T.W.; Abdrashitova, S.A. Mercury in the Aquatic Environment: A Review of Factors Affecting Methylation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 31, 241–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajar, R.; ČETINA, M.; Horvat, M.; Žagar, D. Mass balance of mercury in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Chem. 2007, 107, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droghini, E.; Annibaldi, A.; Prezioso, E.; Tramontana, M.; Frapiccini, E.; De Marco, R.; Illuminati, S.; Truzzi, C.; Spagnoli, F. Mercury Content in Central and Southern Adriatic Sea Sediments in Relation to Seafloor Geochemistry and Sedimentology. Molecules 2019, 24, 4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardellicchio, N.; DeCataldo, A.; Di Leo, A.; Misino, A. Accumulation and tissue distribution of mercury and selenium in striped dolphins (Stenella coeruleoalba) from the Mediterranean Sea (southern Italy). Environ. Pollut. 2002, 116, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, M.M.; Storelli, A.; D’Addabbo, R.; Marano, C.; Bruno, R.; Marcotrigiano, G.O. Trace elements in loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta) from the eastern Mediterranean Sea: Overview and evaluation. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 135, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePew, D.; Basu, N.; Burgess, N.; Campbell, L.M.; Devlin, E.W.; Drevnick, P.; Hammerschmidt, C.R.; Murphy, C.A.; Sandheinrich, M.B.; Wiener, J.G. Toxicity of dietary methylmercury to fish: Derivation of ecologically meaningful threshold concentrations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, B.; Mouneyrac, C.; Perez, T.; Amiard-Triquet, C. Metallothionein concentration in sponges (Spongia officinalis) as a biomarker of metal contamination. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 141, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.; Díez, S.; Soto, D.X.; Catalan, J.; Bayona, J. Assessment of mercury and methylmercury pollution with zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in the Ebro River (NE Spain) impacted by industrial hazardous dumps. Sci. Total. Environ. 2008, 407, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roveta, C.; Annibaldi, A.; Vagnoni, F.; Mantas, T.P.; Domenichelli, F.; Gridelli, S.; Puce, S. Short-term effects of environmental factors on the asexual reproduction of Aurelia sp. polyps. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 36, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibaud, Y. Teneur en mercure dans quelques poissons de consommation courante. Sci. Peche, Bull. Inst. Peches Marit. 1971, 209, 253–3131. [Google Scholar]
- Cumont, G.; Gilles, G.; Bernhard, F.; Briand, M.B.; Stephan, G.; Ramonda, G.; Guillen, G. Bilan de la contamination des poissons de mer par la rnercure al’occasion d’un controle port ant sur 3 annees. Ann. Hyg. Lang. Fr. Med. Nutr. 1975, 11, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cossa, D.; Martin, J.-M. Mercury in the Rhône delta and adjacent marine areas. Mar. Chem. 1991, 36, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, R.; Mazzolai, B.; Edner, H.; Svanberg, S.; Wallinder, E. Atmospheric mercury sources in the Mt. Amiata area, Italy. Sci. Total. Environ. 1998, 213, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, R.; Maserti, B.; Breder, R. Mercury in abiotic and biotic compartments of an area affected by a geochemical anomaly (Mt. Amiata, Italy). Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 1991, 56, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossa, D.; Coquery, M. The Mediterranean Mercury Anomaly, a Geochemical or a Biologocal Issue. In The Mediterranean Sea. Handbook of Environmental Chemistry Vol. 5K; Saliot, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 177–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, R.; Maserti, B.E.; Morelli, M.; Morelli, L.; Nannicini, L.; Scarano, G.; Seritti, A.; Torti, M. Metalli pesanti nelle acque dell’Arcipelago Toscanoe nella Posidonia oceanica dell’Arcipelago Toscano. In Progetto mare Ricerca sullo Stato Biologico, Chimico e Fisico dell’Alto Tirreno Toscano; University of Florence: Florence, Italy, 1993; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Verniani, D. Monitoraggio Acque Marino Costiere Della Toscana Anno 2012. Proposta Di Classificazione Triennio 2010–2012 (D.Lgs. 152/06); Technical report; Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale della Toscana (ARPAT): Florence, Italy, 2013; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Verniani, D. Monitoraggio Acque Marino Costiere Della Toscana Anno 2012. Proposta Di Classificazione Triennio Anno 2013 (D.Lgs. 152/06); Technical report; Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale della Toscana (ARPAT): Florence, Italy, 2014; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccanti, M.; Verniani, D. Monitoraggio Acque Marino Costiere Della Toscana. Attività Di Monitoraggio 2014. Classificazione Provvisoria II Anno Del Triennio 2013–2015; Technical report; Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale della Toscana (ARPAT): Florence, Italy, 2015; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Verniani, D.; Mancusi, C. Monitoraggio Acque Marino Costiere Della Toscana. Attività Di Monitoraggio 2016 e Proposta Di Classificazione; Technical report; Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale della Toscana (ARPAT): Florence, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Megaletti, E.; Tunesi, L. Il Report MSFD 2018: Aggiornamento Della Valutazione Ambientale (Art. 8 Del D.Lgs. 190/2010); Technical report; Istituto Superiore per laProtezione e la Ricerca Ambientale (ISPRA): Rome, Italy, 2019; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Denton, G.R.W.; Breck, W.G. Mercury in tropical marine organisms from north Queensland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1981, 12, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmacher, M.; Batiste, J.; Bosque, M.A.; Domingo, J.L.; Corbella, J. Mercury concentrations in marine species from the coastal area of Tarragona Province, Spain. Dietary intake of mercury through fish and seafood consumption. Sci. Total. Environ. 1994, 156, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugini, M.; Visciano, P.; Manera, M.; Zaccaroni, A.; Olivieri, V.; Amorena, M. Levels of Total Mercury in Marine Organisms from Adriatic Sea, Italy. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, D.; Muricy, G.; Rocha, R.C.; Miekeley, N.F. Marine sponges with contrasting life histories can be complementary biomonitors of heavy metal pollution in coastal ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5785–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, P.A.; Andren, L.; Bonde, G.J.; Jernelov, A.; Reisch, D.J. Monitoring organisms. In Food and Agricultural Organization Technical Conference on Marine Pollution and its Effects on Living Resources and Fishing, Rome, 1970. Supplement 1: Methods of Detection, Measurement and Monitoring of Pollutants in the Marine Environment; Ruivo, M., Ed.; Fishing News Ltd.: London, UK, 1971; pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Haug, A.; Melsom, S.; Omang, S. Estimation of heavy metal pollution in two Norwegian fjord areas by analysis of the brown alga Ascophyllum nodosum. Environ. Pollut. 1974, 7, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.; Balani, M.; Patel, S. Sponge ‘sentinel’ of heavy metals. Sci. Total. Environ. 1985, 41, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, I.V.; Weeks, J.M.; Depledge, M.H. Accumulation of copper, zinc, cadmium and chromium by the marine sponge Halichondria panicea Pallas and the implications for biomonitoring. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capón, R.J.; Elsbury, K.; Butler, M.S.; Lu, C.C.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Rostas, J.A.P.; O’Brien, K.J.; Mudge, L.M.; Sim, A.T.R. Extraordinary levels of cadmium and zinc in a marine sponge, Tedania charcoti Topsent: Inorganic chemical defense agents. Experientia 1993, 49, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, E.; Martí, R.; Uriz, J.; Turon, X. Sublethal effects of contamination on the Mediterranean sponge Crambe crambe: Metal accumulation and biological responses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, E.; Agell, G.; Marti, R.; Uriz, M.J. Response of the Mediterranean sponge Chondrosia reniformis Nardo to copper pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdenal, B.; Diana, C.; Arnoux, A.; Vacelet, J. Pollutant levels in Mediterranean commercial sponges. In New Perspectives in Sponge Biology, Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Biology of Sponges, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, USA, 17–23 November 1985; Rützler, K., Ed.; Smithsonian Inst. Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; pp. 516–524. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, T.; Vacelet, J.; Rebouillon, P. In situ comparative study of several Mediterranean sponges as potential biomonitors of heavy metals. In Sponge Science in the New Millennium; Pansini, M., Pronzato, R., Bavestrello, G., Manconi, R., Eds.; Officine Grafiche Canessa Rapallo: Genova, Italy, 2004; pp. 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, T.; Longet, D.; Schembri, T.; Rebouillon, P.; Vacelet, J. Effects of 12 years’ operation of a sewage treatment plant on trace metal occurrence within a Mediterranean commercial sponge (Spongia officinalis, Demospongiae). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsamo, M.; Fregni, E.; Tongiorgi, P. Marine and freshwater Gastrotricha from the Island of Montecristo (Tuscan Archipelago, Italy), with the description of new species. Boll. di Zool. 1994, 61, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, F.; Westerman, D.S.; Rocchi, S.; Tonarini, S. The Montecristo monzogranite (Northern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy): A collisional pluton in an extensional setting. Geol. J. 1997, 32, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeletti, L.; Ceregato, A.; Ghirelli, M.; Gualandi, B.; Lipparini, E.; Malatesta, D.; Sperotti, A.; Taviani, M. ROV-SCUBA integrated survey of the Montecristo Island Nature Reserve (Tuscan Archipelago National Park, Mediterranean Sea). Underw. Technol. 2010, 29, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IslePark. Available online: http://www.islepark.it (accessed on 14 February 2020).
- Bo, M.; Canese, S.; Bavestrello, G. Discovering Mediterranean black coral forests: Parantipathes larix (Anthozoa: Hexacorallia) in the Tuscan Archipelago, Italy. Ital. J. Zool. 2013, 81, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, E.; Gennaro, P.; Piazzi, L.; Ricevuto, E.; Serena, F. Development of a new biotic index for ecological status assessment of Italian coastal waters based on coralligenous macroalgal assemblages. Eur. J. Phycol. 2014, 49, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turicchia, E.; Abbiati, M.; Sweet, M.; Ponti, M. Mass mortality hits gorgonian forests at Montecristo Island. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 131, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavestrello, G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Calcinai, B.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Cerrano, C.; Morri, C.; Puce, S.; Sára, M. Bio-mineralogy as a structuring factor for marine epibenthic communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 193, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casoli, E.; Modica, M.V.; Belluscio, A.; Capello, M.; Oliverio, M.; Ardizzone, G.; Ventura, D. A massive ingression of the alien species Mytilus edulis L. (Bivalvia: Mollusca) into the Mediterranean Sea following the Costa Concordia cruise-ship disaster. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2016, 17, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illuminati, S.; Annibaldi, A.; Truzzi, C.; Scarponi, G. Recent temporal variations of trace metal content in an Italian white wine. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illuminati, S.; Annibaldi, A.; Truzzi, C.; Libani, G.; Mantini, C.; Scarponi, G. Determination of water-soluble, acid-extractable and inert fractions of Cd, Pb and Cu in Antarctic aerosol by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry after sequential extraction and microwave digestion. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 755, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, C.; Illuminati, S.; Girolametti, F.; Antonucci, M.; Scarponi, G.; Ruschioni, S.; Riolo, P.; Annibaldi, A. Influence of Feeding Substrates on the Presence of Toxic Metals (Cd, Pb, Ni, As, Hg) in Larvae of Tenebrio molitor: Risk Assessment for Human Consumption. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, W.D. Analysis of variance. In Biostatistics, 8th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 303–320. [Google Scholar]
- Piazzi, L.; Balata, D.; Cecchi, E.; Cinelli, F.; Sartoni, G. Species composition and patterns of diversity of macroalgal coralligenous assemblages in the north-western Mediterranean Sea. J. Nat. Hist. 2009, 44, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasolla, G.; Innocenti, G. New records of the invasive crabs Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 and Percnon gibbesi (H. Milne Edwards, 1853) along the Italian coasts. BioInvasions Rec. 2014, 3, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, R.; Napolitano, E.; Marullo, S.; Artale, V.; Vetrano, A. Seasonal Variability of the Tyrrhenian Sea Surface Geostrophic Circulation as Assessed by Altimeter Data. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 1710–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.P.; Burns, K.; Boyle, S.; Brinkman, D.; Webster, N.S. Contamination in sediments, bivalves and sponges of McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 143, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mestre, C.; Maher, W.A.; Roberts, D.; Broad, A.; Krikowa, F.; Davis, A.R. Sponges as sentinels: Patterns of spatial and intra-individual variation in trace metal concentration. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansini, M.; Manconi, R.; Pronzato, R. Porifera I. Calcarea, Demospongiae (partim), Hexactinellida, Homoscleromorpha. Fauna d’Italia, Vol. 46; Calderini-Il Sole 24 Ore: Bologna, Italy, 2011; p. 554. ISBN 978-88-506-5395-9. [Google Scholar]
- Cebrian, E.; Uriz, M.J.; Turon, X. Sponges as biomonitors of heavy metals in spatial and temporal surveys in northwestern Mediterranean: Multispecies comparison. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 2430–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illuminati, S.; Annibaldi, A.; Truzzi, C.; Scarponi, G. Heavy metal distribution in organic and siliceous marine sponge tissues measured by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 111, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysing-Gubala, M.; Poirrier, M.A. The effects of cadmium and mercury on gemmule formation and gemmosclere morphology in Ephydatia fluviatilis (Porifera: Spongillidae). Hydrobiologia 1981, 76, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, E.; Uriz, M.J. Contrasting Effects of Heavy Metals on Sponge Cell Behavior. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 53, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batel, R.; Bihari, N.; Rinkevich, B.; Dapper, J.; Schäcke, H.; Schröder, H.; Müller, W. Modulation of organotin-induced apoptosis by the water pollutant methyl mercury in a human lymphoblastoid tumor cell line and a marine sponge. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 93, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, C.; Annibaldi, A.; Illuminati, S.; Bassotti, E.; Scarponi, G. Square-wave anodic-stripping voltammetric determination of Cd, Pb, and Cu in a hydrofluoric acid solution of siliceous spicules of marine sponges (from the Ligurian Sea, Italy, and the Ross Sea, Antarctica). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibaldi, A.; Truzzi, C.; Illuminati, S.; Bassotti, E.; Finale, C.; Scarponi, G. First Systematic Voltammetric Measurements of Cd, Pb, and Cu in Hydrofluoric Acid-Dissolved Siliceous Spicules of Marine Sponges: Application to Antarctic Specimens. Anal. Lett. 2011, 44, 2792–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacelet, J.; Verdenal, B.; Perinet, G. The iron mineralization of Spongia officinalis L. (Porifera, Dictyoceratida) and its relationships with the collagen skeleton. Biol. Cell 1988, 62, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, D.; Uriz, M.J. Do associated zooxanthellae and the nature of the substratum affect survival, attachment and growth of Cliona viridis (Porifera: Hadromerida)? An experimental approach. Mar. Biol. 1992, 114, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, C.; Schönberg, L.; De Beer, D.; Lawton, A. oxygen microsensor studies on zooxanthellate clionaid sponges from the Costa Brava, Mediterranean Sea 1. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, R.B. Cadmium content of the marine sponge Microciona prolifera, other sponges, water and sediment from the eastern Florida panhandle: Possible effects on Microciona cell aggregation and potential roles of low pH and low salinity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C: Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1999, 124, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Shostak, K.; Gamulin, V.; Lacorn, M.; Skorokhod, A.; Kavsan, V.; Müller, W. Purification, cDNA cloning and expression of a cadmium-inducible cysteine-rich metallothionein-like protein from the marine sponge Suberites domuncula. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 200, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffard, A.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Amiard-Triquet, C. Use of metallothionein in gills from oysters (Crassostrea gigas) as a biomarker: Seasonal and intersite fluctuations. Biomarkers 2002, 7, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, W.G.; Lee, B.; Luoma, S. Subcellular compartmentalization of Cd and Zn in two bivalves. I. Significance of metal-sensitive fractions (MSF) and biologically detoxified metal (BDM). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 249, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, J.; Priya, S.S.; Kiran, G.S.; Thangavelu, T.; Bai, N.S. Sponge-associated marine bacteria as indicators of heavy metal pollution. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 164, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Lurgi, M.; Björk, J.R.; Easson, C.; Astudillo-Garcia, C.; Olson, J.B.; Erwin, P.M.; Lopez-Legentil, S.; Luter, H.; et al. Diversity, structure and convergent evolution of the global sponge microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Gandelman, J.F.; Cruz, K.; Crane, S.; Muricy, G.; Giambiagi-Demarval, M.; Barkay, T.; Laport, M.S. Potential Application in Mercury Bioremediation of a Marine Sponge-Isolated Bacillus cereus strain Pj1. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 69, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Gandelman, J.F.; Giambiagi-Demarval, M.; Muricy, G.; Barkay, T.; Laport, M.S. Mercury and methylmercury detoxification potential by sponge-associated bacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabili, L.; Pizzolante, G.; Morgante, A.; Nonnis Marzano, C.; Longo, C.; Aresta, A.M.; Zambonin, C.; Corriero, G.; Alifano, P. Lindane Bioremediation Capability of Bacteria Associated with the Demosponge Hymeniacidon perlevis. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Location | Methodology | Hg (mg·kg−1) dw | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agelas oroides | Montecristo Island, Tuscany (Italy) | Mean ± SD | 0.29 ± 0.03 | This study |
| Coutiou, Marseille (France) | Mean ± SD | 1.7 ± 0.2 | [37] | |
| Chondrosia reniformis | Giglio Island, Tuscany (Italy) | Mean ± SD | 0.73 ± 0.05 | This study |
| 0.58 ± 0.02 | ||||
| 0.39 ± 0.02 | ||||
| Coutiou, Marseille (France) | Mean ± SD | 0.8 ± 0.1 | [37] | |
| Cliona viridis | Montecristo Island, Tuscany (Italy) | Mean ± SD | 0.033 ± 0.001 | This study |
| Giglio Island, Tuscany (Italy) | 0.0167 ± 0.0003 | |||
| Coutiou, Marseille (France) | Mean ± SD | 0.3 ± 0.4 | [37] | |
| Sarcotragus spinosulus | Montecristo Island, Tuscany (Italy) | Mean ± SD | 0.64 ± 0.01 | This study |
| Cacospongia scalaris | Coutiou, Marseille (France) | Mean ± SD | 0.8 ± 0.0 | [37] |
| Spongia (Spongia) lamella | Marseille and Saint Tropez (France) | Max | 0.52 | [36] |
| Coutiou, Marseille (France) | Mean ± SD | 0.3 ± 0.0 | [37] | |
| Spongia (Spongia) nitens | Marseille and Saint Tropez (France) | Max | 0.52 | [36] |
| Spongia (Spongia) officinalis | Marseille and Saint Tropez (France) | Max | 0.52 | [36] |
| Coutiou, Marseille (France) | Mean ± SD | 0.9 ± 0.1 | [37] | |
| Coutiou, Marseille (France) | Mean ± SD | 0.8 ± 0.1 | [38] | |
| Maire, Marseille (France) | 0.5 ± 0.1 | |||
| Plane, Marseille (France) | 0.9 ± 0.3 | |||
| Jarre, Marseille (France) | 0.6 ± 0.1 | |||
| Riou, Marseille (France) | 0.5 ± 0.1 | |||
| Veyron, Marseille (France) | 0.6 ± 0.1 | |||
| Lavera, Marseille (France) | 0.5 ± 0.1 | |||
| Niolon, Marseille (France) | 1.1 ± 0.5 | |||
| Port-Cros, Saint Tropez (France) | 0.6 ± 0.4 | |||
| Coutiou, Marseille (France) | Mean ± SD | 0.4 ± 0.1 | [10] | |
| Port-Cros, Saint Tropez (France) | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roveta, C.; Pica, D.; Calcinai, B.; Girolametti, F.; Truzzi, C.; Illuminati, S.; Annibaldi, A.; Puce, S. Hg Levels in Marine Porifera of Montecristo and Giglio Islands (Tuscan Archipelago, Italy). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124342
Roveta C, Pica D, Calcinai B, Girolametti F, Truzzi C, Illuminati S, Annibaldi A, Puce S. Hg Levels in Marine Porifera of Montecristo and Giglio Islands (Tuscan Archipelago, Italy). Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(12):4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124342
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoveta, Camilla, Daniela Pica, Barbara Calcinai, Federico Girolametti, Cristina Truzzi, Silvia Illuminati, Anna Annibaldi, and Stefania Puce. 2020. "Hg Levels in Marine Porifera of Montecristo and Giglio Islands (Tuscan Archipelago, Italy)" Applied Sciences 10, no. 12: 4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124342
APA StyleRoveta, C., Pica, D., Calcinai, B., Girolametti, F., Truzzi, C., Illuminati, S., Annibaldi, A., & Puce, S. (2020). Hg Levels in Marine Porifera of Montecristo and Giglio Islands (Tuscan Archipelago, Italy). Applied Sciences, 10(12), 4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124342